Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 131-140.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.14
Tong QIAO1,3( ), Lin YIN1, Keni ZHANG1, Minzhu NIU3, Ju HUANG2, Zhijun Geng2, Jing LI1,2, Jianguo HU1,2(
), Lin YIN1, Keni ZHANG1, Minzhu NIU3, Ju HUANG2, Zhijun Geng2, Jing LI1,2, Jianguo HU1,2( )
)
Received:2025-05-19
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-16
Contact:
Jianguo HU
E-mail:qt1231126@163.com;jghu9200@bbmu.edu.cn
Tong QIAO, Lin YIN, Keni ZHANG, Minzhu NIU, Ju HUANG, Zhijun Geng, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. Poricoic acid A alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by regulating AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy and inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2026, 46(1): 131-140.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.14
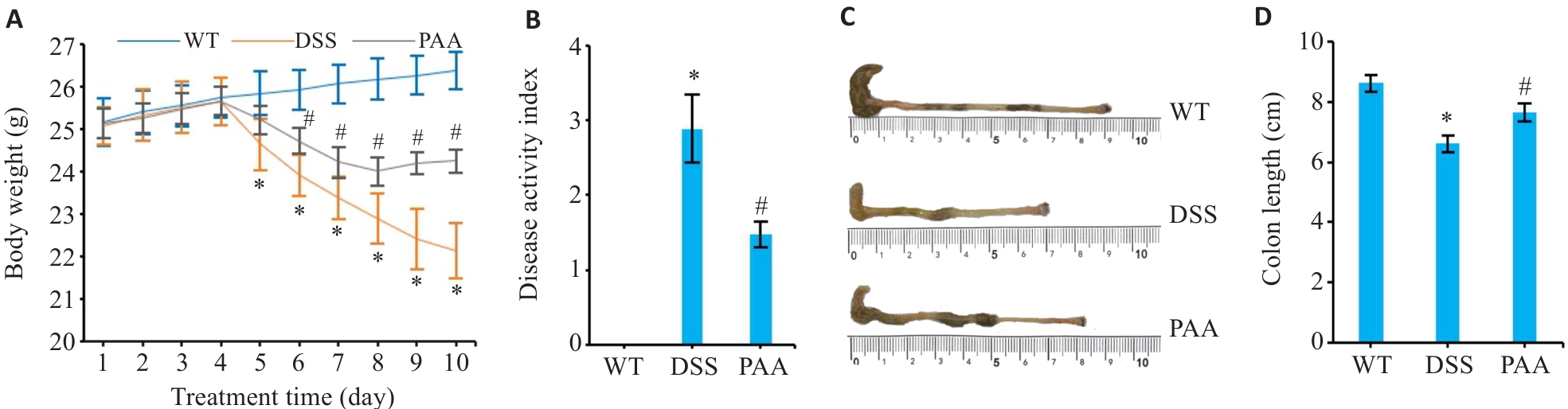
