Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 74-82.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.08
Previous Articles Next Articles
Nan LI1,2( ), Liang ZHANG3, Qiaofeng GUO2, Yue ZHOU2(
), Liang ZHANG3, Qiaofeng GUO2, Yue ZHOU2( ), Changjiang LIU1
), Changjiang LIU1
Received:2025-09-11
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-16
Contact:
Yue ZHOU
E-mail:linan@xjtu.edu.cn;zhouy@bsu.edu.cn
Nan LI, Liang ZHANG, Qiaofeng GUO, Yue ZHOU, Changjiang LIU. Aerobic exercise regulates macrophage polarization and improves insulin resistance in mice: the mediating role of miR-221-3p[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2026, 46(1): 74-82.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.08
| Gene | Primer sequences (5'-3') | |
|---|---|---|
| miR-221-3p | RT | CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGGAAACCCA |
| F | ACACTCCAGCTGGGAGCTACATTGTCTGC | |
| U6 | F | CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA |
| R | AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT | |
| Tnf-α | F | CCCTCACACTCAGATCATCTTCT |
| R | GCTACGACGTGGGCTACAG | |
| Arg-1 | F | ACAGCAGAGGAGGTGAAGAGTAC |
| R | AGTCAGTCCCTGGCTTATGGT | |
| Socs1 | F | CTGCGGCTTCTATTGGGGAC |
| R | AAAAGGCAGTCGAAGGTCTCG | |
| β-actin | F | GTGCTATGTTGCTCTAGACTTCG |
| R | ATGCCACAGGATTCCATACC | |
Tab.1 Primers sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Primer sequences (5'-3') | |
