Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 141-149.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.15
Yunneng CUI1,2( ), Minqing FENG3,4,5, Liangfeng YAO2, Jiewen YAN2, Wenhan LI6, Yanping HUANG6(
), Minqing FENG3,4,5, Liangfeng YAO2, Jiewen YAN2, Wenhan LI6, Yanping HUANG6( )
)
Received:2025-06-20
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-16
Contact:
Yanping HUANG
E-mail:letitb@163.com;yale.huangyp@fosu.edu.cn
Yunneng CUI, Minqing FENG, Liangfeng YAO, Jiewen YAN, Wenhan LI, Yanping HUANG. Enhancement of radiomics-based machine learning models for predicting efficacy of high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of uterine fibroids using undersampling methods[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2026, 46(1): 141-149.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.15
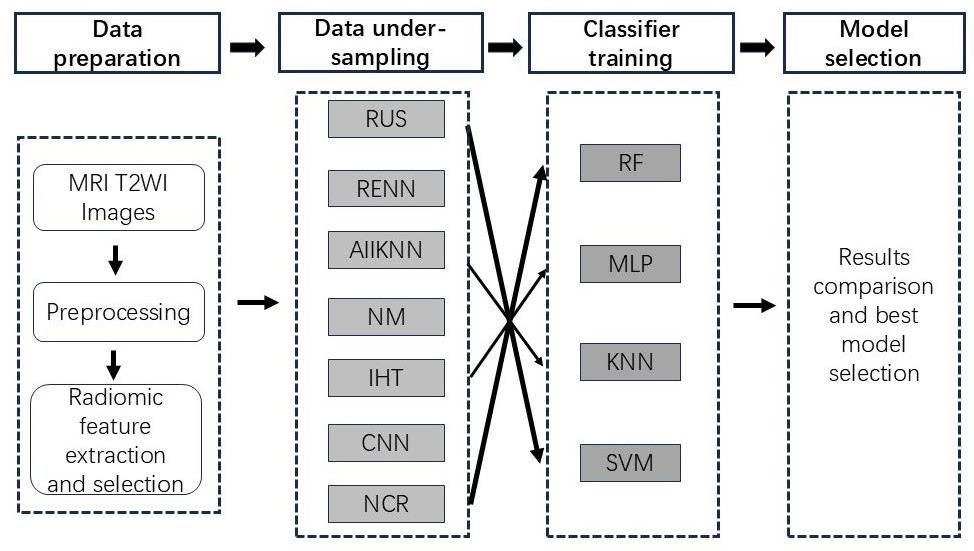
Fig.1 Diagram of the main data processing procedures in this study. Seven undersampling methods are used in combination with 4 types of classifiers to construct predictive models for HIFU treatment of uterine fibroids.
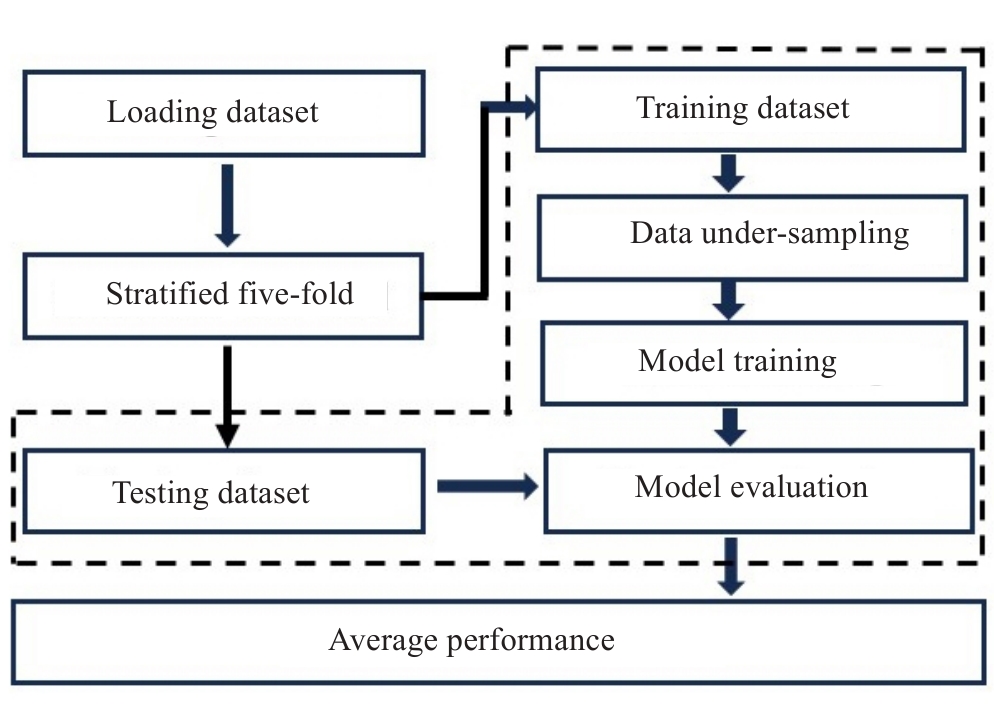
Fig.3 Flowchart of model establishment and evaluation in this study. The procedures boxed using dotted lines are repeated 5 times for the 5-fold cross-validation scheme.
