Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 313-321.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.02.12
Junjie GAO( ), Kai YE, Jing WU(
), Kai YE, Jing WU( )
)
Received:2024-09-03
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-03-03
Contact:
Jing WU
E-mail:631517383@qq.com;wjwjwj1973@126.com
Supported by:Junjie GAO, Kai YE, Jing WU. Quercetin inhibits proliferation and migration of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells by regulating TP53 gene[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 313-321.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.02.12
| Exposure | Outcome | Gen | Method | Nsnp | b | Se | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9816_37_ISOC1_ISOC1 | KIRC | ISOC1 | IVW | 8 | 0.736746 | 0.171048 | 1.65E-05 |
| 6354_13_HEPHL1_HPHL1 | KIRC | HEPHL1 | IVW | 5 | -1.28851 | 0.310833 | 3.39E-05 |
| 17742_2_RRAS_RRAS | KIRC | RRAS | IVW | 5 | -1.33358 | 0.325935 | 4.29E-05 |
| 12621_55_PPP2R1A_PP2AAA | KIRC | PPP2R1A | IVW | 4 | -0.9648 | 0.243754 | 7.56E-05 |
| 5345_51_CKAP2_CKAP2 | KIRC | CKAP2 | IVW | 15 | -0.66094 | 0.169567 | 9.71E-05 |
| 12807_89_ARHGAP30_RHG30 | KIRC | ARHGAP30 | IVW | 3 | 1.721247 | 0.446005 | 0.000114 |
| 6123_69_TP53_p53 | KIRC | TP53 | IVW | 7 | 1.201512 | 0.311593 | 0.000115 |
| 9511_61_NXPH2_NXPH2 | KIRC | NXPH2 | IVW | 18 | -0.39638 | 0.103952 | 0.000137 |
| 6388_21_CCDC126_CC126 | KIRC | CCDC126 | IVW | 18 | -0.46547 | 0.124775 | 0.000191 |
| 13673_21_CCT7_TCPH | KIRC | CCT7 | IVW | 4 | -1.0039 | 0.269598 | 0.000196 |
| 7083_74_MATN4_MATN4 | KIRC | MATN4 | IVW | 7 | 0.634937 | 0.174364 | 0.000271 |
| 4568_17_SLITRK5_SLIK5 | KIRC | SLITRK5 | IVW | 12 | 0.821988 | 0.226306 | 0.000281 |
