Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 785-798.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.14
Niandong RAN1( ), Jie LIU1,2,3, Jian XU1,2,3, Yongping ZHANG1,2,3, Jiangtao GUO1(
), Jie LIU1,2,3, Jian XU1,2,3, Yongping ZHANG1,2,3, Jiangtao GUO1( )
)
Received:2024-11-14
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
Jiangtao GUO
E-mail:252834816@qq.com;jtguo1987@163.com
Niandong RAN, Jie LIU, Jian XU, Yongping ZHANG, Jiangtao GUO. n-butanol fraction of ethanol extract of Periploca forrestii Schltr.: its active components, targets and pathways for treating Alcheimer's disease in rats[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 785-798.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.14
| Serial number | Retention time | Molecular formula | Measured value | Error value/ppm | Feature fragment(m/z) | Compound name | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.68 | C16H18O9 | 353.08691[M-H]- | -3.45 | 192.05919, 191.05542, 179.03412,173.04466, 93.03349 | Chlorogenic acid | [ |
| 2 | 1.73 | C16H18O9 | 353.40290[M-H]- | -2.56 | 191.05544, 179.03429, 135.04407, 91.98469,85.02808, 57.03342 | Neochlorogenic acid | [ |
| 3 | 9.18 | C17H20O9 | 369.11716[M+H]+ | 2.12 | 145.09915, 149.02530, 179.06972, 164.83426 | 3-O-Caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester | [ |
| 4 | 11.15 | C10H8O4 | 193.07759[M+H]+ | 4.73 | 178.24461, 161.94366, 150.83627 | Scopoletin | [ |
| 5 | 11.98 | C35H60O6 | 577.98993[M+H]+ | 1.98 | 413.25134, 319.17458, 295.77209 | Daucosterol | [ |
| 6 | 13.67 | C15H10O6 | 287.47942[M+H]+ | 4.34 | 164.8902, 152.63197 | Kaempferol | [ |
| 7 | 14.33 | C9H10O3 | 167.98975[M+H]+ | 1.09 | 167.10678, 165.98264, 148.96109,121.96677, 125.96402, 91.05489 | Paeonol | [ |
| 8 | 14.55 | C29H50O | 415.21033[M+H]+ | 1.21 | 119.08556, 91.05432 | Beta-Sitosterol | [ |
| 9 | 14.76 | C15H10O7 | 303.23000[M+H]+ | 3.06 | 301.29196, 257.51855, 151.59630, 107.08958 | Quercetin | [ |
| 10 | 16.55 | C30H48O3 | 457.53849[M+H]+ | 1.84 | 439.68873, 411.50410, 393.35737, 191.18426 | Ursolic Acid | [ |
| 11 | 18.87 | C21H20O11 | 449.10769[M+H]+ | 1.63 | 287.16988, 153.36526, 135.96421 | Kaempferol 3-O-β- D-glucopyranoside | [ |
| 12 | 21.57 | C15H12O4 | 257.26276[M+H]+ | 3.94 | 257.26599, 210.88354, 120.98715 | Isoliquiritigenin | [ |
| 13 | 23.67 | C16H12O5 | 285.28204[M+H]+ | 3.58 | 240.88678, 282.27838 | Questin | [ |
| 14 | 24.41 | C16H12O5 | 283.05704[M-H]- | -3.41 | 267.04141, 239.87805 | Wogonin | [ |
| 15 | 27.46 | C16H12O5 | 284.29410[M+H]+ | 1.19 | 285.29733, 238.87862, 164.61707 | Physcion | [ |
