Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 347-358.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.02.16
Ying LIU1,2( ), Borui LI1, Yongcai LI1, Lubo CHANG1, Jiao WANG1, Lin YANG1, Yonggang YAN1,2, Kai QV3, Jiping LIU1,4, Gang ZHANG1(
), Borui LI1, Yongcai LI1, Lubo CHANG1, Jiao WANG1, Lin YANG1, Yonggang YAN1,2, Kai QV3, Jiping LIU1,4, Gang ZHANG1( ), Xia SHEN1,2(
), Xia SHEN1,2( )
)
Received:2024-11-17
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-03-03
Contact:
Gang ZHANG, Xia SHEN
E-mail:farewell991007@163.com;jay_gumling2003@aliyun.com;jxrain@163.com
Ying LIU, Borui LI, Yongcai LI, Lubo CHANG, Jiao WANG, Lin YANG, Yonggang YAN, Kai QV, Jiping LIU, Gang ZHANG, Xia SHEN. Jiawei Xiaoyao Pills improves depression-like behavior in rats by regulating neurotransmitters, inhibiting inflammation and oxidation and modulating intestinal flora[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 347-358.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.02.16
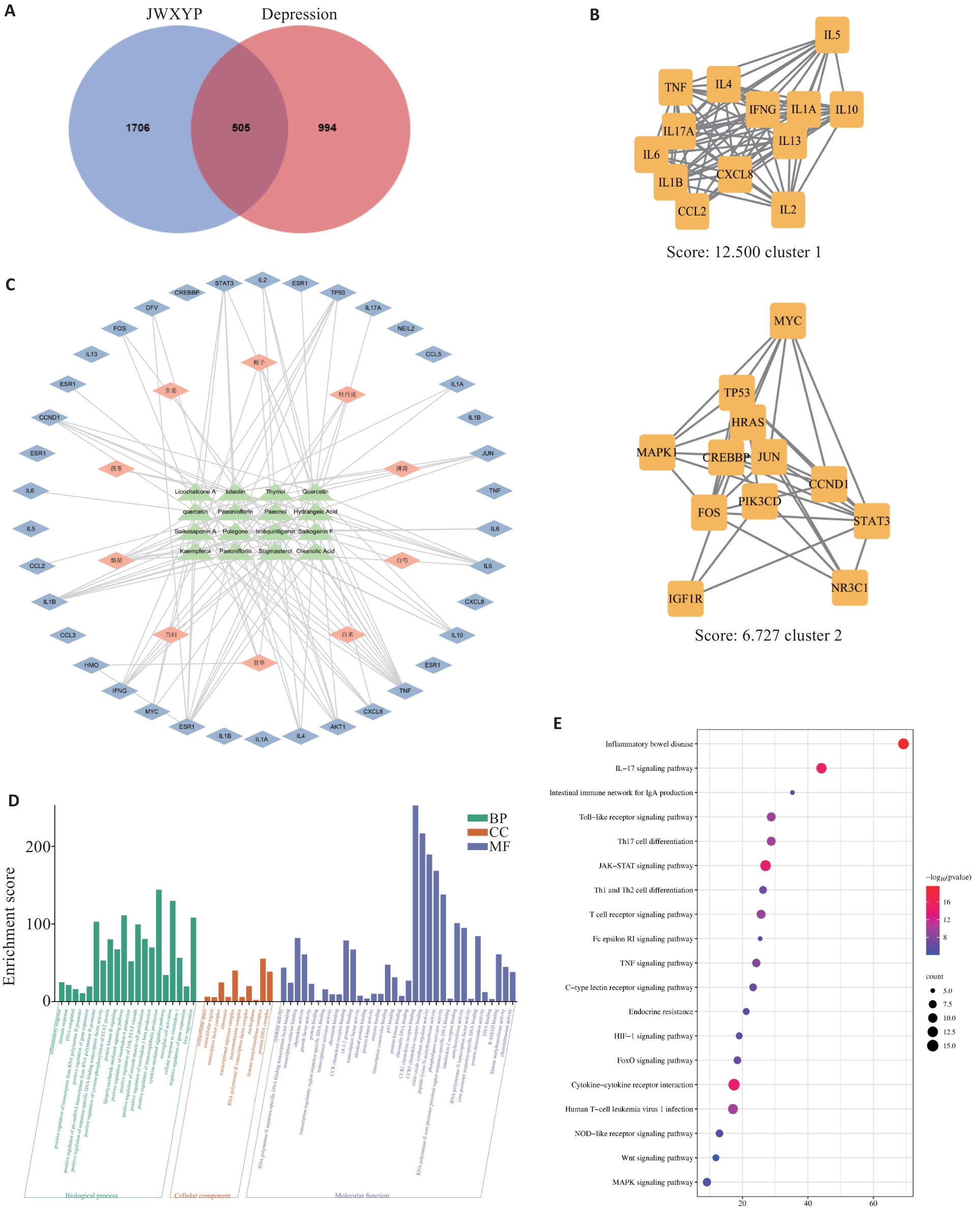
Fig.1 Network pharmacology results. A: JWXYP and depression intersection genes. B: MCODE algorithm for screening the key targets. C: Chinese medicine-component-target network diagram. D: GO analysis of the key genes. E: Bubble map of KEGG analysis of the key genes.
