Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (11): 2172-2183.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.14
Jianguo QIU1,2( ), Yitong QIU1, Guorong LI1, Linsheng ZHANG1, Xue ZHENG1,3, Yongjiang YAO1, Xidan WANG2, Haiyang HUANG2, Fengmin ZHANG2, Jiyan SU4, Xuebao ZHENG1,3(
), Yitong QIU1, Guorong LI1, Linsheng ZHANG1, Xue ZHENG1,3, Yongjiang YAO1, Xidan WANG2, Haiyang HUANG2, Fengmin ZHANG2, Jiyan SU4, Xuebao ZHENG1,3( ), Xiaoqi HUANG1,3(
), Xiaoqi HUANG1,3( )
)
Received:2024-07-07
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-11-29
Contact:
Xuebao ZHENG, Xiaoqi HUANG
E-mail:1194883143@qq.com;xuebaozheng@ gzucm.edu.cn;huangxiaoqi@gzucm.edu.cn
Supported by:Jianguo QIU, Yitong QIU, Guorong LI, Linsheng ZHANG, Xue ZHENG, Yongjiang YAO, Xidan WANG, Haiyang HUANG, Fengmin ZHANG, Jiyan SU, Xuebao ZHENG, Xiaoqi HUANG. Huangqin Decoction alleviates ulcerative colitis in mice by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2172-2183.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.14
| Weight loss (%) | Feces consistency | Hemafecia | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Normal | N/A | 0 |
| 1-5 | Mild soft | Slight bleeding | 1 |
| 5-10 | Soft and wet | Moderate bleeding | 2 |
| 10-20 | Half loose stool | Gross bleeding | 3 |
| >20 | loose stool | Blood clot around anus | 4 |
Tab.1 Quantitative table of DAI score
| Weight loss (%) | Feces consistency | Hemafecia | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Normal | N/A | 0 |
| 1-5 | Mild soft | Slight bleeding | 1 |
| 5-10 | Soft and wet | Moderate bleeding | 2 |
| 10-20 | Half loose stool | Gross bleeding | 3 |
| >20 | loose stool | Blood clot around anus | 4 |
| Inflammation degree | Inflammation range | Colonic crypt damage | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | Normal | 0 |
| Mild inflammation | Inflammation of the mucosa | One-third of crypt damage | 1 |
| Moderate inflammation | Inflammation of the mucosa and submucosa | Two thirds of crypt damage | 2 |
| Severe inflammation | Inflammation of the mucosa and intestinal wall | Crypts disappeared but epithelium remains | 3 |
| Acute severe inflammation | Transmural inflammation | Both crypts and epithelium disappeared | 4 |
Tab.2 Histopathological score of the colon
