Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2738-2746.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.21
Xinxin LIU1( ), Yingrui XU2, Hongna SHENG3, Hao LIU1(
), Yingrui XU2, Hongna SHENG3, Hao LIU1( )
)
Received:2025-04-21
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Hao LIU
E-mail:1165462226@qq.com;13651138303@163.com
Xinxin LIU, Yingrui XU, Hongna SHENG, Hao LIU. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell grafting alleviates inflammatory response in type 1 diabetic mice by suppressing M1 macrophage polarization through Chi3l1[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2738-2746.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.21
| Primer | Sequence (5'→3') | |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | Forword: | ACACTCCAGCTGGGGCTGTACTGACTTGATG |
| Reverse: | CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCG GCAATTCAGTTGAGCATCAGAT | |
| Chi3l1 | Forword: | AAGCAACGATCACATCGACAC |
| Reverse: | TCAGGTTGGGGTTCCTGTTCT | |
| iNOS | Forword: | CCAACAATACAAGATGACCCT |
| Reverse: | TTCTGGAACATTCTGTGCTG | |
| Arg-1 | Forword: | GAACTGAAAGGAAAGTTCCCA |
| Reverse: | AATGTACACGATGTCTTTGGC | |
| TNF-α | Forword: | GGCAGGTCTACTTTFFAGTCATTGC |
| Reverse: | ACATTCGAGGCTCCAGTGAATTCGG | |
| IL-6 | Forword: | TACCACTTCACAAGTCGGA |
| Reverse: | AATTGCCATTGCACAACTC | |
| IL-10 | Forword: | TTAATAAGCTCCAAGACCAAGG |
| Reverse: | CATCATGTATGCTTCTATGCAG | |
| IL-13 | Forword: | TCCCTCAAGTTCTTTGTTCG |
| Reverse: | CGCACCTTTCTGGTTACAC | |
| IL-1β | Forword: | CCTCAAAGGAAAGAATCTATACCTG |
| Reverse: | CTTGGGATCCACACTCTCC | |