| 16 | 35.12 | C9H8O3 | 165.11798[M+H]+ | 5.85 | 165.12164, 148.08638 | Trans-4- Hydroxycinnamic acid | [ |
| 17 | 35.37 | C18H34O2 | 283.04980[M+H]+ | 2.08 | 281.04965, 265.01825 | Oleic acid | [ |
Tab.1 Information of the 17 compounds identified in n-butanol fraction of Periploca forrestii Schltr. ethanol extract
| Serial number | Retention time | Molecular formula | Measured value | Error value/ppm | Feature fragment(m/z) | Compound name | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.68 | C16H18O9 | 353.08691[M-H]- | -3.45 | 192.05919, 191.05542, 179.03412,173.04466, 93.03349 | Chlorogenic acid | [ |
| 2 | 1.73 | C16H18O9 | 353.40290[M-H]- | -2.56 | 191.05544, 179.03429, 135.04407, 91.98469,85.02808, 57.03342 | Neochlorogenic acid | [ |
| 3 | 9.18 | C17H20O9 | 369.11716[M+H]+ | 2.12 | 145.09915, 149.02530, 179.06972, 164.83426 | 3-O-Caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester | [ |
| 4 | 11.15 | C10H8O4 | 193.07759[M+H]+ | 4.73 | 178.24461, 161.94366, 150.83627 | Scopoletin | [ |
| 5 | 11.98 | C35H60O6 | 577.98993[M+H]+ | 1.98 | 413.25134, 319.17458, 295.77209 | Daucosterol | [ |
| 6 | 13.67 | C15H10O6 | 287.47942[M+H]+ | 4.34 | 164.8902, 152.63197 | Kaempferol | [ |
| 7 | 14.33 | C9H10O3 | 167.98975[M+H]+ | 1.09 | 167.10678, 165.98264, 148.96109,121.96677, 125.96402, 91.05489 | Paeonol | [ |
| 8 | 14.55 | C29H50O | 415.21033[M+H]+ | 1.21 | 119.08556, 91.05432 | Beta-Sitosterol | [ |
| 9 | 14.76 | C15H10O7 | 303.23000[M+H]+ | 3.06 | 301.29196, 257.51855, 151.59630, 107.08958 | Quercetin | [ |
| 10 | 16.55 | C30H48O3 | 457.53849[M+H]+ | 1.84 | 439.68873, 411.50410, 393.35737, 191.18426 | Ursolic Acid | [ |
| 11 | 18.87 | C21H20O11 | 449.10769[M+H]+ | 1.63 | 287.16988, 153.36526, 135.96421 | Kaempferol 3-O-β- D-glucopyranoside | [ |
| 12 | 21.57 | C15H12O4 | 257.26276[M+H]+ | 3.94 | 257.26599, 210.88354, 120.98715 | Isoliquiritigenin | [ |
| 13 | 23.67 | C16H12O5 | 285.28204[M+H]+ | 3.58 | 240.88678, 282.27838 | Questin | [ |
| 14 | 24.41 | C16H12O5 | 283.05704[M-H]- | -3.41 | 267.04141, 239.87805 | Wogonin | [ |
| 15 | 27.46 | C16H12O5 | 284.29410[M+H]+ | 1.19 | 285.29733, 238.87862, 164.61707 | Physcion | [ |
| 16 | 35.12 | C9H8O3 | 165.11798[M+H]+ | 5.85 | 165.12164, 148.08638 | Trans-4- Hydroxycinnamic acid | [ |
| 17 | 35.37 | C18H34O2 | 283.04980[M+H]+ | 2.08 | 281.04965, 265.01825 | Oleic acid | [ |
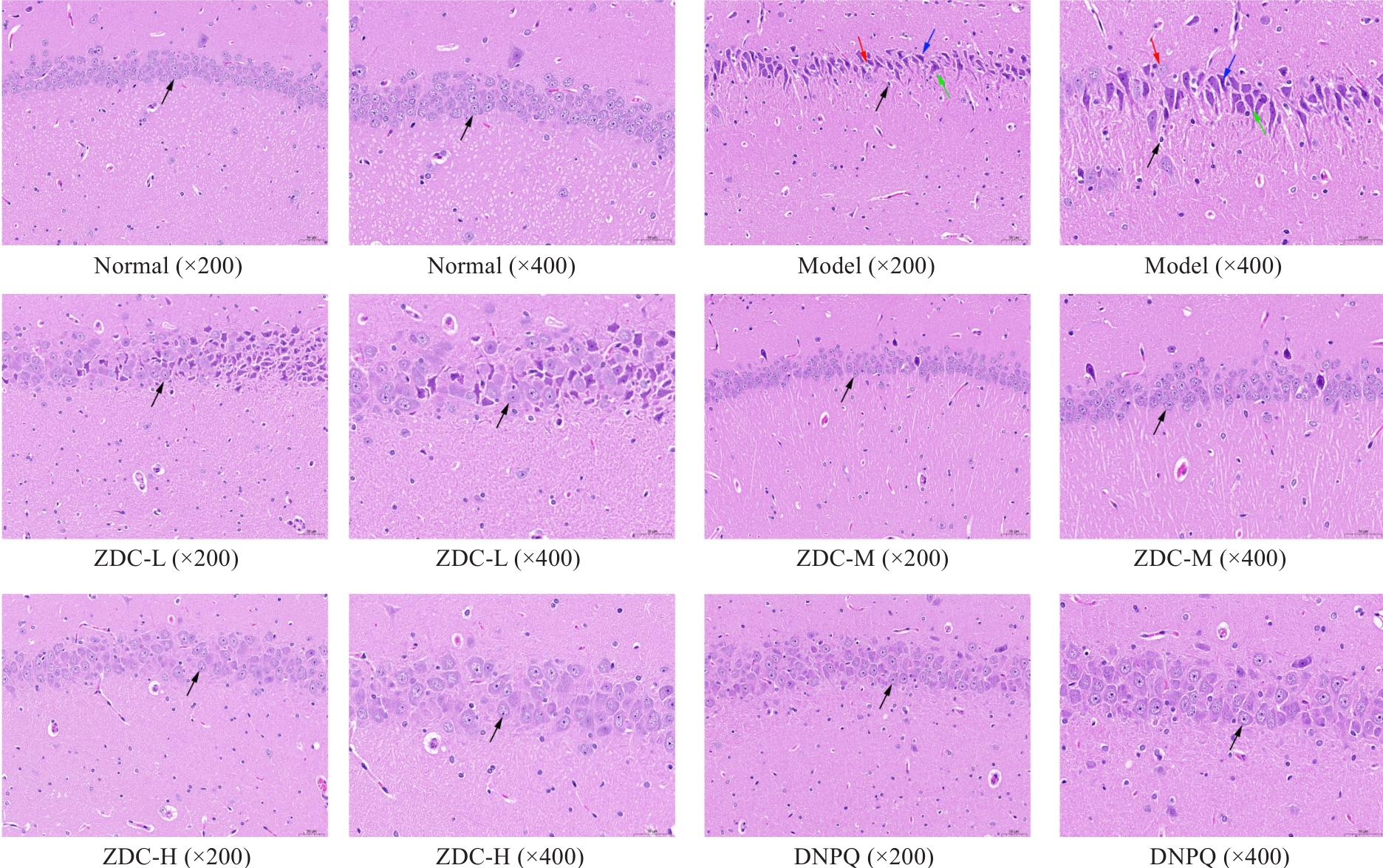
Fig.4 HE staining of rat hippocampus in each group. Nucleus (black arrow), cytoplasm (blue arrow), cell body (red arrow), irregular cell (green arrow).