| Compound | MW | OB(%) | BBB | DL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | 302.25 | 46.43 | -0.77 | 0.28 |
| Luteolin | 286.25 | 36.16 | -0.84 | 0.25 |
| Kaempferol | 286.25 | 41.88 | -0.55 | 0.24 |
| Thymol | 150.24 | 41.47 | 1.68 | 0.03 |
| Stigmasterol | 412.77 | 43.83 | 1 | 0.76 |
| Paeonol | 166.19 | 28.79 | 0.84 | 0.04 |
| Oleanolic acid | 456.78 | 29.02 | 0.07 | 0.76 |
| Saikosaponin A | 781.1 | 32.39 | -2.93 | 0.09 |
| Pulegone | 152.26 | 51.6 | 1.74 | 0.03 |
| Isoliquiritigenin | 256.27 | 85.32 | -0.41 | 0.15 |
| Paeoniflorin | 480.51 | 53.87 | -1.86 | 0.79 |
| Saikogenin F | 472.78 | 25.88 | -0.71 | 0.63 |
| Licochalcone A | 338.43 | 40.79 | -0.21 | 0.29 |
Tab.1 Physicochemical properties of the bioactive compounds in Jiawei Xiaoyao Pills (JWXYP)
| Compound | MW | OB(%) | BBB | DL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | 302.25 | 46.43 | -0.77 | 0.28 |
| Luteolin | 286.25 | 36.16 | -0.84 | 0.25 |
| Kaempferol | 286.25 | 41.88 | -0.55 | 0.24 |
| Thymol | 150.24 | 41.47 | 1.68 | 0.03 |
| Stigmasterol | 412.77 | 43.83 | 1 | 0.76 |
| Paeonol | 166.19 | 28.79 | 0.84 | 0.04 |
| Oleanolic acid | 456.78 | 29.02 | 0.07 | 0.76 |
| Saikosaponin A | 781.1 | 32.39 | -2.93 | 0.09 |
| Pulegone | 152.26 | 51.6 | 1.74 | 0.03 |
| Isoliquiritigenin | 256.27 | 85.32 | -0.41 | 0.15 |
| Paeoniflorin | 480.51 | 53.87 | -1.86 | 0.79 |
| Saikogenin F | 472.78 | 25.88 | -0.71 | 0.63 |
| Licochalcone A | 338.43 | 40.79 | -0.21 | 0.29 |
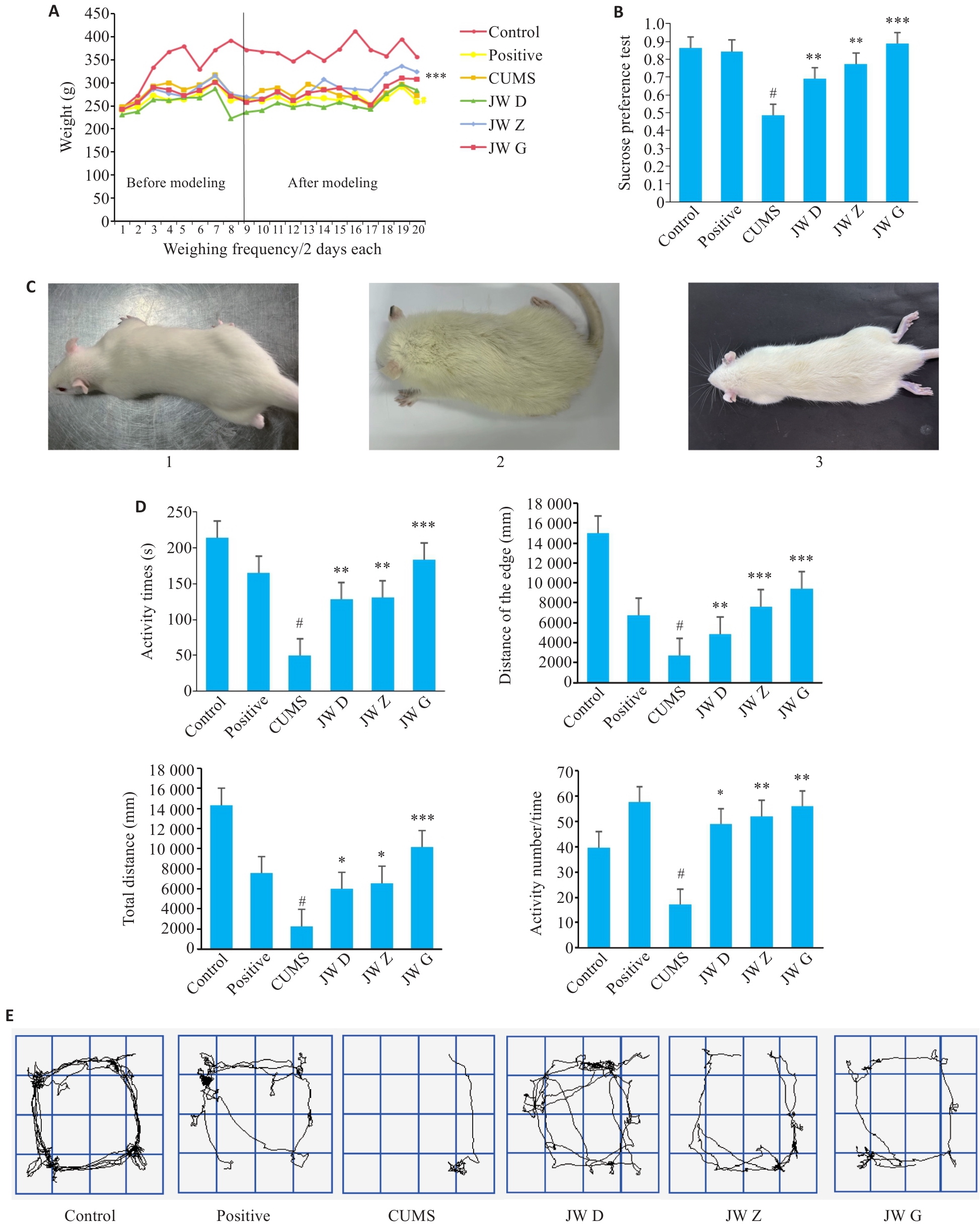
Fig.2 Establishment of depression rat models and behavioral test results of the rats. A: Body weight curves of rats in each group. B: Sugar water preference test. C: External hair of rats before modeling (1), after modeling (2) and after drug treatment (3). D: Open- field test of the rats (activity time, distance of the edge, total distance, and number of activities). E: Trajectory diagram of the rats in open field test. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs model group (CUMS); #P<0.05 vs control group.
