Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1297-1306.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.19
Minzhu NIU1,4,5( ), Lixia YIN2, Tong QIAO4, Lin YIN2, Keni ZHANG2, Jianguo HU1,2, Chuanwang SONG4, Zhijun GENG1,3, Jing LI1,2(
), Lixia YIN2, Tong QIAO4, Lin YIN2, Keni ZHANG2, Jianguo HU1,2, Chuanwang SONG4, Zhijun GENG1,3, Jing LI1,2( )
)
Received:2025-01-20
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-06-27
Contact:
Jing LI
E-mail:nmz8033@163.com;lijingbyfy@bbmc.edu.cn
Minzhu NIU, Lixia YIN, Tong QIAO, Lin YIN, Keni ZHANG, Jianguo HU, Chuanwang SONG, Zhijun GENG, Jing LI. Ecliptasaponin A ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice by suppressing M1 macrophage polarization via inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1297-1306.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.19

Fig.1 ESA significantly reduces percentage of M1-type macrophages in RAW264.7 cells induced by LPS and IFN-γ. A: Morphology of macrophages from each group (scale bar=50 μm). B: Percentages of F4/80+CD86+ macrophages detected by flow cytometry. *P<0.05 vs M0 group. #P<0.05 vs M1 group.
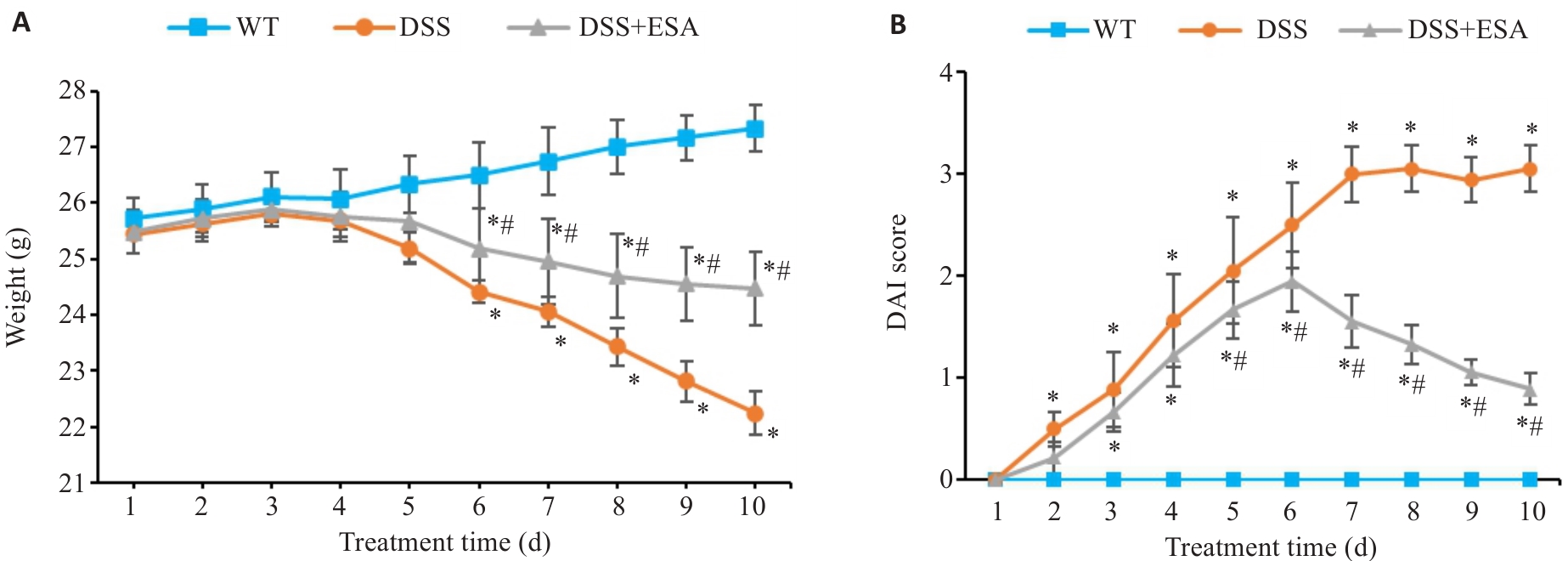
Fig.2 Effect of ESA on the disease status of DSS model mice. A: Changes of body weight. B: Changes of DAI scores. WT: Control group; DSS: DSS-induced model group; DSS+ESA: ESA treatment group. *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
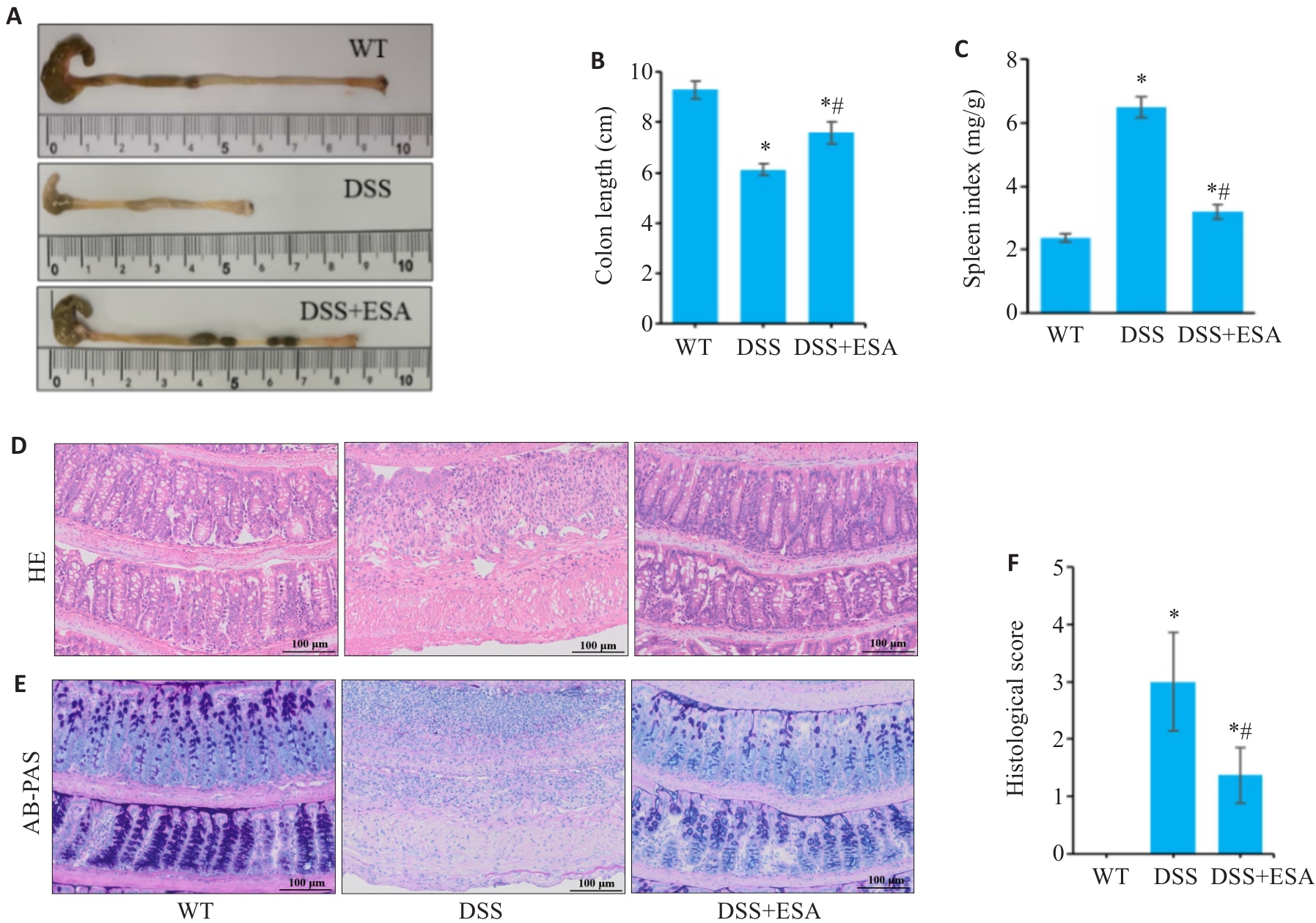
Fig.3 ESA improves pathological phenotype of DSS-induced colitis in mice. A, B: Representative images of mouse colons in each group. C: Changes of spleen index. D: HE staining of the colon tissues. E: AB-PAS staining of colon tissue from each groups. F: Histopathological scores in different groups. *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs DSS group. (scale bar=100 μm).