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUS-KNN | 0.792(0.586-0.958) | 0.679 | 0.728 | 0.664 |
| RENN-KNN | 0.736(0.519-0.925) | 0.643 | 0.678 | 0.637 |
| AllKNN-KNN | 0.708(0.465-0.909) | 0.679 | 0.750 | 0.655 |
| NM-KNN | 0.769(0.558-0.939) | 0.679 | 0.782 | 0.646 |
| CNN-KNN | 0.822(0.635-0.964) | 0.714 | 0.675 | 0.733 |
| NCR-KNN | 0.734(0.507-0.927) | 0.664 | 0.618 | 0.684 |
| IHT-KNN | 0.710(0.479-0.909) | 0.664 | 0.728 | 0.646 |
| KNN-baseline | 0.784(0.571-0.955) | 0.750 | 0.143 | 0.962 |
Tab.1 Performances of different models associated with KNN learning
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUS-KNN | 0.792(0.586-0.958) | 0.679 | 0.728 | 0.664 |
| RENN-KNN | 0.736(0.519-0.925) | 0.643 | 0.678 | 0.637 |
| AllKNN-KNN | 0.708(0.465-0.909) | 0.679 | 0.750 | 0.655 |
| NM-KNN | 0.769(0.558-0.939) | 0.679 | 0.782 | 0.646 |
| CNN-KNN | 0.822(0.635-0.964) | 0.714 | 0.675 | 0.733 |
| NCR-KNN | 0.734(0.507-0.927) | 0.664 | 0.618 | 0.684 |
| IHT-KNN | 0.710(0.479-0.909) | 0.664 | 0.728 | 0.646 |
| KNN-baseline | 0.784(0.571-0.955) | 0.750 | 0.143 | 0.962 |
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUS-RF | 0.768(0.556-0.932) | 0.636 | 0.696 | 0.617 |
| RENN-RF | 0.722(0.504-0.907) | 0.543 | 0.793 | 0.465 |
| AllKNN-RF | 0.692(0.476-0.883) | 0.593 | 0.675 | 0.569 |
| NM-RF | 0.701(0.475-0.892) | 0.579 | 0.586 | 0.580 |
| CNN-RF | 0.772(0.566-0.942) | 0.700 | 0.725 | 0.694 |
| NCR-RF | 0.672(0.466-0.876) | 0.614 | 0.504 | 0.656 |
| IHT-RF | 0.656(0.430-0.854) | 0.550 | 0.750 | 0.482 |
