Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 514-521.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.09
Lin SHEN1( ), Cuihao SONG1(
), Cuihao SONG1( ), Congmin WANG2, Xi GAO3, Junhong AN4, Chengxin LI1(
), Congmin WANG2, Xi GAO3, Junhong AN4, Chengxin LI1( ), Bin LIANG5(
), Bin LIANG5( ), Xia LI6(
), Xia LI6( )
)
Received:2024-12-16
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
Chengxin LI, Bin LIANG, Xia LI
E-mail:linlinshen1995@126.com;18110026396@163.com;chengxinderm@163.com;echo_lb666@163.com;1648248514@qq.com
Supported by:Lin SHEN, Cuihao SONG, Congmin WANG, Xi GAO, Junhong AN, Chengxin LI, Bin LIANG, Xia LI. Risk factors for malnutrition in ulcerative colitis complicated with pyoderma gangrenosum and construction of a lasso regression-based prediction model[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 514-521.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.09
| Project | Unhealthy group (n=185) | Good group (n=92) | t/x2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 5.988 | 0.014 | ||
| Male | 109 (58.92) | 68 (73.91) | ||
| Female | 76 (41.08) | 24 (26.09) | ||
| Age (year) | 59.63±14.62 | 52.82±13.94 | 3.165 | 0.002 |
| Education level | 6.243 | 0.044 | ||
| Elementary school or below | 99 (53.51) | 37 (40.22) | ||
| High school | 58 (31.35) | 31 (33.70) | ||
| University | 28 (15.14) | 24 (26.01) | ||
| Marital status in the past year | 6.104 | 0.047 | ||
| Unmarried | 16 (8.65) | 3 (3.26) | ||
| Divorced/widowed | 34 (18.38) | 10 (10.87) | ||
| In marriage | 135 (72.97) | 79 (85.87) | ||
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 21.80±3.47 | 24.52±2.95 | -10.416 | <0.001 |
| Residential area in the past year | 11.457 | 0.003 | ||
| Rural area | 92 (49.73) | 33 (35.87) | ||
| Town | 37 (20.00) | 12 (13.04) | ||
| Urban area | 56 (30.27) | 47 (51.09) | ||
| Residential partner in the past year | 7.497 | 0.024 | ||
| Live alone | 41 (22.16) | 9 (9.78) | ||
| Friends/relatives | 10 (5.41) | 3 (3.26) | ||
| Spouse/children | 134 (72.43) | 80 (86.96) | ||
| Economic pressure in the past year | 25.668 | <0.001 | ||
| No | 30 (16.22) | 39 (42.39) | ||
| General | 67 (36.22) | 31 (33.70) | ||
| Larger | 88 (47.56) | 22 (23.91) |
Tab.1 Comparison of general demographic data between the two groups [Mean±SD, n(%)]
| Project | Unhealthy group (n=185) | Good group (n=92) | t/x2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 5.988 | 0.014 | ||
| Male | 109 (58.92) | 68 (73.91) | ||
| Female | 76 (41.08) | 24 (26.09) | ||
| Age (year) | 59.63±14.62 | 52.82±13.94 | 3.165 | 0.002 |
| Education level | 6.243 | 0.044 | ||
| Elementary school or below | 99 (53.51) | 37 (40.22) | ||
| High school | 58 (31.35) | 31 (33.70) | ||
| University | 28 (15.14) | 24 (26.01) | ||
| Marital status in the past year | 6.104 | 0.047 | ||
| Unmarried | 16 (8.65) | 3 (3.26) | ||
| Divorced/widowed | 34 (18.38) | 10 (10.87) | ||