|---|---|---|
| miR-221-3p | RT | CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGGAAACCCA |
| F | ACACTCCAGCTGGGAGCTACATTGTCTGC | |
| U6 | F | CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA |
| R | AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT | |
| Tnf-α | F | CCCTCACACTCAGATCATCTTCT |
| R | GCTACGACGTGGGCTACAG | |
| Arg-1 | F | ACAGCAGAGGAGGTGAAGAGTAC |
| R | AGTCAGTCCCTGGCTTATGGT | |
| Socs1 | F | CTGCGGCTTCTATTGGGGAC |
| R | AAAAGGCAGTCGAAGGTCTCG | |
| β-actin | F | GTGCTATGTTGCTCTAGACTTCG |
| R | ATGCCACAGGATTCCATACC | |
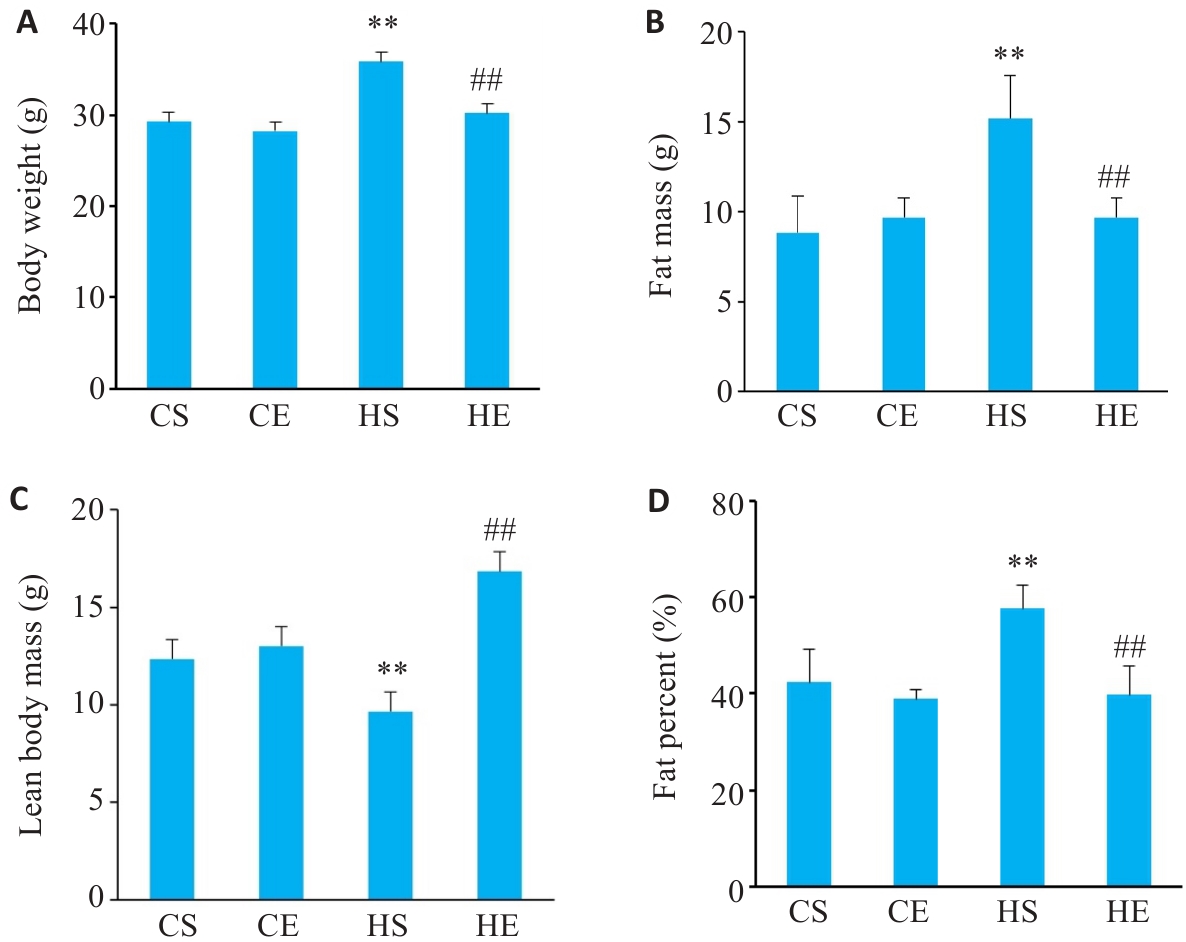
Fig.1 Changes in body weight of the mice in each group (n=6). A: Changes in body weight. B: Changes in fat mass. C: Changes in lean body mass. D: Changes in fat percent. CS: Normally fed sedentary group without exercise; CE: Normally fed sedentary group with aerobic exercise; HS: High-fat diet sedentary group; HE: High-fat diet group with aerobic exercise. **P<0.01 vs CS group, ##P<0.01 vs HS group.
| Parameter | CS | CE | HS | HE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting blood glucose (mmol/L) | 6.70±0.38 | 6.13±0.44 | 13.10±0.99** | 7.56±0.69## |
| Insulin (μIU/mL) | 7.74±0.62 | 8.27±2.70 | 24.73±2.41** | 11.70±3.30**## |
| HOMA-IR | 2.32±0.22 | 2.24±0.72 | 14.46±2.27** | 3.87±0.84*## |
| TC (mmol/L) | 3.08±0.13 | 3.02±0.53 | 4.67±0.40** | 3.90±0.70**## |