| RF-baseline | 0.731(0.518-0.909) | 0.750 | 0.336 | 0.895 |
Tab.2 Performances of different models associated with RF learning
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUS-RF | 0.768(0.556-0.932) | 0.636 | 0.696 | 0.617 |
| RENN-RF | 0.722(0.504-0.907) | 0.543 | 0.793 | 0.465 |
| AllKNN-RF | 0.692(0.476-0.883) | 0.593 | 0.675 | 0.569 |
| NM-RF | 0.701(0.475-0.892) | 0.579 | 0.586 | 0.580 |
| CNN-RF | 0.772(0.566-0.942) | 0.700 | 0.725 | 0.694 |
| NCR-RF | 0.672(0.466-0.876) | 0.614 | 0.504 | 0.656 |
| IHT-RF | 0.656(0.430-0.854) | 0.550 | 0.750 | 0.482 |
| RF-baseline | 0.731(0.518-0.909) | 0.750 | 0.336 | 0.895 |
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUS-SVM | 0.791(0.595-0.955) | 0.728 | 0.807 | 0.702 |
| RENN-SVM | 0.702(0.363-0.828) | 0.593 | 0.843 | 0.513 |
| AllKNN-SVM | 0.708(0.490-0.895) | 0.629 | 0.778 | 0.579 |
| NM-SVM | 0.797(0.600-0.950) | 0.664 | 0.836 | 0.607 |
| CNN-SVM | 0.782(0.577-0.950) | 0.757 | 0.700 | 0.780 |
| NCR-SVM | 0.714(0.495-0.902) | 0.671 | 0.643 | 0.684 |
| IHT-SVM | 0.734(0.511-0.912) | 0.621 | 0.778 | 0.568 |
| SVM-baseline | 0.712(0.485-0.910) | 0.743 | 0 | 1 |
Tab.3 Performances of different models associated with SVM learning
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUS-SVM | 0.791(0.595-0.955) | 0.728 | 0.807 | 0.702 |
| RENN-SVM | 0.702(0.363-0.828) | 0.593 | 0.843 | 0.513 |
| AllKNN-SVM | 0.708(0.490-0.895) | 0.629 | 0.778 | 0.579 |
| NM-SVM | 0.797(0.600-0.950) | 0.664 | 0.836 | 0.607 |