| In marriage | 135 (72.97) | 79 (85.87) | ||
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 21.80±3.47 | 24.52±2.95 | -10.416 | <0.001 |
| Residential area in the past year | 11.457 | 0.003 | ||
| Rural area | 92 (49.73) | 33 (35.87) | ||
| Town | 37 (20.00) | 12 (13.04) | ||
| Urban area | 56 (30.27) | 47 (51.09) | ||
| Residential partner in the past year | 7.497 | 0.024 | ||
| Live alone | 41 (22.16) | 9 (9.78) | ||
| Friends/relatives | 10 (5.41) | 3 (3.26) | ||
| Spouse/children | 134 (72.43) | 80 (86.96) | ||
| Economic pressure in the past year | 25.668 | <0.001 | ||
| No | 30 (16.22) | 39 (42.39) | ||
| General | 67 (36.22) | 31 (33.70) | ||
| Larger | 88 (47.56) | 22 (23.91) |
| Project | unhealthy group (n=185) | Good group (n=92) | t/x2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise frequency in past year | 3.714 | 0.156 | ||
| Less | 43 (23.24) | 16 (17.39) | ||
| General | 81 (43.78) | 35 (38.04) | ||
| Often | 61 (32.98) | 41 (44.57) | ||
| Types of food in past year | 26.339 | <0.001 | ||
| Less | 85 (45.95) | 27 (29.35) | ||
| General | 66 (35.68) | 21 (22.83) | ||
| Often | 34 (18.37) | 44 (47.82) | ||
| Dietary preference in past year | 7.407 | 0.025 | ||
| Less | 48 (25.95) | 11 (11.96) | ||
| General | 62 (33.51) | 34 (36.96) | ||
| Often | 75 (40.54) | 47 (51.08) | ||
| Smoking in past year | 0.827 | 0.661 | ||
| Less | 109 (58.92) | 58 (63.04) | ||
| General | 42 (22.70) | 21 (22.83) | ||
| Often | 34 (18.38) | 13 (14.13) | ||
| Drinking in the past year | 9.568 | 0.008 | ||
| Less | 95 (51.35) | 62 (67.39) | ||
| General | 48 (25.95) | 22 (23.91) | ||
| Often | 42 (22.70) | 8 (8.70) |
Tab.2 Comparison of living and eating habits of the patients between the two groups [n(%)]
| Project | unhealthy group (n=185) | Good group (n=92) | t/x2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise frequency in past year | 3.714 | 0.156 | ||
| Less | 43 (23.24) | 16 (17.39) | ||
| General | 81 (43.78) | 35 (38.04) | ||
| Often | 61 (32.98) | 41 (44.57) | ||
| Types of food in past year | 26.339 | <0.001 | ||
| Less | 85 (45.95) | 27 (29.35) | ||
| General | 66 (35.68) | 21 (22.83) | ||
| Often | 34 (18.37) | 44 (47.82) | ||
| Dietary preference in past year | 7.407 | 0.025 | ||
| Less | 48 (25.95) | 11 (11.96) | ||
| General | 62 (33.51) | 34 (36.96) | ||
| Often | 75 (40.54) | 47 (51.08) | ||
| Smoking in past year | 0.827 | 0.661 | ||
| Less | 109 (58.92) | 58 (63.04) | ||
| General | 42 (22.70) | 21 (22.83) | ||
| Often | 34 (18.38) | 13 (14.13) | ||
| Drinking in the past year | 9.568 | 0.008 | ||
| Less | 95 (51.35) | 62 (67.39) | ||
| General | 48 (25.95) | 22 (23.91) | ||
| Often | 42 (22.70) | 8 (8.70) |
| Project | Unhealthy group (n=185) | Good group (n=92) | t/x2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of ulcerative colitis (months) | 93.19±48.83 | 49.01±31.29 | 12.18 | 0.000 |