Tab.1 Primer sequences for qPCR
| Primer | Sequence (5'→3') | |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | Forword: | ACACTCCAGCTGGGGCTGTACTGACTTGATG |
| Reverse: | CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCG GCAATTCAGTTGAGCATCAGAT | |
| Chi3l1 | Forword: | AAGCAACGATCACATCGACAC |
| Reverse: | TCAGGTTGGGGTTCCTGTTCT | |
| iNOS | Forword: | CCAACAATACAAGATGACCCT |
| Reverse: | TTCTGGAACATTCTGTGCTG | |
| Arg-1 | Forword: | GAACTGAAAGGAAAGTTCCCA |
| Reverse: | AATGTACACGATGTCTTTGGC | |
| TNF-α | Forword: | GGCAGGTCTACTTTFFAGTCATTGC |
| Reverse: | ACATTCGAGGCTCCAGTGAATTCGG | |
| IL-6 | Forword: | TACCACTTCACAAGTCGGA |
| Reverse: | AATTGCCATTGCACAACTC | |
| IL-10 | Forword: | TTAATAAGCTCCAAGACCAAGG |
| Reverse: | CATCATGTATGCTTCTATGCAG | |
| IL-13 | Forword: | TCCCTCAAGTTCTTTGTTCG |
| Reverse: | CGCACCTTTCTGGTTACAC | |
| IL-1β | Forword: | CCTCAAAGGAAAGAATCTATACCTG |
| Reverse: | CTTGGGATCCACACTCTCC | |
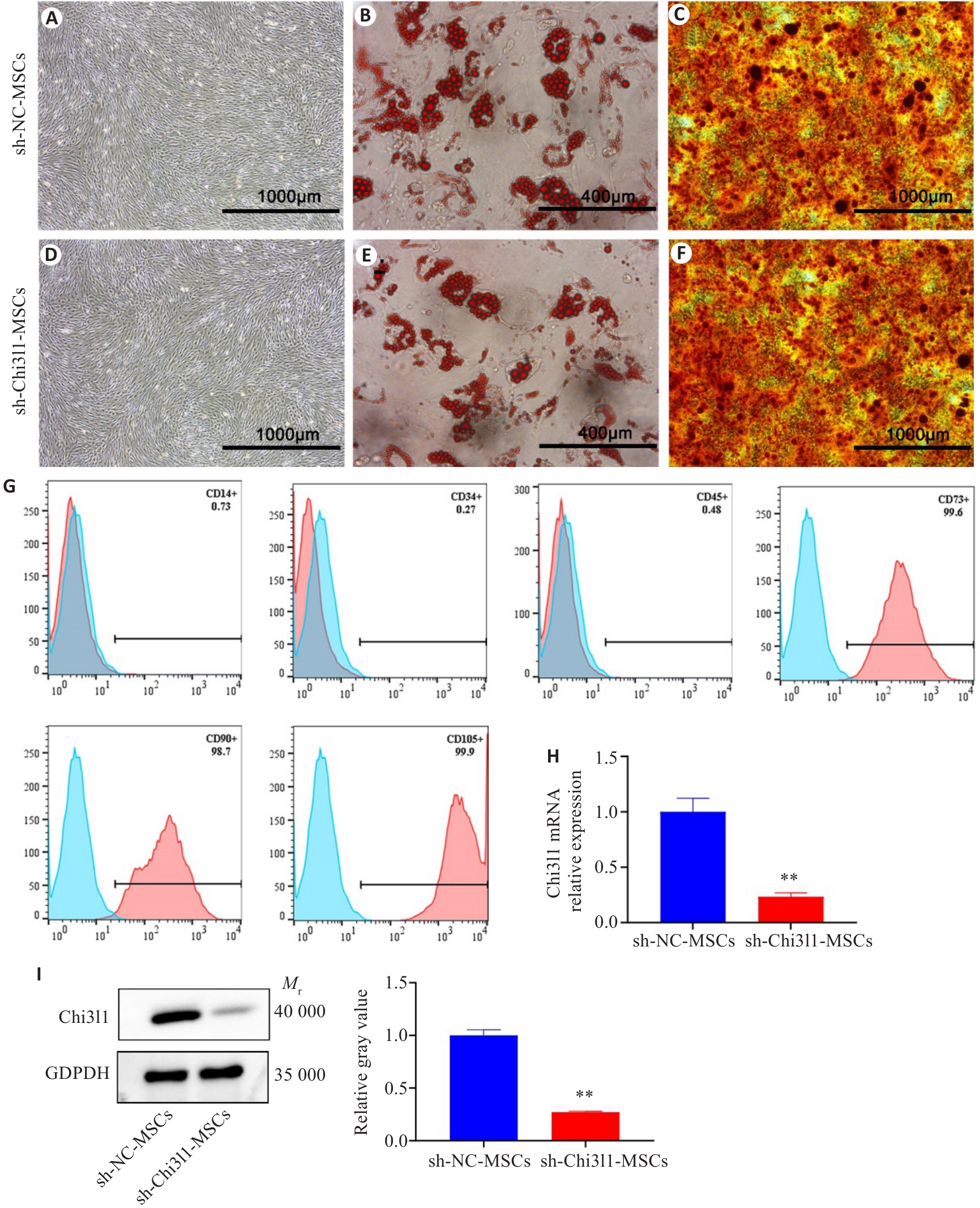
Fig.1 Identification of MSCs with stable Chi3l1 knockdown. A: Morphology of sh-NC-MSCs. B: Oil Red O staining of sh-NC-MSCs after adipogenic induction. C: Alizarin Red S staining of sh-NC-MSCs after osteogenic induction. D: Morphology of sh-Chi3l1-MSCs. E: Oil Red O staining of sh-Chi3l1-MSCs after adipogenic induction. F: Alizarin Red S staining of sh-Chi3l1-MSCs after osteogenic induction. G: Detection of surface markers on sh-Chi3l1-MSCs by flow cytometry. H: Chi3l1 mRNA expression level in sh-Chi3l1-MSCs. I: Protein level of Chi3l1 in sh-Chi3l1-MSCs detected by Western blotting. **P<0.01 vs sh-NC-MSCs.
