Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 554-565.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.13
Jiachun LUO( ), Sodnomjamts Batzaya, Xuefeng GAO, Jingyu CHEN, Zhengying YU, Shasha XIONG, Hong CAO(
), Sodnomjamts Batzaya, Xuefeng GAO, Jingyu CHEN, Zhengying YU, Shasha XIONG, Hong CAO( )
)
Received:2024-11-19
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
Hong CAO
E-mail:q929188753@163.com;gzhcao@smu.edu.cn
Supported by:Jiachun LUO, Sodnomjamts Batzaya, Xuefeng GAO, Jingyu CHEN, Zhengying YU, Shasha XIONG, Hong CAO. Akkermansia muciniphila gavage improves gut-brain interaction disorders in gp120 transgenic mice[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 554-565.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.13
| Gene | Primer sequences (5'-3')-F | Primer sequences (3'-5')-R |
|---|---|---|
| Occludin | TTTCCTGCGGTGACTTCTCC | GGGGAACGTGGCCGATATAA |
| ZO-1 | CTCAAGTTCCTGAAGCCCGT | GCAAAAGACCAACCGTCAGG |
| TNF-α | CCTGTAGCCCACGTCGTAG | GGGAGTAGACAAGGTACAACCC |
| INF-γ | ATGAACGCTACACACTGCATC | CCATCCTTTTGCCAGTTCCTC |
| IL-10 | CTTACTGACTGGCATGAGGATCA | GCAGCTCTAGGAGCATGTGG |
| GAPDH | AGCTTGTCATCAACGGGAAG | TTTGATGTTAGTGGGGTCTCG |
Tab.1 Primers used for qPCR
| Gene | Primer sequences (5'-3')-F | Primer sequences (3'-5')-R |
|---|---|---|
| Occludin | TTTCCTGCGGTGACTTCTCC | GGGGAACGTGGCCGATATAA |
| ZO-1 | CTCAAGTTCCTGAAGCCCGT | GCAAAAGACCAACCGTCAGG |
| TNF-α | CCTGTAGCCCACGTCGTAG | GGGAGTAGACAAGGTACAACCC |
| INF-γ | ATGAACGCTACACACTGCATC | CCATCCTTTTGCCAGTTCCTC |
| IL-10 | CTTACTGACTGGCATGAGGATCA | GCAGCTCTAGGAGCATGTGG |
| GAPDH | AGCTTGTCATCAACGGGAAG | TTTGATGTTAGTGGGGTCTCG |
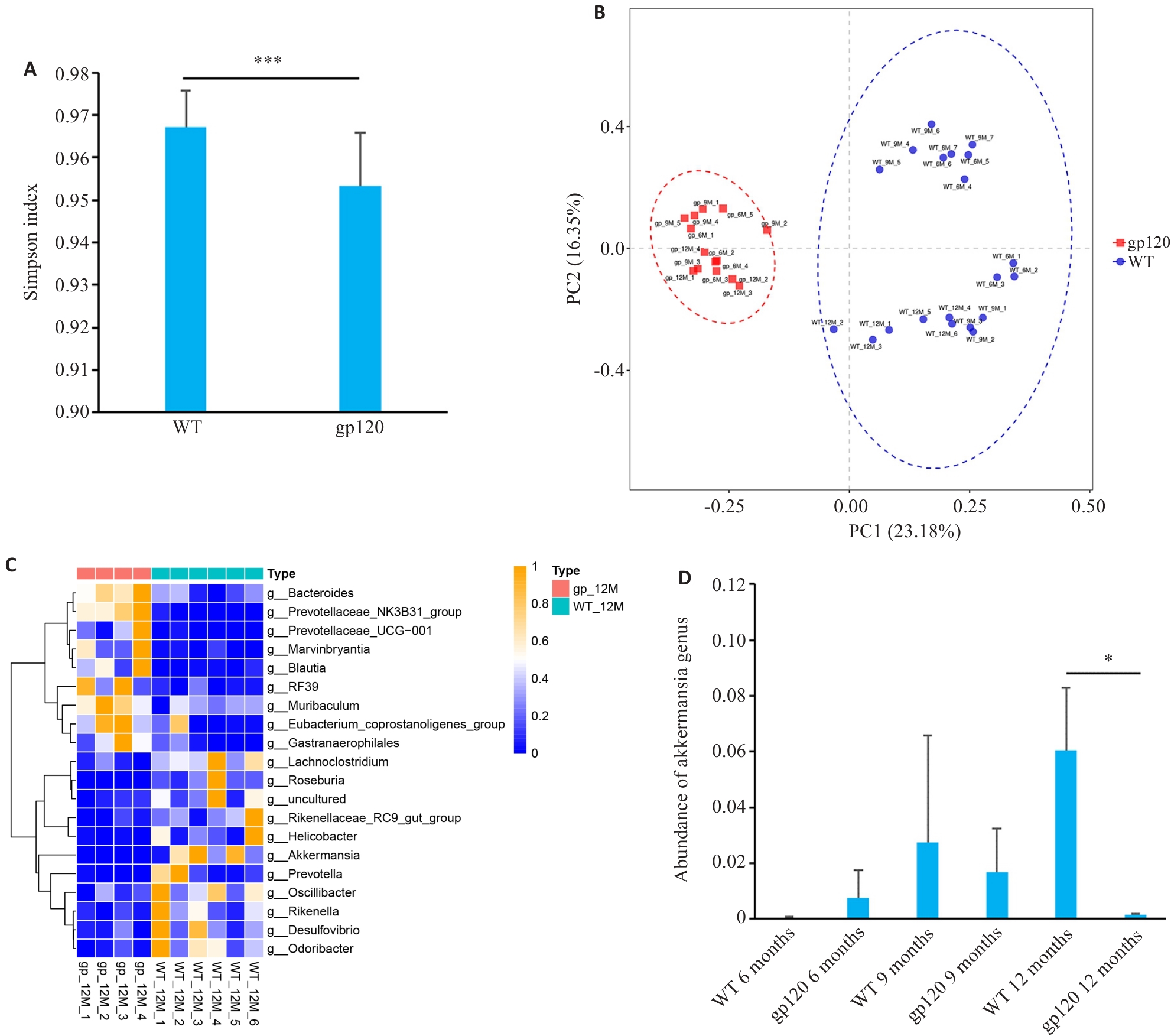
Fig.1 Analysis of diversity and abundance of intestinal microbiota in gp120tg mice and WT mice. A: Simpson's diversity index of the microbiome in gp120tg mice (n=14) and WT mice (n=20). B: Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) using unweighted UniFrac distance in gp120tg mice (n=14) and WT mice (n=20). C: Heatmap for comparison of microbiota abundance at the genus level between 12-month-old gp120tg mice (n=4) and WT mice (n=6). D: Abundance of Akkermansia genus in different groups of mice (n=3-4). *P<0.05, ***P < 0.001.