| TG (mmol/L) | 0.59±0.07 | 0.60±0.09 | 0.88±0.19** | 0.72±0.07## |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 2.87±0.47 | 2.86±0.27 | 3.76±0.73** | 3.56±0.23 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 0.15±0.08 | 0.14±0.06 | 0.32±0.13 | 0.31±0.13 |
Tab.2 Changes in the indicators of the mice in each group
| Parameter | CS | CE | HS | HE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting blood glucose (mmol/L) | 6.70±0.38 | 6.13±0.44 | 13.10±0.99** | 7.56±0.69## |
| Insulin (μIU/mL) | 7.74±0.62 | 8.27±2.70 | 24.73±2.41** | 11.70±3.30**## |
| HOMA-IR | 2.32±0.22 | 2.24±0.72 | 14.46±2.27** | 3.87±0.84*## |
| TC (mmol/L) | 3.08±0.13 | 3.02±0.53 | 4.67±0.40** | 3.90±0.70**## |
| TG (mmol/L) | 0.59±0.07 | 0.60±0.09 | 0.88±0.19** | 0.72±0.07## |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 2.87±0.47 | 2.86±0.27 | 3.76±0.73** | 3.56±0.23 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 0.15±0.08 | 0.14±0.06 | 0.32±0.13 | 0.31±0.13 |
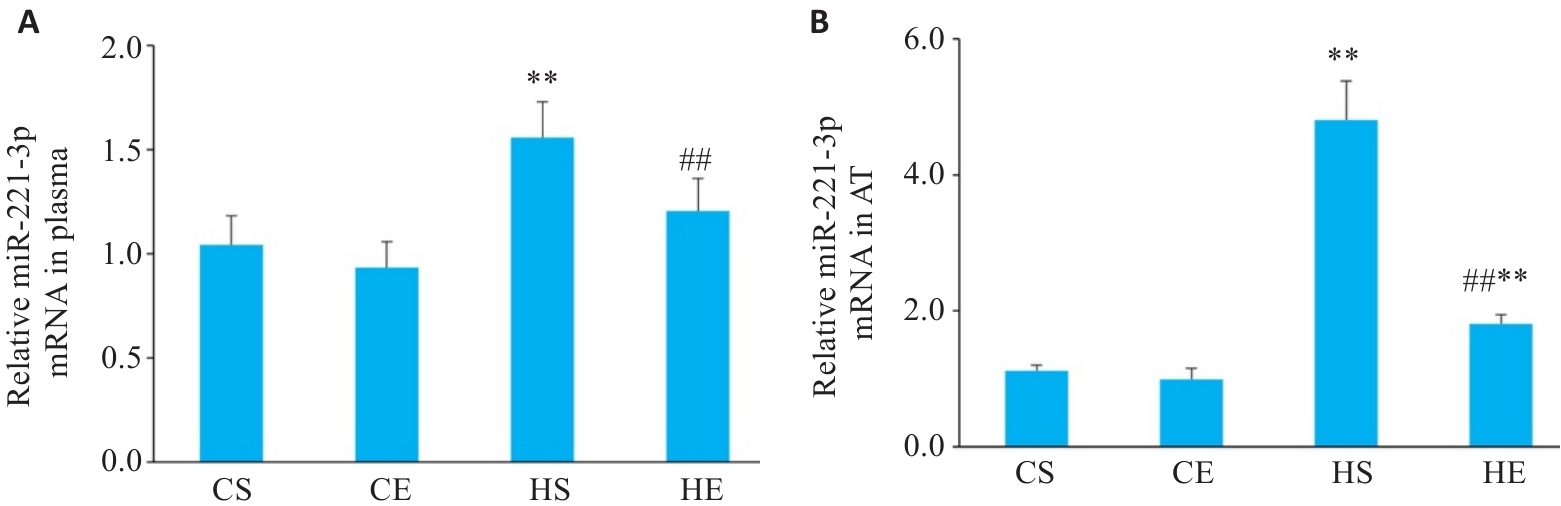
Fig.2 Changes in miR-221-3p levels in each group. A: Expression levels of miR-221-3p in plasma (n=6). B: Expression levels of miR-221-3p in adipose tissue (AT). **P<0.01 vs CS group, ##P<0.01 vs HS group.
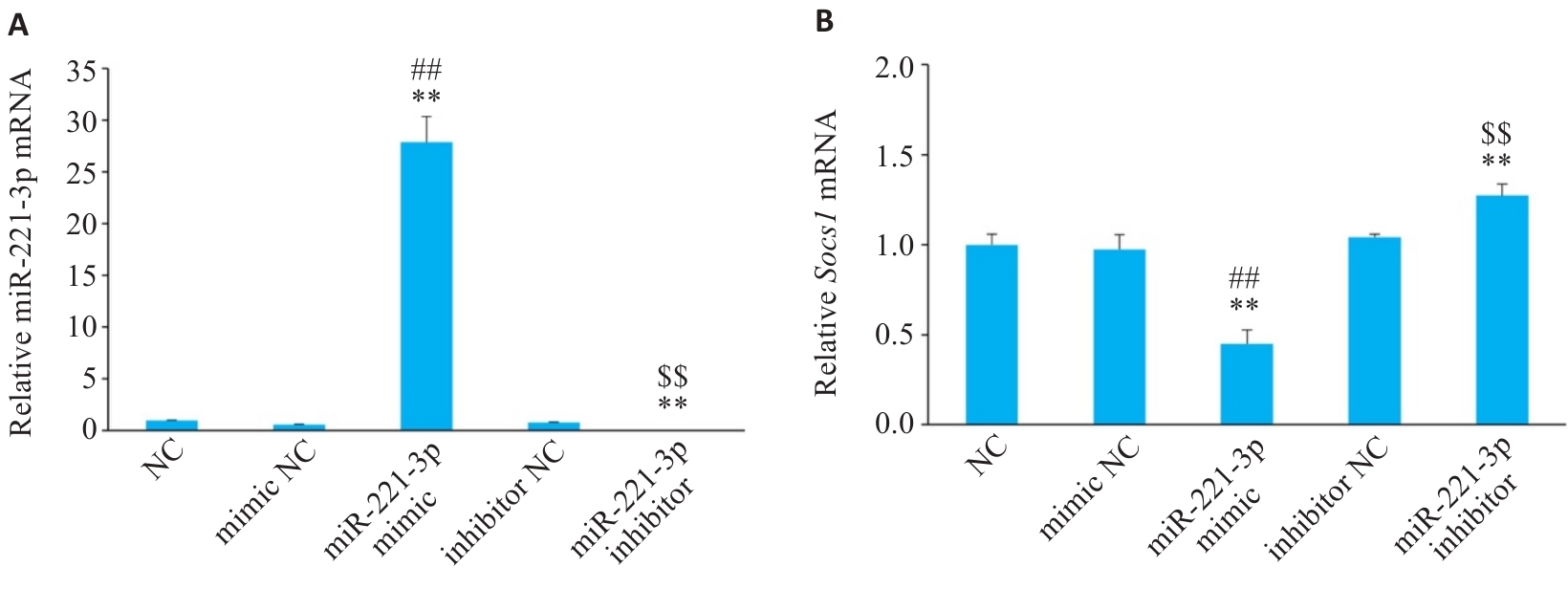
Fig.4 Relative mRNA levels of miR-221-3p (A) and Socs1 (B) enriched in RAW 264.7 cells (n=3). **P<0.01 vs NC group, ##P<0.01 vs mimic NC group, $$P<0.01 vs inhibitor NC group.
