Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 1867-1879.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.07
Received:2025-03-27
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Hua JIN
E-mail:qinhu992024@163.com;ya790312@sina.com
Supported by:Qin HU, Hua JIN. Qingshen Granules improves renal function of patients with chronic kidney disease damp-heat syndrome by activating the miR-23b and Nrf2 pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1867-1879.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.07
| Group | Age (year) | Course | Gender | CKD staging | Underlying medical conditions | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | 3 | 4 | 5 | Chronic nephritis | Hypertension | Diabetes | Polycystic kidney disease | |||||
| Normal (n=20) | 51.55±8.17 | - | 11 | 9 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Control (n=30) | 48.73±9.13 | 3.74±1.92 | 17 | 13 | 1 | 17 | 12 | 12 | 7 | 7 | 4 | ||
| Observation (n=30) | 50.03±9.64 | 3.91±2.04 | 16 | 14 | 5 | 11 | 14 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 4 | ||
Tab.1 Comparison of general data of the participants
| Group | Age (year) | Course | Gender | CKD staging | Underlying medical conditions | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | 3 | 4 | 5 | Chronic nephritis | Hypertension | Diabetes | Polycystic kidney disease | |||||
| Normal (n=20) | 51.55±8.17 | - | 11 | 9 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Control (n=30) | 48.73±9.13 | 3.74±1.92 | 17 | 13 | 1 | 17 | 12 | 12 | 7 | 7 | 4 | ||
