Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2639-2645.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.11
Fei WANG1( ), Weiran LI1, Xiang SHANG1, Fei LI2(
), Weiran LI1, Xiang SHANG1, Fei LI2( )
)
Received:2025-06-29
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Fei LI
E-mail:wangr05@qq.com;leagcen@163.com
Fei WANG, Weiran LI, Xiang SHANG, Fei LI. Development and validation of a risk prediction model for cognitive impairment in rural elderly Chinese populations: evidence from the CHARLS study[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2639-2645.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.11
| Variable | No Cognitive impairment (n=1331) | Cognitive impairment (n=229) | P# | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 601 (45.2) | 147 (64.2) | <0.001 |
| Male | 730 (54.8) | 82 (35.8) | ||
| Age (year) | 66 (62, 71) | 70 (64, 76) | <0.001 | |
| Marital status | Unmarried | 205 (15.4) | 66 (28.8) | <0.001 |
| Married/Other | 1126 (84.6) | 163 (71.2) | ||
| Education | Below primary | 405 (30.4) | 182 (79.5) | <0.001 |
| Primary school | 375 (28.2) | 38 (16.6) | ||
| Middle school | 304 (22.8) | 6 (2.6) | ||
| High school and above | 247 (18.6) | 3 (1.3) | ||
| Life satisfaction | Low | 119 (8.9) | 38 (16.6) | 0.002 |
| Moderate | 911 (68.4) | 141 (61.6) | ||
| High | 301 (22.6) | 50 (21.8) | ||
| Smoking | No | 971 (73.0) | 172 (75.1) | 0.496 |
| Yes | 360 (27.0) | 57 (24.9) | ||
| Alcohol drinking | No | 897 (67.4) | 187 (81.7) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 434 (32.6) | 42 (18.3) | ||
| Sleep duration | <6 h | 368 (27.6) | 89 (38.9) | <0.001 |
| 6-8 h | 887 (66.6) | 117 (51.1) | ||
| >8 h | 76 (5.7) | 23 (10.0) | ||
| Social activities | No | 583 (43.8) | 135 (59.0) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 748 (56.2) | 94 (41.0) | ||
| Tap water access | No | 234 (17.6) | 69 (30.1) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 1097 (82.4) | 160 (69.9) | ||
| Hypertension | No | 559 (42.0) | 73 (31.9) | 0.004 |
| Yes | 772 (58.0) | 156 (68.1) | ||
| Diabetes | No | 1095 (82.3) | 192 (83.8) | 0.563 |
| Yes | 236 (17.7) | 37 (16.2) | ||
| Cancer | No | 1313 (98.6) | 227 (99.1) | 0.756 |
| Yes | 18 (1.4) | 2 (0.9) | ||
| Lung disease | No | 1166 (87.6) | 197 (86.0) | 0.507 |
| Yes | 165 (12.4) | 32 (14.0) | ||
| Heart disease | No | 1035 (77.8) | 183 (79.9) | 0.467 |
| Yes | 296 (22.2) | 46 (20.1) | ||
| Stroke | No | 1277 (95.9) | 220 (96.1) | 0.928 |
| Yes | 54 (4.1) | 9 (3.9) | ||
| Arthritis | No | 898 (67.5) | 146 (63.8) | 0.270 |
| Yes | 433 (32.5) | 83 (36.2) | ||
| Dyslipidemia | No | 1083 (81.4) | 203 (88.6) | 0.007 |
| Yes | 248 (18.6) | 26 (11.4) | ||
| Liver disease | No | 1271 (95.5) | 222 (96.9) | 0.317 |
| Yes | 60 (4.5) | 7 (3.1) | ||
| Kidney disease | No | 1246 (93.6) | 215 (93.9) | 0.876 |
| Yes | 85 (6.4) | 14 (6.1) | ||
| Gastrointestinal disease | No | 1066 (80.1) | 170 (74.2) | 0.044 |
| Yes | 265 (19.9) | 59 (25.8) | ||
| Asthma | No | 1260 (94.7) | 218 (95.2) | 0.740 |
| Yes | 71 (5.3) | 11 (4.8) | ||