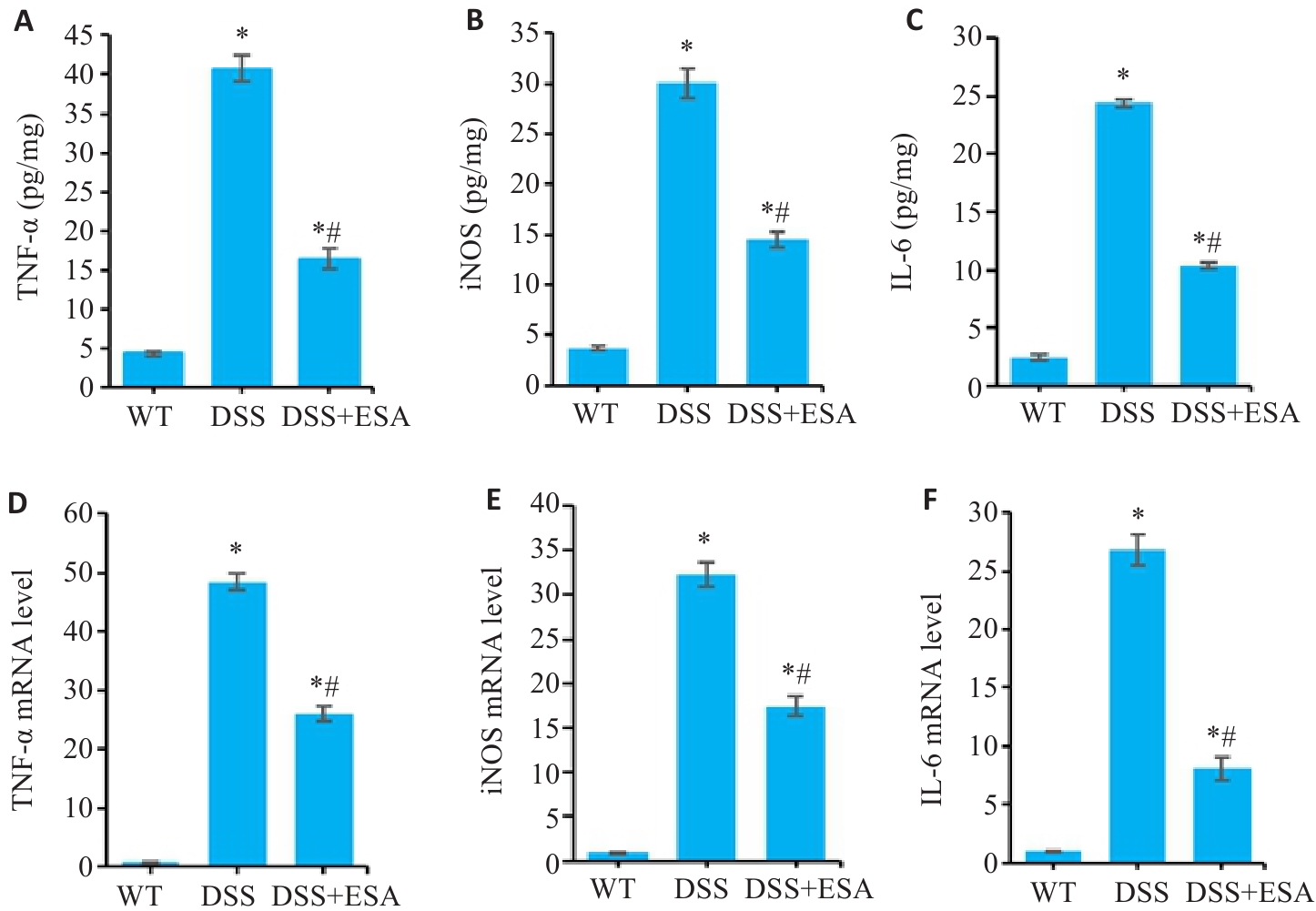
Fig.4 Effect of ESA on intestinal mucosal inflammatory mediators in DSS model mice. A-C: Concentrations of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, iNOS and IL-6 in the colon tissues detected by ELISA. D-F: The mRNA levels of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, iNOS and IL-6 in different groups. *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
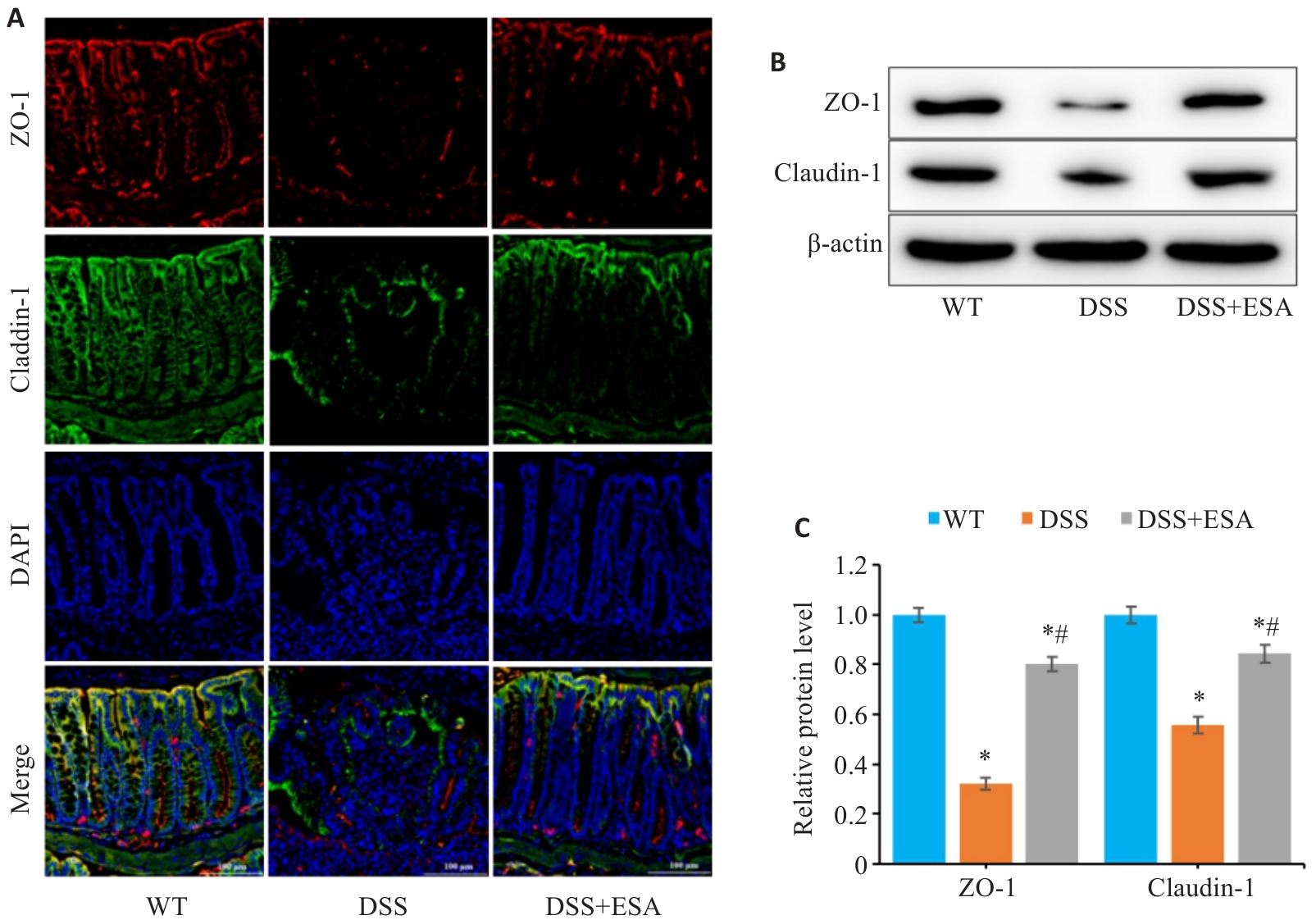
Fig.5 ESA improves gut barrier disruption in mice with DSS-induced colitis. A: Immunofluorescence staining showing expression of ZO-1 and claudin-1 proteins in the colon tissues. B, C: Relative expression levels of ZO-1 and claudin-1 proteins in colon mucosa detected by Western blotting. *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs DSS group (scale bar=100 μm).

