Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1173-1181.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.06.19
Guoxin LIANG1,2,3( ), Hongyue TANG3,4, Chang GUO2,3, Mingming ZHANG3
), Hongyue TANG3,4, Chang GUO2,3, Mingming ZHANG3
Received:2024-01-03
Online:2024-06-20
Published:2024-07-01
Contact:
Mingming ZHANG
E-mail:lgx202309@163.com
Guoxin LIANG, Hongyue TANG, Chang GUO, Mingming ZHANG. MiR-224-5p overexpression inhibits oxidative stress by regulating the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 axis to attenuate hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte injury[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1173-1181.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.06.19
| Clinical parameters | STEMI (n=80) | NSTEMI (n=80) | HC (n=80) | P1 | P2 | P3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 60.5±11.46 | 58.58±12.19 | 59.24±12.85 | 0.514 | 0.739 | 0.306 |
| Gender (male/female) | 44/36 | 41/39 | 43/37 | 0.950 | 0.874 | 0.635 |
| Hypertension | 75% (60) | 72% (58) | 0 | ≠ | ≠ | 0.720 |
| Tobacco | 70% (56) | 65% (52) | 50% (40) | 0.001 | 0.055 | 0.971 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 40% (32) | 30% (24) | 0 | ≠ | ≠ | 0.185 |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 80% (64) | 75% (60) | 0 | ≠ | ≠ | 0.449 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 25.2±4.2 | 24.5±3.4 | 22.4±1.8 | 0.795 | 0.839 | 0.973 |
| Previous MI | 10% (8) | 6% (4) | 0 | ≠ | ≠ | 0.378 |
| Previous PTCA | 6 | 4 | 0 | ≠ | ≠ | 0.744 |
| Previous CABG | 5% (4) | 2% (2) | 0 | ≠ | ≠ | 0.701 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 18.17±5.52 | 18.51±4.86 | 2.13±1.36 | <0.05 | <0.005 | 0.680 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 5.75±1.85 | 5.68±1.82 | 4.81±0.48 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.810 |
| CK(U/L) | 483.9±57.27 | 474.9±50.49 | 127.29±26.33 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.293 |