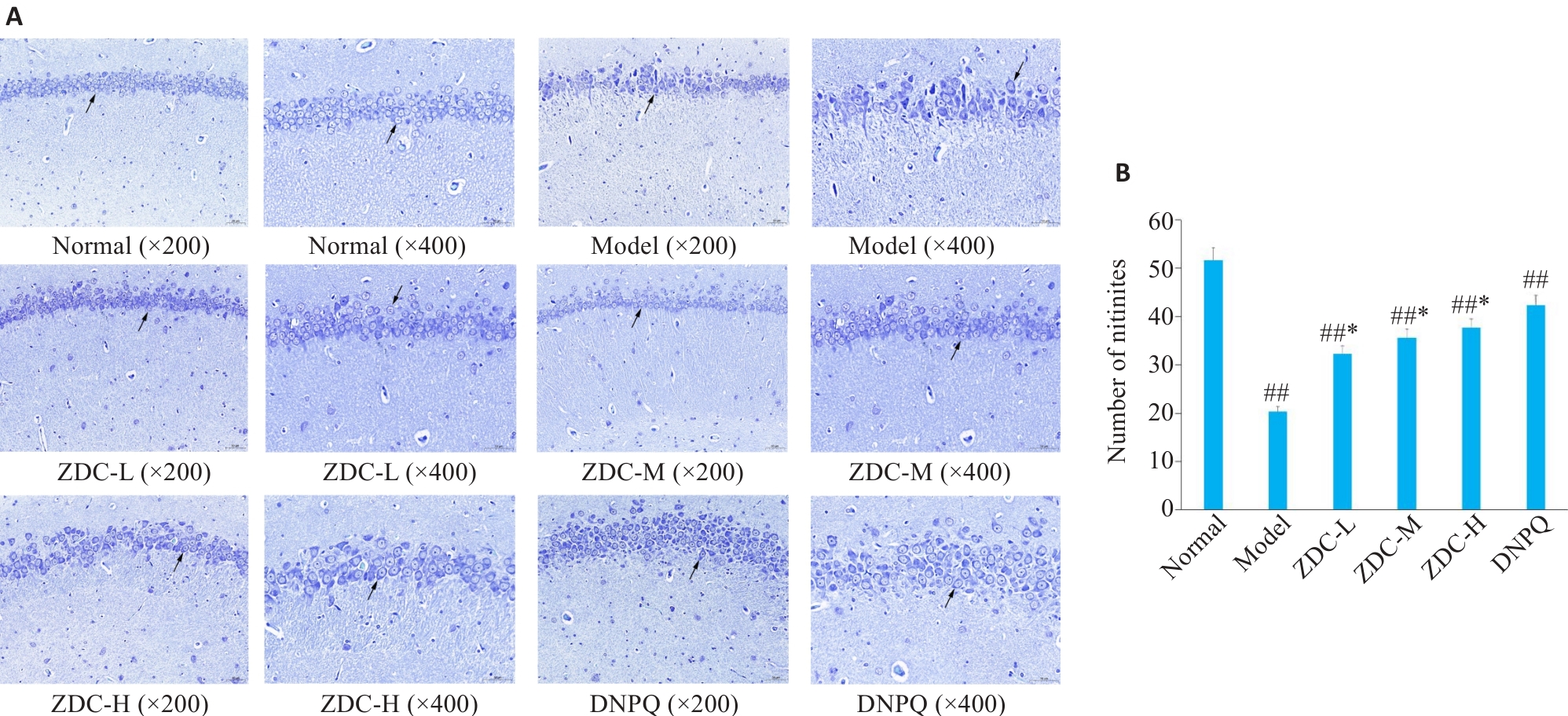
Fig.5 Nissl staining of rat hippocampal tissues (A) and statistics of the number of Nissl bodies (arrows)(B) in each group. ##P<0.01 vs Normal group; *P<0.05 vs Model group.
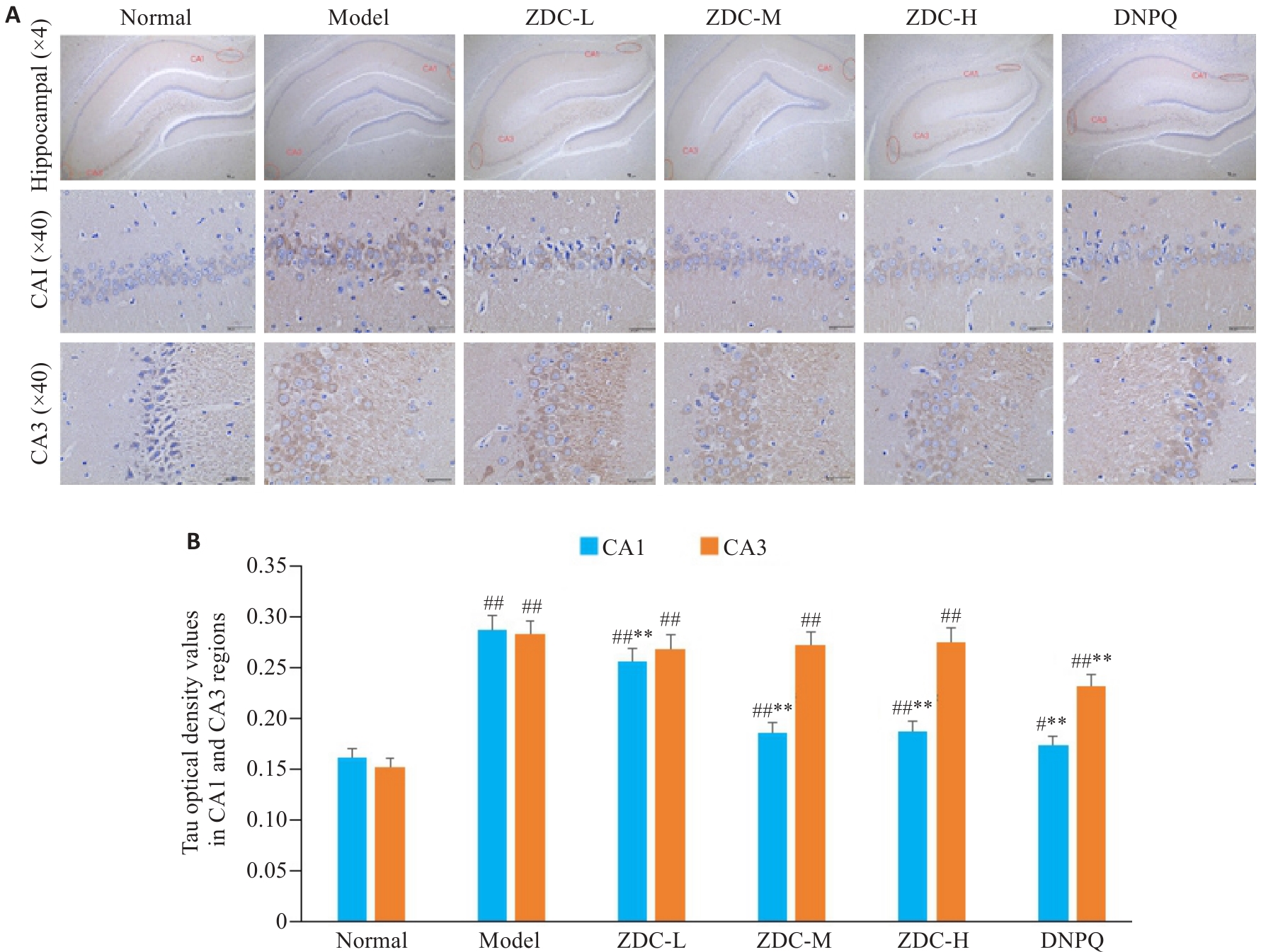
Fig.6 Tau protein deposition in rat hippocampus detected by immunohistochemistry (A) and Tau optical density values in CA1 and CA3 regions (B) in each group. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs Normal group; **P<0.01 vs Model group.