Fig.1 Therapeutic effects of PAA on DSS-induced colitis in mice. A: Changes in body weight of the mice. B: Disease activity index (DAI) scoring. C: Macroscopic evaluation of colon morphology. D: Quantitative analysis of colon length. WT: Wild type group; DSS: DSS-induced model group; PAA: Treatment group DSS. n=6, *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
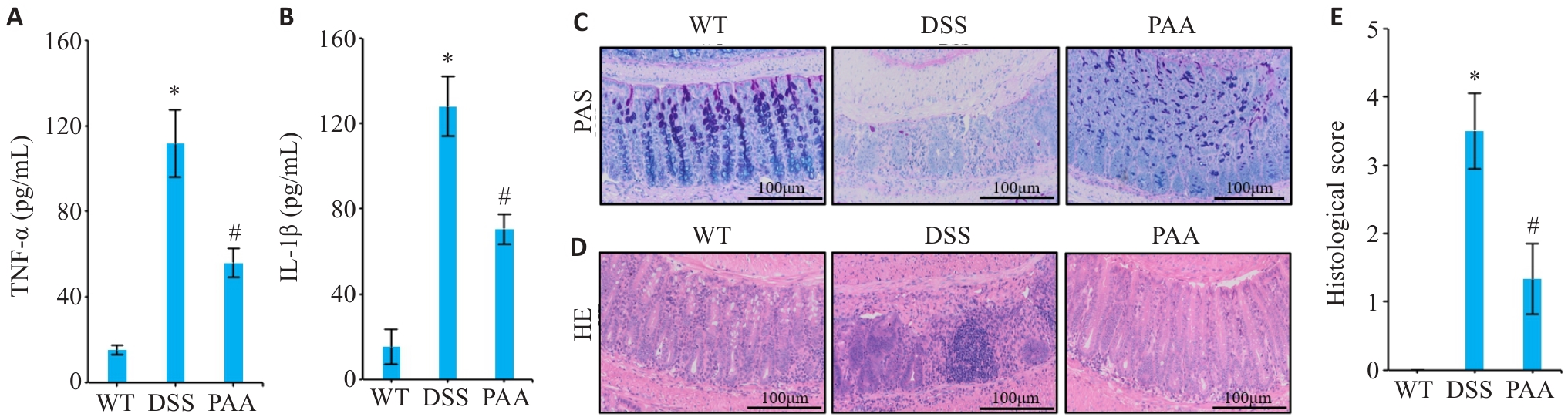
Fig.2 Effects of PAA intervention on intestinal histopathological damage and expression of inflammatory factors in DSS mice. A, B: ELISA results of TNF-α (A) and IL-1β (B) in mice intestinal mucosa. C: AB-PAS staining of colon tissues in different groups. D: HE staining of colon tissues in different groups. E: Histopathological scores of colon tissues. n=6, *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
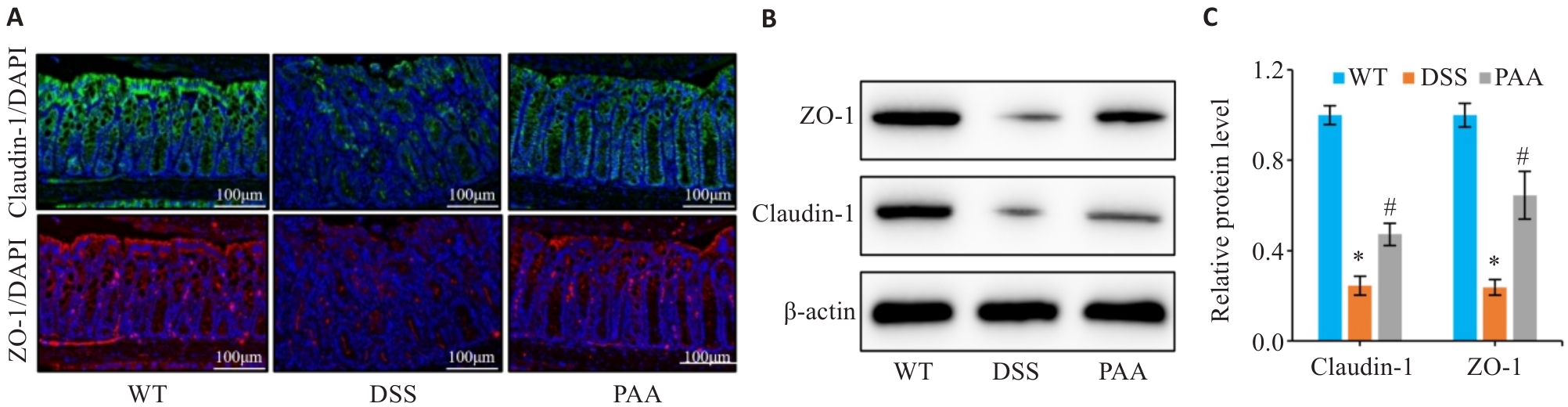
Fig.3 Effect of PAA on intestinal barrier function in DSS-induced colitis mice. A: Immunofluorescence staining of ZO-1 and claudin-1 in the colon. B, C: Quantitative