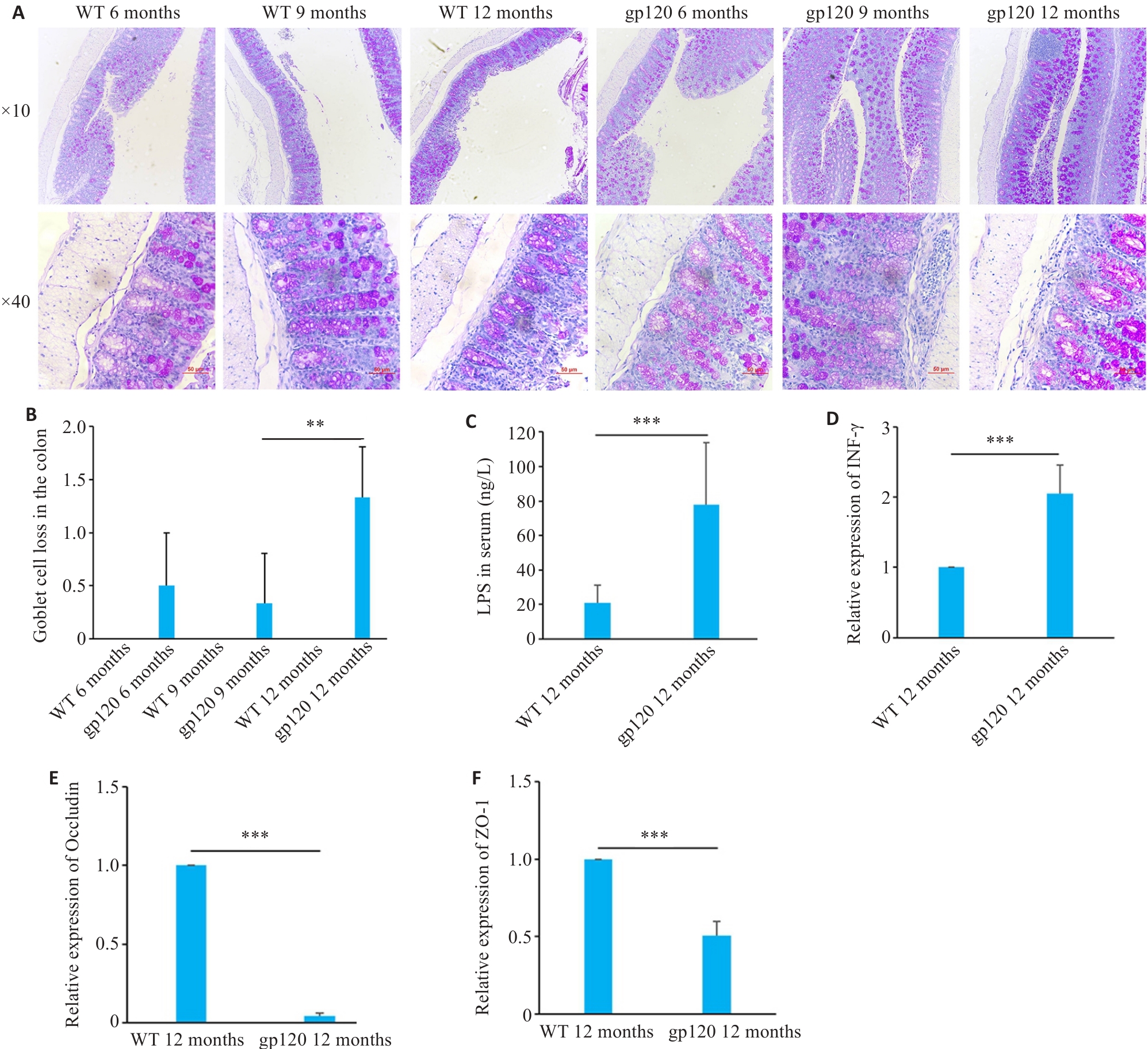
Fig.2 Expression of intestinal barrier-related indexes in gp120tg mice and WT mice. A: PAS staining of mouse colon tissues. B: Quantification of goblet cell loss of mouse colon tissues (n=3-4). C: ELISA validation of LPS levels in mouse serum (n=5). D-F: Quantification of INF-γ, occludin and ZO-1 expression levels in the mouse colon (n=3). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
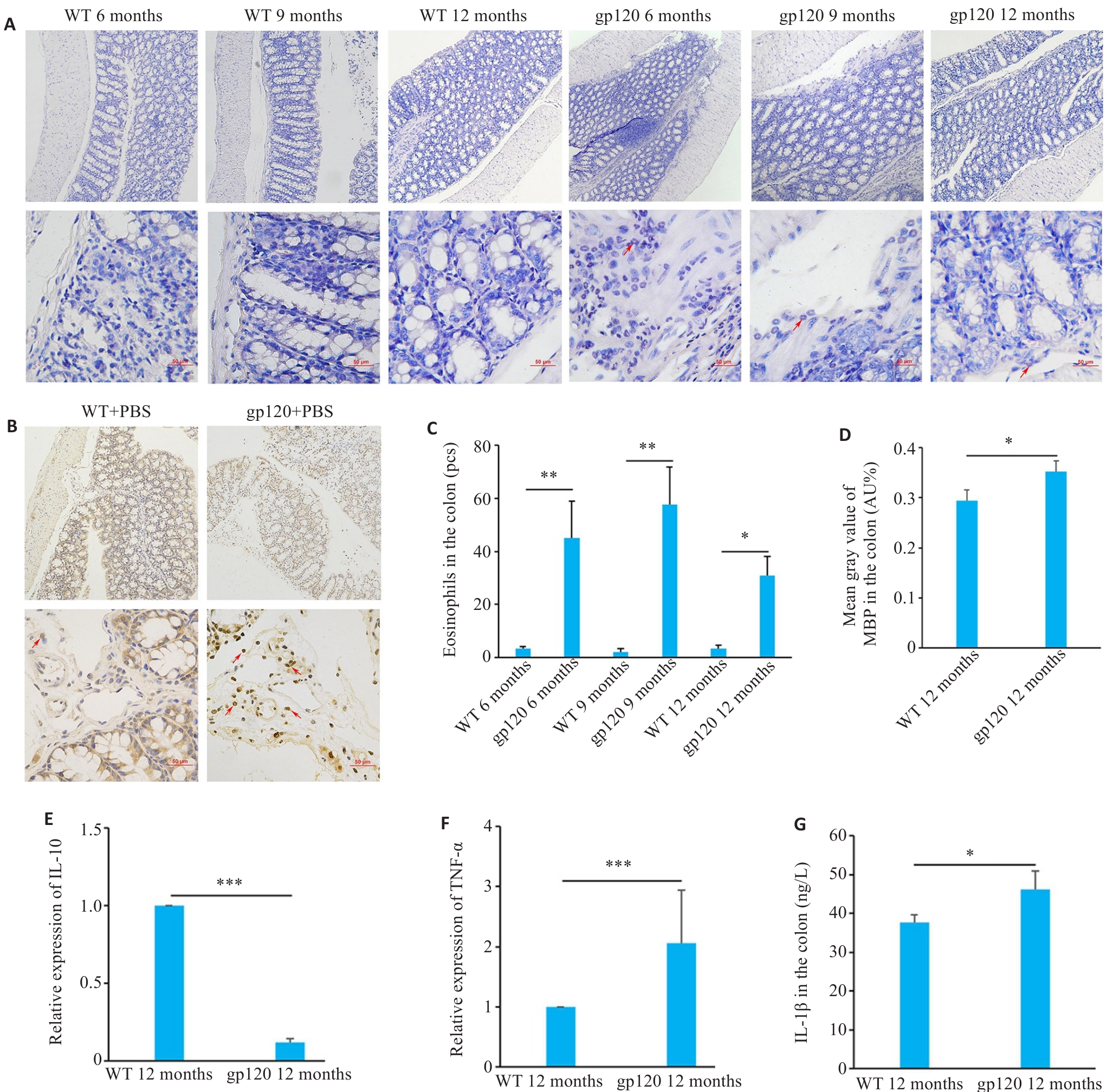
Fig.3 Expression of inflammation- and immune response-related indexes in gp120tg mice and WT mice. A: Hematoxylin-chromotrope staining of mouse colon tissues (scale bar=50 μm). B: MBP staining of the mouse colon tissues (MBP-positive areas are brown or reddish-brown; scale bar=50 μm). C: Quantification of eosinophils in the mouse colon tissues (n=3 or 4). D: Mean gray value of MBP in the colon (n=3). E, F: Quantification of IL-10 and TNF-α expression levels in the mouse colon (n=3). G: ELISA validation of IL-1β levels in the mouse colon (n=4). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
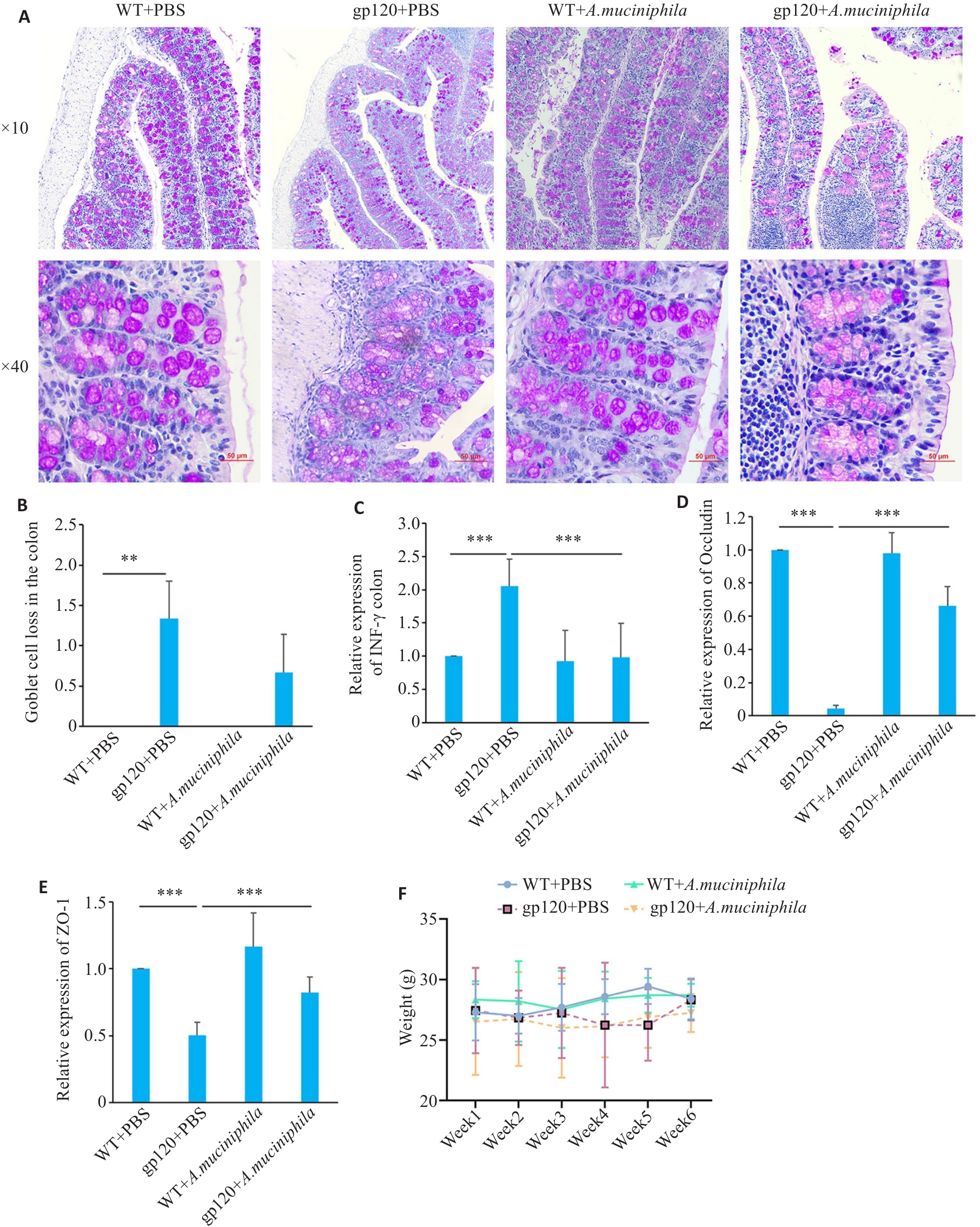
Fig.4 Effects of oral gavage of A.muciniphila on expression of gut barrier-related indexes in the colon of 12-month-old gp120tg mice and WT mice. A: PAS staining of mouse colon tissues (scale bar=50 μm). B: Quantification of goblet cell loss in mouse colon tissues (n=3 or 4). C-E: Quantification of INF-γ, occludin and ZO-1 expression levels in mouse colon (n=3). Mice were gavaged once a day with A. muciniphila (2×108 CFU per mouse) for 6 weeks. F: Changes of body weight of the mice during oral gavage of A.muciniphila. **P<0.01, ***P< 0.001.
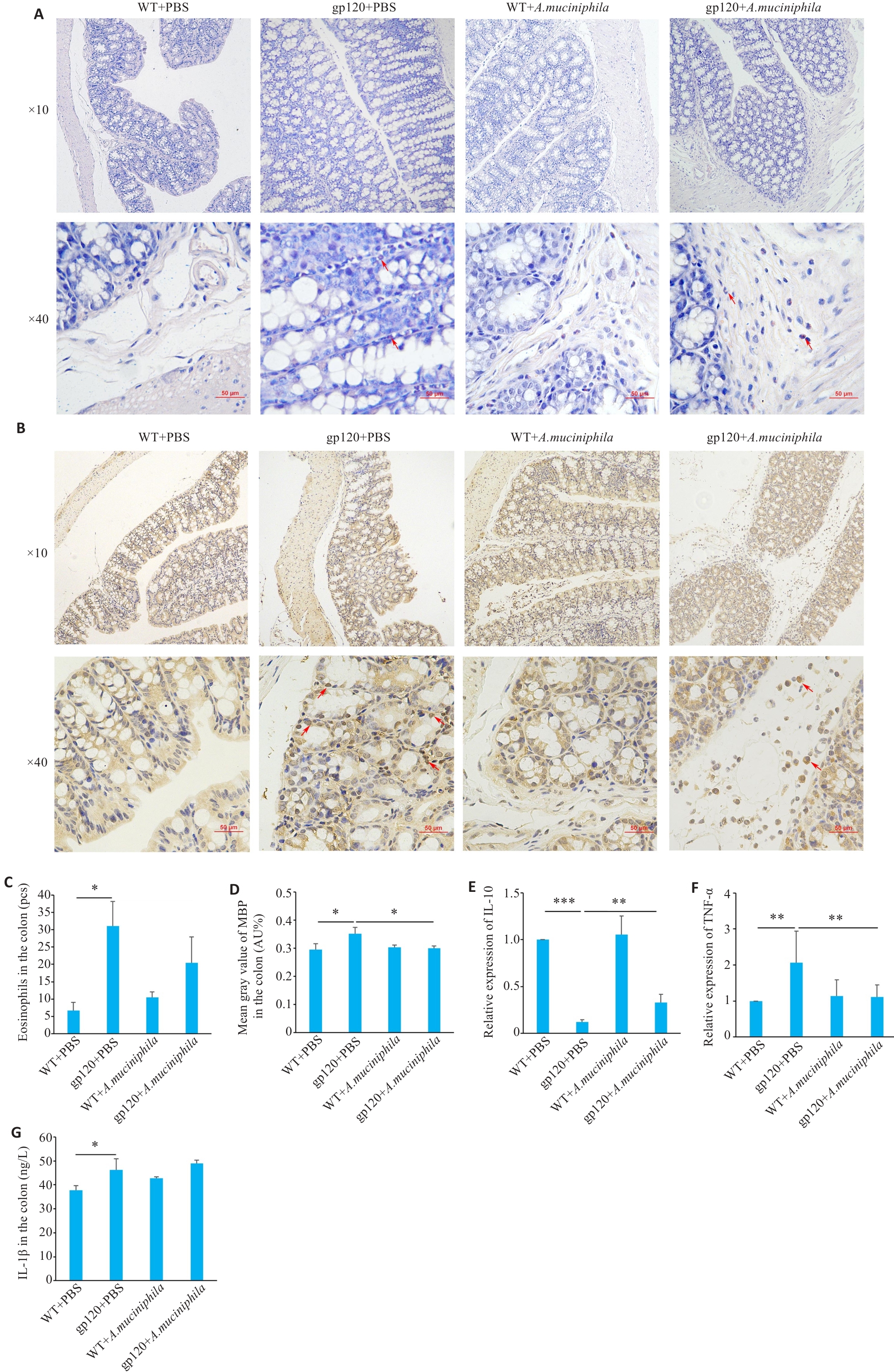
Fig.5 Effects of oral gavage of A.muciniphila onexpression of inflammation- and immune response-related indexes in 12-month-old gp120tg mice and WT mice. A: Hematoxylin-chromotrope staining of mouse colon tissues. B: MBP staining in the mouse colon tissues. C: Quantification of eosinophils in the mouse colon tissues (n=3 or 4). D: Mean gray value of MBP in the colon (n=3). E, F: Quantification of IL-10 and TNF-α expression levels in mouse colon (n=3). G: ELISA validation of IL-1β levels in mouse colon (n=3 or 4). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