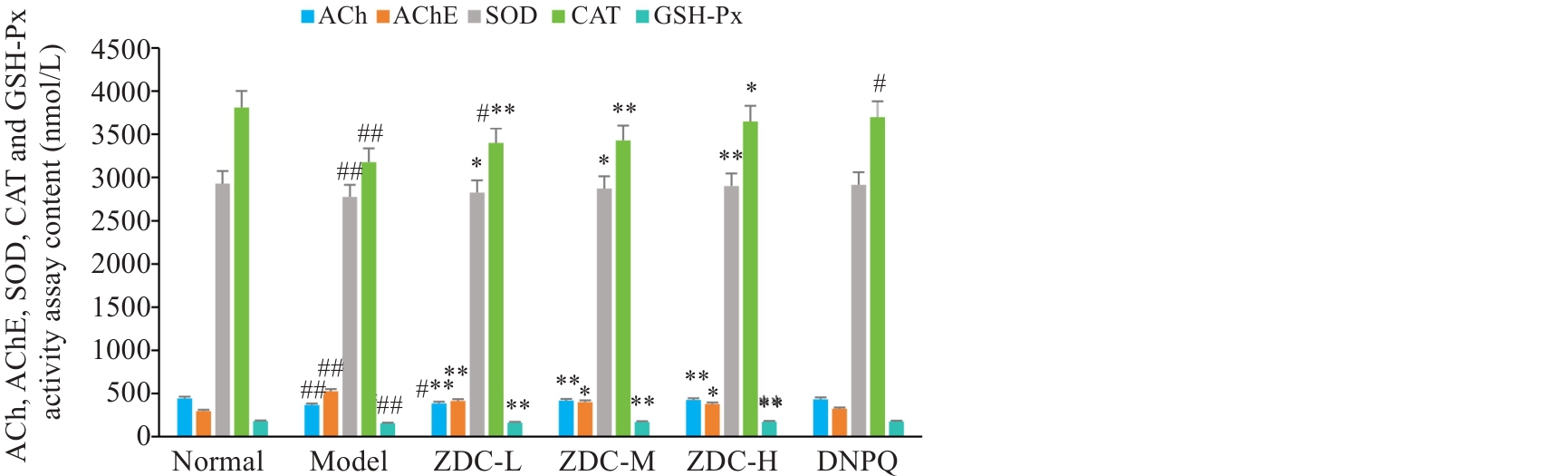
Fig.7 ACh, AChE, SOD, CAT and GSH-Px activities in rat hippocampus in each group. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs Normal group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Model group.
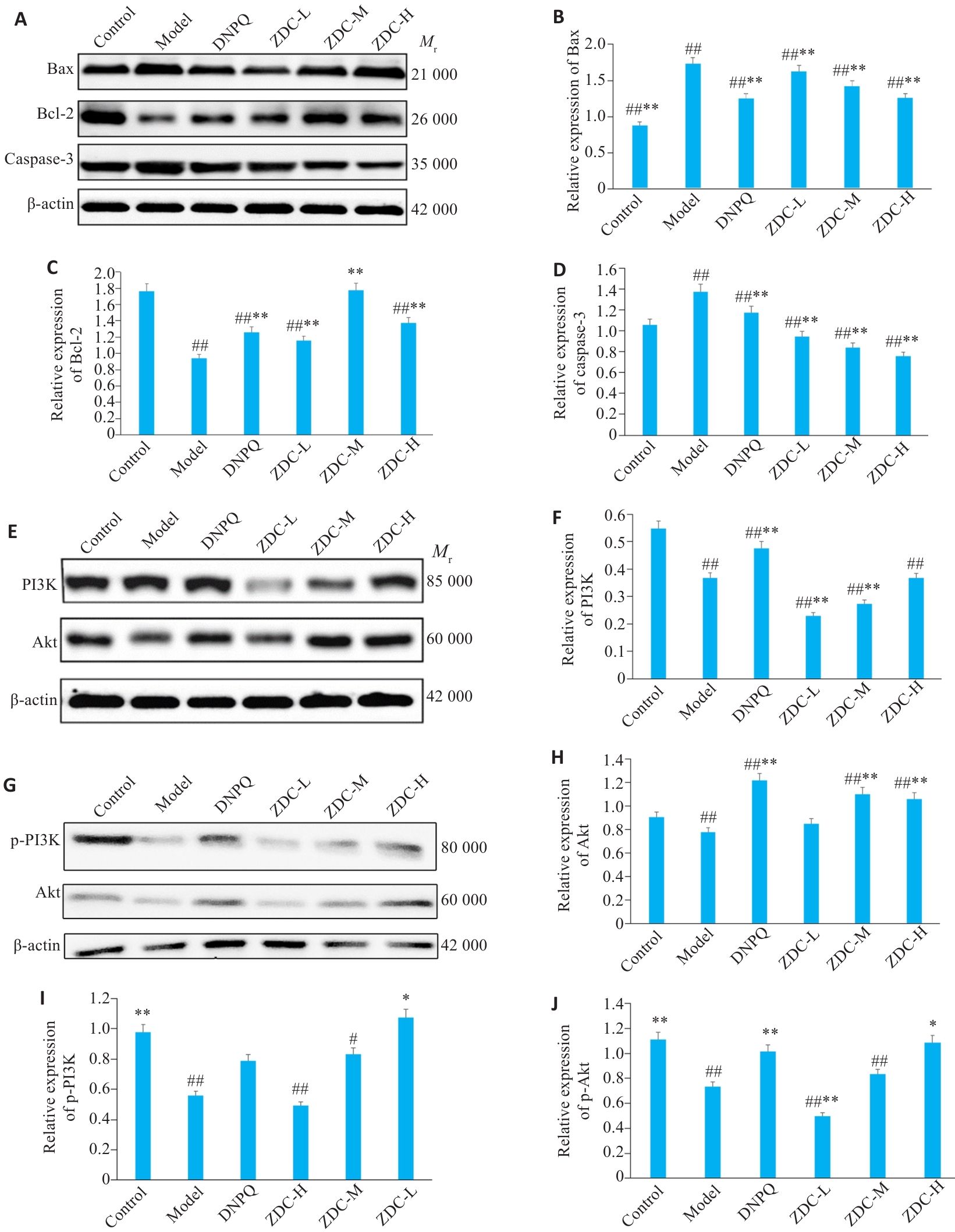
Fig.8 Western blotting for detecting protein expression levels in the hippocampus in each group. A-D: Bcl-2, Bax and caspase-3 protein bands and their relative expression levels. E-J: PI3K, Akt, p-PI3K and p-Akt protein bands and their relative expression levels. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs Control group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Model group.