| Inflammation degree | Inflammation range | Colonic crypt damage | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | Normal | 0 |
| Mild inflammation | Inflammation of the mucosa | One-third of crypt damage | 1 |
| Moderate inflammation | Inflammation of the mucosa and submucosa | Two thirds of crypt damage | 2 |
| Severe inflammation | Inflammation of the mucosa and intestinal wall | Crypts disappeared but epithelium remains | 3 |
| Acute severe inflammation | Transmural inflammation | Both crypts and epithelium disappeared | 4 |
| Gene | Orientation | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| MUC2 | Forward | AGGGCTCGGAACTCCAGAAA |
| Reverse | CCAGGGAATCGGTAGACATCG | |
| TFF3 | Forward | TTGCTGGGTCCTCTGGGATAG |
| Reverse | TACACTGCTCCGATGTGACAG | |
| AGR2 | Forward | ACAACTGACAAGCACCTTTCTC |
| Reverse | GTTTGAGTATCGTCCAGTGATGT | |
| GRP78 | Forward | ACTTGGGGACCACCTATTCCT |
| Reverse | GTTGCCCTGATCGTTGGCTA | |
| CHOP | Forward | AAGCCTGGTATGAGGATCTGC |
| Reverse | TTCCTGGGGATGAGATATAGGTG | |
| Caspase-12 | Forward | TTGGAAGGTAGGCAAGACTGGTTC |
| Reverse | TCAGTTCACCTGGGACCTCAAATG | |
| ATF4 | Forward | AACCTATAAAGGCTTGCGGC |
| Reverse | GATTTCGTGAAGAGCGCCAT | |
| XBP1s | Forward | AAGAACACGCTTGGGAATGG |
| Reverse | CTGCACCTGCTGCGGAC |
Tab.3 Primer sequence
| Gene | Orientation | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| MUC2 | Forward | AGGGCTCGGAACTCCAGAAA |
| Reverse | CCAGGGAATCGGTAGACATCG | |
| TFF3 | Forward | TTGCTGGGTCCTCTGGGATAG |
| Reverse | TACACTGCTCCGATGTGACAG | |
| AGR2 | Forward | ACAACTGACAAGCACCTTTCTC |
| Reverse | GTTTGAGTATCGTCCAGTGATGT | |
| GRP78 | Forward | ACTTGGGGACCACCTATTCCT |
| Reverse | GTTGCCCTGATCGTTGGCTA | |
| CHOP | Forward | AAGCCTGGTATGAGGATCTGC |
| Reverse | TTCCTGGGGATGAGATATAGGTG | |
| Caspase-12 | Forward | TTGGAAGGTAGGCAAGACTGGTTC |
| Reverse | TCAGTTCACCTGGGACCTCAAATG | |
| ATF4 | Forward | AACCTATAAAGGCTTGCGGC |
| Reverse | GATTTCGTGAAGAGCGCCAT | |
| XBP1s | Forward | AAGAACACGCTTGGGAATGG |
| Reverse | CTGCACCTGCTGCGGAC |
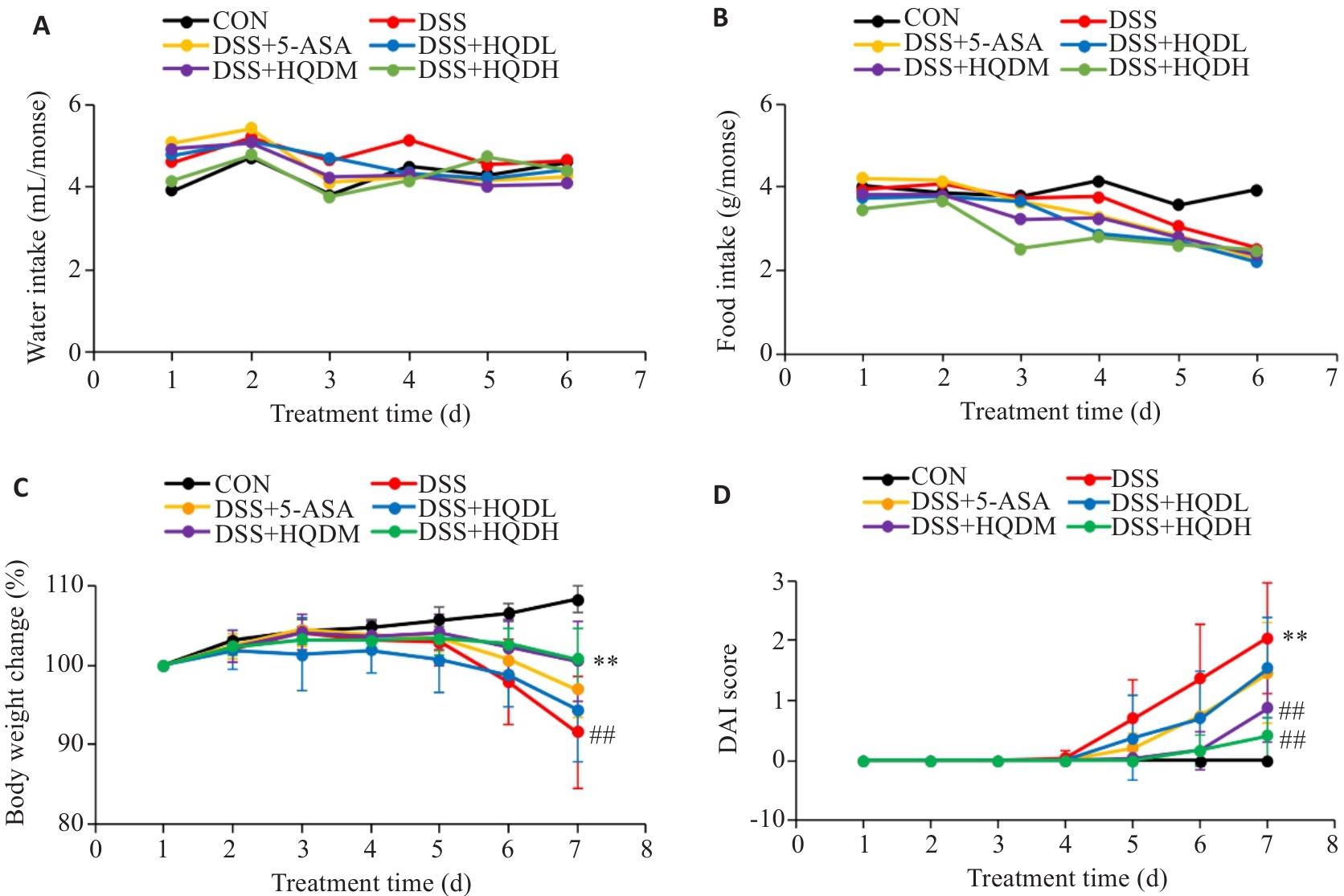
Fig.1 Changes of water intake (A), food intake (B), body weight (C) and DAI score (D) of the mice during modeling (Mean±SD, n=8). ##P<0.01 vs CON group; **P<0.01 vs DSS group.