Fig.6 Effect of ESA on M1 macrophages in the mesenteric lymph nodes of DSS model mice. The percentages of F4/80+CD86+ macrophages in mesenteric lymph nodes were detected by flow cytometry. *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
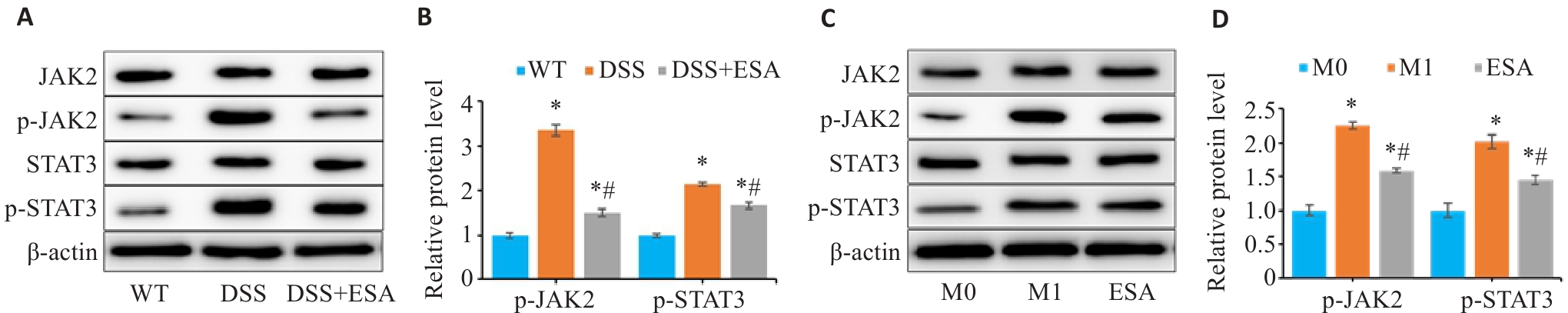
Fig.7 ESA suppresses JAK2/STAT3 pathway activation by blocking its phosphorylation in vitro and in vivo. A, B: Relative expression levels of JAK2, p-JAK2, STAT3, and p-STAT3 proteins in mouse colon tissue detected by Western blotting (*P<0.05 vs WT group; #P<0.05 vs DSS group). C, D: Relative expression levels of JAK2, p-JAK2, STAT3, p-STAT3 proteins in RAW264.7 cells detected by Western blotting (*P<0.05 vs M0 group. #P<0.05 vs M1 group).