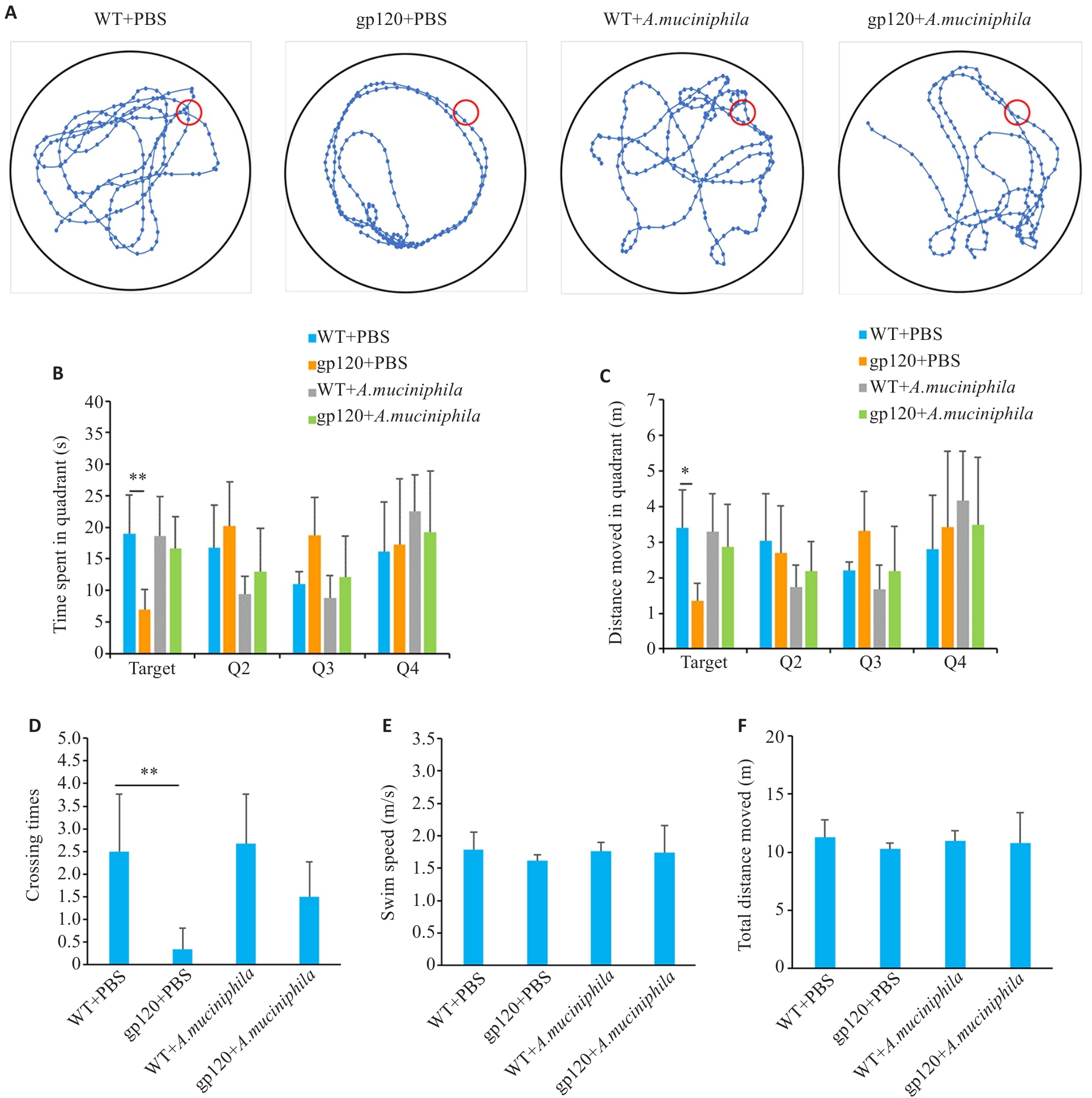
Fig.6 Effects of oral gavage of A.muciniphila on learning and spatial memory abilities of 12-month-old gp120tg mice and WT mice. A: Movement trajectory diagrams of the mice in the spatial exploration experiments (n=6). B: Movement time in each quadrant in the spatial exploration experiments (n=6). C: Movement distance in each quadrant in the spatial exploration experiments (n=6). D: Crossing times of the platform in the spatial exploration experiments (n=6). E: Swimming speed of the mice in the spatial exploration experiments (n=6). F: Total distance moved of the mice in the spatial exploration experiments (n=6). *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
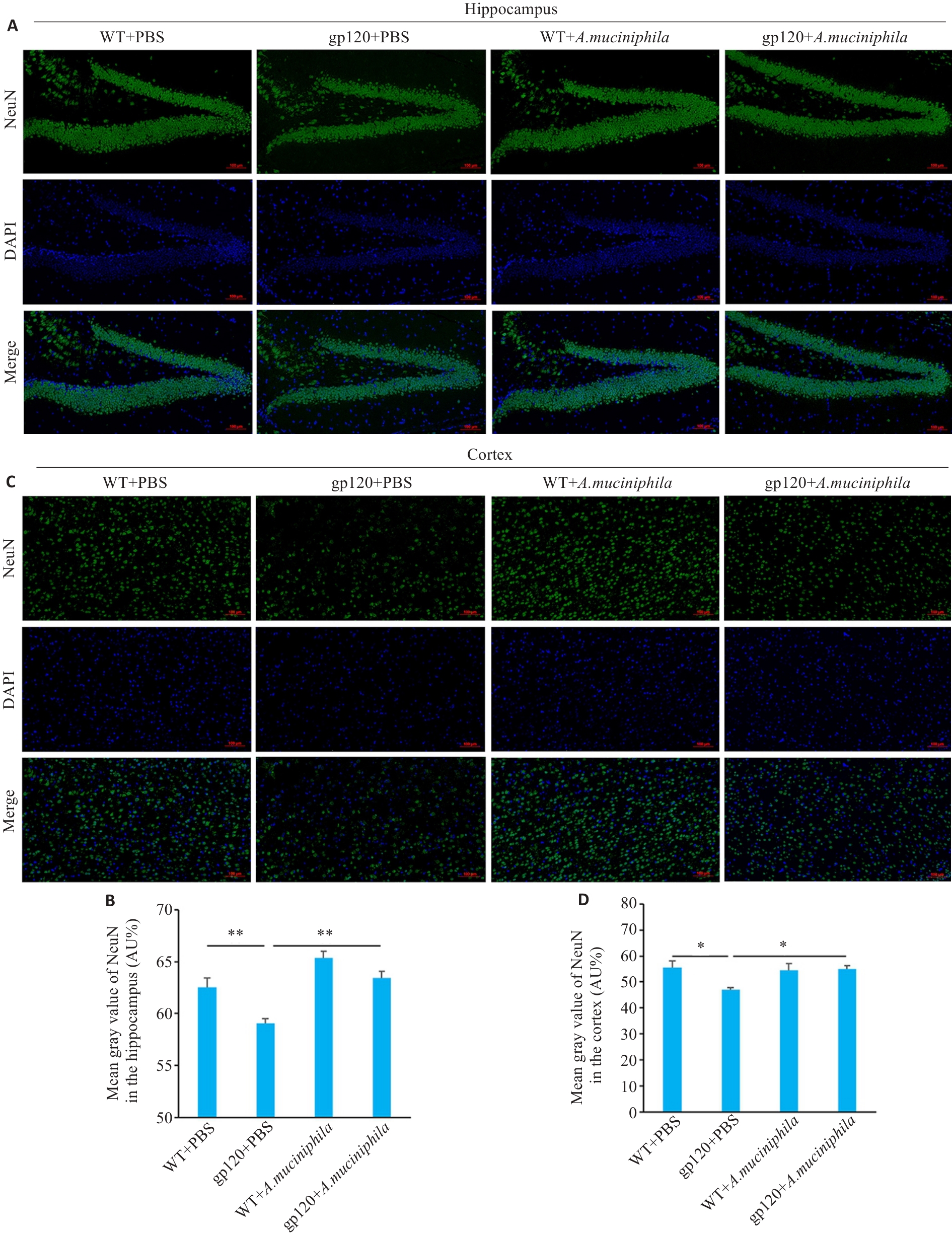
Fig.7 Effects of A.muciniphila gavage on neuronal damage in 12-month-old gp120tg mice and WT mice. A: Immunofluorescence showing the distribution of NeuN in the mouse hippocampus (scale bar=100 μm). B: Mean gray value of NeuN in the mouse hippocampus (n=3). C: Immunofluorescence showing the distribution of NeuN in the mouse cortex (scale bar=100 μm). D: Mean gray value of NeuN in the mouse cortex (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
| 1 | Namagga JK, Rukundo GZ, Niyonzima V, et al. Depression and HIV associated neurocognitive disorders among HIV infected adults in rural southwestern Uganda: a cross-sectional quantitative study[J]. BMC Psychiatry, 2021, 21(1): 350. |
| 2 | Ji J, Zhang Y, Ma Y, et al. People who living with HIV/AIDS also have a high prevalence of anxiety disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Psychiatry, 2024, 15: 1259290. |