analysis of ZO-1 and claudin-1 expression levels in the intestinal mucosa by Western blotting. n=6, *P<0.05 vs WT group; #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
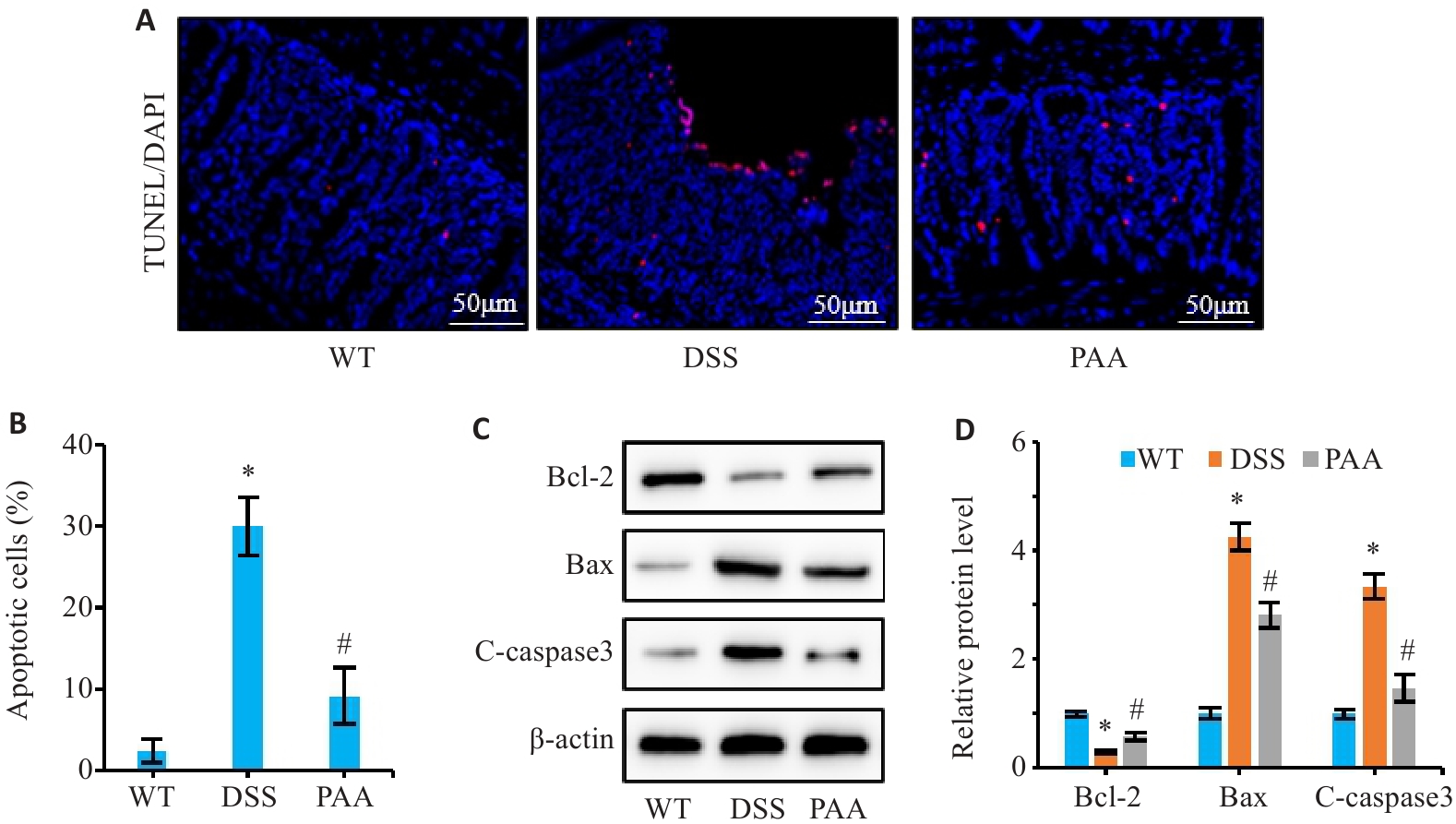
Fig.4 Effect of PAA on intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis in DSS-induced colitis mice. A: TUNEL staining of colon tissues. B: Quantitative analysis of intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis rate. C, D: Western blotting of Bcl-2, Bax, and cleaved caspase-3 (C-caspase3) expression levels in colonic mucosa. n=6, *P<0.05 vs WT group; #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
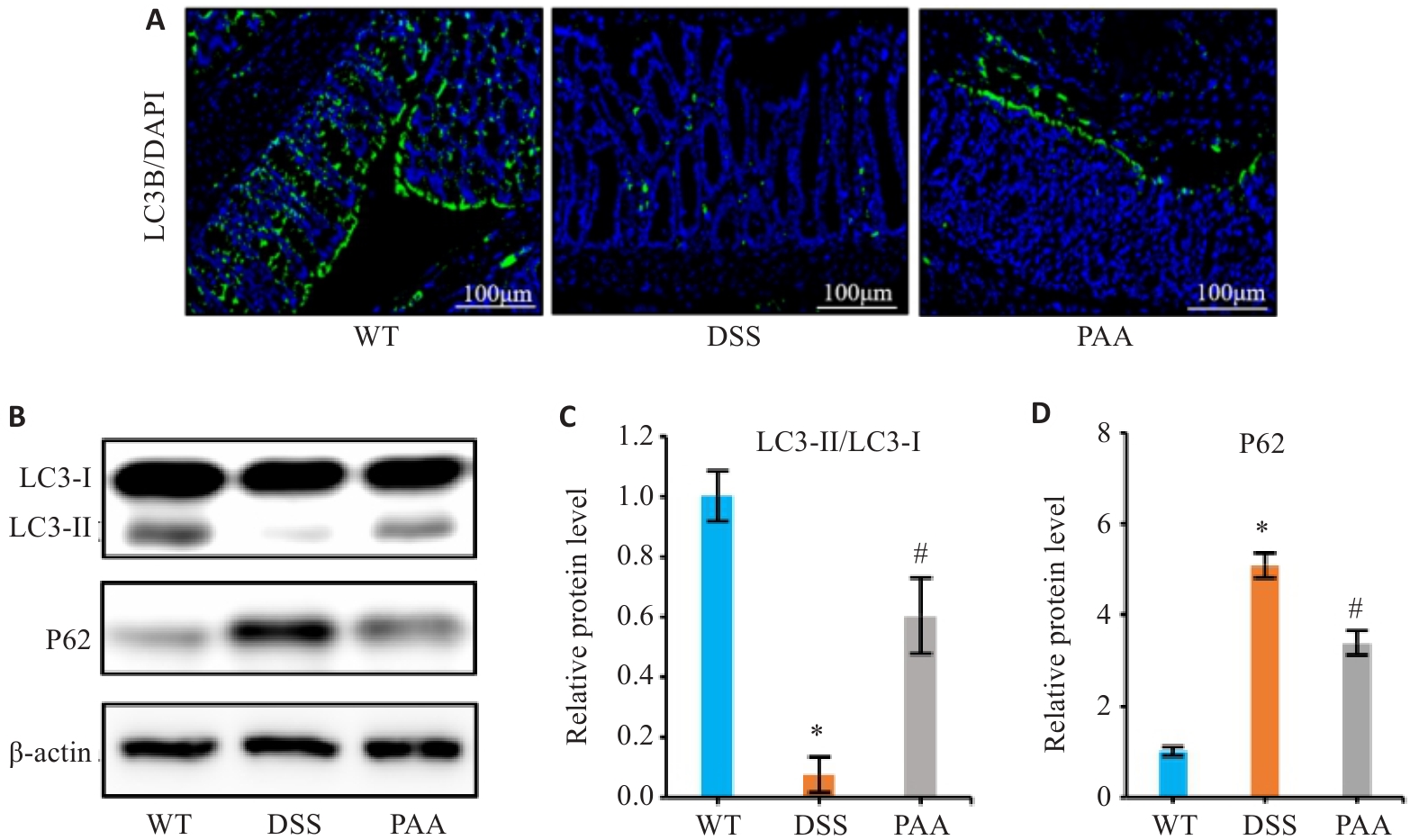
Fig.5 Effects of PAA on cellular autophagy in DSS-induced colitis mouse models. A: Immunofluorescence images of LC3B in the colon. B: Western blotting of LC3-I, LC3-II, and P62 expressions in the intestinal mucosa. C: Quantitative analysis of the LC3-II/LC3-I protein ratio. D: Quantitative analysis of P62 protein expression. n=6, *P<0.05 vs WT group; #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