| 15460_9_DPP4_CD26 | KIRC | DPP4 | IVW | 3 | -1.75547 | 0.495302 | 0.000394 |
| 18408_26_ARF4_ARF4 | KIRC | ARF4 | IVW | 8 | -0.76964 | 0.218311 | 0.000423 |
| 8040_9_LEMD1_LEMD1 | KIRC | LEMD1 | IVW | 3 | -2.26505 | 0.647584 | 0.000469 |
| 6578_29_TNMD_TNMD | KIRC | TNMD | IVW | 3 | -1.94913 | 0.558892 | 0.000488 |
| 9012_1_PRPF6_PRP6 | KIRC | PRPF6 | IVW | 2 | -2.88761 | 0.828756 | 0.000493 |
| 8535_102_DMKN_Dermokine | KIRC | DMKN | IVW | 2 | -1.63853 | 0.479425 | 0.000632 |
| 8748_45_CD74_HG2A | KIRC | CD74 | IVW | 3 | -2.22233 | 0.652226 | 0.000656 |
| 10085_25_STAR_STAR | KIRC | STAR | IVW | 5 | -1.39378 | 0.418791 | 0.000874 |
| 18198_51_HBQ1_HBAT | KIRC | HBQ1 | IVW | 8 | -0.86326 | 0.261832 | 0.000977 |
| 18380_78_ALB_Albumin | KIRC | ALB | IVW | 11 | -0.41249 | 0.13172 | 0.001739 |
| 12587_65_ARL2_ARL2 | KIRC | ARL2 | IVW | 12 | -0.47391 | 0.152486 | 0.001884 |
| 12041_33_HSPA1L_HS71L | KIRC | HSPA1L | IVW | 11 | -0.55241 | 0.178001 | 0.001913 |
| 10842_7_GCNT4_GCNT4 | KIRC | GCNT4 | IVW | 4 | -1.6224 | 0.541404 | 0.00273 |
| 11160_56_RNF122_RN122 | KIRC | RNF122 | IVW | 6 | -0.87475 | 0.299384 | 0.00348 |
Tab.1 Result of Mendelian randomization between plasma proteins and ccRCC
| Exposure | Outcome | Gen | Method | Nsnp | b | Se | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9816_37_ISOC1_ISOC1 | KIRC | ISOC1 | IVW | 8 | 0.736746 | 0.171048 | 1.65E-05 |
| 6354_13_HEPHL1_HPHL1 | KIRC | HEPHL1 | IVW | 5 | -1.28851 | 0.310833 | 3.39E-05 |
| 17742_2_RRAS_RRAS | KIRC | RRAS | IVW | 5 | -1.33358 | 0.325935 | 4.29E-05 |
| 12621_55_PPP2R1A_PP2AAA | KIRC | PPP2R1A | IVW | 4 | -0.9648 | 0.243754 | 7.56E-05 |
| 5345_51_CKAP2_CKAP2 | KIRC | CKAP2 | IVW | 15 | -0.66094 | 0.169567 | 9.71E-05 |
| 12807_89_ARHGAP30_RHG30 | KIRC | ARHGAP30 | IVW | 3 | 1.721247 | 0.446005 | 0.000114 |