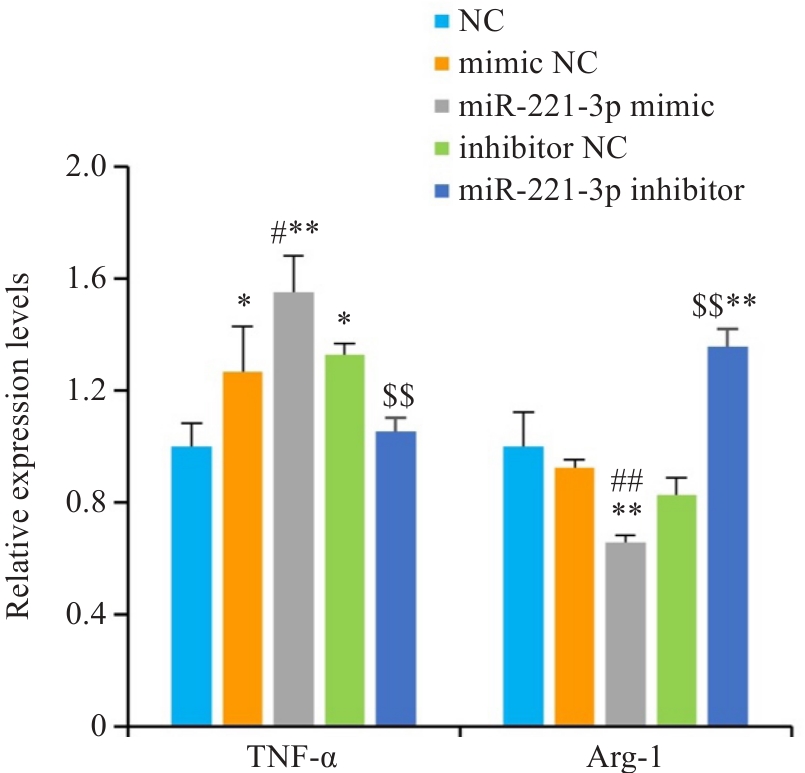
Fig.5 Relative mRNA levels of Tnf-α and Arg-1 enriched in RAW 264.7 cells (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs NC group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs mimic NC group, $$P<0.01 vs inhibitor NC group.
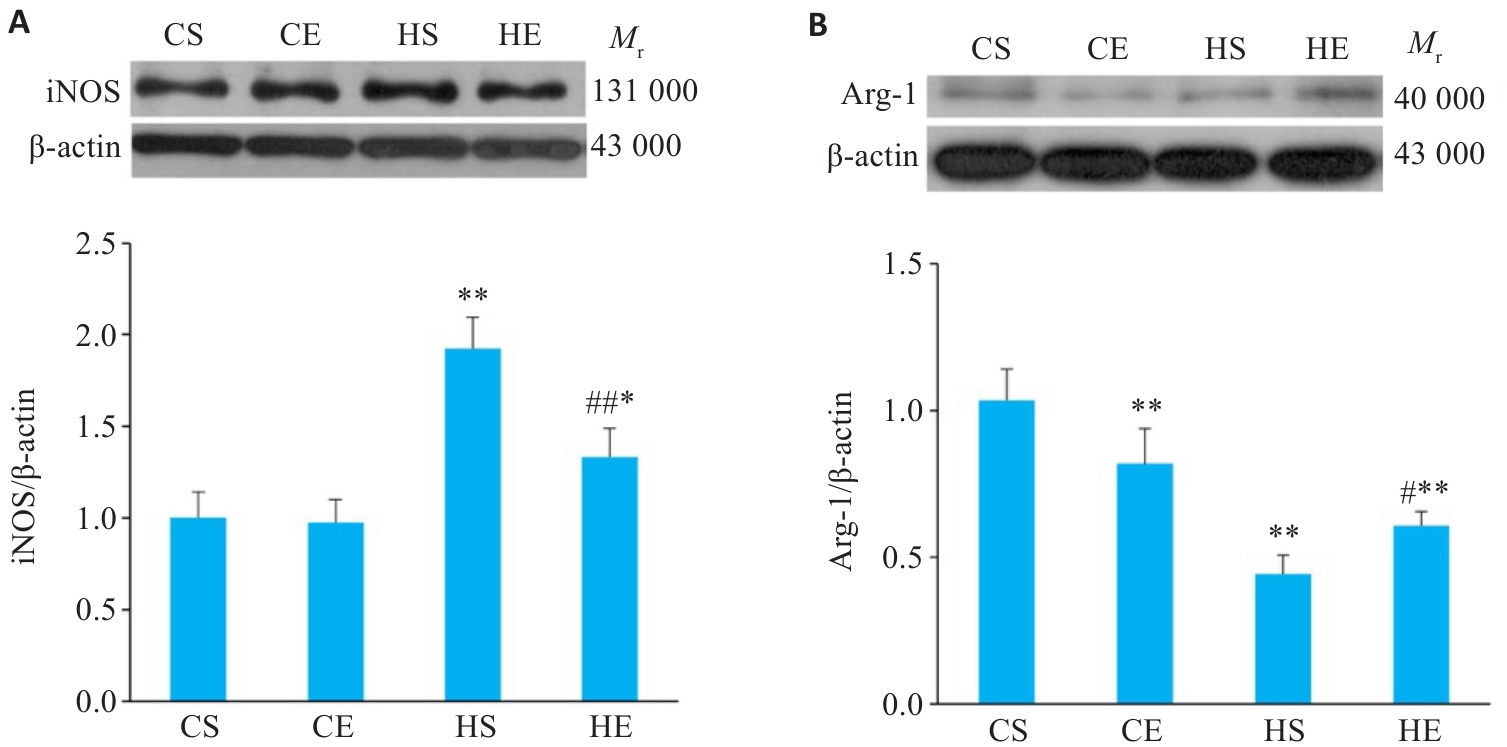
Fig.6 Changes of macrophage polarization-related proteins in the adipose tissue of mice after aerobic exercise intervention. A: Expression of iNOS proteins in adipose tissue. B: Expression of Arg-1 proteins in adipose tissue. n=6. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs CS group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs HS group.
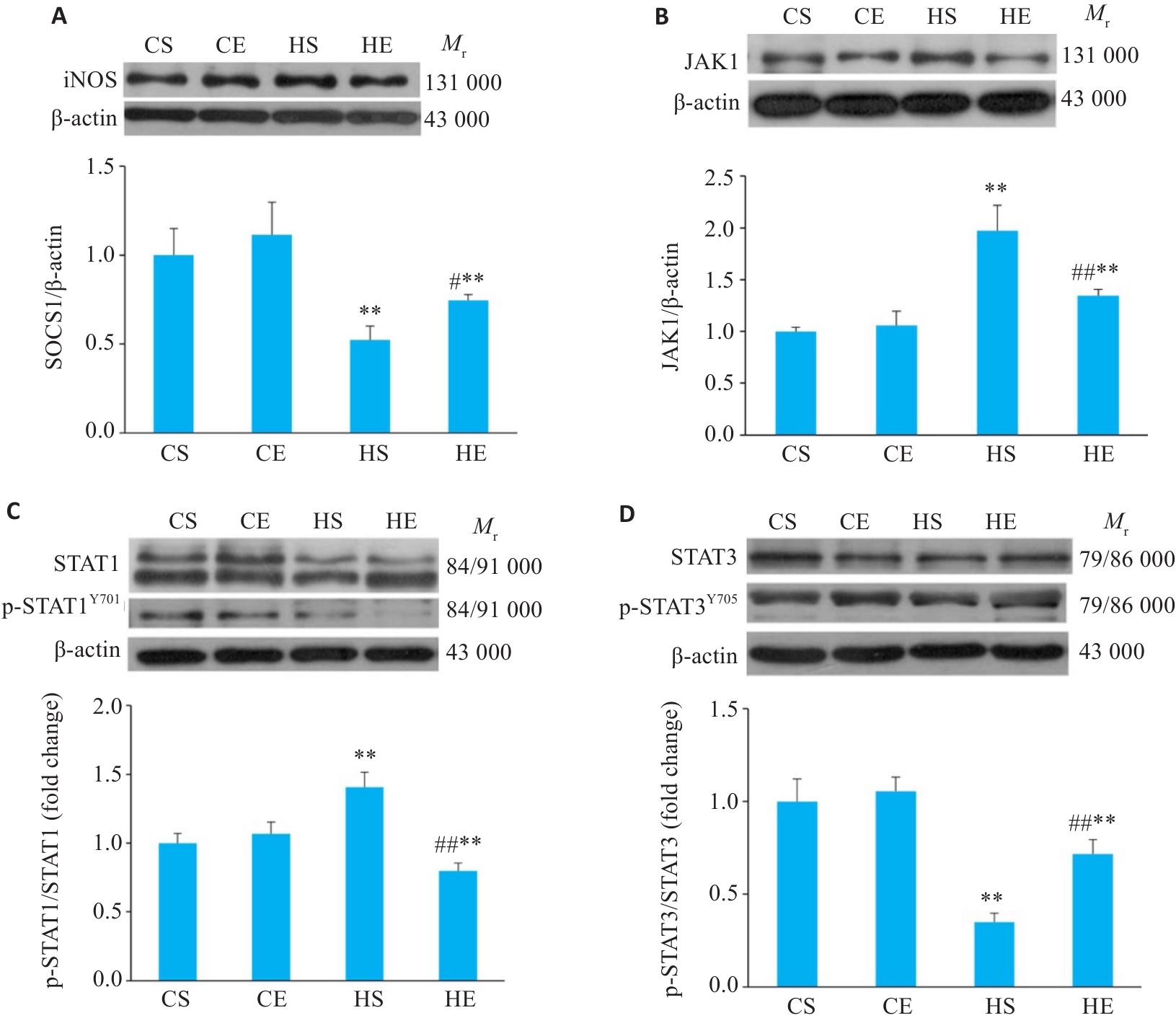
Fig.7 Comparison of the expression levels of JAK/STAT pathway proteins SOCS1 (A), JAK1 (B), p-STAT1/STAT1 (C), and p-STAT3/STAT3 (D) in the adipose tissue of the mice. n=6. **P<0.01 vs CS group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs HS group.