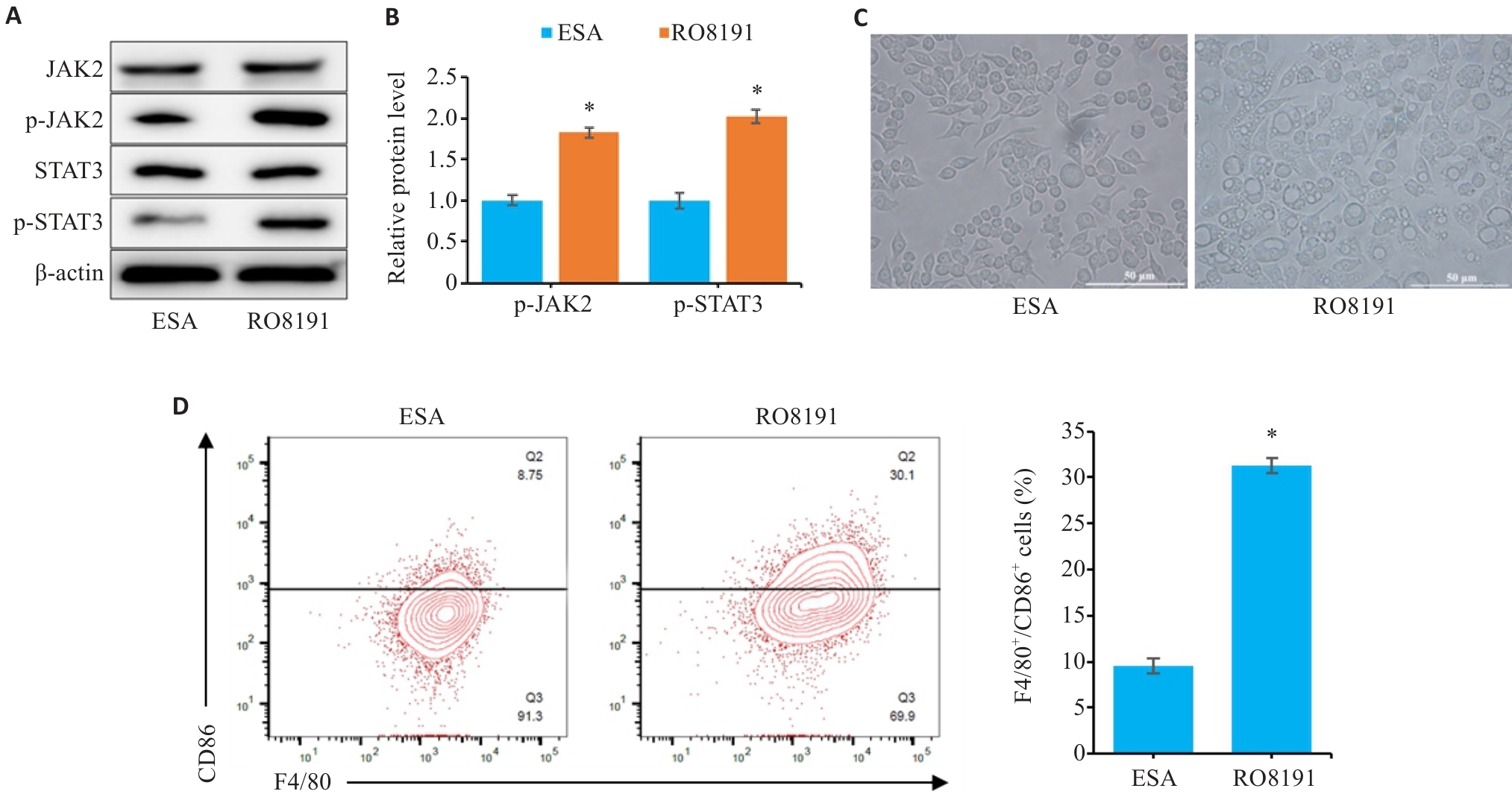
Fig.8 JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway is involved in ESA-mediated inhibition of M1-type macrophage polarization of RAW264.7 cells. A, B: Relative expressions of JAK2, p-JAK2, STAT3 and p-STAT3 proteins detected by Western blotting in RAW264.7 cells. C: Morphology of the macrophages (×400). D: Proportion of F4/80+CD86+ cells in each group. *P<0.05 vs ESA group (Scale bar=50 μm).