| 6123_69_TP53_p53 | KIRC | TP53 | IVW | 7 | 1.201512 | 0.311593 | 0.000115 |
| 9511_61_NXPH2_NXPH2 | KIRC | NXPH2 | IVW | 18 | -0.39638 | 0.103952 | 0.000137 |
| 6388_21_CCDC126_CC126 | KIRC | CCDC126 | IVW | 18 | -0.46547 | 0.124775 | 0.000191 |
| 13673_21_CCT7_TCPH | KIRC | CCT7 | IVW | 4 | -1.0039 | 0.269598 | 0.000196 |
| 7083_74_MATN4_MATN4 | KIRC | MATN4 | IVW | 7 | 0.634937 | 0.174364 | 0.000271 |
| 4568_17_SLITRK5_SLIK5 | KIRC | SLITRK5 | IVW | 12 | 0.821988 | 0.226306 | 0.000281 |
| 15460_9_DPP4_CD26 | KIRC | DPP4 | IVW | 3 | -1.75547 | 0.495302 | 0.000394 |
| 18408_26_ARF4_ARF4 | KIRC | ARF4 | IVW | 8 | -0.76964 | 0.218311 | 0.000423 |
| 8040_9_LEMD1_LEMD1 | KIRC | LEMD1 | IVW | 3 | -2.26505 | 0.647584 | 0.000469 |
| 6578_29_TNMD_TNMD | KIRC | TNMD | IVW | 3 | -1.94913 | 0.558892 | 0.000488 |
| 9012_1_PRPF6_PRP6 | KIRC | PRPF6 | IVW | 2 | -2.88761 | 0.828756 | 0.000493 |
| 8535_102_DMKN_Dermokine | KIRC | DMKN | IVW | 2 | -1.63853 | 0.479425 | 0.000632 |
| 8748_45_CD74_HG2A | KIRC | CD74 | IVW | 3 | -2.22233 | 0.652226 | 0.000656 |
| 10085_25_STAR_STAR | KIRC | STAR | IVW | 5 | -1.39378 | 0.418791 | 0.000874 |
| 18198_51_HBQ1_HBAT | KIRC | HBQ1 | IVW | 8 | -0.86326 | 0.261832 | 0.000977 |
| 18380_78_ALB_Albumin | KIRC | ALB | IVW | 11 | -0.41249 | 0.13172 | 0.001739 |
| 12587_65_ARL2_ARL2 | KIRC | ARL2 | IVW | 12 | -0.47391 | 0.152486 | 0.001884 |
| 12041_33_HSPA1L_HS71L | KIRC | HSPA1L | IVW | 11 | -0.55241 | 0.178001 | 0.001913 |
| 10842_7_GCNT4_GCNT4 | KIRC | GCNT4 | IVW | 4 | -1.6224 | 0.541404 | 0.00273 |
| 11160_56_RNF122_RN122 | KIRC | RNF122 | IVW | 6 | -0.87475 | 0.299384 | 0.00348 |
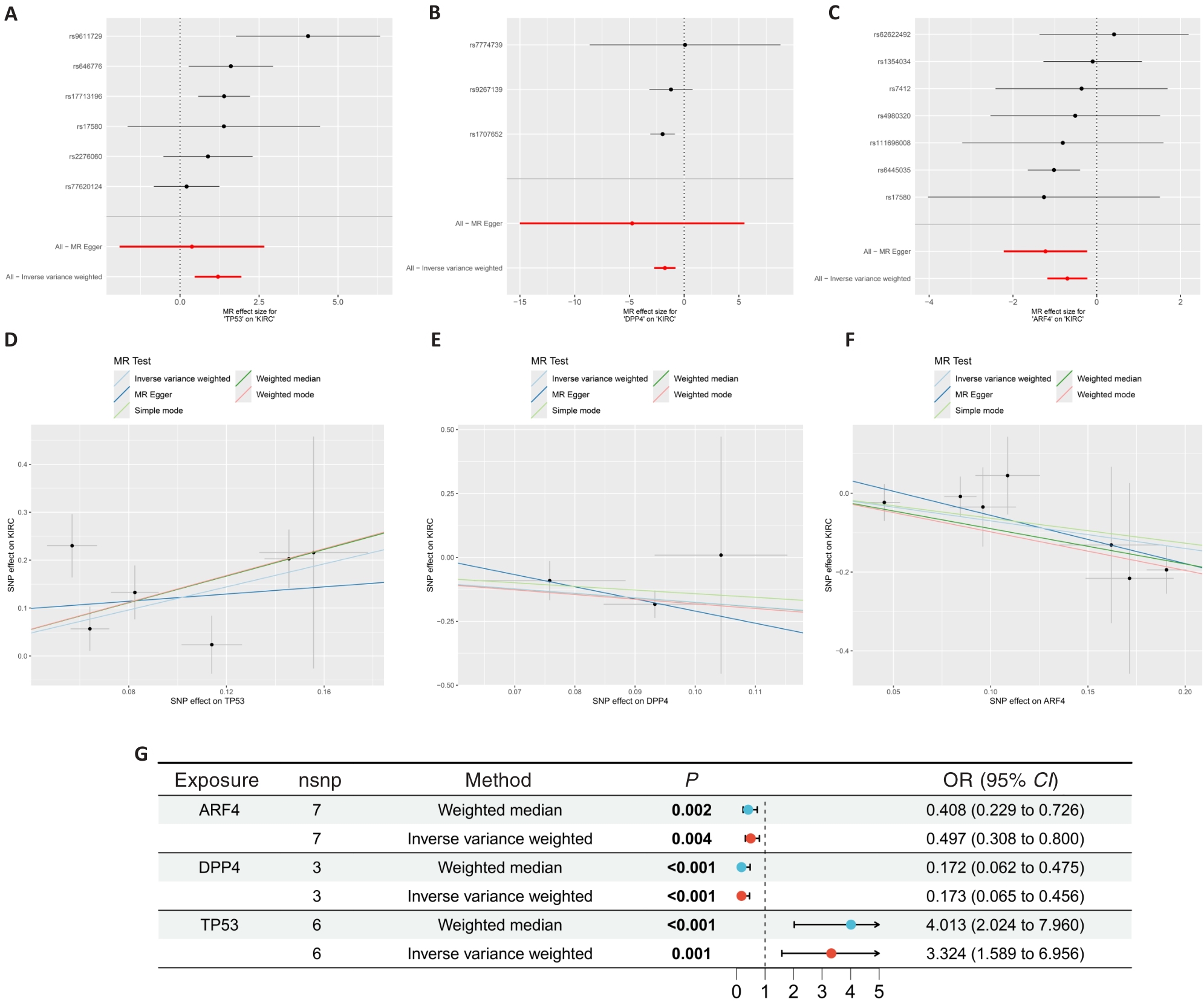