| CNN-SVM | 0.782(0.577-0.950) | 0.757 | 0.700 | 0.780 |
| NCR-SVM | 0.714(0.495-0.902) | 0.671 | 0.643 | 0.684 |
| IHT-SVM | 0.734(0.511-0.912) | 0.621 | 0.778 | 0.568 |
| SVM-baseline | 0.712(0.485-0.910) | 0.743 | 0 | 1 |
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUS-MLP | 0.791(0.593-0.949) | 0.657 | 0.721 | 0.634 |
| RENN-MLP | 0.723(0.504-0.910) | 0.607 | 0.818 | 0.541 |
| AllKNN-MLP | 0.729(0.520-0.911) | 0.664 | 0.807 | 0.616 |
| NM-MLP | 0.822(0.632-0.960) | 0.729 | 0.786 | 0.713 |
| CNN-MLP | 0.782(0.570-0.954) | 0.679 | 0.728 | 0.666 |
| NCR-MLP | 0.730(0.499-0.913) | 0.693 | 0.614 | 0.722 |
| IHT-MLP | 0.736(0.530-0.909) | 0.629 | 0.811 | 0.568 |
| MLP-baseline | 0.710(0.467-0.911) | 0.736 | 0.414 | 0.847 |
Tab.4 Performances of different models associated with MLP learning
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUS-MLP | 0.791(0.593-0.949) | 0.657 | 0.721 | 0.634 |
| RENN-MLP | 0.723(0.504-0.910) | 0.607 | 0.818 | 0.541 |
| AllKNN-MLP | 0.729(0.520-0.911) | 0.664 | 0.807 | 0.616 |
| NM-MLP | 0.822(0.632-0.960) | 0.729 | 0.786 | 0.713 |
| CNN-MLP | 0.782(0.570-0.954) | 0.679 | 0.728 | 0.666 |
| NCR-MLP | 0.730(0.499-0.913) | 0.693 | 0.614 | 0.722 |
| IHT-MLP | 0.736(0.530-0.909) | 0.629 | 0.811 | 0.568 |
| MLP-baseline | 0.710(0.467-0.911) | 0.736 | 0.414 | 0.847 |
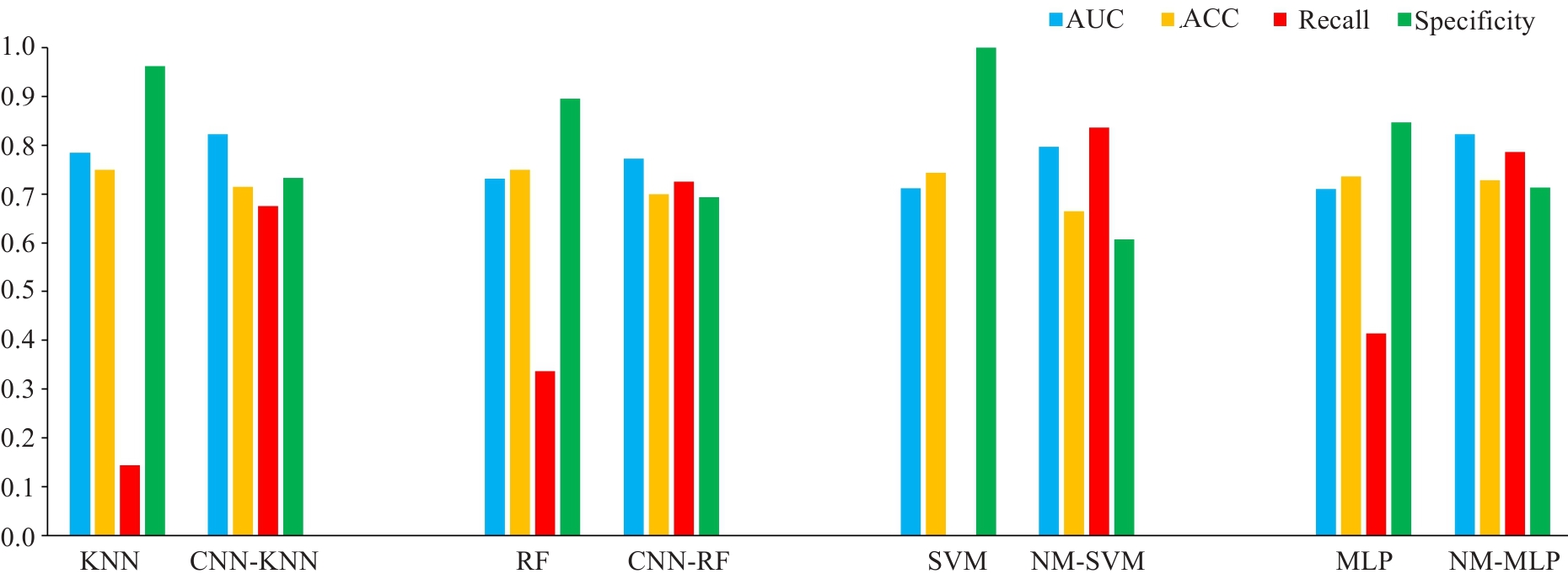
Fig.5 Comparison of prediction performances (AUC, accuracy, recall and specificity) among KNN, RF, SVM and MLP models without and with under-sampling. ACC: Accuracy.