| [1] | Xu Y, Lu JL, Li M, et al. Diabetes in China part 1: epidemiology and risk factors[J]. Lancet Public Health, 2024, 9(12): e1089-97. doi:10.1016/s2468-2667(24)00250-0 |
| [2] | Wu H, Ballantyne CM. Metabolic inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity[J]. Circ Res, 2020, 126(11): 1549-64. doi:10.1161/circresaha.119.315896 |
| [3] | Feehan KT, Gilroy DW. Is resolution the end of inflammation[J]? Trends Mol Med, 2019, 25(3): 198-214. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2019.01.006 |
| [4] | Anderson E, Durstine JL. Physical activity, exercise, and chronic diseases: a brief review[J]. Sports Med Health Sci, 2019, 1(1): 3-10. doi:10.1016/j.smhs.2019.08.006 |
| [5] | Yaribeygi H, Atkin SL, Simental-Mendía LE, et al. Molecular mechanisms by which aerobic exercise induces insulin sensitivity[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(8): 12385-92. doi:10.1002/jcp.28066 |
| [6] | 王 平, 李佳欣, 陈小龙, 等. 转录因子EB在有氧运动改善高脂饮食诱导小鼠骨骼肌胰岛素抵抗中的作用 [J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2024, 43(3): 193-204. |
| [7] | 李 楠, 史海燕, 周 越. 运动介导microRNAs改善慢性炎症及骨骼肌胰岛素抵抗的研究进展 [J]. 生命科学, 2022, 34(3): 324-31. |
| [8] | Li N, Shi H, Guo Q, et al. Aerobic exercise prevents chronic inflammation and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of high-fat diet mice[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14(18): 3730. doi:10.3390/nu14183730 |
| [9] | Quah S, Subramanian G, Tan JSL, et al. microRNAs: a symphony orchestrating evolution and disease dynamics[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2025, 31(1): 21-35. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2024.07.004 |
| [10] | Agbu P, Carthew RW. microRNA-mediated regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2021, 22(6): 425-38. doi:10.1038/s41580-021-00354-w |
| [11] | Wang J, Li L, Zhang Z, et al. Extracellular vesicles mediate the communication of adipose tissue with brain and promote cognitive impairment associated with insulin resistance[J]. Cell Metab, 2022, 34(9): 1264-79.e8. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2022.08.004 |
| [12] | Huang F, Zhu P, Wang J, et al. Postnatal overfeeding induces hepatic microRNA-221 expression and impairs the PI3K/AKT pathway in adult male rats[J]. Pediatr Res, 2021, 89(1): 143-9. doi:10.1038/s41390-020-0877-7 |
| [13] | Wilson HM. SOCS proteins in macrophage polarization and function[J]. Front Immunol, 2014, 5: 357. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00357 |
| [14] | Cai MC, Shi Y, Zheng TH, et al. Mammary epithelial cell derived exosomal miR-221 mediates M1 macrophage polarization via SOCS1/STATs to promote inflammatory response[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020, 83: 106493. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106493 |
| [15] | Li N, Zhang L, Guo Q, et al. Aerobic exercise improves inflammation and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle by regulating miR-221-3p via JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Front Physiol. 2025;16:1534911. doi:10.3389/fphys.2025.1534911 |
| [16] | Høydal MA, Wisløff U, Kemi OJ, et al. Running speed and maximal oxygen uptake in rats and mice: practical implications for exercise training[J]. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil, 2007, 14(6): 753-60. doi:10.1097/hjr.0b013e3281eacef1 |
| [17] | Hariri N, Thibault L. High-fat diet-induced obesity in animal models[J]. Nutr Res Rev, 2010, 23(2): 270-99. doi:10.1017/s0954422410000168 |
| [18] | Speakman JR. Use of high-fat diets to study rodent obesity as a model of human obesity[J]. Int J Obes: Lond, 2019, 43(8): 1491-2. doi:10.1038/s41366-019-0363-7 |
| [19] | Lichtenstein AH, Schwab US. Relationship of dietary fat to glucose metabolism[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2000, 150(2): 227-43. doi:10.1016/s0021-9150(99)00504-3 |
| [20] | Binwal M, Babu V, Israr KM, et al. Taxoids-rich extract from Taxus wallichiana alleviates high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance in C57BL/6 mice through inhibition of low-grade inflammation[J]. Inflammopharmacology, 2023, 31(1): 451-64. doi:10.1007/s10787-022-01119-3 |