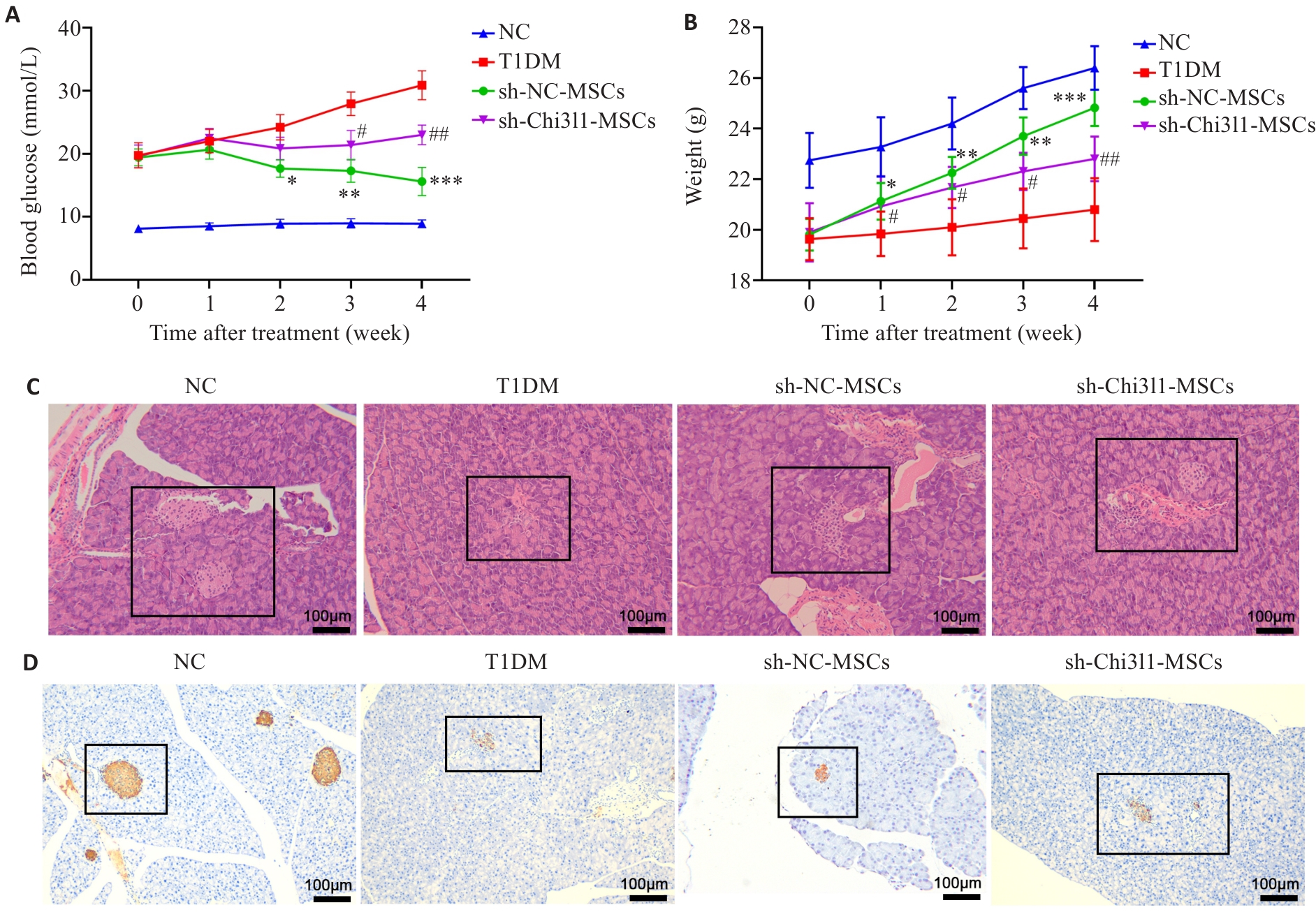
Fig.2 Chi3l1 knockdown attenuates therapeutic efficacy of MSCs in T1DM mice. A: Blood glucose levels of the mice in each group over the course of treatment. B: Body weight changes of the mice in each group (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs T1DM group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs sh-NC-MSCs group). C: Pancreatic pathological changes in each group (HE staining, original magnification: ×100). D: Insulin content in the pancreas of the mice in each group detected by immunohistochemical staining (×100).