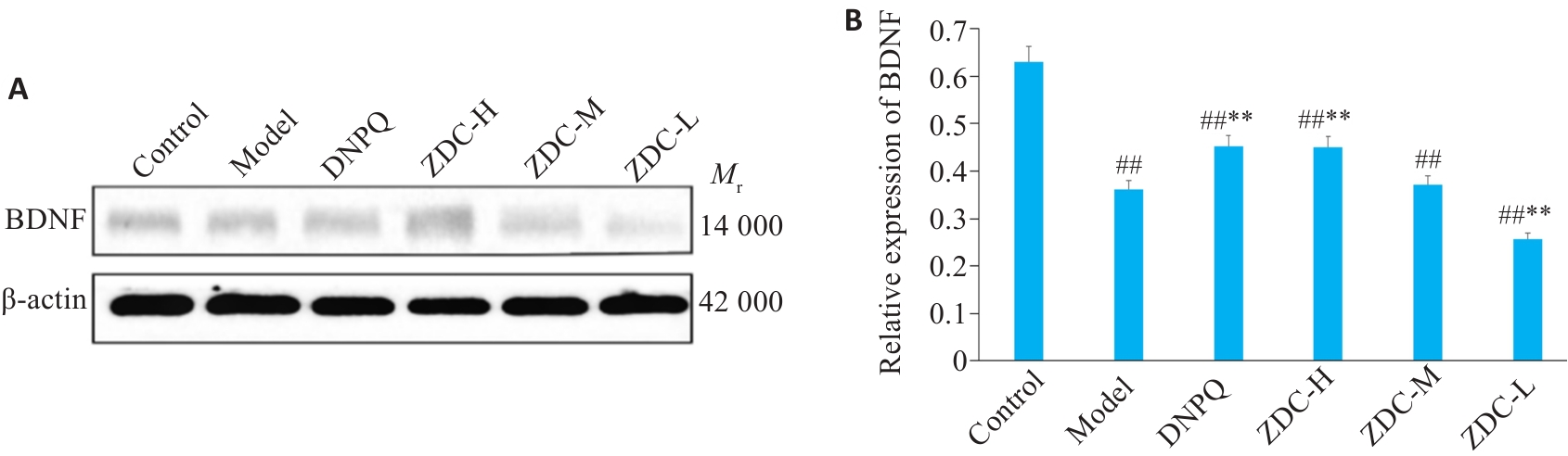
Fig.9 Expression levels of BDNF protein in the hippocampus in each group detected by Western blotting. ##P<0.01 vs Control group; **P<0.01 vs Model group.
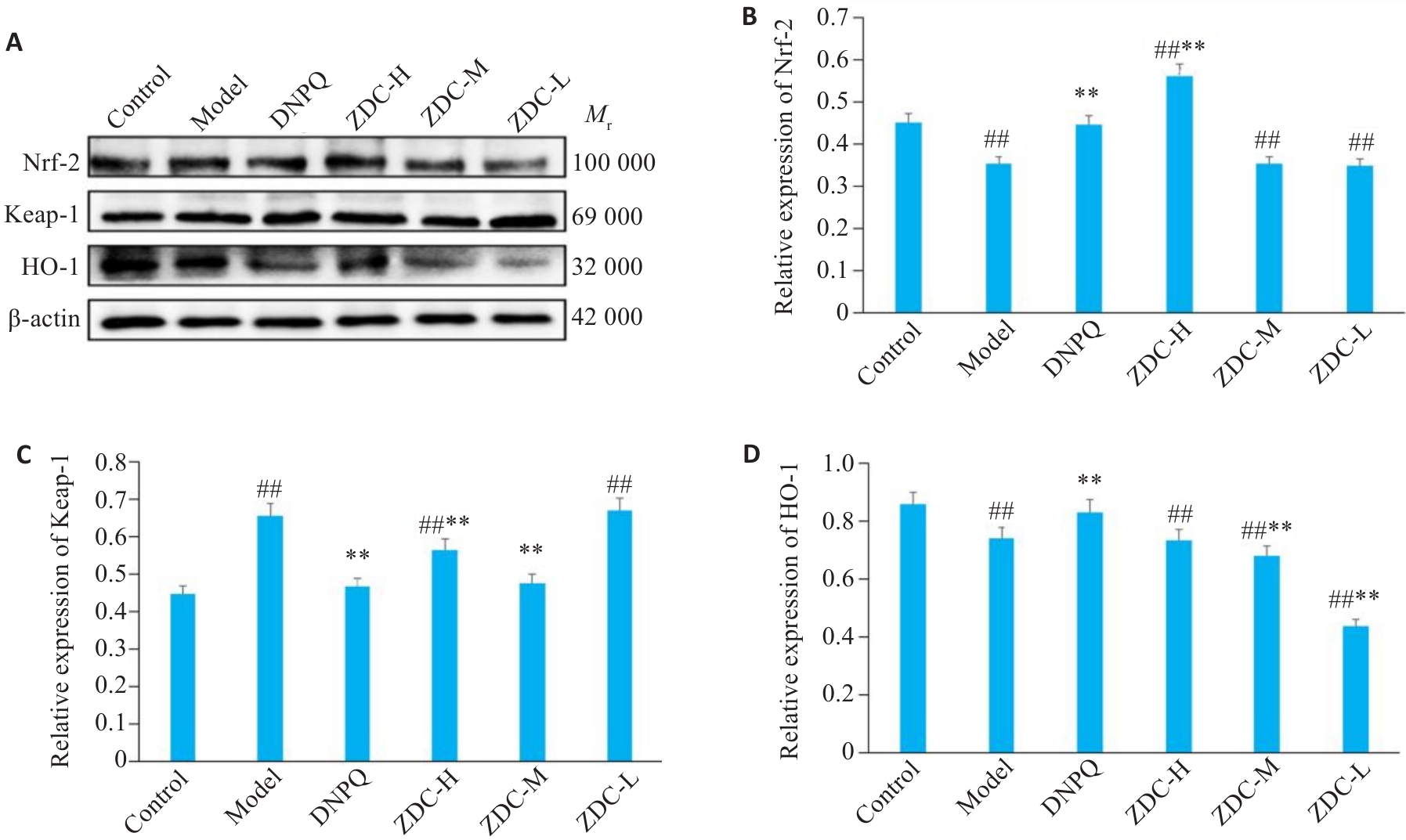
Fig.10 Expression levels of Nrf-2, Keap-1, and HO-1 in the hippocampus in each group detected by Western blotting. ##P<0.01 vs Control group; **P<0.01 vs Model group.