| [21] | Villareal DT, Aguirre L, Gurney AB, et al. Aerobic or resistance exercise, or both, in dieting obese older adults[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 376(20): 1943-55. doi:10.1056/nejmoa1616338 |
| [22] | Brouwers B, Schrauwen-Hinderling VB, Jelenik T, et al. Exercise training reduces intrahepatic lipid content in people with and people without nonalcoholic fatty liver[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2018, 314(2): E165-73. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00266.2017 |
| [23] | Gopalan V, Yaligar J, Michael N, et al. A 12-week aerobic exercise intervention results in improved metabolic function and lower adipose tissue and ectopic fat in high-fat diet fed rats[J]. Biosci Rep, 2021, 41(1): BSR20201707. doi:10.1042/bsr20201707 |
| [24] | Yao F, Yu Y, Feng LJ, et al. Adipogenic miR-27a in adipose tissue upregulates macrophage activation via inhibiting PPARγ of insulin resistance induced by high-fat diet-associated obesity[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2017, 355(2): 105-12. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.03.060 |
| [25] | Kiran S, Kumar V, Kumar S, et al. Adipocyte, immune cells, and miRNA crosstalk: a novel regulator of metabolic dysfunction and obesity[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(5): 1004. doi:10.3390/cells10051004 |
| [26] | Ying W, Gao H, Dos Reis FCG, et al. miR-690, an exosomal-derived miRNA from M2-polarized macrophages, improves insulin sensitivity in obese mice[J]. Cell Metab, 2021, 33(4): 781-90.e5. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.12.019 |
| [27] | Galardi S, Mercatelli N, Giorda E, et al. miR-221 and miR-222 expression affects the proliferation potential of human prostate carcinoma cell lines by targeting p27Kip1[J]. J Biol Chem, 2007, 282(32): 23716-24. doi:10.1074/jbc.m701805200 |
| [28] | Wang T, Jiang L, Wei X, et al. Inhibition of miR-221 alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury via inactivation of SOCS1/NF‑κB signaling pathway[J]. Cell Cycle, 2019, 18(16): 1893-907. doi:10.1080/15384101.2019.1632136 |
| [29] | Li YY, Yan CH, Fan JH, et al. miR-221-3p targets Hif-1α to inhibit angiogenesis in heart failure[J]. Lab Investig, 2021, 101(1): 104-15. doi:10.1038/s41374-020-0450-3 |
| [30] | Wang N, Liang H, Zen K. Molecular mechanisms that influence the macrophage m1-m2 polarization balance[J]. Front Immunol, 2014, 5: 614. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00614 |
| [31] | Liu W, Long Q, Zhang W, et al. miRNA-221-3p derived from M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophage exosomes aggravates the growth and metastasis of osteosarcoma through SOCS3/JAK2/STAT3 axis[J]. Aging: Albany NY, 2021, 13(15): 19760-75. doi:10.18632/aging.203388 |
| [32] | Meerson A, Traurig M, Ossowski V, et al. Human adipose microRNA-221 is upregulated in obesity and affects fat metabolism downstream of leptin and TNF‑α[J]. Diabetologia, 2013, 56(9): 1971-9. doi:10.1007/s00125-013-2950-9 |
| [33] | Olefsky JM, Glass CK. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance[J]. Annu Rev Physiol, 2010, 72: 219-46. doi:10.1146/annurev-physiol-021909-135846 |
| [34] | Yan B, Ma H, Jiang S, et al. microRNA-221 restricts human cytomegalovirus replication via promoting type I IFN production by targeting SOCS1/NF-κB pathway[J]. Cell Cycle, 2019, 18(22): 3072-84. doi:10.1080/15384101.2019.1667706 |
| [35] | Liau NPD, Laktyushin A, Lucet IS, et al. The molecular basis of JAK/STAT inhibition by SOCS1[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 1558. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-04013-1 |
| [36] | Dodington DW, Desai HR, Woo M. JAK/STAT-emerging players in metabolism[J]. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2018, 29(1): 55-65. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2017.11.001 |
| [1] | Qin HU, Hua JIN. Qingshen Granules improves renal function of patients with chronic kidney disease damp-heat syndrome by activating the miR-23b and Nrf2 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1867-1879. |