| 1 | Glassner KL, Abraham BP, Quigley EMM. The microbiome and inflammatory bowel disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2020, 145(1): 16-27. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2019.11.003 |
| 2 | Ordás I, Eckmann L, Talamini M, et al. Ulcerative colitis[J]. Lancet, 2012, 380(9853): 1606-19. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(12)60150-0 |
| 3 | Xu L, He B, Sun Y, et al. Incidence of inflammatory bowel disease in urban China: a nationwide population-based study[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 21(13): 3379-86. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2023.08.013 |
| 4 | Wangchuk P, Yeshi K, Loukas A. Ulcerative colitis: clinical biomarkers, therapeutic targets, and emerging treatments[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2024, 45(10): 892-903. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2024.08.003 |
| 5 | Saez A, Herrero-Fernandez B, Gomez-Bris R, et al. Pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease: innate immune system[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(2): 1526. doi:10.3390/ijms24021526 |
| 6 | Zhou X, Li WY, Wang S, et al. YAP aggravates inflammatory bowel disease by regulating M1/M2 macrophage polarization and gut microbial homeostasis[J]. Cell Rep, 2019, 27(4): 1176-89. e5. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2019.03.028 |
| 7 | Krausgruber T, Blazek K, Smallie T, et al. IRF5 promotes inflammatory macrophage polarization and TH1-TH17 responses[J]. Nat Immunol, 2011, 12(3): 231-8. doi:10.1038/ni.1990 |
| 8 | Pan XH, Zhu Q, Pan LL, et al. Macrophage immunometabolism in inflammatory bowel diseases: From pathogenesis to therapy[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2022, 238: 108176. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108176 |
| 9 | Zhang K, Guo J, Yan W, et al. Macrophage polarization in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2023, 21(1): 367. doi:10.1186/s12964-023-01386-9 |
| 10 | Ruan S, Xu L, Sheng Y, et al. Th1 promotes M1 polarization of intestinal macrophages to regulate colitis-related mucosal barrier damage[J]. Aging: Albany NY, 2023, 15(14): 6721-35. doi:10.18632/aging.204629 |
| 11 | Guo HR, Guo H, Xie Y, et al. Mo3Se4 nanoparticle with ROS scavenging and multi-enzyme activity for the treatment of DSS-induced colitis in mice[J]. Redox Biol, 2022, 56: 102441. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2022.102441 |
| 12 | Yang Y, Ma Q, Wang Q, et al. Mannose enhances intestinal immune barrier function and dextran sulfate sodium salt-induced colitis in mice by regulating intestinal microbiota[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1365457. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1365457 |
| 13 | You XY, Xue Q, Fang Y, et al. Preventive effects of Ecliptae Herba extract and its component, ecliptasaponin A, on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2015, 175: 172-80. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2015.08.034 |
| 14 | Han J, Lv W, Sheng H, et al. Ecliptasaponin A induces apoptosis through the activation of ASK1/JNK pathway and autophagy in human lung cancer cells[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2019, 7(20): 539. doi:10.21037/atm.2019.10.07 |
| 15 | Xi FM, Li CT, Han J, et al. Thiophenes, polyacetylenes and terpenes from the aerial parts of Eclipata prostrata[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2014, 22(22): 6515-22. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2014.06.051 |
| 16 | Ge SM, Wu SH, Yin Q, et al. Ecliptasaponin A protects heart against acute ischemia-induced myocardial injury by inhibition of the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 335: 118612. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118612 |
| 17 | Ge ST, Yang YT, Zuo LG, et al. Sotetsuflavone ameliorates Crohn’s disease-like colitis by inhibiting M1 macrophage-induced intestinal barrier damage via JNK and MAPK signalling[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2023, 940: 175464. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175464 |
| 18 | Lei X, Zou F, Tang X, et al. CD3D silencing alleviates diabetic nephropathy via inhibition of JAK/STAT pathway[J]. FASEB J, 2024, 38(21): e70169. doi:10.1096/fj.202401879r |
| 19 | Wirtz S, Popp V, Kindermann M, et al. Chemically induced mouse models of acute and chronic intestinal inflammation[J]. Nat Protoc, 2017, 12(7): 1295-309. doi:10.1038/nprot.2017.044 |
| 20 | Chougule PR, Sangaraju R, Patil PB, et al. Effect of ethyl gallate and propyl gallate on dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced ulcerative colitis in C57BL/6J mice: preventive and protective[J]. Inflammopharmacology, 2023, 31(4): 2103-20. doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01254-5 |
| 21 | Kobayashi T, Siegmund B, Le Berre C, et al. Ulcerative colitis[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2020, 6: 74. doi:10.1038/s41572-020-0205-x |