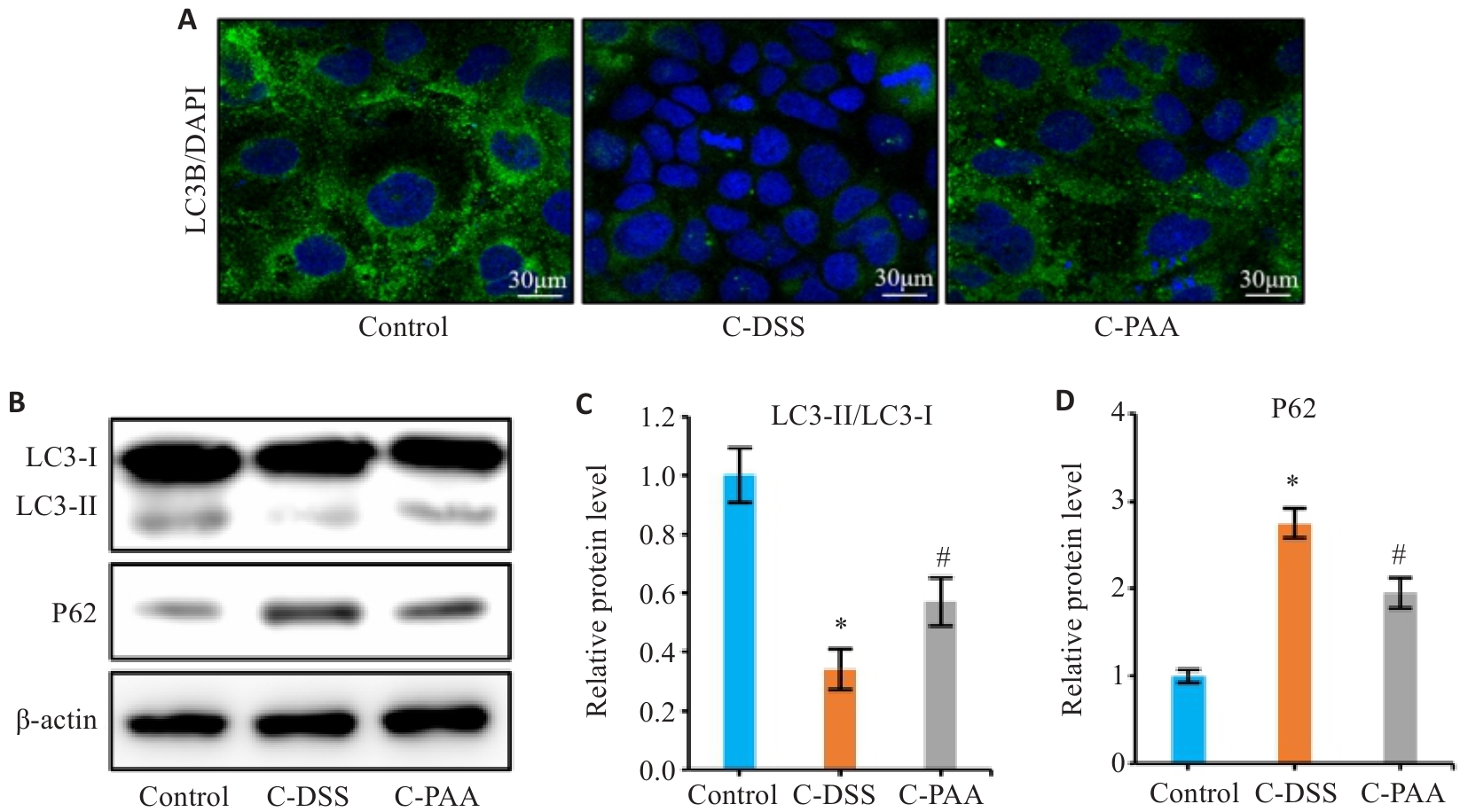
Fig.6 Effect of PAA on autophagy in DSS-induced Caco-2 cells. A: Immunofluorescence staining of LC3B in Caco-2 cells. B: Western blotting of LC3-I, LC3-II, and P62 expression. C: Quantitative analysis of the LC3-II/LC3-I ratio. D: Quantitative analysis of P62 protein level. Control: Normal control group; C-DSS: DSS-induced model group; C-PAA: PAA treatment group. n=3, *P<0.05 vs Control group; #P<0.05 vs C-DSS group.
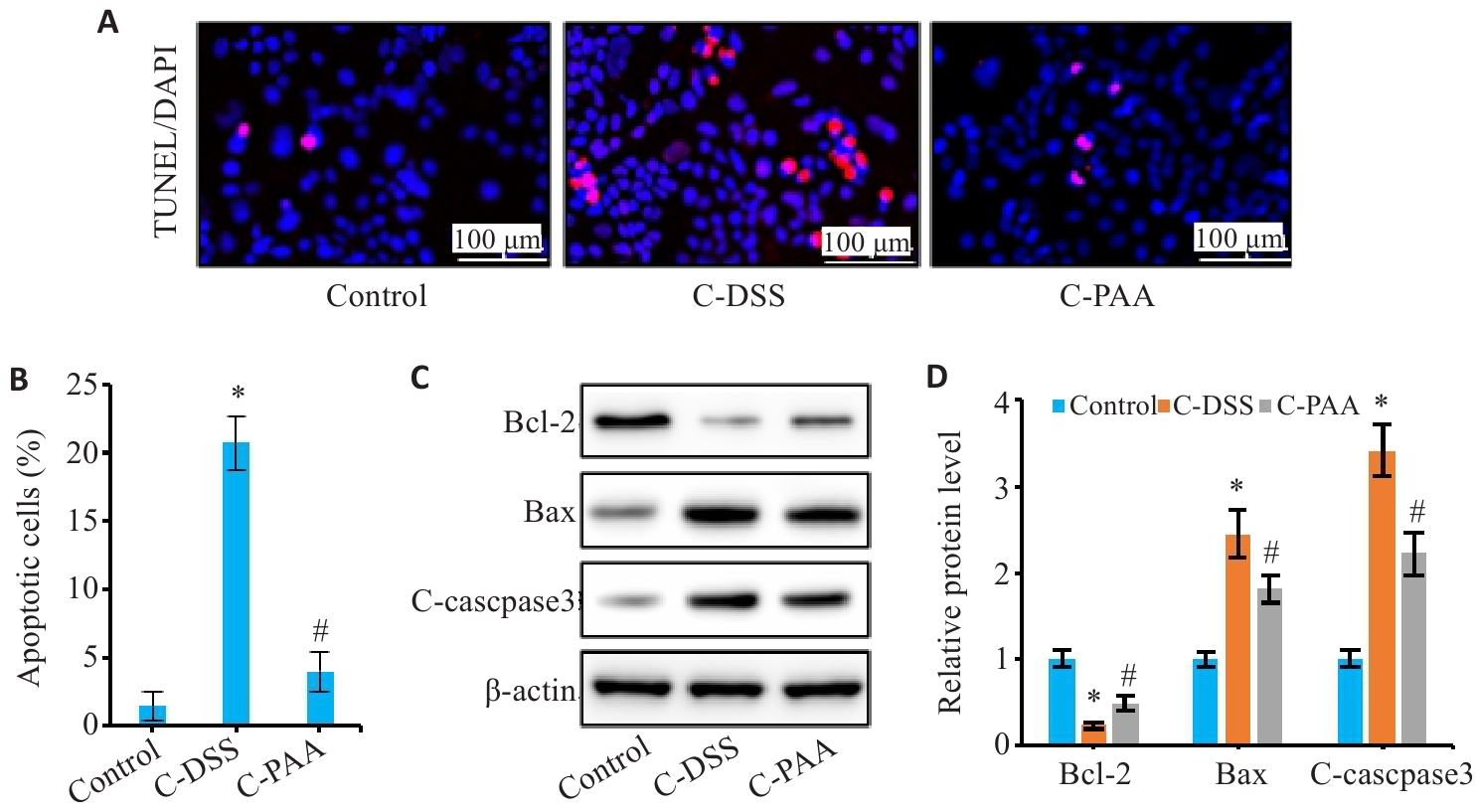
Fig.7 Effect of PAA on DSS-induced apoptosis of Caco-2 cells. A: TUNEL staining of Caco-2 cells. B: Quantitative analysis of apoptosis rate. C: Western blotting of Bcl-2, Bax, and C-caspase3 expressions. D: Relative protein expression levels of Bcl-2, Bax, and C-caspase3. n=3, *P<0.05 vs Control group; #P<0.05 vs C-DSS group.