| CK-MB(U/L) | 76.43±23.85 | 73.71±20.68 | 9.82±4.88 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.472 |
| cTnI (mg/mL) | 163.66±21.50 | 160.73±23.88 | 26.40±13.77 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.403 |
Tab.1 Clinical parameters of the participants
| Clinical parameters | STEMI (n=80) | NSTEMI (n=80) | HC (n=80) | P1 | P2 | P3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 60.5±11.46 | 58.58±12.19 | 59.24±12.85 | 0.514 | 0.739 | 0.306 |
| Gender (male/female) | 44/36 | 41/39 | 43/37 | 0.950 | 0.874 | 0.635 |
| Hypertension | 75% (60) | 72% (58) | 0 | ≠ | ≠ | 0.720 |
| Tobacco | 70% (56) | 65% (52) | 50% (40) | 0.001 | 0.055 | 0.971 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 40% (32) | 30% (24) | 0 | ≠ | ≠ | 0.185 |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 80% (64) | 75% (60) | 0 | ≠ | ≠ | 0.449 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 25.2±4.2 | 24.5±3.4 | 22.4±1.8 | 0.795 | 0.839 | 0.973 |
| Previous MI | 10% (8) | 6% (4) | 0 | ≠ | ≠ | 0.378 |
| Previous PTCA | 6 | 4 | 0 | ≠ | ≠ | 0.744 |
| Previous CABG | 5% (4) | 2% (2) | 0 | ≠ | ≠ | 0.701 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 18.17±5.52 | 18.51±4.86 | 2.13±1.36 | <0.05 | <0.005 | 0.680 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 5.75±1.85 | 5.68±1.82 | 4.81±0.48 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.810 |
| CK(U/L) | 483.9±57.27 | 474.9±50.49 | 127.29±26.33 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.293 |
| CK-MB(U/L) | 76.43±23.85 | 73.71±20.68 | 9.82±4.88 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.472 |
| cTnI (mg/mL) | 163.66±21.50 | 160.73±23.88 | 26.40±13.77 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.403 |
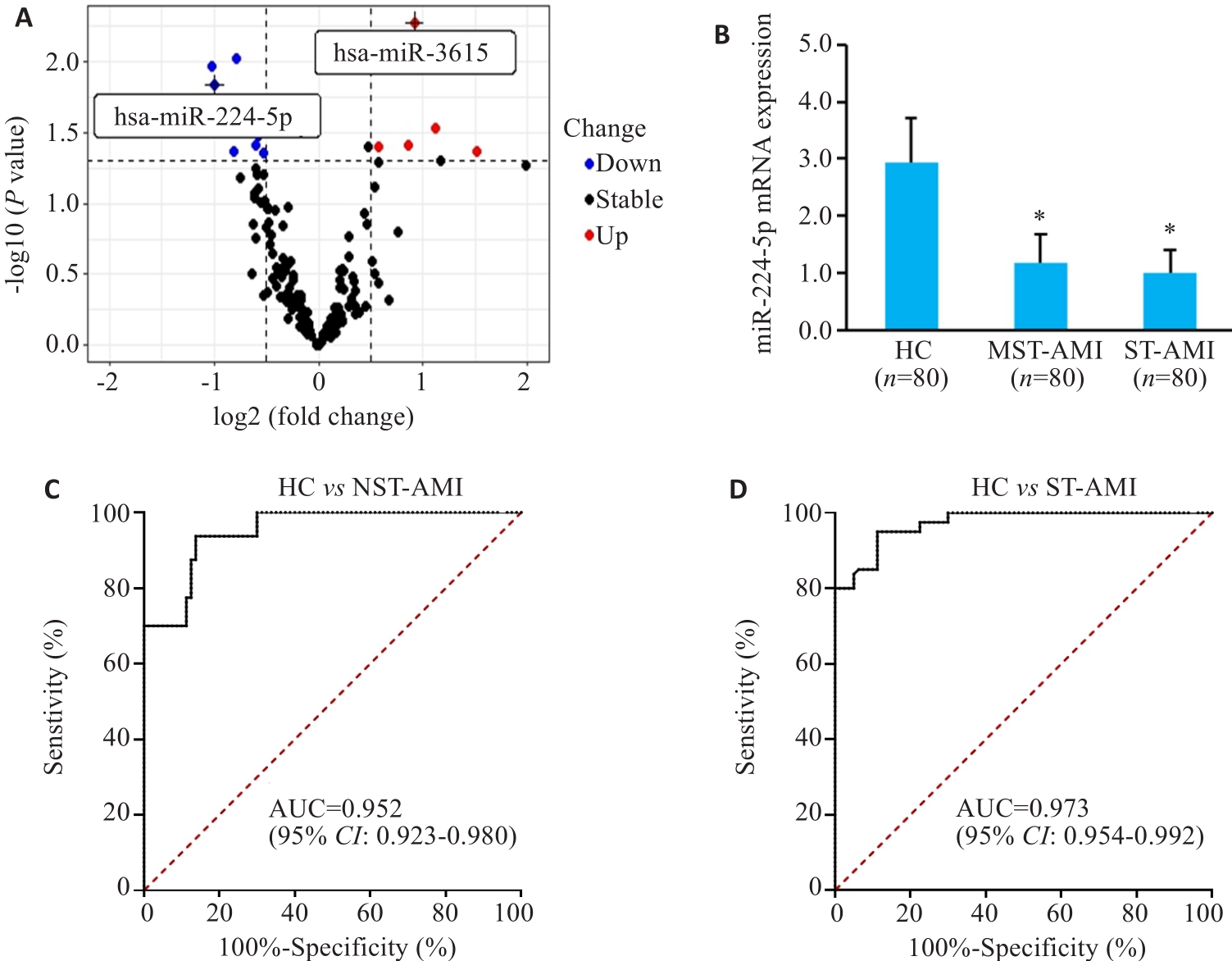
Fig.1 Expression level of miR-224-5p and its clinical diagnostic value. A: High-throughput data analysis. B: miR-224-5p expression levels.*P<0.05 vs HC group; C: AUC of HC vs STEMI; D: AUC of HC vs NSTEMI.