| Hip fracture | No | 1315 (98.8) | 223 (97.4) | 0.120 |
| Yes | 16 (1.2) | 6 (2.6) | ||
| Visual impairment | No | 324 (24.3) | 35 (15.3) | 0.003 |
| Yes | 1,007 (75.7) | 194 (84.7) | ||
| Hearing impairment | No | 606 (45.5) | 83 (36.2) | 0.009 |
| Yes | 725 (54.5) | 146 (63.8) | ||
| Depression | No | 975 (73.3) | 104 (45.4) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 356 (26.7) | 125 (54.6) | ||
| Pain | No | 1033 (77.6) | 148 (64.6) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 298 (22.4) | 81 (35.4) | ||
| Self-rated health | Poor | 295 (22.2) | 74 (32.3) | 0.001 |
| Fair | 720 (54.1) | 117 (51.1) | ||
| Good | 316 (23.7) | 38 (16.6) | ||
| ADL | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.00 (0.00, 1.00) | <0.001 | |
| IADL | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.00 (0.00, 2.00) | <0.001 | |
| Waist circumference | 87 (83, 93) | 87 (81, 92) | 0.003 | |
| BMI | 24.6 (22.3, 25.9) | 23.4 (20.8, 24.8) | <0.001 | |
| Handgrip strength | 29 (24, 33) | 23 (19, 27) | <0.001 | |
| SBP | 135 (124, 144) | 140 (126, 153) | <0.001 | |
| DBP | 76 (70, 82) | 77 (71, 84) | 0.007 | |
| Disability | No | 1136 (85.3) | 160 (69.9) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 195 (14.7) | 69 (30.1) | ||
| History of falls | No | 1133 (85.1) | 182 (79.5) | 0.030 |
| Yes | 198 (14.9) | 47 (20.5) | ||
| Tooth loss | No | 1199 (90.1) | 177 (77.3) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 132 (9.9) | 52 (22.7) |
Tab.1 Baseline characteristics of the participants in the training set
| Variable | No Cognitive impairment (n=1331) | Cognitive impairment (n=229) | P# | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 601 (45.2) | 147 (64.2) | <0.001 |
| Male | 730 (54.8) | 82 (35.8) | ||
| Age (year) | 66 (62, 71) | 70 (64, 76) | <0.001 | |
| Marital status | Unmarried | 205 (15.4) | 66 (28.8) | <0.001 |
| Married/Other | 1126 (84.6) | 163 (71.2) | ||
| Education | Below primary | 405 (30.4) | 182 (79.5) | <0.001 |
| Primary school | 375 (28.2) | 38 (16.6) | ||
| Middle school | 304 (22.8) | 6 (2.6) | ||
| High school and above | 247 (18.6) | 3 (1.3) | ||
| Life satisfaction | Low | 119 (8.9) | 38 (16.6) | 0.002 |
| Moderate | 911 (68.4) | 141 (61.6) | ||
| High | 301 (22.6) | 50 (21.8) | ||
| Smoking | No | 971 (73.0) | 172 (75.1) | 0.496 |
| Yes | 360 (27.0) | 57 (24.9) | ||
| Alcohol drinking | No | 897 (67.4) | 187 (81.7) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 434 (32.6) | 42 (18.3) | ||
| Sleep duration | <6 h | 368 (27.6) | 89 (38.9) | <0.001 |
| 6-8 h | 887 (66.6) | 117 (51.1) | ||
| >8 h | 76 (5.7) | 23 (10.0) | ||
| Social activities | No | 583 (43.8) | 135 (59.0) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 748 (56.2) | 94 (41.0) | ||
| Tap water access | No | 234 (17.6) | 69 (30.1) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 1097 (82.4) | 160 (69.9) | ||
| Hypertension | No | 559 (42.0) | 73 (31.9) | 0.004 |
| Yes | 772 (58.0) | 156 (68.1) | ||
| Diabetes | No | 1095 (82.3) | 192 (83.8) | 0.563 |
| Yes | 236 (17.7) | 37 (16.2) | ||