Fig.3 Mendelian randomization results on ccRCC. A-C: Forest plot showing the results of Mendelian randomization of the core genes. D-F: Scatter plots of Mendelian randomization results on core targets and ccRCC. G: Forest plot showing Mendelian randomization results of the core genes.
| Id.exposure | Outcome | Exposure | Method | Q | Q_pval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18408_26_ARF4_ARF4 | KIRC | ARF4 | MR Egger | 2.46079 | 0.782388313 |
| 18408_26_ARF4_ARF4 | KIRC | ARF4 | Inverse variance weighted | 3.836625 | 0.698774273 |
| 15460_9_DPP4_CD26 | KIRC | DPP4 | MR Egger | 0.27862 | 0.597607084 |
| 15460_9_DPP4_CD26 | KIRC | DPP4 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.608893 | 0.737531351 |
| 6123_69_TP53_p53 | KIRC | TP53 | MR Egger | 9.021383 | 0.060567227 |
| 6123_69_TP53_p53 | KIRC | TP53 | Inverse variance weighted | 10.29088 | 0.06740046 |
Tab. 2 Heterogeneity analysis of Mendelian randomization between plasma proteins and ccRCC
| Id.exposure | Outcome | Exposure | Method | Q | Q_pval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18408_26_ARF4_ARF4 | KIRC | ARF4 | MR Egger | 2.46079 | 0.782388313 |
| 18408_26_ARF4_ARF4 | KIRC | ARF4 | Inverse variance weighted | 3.836625 | 0.698774273 |
| 15460_9_DPP4_CD26 | KIRC | DPP4 | MR Egger | 0.27862 | 0.597607084 |
| 15460_9_DPP4_CD26 | KIRC | DPP4 | Inverse variance weighted | 0.608893 | 0.737531351 |
| 6123_69_TP53_p53 | KIRC | TP53 | MR Egger | 9.021383 | 0.060567227 |
| 6123_69_TP53_p53 | KIRC | TP53 | Inverse variance weighted | 10.29088 | 0.06740046 |
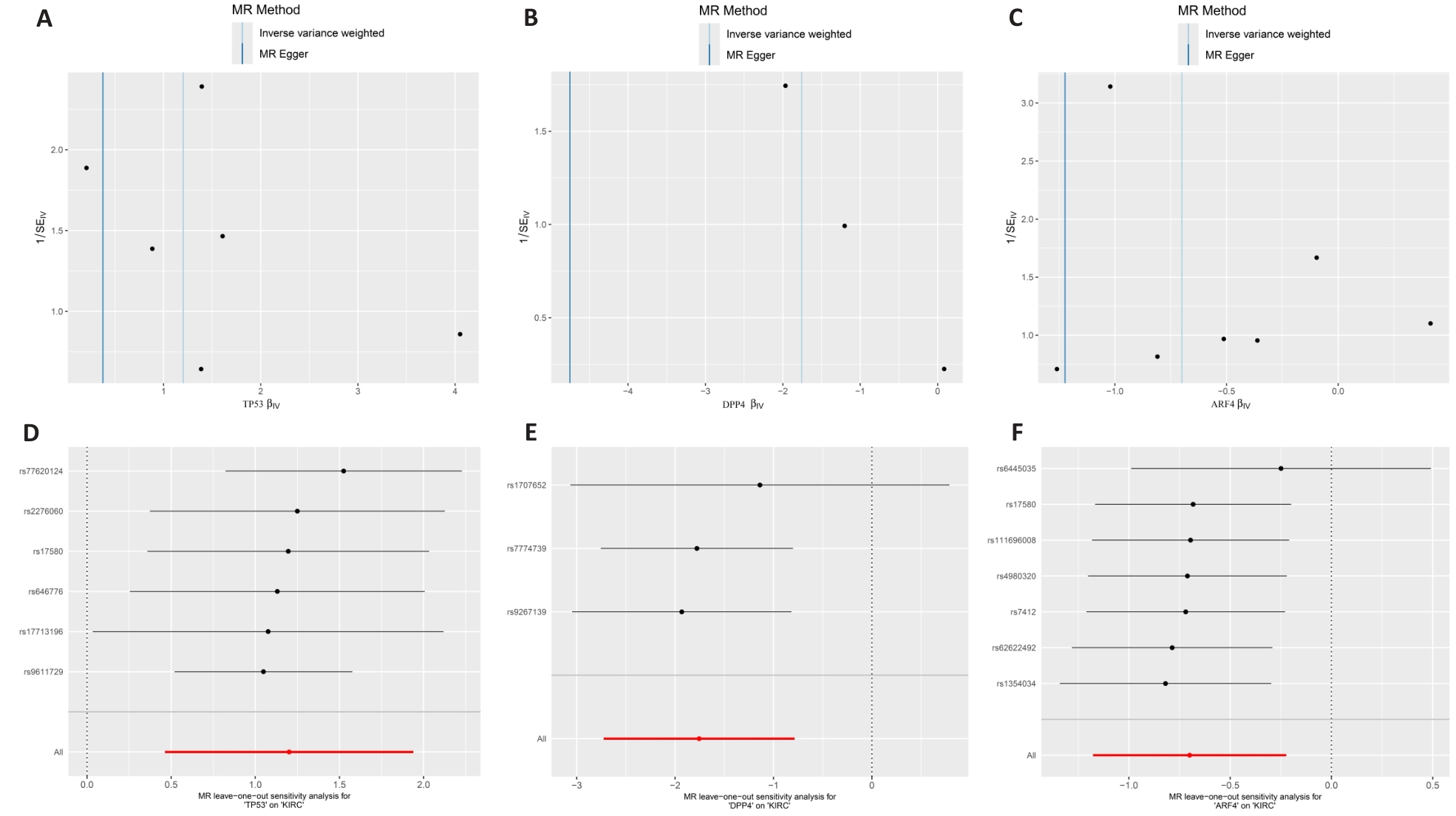
Fig.4 Sensitivity analysis of Mendelian randomization. A-C: MR funnel plot for core targets and ccRCC. D-F: Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis for potential core genes and ccRCC.