| 3 | Myszka DG, Sweet RW, Hensley P, et al. Energetics of the HIV gp120-CD4 binding reaction[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2000, 97(16): 9026-31. |
| 4 | He XL, Yang WJ, Zeng ZJ, et al. NLRP3-dependent pyroptosis is required for HIV-1 gp120-induced neuropathology[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2020, 17: 283-99. |
| 5 | Tan SY, Li WJ, Yang C, et al. gp120-derived amyloidogenic peptides form amyloid fibrils that increase HIV-1 infectivity[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2024, 21: 479-94. |
| 6 | Ellis RJ, Marquine MJ, Kaul M, et al. Mechanisms underlying HIV-associated cognitive impairment and emerging therapies for its management[J]. Nat Rev Neurol, 2023, 19: 668-87. |
| 7 | Maung R, Hoefer MM, Sanchez AB, et al. CCR5 knockout prevents neuronal injury and behavioral impairment induced in a transgenic mouse model by a CXCR4-using HIV-1 glycoprotein 120[J]. J Immunol, 2014, 193(4): 1895-910. |
| 8 | Toggas SM, Masliah E, Rockenstein EM, et al. Central nervous system damage produced by expression of the HIV-1 coat protein gp120 in transgenic mice[J]. Nature, 1994, 367(6459): 188-93. |
| 9 | Bonnechère B, Amin N, van Duijn C. What are the key gut microbiota involved in neurological diseases? A systematic review[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(22): 13665. |
| 10 | Yang H, Li S, Le W. Intestinal permeability, dysbiosis, inflammation and enteric Glia cells: the intestinal etiology of Parkinson's disease[J]. Aging Dis, 2022, 13(5): 1381-90. |
| 11 | Rocafort M, Noguera-Julian M, Rivera J, et al. Evolution of the gut microbiome following acute HIV-1 infection[J]. Microbiome, 2019, 7(1): 73. |
| 12 | Guo XY, Guo YT, Wang ZR, et al. Severe intestinal barrier damage in HIV-infected immunological non-responders[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(10): e20790. |
| 13 | Van Oudenhove L, Crowell MD, Drossman DA, et al. Biopsychosocial aspects of functional gastrointestinal disorders[J]. Gastroenterology, 2016: S0016-5085(16)00218-3. |