| Cancer | No | 1313 (98.6) | 227 (99.1) | 0.756 |
| Yes | 18 (1.4) | 2 (0.9) | ||
| Lung disease | No | 1166 (87.6) | 197 (86.0) | 0.507 |
| Yes | 165 (12.4) | 32 (14.0) | ||
| Heart disease | No | 1035 (77.8) | 183 (79.9) | 0.467 |
| Yes | 296 (22.2) | 46 (20.1) | ||
| Stroke | No | 1277 (95.9) | 220 (96.1) | 0.928 |
| Yes | 54 (4.1) | 9 (3.9) | ||
| Arthritis | No | 898 (67.5) | 146 (63.8) | 0.270 |
| Yes | 433 (32.5) | 83 (36.2) | ||
| Dyslipidemia | No | 1083 (81.4) | 203 (88.6) | 0.007 |
| Yes | 248 (18.6) | 26 (11.4) | ||
| Liver disease | No | 1271 (95.5) | 222 (96.9) | 0.317 |
| Yes | 60 (4.5) | 7 (3.1) | ||
| Kidney disease | No | 1246 (93.6) | 215 (93.9) | 0.876 |
| Yes | 85 (6.4) | 14 (6.1) | ||
| Gastrointestinal disease | No | 1066 (80.1) | 170 (74.2) | 0.044 |
| Yes | 265 (19.9) | 59 (25.8) | ||
| Asthma | No | 1260 (94.7) | 218 (95.2) | 0.740 |
| Yes | 71 (5.3) | 11 (4.8) | ||
| Hip fracture | No | 1315 (98.8) | 223 (97.4) | 0.120 |
| Yes | 16 (1.2) | 6 (2.6) | ||
| Visual impairment | No | 324 (24.3) | 35 (15.3) | 0.003 |
| Yes | 1,007 (75.7) | 194 (84.7) | ||
| Hearing impairment | No | 606 (45.5) | 83 (36.2) | 0.009 |
| Yes | 725 (54.5) | 146 (63.8) | ||
| Depression | No | 975 (73.3) | 104 (45.4) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 356 (26.7) | 125 (54.6) | ||
| Pain | No | 1033 (77.6) | 148 (64.6) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 298 (22.4) | 81 (35.4) | ||
| Self-rated health | Poor | 295 (22.2) | 74 (32.3) | 0.001 |
| Fair | 720 (54.1) | 117 (51.1) | ||
| Good | 316 (23.7) | 38 (16.6) | ||
| ADL | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.00 (0.00, 1.00) | <0.001 | |
| IADL | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.00 (0.00, 2.00) | <0.001 | |
| Waist circumference | 87 (83, 93) | 87 (81, 92) | 0.003 | |
| BMI | 24.6 (22.3, 25.9) | 23.4 (20.8, 24.8) | <0.001 | |
| Handgrip strength | 29 (24, 33) | 23 (19, 27) | <0.001 | |
| SBP | 135 (124, 144) | 140 (126, 153) | <0.001 | |
| DBP | 76 (70, 82) | 77 (71, 84) | 0.007 | |
| Disability | No | 1136 (85.3) | 160 (69.9) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 195 (14.7) | 69 (30.1) | ||
| History of falls | No | 1133 (85.1) | 182 (79.5) | 0.030 |
| Yes | 198 (14.9) | 47 (20.5) | ||
| Tooth loss | No | 1199 (90.1) | 177 (77.3) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 132 (9.9) | 52 (22.7) |

Fig.1 Feature selection process based on LASSO regression. A: Optimal penalty parameter λ selected based on 10-fold cross-validation. The left dashed line indicates the λ corresponding to the minimum mean cross-validated error, and the right dashed line represents λ1se, the largest λ within one standard error of the minimum. B: LASSO coefficient profile plot showing how the coefficients of each variable evolve as the λ value changes. The dashed line marks the selected optimal λ. C: Key variables selected by LASSO and their corresponding regression coefficients. Negative coefficients indicate risk factors, and positive coefficients represent protective factors.