Fig. 2 Effect of Huangqin Decoction on colon length and pathology in UC mice. A: Colon length of the mice in each group. B: Statistics of colon length in each group. C: Histopathological score of the colon in each group (Mean±SD, n=8). D: HE staining of the colon tissues in each group (Original magnification: ×100 or 200). ##P<0.01 vs CON group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs DSS group.

Fig.3 Effect of Huangqin decoction on apoptosis of colonic epithelial cells in UC mice. A: TUNEL staining of the colon tissue in each group (×400 or 200). B: Mean fluorescence intensity in each group (Mean±SD, n=3) . ##P<0.01 vs CON group;**P<0.01 vs DSS group.

Fig.5 Effect of Huangqin Decoction on mucin and goblet cell secretion in UC mice (Mean±SD, n=3). A: AB-PAS staining of mice in each group (×100, ×200). B:Expression of MUC2 MRNA. C: Expression of TFF3 MRNA. D: Expression of AGR2 mRNA. #P<0.005, ##P<0.01 vs CON group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs DSS group.

Fig 6 Effect of Huangqin Decoction on mechanical barrier function of the colonic epithelium in UC mice (Mean±SD, n=3). ##P<0.01 vs CON group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs DSS group. A: E-cadherin. B: Occludin. C: Claudin-1.

Fig.7 Effect of Huangqin Decoction on expression of GRP78 mRNA and protein in UC mice (Mean±SD, n=6). A: Immunohistochemistry staining of GRP78 protein of mice in each group (×200, ×400). B: Area fraction of GRP78 protein of mice in each group. C: Expression of GRP78 mRNA; ##P<0.01 vs CON group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs DSS group.

Fig.8 Effect of Huangqin decoction on protein and mRNA expressions related to endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway in UC mice (Mean±SD, n=3). ##P<0.01 vs CON group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs DSS group. A: p-PERK/PERK. B: p-IRElα/IRElα. C: p-eIF2α/eIF2α. D: ATF4 mRNA level (fold change). E: XBPls mRNA level (fold change).

Fig.9 Effect of Huangqin Decoction on CHOP and Caspase-12 expressions in UC mice (Mean±SD, n=3). A: Immunohistochemistry staining of CHOP and Caspase-12 protein of mice in each group (×200, ×400). B-C: Area fraction of immunohistochemistry staining of CHOP and Caspase-12 protein of mice in each group. D-E: Expression of CHOP and Caspase-12 mRNA; ##P<0.01 vs CON group; **P<0.01 vs DSS group.

Fig 10 Effect of Huangqin Decoction on Bcl-2, Bax and Caspase-3 expressions in UC mice (Mean±SD, n=3). ##P<0.01 vs CON group; **P<0.01 vs DSS group. A: Bcl-2/Bax. B: Cleaved-Caspase-3/β-tubulin.
