Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (9): 1729-1737.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.09.13
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xueli ZHOU1( ), Hua LI3, Qingyu CHEN2, Meina JIN1, Haibo LI1, Wei BAI1, Chuxuan JIA1, Cuiying WEI1(
), Hua LI3, Qingyu CHEN2, Meina JIN1, Haibo LI1, Wei BAI1, Chuxuan JIA1, Cuiying WEI1( )
)
Received:2024-03-05
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-09-30
Contact:
Cuiying WEI
E-mail:15540887135@163.com;weicuiying9@163.com
Supported by:Xueli ZHOU, Hua LI, Qingyu CHEN, Meina JIN, Haibo LI, Wei BAI, Chuxuan JIA, Cuiying WEI. Effects of chronic intermittent hypoxia and reoxygenation on insulin resistance and skeletal muscle miR-27a-3p/PPARγ/IRS1/PI3K/AKT expressions in rats[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1729-1737.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.09.13
| Gene | Primer sequence 5'-3' |
|---|---|
| miR-27a-3p-F | ACACTCCAGCTGGGTTCACAGTGGCTAAG |
| miR-27a-3p-R | CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGGCGGAACT |
| U6-F | CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA |
| U6-R | AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT |
| PPARγ-F | TTTCAAGGGTGCCAGTTTCG |
| PPARγ-R | GGAGGCCAGCATGGTGTAGAT |
| GAPDH-F | CTGGAGAAACCTGCCAAGTATG |
| GAPDH-R | GGTGGAAGAATGGGAGTTGCT |
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Primer sequence 5'-3' |
|---|---|
| miR-27a-3p-F | ACACTCCAGCTGGGTTCACAGTGGCTAAG |
| miR-27a-3p-R | CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGGCGGAACT |
| U6-F | CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA |
| U6-R | AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT |
| PPARγ-F | TTTCAAGGGTGCCAGTTTCG |
| PPARγ-R | GGAGGCCAGCATGGTGTAGAT |
| GAPDH-F | CTGGAGAAACCTGCCAAGTATG |
| GAPDH-R | GGTGGAAGAATGGGAGTTGCT |
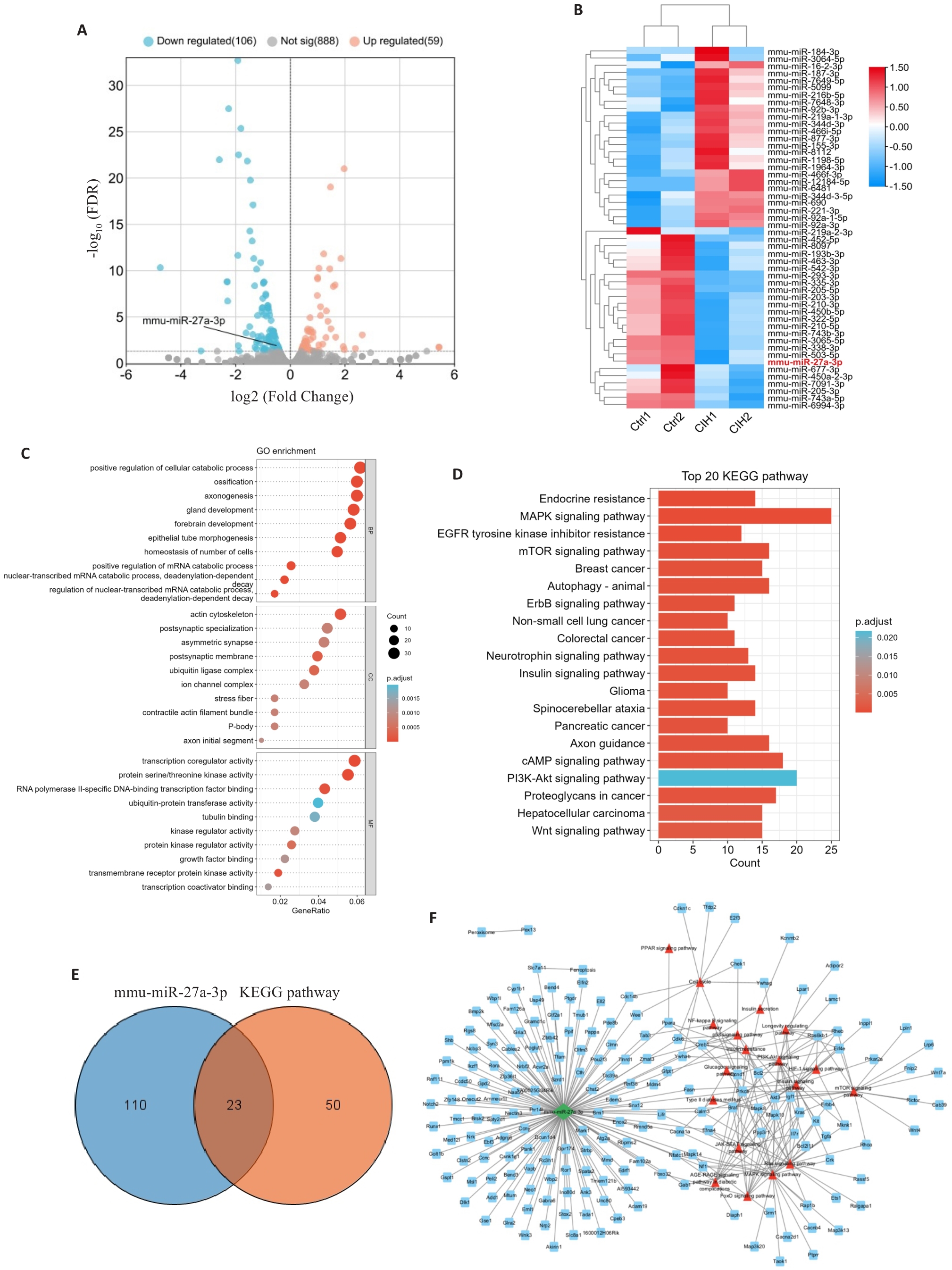
