Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 453-460.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.02
Qi CHEN1,2( ), Tiantian XIA3,4(
), Tiantian XIA3,4( ), Yongqiang ZHOU4, Mingyang CHANG5, Nan HU2, Yanmei YANG2, Zhong LI2, Yue GAO4(
), Yongqiang ZHOU4, Mingyang CHANG5, Nan HU2, Yanmei YANG2, Zhong LI2, Yue GAO4( ), Bin GU2(
), Bin GU2( )
)
Received:2024-11-27
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
Yue GAO, Bin GU
E-mail:CC313nn@163.com;xiatianttx@163.com;gaoyue@ bmi.ac.cn;gubinmail301@163.com
Qi CHEN, Tiantian XIA, Yongqiang ZHOU, Mingyang CHANG, Nan HU, Yanmei YANG, Zhong LI, Yue GAO, Bin GU. Prevotella nigrescens exacerbates periodontal inflammation and impairs cognitive function in mice[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 453-460.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.02

Fig.2 HE staining of periodontal histological sections of the mice at 6 weeks after modeling (scale bar=200 μm for upper and lower panels; P: Periodontitis).
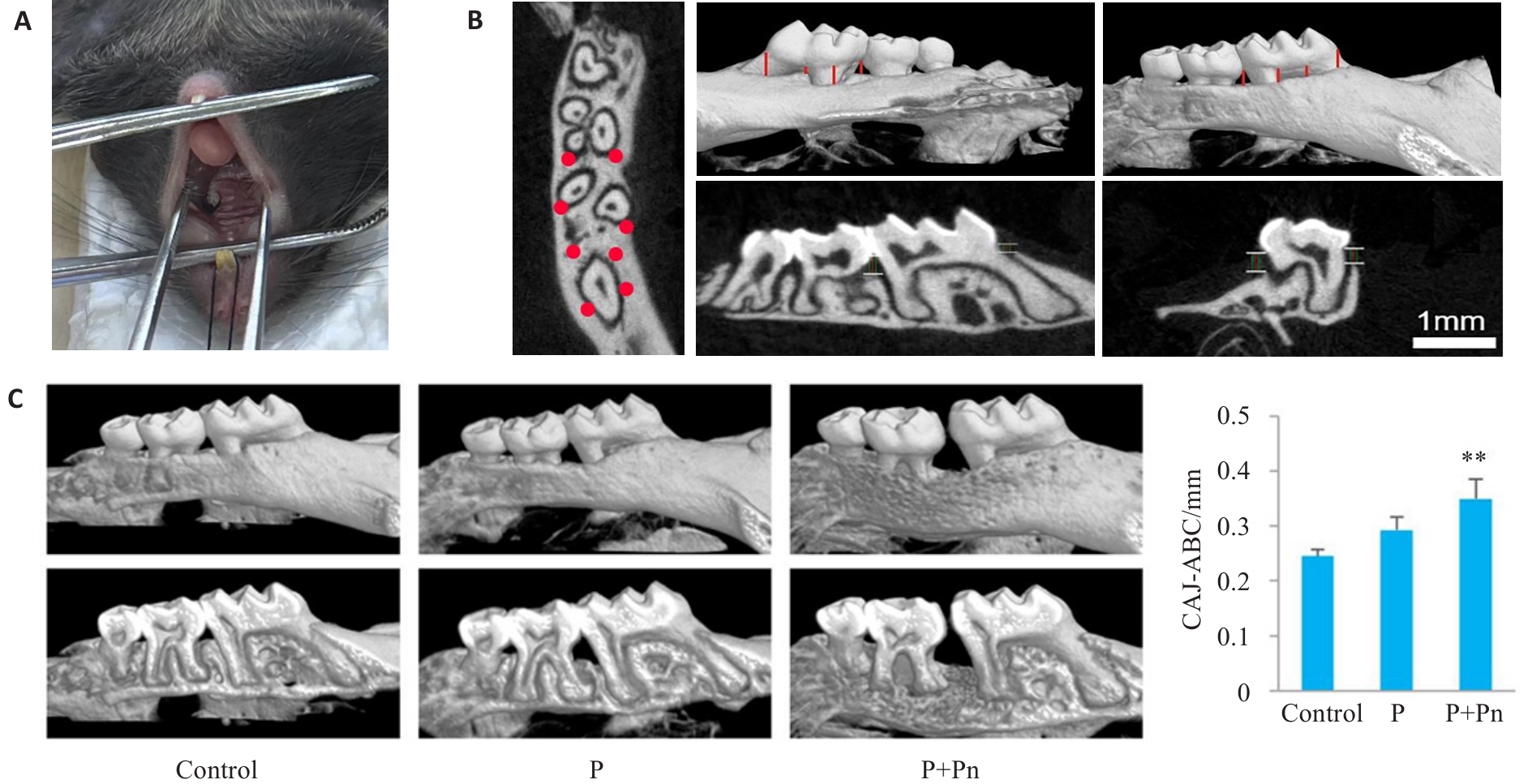
Fig.3 Establishment of a mouse periodontitis model and Micro-CT scan and 3D reconstruction analysis. A: Periodontitis in a mouse model. B: Micro-CT scan and 3D reconstruction for measurement of positional markings. C: Analysis of periodontal bone defects by Micro-CT and the distance from the enamel bone boundary to the top of the alveolar ridge (CAJ-ABC). **P<0.01 vs control group. P: Periodontitis.