| [1] | Giuliani E, As-Sanie S, Marsh EE. Epidemiology and management of uterine fibroids[J]. Int J Gynaecol Obstet, 2020, 149(1): 3-9. doi:10.1002/ijgo.13102 |
| [2] | Management of symptomatic uterine leiomyomas: ACOG practice bulletin, number 228[J]. Obstet Gynecol, 2021, 137(6): e100-15. doi:10.1097/aog.0000000000004401 |
| [3] | Grube M, Neis F, Brucker SY, et al. Uterine fibroids - current trends and strategies[J]. Surg Technol Int, 2019, 34: 257-63. |
| [4] | Haviv E, Schwarzman P, Bernstein EH, et al. Subsequent pregnancy outcomes after abdominal vs. laparoscopic myomectomy[J]. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med, 2022, 35(25): 8219-25. doi:10.1080/14767058.2021.1967315 |
| [5] | Hajian-Tilaki K. Sample size estimation in diagnostic test studies of biomedical informatics[J]. J Biomed Inform, 2014, 48: 193-204. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2014.02.013 |
| [6] | Liu L, Wang T, Lei B. Ultrasound-guided microwave ablation in the management of symptomatic uterine myomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Minim Invasive Gynecol, 2021, 28(12): 1982-92. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2021.06.020 |
| [7] | Jenne JW, Preusser T, Günther M. High-intensity focused ultrasound: principles, therapy guidance, simulations and applications[J]. Z Für Med Phys, 2012, 22(4): 311-22. doi:10.1016/j.zemedi.2012.07.001 |
| [8] | Machtinger R, Inbar Y, Cohen-Eylon S, et al. MR-guided focus ultrasound (MRgFUS) for symptomatic uterine fibroids: predictors of treatment success[J]. Hum Reprod, 2012, 27(12): 3425-31. doi:10.1093/humrep/des333 |
| [9] | Mindjuk I, Trumm CG, Herzog P, et al. MRI predictors of clinical success in MR-guided focused ultrasound (MRgFUS) treatments of uterine fibroids: results from a single centre[J]. Eur Radiol, 2015, 25(5): 1317-28. doi:10.1007/s00330-014-3538-6 |
| [10] | Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, et al. Radiomics: Extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2012, 48(4): 441-6. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2011.11.036 |
| [11] | Avanzo M, Wei L, Stancanello J, et al. Machine and deep learning methods for radiomics[J]. Med Phys, 2020, 47(5): e185-202. doi:10.1002/mp.13678 |
| [12] | Yip SS, Aerts HJ. Applications and limitations of radiomics[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2016, 61(13): R150-66. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/61/13/r150 |
| [13] | Hocquelet A, Denis de Senneville B, Frulio N, et al. Magnetic resonance texture parameters are associated with ablation efficiency in MR-guided high-intensity focussed ultrasound treatment of uterine fibroids[J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2017, 33(2): 142-9. doi:10.1080/02656736.2016.1241432 |
| [14] | Li ZC, Zhang J, Song Y, et al. Utilization of radiomics to predict long-term outcome of magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound ablation therapy in adenomyosis[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(1): 392-402. doi:10.1007/s00330-020-07076-1 |
| [15] | Zheng Y, Chen L, Liu M, et al. Prediction of clinical outcome for high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of uterine leiomyomas using multiparametric MRI radiomics-based machine leaning model[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 618604. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.618604 |
| [16] | Li DC, Liu CW, Hu SC. A learning method for the class imbalance problem with medical data sets[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2010, 40(5): 509-18. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2010.03.005 |
| [17] | Galar M, Fernandez A, Barrenechea E, et al. A review on ensembles for the class imbalance problem: bagging-, boosting-, and hybrid-based approaches[J]. IEEE Trans Syst, Man, Cybern C, 42(4): 463-84. doi:10.1109/tsmcc.2011.2161285 |
| [18] | Funaki K, Fukunishi H, Funaki T, et al. Magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound surgery for uterine fibroids: relationship between the therapeutic effects and signal intensity of preexisting T2-weighted magnetic resonance images[J]. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2007, 196(2): 184.e1-6. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2006.08.030 |
| [19] | Kim YS, Lim HK, Park MJ, et al. Screening magnetic resonance imaging-based prediction model for assessing immediate therapeutic response to magnetic resonance imaging-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of uterine fibroids[J]. Invest Radiol, 2016, 51(1): 15-24. doi:10.1097/rli.0000000000000199 |
| [20] | Jiang Y, Qin S, Wang Y, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI for predicting the efficacy of high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation for uterine fibroids[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1178649. doi:10.3389/fonc.2023.1178649 |