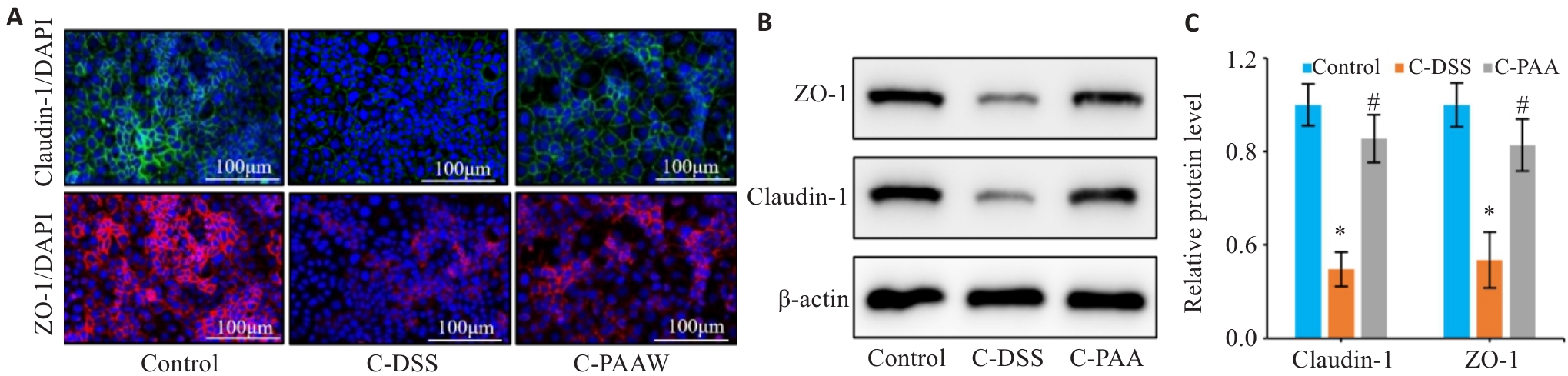
Fig. 8 Therapeutic effects of PAA on DSS-induced barrier damage in Caco-2 cells. A: Immunofluorescence staining of ZO-1 and claudin-1 in Caco-2 cells (Scale bar=100 μm). B, C: Western blotting for detecting protein expression levels of ZO-1 (B) and claudin-1 (C) in Caco-2 cells. n=3, *P<0.05 vs Control group. #P<0.05 vs C-DSS group.
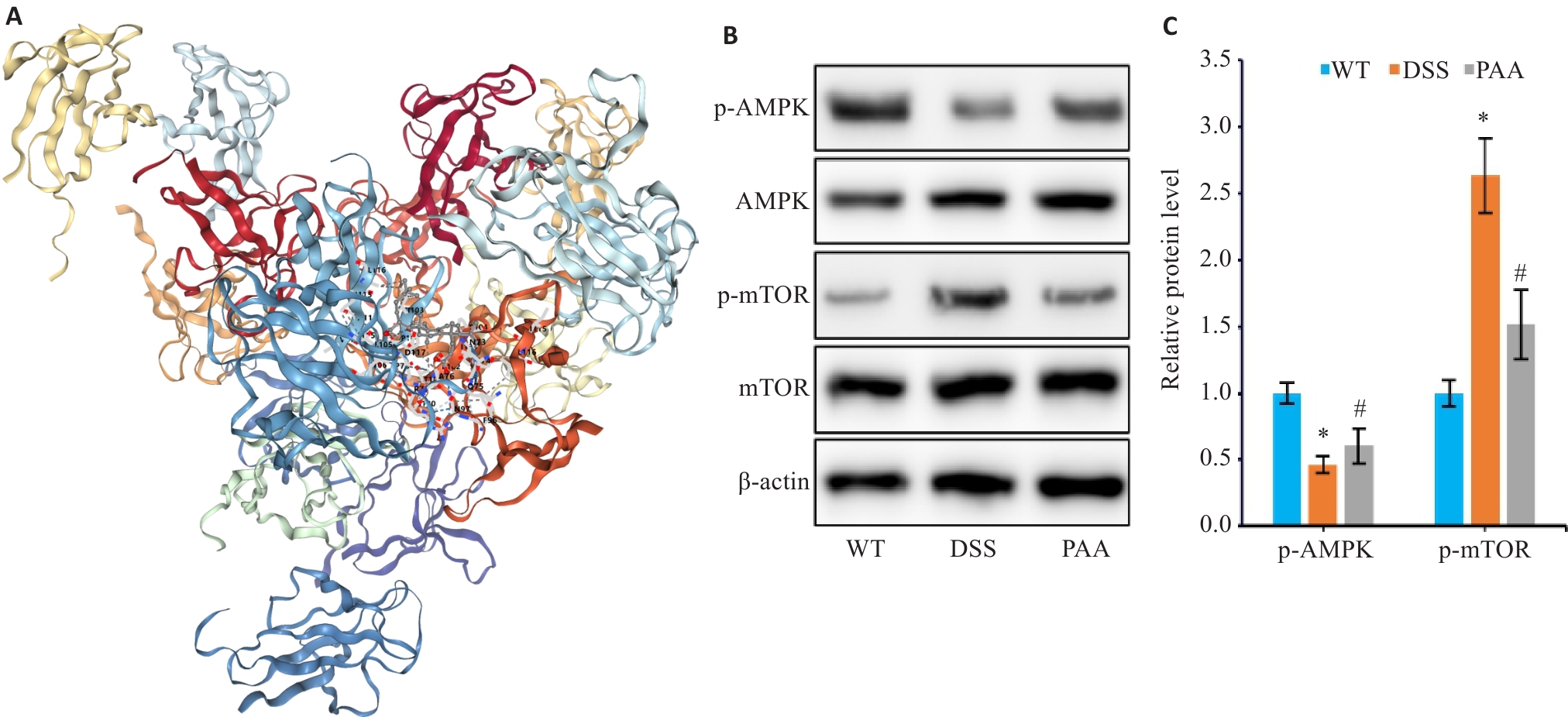
Fig.9 Effect of PAA on the AMPK/mTOR pathway in the mouse models. A: Molecular docking analysis of PAA with AMPK. B, C: Western blotting for detecting protein expression levels of p-AMPK, AMPK, p-mTOR, and mTOR in mouse colon tissues. n=6, *P<0.05 vs WT group; #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
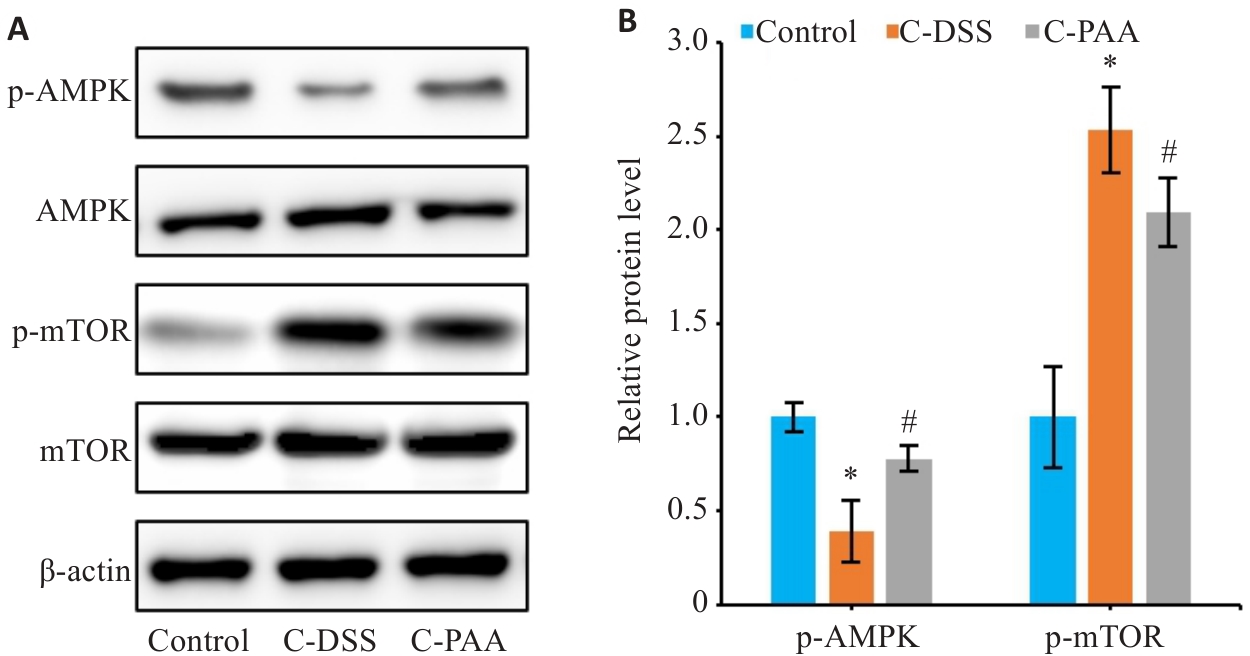
Fig.10 Effects of PAA treatment on AMPK/mTOR signaling in DSS-induced Caco-2 cells. A: Western blotting for p-AMPK, AMPK, p-mTOR, and mTOR expressions. B: Quantitative analysis of p-AMPK/AMPK and p-mTOR/mTOR protein expression ratios. n=3, *P<0.05 vs Control group. #P<0.05 vs C-DSS group.