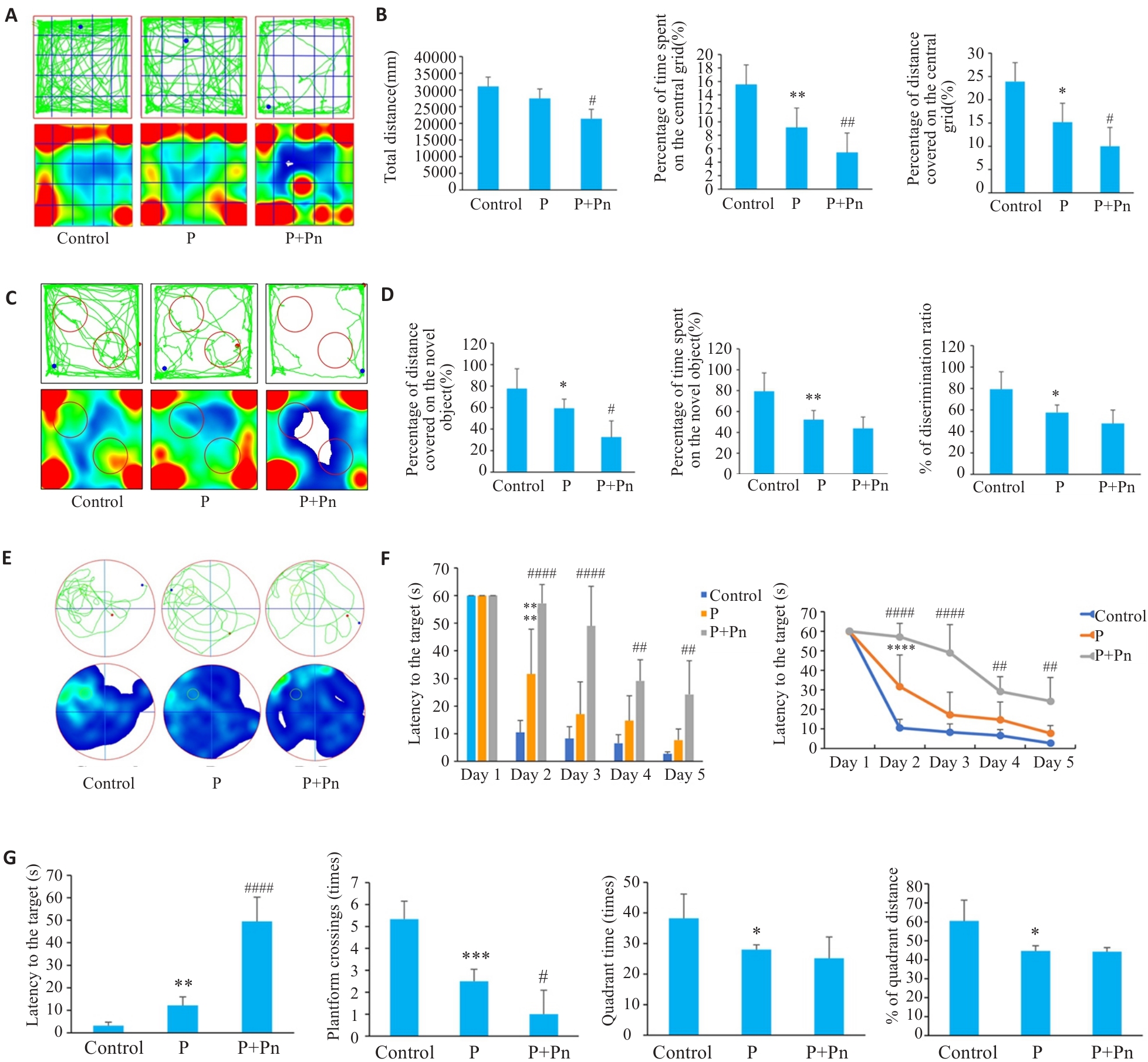
Fig.5 Learning and memory functions of mice with periodontitis modeled using the two methods. A: Open field test. B: representative tracking images of movement over 5 min, total distance covered, percent distance covered on the central grid, percent time spent on the central grid. C: New object recognition test (NORT). D: Percentage of distance covered around a new object, discrimination index (DI), percentage of times a new object was explored. E: Morris water maze test (MWM). F: Platform finding latency 5 days prior to training. G: Percentage of platform finding latency, number of platform traversals, time spent in target quadrant activity, and percentage of distance traveled in target quadrant activity. (*P<0.05,**P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ####P<0.0001 vs P group. P: Periodontitis group; P+Pn: Periodontitis + Pn bacteria group).