| Lesion site of colitis | 15.374 | 0.000 | ||
| Rectum | 34 (18.38) | 37 (40.22) | ||
| Colon | 151 (81.62) | 55 (59.78) | ||
| Colitis activity | 48.751 | 0.000 | ||
| Mild | 41 (22.16) | 55 (59.78) | ||
| Moderate | 85 (45.95) | 34 (36.96) | ||
| Severe | 59 (31.89) | 3 (3.26) | ||
| Course of pyoderma gangrenosum (months) | 10.99±4.94 | 6.11±3.26 | 8.591 | 0.000 |
| Classification of pyoderma | 5.704 | 0.058 | ||
| Kuitang type | 78 (42.16) | 29 (31.52) | ||
| Pustular type | 42 (22.70) | 17 (18.48) | ||
| Proliferative type | 65 (35.14) | 46 (50.00) | ||
| Number of chronic diseases (types) | 4.18±2.85 | 2.89±2.02 | 6.814 | 0.000 |
| Self care ability | 14.304 | 0.001 | ||
| Unable to care on self | 11 (5.95) | 1 (1.09) | ||
| Partially self-care | 62 (33.51) | 15 (16.30) | ||
| Completely self-care | 112 (60.5) | 76 (82.61) | ||
| Sds score | 59.78±13.81 | 50.85±12.68 | 5.206 | 0.000 |
| Sas score | 62.98±12.26 | 51.83±11.33 | 6.004 | 0.000 |
| Denture or dental problems | 34 (18.38) | 5 (5.43) | 8.510 | 0.004 |
| Sleep quality in recent half a year | 47.101 | 0.000 | ||
| Poor | 85 (45.95) | 22 (23.91) | ||
| General | 94 (50.81) | 41 (44.57) | ||
| Better | 6 (3.24) | 29 (31.52) |
Tab.3 Comparison of disease-related data between the two groups [Mean±SD, n(%)]
| Project | Unhealthy group (n=185) | Good group (n=92) | t/x2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of ulcerative colitis (months) | 93.19±48.83 | 49.01±31.29 | 12.18 | 0.000 |
| Lesion site of colitis | 15.374 | 0.000 | ||
| Rectum | 34 (18.38) | 37 (40.22) | ||
| Colon | 151 (81.62) | 55 (59.78) | ||
| Colitis activity | 48.751 | 0.000 | ||
| Mild | 41 (22.16) | 55 (59.78) | ||
| Moderate | 85 (45.95) | 34 (36.96) | ||
| Severe | 59 (31.89) | 3 (3.26) | ||
| Course of pyoderma gangrenosum (months) | 10.99±4.94 | 6.11±3.26 | 8.591 | 0.000 |
| Classification of pyoderma | 5.704 | 0.058 | ||
| Kuitang type | 78 (42.16) | 29 (31.52) | ||
| Pustular type | 42 (22.70) | 17 (18.48) | ||
| Proliferative type | 65 (35.14) | 46 (50.00) | ||
| Number of chronic diseases (types) | 4.18±2.85 | 2.89±2.02 | 6.814 | 0.000 |
| Self care ability | 14.304 | 0.001 | ||
| Unable to care on self | 11 (5.95) | 1 (1.09) | ||
| Partially self-care | 62 (33.51) | 15 (16.30) | ||
| Completely self-care | 112 (60.5) | 76 (82.61) | ||
| Sds score | 59.78±13.81 | 50.85±12.68 | 5.206 | 0.000 |
| Sas score | 62.98±12.26 | 51.83±11.33 | 6.004 | 0.000 |
| Denture or dental problems | 34 (18.38) | 5 (5.43) | 8.510 | 0.004 |
| Sleep quality in recent half a year | 47.101 | 0.000 | ||
| Poor | 85 (45.95) | 22 (23.91) | ||
| General | 94 (50.81) | 41 (44.57) | ||
| Better | 6 (3.24) | 29 (31.52) |
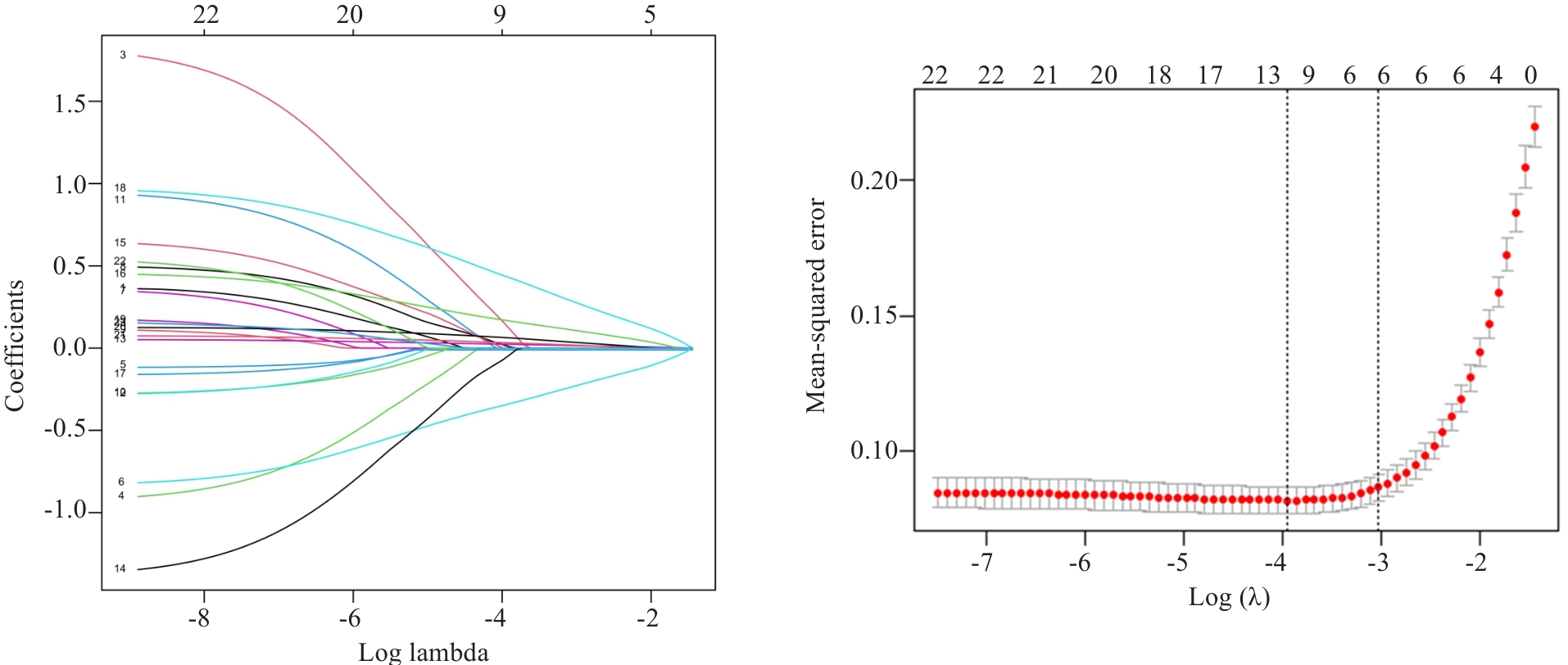
Fig.1 Lasso regression coefficient diagram and cross validation diagram. Lasso regression was used to analyze the association between each index and nutritional risk of the patients.