| Id.exposure | Outcome | Exposure | Egger_intercept | Se | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18408_26_ARF4_ARF4 | KIRC | ARF4 | 0.066322526 | 0.056543 | 0.293645 |
| 15460_9_DPP4_CD26 | KIRC | DPP4 | 0.264971682 | 0.461066 | 0.667936 |
| 6123_69_TP53_p53 | KIRC | TP53 | 0.08422687 | 0.112264 | 0.494821 |
Tab.3 Pleiotropy analysis of Mendelian randomization between plasma proteins and ccRCC
| Id.exposure | Outcome | Exposure | Egger_intercept | Se | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18408_26_ARF4_ARF4 | KIRC | ARF4 | 0.066322526 | 0.056543 | 0.293645 |
| 15460_9_DPP4_CD26 | KIRC | DPP4 | 0.264971682 | 0.461066 | 0.667936 |
| 6123_69_TP53_p53 | KIRC | TP53 | 0.08422687 | 0.112264 | 0.494821 |
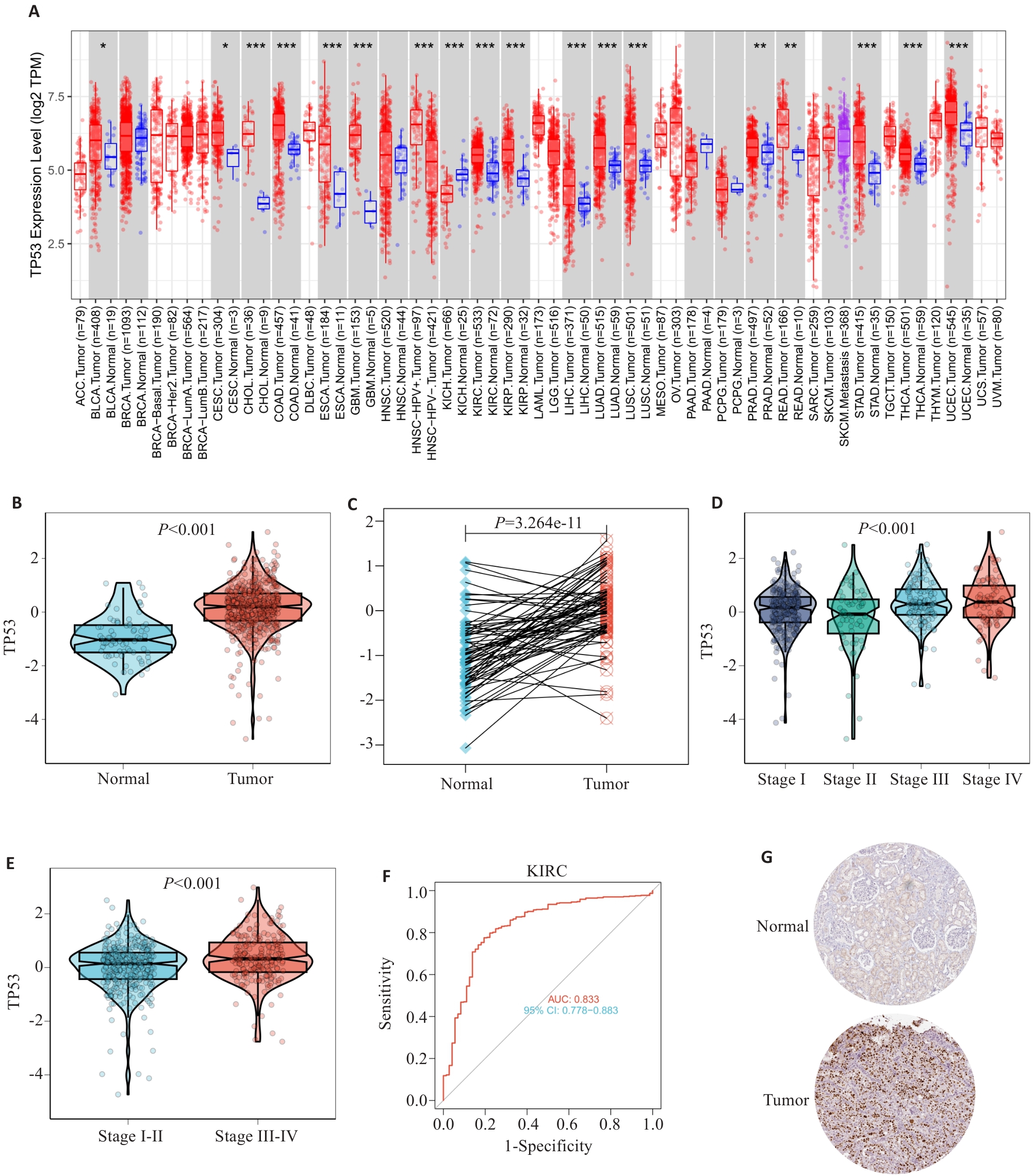
Fig.5 TP53 expression in ccRCC. A: TP53 mRNA evpression in different tumor samples. B: TP53 mRNA expression in ccRCC samples and normal tissues. C: TP53 mRNA expression in ccRCC and paired adjacent normal tissues. D,E: TP53 mRNA expression levels in different ccRCC clinical stages. F: Receiver operating characteristic analysis (ROC) of TP53 in patients with ccRCC (AUC=0.833). G: Immunohistochemical staining of TP53 in renal cancer tissues and normal renal tissues (Original magnification: ×20).