Fig.1 Bioinformatics analysis of differentially expressed mRNAs in chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH). A: CIH exposure regulates miR-27a-3p. B: Heat map showing significant differences in miRNAs between CIH group and control group. C: GO enrichment analysis of the differentially expressed mRNAs. D: KEGG enrichment analysis of the differentially expressed mRNAs. E: Venn diagram of intersecting mRNAs. F: The miR-27a-3p-mRNA pathway regulatory network.
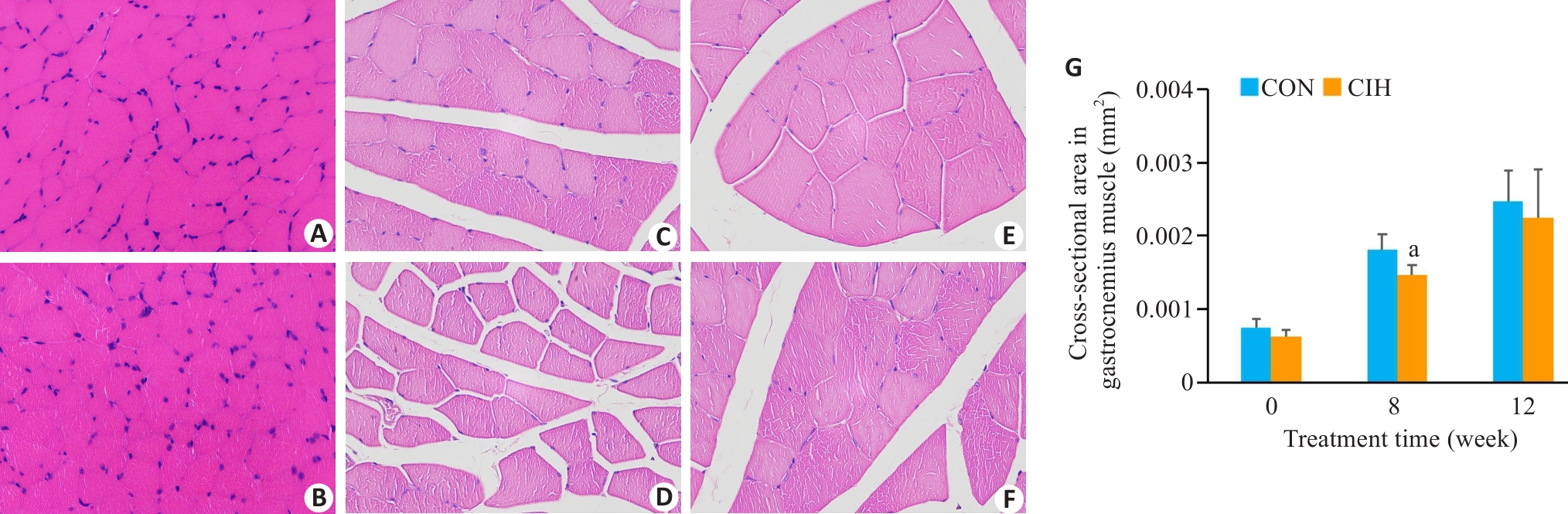
Fig.2 HE staining of the skeletal muscle and analysis of cross-sectional area of the muscle fibers in the two groups (Original magnification: ×400). A: Control group at baseline. B: CIH group at baseline. C: Control group at 8 weeks. D: CIH group at 8 weeks. E: Control group at 12 weeks. F: CIH group at 12 weeks. G: Comparison of the cross-sectional area of the skeletal muscle fibers. aP<0.05 vs control group.
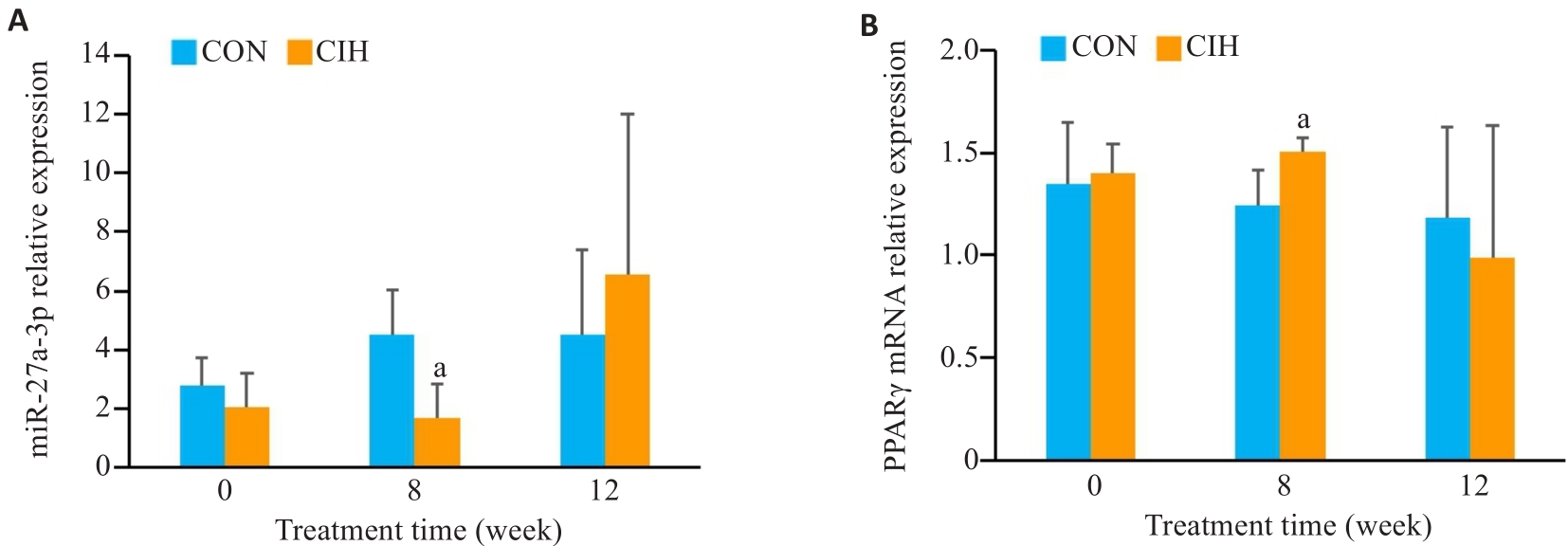
Fig.3 Comparison of miR-27a-3p (A) and PPAR mRNA (B) levels in skeletal muscles in the two groups at different time points detected by RT-qPCR. aP< 0.05 vs control group.