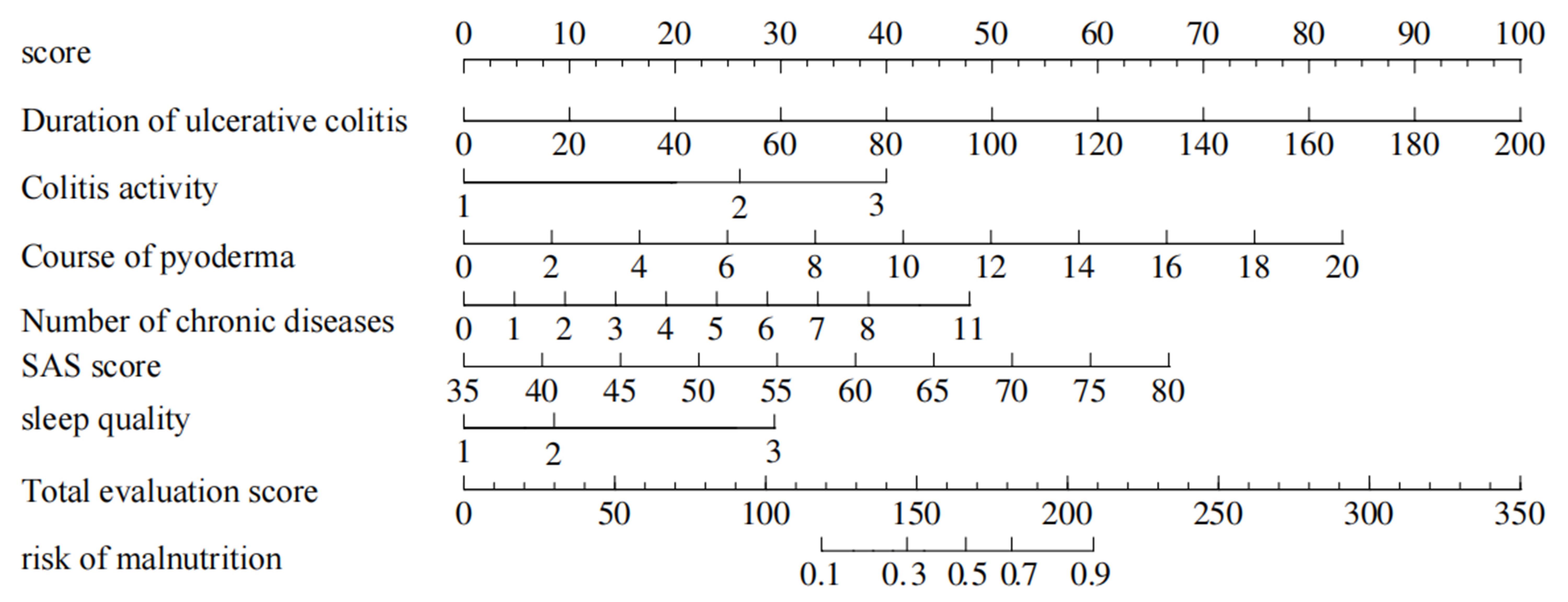
Fig.2 Nomogram prediction model of nutritional risk in patients with ulcerative colitis complicated with pyoderma gangrenosum based on the duration of ulcerative colitis, colitis activity, duration of pyoderma, number of chronic diseases, SAS score and sleep quality, showing the weighted scores of the 6 risk factors and the risk levels of the total score.