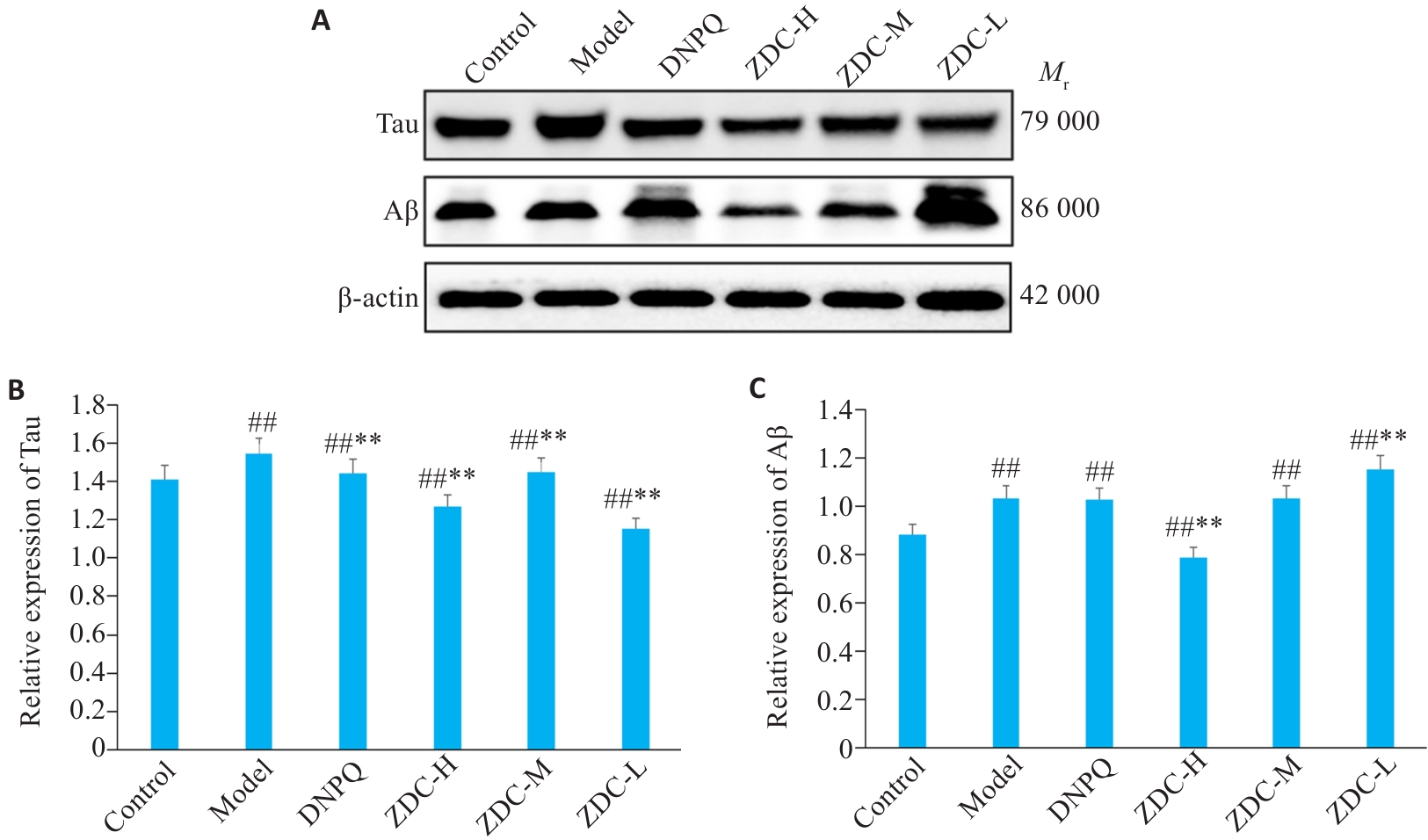
Fig.11 Expression levels of Tau and Aβ protein bands in the hippocampus in each group detected by Western blotting. ##P<0.01 vs Control group; **P<0.01 vs Model group.
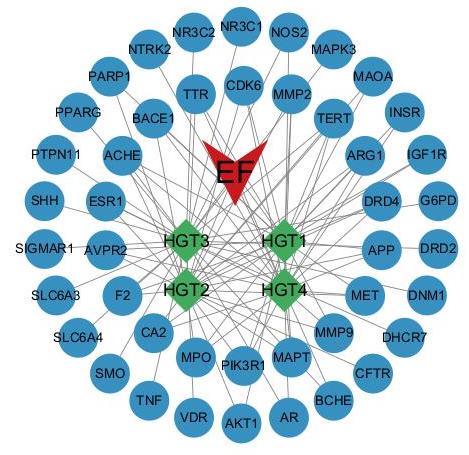
Fig.13 Drug-component-intersection target map. Red "V" shape: n-butanol fraction; Green rhombus: Active components; Blue circle: Targets of the components.