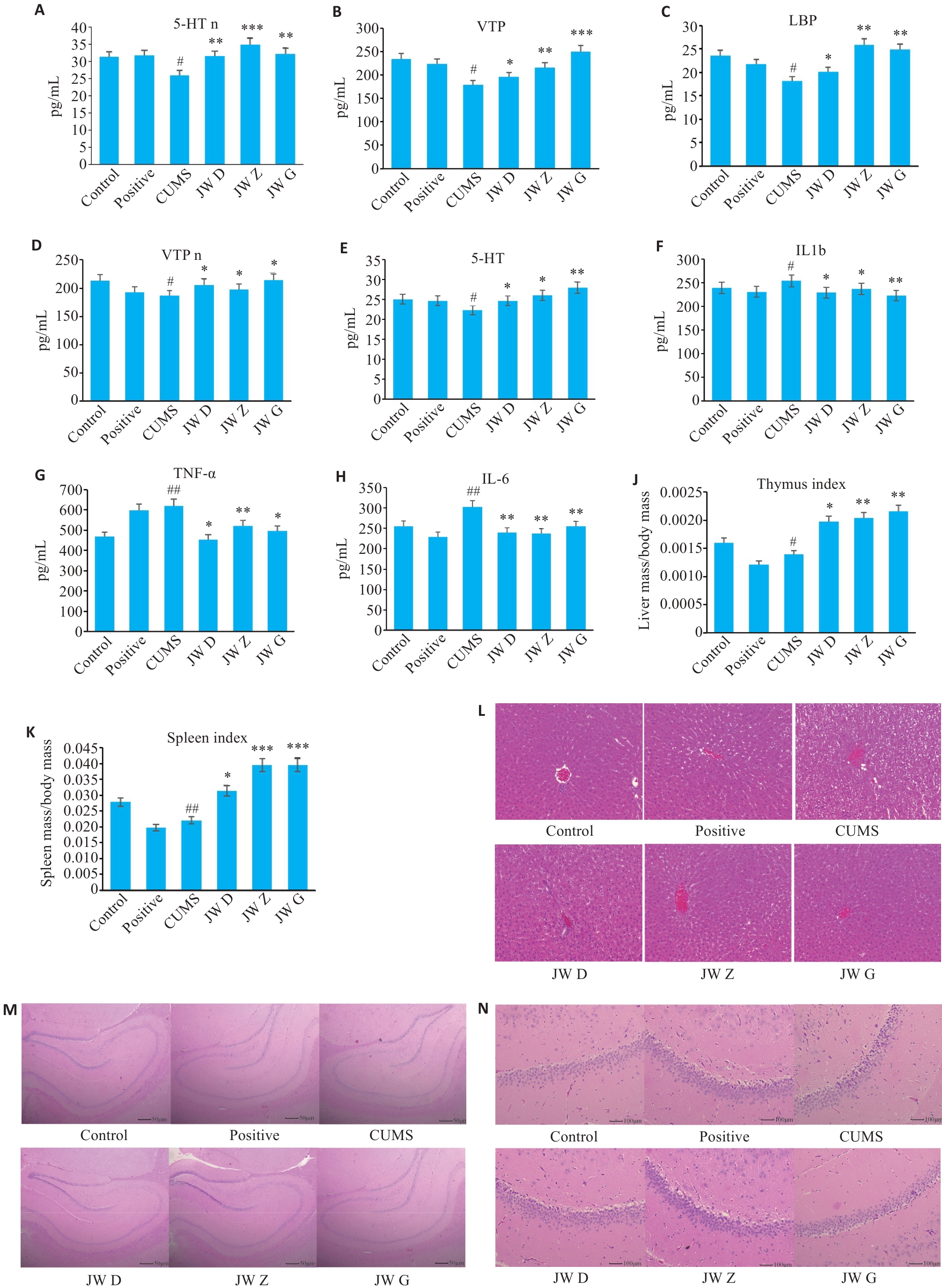
Fig.3 ELISA results, liver and spleen index, liver and hippocampus HE staining results. A, D: Content of VIP and 5-HT in the brain tissues. B, C, E-H: Serum levels of IL-6, TNF-α, VIP, 5-HT, ILβ and LBP. J, K: Thymus index and spleen index. L: HE staining of the liver tissues in each group (Original magnification: ×100). M: HE staining of rat hippocampus (×100). N: HE staining of hippocampal CA1 region of the rats (×200) . *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs model group (CUMS); #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs control group.