| Factors | β | S.E | Z | P | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of ulcerative colitis | 0.065 | 0.017 | 3.922 | 0.000 | 1.067 (1.033-1.102) |
| Colitis activity | |||||
| Mild | 1.000 | ||||
| Moderate | 2.541 | 1.116 | 2.277 | 0.023 | 2.694 (1.425-3.071) |
| Severe | 2.600 | 1.046 | 2.484 | 0.013 | 3.460 (1.731-4.645) |
| Course of pyoderma gangrenosum | 0.539 | 0.164 | 3.280 | 0.001 | 1.715 (1.242-2.367) |
| Number of chronic diseases | 0.621 | 0.188 | 3.302 | 0.000 | 1.861 (1.287-2.690) |
| Sleep quality | |||||
| Better | 1.000 | ||||
| General | 0.742 | 0.950 | 0.781 | 0.435 | 1.101 (0.326-3.529) |
| Poor | 3.814 | 1.187 | 3.214 | 0.001 | 3.336 (1.429-6.088) |
| Sas score | 0.192 | 0.052 | 3.727 | 0.000 | 1.112 (1.025-1.341) |
Tab.4 Results of multivariate logistic regression analysis
| Factors | β | S.E | Z | P | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of ulcerative colitis | 0.065 | 0.017 | 3.922 | 0.000 | 1.067 (1.033-1.102) |
| Colitis activity | |||||
| Mild | 1.000 | ||||
| Moderate | 2.541 | 1.116 | 2.277 | 0.023 | 2.694 (1.425-3.071) |
| Severe | 2.600 | 1.046 | 2.484 | 0.013 | 3.460 (1.731-4.645) |