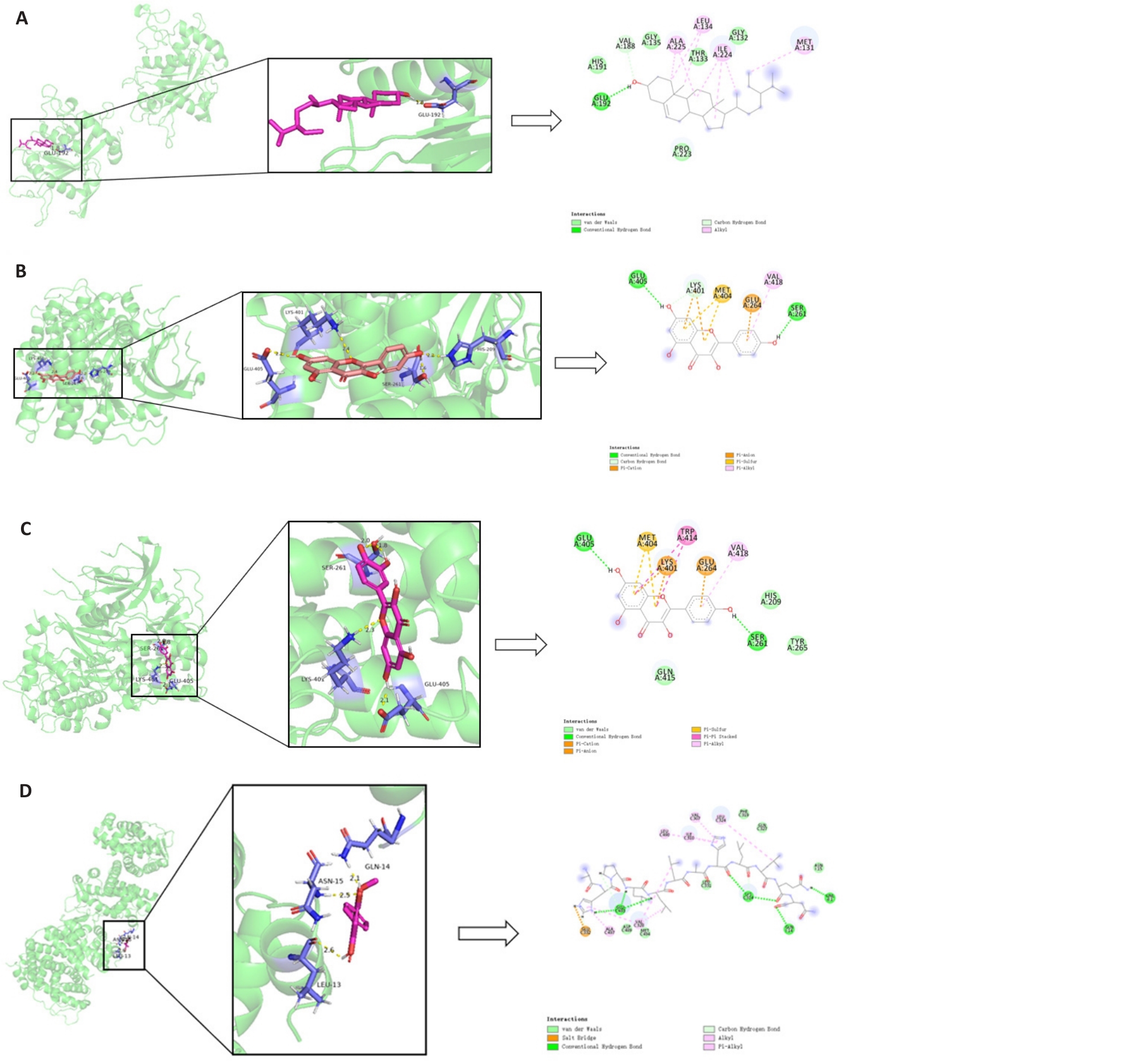
Fig.16 Docking results of the active components with the key target molecules. A: Beta-Sitosterol-TNF. B: kaempferol-AKT1. C: Quercetin-AKT1. D: Wogonin-ESR1.
| 1 | 贵州省药品监督管理局. 贵州省中药材民族药材质量标准2019年版 第二册[M]. 中国医药科技出版社, 2019: 149. |
| 2 | Chen L, Li JS, Ke X, et al. Chemical profiling and the potential active constituents responsible for wound healing in Periploca forrestii Schltr[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2018, 224: 230-41. |
| 3 | Chen HG, Liang Q, Zhou X, et al. Preparative separation of the flavonoid fractions from Periploca forrestii Schltr. ethanol extracts using macroporous resin combined with HPLC analysis and evaluation of their biological activities[J]. J Sep Sci, 2019, 42(3): 650-61. |
| 4 | 贾敏如, 张 艺. 中国民族药辞典[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2016: 603. |
| 5 | 张贵源, 龚莉莉, 党荣敏, 等. 黑骨藤对Pristionchus pacificus线虫神经损伤的治疗实验[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2012, 23(11): 2758-9. |
| 6 | 张贵源, 龚莉莉, 余跃生, 等. 黑骨藤对PC12细胞氧化损伤的保护研究[J]. 宁夏农林科技, 2012, 53(8): 139-40. |
| 7 | Wu H, Cao YJ, Qu YX, et al. Integrating UPLC-QE-Orbitrap-MS technology and network pharmacological method to reveal the mechanism of Bailemian capsule to relieve insomnia[J]. Nat Prod Res, 2022, 36(10): 2554-8. |
| 8 | Liu Y, Sun MY, Sun JQ, et al. Identification of novel serum metabolic signatures to predict chronic kidney disease among Chinese Elders using UPLC-Orbitrap-MS[J]. J Nutr Health Aging, 2024, 28(3): 100036. |
| 9 | 刘灿黄, 章泽恒, 汪 辉, 等. UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS 法定性分析丹膝颗粒的化学成分[J]. 药品评价, 2022, 19(4): 201-9. |
| 10 | 李泮霖, 李楚源, 刘孟华, 等. 基于UFLC-Triple-Q-TOF-MS/MS技术的金银花、山银花化学成分比较[J]. 中南药学, 2016, 14(4): 363-9. |
| 11 | 吴 欢, 占 远, 陈海芳, 等. UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS对紫花地丁中化学成分的快速表征[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2016, 22(24): 70-5. |
| 12 | 贾志鑫, 丛诗语, 潘明霞, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS的速效救心丸化学成分定性分析[J]. 药物评价研究, 2023, 46(2): 330-41. |
| 13 | 王 梦, 田 伟, 甄亚钦, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS技术的彝族药姜味草化学成分分析[J]. 中国药学杂志, 2022, 57(20): 1717-25. |
| 14 | 刘 爽, 戴宇滢, 赵爽同, 等. 基于UHPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap-MS技术分析桂附地黄丸的化学成分及入血成分[J]. 中南药学, 2023, 21(8): 2069-75. |
| 15 | 朱高峰, 蒋成英, 王建塔, 等. UPLC-Q-TOF-MSE技术结合UNIFI数据库定性分析见血清醇提取物化学成分[J]. 广东化工, 2020, 47(20): 36-8. |
| 16 | 肖 岩, 马博稷, 李冰涛, 等. 青钱柳醇提物中化学成分的UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28(16): 196-204. |
| 17 | 张忠立, 石文康, 左月明, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS技术的不同产地肺形草化学成分的研究[J]. 中南药学, 2023, 21(2): 312-9. |
| 18 | 许如玲, 范君婷, 董惠敏, 等. 经典名方黄芪桂枝五物汤标准煎液化学成分的UPLC-Q-TOF-MS分析[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2020, 45(23): 5614-30. |
| 19 | 姜奇瑶, 刘臣臣, 陈惠玲, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS和UPLC的六君子汤化学成分定性与定量分析[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2024,30(06):169-78. |
| 20 | 于小杰. 基于LC-MS技术的芪归银方药效物质基础研究[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2014. |
| 21 | 孔 娇, 刘传鑫, 张 娜, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF/HRMSE小陷胸汤化学成分定性分析[J]. 药物评价研究, 2020, 43(7): 1273-82. |
| 22 | 凌 霄, 李伟霞, 王晓艳, 等. UPLC-Q-TOF-MS分析芍药汤水煎液化学成分[J]. 中国现代中药, 2021, 23(1): 48-56. |
| 23 | 张 宝, 李 悦, 陈婷婷, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-Exactive-Plus-Orbitrap-MS技术分析蛇含委陵菜的化学成分[J]. 中药材, 2023, 46(12): 3014-22. |
| 24 | Wang L, Pan XQ, Jiang LS, et al. The biological activity mechanism of chlorogenic acid and its applications in food industry: a review[J]. Front Nutr, 2022, 9: 943911. |
| 25 | 肖炜明, 卜 平, 龚卫娟. 汉黄芩素抗肿瘤和免疫调节作用的研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2014, 39(16): 3004-9. |
| 26 | 王 玉, 于桂芳, 胡军华, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS及网络药理学探讨麻杏止哮颗粒治疗哮喘的有效成分和作用机制[J]. 中草药, 2023, 54(17): 5508-21. |
| 27 | Dey M, Singh RK. Neurotoxic effects of aluminium exposure as a potential risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Pharmacol Rep, 2022, 74(3): 439-50. |
| 28 | Gilbert PE, Brushfield AM. The role of the CA3 hippocampal subregion in spatial memory: a process oriented behavioral assessment[J]. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry, 2009, 33(5): 774-81. |
| 29 | 周丽莎, 朱书秀, 望庐山. 核桃仁提取物对老年痴呆模型大鼠Ach、ChAT及AchE活性的影响[J]. 中国医院药学杂志, 2011, 31(6): 446-9. |
| 30 | Chen ZR, Huang JB, Yang SL, et al. Role of cholinergic signaling in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(6): 1816. |
| 31 | Meng XW, Cui J, He GB. Bcl-2 is involved in cardiac hypertrophy through PI3K-Akt pathway[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021, 2021: 6615502. |
| 32 | Beroske L, Van den Wyngaert T, Stroobants S, et al. Molecular imaging of apoptosis: the case of caspase-3 radiotracers[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(8): 3948. |