| 1 | Eisenstein M. Ulcerative colitis: towards remission[J]. Nature, 2018, 563(7730): S33. |
| 2 | Ungaro R, Mehandru S, Allen PB, et al. Ulcerative colitis[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389(10080): 1756-70. |
| 3 | Rieder F, Karrasch T, Ben-Horin S, et al. Results of the 2nd scientific workshop of the ECCO (III): basic mechanisms of intestinal healing[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2012, 6(3): 373-85. |
| 4 | Ho GT, Cartwright JA, Thompson EJ, et al. Resolution of inflammation and gut repair in IBD: translational steps towards complete mucosal healing[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2020, 26(8): 1131-43. |
| 5 | Adolph TE, Meyer M, Schwärzler J, et al. The metabolic nature of inflammatory bowel diseases[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 19(12): 753-67. |
| 6 | Solà-Tapias N, Vergnolle N, Denadai-Souza A, et al. The interplay between genetic risk factors and proteolytic dysregulation in the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2020, 14(8): 1149-61. |
| 7 | Larabi A, Barnich N, Nguyen HTT. New insights into the interplay between autophagy, gut microbiota and inflammatory responses in IBD[J]. Autophagy, 2020, 16(1): 38-51. |
| 8 | Eugene SP, Reddy VS, Trinath J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and intestinal inflammation: a perilous union[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 543022. |
| 9 | van der Post S, Jabbar KS, Birchenough G, et al. Structural weakening of the colonic mucus barrier is an early event in ulcerative colitis pathogenesis[J]. Gut, 2019, 68(12): 2142-51. |
| 10 | Ren MT, Gu ML, Zhou XX, et al. Sirtuin 1 alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells in ulcerative colitis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(38): 5800-13. |
| 11 | Naama M, Telpaz S, Awad A, et al. Autophagy controls mucus secretion from intestinal goblet cells by alleviating ER stress[J]. Cell Host Microbe, 2023, 31(3): 433-46. e4. |
| 12 | Coleman OI, Haller D. ER stress and the UPR in shaping intestinal tissue homeostasis and immunity[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2825. |
| 13 | 黄 煌. 黄芩汤的拓展应用与适用人群特征[J]. 南京中医药大学学报, 2022, 38(9): 761-4. |
| 14 | 铉 力, 王晓红, 胡 兵, 等. 复方黄芩汤治疗湿热型溃疡性结肠炎临床观察[J]. 光明中医, 2024, 39(2): 281-4. |
| 15 | 高 勤, 陈一川, 杨 宸, 等. 黄芩汤治疗溃疡性结肠炎疗效与安全性的Meta分析[J]. 海南医学, 2021, 32(10): 1343-9. |
| 16 | Li MY, Li MX, Xu N, et al. Effects of Huangqin Decoction on ulcerative colitis by targeting estrogen receptor alpha and ameliorating endothelial dysfunction based on system pharmacology[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2021, 271: 113886. |
| 17 | Li MY, Luo HJ, Wu X, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Huangqin Decoction on dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice through regulation of the gut microbiota and suppression of the ras-PI3K-akt-HIF-1α and NF‑κB pathways[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 10: 1552. |
| 18 | Li MY, Wu YZ, Qiu JG, et al. Huangqin Decoction ameliorates ulcerative colitis by regulating fatty acid metabolism to mediate macrophage polarization via activating FFAR4-AMPK-PPARα pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 311: 116430. |
| 19 | Li MX, Li MY, Lei JX, et al. Huangqin decoction ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis: role of gut microbiota and amino acid metabolism, mTOR pathway and intestinal epithelial barrier[J]. Phytomedicine, 2022, 100: 154052. |
| 20 | Rodrigues BL, Dotti I, Pascoal LB, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in colonic mucosa of ulcerative colitis patients is mediated by PERK and IRE1 pathway activation[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2022: 6049500. |
| 21 | Lebeaupin C, Proics E, de Bieville CHD, et al. ER stress induces NLRP3 inflammasome activation and hepatocyte death[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2015, 6(9): e1879. |
| 22 | Akbal A, Dernst A, Lovotti M, et al. How location and cellular signaling combine to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2022, 19(11): 1201-14. |
| 23 | Iwasaki Y, Suganami T, Hachiya R, et al. Activating transcription factor 4 links metabolic stress to interleukin-6 expression in macrophages[J]. Diabetes, 2014, 63(1): 152-61. |
| 24 | Oslowski CM, Hara T, O' Sullivan-Murphy B, et al. Thioredoxin-interacting protein mediates ER stress-induced β cell death through initiation of the inflammasome[J]. Cell Metab, 2012, 16(2): 265-73. |
| 25 | Choi EH, Park SJ. TXNIP: a key protein in the cellular stress response pathway and a potential therapeutic target[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2023, 55(7): 1348-56. |
| 26 | Heazlewood CK, Cook MC, Eri R, et al. Aberrant mucin assembly in mice causes endoplasmic reticulum stress and spontaneous inflammation resembling ulcerative colitis[J]. PLoS Med, 2008, 5(3): e54. |
| 27 | Zhao F, Edwards R, Dizon D, et al. Disruption of Paneth and goblet cell homeostasis and increased endoplasmic reticulum stress in Agr2-/ - mice[J]. Dev Biol, 2010, 338(2): 270-9. |