| Course of pyoderma gangrenosum | 0.539 | 0.164 | 3.280 | 0.001 | 1.715 (1.242-2.367) |
| Number of chronic diseases | 0.621 | 0.188 | 3.302 | 0.000 | 1.861 (1.287-2.690) |
| Sleep quality | |||||
| Better | 1.000 | ||||
| General | 0.742 | 0.950 | 0.781 | 0.435 | 1.101 (0.326-3.529) |
| Poor | 3.814 | 1.187 | 3.214 | 0.001 | 3.336 (1.429-6.088) |
| Sas score | 0.192 | 0.052 | 3.727 | 0.000 | 1.112 (1.025-1.341) |
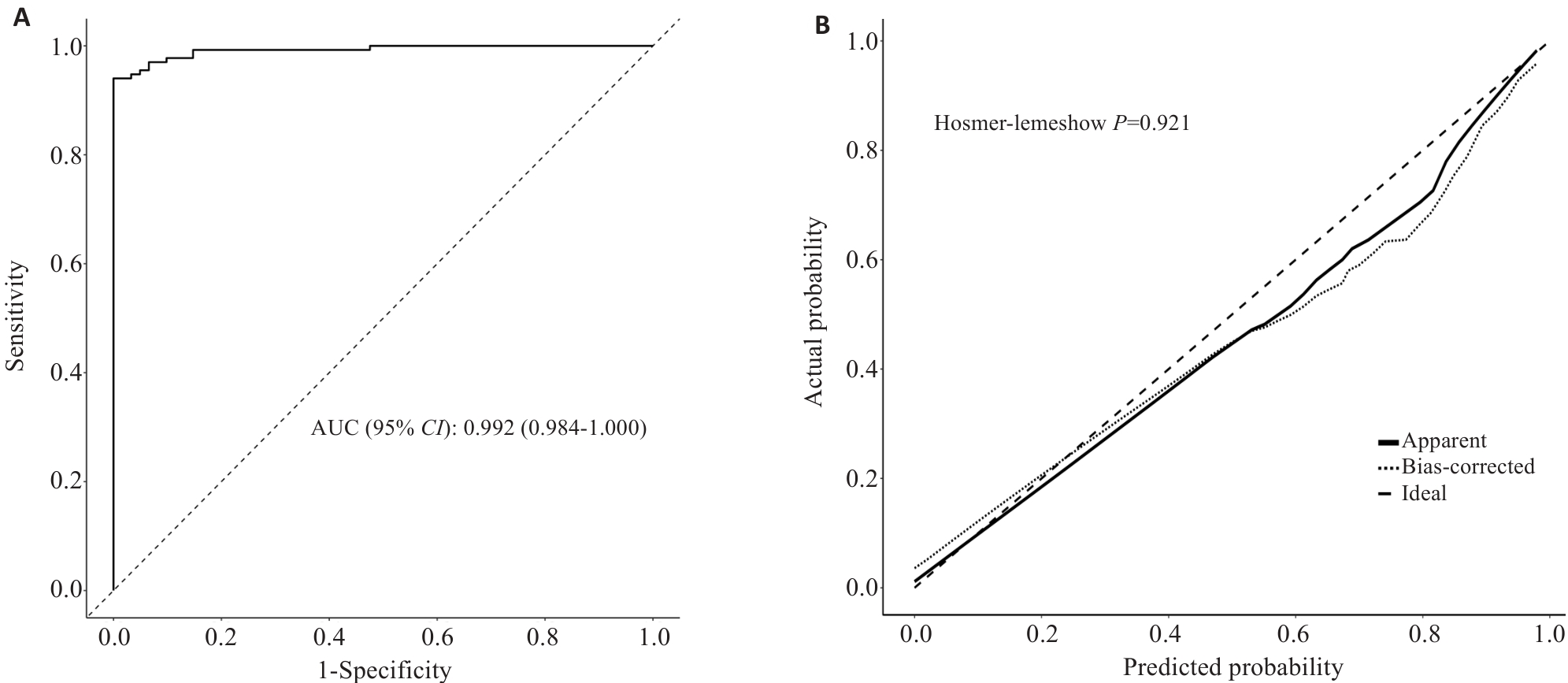
Fig.3 Nomogram model ROC curve and the calibration curve. A: ROC curve analysis of the column chart prediction model for predicting the risk of malnutrition in patients. B: Calibration curve analysis of 1000 repeated sampling validations on the model.
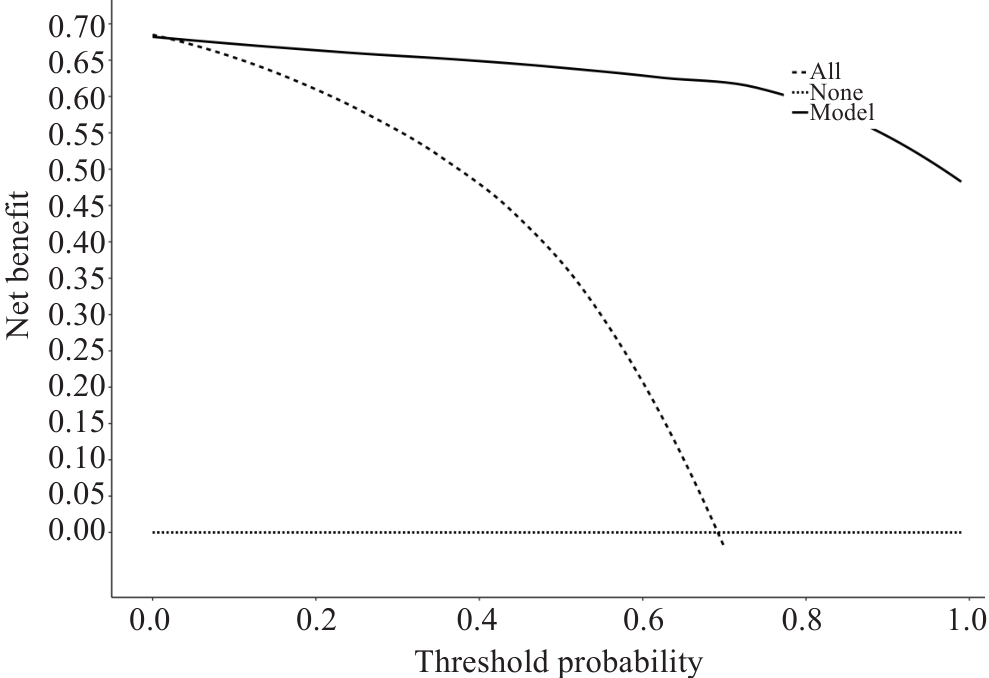
Fig.4 Decision curve analysis of the nomogram model for predicting nutritional risk in the patients. The horizontal dashed line (none line) is the extreme case of all negatives, the oblique dashed line (all line) indicates the extreme case of all positives, the uppermost solid line curve (model line) indicates how the established prediction model makes decisions, and when the model line is higher than the all line, it indicates that the model prediction can be clinically beneficial.