| 14 | Mohamed AA, Oduor C, Kinyanjui D. HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders at Moi teaching and referral hospital, Eldoret, Kenya[J]. BMC Neurol, 2020, 20(1): 280. |
| 15 | Vujkovic-Cvijin I, Sortino O, Verheij E, et al. HIV-associated gut dysbiosis is independent of sexual practice and correlates with noncommunicable diseases[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11: 2448. |
| 16 | Vázquez-Castellanos JF, Serrano-Villar S, Jiménez-Hernández N, et al. Interplay between gut microbiota metabolism and inflammation in HIV infection[J]. ISME J, 2018, 12: 1964-76. |
| 17 | Ouyang J, Lin J, Isnard S, et al. The bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila: a sentinel for gut permeability and its relevance to HIV-related inflammation[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 645. |
| 18 | Zheng M, Han R, Yuan Y, et al. The role of Akkermansia muciniphila in inflammatory bowel disease: Current knowledge and perspectives[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 1089600. |
| 19 | Xu R, Zhang Y, Chen S, et al. The role of the probiotic Akkermansia muciniphila in brain functions: insights underpinning therapeutic potential[J]. Crit Rev Microbiol, 2023, 49(2): 151-76. |
| 20 | Mo C, Lou X, Xue J, et al. The influence of Akkermansia muciniphila on intestinal barrier function[J]. Gut Pathog, 2024, 16(1): 41. |
| 21 | Erben U, Loddenkemper C, Doerfel K, et al. A guide to histomorphological evaluation of intestinal inflammation in mouse models[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2014, 7(8): 4557-76. |
| 22 | Barbaro MR, Cremon C, Marasco G, et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying loss of vascular and epithelial integrity in irritable bowel syndrome[J]. Gastroenterology, 2024, 167(6): 1152-66. |
| 23 | Vanheel H, Vicario M, Vanuytsel T, et al. Impaired duodenal mucosal integrity and low-grade inflammation in functional dyspepsia[J]. Gut, 2014, 63(2): 262-71. |