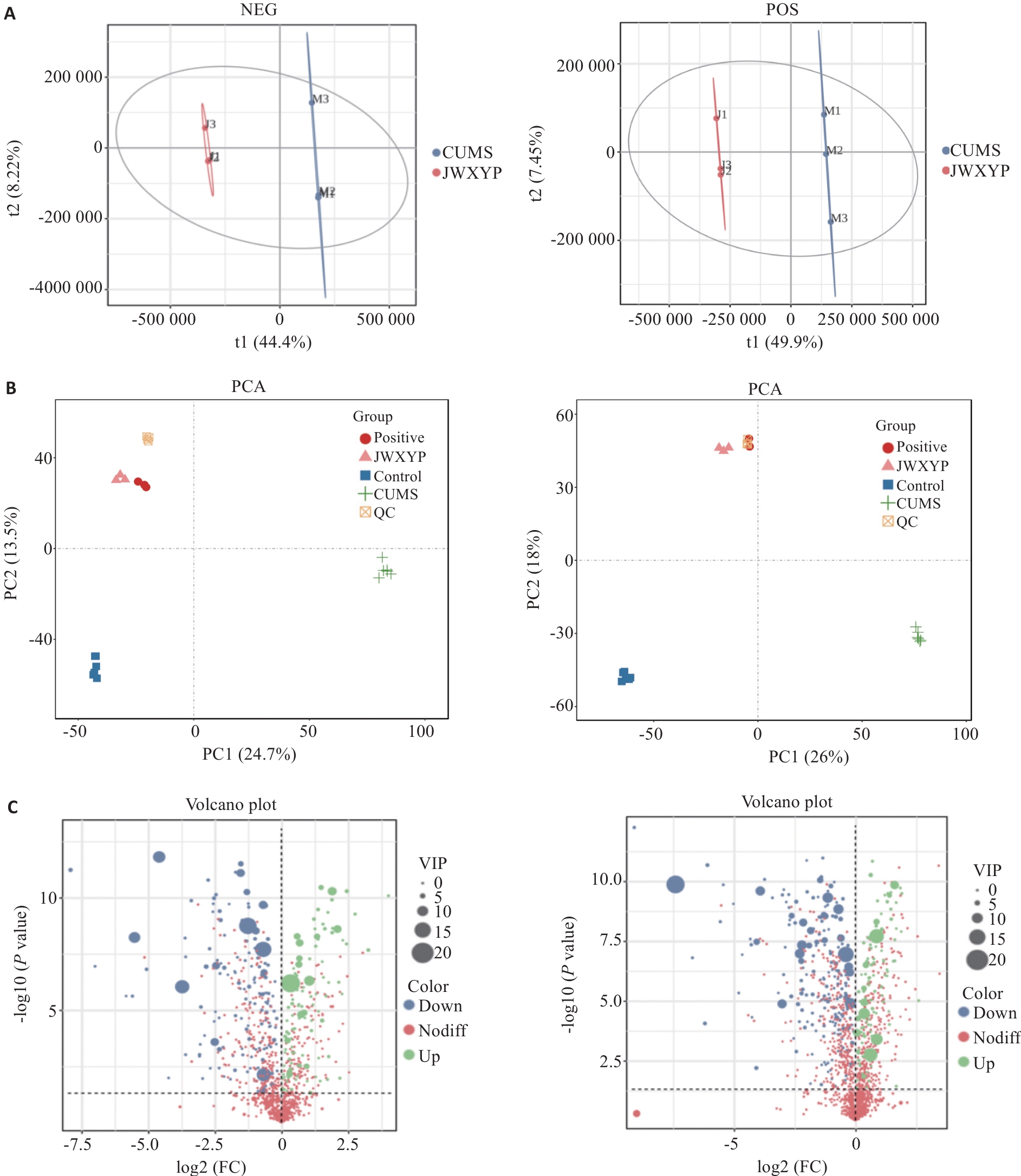
Fig.4 Identification of differential metabolites and multivariate statistical analysis. A: Principal component analysis. B: Partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA). C: Differential metabolite volcano plot analysis. The threshold of the difference was VIP≥1 and T-test P<0.05 in the OPLS-DA model.
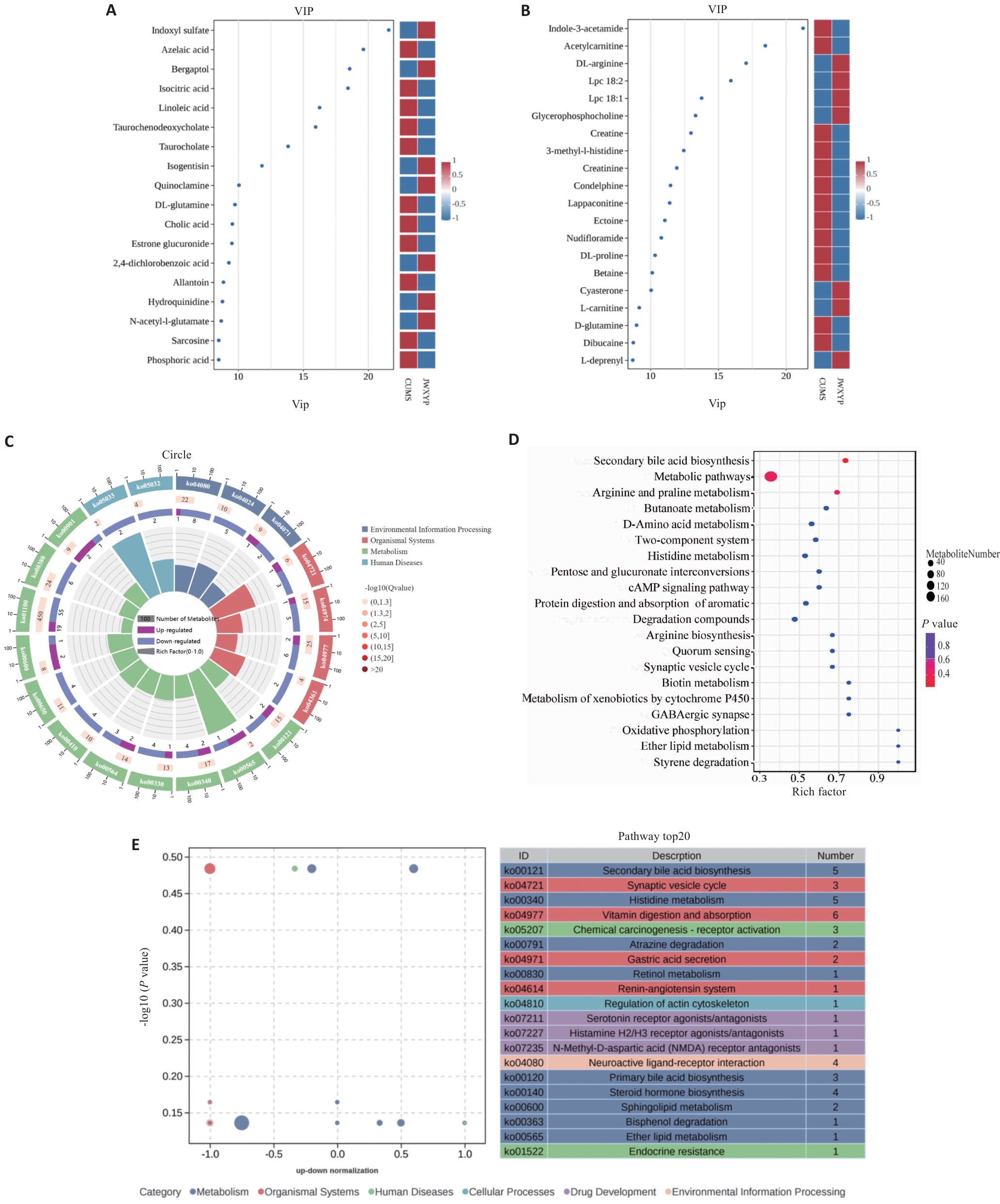
Fig.5 Effects of serum metabolites and metabolic pathway analysis. A: VIP (importance of variables in projection) diagram of OPLS-DA in POS mode. B: VIP diagram of OPLS-DA in NEG mode. C: KEGG enrichment circle diagram (CUMS vs JWJWXYP). D: KEGG enriched