| 1 | 中国中西医结合学会. 溃疡性结肠炎中西医结合诊疗专家共识[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2023, 43(1): 5-11. |
| 2 | 宋泽军, 张明君, 任渝棠, 等. 改良Mayo内镜评分对溃疡性结肠炎有较高的评估价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(7): 997-1005. |
| 3 | 焦雨竹, 杨 青. 坏疽性脓皮病治疗进展[J]. 中国麻风皮肤病杂志, 2024, 40(3): 216-20. |
| 4 | 单 玮, 雷春明, 肖 文, 等. 阙华发辨治溃疡性结肠炎并发坏疽性脓皮病经验[J]. 辽宁中医杂志, 2022, 49(3): 30-2. |
| 5 | Xu HM, Huang HL, Xu J, et al. Cross-talk between butyric acid and gut microbiota in ulcerative colitis following fecal microbiota transplantation[J]. Front Microbiol, 2021, 12: 658292. |
| 6 | Chen QY, Fan YY, Zhang BZ, et al. Capsulized fecal microbiota transplantation induces remission in patients with ulcerative colitis by gut microbial colonization and metabolite regulation[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2023, 11(3): e0415222. |
| 7 | 袁 伟, 李 娟, 杨小娟, 等. 肠内营养对活动期溃疡性结肠炎伴营养不良患者营养状况、肠黏膜屏障功能和肠道菌群的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2022, 22(14): 2658-62. |
| 8 | 刘仁娟, 田字彬, 王丹丹, 等. 溃疡性结肠炎病人生物电阻抗相位角与营养状况的关系研究[J]. 肠外与肠内营养, 2023, 30(6): 328-33. |
| 9 | 张文玉, 马贤纵, 谢 惠, 等. 炎症性肠病患者营养障碍的研究[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2024, 33(6): 641-5. |
| 10 | 楚俊红, 王丽敏, 樊虹雨, 等. 活动期溃疡性结肠炎住院病人营养风险研究[J]. 护理研究, 2022, 36(22): 4131-3. |
| 11 | Kondrup J, Rasmussen HH, Hamberg O, et al. Nutritional risk screening (NRS 2002): a new method based on an analysis of controlled clinical trials[J]. Clin Nutr, 2003, 22(3): 321-36. |
| 12 | 李军祥, 陈 誩. 溃疡性结肠炎中西医结合诊疗共识意见(2017年)[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2018, 26(2): 105-11, 120. |
| 13 | Jockenhöfer F, Wollina U, Salva KA, et al. The PARACELSUS score: a novel diagnostic tool for pyoderma gangrenosum[J]. Br J Dermatol, 2019, 180(3): 615-20. |
| 14 | 王征宇, 迟玉芬. 抑郁自评量表(SDS)[J]. 上海精神医学, 1984, 2: 71-2. |
| 15 | Dunstan DA, Scott N. Norms for zung's self-rating anxiety scale[J]. BMC Psychiatry, 2020, 20(1): 90. |
| 16 | Sachan A, Thungapathra M, Kaur H, et al. Comprehensive assessment of nutritional and functional status of patients with ulcerative colitis and their impact on quality of life[J]. Indian J Gastroenterol, 2024, 43(1): 254-63. |
| 17 | Li XJ, Hu YD, Shi XD, et al. Prevalence and relevant factors of micronutrient deficiencies in hospitalized patients with inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Nutrition, 2022, 99/100: 111671. |
| 18 | 刘仁娟, 田字彬, 荆 雪, 等. GLIM标准诊断的营养不良与溃疡性结肠炎住院患者疾病活动度及不良临床结局的关系[J]. 中华临床营养杂志, 2024, 32(2): 98-104. |
| 19 | Ünal NG, Oruç N, Tomey O, et al. Malnutrition and sarcopenia are prevalent among inflammatory bowel disease patients with clinical remission[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 33(11): 1367-75. |
| 20 | Kamel AY, Johnson ZD, Hernandez I, et al. Micronutrient deficiencies in inflammatory bowel disease: an incidence analysis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2024, 36(10): 1186-92. |
| 21 | Zerouga I, Valeur J, Sommer C, et al. Dietary intake and nutritional status in patients with newly diagnosed inflammatory bowel disease: insights from the IBSEN III study[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2024, 59(6): 652-60. |
| 22 | Day AS, Davis R, Costello SP, et al. The adequacy of habitual dietary fiber intake in individuals with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review[J]. J Acad Nutr Diet, 2021, 121(4): 688-708. e3. |
| 23 | Jabłońska B, Mrowiec S. Nutritional status and its detection in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases[J]. Nutrients, 2023, 15(8): 1991. |
| 24 | Whelan K, Murrells T, Morgan M, et al. Food-related quality of life is impaired in inflammatory bowel disease and associated with reduced intake of key nutrients[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2021, 113(4): 832-44. |
| 25 | Gold SL, Rabinowitz LG, Manning L, et al. High prevalence of malnutrition and micronutrient deficiencies in patients with inflammatory bowel disease early in disease course[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2023, 29(3): 423-9. |
| 26 | Dhaliwal A, Quinlan JI, Overthrow K, et al. Sarcopenia in inflammatory bowel disease: a narrative overview[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(2): 656. |