| 24 | Vanuytsel T, Bercik P, Boeckxstaens G. Understanding neuroimmune interactions in disorders of gut-brain interaction: from functional to immune-mediated disorders[J]. Gut, 2023, 72(4): 787-98. |
| 25 | Lechuga S, Braga-Neto MB, Naydenov NG, et al. Understanding disruption of the gut barrier during inflammation: Should we abandon traditional epithelial cell lines and switch to intestinal organoids?[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1108289. |
| 26 | Awad K, Barmeyer C, Bojarski C, et al. Epithelial barrier dysfunction in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D) via downregulation of claudin-1[J]. Cells, 2023, 12(24): 2846. |
| 27 | Han X, Lee A, Huang S, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG prevents epithelial barrier dysfunction induced by interferon-gamma and fecal supernatants from irritable bowel syndrome patients in human intestinal enteroids and colonoids[J]. Gut Microbes, 2019, 10(1): 59-76. |
| 28 | Madara JL, Stafford J. Interferon-gamma directly affects barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers[J]. J Clin Invest, 1989, 83(2): 724-7. |
| 29 | Pabst O, Cerovic V. Interferon-γ sensing by epithelial cells tames gut inflammation[J]. Nat Immunol, 2024, 25: 9-10. |
| 30 | Smolinska S, Winiarska E, Globinska A, et al. Histamine: a mediator of intestinal disorders-a review[J]. Metabolites, 2022, 12(10): 895. |
| 31 | Salvo-Romero E, Rodiño-Janeiro BK, Albert-Bayo M, et al. Eosinophils in the gastrointestinal tract: key contributors to neuro-immune crosstalk and potential implications in disorders of brain-gut interaction[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(10): 1644. |
| 32 | Furuta GT, Nieuwenhuis EE, Karhausen J, et al. Eosinophils alter colonic epithelial barrier function: role for major basic protein[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2005, 289(5): G890-7. |