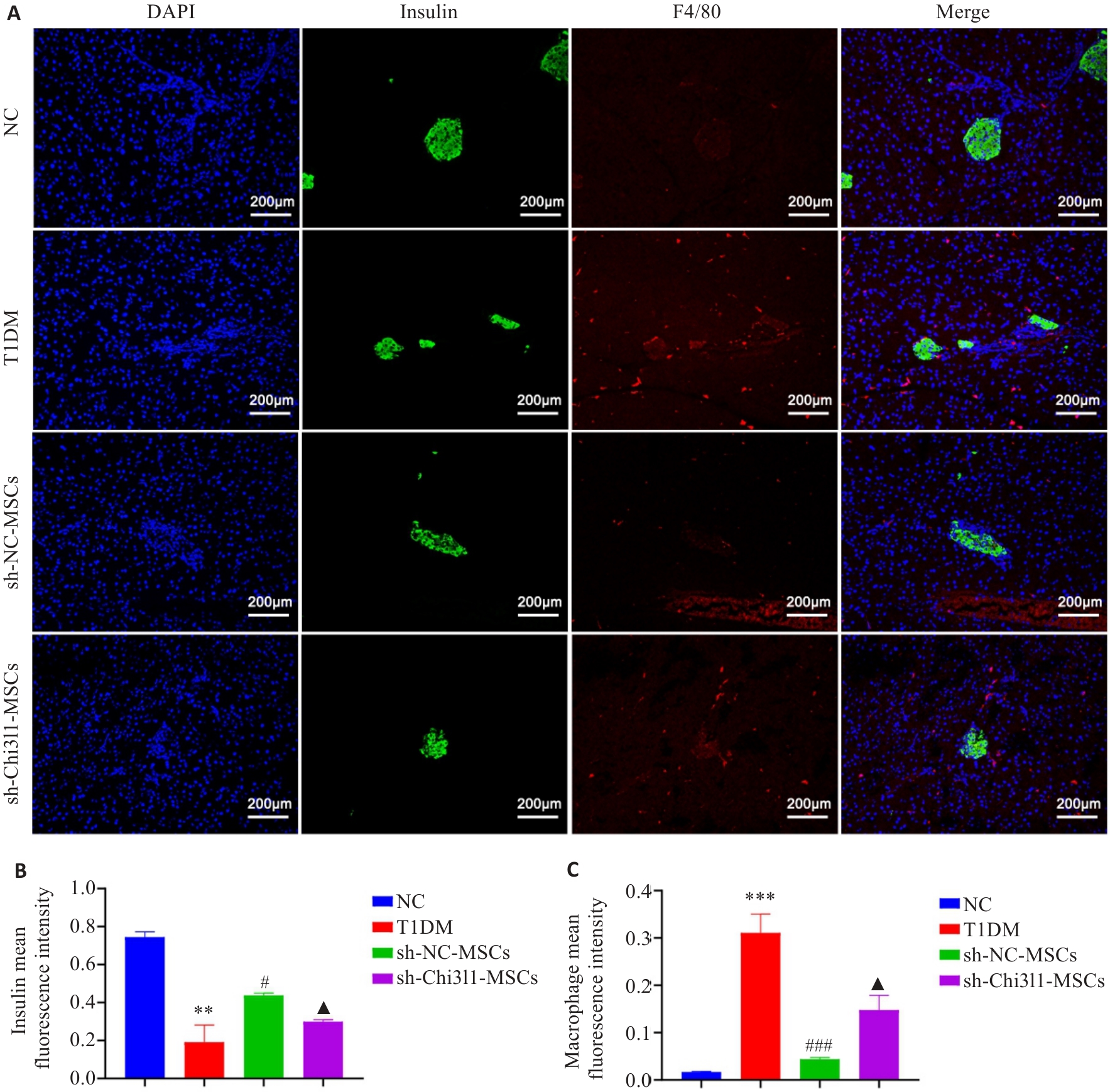
Fig.3 Changes in insulin content and macrophage infiltration in pancreatic tissues of mice. A: Insulin content (green) and macrophage infiltration (red) in pancreatic tissues of mice from each group detected by immunofluorescence staining (×200). B. Statistical analysis of insulin content within individual islets of mice in each group. C: Quantitative analysis of the mean immunofluorescence intensity of macrophages in pancreatic tissues across the groups. **P<0.01,***P<0.001 vs NC group; #P<0.05, ###P<0.001 vs T1DM group; ▲P<0.05 vs sh-NC-MSCs group.