| 27 | Hashash JG, Elkins J, Lewis JD, et al. AGA clinical practice update on diet and nutritional therapies in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: expert review[J]. Gastroenterology, 2024, 166(3): 521-32. |
| 28 | Skrzypczak D, Ratajczak AE, Szymczak-Tomczak A, et al. A vicious cycle of osteosarcopeniain inflammatory bowel diseases-aetiology, clinical implications and therapeutic perspectives[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(2): 293. |
| 29 | 荫士安, 董彩霞, 杨振宇. 遏制人群慢性病上升态势的全生命周期预防建议[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2024, 58(1): 107-13. |
| 30 | 王禹毅, 卜志军, 李元晞, 等. 临床预测模型变量筛选方法及比较[J]. 现代中医临床, 2024, 31(2): 6-12. |
| [1] | Na ZHAO, Mengdi SHEN, Rui ZHAO, Di AO, Zetan LUO, Yinliang ZHANG, Zhidong XU, Fangtian FAN, Hailun ZHENG. column:Sanguinarine alleviates ulcerative colitis in mice by regulating the Nrf2/NF-κB pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1467-1475. |
| [2] | Guanzheng YU, Weiqiang CHENG, Xing TU, Man ZHANG, Hong LI, Juan NIE. Therapeutic mechanism of Cynanchum wilfordii for ulcerative colitis: an analysis using UPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology and metabolomics [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1485-1496. |
| [3] | Jianguo QIU, Yitong QIU, Guorong LI, Linsheng ZHANG, Xue ZHENG, Yongjiang YAO, Xidan WANG, Haiyang HUANG, Fengmin ZHANG, Jiyan SU, Xuebao ZHENG, Xiaoqi HUANG. Huangqin Decoction alleviates ulcerative colitis in mice by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2172-2183. |
| [4] | SONG Zejun, DONG Haibin, MA Na, REN Yutang, JIANG Bo. Value of Improved Mayo Endoscopic Score for evaluating treatment efficacy for active ulcerative colitis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(7): 1204-1213. |
| [5] | SONG Zejun, ZHANG Mingjun, REN Yutang, JIANG Bo. Improved Mayo Endoscopic Score has a higher value for evaluating clinical severity of ulcerative colitis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(7): 997-1005. |
| [6] | KUERBANNAIMU Kaheman, ZHAO Jianfeng, MUKAIDAISI Aihemaiti, WANG Hanming, ZHU Jiwei, PAN Wentao, KASIMUJIANG Aximujiang. E.faecium QH06 alleviates TNBS-induced colonic mucosal injury in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(7): 976-987. |
| [7] | ZHAO Chenling, DONG Ting, SUN Lunyan, HU Huibing, WANG Qiong, TIAN Liwei, JIANG Zhangsheng. Establishment and validation of a predictive nomogram for liver fibrosis in patients with Wilson disease and abnormal lipid metabolism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(11): 1720-1725. |
| [8] | DENG Ya, WANG Chunyan, FU Yiming, LI Zhongbin, JI Dong. A high relapse risk of chronic drug-induced liver injury is correlated with a greater severity of liver fibrosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(11): 1655-1661. |
| [9] | . rCsHscB derived from Clonorchis sinensis has therapeutic effect on dextran sodium sulfate-induced chronic ulcerative colitis in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(5): 664-670. |
| [10] | . Establishment of naive Bayes classifier-based risk prediction model for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(4): 607-612. |
| [11] | . Huangqin decoction alleviates ulcerative colitis by regulating ILC3s-TH cell response [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(2): 256-263. |
| [12] | . Mechanism of Jiawei Huangqin decoction for treating ulcerative colitis in mice: the role of STAT3/NF-kB/IL-6 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(02): 196-202. |
| [13] | . Kirenol relieves dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice by inhibiting inflammatory cytokines and inducing CD4+ T lymphocyte apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2019, 39(12): 1387-1392. |
| [14] | . Red blood cell distribution width is a independent prognostic indicator for mortality in patients with HBV related acute-on-chronic liver failure [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2018, 38(11): 1354-. |
| [15] | . Expressions of inflammatory cytokines in intestinal mucosa and their prognostic value in patients with ulcerative colitis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2016, 36(12): 1712-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||