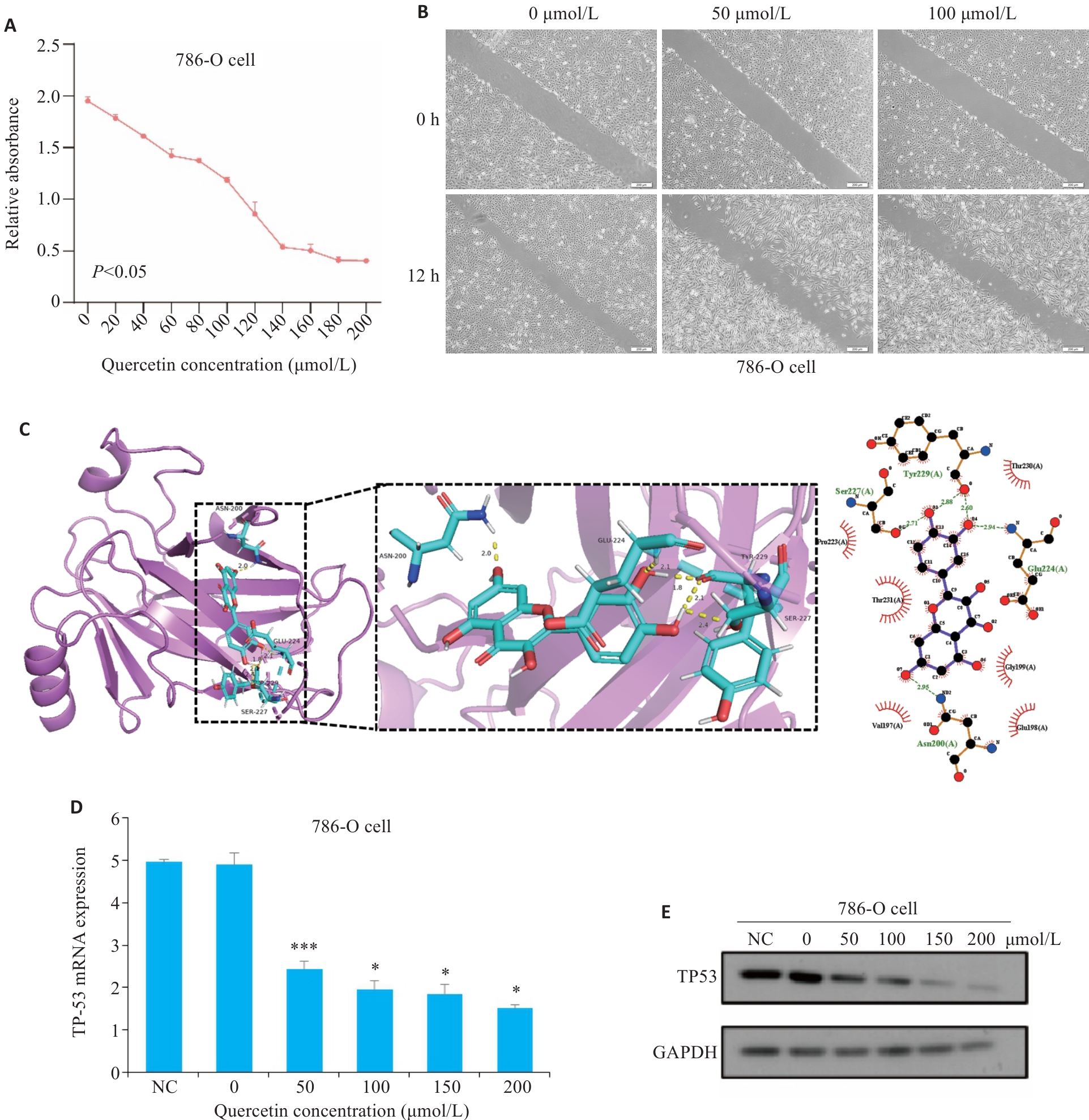
Fig.6 Cell experiments and molecular docking validation. A: Viability of 786-O cells measured using CCK-8 assay after 24 h of quercetin treatment. B: Wound healing assay for assessing migration capacity of 786-O cells after quercetin treatment for 12 h (scale bar=200 μm). C: Docking of quercetin with TP53 molecule. D: Effect of different concentrations of quercetin on TP53 mRNA expression in 786-O cells detected using RT-qPCR (*P<0.05,***P<0.001 vs 0 μmol/L). E: Effect of different concentrations of quercetin on TP53 protein expression in 786-O cells detected using Western blotting.