| Observation (n=30) | 50.03±9.64 | 3.91±2.04 | 16 | 14 | 5 | 11 | 14 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 4 | ||
| miRNA_id | log2 Fold Change | qValue | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-let-7b-3p | 8.206372 | 1.35×10-5 | Up |
| hsa-let-7f-2-3p | 9.086326 | 0.0016 | Up |
| …… | …… | …… | …… |
| hsa-miR-20a-5p | 10.3875 | 1.37×10-5 | Up |
| hsa-miR-21-5p | 5.334294 | 0.000371 | Up |
| hsa-miR-23b-5p | -4.50953 | 0.003782 | Down |
| hsa-miR-26b-5p | 4.938481 | 0.003172 | Up |
| hsa-miR-27a-3p | 4.084065 | 0.005144 | Up |
| hsa-miR-30d-3p | -2.49269 | 0.049808 | Down |
Tab.2 Expression of differential miRNAs between the two groups
| miRNA_id | log2 Fold Change | qValue | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-let-7b-3p | 8.206372 | 1.35×10-5 | Up |
| hsa-let-7f-2-3p | 9.086326 | 0.0016 | Up |
| …… | …… | …… | …… |
| hsa-miR-20a-5p | 10.3875 | 1.37×10-5 | Up |
| hsa-miR-21-5p | 5.334294 | 0.000371 | Up |
| hsa-miR-23b-5p | -4.50953 | 0.003782 | Down |
| hsa-miR-26b-5p | 4.938481 | 0.003172 | Up |
| hsa-miR-27a-3p | 4.084065 | 0.005144 | Up |
| hsa-miR-30d-3p | -2.49269 | 0.049808 | Down |
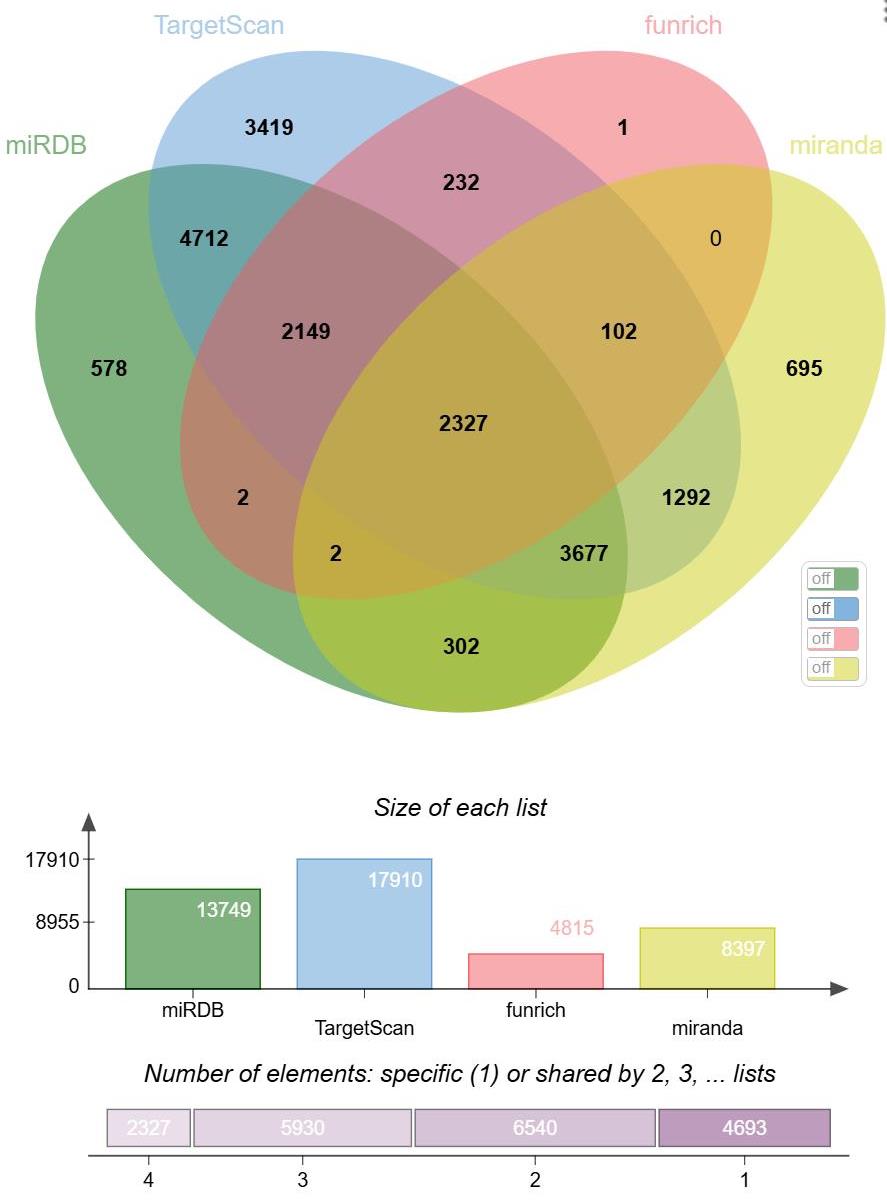
Fig.2 Venn diagram of miRNA target gene prediction. 1: Elements exist only in a single list (one of miRDB, TargetScan, funrich, miranda) and are not shared with other lists. 2: Elements exist in two lists simultaneously. 3: Elements exist in three lists simultaneously. 4: Elements exist in four lists simultaneously.