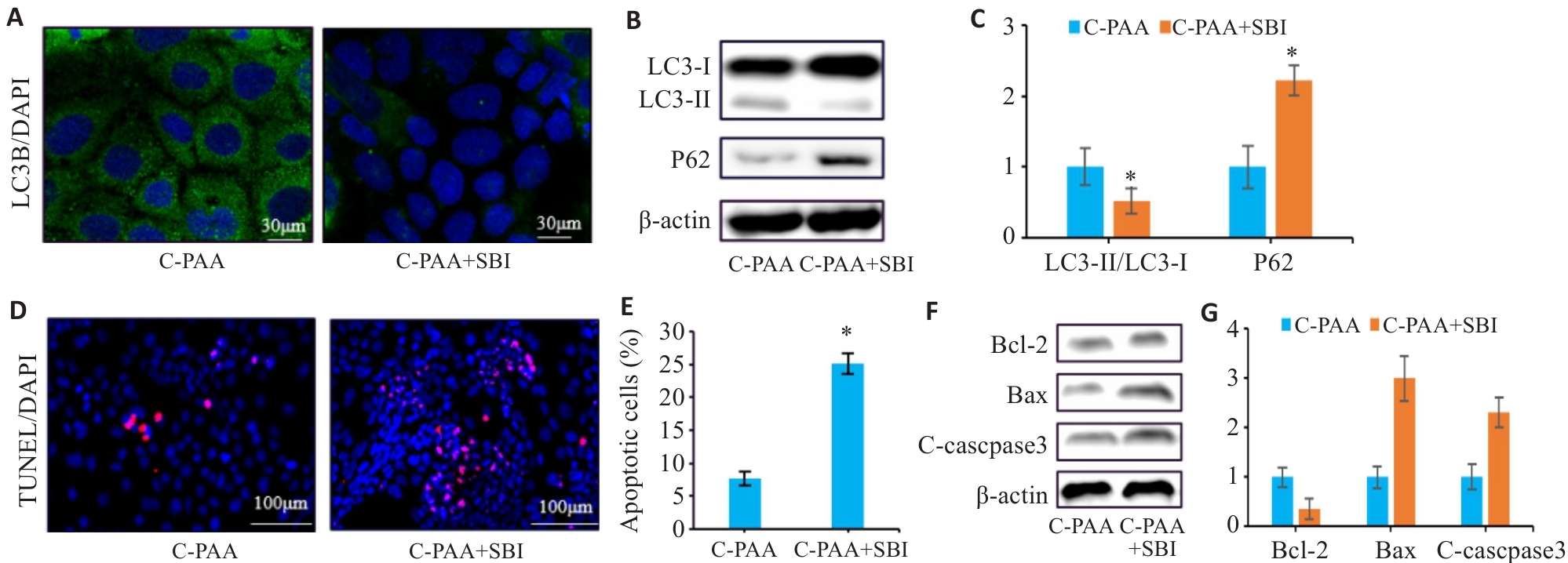
Fig.11 PAA regulates autophagy and apoptosis in Caco-2 cells by activating the AMPK/mTOR pathway. A: Immunofluorescence staining of LC3B in Caco-2 cells. B: Western blotting for LC3-I, LC3-II, and P62 expressions. C: Quantitative analysis of the LC3-II/LC3-I ratio. D: TUNEL staining of Caco-2 cells. E: Quantitative analysis of apoptosis rate. F: Western blotting for Bcl-2, Bax, and C-caspase3 expressions. G: Relative protein expression levels of Bcl-2, Bax, and C-caspase3. C-PAA: PAA treatment group; C-PAA+SBI: PAA treatment group+SBI-0206965. n=3, *P<0.05 vs C-PAA group.
| [1] | Saha K, Subramenium Ganapathy A, Wang A, et al. Autophagy reduces the degradation and promotes membrane localization of occludin to enhance the intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier against paracellular macromolecule flux[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2023, 17(3): 433-49. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjac148 |
| [2] | Xu J, Li S, Jin W, et al. Epithelial Gab1 calibrates RIPK3-dependent necroptosis to prevent intestinal inflammation[J]. JCI Insight, 2023, 8(6): e162701. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.162701 |
| [3] | Tran S, Juliani J, Fairlie WD, et al. The emerging roles of autophagy in intestinal epithelial cells and its links to inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Biochem Soc Trans, 2023, 51(2): 811-26. doi:10.1042/bst20221300 |
| [4] | Zhang Y, Li XZ, Li YT, et al. DNA damage-regulated autophagy modulator 1 (DRAM1) mediates autophagy and apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2021, 66(10): 3375-90. doi:10.1007/s10620-020-06697-2 |
| [5] | Chen SL, Li CM, Li W, et al. How autophagy, a potential therapeutic target, regulates intestinal inflammation[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1087677. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1087677 |
| [6] | Khan S, Mentrup HL, Novak EA, et al. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase contributes to epithelial homeostasis in intestinal inflammation via Beclin-1-mediated autophagy[J]. FASEB J, 2022, 36(5): e22282. doi:10.1096/fj.202200138r |
| [7] | Gorrepati VS, Soriano C, Johri A, et al. Abdominal pain and anxious or depressed state are independently associated with weight loss in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Crohns Colitis 360, 2020, 2(2): otaa047. doi:10.1093/crocol/otaa047 |
| [8] | Oligschlaeger Y, Yadati T, Houben T, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease: a stressed "gut/feeling"[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(7): E659. doi:10.3390/cells8070659 |
| [9] | Goll R, Moe ØK, Johnsen KM, et al. Pharmacodynamic mechanisms behind a refractory state in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2022, 22(1): 464. doi:10.1186/s12876-022-02559-5 |
| [10] | Yibcharoenporn C, Muanprasat C, Moonwiriyakit A, et al. AMPK in intestinal health and disease: a multifaceted therapeutic target for metabolic and inflammatory disorders[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2025, 19: 3029-58. doi:10.2147/dddt.s507489 |
| [11] | Olivier S, Diounou H, Pochard C, et al. Intestinal epithelial AMPK deficiency causes delayed colonic epithelial repair in DSS-induced colitis[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(4): 590. doi:10.3390/cells11040590 |
| [12] | Accordi B, Galla L, Milani G, et al. AMPK inhibition enhances apoptosis in MLL-rearranged pediatric B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells[J]. Leukemia, 2013, 27(5): 1019-27. doi:10.1038/leu.2012.338 |
| [13] | 曹霞, 邱 榕, 陶云平, 等. 基于Th17/Treg平衡的调节探讨参苓白术散治疗溃疡性结肠炎的疗效及作用机制[J]. 中药材, 2025, 48(1):237-41. |
| [14] | Zhang L, Yin M, Feng X, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of four triterpenoids isolated from Poriae cutis [J]. Foods, 2021, 10(12): 3155. doi:10.3390/foods10123155 |
| [15] | Jin Q, Yin JZ, Liu ZZ. Poricoic acid A promotes angiogenesis and myocardial regeneration by inducing autophagy in myocardial infarction[J]. Tissue Cell, 2024, 88: 102401. doi:10.1016/j.tice.2024.102401 |
| [16] | Chen DQ, Wang YN, Vaziri ND, et al. Poricoic acid A activates AMPK to attenuate fibroblast activation and abnormal extracellular matrix remodelling in renal fibrosis[J]. Phytomedicine, 2020, 72: 153232. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153232 |
| [17] | Wu YW, Xu YC, Deng HH, et al. Poricoic acid a ameliorates high glucose-induced podocyte injury by regulating the AMPKα/FUNDC1 pathway[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2024, 51(1): 1003. doi:10.1007/s11033-024-09921-8 |
| [18] | 程 扬, 宾东华, 尹园缘, 等. 参苓白术散对克罗恩病大鼠肠道炎症及PI3K/Akt信号通路的影响[J]. 中医药导报, 2024, 30(4): 30-4. |
| [19] | Roselli M, Maruszak A, Grimaldi R, et al. Galactooligosaccharide treatment alleviates DSS-induced colonic inflammation in caco-2 cell model[J]. Front Nutr, 2022, 9: 862974. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.862974 |