| 22 | Le Berre C, Honap S, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Ulcerative colitis[J]. Lancet, 2023, 402(10401): 571-84. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(23)00966-2 |
| 23 | Dai N, Haidar O, Askari A, et al. Colectomy rates in ulcerative colitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2023, 55(1): 13-20. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2022.08.039 |
| 24 | Asano K, Takahashi N, Ushiki M, et al. Intestinal CD169+ macrophages initiate mucosal inflammation by secreting CCL8 that recruits inflammatory monocytes[J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6: 7802. doi:10.1038/ncomms8802 |
| 25 | Goddard ZR, Searcey M, Osbourn A. Advances in triterpene drug discovery[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2024, 45(11): 964-8. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2024.10.003 |
| 26 | Martin LBB, Kikuchi S, Rejzek M, et al. Complete biosynthesis of the potent vaccine adjuvant QS-21[J]. Nat Chem Biol, 2024, 20(4): 493-502. doi:10.1038/s41589-023-01538-5 |
| 27 | Hirata K, Helal F, Hadgraft J, et al. Formulation of carbenoxolone for delivery to the skin[J]. Int J Pharm, 2013, 448(2): 360-5. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.03.045 |
| 28 | Chen Y, Hu Z, Li R, et al. The effects of carbenoxolone against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in a mouse model[J]. Neuroimmunomodulation, 2020, 27(1): 19-27. doi:10.1159/000505333 |
| 29 | Kou RW, Li ZQ, Wang JL, et al. Ganoderic acid a mitigates inflammatory bowel disease through modulation of AhR activity by microbial tryptophan metabolism[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2024, 72(32): 17912-23. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.4c01166 |
| 30 | Stronati L, Palone F, Negroni A, et al. Dipotassium glycyrrhizate improves intestinal mucosal healing by modulating extracellular matrix remodeling genes and restoring epithelial barrier functions[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 939. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.00939 |
| 31 | Hong GU, Lee JY, Kang H, et al. Inhibition of osteoarthritis-related molecules by isomucronulatol 7-O-β-d-glucoside and ecliptasaponin a in IL-1β-stimulated chondrosarcoma cell model[J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(11): E2807. doi:10.3390/molecules23112807 |
| 32 | De Schepper S, Verheijden S, Aguilera-Lizarraga J, et al. Self-maintaining gut macrophages are essential for intestinal homeostasis[J]. Cell, 2019, 176(3): 676. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.010 |
| 33 | Tao Q, Liang Q, Fu Y, et al. Puerarin ameliorates colitis by direct suppression of macrophage M1 polarization in DSS mice[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 135: 156048. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156048 |
| 34 | Westendorp BF, Büller NVJA, Karpus ON, et al. Indian hedgehog suppresses a stromal cell-driven intestinal immune response[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 5(1): 67-82.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jcmgh.2017.08.004 |
| 35 | Huang B, Chen Z, Geng L, et al. Mucosal profiling of pediatric-onset colitis and IBD reveals common pathogenics and therapeutic pathways[J]. Cell, 2019, 179(5): 1160-76.e24. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.027 |
| 36 | Xue C, Yao Q, Gu X, et al. Evolving cognition of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway: autoimmune disorders and cancer[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 204. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01468-7 |
| 37 | Huang B, Lang X, Li X. The role of IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in cancers[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 1023177. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.1023177 |
| 38 | Lu MN, Xie KG, Lu XZ, et al. Notoginsenoside R1 counteracts mesenchymal stem cell-evoked oncogenesis and doxorubicin resistance in osteosarcoma cells by blocking IL-6 secretion-induced JAK2/STAT3 signaling[J]. Investig New Drugs, 2021, 39(2): 416-25. doi:10.1007/s10637-020-01027-9 |
| 39 | Salas A, Hernandez-Rocha C, Duijvestein M, et al. JAK-STAT pathway targeting for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 17(6): 323-37. doi:10.1038/s41575-020-0273-0 |
| 40 | Huang XL, Lin R, Liu H, et al. Resatorvid (TAK-242) ameliorates ulcerative colitis by modulating macrophage polarization and T helper cell balance via TLR4/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Inflammation, 2024, 47(6): 2108-28. doi:10.1007/s10753-024-02028-z |
| 41 | Wang Y, Song X, Xia Y, et al. Complanatuside A ameliorates 2, 4, 6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis in mice by regulating the Th17/Treg balance via the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. FASEB J, 2024, 38(10): e23667. doi:10.1096/fj.202301127rr |