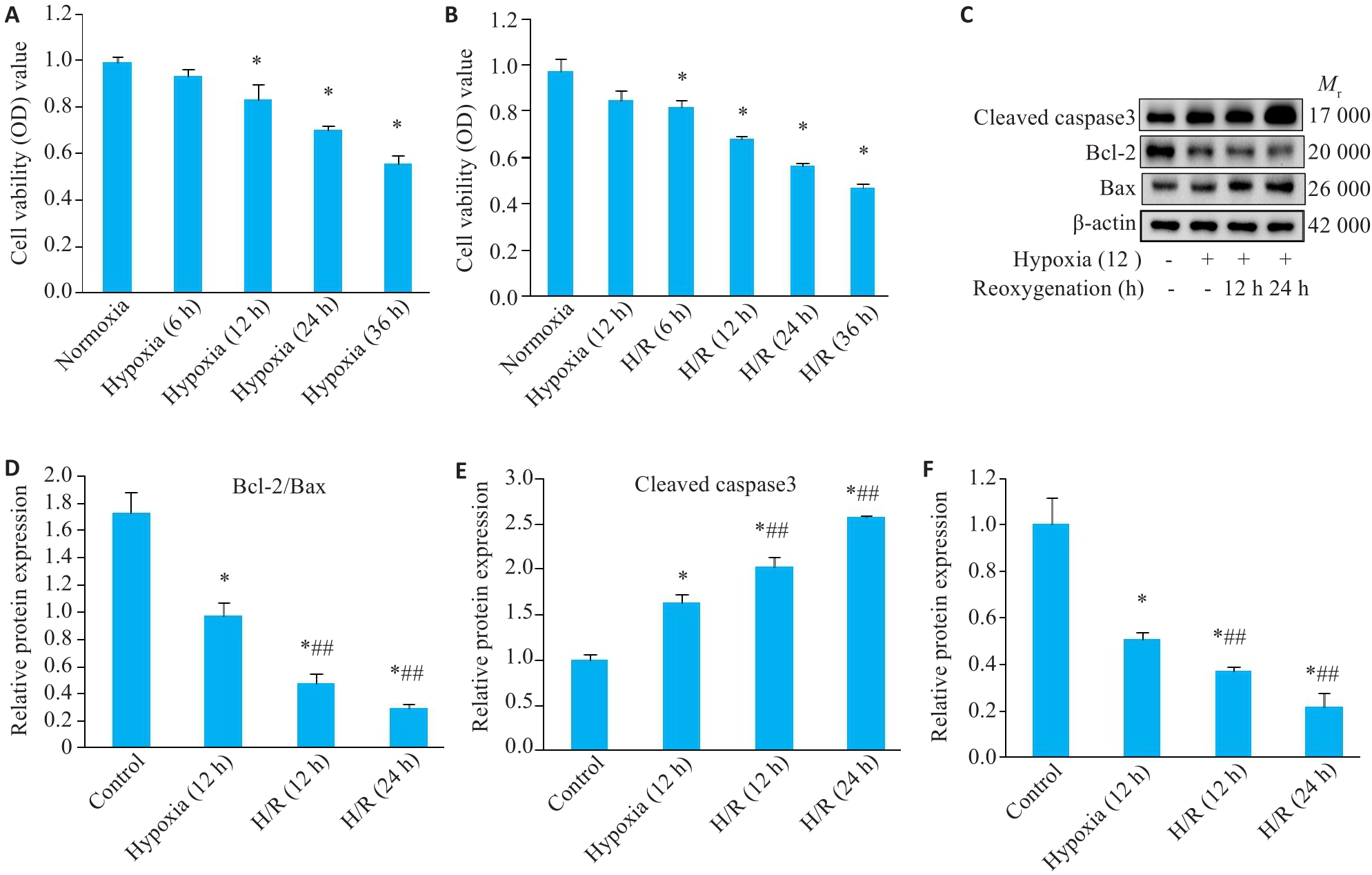
Fig.2 Hypoxia/reoxygenation decreases viability and promotes apoptosis of cultured cardiomyocytes. A, B: MTT colorimetric assay to determine cell viability (Mean±SD, n=6). C: Western blotting for detecting protein expressions of cleaved caspase3, Bcl-2, and Bax. D-F: Relative expressions of Bcl2/Bax proteins, cleaved caspase3 and miR-224-5p in H9c2 cells in each group (Mean±SD, n=3). compared with Control group, *P<0.05; ##P<0.05 vs Hypoxia (12 h) group.