bubble diagram of the top 20 pathways with the smallest Q value. E: Metabolic pathway and classification between JWXYP and CUMS groups.
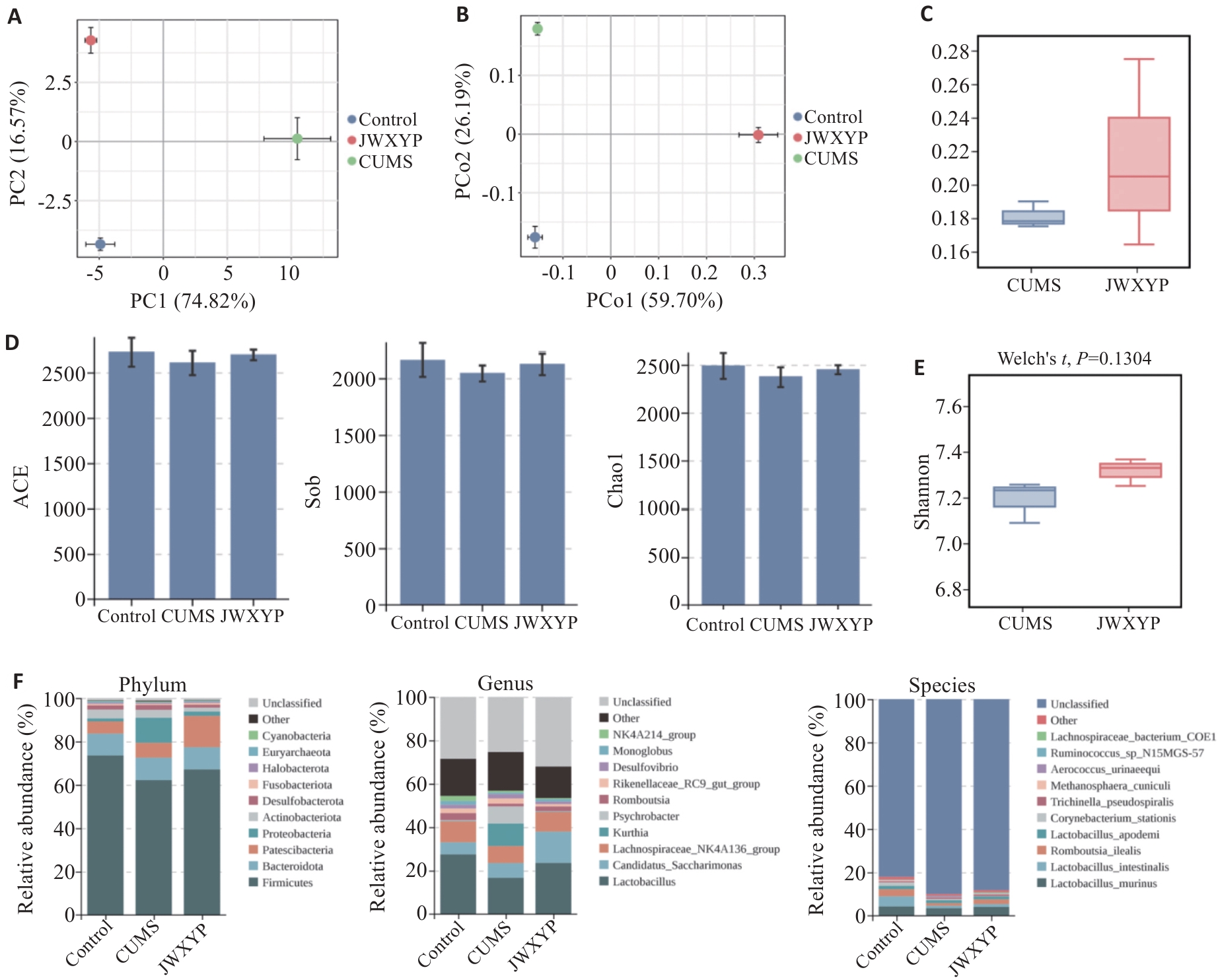
Fig.6 Intestinal flora species abundance and differential species. A: Distribution of samples in PC1 and PC2 dimensions. B: PCA analysis and PCoA analysis of the distribution of samples in PCo1 and PCo2 dimensions. C: β diversity box plot. D: Shaanon diversity index: ACE, Sob, Chao1 and Shannon index of Control, CIHMS and JWXYP groups. E: Distribution of Shannon index. F: Relative abundance of species at the phylum, class and species levels in control, CUMS and JWXYP groups.