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.06 | 1.03, 1.09 | <0.001 |
| Education (Reference: Below Primary School) | |||
| Primary school | 0.29 | 0.19, 0.43 | <0.001 |
| Middle school | 0.06 | 0.03, 0.15 | <0.001 |
| High school and above | 0.04 | 0.01, 0.13 | <0.001 |
| Alcohol drinking (Reference: No) | 0.64 | 0.42, 0.96 | 0.032 |
| SBP | 1.01 | 1.00, 1.02 | 0.005 |
| Handgrip strength | 0.97 | 0.95,0.99 | 0.003 |
| Depression (Reference: No) | 2.06 | 1.45, 2.94 | <0.001 |
Tab.2 Logistic regression analysis of risk factors for cognitive impairment in the elderly individuals
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.06 | 1.03, 1.09 | <0.001 |
| Education (Reference: Below Primary School) | |||
| Primary school | 0.29 | 0.19, 0.43 | <0.001 |
| Middle school | 0.06 | 0.03, 0.15 | <0.001 |
| High school and above | 0.04 | 0.01, 0.13 | <0.001 |
| Alcohol drinking (Reference: No) | 0.64 | 0.42, 0.96 | 0.032 |
| SBP | 1.01 | 1.00, 1.02 | 0.005 |
| Handgrip strength | 0.97 | 0.95,0.99 | 0.003 |
| Depression (Reference: No) | 2.06 | 1.45, 2.94 | <0.001 |
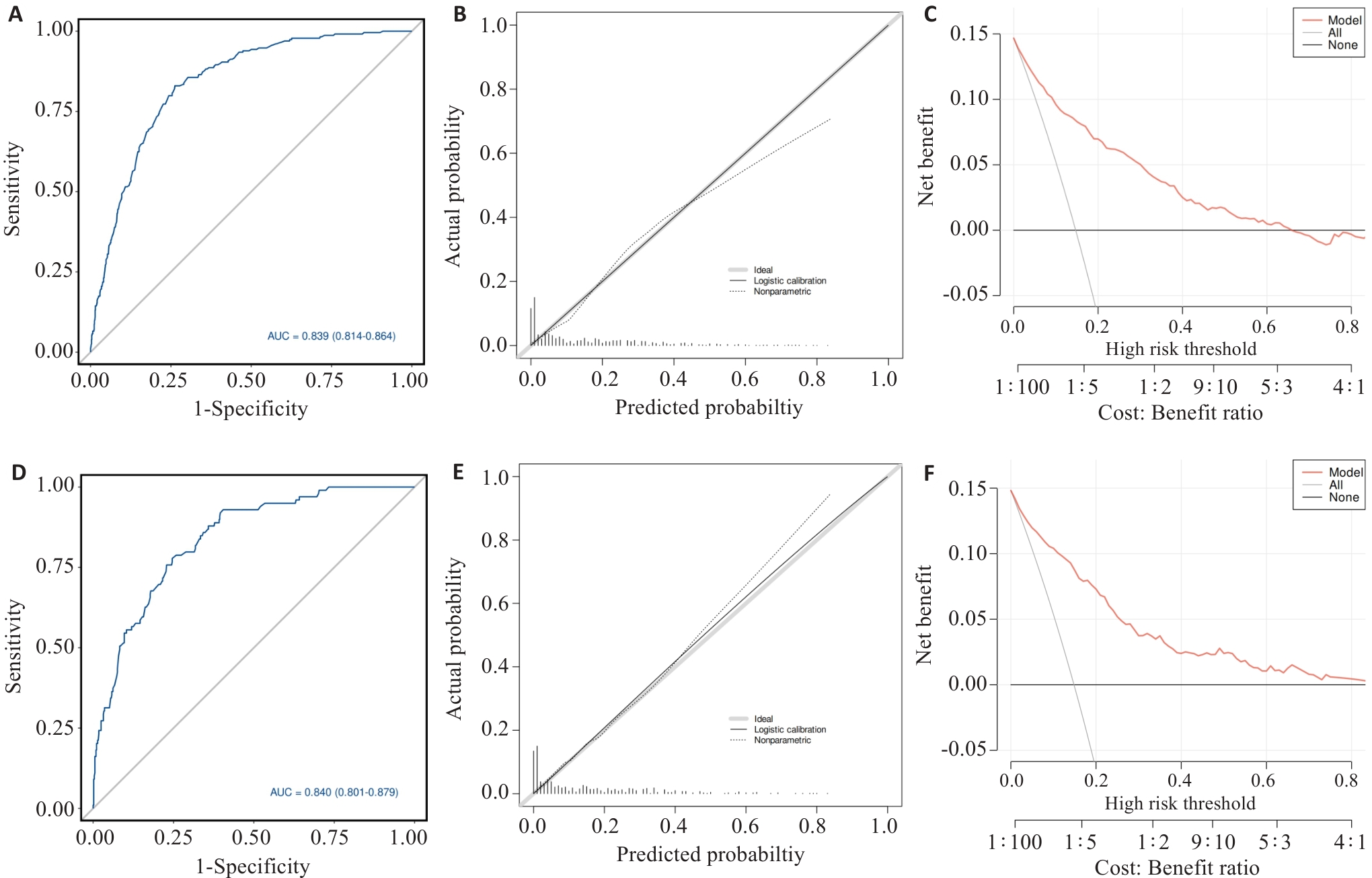
Fig.3 Performance evaluation of the predictive model in the training and validation cohorts. A: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve in the training set. B: Calibration curve in the training set. C: Decision curve analysis (DCA) in the training set. D: ROC curve in the internal validation set. E: Calibration curve in the internal validation set. F: DCA in the internal validation set.
| [1] | Jiang Y, Cui M, Tian W, et al. Lifestyle, multi-omics features, and preclinical dementia among Chinese: The Taizhou Imaging Study[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2021, 17(1): 18-28. doi:10.1002/alz.12171 |
| [2] | Jia L, Du Y, Chu L, et al. Prevalence, risk factors, and management of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 60 years or older in China: a cross-sectional study[J]. Lancet Public Health, 2020, 5(12): e661-71. doi:10.1016/s2468-2667(20)30185-7 |
| [3] | 王英全,梁景宏,贾瑞霞,等.2020-2050年中国阿尔茨海默病患病情况预测研究[J].阿尔茨海默病及相关病,2019,2(01):289-98. |
| [4] | Ren Y, Dong Y, Hou T, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and progression of cognitive impairment, No dementia among rural-dwelling Chinese older adults[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2022, 85(4): 1583-92. doi:10.3233/jad-215236 |
| [5] | 首都医科大学宣武医院国家神经疾病医学中心, 中国疾病预防控制中心慢性非传染性疾病预防控制中心, 国家卫生健康委能力建设和继续教育中心, 等. 中国阿尔茨海默病蓝皮书(精简版)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2024, 104(29): 2701-27. |
| [6] | Xue C, Li J, Hao M, et al. High prevalence of subjective cognitive decline in older Chinese adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Public Health, 2023, 11: 1277995. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2023.1277995 |
| [7] | Pu LN, Pan DG, Wang HH, et al. A predictive model for the risk of cognitive impairment in community middle-aged and older adults[J]. Asian J Psychiatry, 2023, 79: 103380. doi:10.1016/j.ajp.2022.103380 |