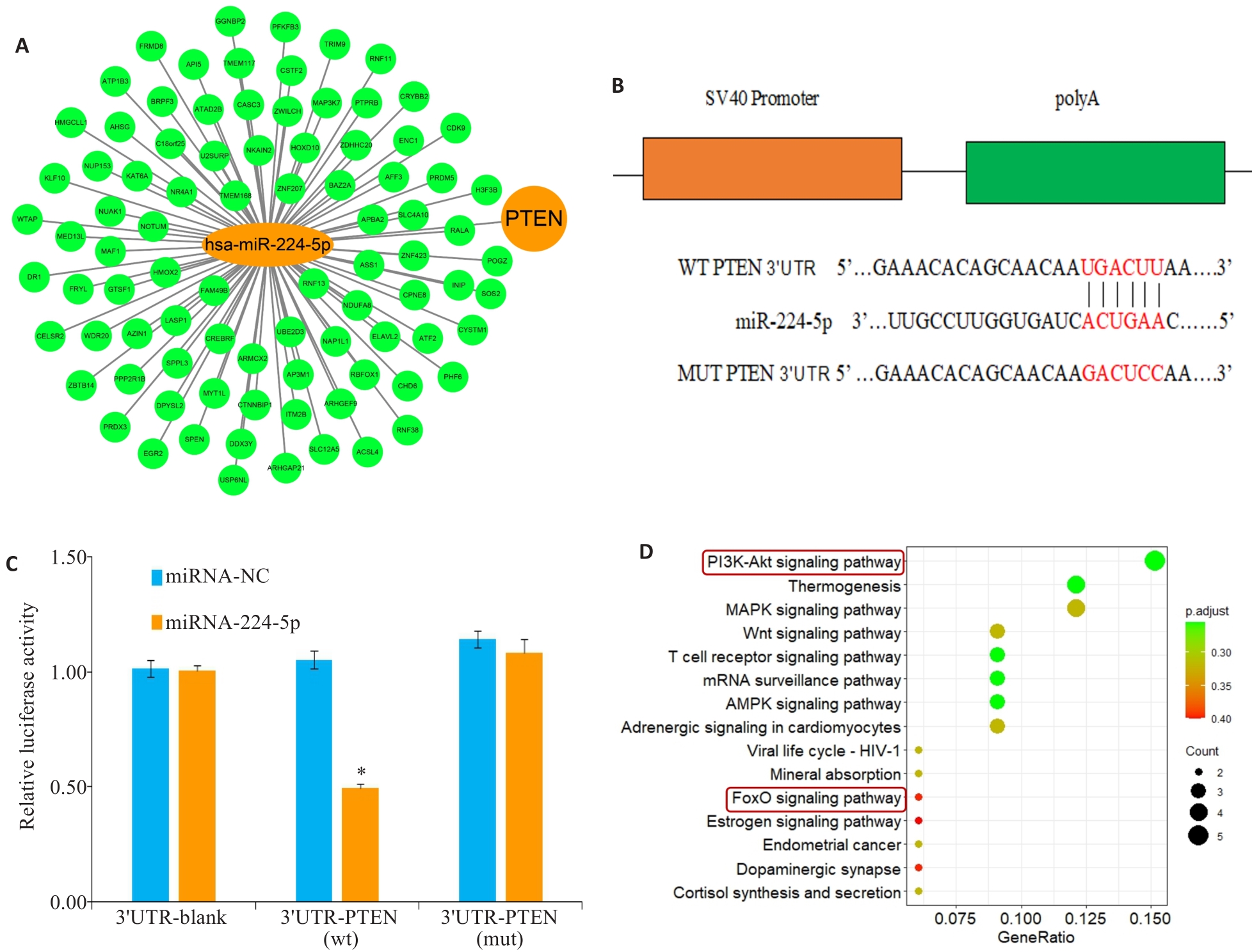
Fig3 Target gene of miR-224-5p and KEGG enrichment analysis. A: MiR-224-5p gene regulatory network. B: Binding sequences of PTEN mRNA 3'-UTR and miR-224-5p. C: PTEN-Wt or PTEN- Mut reporter Vector cotransfected into H9C2 cells with vehicle (control), miR-224-5p mimic, or negative control (miRNA-NC). Luciferase activity was normalized to the activity in the control group. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=3). D: KEGG pathway enrichment analysis. *P<0.05 vs miR-NC group.