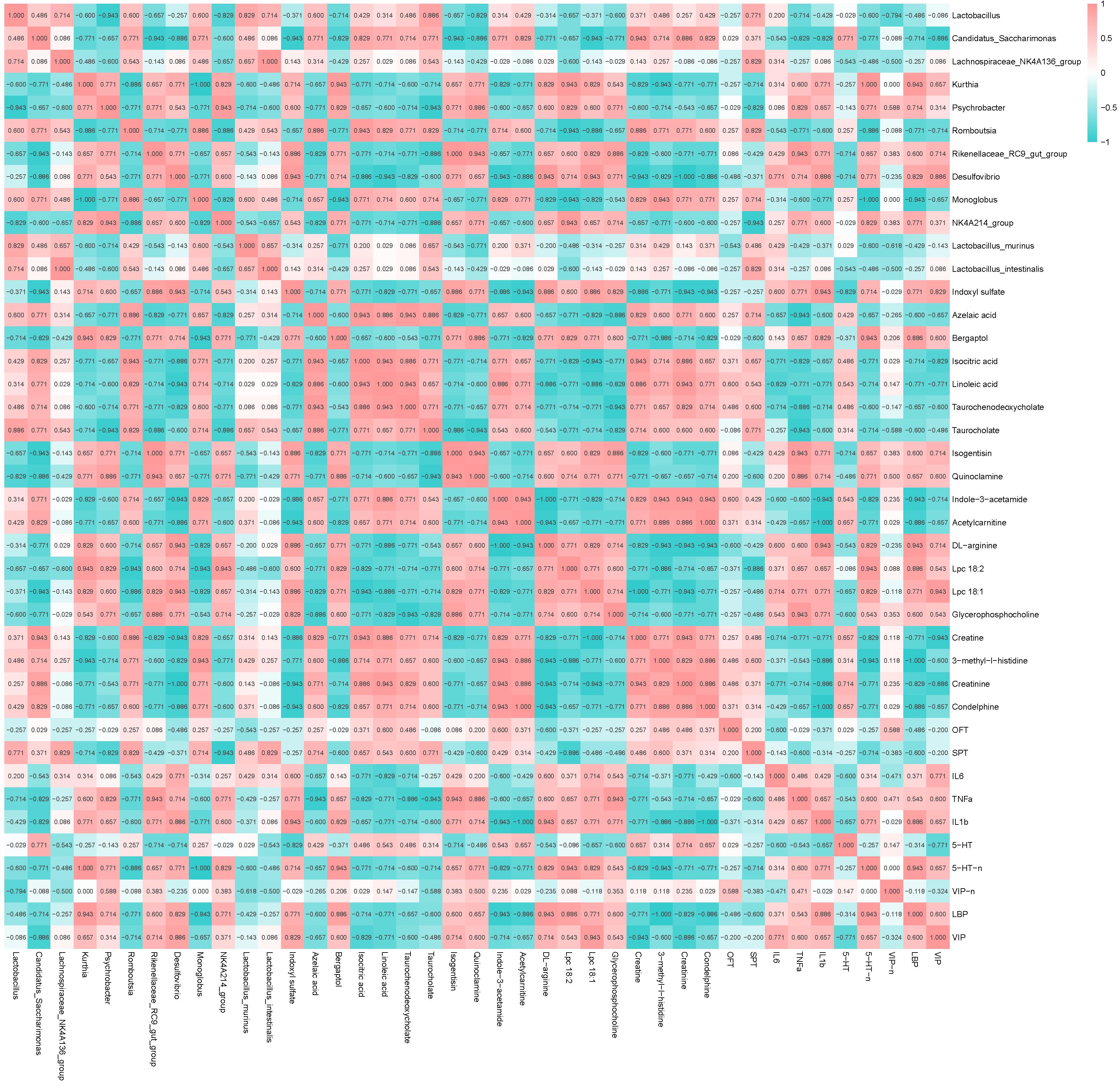
Fig.7 Spearman analysis of depression-related components, differential metabolites and differential intestinal flora in JWXYP-treated rats with CUMS-induced depression. P value and color depth represent the degree of correlation.*P<0.05, **P<0.01,***P<0.001, JW vs CUMS group.