| [8] | 赵晓晴, 郭桐桐, 张欣怡, 等. 社区老年人认知障碍风险预测模型的构建与验证研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2776-90. |
| [9] | Geethadevi GM, Peel R, Bell JS, et al. Validity of three risk prediction models for dementia or cognitive impairment in Australia[J]. Age Ageing, 2022, 51(12): afac307. doi:10.1093/ageing/afac307 |
| [10] | Zhao Y, Hu Y, Smith JP, et al. Cohort profile: the China health and retirement longitudinal study (CHARLS)[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2014, 43(1): 61-8. doi:10.1093/ije/dys203 |
| [11] | Chu L, Wu Y, Karjalainen H, et al. Lifespan exposures to rural-urban conditions and later-life cognitive function[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2025, 21(6): e70267. doi:10.1002/alz.70267 |
| [12] | Li L, Zhuang L, Xu Z, et al. U-shaped relationship between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cognitive impairment in Chinese middle-aged and elderly: a cross-sectional study[J]. BMC Public Health, 2024, 24(1): 1624. doi:10.1186/s12889-024-19164-8 |
| [13] | Zhou S, Song S, Jin Y, et al. Prospective association between social engagement and cognitive impairment among middle-aged and older adults: evidence from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study[J]. BMJ Open, 2020, 10(11): e040936. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-040936 |
| [14] | 史路平, 姚水洪, 王 薇. 中国老年人群轻度认知障碍患病率及发展趋势的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(1): 109-14. doi:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.315 |
| [15] | Jia LF, Quan MN, Fu Y, et al. Dementia in China: epidemiology, clinical management, and research advances[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2020, 19(1): 81-92. doi:10.1016/s1474-4422(19)30290-x |
| [16] | 公维军. 衰老相关认知功能障碍的发病机制与康复治疗[J]. 康复学报, 2024, 34(6): 529-35. |
| [17] | Arlt FA, Sperber PS, von Rennenberg R, et al. Serum anti-NMDA receptor antibodies are linked to memory impairment 12 months after stroke[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2025, 30(4): 1359-68. doi:10.1038/s41380-024-02744-w |
| [18] | 李 月. 我国老年人认知障碍特征分析及政策研究[J]. 人口与健康, 2020, (5): 54-7. |
| [19] | Cai Y, Fang L, Li A, et al. Educational attainment, Aβ, tau, and structural brain reserve in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2025, 21(2): e14400. doi:10.1002/alz.14400 |
| [20] | Cui L, Hou NN, Wu HM, et al. Prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease in China: an updated systematical analysis[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2020, 12: 603854. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2020.603854 |
| [21] | Zhang R, Shen L, Miles T, et al. Association of low to moderate alcohol drinking with cognitive functions from middle to older age among US adults[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2020, 3(6): e207922. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.7922 |
| [22] | Huang Z, Chen R, Ho M, et al. Dynamic responses of striatal cholinergic interneurons control behavioral flexibility[J]. Sci Adv, 2024, 10(51): eadn2446. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adn2446 |