| Key ingredients | Target | Affinity (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| ACTB | -2.88 | |
| PTEN | -2.55 | |
| Quercetin | PPARG | -5.31 |
| PIK3CA | -4.9 | |
Kaempferol Apigenin Luteolin | NFE2L2 ACTB PTEN PPARG PIK3CA NFE2L2 ACTB PTEN PPARG PIK3CA NFE2L2 ACTB PTEN PPARG PIK3CA NFE2L2 | -4.8 -3.61 -3.5 -4.1 -2.63 -4.96 -3.21 -2.34 -4.13 -4.05 -6.0 -4.34 -3.58 -4.26 -4.19 -5.38 |
Tab.3 Binding energy of the active ingredients to the core targets
| Key ingredients | Target | Affinity (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| ACTB | -2.88 | |
| PTEN | -2.55 | |
| Quercetin | PPARG | -5.31 |
| PIK3CA | -4.9 | |
Kaempferol Apigenin Luteolin | NFE2L2 ACTB PTEN PPARG PIK3CA NFE2L2 ACTB PTEN PPARG PIK3CA NFE2L2 ACTB PTEN PPARG PIK3CA NFE2L2 | -4.8 -3.61 -3.5 -4.1 -2.63 -4.96 -3.21 -2.34 -4.13 -4.05 -6.0 -4.34 -3.58 -4.26 -4.19 -5.38 |
| Group | TCM syndrome scores | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | ||
| Control | 11.98±1.69 | 10.87±2.14 | |
| Observation | 12.60±1.11 | 8.53±2.19*▲ | |
Tab.4 Comparison of TCM syndrome scores (n=30, Mean±SD)
| Group | TCM syndrome scores | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | ||
| Control | 11.98±1.69 | 10.87±2.14 | |
| Observation | 12.60±1.11 | 8.53±2.19*▲ | |
| Group | Scr (μmol/L) | eGFR(mL/min) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | △Scr | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | △eGFR | |||
| Control | 328.51±109.32 | 322.25±110.45 | 6.26±20.57 | 19.33±9.20 | 19.78±9.19 | 0.45±1.51 | ||
| Observation | 317.81±114.33 | 298.47±108.61* | 19.34±23.86▲ | 20.02±9.31 | 21.68±10.15* | 1.65±2.15▲ | ||
Tab.5 Comparison of Scr and eGFR between the two groups of patients (n=30, Mean±SD)
| Group | Scr (μmol/L) | eGFR(mL/min) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | △Scr | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | △eGFR | |||
| Control | 328.51±109.32 | 322.25±110.45 | 6.26±20.57 | 19.33±9.20 | 19.78±9.19 | 0.45±1.51 | ||
| Observation | 317.81±114.33 | 298.47±108.61* | 19.34±23.86▲ | 20.02±9.31 | 21.68±10.15* | 1.65±2.15▲ | ||
| Group | n | Nrf2/β-actin | HO-1/β-actin | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | |||
| Normal | 20 | 1.04±0.06 | - | 1.10±0.09 | - | |
| Control | 30 | 0.42±0.07△ | 0.48±0.09* | 0.32±0.06 | 0.36±0.11* | |
| Observation | 30 | 0.45±0.07△ | 0.55±0.12*▲ | 0.33±0.06 | 0.42±0.10*▲ | |
Tab.6 Comparison of Nrf2 and HO-1 in PBMCs among the 3 groups (Mean±SD)
| Group | n | Nrf2/β-actin | HO-1/β-actin | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | |||
| Normal | 20 | 1.04±0.06 | - | 1.10±0.09 | - | |
| Control | 30 | 0.42±0.07△ | 0.48±0.09* | 0.32±0.06 | 0.36±0.11* | |
| Observation | 30 | 0.45±0.07△ | 0.55±0.12*▲ | 0.33±0.06 | 0.42±0.10*▲ | |
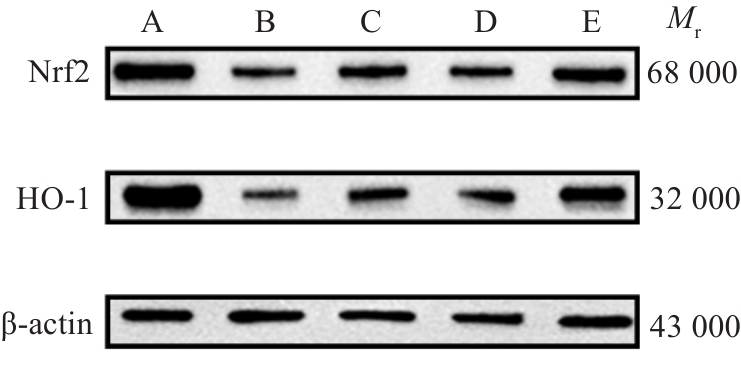
Fig.9 Nrf2 and HO-1 in the PBMCs in each group. A:Normal group. B: Control group(Pre-treatment).C: Control group (Post-treatment). D:Observation group(Pre-treatment). E: Observation group(Post-treatment).