| 1 | Chang LJ, Wei Y, Hashimoto K. Brain-gut-microbiota axis in depression: a historical overview and future directions[J]. Brain Res Bull, 2022, 182: 44-56. |
| 2 | Kim IB, Park SC, Kim YK. Microbiota-gut-brain axis in major depression: a new therapeutic approach[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2023, 1411: 209-24. |
| 3 | Liu SH, Guo RJ, Liu F, et al. Gut microbiota regulates depression-like behavior in rats through the neuroendocrine-immune-mitocho-ndrial pathway[J]. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat, 2020, 16: 859-69. |
| 4 | 吴 丹, 高 耀, 向 欢, 等. 逍遥散“异病同治” 抑郁症和糖尿病的网络药理学作用机制研究[J]. 中草药, 2019, 50(8): 1818-27. |
| 5 | 于冰清, 邵欣欣, 付晓凡, 等. 抗抑郁中药复方的组方特点及作用机制研究[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(11): 3344-52. |
| 6 | 宋)宋太医局编 (宋)陈 承, (宋)裴宗元, 宋)陈师文校正. 太平惠民和剂局方[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社, 2020. |
| 7 | Li ZX, Zhao YX, Cheng JL, et al. Integrated plasma metabolomics and gut microbiota analysis: the intervention effect of Jiawei Xiaoyao San on liver depression and spleen deficiency liver cancer rats[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 906256. |
| 8 | Xie JQ, Xu DD, Wang C, et al. Jiawei Xiaoyao San in treatment of anxiety disorder and anxiety: a review[J]. Chin Herb Med, 2023, 15(2): 214-21. |
| 9 | 平 凡, 朱 琳, 沈 霞, 等. 基于炎症因子、雌激素及骨稳态的多向调控研究肉桂-熟地黄防治骨质疏松的分子作用机制[J]. 药学学报, 2022, 57(12): 3644-52. |
| 10 | 王艳霞, 沈 霞, 颜永刚, 等. 基于UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS的大黄治疗血瘀证的多元统计分析及代谢调控机制研究[J]. 药学学报, 2022, 57(4): 1115-22. |
| 11 | 朱 琳, 刘 莹, 申 洁, 等. 基于功效实验-网络药理学-HPLC探讨大黄-桃仁配伍活血化瘀的物质基础及分子作用机制[J]. 药学学报, 2024, 59(7): 2126-34. |
| 12 | 沈 霞, 裴丽珊, 高 静, 等. 基于系统药理学逍遥散治疗抑郁症的分子机制初探[J]. 中南药学, 2019, 17(9): 1476-84. |
| 13 | 裴丽珊, 沈 霞, 颜永刚, 等. 基于血管内皮生长因子信号通路/肿瘤坏死因子信号通路的桃核承气汤防治脑卒中双向调节分子网络机制[J]. 药学学报, 2020, 55(5): 898-906. |
| 14 | Yan LJ, Xu X, He ZY, et al. Antidepressant-like effects and cognitive enhancement of coadministration of Chaihu Shugan San and fluoxetine: dependent on the BDNF-ERK-CREB signaling pathway in the hippocampus and frontal cortex[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 2794263. |
| 15 | Zhou XM, Liu CY, Liu YY, et al. Xiaoyaosan alleviates hippocampal glutamate-induced toxicity in the CUMS rats via NR2B and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 586788. |
| 16 | 乔明亮, 梁 硕, 孟 毅, 等. 柴胡皂苷A调节cAMP/PKA/CREB信号通路对失眠大鼠的改善作用及机制研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2024, 35(5): 633-8. |
| 17 | 于泽胜, 路腾飞, 周好波, 等. 柴胡白芍药对对慢性温和不可预知性应激抑郁模型大鼠脑内单胺类神经递质的影响[J]. 中草药, 2016, 47(16): 2887-92. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2016.16.019 |
| 18 | 左洁仪, 徐汪洋, 陈洪栋, 等. 槲皮素通过调控FoxO3a/TXNIP通路对神经细胞焦亡的影响[J]. 中药材, 2024, 47(5): 1271-6. |
| 19 | 李 红, 万珊珊, 刘志新, 等. 甘草查尔酮A通过PI3K/Akt信号通路对胶质瘤U87细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭和氧化损伤的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2024, 40(5): 678-82. |
| 20 | 何 芳, 丁 敏, 甄海宁, 等. 芍药苷通过STAT3抑制IL-13诱导的BEAS-2B细胞氧化应激和自噬[J]. 中国医院药学杂志, 2024, 44(13): 1535-40. |
| 21 | 庞彬彬, 陈 震, 邢怡桥. 芍药苷调节RhoA/ROCK信号通路对实验性自身免疫性葡萄膜炎小鼠Th17/Treg免疫平衡的影响[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2024, 35(4): 506-12. |
| 22 | Yang J, Zheng P, Li YF, et al. Landscapes of bacterial and metabolic signatures and their interaction in major depressive disorders[J]. Sci Adv, 2020, 6(49): eaba8555. |
| 23 | Amin N, Liu J, Bonnechere B, et al. Interplay of metabolome and gut microbiome in individuals with major depressive disorder vs control individuals[J]. JAMA Psychiatry, 2023, 80(6): 597-609. |
| 24 | 郭天灏, 程海波. 肠道菌群与氨基酸代谢的相互作用研究进展[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2023, 38(10): 4851-7. |
| 25 | Vang S, Longley K, Steer CJ, et al. The unexpected uses of urso- and tauroursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of non-liver diseases[J]. Glob Adv Health Med, 2014, 3(3): 58-69. |
| 26 | Cheng L, Huang C, Chen Z. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced depression like behavior in mice via the inhibition of neuroinflammation and oxido-nitrosative stress[J]. Pharmacology, 2019, 103(1/2): 93-100. |
| 27 | Peng LY, Shi HT, Tan YR, et al. Baicalin inhibits APEC-induced lung injury by regulating gut microbiota and SCFA production[J]. Food Funct, 2021, 12(24): 12621-33. |
| 28 | Amin N, Liu J, Bonnechere B, et al. Interplay of metabolome and gut microbiome in individuals with major depressive disorder vs control individuals[J]. JAMA Psychiatry, 2023, 80(6): 597-609. |
| 29 | 李雅青, 王玉静, 许嘉乾, 等. 乳酸菌对抑郁症的影响及其可能的作用机制[J]. 微生物学通报,2024: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.240596 . |
| 30 | Mela DJ. A proposed simple method for objectively quantifying free sugars in foods and beverages[J]. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2020, 74(9): 1366-8. |
| 31 | 吴振宁, 王 琦, 秦雪梅, 等. 肠道菌群及其代谢产物在中药治疗抑郁症中的研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2023, 54(14): 4713-21. |
| 32 | Raidoo S, Tschann M, Kaneshiro B, et al. Impact of insurance coverage for abortion in hawai'i on gestational age at presentation and type of abortion, 2010-2013[J]. Hawaii J Health Soc Welf, 2020, 79(4): 117-22. |
| 33 | Gao K, Mu CL, Farzi A, et al. Tryptophan metabolism: a link between the gut microbiota and brain[J]. Adv Nutr, 2020, 11(3): 709-23. |