| 28 | Hu XM, Deng JL, Yu TM, et al. ATF4 deficiency promotes intestinal inflammation in mice by reducing uptake of glutamine and expression of antimicrobial peptides[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 156(4): 1098-111. |
| 29 | Kaser A, Lee AH, Franke A, et al. XBP1 links ER stress to intestinal inflammation and confers genetic risk for human inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Cell, 2008, 134(5): 743-56. |
| 30 | Zhang Q, Liu JN, Chen SL, et al. Caspase-12 is involved in stretch-induced apoptosis mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Apoptosis, 2016, 21(4): 432-42. |
| 31 | Yang L, Wang J, Yang J, et al. Antioxidant metallothionein alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced myocardial apoptosis and contractile dysfunction[J]. Free Radic Res, 2015, 49(10): 1187-98. |
| 32 | Sano R, Reed J C. ER stress-induced cell death mechanisms[J]. Biochimica et biophysica acta, 2013, 1833(12): 3460-70. |
| [1] | Na ZHAO, Mengdi SHEN, Rui ZHAO, Di AO, Zetan LUO, Yinliang ZHANG, Zhidong XU, Fangtian FAN, Hailun ZHENG. column:Sanguinarine alleviates ulcerative colitis in mice by regulating the Nrf2/NF-κB pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1467-1475. |
| [2] | Guanzheng YU, Weiqiang CHENG, Xing TU, Man ZHANG, Hong LI, Juan NIE. Therapeutic mechanism of Cynanchum wilfordii for ulcerative colitis: an analysis using UPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology and metabolomics [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1485-1496. |
| [3] | Shuo LIU, Jing LI, Xingwang WU. Swertiamarin ameliorates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced colitis in mice by inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1545-1552. |
| [4] | Xiaofan CONG, Teng CHEN, Shuo LI, Yuanyuan WANG, Longyun ZHOU, Xiaolong LI, Pei ZHANG, Xiaojin SUN, Surong ZHAO. Dihydroartemisinin enhances sensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma HNE1/DDP cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by promoting ROS production [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1553-1560. |
| [5] | Linyu XIAO, Ting DUAN, Yongsheng XIA, Yue CHEN, Yang SUN, Yibo XU, Lei XU, Xingzhou YAN, Jianguo HU. Linarin inhibits microglia activation-mediated neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis in mouse spinal cord injury by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1589-1598. |
| [6] | Mengdong ZHENG, Yan LIU, Jiaojiao LIU, Qiaozhen KANG, Ting WANG. Effect of deletion of protein 4.1R on proliferation, apoptosis and glycolysis of hepatocyte HL-7702 cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1355-1360. |
| [7] | Yuanguo WANG, Peng ZHANG. Ferroptosis suppressor genes are highly expressed in esophageal cancer to inhibit tumor cell ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1389-1396. |
| [8] | Zhijun REN, Jianxin DIAO, Yiting WANG. Xionggui Decoction alleviates heart failure in mice with myocardial infarction by inhibiting oxidative stress-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1416-1424. |
| [9] | Guiling CHEN, Xiaofeng LIAO, Pengtao SUN, Huan CEN, Shengchun SHU, Bijing LI, Jinhua LI. Solasonine promotes apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating the Bcl-2/Bax/caspase-3 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1109-1116. |
| [10] | Lingjun LU, Xiaodi YANG, Huaping ZHANG, Yuan LIANG, Xiulan SHI, Xin ZHOU. Recombinant Schistosoma japonicum cystatin alleviates acute liver injury in mice by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammation and hepatocyte apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1126-1134. |
| [11] | Guoxin LIANG, Hongyue TANG, Chang GUO, Mingming ZHANG. MiR-224-5p overexpression inhibits oxidative stress by regulating the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 axis to attenuate hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte injury [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1173-1181. |
| [12] | Wei ZHOU, Jun NIE, Jia HU, Yizhi JIANG, Dafa ZHANG. Differential expressions of endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated genes in aortic dissection and their correlation with immune cell infiltration [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 859-866. |
| [13] | ZHANG Xiaoyan, WANG Xie, WANG Jie, SHAO Nan, CAI Biao, XIE Daojun. Huangpu Tongqiao Capsule improves cognitive impairment in rats with Wilson disease by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 447-454. |
| [14] | CHEN Guodong, LUO Suxin. Colchicine alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by activating AMPK [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 226-235. |
| [15] | Xiuqi SUN, Jing CAI, Anbang ZHANG, Bo PANG, Chunyan CHENG, Qiqi CHA, Fei QUAN, Tao YE. Electroacupuncture pretreatment alleviates post-stroke spasticity in rats by inhibiting NF‑κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway-mediated inflammation and neuronal apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2102-2109. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||