| 42 | 罗雪菲, 王 伟, 赵晓芳, 等. 基于网络药理学探讨桃莲绞复方增强全成分肿瘤细胞疫苗抗结直肠癌作用分子机制[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(2): 459-68. doi:10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.02.020 |
| 43 | Xiao QP, Luo L, Zhu XY, et al. Formononetin alleviates ulcerative colitis via reshaping the balance of M1/M2 macrophage polarization in a gut microbiota-dependent manner[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 135: 156153. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156153 |
| 44 | Xiao QP, Huang JQ, Zhu XY, et al. Formononetin ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis via enhancing antioxidant capacity, promoting tight junction protein expression and reshaping M1/M2 macrophage polarization balance[J]. Int Immuno-pharmacol, 2024, 142: 113174. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113174 |
| [1] | Shuyu TU, Xiangyu CHEN, Chenghui LI, Danping HUANG, Li ZHANG. Buyang Huanwu Decoction delays vascular aging in rats through exosomal miR-590-5p signal-mediated macrophage polarization [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1251-1259. |
| [2] | Jiawen YU, Yi ZHOU, Chunmei QIAN, Lan MU, Renye QUE. Effects of liver fibrosis induced by iron overload on M2 polarization of macrophages in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 684-691. |
| [3] | Fei CHU, Xiaohua CHEN, Bowen SONG, Jingjing YANG, Lugen ZUO. Moslosooflavone ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by suppressing intestinal epithelium apoptosis via inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 819-828. |
| [4] | Lixia YIN, Minzhu NIU, Keni ZHANG, Zhijun GENG, Jianguo HU, Jiangyan LI, Jing LI. Cimifugin ameliorates Crohn's disease-like colitis in mice by modulating Th-cell immune balance via inhibiting the MAPK pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 595-602. |
| [5] | Yu BIN, Ziwen LI, Suwei ZUO, Sinuo SUN, Min LI, Jiayin SONG, Xu LIN, Gang XUE, Jingfang WU. High expression of apolipoprotein C1 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells by activating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 359-370. |
| [6] | Shuo LIU, Jing LI, Xingwang WU. Swertiamarin ameliorates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced colitis in mice by inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1545-1552. |
| [7] | XI Jin, ZHANG Min, ZHANG Yongyu, ZHANG Chen, ZHANG Yulu, WANG Rui, SHEN Lin, LI Jing, SONG Xue. Upregulating KLF11 ameliorates intestinal inflammation in mice with 2, 4, 6-trinitrobenesulfonic acid-induced colitis by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(4): 765-772. |
| [8] | Minzhu NIU, Lixia YIN, Ting DUAN, Ju HUANG, Jing LI, Zhijun GENG, Jianguo HU, Chuanwang SONG. Asperosaponin VI alleviates TNBS-induced Crohn's disease-like colitis in mice by reducing intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis via inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2335-2346. |
| [9] | SHAO Rongrong, YANG Zi, ZHANG Wenjing, ZHANG Nuo, ZHAO Yajing, ZHANG Xiaofeng, ZUO Lugen, GE Sitang. Pachymic acid protects against Crohn's disease-like intestinal barrier injury and colitis in mice by suppressing intestinal epithelial cell apoptosisviainhibiting PI3K/AKT signaling [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(6): 935-942. |
| [10] | LI jingyi, YANG Siyuan, HAN Zhen, JIANG Tianle, ZHU Yao, ZHOU Zihang, ZHOU Jingping. Akt2 inhibitor promotes M2 macrophage polarization in rats with periapical inflammation by reducing miR-155-5p expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(4): 568-576. |
| [11] | ZHANG Mengying, LI Zhi, PEI Weiya, LI Xueqin, YANG Hui, ZHU Xiaolong, LÜ Kun. M2 macrophage-derived exosomal lncRNA NR_028113.1 promotes macrophage polarization possibly by activating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(3): 393-399. |
| [12] | ZHAO Jialin, CHEN Ping, XU Guangli, SUN Jianhua, RUAN Yuanyuan, XUE Miaomiao, WU Yueliang. Bushen Huoxue Fang improves recurrent miscarriage in mice by down-regulating the JAK2/STAT3 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(2): 265-270. |
| [13] | XIAO Shuzhe, CHENG Yanling, ZHU Yun, TANG Rui, GU Jianbiao, LAN Lin, HE Zhihua, LIU Danqiong, GENG Lanlan, CHENG Yang, GONG Sitang. Fibroblasts overpressing WNT2b cause impairment of intestinal mucosal barrier [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(2): 206-212. |
| [14] | WANG Jie, LIU Jian, WEN Jianting, WANG Xin. Triptolide inhibits inflammatory response and migration of fibroblast like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis through the circRNA 0003353/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(3): 367-374. |
| [15] | . Changes of guanylate cyclase C in colon tissues of rats with intestinal injury associated with severe acute pancreatitis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(3): 376-383. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||