| Group | n | ROS (U/mL) | PON-1 (U/L) | AOPP (μmol/L) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | ||||
| Normal | 20 | 21707.25±844.70 | - | 79.40±5.25 | - | 2045.52±156.85 | - | ||
| Control | 30 | 36181.78±2904.00△ | 35090.40±3001.58* | 47.94±9.58 | 50.84±12.18* | 3596.73±236.77 | 3493.55±236.38* | ||
| Observation | 30 | 36019.23±2370.14△ | 30176.07±2850.72*▲ | 51.28±9.24 | 60.50±13.29*▲ | 3527.61±347.18 | 2825.24±311.16*▲ | ||
Tab.7 Comparison of serum ROS, PON-1 and AOPP levels among the 3 groups before and after treatment (Mean±SD)
| Group | n | ROS (U/mL) | PON-1 (U/L) | AOPP (μmol/L) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | ||||
| Normal | 20 | 21707.25±844.70 | - | 79.40±5.25 | - | 2045.52±156.85 | - | ||
| Control | 30 | 36181.78±2904.00△ | 35090.40±3001.58* | 47.94±9.58 | 50.84±12.18* | 3596.73±236.77 | 3493.55±236.38* | ||
| Observation | 30 | 36019.23±2370.14△ | 30176.07±2850.72*▲ | 51.28±9.24 | 60.50±13.29*▲ | 3527.61±347.18 | 2825.24±311.16*▲ | ||
| Group | n | miR-23b-5p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | ||
| Normal | 20 | 1.05±0.19 | - |
| Control | 30 | 0.35±0.09△ | 0.39±0.14 |
| Observation | 30 | 0.38±0.11△ | 0.53±0.19*▲ |
Tab.8 Comparison of miR-23b-5p in PBMCs among the 3 groups (Mean±SD)
| Group | n | miR-23b-5p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | ||
| Normal | 20 | 1.05±0.19 | - |
| Control | 30 | 0.35±0.09△ | 0.39±0.14 |
| Observation | 30 | 0.38±0.11△ | 0.53±0.19*▲ |
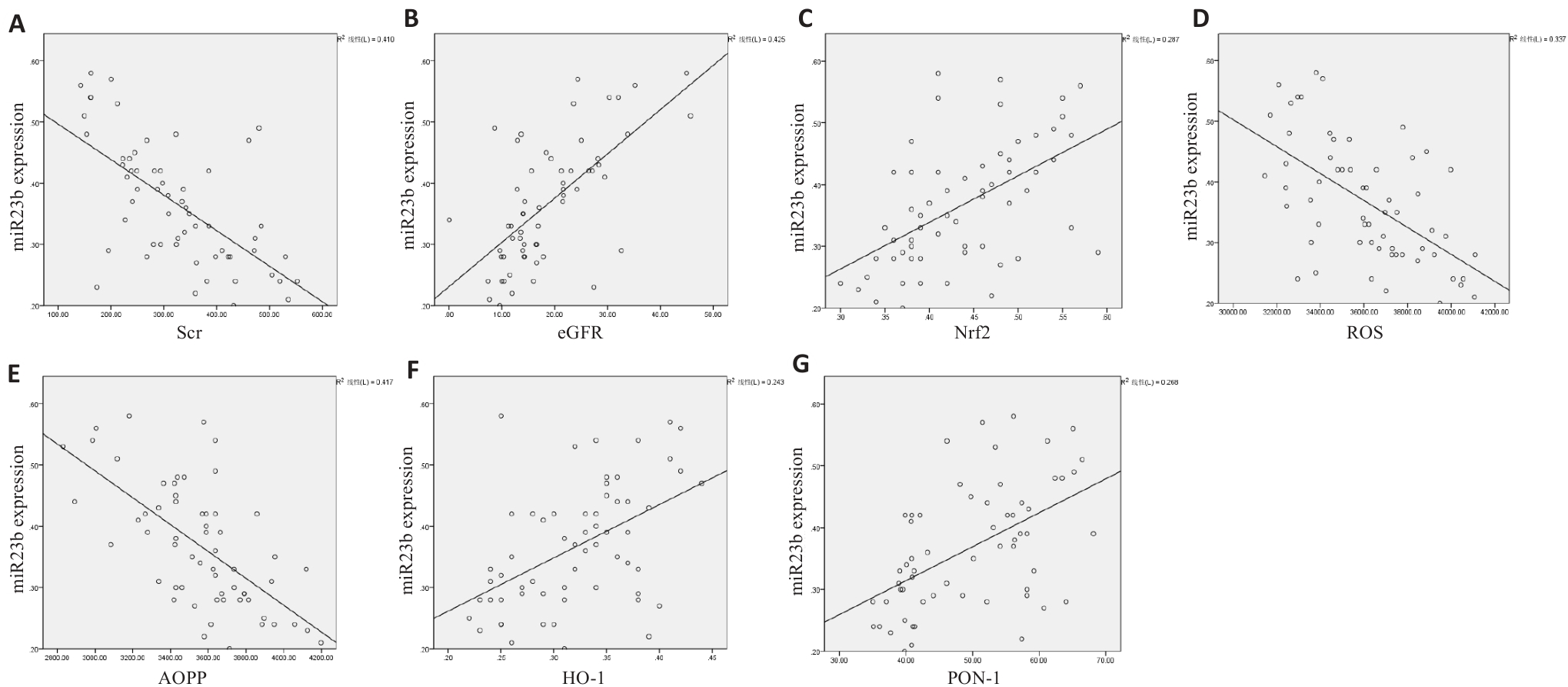
Fig10 Correlation analysis of miR-23b-5p expression. A: miR-23b-5p and Scr (negative correlation). B: miR-23b-5p and eGFR (positive correlation). C: miR-23b-5p and Nrf2 (positive correlation). D: miR-23b-5p and ROS (negative correlation). E: miR-23b-5p and AOPP (negative correlation). F: miR-23b-5p and HO-1 (positive correlation). G: miR-23b-5p and PON1 (positive correlation).
| [1] | GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10225): 709-33. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(19)32977-0 |
| [2] | Ruiz-Ortega M, Rayego-Mateos S, Lamas S, et al. Targeting the progression of chronic kidney disease[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2020, 16(5): 269-88. doi:10.1038/s41581-019-0248-y |
| [3] | Zhao H, Ma SX, Shang YQ, et al. microRNAs in chronic kidney disease[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2019, 491: 59-65. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2019.01.008 |
| [4] | Aranda-Rivera AK, Cruz-Gregorio A, Pedraza-Chaverri J, et al. Nrf2 activation in chronic kidney disease: promises and pitfalls[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2022, 11(6): 1112. doi:10.3390/antiox11061112 |
| [5] | DiseaseKidney: Improving Global Outcomes CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease[J]. Kidney Int, 2024, 105(4S): S117-314. |
| [6] | 王亿平, 陈 芳, 王 东, 等. 清肾颗粒对慢性肾衰竭湿热证患者氧化应激的干预作用[J]. 中成药, 2017, 39(1): 46-50. |