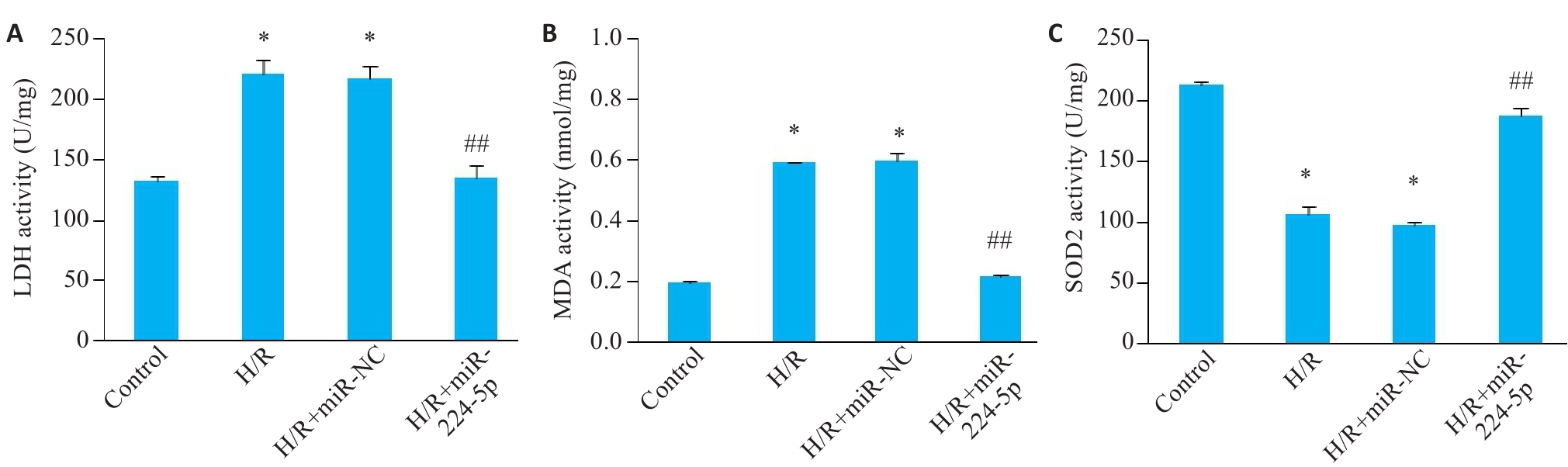
Fig.4 Levels of LDH, MDA, and SOD2 in H9c2 cells in each group (Mean±SD, n=6). A: LDH activity. B: MDA content. C: SOD2 activity measurement. *P<0.05 vs Control group; ##P<0.05 vs H/R+miR-NC group.
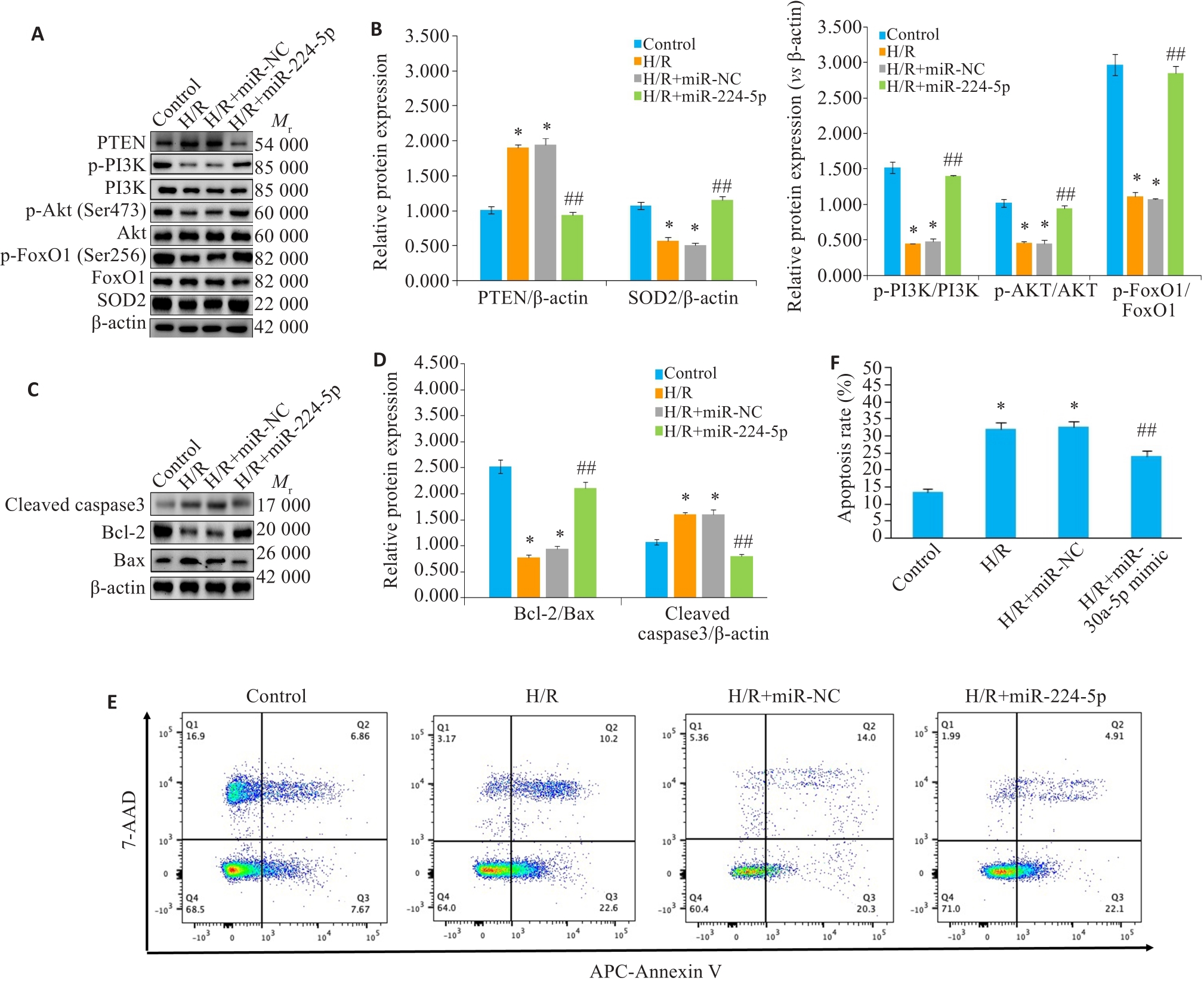
Fig5 Effect of overexpression of miR-224-5p on hypoxia/hypoxia-induced oxidative stress and apoptotic proteins in H9c2 cells in each group (Mean±SD, n=3). A, B: Western blotting for detecting oxidative stress pathway protein expressions. C, D: Western blotting for detecting cleaved caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 protein expressions. E, F: Flow cytometry for analyzing apoptosis rate in H9c2 cells in each group (Mean±SD, n=3); *P<0.05 compared with Control group; #P<0.05 vs H/R+ miR-NC group, ##P<0.05.
| 1 | WHO CVD Risk Chart Working Group. World Health Organization cardiovascular disease risk charts: revised models to estimate risk in 21 global regions[J]. Lancet Glob Health, 2019, 7(10): e1332-e1345. |
| 2 | Valikeserlis I, Athanasiou AA, Stakos D. Cellular mechanisms and pathways in myocardial reperfusion injury[J]. Coron Artery Dis, 2021, 32(6): 567-77. |
| 3 | Liu Y, Li L, Wang Z, et al. Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury; Molecular mechanisms and prevention[J]. Microvasc Res, 2023, 149: 104565. |
| 4 | Zhang WL, Chen CY, Wang J, et al. Mitophagy in cardiomyocytes and in platelets: a major mechanism of cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. Physiology, 2018, 33(2): 86-98. |
| 5 | Wang L, Niu HP, Zhang J. Homocysteine induces mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through stimulating ROS production and the ERK1/2 signaling pathway[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2020, 20(2): 938-44. |
| 6 | Jiang W, Zhang YX, Zhang W, et al. Hirsutine ameliorates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through improving mitochondrial function via CaMKII pathway[J]. Clin Exp Hypertens, 2023, 45(1): 2192444. |
| 7 | Zhao P, Zhang BL, Liu K, et al. Overexpression of miR-638 attenuated the effects of hypoxia/reoxygenation treatment on cell viability, cell apoptosis and autophagy by targeting ATG5 in the human cardiomyocytes[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2018, 22(23): 8462-71. |
| 8 | Zhai CL, Sun YG, Qian G, et al. LncRNA AK087124/miR-224-5p/PTEN axis modulates endothelial cell injury in atherosclerosis through apoptosis and AKT signaling pathway[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2021, 705: 108916. |
| 9 | Mao CY, Zhang TT, Li DJ, et al. Extracellular vesicles from hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells alleviates myocardial injury by targeting thioredoxin-interacting protein-mediated hypoxia-inducible factor-1α pathway[J]. World J Stem Cells, 2022, 14(2): 183-99. |
| 10 | Cheng JW, Ma HB, Yan M, et al. Circ_0007624 suppresses the development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via targeting miR-224-5p/CPEB3 to inactivate the EGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling[J]. Cell Signal, 2022, 99: 110448. |