| 34 | Zhang FL, Chen XW, Wang YF, et al. Microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites indole-3-lactic acid is associated with intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury via positive regulation of YAP and Nrf2[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21(1): 264. |
| 35 | Wang QW, Jia DJC, He JM, et al. Lactobacillus intestinalis primes epithelial cells to suppress colitis-related Th17 response by host-microbe retinoic acid biosynthesis[J]. Adv Sci, 2023, 10(36): e2303457. |
| 36 | 国立东, 王丽群. 综述乳酸菌对抑郁症的改善作用[J]. 中国食品学报, 2020, 20(7): 317-25. |
| 37 | Michaudel C, Sokol H. The gut microbiota at the service of immunometabolism[J]. Cell Metab, 2020, 32(4): 514-23. |
| 38 | Mihajlovic M, Wyss HM, Sijbesma RP. Effects of surfactant and urea on dynamics and viscoelastic properties of hydrophobically assembled supramolecular hydrogel[J]. Macromolecules, 2018, 51(13): 4813-20. |
| [1] | Haonan¹ XU, Fang³ ZHANG, Yuying² HUANG, Qisheng⁴ YAO, Yueqin⁴ GUAN, Hao CHEN. Thesium chinense Turcz. alleviates antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice by modulating gut microbiota structure and regulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [2] | Junjie GAO, Kai YE, Jing WU. Quercetin inhibits proliferation and migration of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells by regulating TP53 gene [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [3] | Qiao CHU, Xiaona WANG, Jiaying XU, Huilin PENG, Yulin ZHAO, Jing ZHANG, Guoyu LU, Kai WANG. Pulsatilla saponin D inhibits invasion and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells through multiple targets and pathways [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [4] | Xiupeng LONG, Shun TAO, Shen YANG, Suyun LI, Libing RAO, Li LI, Zhe ZHANG. Quercetin improves heart failure by inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis via suppressing the MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 187-196. |
| [5] | Meng XU, Lina CHEN, Jinyu WU, Lili LIU, Mei SHI, Hao ZHOU, Guoliang ZHANG. Mechanism of Hedyotis diffusa-Scutellaria barbata D. Don for treatment of primary liver cancer: analysis with network pharmacology, molecular docking and in vitro validation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 80-89. |
| [6] | Qing LIU, Jing LIU, Yihang ZHENG, Jin LEI, Jianhua HUANG, Siyu LIU, Fang LIU, Qunlong PENG, Yuanfang ZHANG, Junjie WANG, Yujuan LI. Quercetin mediates the therapeutic effect of Centella asiatica on psoriasis by regulating STAT3 phosphorylation to inhibit the IL-23/IL-17A axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 90-99. |
| [7] | Xingmei CHEN, Qinwen LIU, Yi LI, Xiaoyu ZHONG, Qiling FAN, Ke MA, Liuting LUO, Daogang GUAN, Zhibo ZHU. Analysis of core functional components in Yinchenhao Decoction and their pathways for treating liver fibrosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1508-1517. |
| [8] | Shanyuan ZHANG, Qiaoyan CAI, Jianghan QI, Kaixin YIN, Chenchen HE, Zhuye GAO, Ling ZHANG, Jianfeng CHU. Pharmacodynamics of Qingxin Jieyu Granules for treatment of atherosclerosis and its regulatory mechanism for lipid metabolism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1518-1528. |
| [9] | Yuming ZHANG, Shicheng XIA, Linlin ZHANG, Mengxi CHEN, Xiaojing LIU, Qin GAO, Hongwei YE. Protective effect of Lonicerae japonicae flos extract against doxorubicin-induced liver injury in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1571-1581. |
| [10] | Jinjin WANG, Wenfei CUI, Xuewei DOU, Binglei YIN, Yuqi NIU, Ling NIU, Guoli YAN. Euonymus alatus delays progression of diabetic kidney disease in mice by regulating EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1243-1255. |
| [11] | Linyue WANG, Wenyue QI, Jihua GAO, Maosheng TIAN, Jiancheng XU. Tongyangxiao Lotion promotes postoperative wound healing in a rat model of anal fistula by downregulating inflammatory factors and suppressing inflammation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1256-1265. |
| [12] | Wenxiang ZHANG, Huixian GU, Pengde CHEN, Siyu WU, Hongyan MA, Lan YAO. Compound Yuye Decoction protects diabetic rats against cardiomyopathy by inhibiting myocardial apoptosis and inflammation via regulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1306-1314. |
| [13] | Yan HUANG, Lulu QIN, Shaoxing GUAN, Yanping GUANG, Yuru WEI, Ailing CAO, Dongmei LI, Guining WEI, Qibiao SU. Therapeutic mechanism of aqueous extract of Semiliquidambar cathayensis Chang root for pancreatic cancer: the active components, therapeutic targets and pathways [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1336-1344. |
| [14] | Zhijun REN, Jianxin DIAO, Yiting WANG. Xionggui Decoction alleviates heart failure in mice with myocardial infarction by inhibiting oxidative stress-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1416-1424. |
| [15] | Ruibo LI, Ge GAO, Xi XIE, Haibin LUO. Oral submucosal fibrosis induced by active components in areca nut: a network pharmacology-based analysis and validation of the mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 930-940. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||