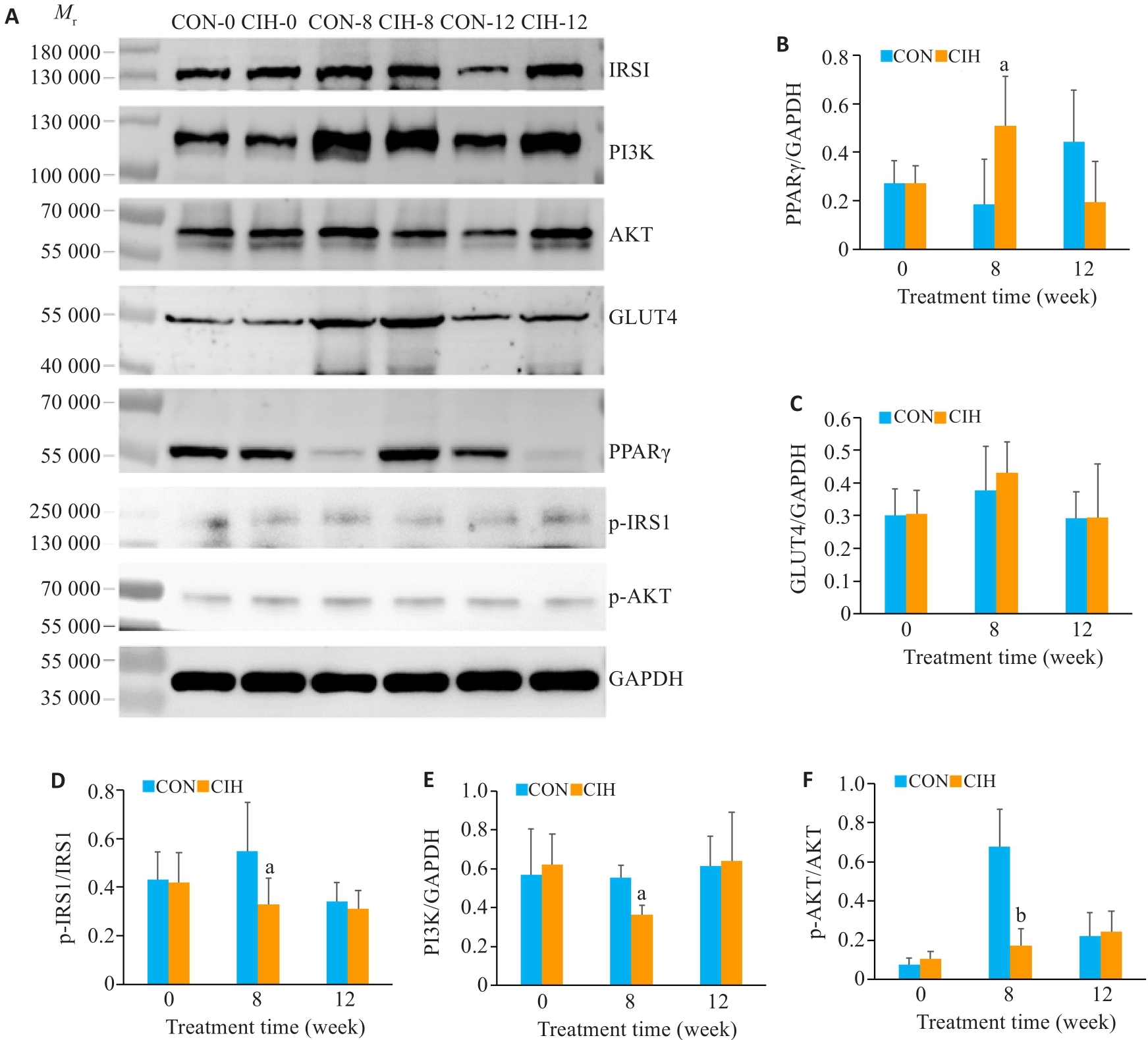
Fig.5 Western blotting for detecting expression levels of PPARγ, GLUT4, p-IRS1/IRS1, PI3K and p-AKT/AKT proteins in the skeletal muscles in the two groups at different time points. A: Western blots of PPARγ, GLUT4, p-IRS1/IRS1, PI3K and p-AKT/AKT in the skeletal muscles. B-F: Relative protein expression levels of PPARγ, GLUT4, p-IRS1/IRS1, PI3K and p-AKT/AKT, respectively. aP<0.05,bP<0.01 vs control group.