| 11 | Zhou G, Wu H, Yang J, et al. Liraglutide attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the inhibition of necroptosis by activating GLP-1R/PI3K/akt pathway[J]. Cardiovasc Toxicol, 2023, 23(3/4): 161-75. |
| 12 | Guo LT, Wang SQ, Su J, et al. Baicalin ameliorates neuroinflammation-induced depressive-like behavior through inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 expression via the PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 pathway[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2019, 16(1): 95. |
| 13 | Zeng H, Yang Y, Tou FF, et al. Bone marrow stromal cell-derived exosomes improve oxidative stress and pyroptosis in doxorubicin-induced myocardial injury in vitro by regulating the transcription of GSDMD through the PI3K-AKT-Foxo1 pathway[J]. Immun Inflamm Dis, 2023, 11(3): e810. |
| 14 | Tan Y, Bie YL, Chen L, et al. Lingbao Huxin pill alleviates apoptosis and inflammation at infarct border zone through SIRT1-mediated FOXO1 and NF-κB pathways in rat model of acute myocardial infarction[J]. Chin J Integr Med, 2022, 28(4): 330-8. |
| 15 | Liu LL, Qiao S, Wang ML, et al. MiR224-5p inhibitor restrains neuronal apoptosis by targeting NR4A1 in the oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) model[J]. Front Neurosci, 2020, 14: 613. |
| 16 | Hou ZX, Qin XH, Hu YY, et al. Longterm exercise-derived exosomal miR-342-5p: a novel exerkine for cardioprotection[J]. Circ Res, 2019, 124(9): 1386-400. |
| 17 | Gao Y, Yin H, Zhang YF, et al. Dexmedetomidine protects hippocampal neurons against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis through activation HIF-1α/p53 signaling[J]. Life Sci, 2019, 232: 116611. |
| 18 | Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018)[J]. Eur Heart J, 2019, 40(3): 237-69. |
| 19 | Lv XB, Niu QH, Zhang M, et al. Critical functions of microRNA-30a-5p-E2F3 in cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2021, 37(2): 92-100. |
| 20 | Wu MY, Yiang GT, Liao WT, et al. Current mechanistic concepts in ischemia and reperfusion injury[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 46(4): 1650-67. |
| 21 | Monier B, Suzanne M. Orchestration of force generation and nuclear collapse in apoptotic cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(19): 10257. |
| 22 | Zhu L, Hao J, Cheng MJ, et al. Hyperglycemia-induced Bcl-2/Ba x -mediated apoptosis of Schwann cells via mTORC1/S6K1 inhibition in diabetic peripheral neuropathy[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2018, 367(2): 186-95. |
| 23 | Lu HL, Zhang JF, Xuan FF. MiR-7a-5p attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by targeting VDAC1[J]. Cardiovasc Toxicol, 2022, 22(2): 108-17. |
| 24 | Li GB, Jin JL, Liu SX, et al. Inhibition of miR-1224 suppresses hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes through targeting GPX4[J]. Exp Mol Pathol, 2021, 121: 104645. |