| 33 | Qin TT, Fang F, Song MT, et al. Umbelliferone reverses depression-like behavior in chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced rats by attenuating neuronal apoptosis via regulating ROCK/Akt pathway[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2017, 317: 147-56. |
| 34 | Sakon JJ, Suzuki WA. Neural evidence for recognition of naturalistic videos in monkey hippocampus[J]. Hippocampus, 2021, 31(8): 916-32. |
| 35 | Qiao CM, Zhou Y, Quan W, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation from aged mice render recipient mice resistant to MPTP-induced nigrostriatal degeneration via a neurogenesis-dependent but inflammation-independent manner[J]. Neurotherapeutics, 2023, 20(5): 1405-26. |
| 36 | Qiao CM, Huang WY, Zhou Y, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila is beneficial to a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease, via alleviated neuroinflammation and promoted neurogenesis, with involvement of SCFAs[J]. Brain Sci, 2024, 14(3): 238. |
| [1] | Pengwei HUANG, Jie CHEN, Jinhu ZOU, Xuefeng GAO, Hong CAO. Quercetin mitigates HIV-1 gp120-induced rat astrocyte neurotoxicity via promoting G3BP1 disassembly in stress granules [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 304-312. |
| [2] | Jiajin LIU, Changhong MIAO, Jiankang XU, Weijie YU, Jixin CHEN, Haozhi TANG, Aifeng LIU. Causal relationship between gut microbiota and pigmented villonodular synovitis: a Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1397-1406. |
| [3] | ZHU Jiwei, LU Manlu, JIAO Qianqian, SUN Yunliang, LIU Lu, DING Honghong, YU Yan, PAN Lei. Analysis of gut target microbiota and species difference in patients with obstructive sleep apnea based on 16S rRNA sequencing [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 146-155. |
| [4] | WANG Min, ZHANG Qian, XU Guiling, HUANG Shuyu, ZHAO Wenqu, LIANG Jianpeng, HUANG Junwen, CAI Shaoxi, ZHAO Haijin. Association between vitamin D level and blood eosinophil count in healthy population and patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(5): 727-732. |