| 1 | Charčiūnaitė K, Gauronskaitė R, Šlekytė G, et al. Evaluation of obstructive sleep apnea phenotypes treatment effectiveness[J]. Medicina, 2021, 57(4): 335. |
| 2 | Laratta CR, Ayas NT, Povitz M, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in adults[J]. CMAJ, 2017, 189(48): E1481- 8. |
| 3 | Domínguez-Mayoral A, Sánchez-Gómez J, Guerrero P, et al. High prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in Spain's Stroke Belt[J]. J Int Med Res, 2021, 49(10): 3000605211053090. |
| 4 | Wang Y, Yang QC, Feng J, et al. The prevalence and clinical features of hypertension in patients with obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome and related nursing strategies[J]. J Nurs Res, 2016, 24(1): 41-7. |
| 5 | Qian YJ, Yi HL, Zou JY, et al. Independent association between sleep fragmentation and dyslipidemia in patients with obstructive sleep apnea[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 26089. |
| 6 | Woo HG, Song TJ, Jung JS, et al. Association between the high risk for obstructive sleep apnea and intracranial carotid artery calcification in patients with acute ischemic stroke[J]. Schlaf Atmung, 2021, 25(1): 299-307. |
| 7 | Gabryelska A, Chrzanowski J, Sochal M, et al. Nocturnal oxygen saturation parameters as independent risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus among obstructive sleep apnea patients[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(17): 3770. |
| 8 | Lu XX, Wang X, Xu T, et al. Circulating C3 and glucose metabolism abnormalities in patients with OSAHS[J]. Schlaf Atmung, 2018, 22(2): 345-51. |
| 9 | Lv RJ, Liu XY, Zhang Y, et al. Pathophysiological mechanisms and therapeutic approaches in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 218. |
| 10 | Murphy AM, Thomas A, Crinion SJ, et al. Intermittent hypoxia in obstructive sleep apnoea mediates insulin resistance through adipose tissue inflammation[J]. Eur Respir J, 2017, 49(4): 1601731. |
| 11 | Li XM, Zhang X, Hou XZ, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea-increased DEC1 regulates systemic inflammation and oxidative stress that promotes development of pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Apoptosis, 2023, 28(3/4): 432-46. |
| 12 | Schulte R, Wohlleber D, Unrau L, et al. Pioglitazone-mediated peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ activation aggravates murine immune-mediated hepatitis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(7): 2523. |
| 13 | Regazzi R. MicroRNAs as therapeutic targets for the treatment of diabetes mellitus and its complications[J]. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2018, 22(2): 153-60. |
| 14 | Massart J, Sjögren RJO, Lundell LS, et al. Altered miR-29 expression in type 2 diabetes influences glucose and lipid metabolism in skeletal muscle[J]. Diabetes, 2017, 66(7): 1807-18. |
| 15 | Zhou T, Meng XH, Che H, et al. Regulation of insulin resistance by multiple MiRNAs via targeting the GLUT4 signalling pathway[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2016, 38(5): 2063-78. |
| 16 | Liu KX, Chen GP, Lin PL, et al. Detection and analysis of apoptosis- and autophagy-related miRNAs of mouse vascular endothelial cells in chronic intermittent hypoxia model[J]. Life Sci, 2018, 193: 194-9. |
| 17 | Gao HB, Han ZL, Huang S, et al. Intermittent hypoxia caused cognitive dysfunction relate to miRNAs dysregulation in hippocampus[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2017, 335: 80-7. |
| 18 | Wu X, Chang SC, Jin JF, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome mediates chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced renal injury implication of the microRNA-155/FOXO3a signaling pathway[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(12): 9404-15. |