| [7] | 金 华, 王亿平, 王 东, 等. 清肾颗粒对慢性肾衰竭湿热证患者氧化应激介导的NF-κB信号通路活化的影响[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2017, 28(12): 2841-3. |
| [8] | 李文娟, 王亿平. 湿热证与慢性肾衰竭病证关系浅析[J]. 安徽中医学院学报, 2004, 23(2): 58-9. |
| [9] | 邵光新.慢性肾功能衰竭中医证候学临床回顾性调查研究[D].合肥:安徽中医学院,2007. |
| [10] | 慢性肾脏病蛋白营养治疗专家共识[J]. 国外医学 内分泌学分册, 2005, 25(6): 437-8. |
| [11] | 中国高血压防治指南修订委员会, 高血压联盟(中 国, 中国医疗保健国际交流促进会高血压病学分会, 等. 中国高血压防治指南(2024年修订版)[J]. 中华高血压杂志: 中英文, 2024, 32(7): 603-700. |
| [12] | 孙雪峰. 《中国肾性贫血诊疗的临床实践指南》解读[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2021, 41(9): 785-8. |
| [13] | National Clinical Research Center of Kidney Diseases. 中国慢性肾脏病矿物质和骨异常诊治指南概要[J]. 肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志, 2019, 28(1): 52-7. |
| [14] | Lai KM, Wang JJ, Lin SY, et al. Sensing of mitochondrial DNA by ZBP1 promotes RIPK3-mediated necroptosis and ferroptosis in response to diquat poisoning[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2024, 31(5): 635-50. doi:10.1038/s41418-024-01279-5 |
| [15] | Zhang JC, Zhao XM, Zhu HL, et al. Apigenin protects against renal tubular epithelial cell injury and oxidative stress by high glucose via regulation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2019, 25: 5280-8. doi:10.12659/msm.915038 |
| [16] | Jin H, Wang YP, Wang D, et al. Effects of Qingshen Granules on the oxidative stress-NF/kB signal pathway in unilateral ureteral obstruction rats[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2018, 2018: 4761925. doi:10.1155/2018/4761925 |
| [17] | Lin DW, Hsu YC, Chang CC, et al. Insights into the molecular mechanisms of NRF2 in kidney injury and diseases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(7): 6053. doi:10.3390/ijms24076053 |
| [18] | Ryoo IG, Shin DH, Kang KS, et al. Involvement of Nrf2-GSH signaling in TGFβ1-stimulated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition changes in rat renal tubular cells[J]. Arch Pharm Res, 2015, 38(2): 272-81. doi:10.1007/s12272-014-0380-y |
| [19] | Wang J, Zhu HB, Huang LQ, et al. Nrf2 signaling attenuates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and renal interstitial fibrosis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathways[J]. Exp Mol Pathol, 2019, 111: 104296. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104296 |
| [20] | 陈 诺, 金 华, 呼 琴, 等. 清肾颗粒对腺嘌呤致肾纤维化大鼠Nrf2/ARE信号通路及氧化应激的干预作用[J]. 中医药临床杂志, 2023, 35(5): 976-82. |
| [21] | Yu DM, Yang XH, Zhu Y, et al. Knockdown of plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 (PVT1) inhibits high glucose-induced proliferation and renal fibrosis in HRMCs by regulating miR-23b-3p/early growth response factor 1 (EGR1)[J]. Endocr J, 2021, 68(5): 519-29. doi:10.1507/endocrj.ej20-0642 |
| [22] | Zhao BH, Li HZ, Liu JT, et al. microRNA-23b targets ras GTPase-activating protein SH3 domain-binding protein 2 to alleviate fibrosis and albuminuria in diabetic nephropathy[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2016, 27(9): 2597-608. doi:10.1681/asn.2015030300 |