| 25 | Gong NJ, Yang XH, Li XY, et al. MicroRNA-590-3p relieves hypoxia/reoxygenation induced cardiomyocytes apoptosis and autophagy by targeting HIF-1α[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2021, 22(4): 1077. |
| 26 | 高晓阳, 赵晓璐, 张春艳, 等. 槲皮素诱导肝星状细胞凋亡: 基于调控miR-146影响PI3K/Akt信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1725-33. |
| 27 | 杨 子, 赵天豪, 程 阳, 等. 香叶木素通过调节小鼠的肠道免疫平衡减轻克罗恩病样结肠炎:基于抑制PI3K/AKT通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 474-82. |
| 28 | Xu YX, Jiang YP, Wang YZ, et al. LINC00473 rescues human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from apoptosis induced by dexamethasone through the PEBP1-mediated Akt/Bad/Bcl-2 signaling pathway[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2021, 47(1): 171-82. |
| 29 | Yang WB, Wu ZJ, Yang K, et al. BMI1 promotes cardiac fibrosis in ischemia-induced heart failure via the PTEN-PI3K/Akt-mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2019, 316(1): H61-H69. |
| 30 | Sun L, Wang H, Xu D, et al. Lapatinib induces mitochondrial dysfunction to enhance oxidative stress and ferroptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocytes via inhibition of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Bioengineered, 2022, 13(1): 48-60. |
| 31 | Peng B, Rao L, Yang JL, et al. Columbianadin attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiac injury, oxidative stress, and apoptosis via Sirt1/FOXO1 signaling pathway[J]. Acta Cir Bras, 2023, 38: e382223. |
| 32 | Hu B, Tian T, Li XT, et al. Dexmedetomidine postconditioning attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating the Nrf2/Sirt3/SOD2 signaling pathway in the rats[J]. Redox Rep, 2023, 28(1): 2158526. |
| [1] | Guiling CHEN, Xiaofeng LIAO, Pengtao SUN, Huan CEN, Shengchun SHU, Bijing LI, Jinhua LI. Solasonine promotes apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating the Bcl-2/Bax/caspase-3 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1109-1116. |
| [2] | Lingjun LU, Xiaodi YANG, Huaping ZHANG, Yuan LIANG, Xiulan SHI, Xin ZHOU. Recombinant Schistosoma japonicum cystatin alleviates acute liver injury in mice by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammation and hepatocyte apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1126-1134. |
| [3] | ZHANG Xiaoyan, WANG Xie, WANG Jie, SHAO Nan, CAI Biao, XIE Daojun. Huangpu Tongqiao Capsule improves cognitive impairment in rats with Wilson disease by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 447-454. |
| [4] | CHEN Guodong, LUO Suxin. Colchicine alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by activating AMPK [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 226-235. |
| [5] | LING Xuguang, XU Wenwen, PANG Guanlai, HONG Xuxing, LIU Fengqin, LI Yang. Tea polyphenols ameliorates acute lung injury in septic mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasomes [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 381-386. |