| 33 | Fan SS, Liu XY, Wang Y, et al. Thymus quinquecostatus Celak. ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via dual antioxidant actions: Activating Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and directly scavenging ROS[J]. Phytomedicine, 2021, 91: 153673. |
| [1] | Haonan¹ XU, Fang³ ZHANG, Yuying² HUANG, Qisheng⁴ YAO, Yueqin⁴ GUAN, Hao CHEN. Thesium chinense Turcz. alleviates antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice by modulating gut microbiota structure and regulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [2] | Junjie GAO, Kai YE, Jing WU. Quercetin inhibits proliferation and migration of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells by regulating TP53 gene [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [3] | Ying LIU, Borui LI, Yongcai LI, Lubo CHANG, Jiao WANG, Lin YANG, Yonggang YAN, Kai QV, Jiping LIU, Gang ZHANG, Xia SHEN. Jiawei Xiaoyao Pills improves depression-like behavior in rats by regulating neurotransmitters, inhibiting inflammation and oxidation and modulating intestinal flora [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 347-358. |
| [4] | Qiao CHU, Xiaona WANG, Jiaying XU, Huilin PENG, Yulin ZHAO, Jing ZHANG, Guoyu LU, Kai WANG. Pulsatilla saponin D inhibits invasion and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells through multiple targets and pathways [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [5] | Xiupeng LONG, Shun TAO, Shen YANG, Suyun LI, Libing RAO, Li LI, Zhe ZHANG. Quercetin improves heart failure by inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis via suppressing the MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 187-196. |
| [6] | Meng XU, Lina CHEN, Jinyu WU, Lili LIU, Mei SHI, Hao ZHOU, Guoliang ZHANG. Mechanism of Hedyotis diffusa-Scutellaria barbata D. Don for treatment of primary liver cancer: analysis with network pharmacology, molecular docking and in vitro validation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 80-89. |
| [7] | Qing LIU, Jing LIU, Yihang ZHENG, Jin LEI, Jianhua HUANG, Siyu LIU, Fang LIU, Qunlong PENG, Yuanfang ZHANG, Junjie WANG, Yujuan LI. Quercetin mediates the therapeutic effect of Centella asiatica on psoriasis by regulating STAT3 phosphorylation to inhibit the IL-23/IL-17A axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 90-99. |
| [8] | Guanzheng YU, Weiqiang CHENG, Xing TU, Man ZHANG, Hong LI, Juan NIE. Therapeutic mechanism of Cynanchum wilfordii for ulcerative colitis: an analysis using UPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology and metabolomics [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1485-1496. |
| [9] | Xingmei CHEN, Qinwen LIU, Yi LI, Xiaoyu ZHONG, Qiling FAN, Ke MA, Liuting LUO, Daogang GUAN, Zhibo ZHU. Analysis of core functional components in Yinchenhao Decoction and their pathways for treating liver fibrosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1508-1517. |
| [10] | Shanyuan ZHANG, Qiaoyan CAI, Jianghan QI, Kaixin YIN, Chenchen HE, Zhuye GAO, Ling ZHANG, Jianfeng CHU. Pharmacodynamics of Qingxin Jieyu Granules for treatment of atherosclerosis and its regulatory mechanism for lipid metabolism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1518-1528. |
| [11] | Yuming ZHANG, Shicheng XIA, Linlin ZHANG, Mengxi CHEN, Xiaojing LIU, Qin GAO, Hongwei YE. Protective effect of Lonicerae japonicae flos extract against doxorubicin-induced liver injury in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1571-1581. |
| [12] | Jinjin WANG, Wenfei CUI, Xuewei DOU, Binglei YIN, Yuqi NIU, Ling NIU, Guoli YAN. Euonymus alatus delays progression of diabetic kidney disease in mice by regulating EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1243-1255. |
| [13] | Linyue WANG, Wenyue QI, Jihua GAO, Maosheng TIAN, Jiancheng XU. Tongyangxiao Lotion promotes postoperative wound healing in a rat model of anal fistula by downregulating inflammatory factors and suppressing inflammation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1256-1265. |
| [14] | Wenxiang ZHANG, Huixian GU, Pengde CHEN, Siyu WU, Hongyan MA, Lan YAO. Compound Yuye Decoction protects diabetic rats against cardiomyopathy by inhibiting myocardial apoptosis and inflammation via regulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1306-1314. |
| [15] | Yan HUANG, Lulu QIN, Shaoxing GUAN, Yanping GUANG, Yuru WEI, Ailing CAO, Dongmei LI, Guining WEI, Qibiao SU. Therapeutic mechanism of aqueous extract of Semiliquidambar cathayensis Chang root for pancreatic cancer: the active components, therapeutic targets and pathways [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1336-1344. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||