| [23] | Liu HF, Wang XH, Liu SF, et al. Effects and mechanism of miR-23b on glucose-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2016, 70: 149-60. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2015.11.016 |
| [24] | Li HZ, Chen ZC, Chen WT, et al. microRNA-23b-3p deletion induces an IgA nephropathy-like disease associated with dysregulated mucosal IgA synthesis[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2021, 32(10): 2561-78. doi:10.1681/asn.2021010133 |
| [25] | Li M, Peng YF, Chen WJ, et al. Active Nrf2 signaling flexibly regulates HO-1 and NQO-1 in hypoxic Gansu Zokor (Eospalax cansus)[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol, 2023, 264: 110811. doi:10.1016/j.cbpb.2022.110811 |
| [26] | Zhao YF, Fan XT, Wang QM, et al. ROS promote hyper-methylation of NDRG2 promoters in a DNMTS-dependent manner: Contributes to the progression of renal fibrosis[J]. Redox Biol, 2023, 62: 102674. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2023.102674 |
| [27] | Xiang Q, Cheng ZR, Wang JT, et al. Allicin attenuated advanced oxidation protein product-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial apoptosis in human nucleus pulposus cells[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2020, 2020: 6685043. doi:10.1155/2020/6685043 |
| [28] | Zuo J, Chaykovska L, Chu C, et al. Head-to-head comparison of oxidative stress biomarkers for all-cause mortality in hemodialysis patients[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2022, 11(10): 1975. doi:10.3390/antiox11101975 |
| [29] | Morris G, Puri BK, Bortolasci CC, et al. The role of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, apolipoprotein A and paraoxonase-1 in the pathophysiology of neuroprogressive disorders[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2021, 125: 244-63. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.02.037 |
| [1] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | Liming WANG, Hongrui CHEN, Yan DU, Peng ZHAO, Yujie WANG, Yange TIAN, Xinguang LIU, Jiansheng LI. Yiqi Zishen Formula ameliorates inflammation in mice with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [3] | Yinfu ZHU, Yiran LI, Yi WANG, Yinger HUANG, Kunxiang GONG, Wenbo HAO, Lingling SUN. Therapeutic mechanism of hederagenin, an active component in Guizhi Fuling Pellets, against cervical cancer in nude mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [4] | Lijun HE, Xiaofei CHEN, Chenxin YAN, Lin SHI. Inhibitory effect of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction against non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and the possible molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [5] | Guoyong LI, Renling LI, Yiting LIU, Hongxia KE, Jing LI, Xinhua WANG. Therapeutic mechanism of Arctium lappa extract for post-viral pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis: a metabolomics, network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [6] | Liping