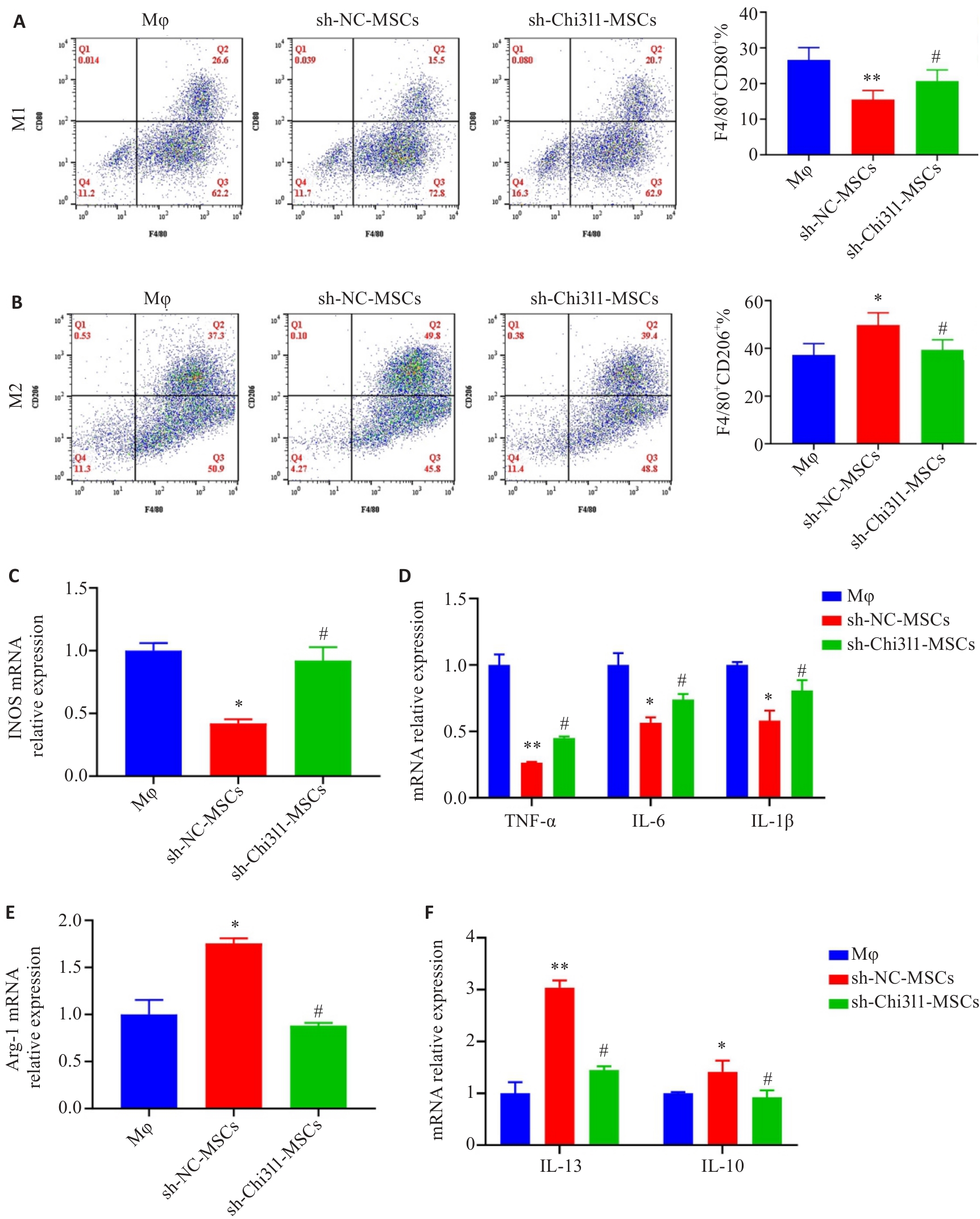
Fig.4 Chi3l1 influences hUC-MSCs-mediated regulation of macrophage polarization. A: Frequency of M1-type macrophages analyzed using flow cytometry. B: Frequency of M2-type macrophages analyzed using flow cytometry. C: Expression of iNOS mRNA detected with qPCR. D: Expressions of mRNAs for inflammatory cytokines detected by qPCR. E: Expression of Arg-1 mRNA detected with qPCR. F: Expressions of mRNAs for anti-inflammatory cytokines detected by qPCR. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Mφ group; #P<0.05 vs sh-NC-MSCs group.