| [23] | Li CL, Zhu YD, Ma YJ, et al. Association of cumulative blood pressure with cognitive decline, dementia, and mortality[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2022, 79(14): 1321-35. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2022.01.045 |
| [24] | Zheng G, Zhou B, Fang Z, et al. Long-term visit-to-visit blood pressure variability and cognitive decline among patients with hypertension: a pooled analysis of 3 national prospective cohorts[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2024, 13(13): e035504. doi:10.1161/jaha.124.035504 |
| [25] | Duchowny KA, Ackley SF, Brenowitz WD, et al. Associations between handgrip strength and dementia risk, cognition, and neuroimaging outcomes in the UK biobank cohort study[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2022, 5(6): e2218314. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.18314 |
| [26] | Kuo K, Zhang YR, Chen SD, et al. Associations of grip strength, walking pace, and the risk of incident dementia: a prospective cohort study of 340212 participants[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2023, 19(4): 1415-27. doi:10.1002/alz.12793 |
| [27] | Liou YJ, Tsai SJ, Bai YM, et al. Dementia risk in middle-aged patients with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder: a cohort study of 84, 824 subjects[J]. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci, 2023, 273(1): 219-27. doi:10.1007/s00406-022-01389-6 |
| [28] | Li JM, Hu T, Zhou XN, et al. The involvement of NLRP3 inflammasome in CUMS-induced AD-like pathological changes and related cognitive decline in mice[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2023, 20(1): 112. doi:10.1186/s12974-023-02791-0 |
| [1] | Yunhong YU, Wei XIE, Hui LI. Chaihu Shugan Decoction improves cognitive impairment after epilepsy in rats by regulating hippocampal NMDAR subunits via upregulating ASIC1 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1506-1512. |
| [2] | Zhenyan MA, Xin A, Lei ZHAO, Hongbo ZHANG, Ke LIU, Yiqing ZHAO, Geng QIAN. A cardiac magnetic resonance-based risk prediction model for left ventricular adverse remodeling following percutaneous coronary intervention for acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: a multi-center prospective study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 669-683. |
| [3] | Qi CHEN, Tiantian XIA, Yongqiang ZHOU, Mingyang CHANG, Nan HU, Yanmei YANG, Zhong LI, Yue GAO, Bin GU. Prevotella nigrescens exacerbates periodontal inflammation and impairs cognitive function in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 453-460. |
| [4] | Jiachun LUO, Sodnomjamts Batzaya, Xuefeng GAO, Jingyu CHEN, Zhengying YU, Shasha XIONG, Hong CAO. Akkermansia muciniphila gavage improves gut-brain interaction disorders in gp120 transgenic mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 554-565. |