Fig.6 Histological observations for assessing morphological and functional changes of hippocampal neurons in the brain of the mouse models. A: HE staining of the hippocampal region of the mice in each group (scale bar=200 μm) and the normal neuron numbers in the CA3 region. B: Nissl staining of the hippocampal region of the mice in each group (scale bar=200 μm) and Nissl-positive neuron numbers in the CA3 region. *P<0.05 vs control group; #P<0.05 vs P group.
| 1 | 毛雨婷. 基于PI3K/Akt信号通路探讨加味当归芍药散对系统性红斑狼疮合并认知障碍小鼠的作用机制[D]. 福州: 福建中医药大学, 2023. |
| 2 | Ma WC, Wang C, Xiao JY. A testlet diagnostic classification model with attribute hierarchies[J]. Appl Psychol Meas, 2023, 47(3): 183-99. |
| 3 | Asher S, Stephen R, Mäntylä P, et al. Periodontal health, cognitive decline, and dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2022, 70(9): 2695-709. |
| 4 | Ganesh P, Karthikeyan R, Muthukumaraswamy A, et al. A potential role of periodontal inflammation in Alzheimer's disease: a review[J]. Oral Health Prev Dent, 2017, 15(1): 7-12. |
| 5 | Lu JY, Zhang S, Huang YZ, et al. Periodontitis-related salivary microbiota aggravates Alzheimer's disease via gut-brain axis crosstalk[J]. Gut Microbes, 2022, 14(1): 2126272. |
| 6 | Chen CK, Wu YT, Chang YC. Association between chronic periodontitis and the risk of Alzheimer's disease: a retrospective, population-based, matched-cohort study[J]. Alzheimers Res Ther, 2017, 9(1): 56. |
| 7 | Gil-Montoya JA, Sanchez-Lara I, Carnero-Pardo C, et al. Is periodontitis a risk factor for cognitive impairment and dementia? A case-control study[J]. J Periodontol, 2015, 86(2): 244-53. |
| 8 | Nascimento PC, Castro MML, Magno MB, et al. Association between periodontitis and cognitive impairment in adults: a systematic review[J]. Front Neurol, 2019, 10: 323. |
| 9 | Yakob M, Söder B, Meurman JH, et al. Prevotella nigrescens and Porphyromonas gingivalis are associated with signs of carotid atherosclerosis in subjects with and without periodontitis[J]. J Periodontal Res, 2011, 46(6): 749-55. |
| 10 | Sharma G, Garg N, Hasan S, et al. Fumarate and nitrite reduction by Prevotella nigrescens and Prevotella buccae isolated from Chronic Periodontitis patients[J]. Microb Pathog, 2023, 176: 106022. |
| 11 | Zhang YF, Zhen M, Zhan YL, et al. Population-genomic insights into variation in Prevotella intermedia and Prevotella nigrescens isolates and its association with periodontal disease[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2017, 7: 409. |
| 12 | Xie Y, Chen JZ, He JL, et al. Antimicrobial resistance and prevalence of resistance genes of obligate anaerobes isolated from periodontal abscesses[J]. J Periodontol, 2014, 85(2): 327-34. |
| 13 | Qudeimat MA, Alyahya A, Karched M, et al. Dental plaque microbiota profiles of children with caries-free and caries-active dentition[J]. J Dent, 2021, 104: 103539. |
| 14 | Beydoun MA, Beydoun HA, Hossain S, et al. Clinical and bacterial markers of periodontitis and their association with incident all-cause and Alzheimer's disease dementia in a large national survey[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2020, 75(1): 157-72. |
| 15 | Chi L, Cheng X, Lin LS, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced cognitive impairment is associated with gut dysbiosis, neuroinflammation, and glymphatic dysfunction[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2021, 11: 755925. |
| 16 | Dominy SS, Lynch C, Ermini F, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis in Alzheimer’s disease brains: evidence for disease causation and treatment with small-molecule inhibitors[J]. Sci Adv, 2019, 5(1): eaau3333. |