| [1] | Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Magliano DJ, et al. Diabetes mellitus statistics on prevalence and mortality: facts and fallacies[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2016, 12(10): 616-22. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2016.105 |
| [2] | Harjutsalo V, Maric-Bilkan C, Forsblom C, et al. Impact of sex and age at onset of diabetes on mortality from ischemic heart disease in patients with type 1 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Care, 2014, 37(1): 144-8. doi:10.2337/dc13-0377 |
| [3] | Hummel S, Weiß A, Bonifacio E, et al. Associations of breastfeeding with childhood autoimmunity, allergies, and overweight: The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young (TEDDY) study[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2021, 114(1): 134-42. doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqab065 |
| [4] | Rewers M, Ludvigsson J. Environmental risk factors for type 1 diabetes[J]. Lancet, 2016, 387(10035): 2340-8. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(16)30507-4 |
| [5] | Shi M, Liu ZW, Wang FS. Immunomodulatory properties and therapeutic application of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2011, 164(1): 1-8. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04327.x |
| [6] | Schwartz YS, Svistelnik AV. Functional phenotypes of macrophages and the M1-M2 polarization concept. Part I. Proinflammatory phenotype[J]. Biochemistry (Mosc), 2012, 77(3): 246-60. doi:10.1134/s0006297912030030 |
| [7] | Coulson-Thomas VJ, Coulson-Thomas YM, Gesteira TF, et al. Extrinsic and intrinsic mechanisms by which mesenchymal stem cells suppress the immune system[J]. Ocul Surf, 2016, 14(2): 121-34. doi:10.1016/j.jtos.2015.11.004 |
| [8] | 周 娜, 刘伟江, 李 苹, 等. 间充质干细胞通过调控巨噬细胞极化减轻1型糖尿病模型小鼠炎症反应[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2018, 32(11): 876-84. |
| [9] | Zhao T, Su ZP, Li YC, et al. Chitinase-3 like-protein-1 function and its role in diseases[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2020, 5(1): 201. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00303-7 |
| [10] | Chen YL, Zhang SY, Wang QZ, et al. Tumor-recruited M2 macrophages promote gastric and breast cancer metastasis via M2 macrophage-secreted CHI3L1 protein[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2017, 10(1): 36. doi:10.1186/s13045-017-0408-0 |
| [11] | Liu QL, Chen XY, Liu C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate experimental immune-mediated liver injury via chitinase 3-like protein 1-mediated T cell suppression[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(3): 240. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-03524-y |
| [12] | Furman BL. Streptozotocin-induced diabetic models in mice and rats[J]. Curr Protoc, 2021, 1(4): e78. doi:10.1002/cpz1.78 |
| [13] | Tang YJ, Zhang Z, Yan T, et al. Irisin attenuates type 1 diabetic cardiomyopathy by anti-ferroptosis via SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of p53[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2024, 23(1): 116. doi:10.1186/s12933-024-02183-5 |
| [14] | Cho DI, Kim MR, Jeong HY, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells reciprocally regulate the M1/M2 balance in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2014, 46(1): e70. doi:10.1038/emm.2013.135 |
| [15] | Trouplin V, Boucherit N, Gorvel L, et al. Bone marrow-derived macrophage production[J]. J Vis Exp, 2013(81): e50966. doi:10.3791/50966-v |
| [16] | Pugliese A. Insulitis in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes[J]. Pediatr Diabetes, 2016, 17(Suppl Suppl 22): 31-6. doi:10.1111/pedi.12388 |
| [17] | Scherm MG, Wyatt RC, Serr I, et al. Beta cell and immune cell interactions in autoimmune type 1 diabetes: How they meet and talk to each other[J]. Mol Metab, 2022, 64: 101565. doi:10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101565 |