| [21] | Carré A, Klausner G, Edjlali M, et al. Standardization of brain MR images across machines and protocols: bridging the gap for MRI-based radiomics[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 12340. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-69298-z |
| [22] | Nyul LG, Udupa JK, Zhang X. New variants of a method of MRI scale standardization[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 19(2): 143-50. doi:10.1109/42.836373 |
| [23] | Zwanenburg A, Vallières M, Abdalah MA, et al. The image biomarker standardization initiative: standardized quantitative radiomics for high-throughput image-based phenotyping[J]. Radiology, 2020, 295(2): 328-38. doi:10.1148/radiol.2020191145 |
| [24] | Kira K, Rendell LA. A practical approach to feature selection[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Machine Learning(ML 1992), Aberdeen, Scotland, UK, July 1-3, 1992.[S.l.]: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc, 1992: 249-26. doi:10.1016/b978-1-55860-247-2.50037-1 |
| [25] | Prusa J, Khoshgoftaar TM, Dittman DJ, et al. Using random undersampling to alleviate class imbalance on tweet sentiment data[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Information Reuse and Integration. August 13-15, 2015. San Francisco, CA, USA. IEEE, 2015: 197-202. doi:10.1109/iri.2015.39 |
| [26] | Tomek I. An experiment with the edited nearest-neighbor rule[J]. IEEE Trans Syst, Man, Cybern, SMC-6(6): 448-52. doi:10.1109/tsmc.1976.4309523 |
| [27] | Wilson DL. Asymptotic properties of nearest neighbor rules using edited data[J]. IEEE Trans Syst, Man, Cybern, SMC-2(3): 408-21. doi:10.1109/tsmc.1972.4309137 |
| [28] | Zhang JP, Mani I: kNN approach to unbalanced data distributions: A case study involving information extraction. In: Proceeding of International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2003), Workshop on Learning from Imbalanced Data Sets: 2003; Washington D.C.: ICML; 2003: 1-7. |
| [29] | Hart P. The condensed nearest neighbor rule (Corresp.)[J]. IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 14(3): 515-6. doi:10.1109/tit.1968.1054155 |
| [30] | Laurikkala J. Improving identification of difficult small classes by balancing class distribution[M]//Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2001: 63-6. doi:10.1007/3-540-48229-6_9 |
| [31] | Smith MR, Martinez T, Giraud-Carrier C. An instance level analysis of data complexity[J]. Mach Learn, 2014, 95(2): 225-56. doi:10.1007/s10994-013-5422-z |
| [32] | Tomaszewski MR, Gillies RJ. The biological meaning of radiomic features[J]. Radiology, 2021, 298(3): 505-16. doi:10.1148/radiol.2021202553 |
| [33] | Zhao WP, Chen JY, Chen WZ. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI serves as a predictor of HIFU treatment outcome for uterine fibroids with hyperintensity in T2-weighted images[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2016, 11(1): 328-34. doi:10.3892/etm.2015.2879 |
| [34] | Fribbens C, O'Leary B, Kilburn L, et al. Plasma ESR1 mutations and the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive advanced breast cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2016, 34(25): 2961-8. doi:10.1200/jco.2016.67.3061 |
| [35] | Rogers W, Thulasi Seetha S, Refaee TAG, et al. Radiomics: from qualitative to quantitative imaging[J]. Br J Radiol, 2020, 93(1108): 20190948. doi:10.1259/bjr.20190948 |
| [36] | Zheng Y, Chen L, Liu M, et al. Nonenhanced MRI-based radiomics model for preoperative prediction of nonperfused volume ratio for high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of uterine leiomyomas[J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2021, 38(1): 1349-58. doi:10.1080/02656736.2021.1972170 |
| [37] | Walsh R, Tardy M. A comparison of techniques for class imbalance in deep learning classification of breast cancer[J]. Diagnostics: Basel, 2022, 13(1): 67. doi:10.3390/diagnostics13010067 |
| [38] | Guo HX, Li YJ, Shang J, et al. Learning from class-imbalanced data: review of methods and applications[J]. Expert Syst Appl, 2017, 73: 220-39. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2016.12.035 |
| [39] | Kraiem MS, Sánchez-Hernández F, Moreno-García MN. Selecting the suitable resampling strategy for imbalanced data classification regarding dataset properties. an approach based on association models[J]. Appl Sci, 2021, 11(18): 8546. doi:10.3390/app11188546 |
| [40] | Li M, Wu Z, Wang W, et al. Protein-protein interaction sites prediction based on an under-sampling strategy and random forest algorithm[J]. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform, 2022, 19(6): 3646-54. doi:10.1109/tcbb.2021.3123269 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||