GUAN, Yan YAN, Xinyi LU, Zhifeng LI, Hui GAO, Dong CAO, Chenxi HOU, Jingyu ZENG, Xinyi LI, Yang ZHAO, Junjie WANG, Huilong FANG. Compound Centella asiatica formula alleviates Schistosoma japonicum-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting the inflammation-fibrosis cascade via regulating the TLR4/MyD88 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [7] | Peipei TANG, Yong TAN, Yanyun YIN, Xiaowei NIE, Jingyu HUANG, Wenting ZUO, Yuling LI. Tiaozhou Ziyin recipe for treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency: efficacy, safety and mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [8] | Xiaotao LIANG, Yifan XIONG, Xueqi LIU, Xiaoshan LIANG, Xiaoyu ZHU, Wei XIE. Huoxue Shufeng Granule alleviates central sensitization in chronic migraine mice via TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| [9] | Niandong RAN, Jie LIU, Jian XU, Yongping ZHANG, Jiangtao GUO. n-butanol fraction of ethanol extract of Periploca forrestii Schltr.: its active components, targets and pathways for treating Alcheimer's disease in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 785-798. |
| [10] | Haonan¹ XU, Fang³ ZHANG, Yuying² HUANG, Qisheng⁴ YAO, Yueqin⁴ GUAN, Hao CHEN. Thesium chinense Turcz. alleviates antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice by modulating gut microbiota structure and regulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [11] | Junjie GAO, Kai YE, Jing WU. Quercetin inhibits proliferation and migration of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells by regulating TP53 gene [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [12] | Ying LIU, Borui LI, Yongcai LI, Lubo CHANG, Jiao WANG, Lin YANG, Yonggang YAN, Kai QV, Jiping LIU, Gang ZHANG, Xia SHEN. Jiawei Xiaoyao Pills improves depression-like behavior in rats by regulating neurotransmitters, inhibiting inflammation and oxidation and modulating intestinal flora [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 347-358. |
| [13] | Qiao CHU, Xiaona WANG, Jiaying XU, Huilin PENG, Yulin ZHAO, Jing ZHANG, Guoyu LU, Kai WANG. Pulsatilla saponin D inhibits invasion and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells through multiple targets and pathways [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [14] | Xiupeng LONG, Shun TAO, Shen YANG, Suyun LI, Libing RAO, Li LI, Zhe ZHANG. Quercetin improves heart failure by inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis via suppressing the MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 187-196. |
| [15] | Zhiliang CHEN, Yonggang YANG, Xia HUANG, Yan CHENG, Yuan QU, Qiqi HENG, Yujia FU, Kewei LI, Ning GU. Differential expressions of exosomal miRNAs in patients with chronic heart failure and hyperuricemia: diagnostic values of miR-27a-5p and miR-139-3p [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 43-51. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