| [18] | Bottino R, Knoll MF, Knoll CA, et al. The future of islet transplantation is now[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2018, 5: 202. doi:10.3389/fmed.2018.00202 |
| [19] | Verhoeff K, Marfil-Garza BA, James Shapiro AM. Update on islet cell transplantation[J]. Curr Opin Organ Transplant, 2021, 26(4): 397-404. doi:10.1097/mot.0000000000000891 |
| [20] | Li CH, Gao QY, Jiang H, et al. Changes of macrophage and CD4+ T cell in inflammatory response in type 1 diabetic mice[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 14929. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-19031-9 |
| [21] | Höglund P, Mintern J, Waltzinger C, et al. Initiation of autoimmune diabetes by developmentally regulated presentation of islet cell antigens in the pancreatic lymph nodes[J]. J Exp Med, 1999, 189(2): 331-9. doi:10.1084/jem.189.2.331 |
| [22] | Mallone R, Brezar V, Boitard C. T cell recognition of autoantigens in human type 1 diabetes: clinical perspectives[J]. Clin Dev Immunol, 2011, 2011: 513210. doi:10.1155/2011/513210 |
| [23] | Coope A, Torsoni AS, Velloso LA. Mechanisms in endocrinology: Metabolic and inflammatory pathways on the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes[J]. Eur J Endocrinol, 2016, 174(5): R175-87. doi:10.1530/eje-15-1065 |
| [24] | Calderon B, Suri A, Unanue ER. In CD4+ T-cell-induced diabetes, macrophages are the final effector cells that mediate islet beta-cell killing: studies from an acute model[J]. Am J Pathol, 2006, 169(6): 2137-47. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2006.060539 |
| [25] | Wang FX, Sun F, Luo JH, et al. Loss of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 (Ubc9) in macrophages exacerbates multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes by attenuating M2 macrophage polarization[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10(12): 892. doi:10.1038/s41419-019-2130-z |
| [26] | Sicco CL, Reverberi D, Balbi C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles as mediators of anti-inflammatory effects: endorsement of macrophage polarization[J]. Stem Cells Transl Med, 2017, 6(3): 1018-28. doi:10.1002/sctm.16-0363 |
| [27] | Zhang CY, Han X, Yang L, et al. Circular RNA circPPM1F modulates M1 macrophage activation and pancreatic islet inflammation in type 1 diabetes mellitus[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(24): 10908-24. doi:10.7150/thno.48264 |
| [28] | Zhao JX, Li XL, Hu JX, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes attenuate myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury through miR-182-regulated macrophage polarization[J]. Cardio-vasc Res, 2019, 115(7): 1205-16. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvz040 |
| [29] | Liu F, Qiu HB, Xue M, et al. MSC-secreted TGF-β regulates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophage M2-like polarization via the Akt/FoxO1 pathway[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2019, 10(1): 345. doi:10.1186/s13287-019-1447-y |
| [30] | Freytes DO, Kang JW, Marcos-Campos I, et al. Macrophages modulate the viability and growth of human mesenchymal stem cells[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2013, 114(1): 220-9. doi:10.1002/jcb.24357 |
| [31] | Ma B, Herzog EL, Lee CG, et al. Role of chitinase 3-like-1 and semaphorin 7a in pulmonary melanoma metastasis[J]. Cancer Res, 2015, 75(3): 487-96. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-13-3339 |
| [32] | Cohen N, Shani O, Raz Y, et al. Fibroblasts drive an immunosuppressive and growth-promoting microenvironment in breast cancer via secretion of Chitinase 3-like 1[J]. Oncogene, 2017, 36(31): 4457-68. doi:10.1038/onc.2017.65 |
| [1] | . Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into neuron-like cells after induction with B27-supplemented serum-free medium [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(09): 1340-1345. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||