| 1 | Marston Linehan W, Schmidt LS, Crooks DR, et al. The metabolic basis of kidney cancer[J]. Cancer Discov, 2019, 9(8): 1006-21. |
| 2 | Singh D, Vignat J, Lorenzoni V, et al. Global estimates of incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in 2020: a baseline analysis of the WHO Global Cervical Cancer Elimination Initiative[J]. Lancet Glob Health, 2023, 11(2): e197-206. |
| 3 | Capitanio U, Montorsi F. Renal cancer[J]. Lancet, 2016, 387(10021): 894-906. |
| 4 | Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, et al. European association of urology guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: the 2022 update[J]. Eur Urol, 2022, 82(4): 399-410. |
| 5 | Motzer RJ, Penkov K, Haanen J, et al. Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 380(12): 1103-15. |
| 6 | Panossian A, Wikman G. Pharmacology of Schisandra chinensis bail.: an overview of Russian research and uses in medicine[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2008, 118(2): 183-212. |
| 7 | Li Y, Yao JY, Han CY, et al. Quercetin, inflammation and immunity[J]. Nutrients, 2016, 8(3): 167. |
| 8 | Lim H, Min DS, Yun HE, et al. Impressic acid from Acanthopanax koreanum, possesses matrix metalloproteinase-13 down-regulating capacity and protects cartilage destruction[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2017, 209: 73-81. |
| 9 | Wong CK. Simplifying electrocardiographic assessment in STEMI reperfusion management: Pros and cons[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2017, 227: 30-6. |
| 10 | Vandemoortele A, Babat P, Yakubu M, et al. Reactivity of free malondialdehyde during in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2017, 65(10): 2198-204. |
| 11 | Ru JL, Li P, Wang JN, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines[J]. J Cheminform, 2014, 6: 13. |
| 12 | Wang X, Shen YH, Wang SW, et al. PharmMapper 2017 update: a web server for potential drug target identification with a comprehensive target pharmacophore database[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45(W1): W356-60. |
| 13 | Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V. SwissTargetPrediction: updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47(W1): W357-64. |
| 14 | Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, et al. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018, 46(D1): D1074-82. |
| 15 | Gilson MK, Liu TQ, Baitaluk M, et al. BindingDB in 2015: a public database for medicinal chemistry, computational chemistry and systems pharmacology[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2016, 44(D1): D1045-53. |
| 16 | Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, et al. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility[J]. J Comput Chem, 2009, 30(16): 2785-91. |
| 17 | Seeliger D, de Groot BL. Ligand docking and binding site analysis with PyMOL and Autodock/Vina[J]. J Comput Aided Mol Des, 2010, 24(5): 417-22. |
| 18 | Larson AJ, David Symons J, Jalili T. Therapeutic potential of quercetin to decrease blood pressure: review of efficacy and mechanisms[J]. Adv Nutr, 2012, 3(1): 39-46. |
| 19 | Russo M, Spagnuolo C, Tedesco I, et al. Phytochemicals in cancer prevention and therapy: truth or dare[J]? Toxins, 2010, 2(4): 517-51. |
| 20 | Tang SM, Deng XT, Zhou J, et al. Pharmacological basis and new insights of quercetin action in respect to its anti-cancer effects[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 121: 109604. |
| 21 | Levine AJ. p53: 800 million years of evolution and 40 years of discovery[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2020, 20(8): 471-80. |
| 22 | Network CGAR. Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Nature, 2013, 499(7456): 43-9. |
| 23 | Wang B, Song Q, Wei YA, et al. Comprehensive investigation into cuproptosis in the characterization of clinical features, molecular characteristics, and immune situations of clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 948042. |
| 24 | Paul JY, Harding R, Tushemereirwe W, et al. Banana21: from gene discovery to deregulated golden bananas[J]. Front Plant Sci, 2018, 9: 558. |
| 25 | D’Andrea G. Quercetin: a flavonol with multifaceted therapeutic applications[J]? Fitoterapia, 2015, 106: 256-71. |
| 26 | Li FZ, Aljahdali IAM, Zhang RY, et al. Kidney cancer biomarkers and targets for therapeutics: survivin (BIRC5), XIAP, MCL-1, HIF1α, HIF2α, NRF2, MDM2, MDM4, p53, KRAS and AKT in renal cell carcinoma[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2021, 40(1): 254. |