| [5] | LIN Qiongxi, LUN Jingxian, ZHANG Jimin, HE Xiaolong, GONG Zelong, GAO Xuefeng, CAO Hong. Gut microbiome composition in pre-adolescent children with different meat consumption patterns [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(12): 1801-1808. |
| [6] | . SBi4211 alleviates gp120-induced central nervous system injury via inhibiting S100B/RAGE [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(12): 1693-1702. |
| [7] | . Establishment of a gp120 transgenic mouse model with α7 nAChR knockout [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(08): 1184-1191. |
| [8] | . Gut microbiota—an important contributor to liver diseases [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(04): 595-600. |
| [9] | . Establishment of a vimentin knockout and HIV-1 gp120 transgenic mouse model [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(04): 519-524. |
| [10] | . Gut microbiota in renal transplant recipients, patients with chronic kidney disease and healthy subjects [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2018, 38(12): 1401-. |
| [11] | . Effect of intermittent fasting on physiology and gut microbiota in presenium rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2017, 37(04): 423-. |
| [12] | . A machine learning model using gut microbiome data for predicting changes of trimethylamine-N-oxide in healthy volunteers after choline consumption [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2017, 37(03): 290-. |
| [13] | . Gut microbiota and osteoporosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2017, 37(02): 278-. |
| [14] | . Distribution characteristics of trimethylamine N-oxide and its association with gut microbiota [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2016, 36(04): 455-. |
| [15] | . Virtual screening of small molecular HIV-1 entry inhibitor NC-2 targeting gp120 and its action mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2013, 33(06): 826-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||