| [6] | DUAN Ting, ZHANG Zhen, SHI Jinran, XIAO Linyu, YANG Jingjing, YIN Lixia, ZHANG Xiaofeng, GENG Zhijun, LU Guoyu. High expression of CPNE3 correlates with poor long-term prognosis of gastric cancer by inhibiting cell apoptosis via activating PI3K/AKT signaling [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 129-137. |
| [7] | SUN Xiaopeng, SHI Hang, ZHANG Lei, LIU Zhong, LI Kewei, QIAN Lingling, ZHU Xingyu, YANG Kangjia, FU Qiang, DING Hua. Exosomes from ectoderm mesenchymal stem cells inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial M1 polarization and promotes survival of H2O2-exposed PC12 cells by suppressing inflammatory response and oxidative stress [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 119-128. |
| [8] | YE Hongwei, ZHANG Yuming, YUN Qi, DU Ruoli, LI Lu, LI Yuping, GAO Qin. Resveratrol alleviates hyperglycemia-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis via enhancing SIRT1 expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 45-51. |
| [9] | LIU Xuerou, YANG Yumei, CAI Hui, ZHANG Yaoshuai, FAN Fangtian, LI Xian, LI Shanshan. Aumolertinib inhibits proliferation, invasion and migration and promotes apoptosis of neuroblastoma cells by downregulating MMP2 and MMP9 expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(9): 1493-1499. |
| [10] | LAN Yu, WANG Kaifeng, LAN Zhixian, ZHOU Heqi, SUN Jian. Dealcoholized red wine inhibits occurrence and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma possibly by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1297-1305. |
| [11] | YE Jingjing, XU Wenqin, XI Bangsheng, WANG Nengqian, CHEN Tianbing. Lactate-induced up-regulation of PLEKHA4 promotes proliferation and apoptosis of human glioma cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(7): 1071-1080. |
| [12] | SHAO Rongrong, YANG Zi, ZHANG Wenjing, ZHANG Nuo, ZHAO Yajing, ZHANG Xiaofeng, ZUO Lugen, GE Sitang. Pachymic acid protects against Crohn's disease-like intestinal barrier injury and colitis in mice by suppressing intestinal epithelial cell apoptosisviainhibiting PI3K/AKT signaling [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(6): 935-942. |
| [13] | ZHENG Qingwei, SHAO Yidan, ZHENG Wanting, ZOU Yingxue. Cordycepin, a metabolite of Cordyceps militaris, inhibits xenograft tumor growth of tongue squamous cell carcinoma in nude mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(6): 873-878. |
| [14] | SHI Wenhui, LIU Xiaolian, ZHANG Guiming, YE Linxuan, ZHOU Runhua, LI Yilei, YU Le. RITA selectively inhibits proliferation of BAP1-deficient cutaneous melanoma cells in vitro [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(5): 710-717. |
| [15] | LIU Fang, PENG Lanzhu, XI Jingle. High expression of MYH9 inhibits apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells through activating the AKT/c-Myc pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(4): 527-536. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||