| 27 | Uhlman DL, Nguyen PL, Manivel JC, et al. Association of immunohistochemical staining for p53 with metastatic progression and poor survival in patients with renal cell carcinoma[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 1994, 86(19): 1470-5. |
| 28 | Shvarts O, Seligson D, Lam J, et al. p53 is an independent predictor of tumor recurrence and progression after nephrectomy in patients with localized renal cell carcinoma[J]. J Urol, 2005, 173(3): 725-8. |
| 29 | Noon AP, Vlatković N, Polański R, et al. p53 and MDM2 in renal cell carcinoma: biomarkers for disease progression and future therapeutic targets[J]? Cancer, 2010, 116(4): 780-90. |
| [1] | Haonan¹ XU, Fang³ ZHANG, Yuying² HUANG, Qisheng⁴ YAO, Yueqin⁴ GUAN, Hao CHEN. Thesium chinense Turcz. alleviates antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice by modulating gut microbiota structure and regulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [2] | Pengwei HUANG, Jie CHEN, Jinhu ZOU, Xuefeng GAO, Hong CAO. Quercetin mitigates HIV-1 gp120-induced rat astrocyte neurotoxicity via promoting G3BP1 disassembly in stress granules [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 304-312. |
| [3] | Xiaorui CHEN, Qingzheng WEI, Zongliang ZHANG, Jiangshui YUAN, Weiqing SONG. Overexpression of CHMP2B suppresses proliferation of renal clear cell carcinoma cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 126-136. |
| [4] | Qiao CHU, Xiaona WANG, Jiaying XU, Huilin PENG, Yulin ZHAO, Jing ZHANG, Guoyu LU, Kai WANG. Pulsatilla saponin D inhibits invasion and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells through multiple targets and pathways [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [5] | Xiupeng LONG, Shun TAO, Shen YANG, Suyun LI, Libing RAO, Li LI, Zhe ZHANG. Quercetin improves heart failure by inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis via suppressing the MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 187-196. |
| [6] | Meng XU, Lina CHEN, Jinyu WU, Lili LIU, Mei SHI, Hao ZHOU, Guoliang ZHANG. Mechanism of Hedyotis diffusa-Scutellaria barbata D. Don for treatment of primary liver cancer: analysis with network pharmacology, molecular docking and in vitro validation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 80-89. |
| [7] | Qing LIU, Jing LIU, Yihang ZHENG, Jin LEI, Jianhua HUANG, Siyu LIU, Fang LIU, Qunlong PENG, Yuanfang ZHANG, Junjie WANG, Yujuan LI. Quercetin mediates the therapeutic effect of Centella asiatica on psoriasis by regulating STAT3 phosphorylation to inhibit the IL-23/IL-17A axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 90-99. |
| [8] | Chen YAO, Wenjia LI, Ruiming PANG, Jihong ZHOU. Gluteal tendinitis and primary coxarthrosis may lead to iliotibial band syndrome: a Mendelian randomization study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1821-1830. |
| [9] | Yifan JIANG, Xiaorong LI, Jiayi GENG, Yongfeng CHEN, Bi TANG, Pinfang KANG. Quercetin ameliorates diabetic kidney injury in rats by inhibiting the HMGB1/RAGE/ NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1769-1775. |
| [10] | Xingmei CHEN, Qinwen LIU, Yi LI, Xiaoyu ZHONG, Qiling FAN, Ke MA, Liuting LUO, Daogang GUAN, Zhibo ZHU. Analysis of core functional components in Yinchenhao Decoction and their pathways for treating liver fibrosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1508-1517. |
| [11] | Shanyuan ZHANG, Qiaoyan CAI, Jianghan QI, Kaixin YIN, Chenchen HE, Zhuye GAO, Ling ZHANG, Jianfeng CHU. Pharmacodynamics of Qingxin Jieyu Granules for treatment of atherosclerosis and its regulatory mechanism for lipid metabolism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1518-1528. |
| [12] | Yuming ZHANG, Shicheng XIA, Linlin ZHANG, Mengxi CHEN, Xiaojing LIU, Qin GAO, Hongwei YE. Protective effect of Lonicerae japonicae flos extract against doxorubicin-induced liver injury in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1571-1581. |
| [13] | Weitao ZHONG, Weisong LI, Zelin LI, Qiang WANG, Wangming ZHANG. Causal relationship between sleep phenotype and idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1612-1619. |
| [14] | Jinjin WANG, Wenfei CUI, Xuewei DOU, Binglei YIN, Yuqi NIU, Ling NIU, Guoli YAN. Euonymus alatus delays progression of diabetic kidney disease in mice by regulating EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1243-1255. |
| [15] | Linyue WANG, Wenyue QI, Jihua GAO, Maosheng TIAN, Jiancheng XU. Tongyangxiao Lotion promotes postoperative wound healing in a rat model of anal fistula by downregulating inflammatory factors and suppressing inflammation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1256-1265. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||