| [5] | Yulan WANG, Xiang FANG, Zeming CHEN, Bingkun RUAN, Xinli HAN, Yujie TANG, Luyao ZHU. Qingre Lidan Jiedu Recipe improves high copper load-induced cognitive dysfunction in rats by regulating mitophagy [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(11): 2437-2443. |
| [6] | Shenhao PAN, Yankun LI, Zhewei WU, Yuling MAO, Chunyan WANG. Establishment of a predictive nomogram for clinical pregnancy rate in patients with endometriosis undergoing fresh embryo transfer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1407-1415. |
| [7] | ZHANG Xiaoyan, WANG Xie, WANG Jie, SHAO Nan, CAI Biao, XIE Daojun. Huangpu Tongqiao Capsule improves cognitive impairment in rats with Wilson disease by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 447-454. |
| [8] | LIU Yunze, LI Chengrun, GUO Juntang, LIU Yang. A clinical-radiomics nomogram for differentiating focal organizing pneumonia and lung adenocarcinoma [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 397-404. |
| [9] | ZHANG Haoxuan, LU Jin, JIANG Chengyi, FANG Meifang. Construction and evaluation of an artificial intelligence-based risk prediction model for death in patients with nasopharyngeal cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(2): 271-279. |
| [10] | ZHANG Benlong, LU Yixun, LI Li, GAO Yunhe, LIANG Wenquan, XI Hongqing, WANG Xinxin, ZHANG Kecheng, CHEN Lin. Establishment and validation of a nomogram for predicting prognosis of gastric neuroendocrine neoplasms based on data from 490 cases in a single center [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(2): 183-190. |
| [11] | KONG Dexian, SONG Liping, XIANG Yang. Construction of a prognostic nomogram combining PET/CT metabolic parameters and blood inflammatory markers for non-small cell lung cancer treated with first-line chemotherapy [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(12): 2139-2144. |
| [12] | LIU Zhaojun, ZHOU Xiaoli. A nomogram based on systemic inflammation markers can predict adverse outcomes in patients with heart failure [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(8): 1149-1158. |
| [13] | LUO Chao, WANG Gaoming, HU Liwen, QIANG Yong, ZHENG Chao, SHEN Yi. Development and validation of a prognostic model based on SEER data for patients with esophageal carcinoma after esophagectomy [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(6): 794-804. |
| [14] | MENG Lingfei, ZHU Xueyan, YANG Liming, LI Xinyang, CHENG Siyu, GUO Shizheng, ZHUANG Xiaohua, ZOU Hongbin, CUI Wenpeng. Development and validation of a prediction model for treatment failure in peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis patients: a multicenter study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(4): 546-553. |
| [15] | ZHAO Chenling, DONG Ting, SUN Lunyan, HU Huibing, WANG Qiong, TIAN Liwei, JIANG Zhangsheng. Establishment and validation of a predictive nomogram for liver fibrosis in patients with Wilson disease and abnormal lipid metabolism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(11): 1720-1725. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||