| 17 | Breivik T, Rook GA. Prevaccination with SRL172 (heat-killed Mycobacterium vaccae) inhibits experimental periodontal disease in Wistar rats[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2000, 120(3): 463-7. |
| 18 | Holzhausen M, Júnior CR, Júnior EM, et al. Effect of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition on the development of ligature-induced periodontitis in rats[J]. J Periodontol, 2002, 73(9): 1030-6. |
| 19 | Teixeira FB, Saito MT, Matheus FC, et al. Periodontitis and Alzheimer's disease: a possible comorbidity between oral chronic inflammatory condition and neuroinflammation[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2017, 9: 327. |
| 20 | George AK, Janam P. The short-term effects of non-surgical periodontal therapy on the circulating levels of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in patients with chronic periodontitis[J]. J Indian Soc Periodontol, 2013, 17(1): 36-41. |
| 21 | Olsen I, Singhrao SK. Can oral infection be a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease[J]? J Oral Microbiol, 2015, 7: 29143. |
| 22 | Hu Y, Zhang X, Zhang J, et al. Activated STAT3 signaling pathway by ligature-induced periodontitis could contribute to neuroinflam-mation and cognitive impairment in rats[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2021, 18(1): 80. |
| 23 | Lissner LJ, Wartchow KM, Toniazzo AP, et al. Object recognition and Morris water maze to detect cognitive impairment from mild hippocampal damage in rats: a reflection based on the literature and experience[J]. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 2021, 210: 173273. |
| 24 | Li YD, Briguglio JJ, Romani S, et al. Mechanisms of memory-supporting neuronal dynamics in hippocampal area CA3[J]. Cell, 2024, 187(24): 6804-19. e21. |
| 25 | Zhang J, Yu CB, Zhang X, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide induces cognitive dysfunction, mediated by neuronal inflammation via activation of the TLR4 signaling pathway in C57BL/6 mice[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2018, 15(1): 37. |
| 26 | Ma XY, Shin YJ, Yoo JW, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from Porphyromonas gingivalis induce trigeminal nerve-mediated cognitive impairment[J]. J Adv Res, 2023, 54: 293-303. |
| 27 | Goyal L, Gupta S, Perambudhuru Y. Association between periodontitis and cognitive impairment in adults[J]. Evid Based Dent, 2023, 24(3): 123-4. |
| 28 | Hajishengallis G, Chavakis T. Local and systemic mechanisms linking periodontal disease and inflammatory comorbidities[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2021, 21(7): 426-40. |
| 29 | Nazir MA. Prevalence of periodontal disease, its association with systemic diseases and prevention[J]. Int J Health Sci, 2017, 11(2): 72-80. |
| 30 | Koutsouras GW, Ramos RL, Martinez LR. Role of microglia in fungal infections of the central nervous system[J]. Virulence, 2017, 8(6): 705-18. |
| 31 | Sharma C, Woo H, Kim SR. Addressing blood-brain barrier impairment in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Biomedicines, 2022, 10(4): 742. |
| 32 | Coureuil M, Lécuyer H, Bourdoulous S, et al. A journey into the brain: insight into how bacterial pathogens cross blood-brain barriers[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2017, 15(3): 149-59. |
| 33 | Sheets SM, Potempa J, Travis J, et al. Gingipains from Porphyromonas gingivalis W83 induce cell adhesion molecule cleavage and apoptosis in endothelial cells[J]. Infect Immun, 2005, 73(3): 1543-52. |
| 34 | Talamo BR, Feng WH, Perez-Cruet M, et al. Pathologic changes in olfactory neurons in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 1991, 640: 1-7. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||