| 19 | Li K, Wei P, Qin YW, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling and bioinformatics analysis of dysregulated microRNAs in obstructive sleep apnea patients[J]. Medicine, 2017, 96(34): e7917. |
| 20 | 王 云, 何 燕, 刘师节, 等. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征与糖脂代谢紊乱的机制研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(2): 243-7. |
| 21 | Wang C, Tan J, Miao YY, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea, prediabetes and progression of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Diabetes Investig, 2022, 13(8): 1396-411. |
| 22 | Zeng S, Wang YY, Ai L, et al. Chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced oxidative stress activates TRB3 and phosphorylated JNK to mediate insulin resistance and cell apoptosis in the pancreas[J]. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol, 2024, 51(3): e13843. |
| 23 | 郑莉芳, 陈佩杰, 肖卫华. MicroRNAs对骨骼肌胰岛素抵抗的调控及其机制[J]. 生理学报, 2019, 71(3): 497-504. |
| 24 | Wei J, Hao QY, Chen CK, et al. Epigenetic repression of miR-17 contributed to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-triggered insulin resistance by targeting Keap1-Nrf2/miR-200a axis in skeletal muscle[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(20): 9230-48. |
| 25 | Kong QR, Ji DM, Li FR, et al. MicroRNA-221 promotes myocardial apoptosis caused by myocardial ischemia-reperfusion by down-regulating PTEN[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2019, 23(9): 3967-75. |
| 26 | Liang JT, Tang JM, Shi HJ, et al. MiR-27a-3p targeting RXRα promotes colorectal cancer progression by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(47): 82991-3008. |
| 27 | Han LL, Wang SH, Yao MY, et al. Urinary exosomal microRNA-145-5p and microRNA-27a-3p act as noninvasive diagnostic biomarkers for diabetic kidney disease[J]. World J Diabetes, 2024, 15(1): 92-104. |
| 28 | Ghoreishi E, Shahrokhi SZ, Kazerouni F, et al. Circulating miR-148b-3p and miR-27a-3p can be potential biomarkers for diagnosis of pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes: integrating experimental and in-silico approaches[J]. BMC Endocr Disord, 2022, 22(1): 207. |
| 29 | Chemello F, Grespi F, Zulian A, et al. Transcriptomic analysis of single isolated myofibers identifies miR-27a-3p and miR-142-3p as regulators of metabolism in skeletal muscle[J]. Cell Rep, 2019, 26(13): 3784-97. e8. |
| 30 | LaPierre MP, Stoffel M. MicroRNAs as stress regulators in pancreatic beta cells and diabetes[J]. Mol Metab, 2017, 6(9): 1010-23. |
| 31 | Shahrokhi SZ, Saeidi L, Sadatamini M, et al. Can miR-145-5p be used as a marker in diabetic patients[J]? Arch Physiol Biochem, 2022, 128(5): 1175-80. |
| 32 | Saeidi L, Shahrokhi SZ, Sadatamini M, et al. Can circulating miR-7-1-5p, and miR-33a-5p be used as markers of T2D patients[J]? Arch Physiol Biochem, 2023, 129(3): 771-7. |
| 33 | 汤金梅, 吕 荣, 毕亭亭, 等. PCB118诱发大鼠胰岛素抵抗及对骨骼肌细胞功能的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2021, 41(13): 2808-11. |
| 34 | 谭 健, 莫海兰, 李 洁, 等.慢性间歇性缺氧对大鼠骨骼肌葡萄糖转运蛋白4表达的影响 [J]. 南方医科大学学报,2014, 34 (07):1061-4. |
| 35 | 张 婷. 不同骨骼肌来源的外泌体携带miR-27a-3p调节肌间FAPs成脂分化的研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆医科大学, 2022. |
| 36 | 郑志然. bta-miR-27a-3p靶向INSR在围产期奶牛脂肪肝发病中的作用研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2022. |
| 37 | 王一成, 刘承雨, 黄汉鹏. 线粒体动力学在OSAHS合并肥胖所致腓肠肌损伤中的作用及其机制研究[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2023, 52(12): 120-7. |
| 38 | 栗瑞雪. 间歇低氧大鼠骨骼肌细胞PTP1B及PI3K表达在胰岛素抵抗中的作用[D]. 太原: 山西医科大学, 2016. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||