| [2] | Zhaojun ZHANG, Qiong WU, Miaomiao XIE, Ruyin YE, Chenchen GENG, Jiwen SHI, Qingling YANG, Wenrui WANG, Yurong SHI. Layered double hydroxide-loaded si-NEAT1 regulates paclitaxel resistance and tumor-associated macrophage polarization in breast cancer by targeting miR-133b/PD-L1 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1718-1731. |
| [3] | Shuyu TU, Xiangyu CHEN, Chenghui LI, Danping HUANG, Li ZHANG. Buyang Huanwu Decoction delays vascular aging in rats through exosomal miR-590-5p signal-mediated macrophage polarization [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1251-1259. |
| [4] | Minzhu NIU, Lixia YIN, Tong QIAO, Lin YIN, Keni ZHANG, Jianguo HU, Chuanwang SONG, Zhijun GENG, Jing LI. Ecliptasaponin A ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice by suppressing M1 macrophage polarization via inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1297-1306. |
| [5] | Jiawen YU, Yi ZHOU, Chunmei QIAN, Lan MU, Renye QUE. Effects of liver fibrosis induced by iron overload on M2 polarization of macrophages in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 684-691. |
| [6] | Qian ZHANG, Bowen LIU, Li LEI, Ye WANG, Xinyue ZHANG, Zhangkun MAO, Peng TANG, Jinmei ZHANG, Jiayi YANG, Yanxi PENG, Ze LIU. SERPINE1 overexpression promotes proliferation and paclitaxel resistance of triple-negative breast cancer cells by inducing M2 macrophage polarization [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2551-2560. |
| [7] | Xinxin LIU, Yingrui XU, Hongna SHENG, Hao LIU. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell grafting alleviates inflammatory response in type 1 diabetic mice by suppressing M1 macrophage polarization through Chi3l1 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2738-2746. |
| [8] | Zhiliang CHEN, Yonggang YANG, Xia HUANG, Yan CHENG, Yuan QU, Qiqi HENG, Yujia FU, Kewei LI, Ning GU. Differential expressions of exosomal miRNAs in patients with chronic heart failure and hyperuricemia: diagnostic values of miR-27a-5p and miR-139-3p [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 43-51. |
| [9] | Xueli ZHOU, Hua LI, Qingyu CHEN, Meina JIN, Haibo LI, Wei BAI, Chuxuan JIA, Cuiying WEI. Effects of chronic intermittent hypoxia and reoxygenation on insulin resistance and skeletal muscle miR-27a-3p/PPARγ/IRS1/PI3K/AKT expressions in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1729-1737. |
| [10] | Jing XIAO, Ying LI, Min FANG, Hong GONG, Wen LI, Chunyan ZHANG, Fangyao CHEN, Yan ZHANG, Tuo HAN. Triglyceride-glucose index in non-obese individuals: its association with and predictive value for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1266-1271. |
| [11] | Guoxin LIANG, Hongyue TANG, Chang GUO, Mingming ZHANG. MiR-224-5p overexpression inhibits oxidative stress by regulating the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 axis to attenuate hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte injury [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1173-1181. |
| [12] | HU Sigan, CHENG Zengwei, LI Min, GAO Shiyi, GAO Dasheng, KANG Pinfang. Correlation between insulin resistance and coronary collateral circulation in patients with chronic total coronary occlusion [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(4): 780-786. |
| [13] | FANG Fusheng, WANG Ning, LIU Xingyu, WANGWei, SUN Jing, LI Hong, SUN Banruo, GU Zhaoyan, FU Xiaomin, YAN Shuangtong. Value of C-peptide-based insulin resistance index for evaluating correlation between insulin resistance and serum uric acid level in individuals undergoing health examination [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(9): 1509-1514. |
| [14] | LIN Jiayi, LOU Anni, LI Xu. Lipopolysaccharide stimulates macrophages to secrete exosomes containing miR-155-5p to promote activation and migration of hepatic stellate cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(6): 994-1001. |
| [15] | LI jingyi, YANG Siyuan, HAN Zhen, JIANG Tianle, ZHU Yao, ZHOU Zihang, ZHOU Jingping. Akt2 inhibitor promotes M2 macrophage polarization in rats with periapical inflammation by reducing miR-155-5p expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(4): 568-576. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||