| [20] | Paquette M, El-Houjeiri L, Zirden LC, et al. AMPK-dependent phosphorylation is required for transcriptional activation of TFEB and TFE3[J]. Autophagy, 2021, 17(12): 3957-75. doi:10.1080/15548627.2021.1898748 |
| [21] | Wirtz S, Popp V, Kindermann M, et al. Chemically induced mouse models of acute and chronic intestinal inflammation[J]. Nat Protoc, 2017, 12(7): 1295-309. doi:10.1038/nprot.2017.044 |
| [22] | 张 敏, 刘生宝, 张 诺, 等. 改进型“瑞士卷”法在小鼠肠道组织切片中的应用[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2024, 53(4): 393-7. |
| [23] | Li CL, Liu MG, Deng L, et al. Oxyberberine ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis in rats through suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress via Keap1/Nrf2/NF‑κB signaling pathways[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 116: 154899. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154899 |
| [24] | 韩康宁, 胡俊杰, 李 娟, 等. 二妙四土汤调控JAK/STAT通路治疗湿热型湿疹大鼠的药效与作用机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2025, 31(9): 37-47. |
| [25] | Gareb B, Otten AT, Frijlink HW, et al. Review: local tumor necrosis factor-α inhibition in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2020, 12(6): E539. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics12060539 |
| [26] | 邵荣瑢, 杨 子, 张文静, 等. 茯苓酸缓解小鼠克罗恩病:基于抑制PPII3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 935-42. |
| [27] | 牛民主, 殷丽霞, 段 婷, 等. 川续断皂苷Ⅵ通过抑制PI3K/AKT/NF-κB通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡缓解TNBS诱导的小鼠克罗恩病样结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2335-46. |
| [28] | Robles-Vera I, Jarit-Cabanillas A, Brandi P, et al. Microbiota translocation following intestinal barrier disruption promotes Mincle-mediated training of myeloid progenitors in the bone marrow[J]. Immunity, 2025, 58(2): 381-96. e9. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2024.12.012 |
| [29] | Subramanian S, Geng H, Tan X. Cell death of intestinal epithelial cells in intestinal diseases. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2020. 72(3): 308-24. |
| [30] | Zhao H, Liu T, Yang CE, et al. Poricoic acid A attenuates renal fibrosis by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis[J]. Braz J Med Biol Res, 2024, 57: e14249. doi:10.1590/1414-431x2024e14249 |
| [31] | Liu SS, Jiang TX, Bu F, et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying the BIRC6-mediated regulation of apoptosis and autophagy[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 891. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45222-1 |
| [32] | Langer R, Neppl C, Keller MD, et al. Expression analysis of autophagy related markers LC3B, p62 and HMGB1 indicate an autophagy-independent negative prognostic impact of high p62 expression in pulmonary squamous cell carcinomas[J]. Cancers: Basel, 2018, 10(9): E281. doi:10.3390/cancers10090281 |
| [33] | Cui Y, Cao X, Zhang Y, et al. Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 15 A (PPP1R15A) promoted the progression of gastric cancer by activating cell autophagy under energy stress[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2025, 44(1): 52. doi:10.1186/s13046-025-03320-y |
| [34] | Arab HH, Al-Shorbagy MY, Saad MA. Activation of autophagy and suppression of apoptosis by dapagliflozin attenuates experimental inflammatory bowel disease in rats: Targeting AMPK/mTOR, HMGB1/RAGE and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2021, 335: 109368. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109368 |
| [35] | Wang Y, Liu Z, Shu S, et al. AMPK/mTOR signaling in autophagy regulation during cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury[J]. Front Physiol, 2020, 11: 619730. doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.619730 |
| [36] | Liu H, Wang Q, Shi G, et al. Emodin ameliorates renal damage and podocyte injury in a rat model of diabetic nephropathy via regulating AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy signaling pathway[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes, 2021, 14: 1253-66. doi:10.2147/dmso.s299375 |
| [37] | Zafar H, Saier MH Jr. GutBacteroidesspecies in health and disease[J]. Gut Microbes, 2021, 13: 1848158. doi:10.1080/19490976.2020.1848158 |
| [1] | Xiaoyu CHANG, Hanwen ZHANG, Hongting CAO, Ling HOU, Xin MENG, Hong TAO, Yan LUO, Guanghua LI. Heat stress affects expression levels of circadian clock gene Bmal1 and cyclins in rat thoracic aortic endothelial cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1353-1362. |
| [2] | Weiyi LI, Lu JIANG, Zongxing ZHANG, Dan CHEN, Zhuoma BAO, Li HUANG, Lin YUAN. Qianggu Kangshu Formula attenuates osteoclast differentiation in rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting the HIF-1α/BNIP3 autophagy signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1389-1396. |
| [3] | Xinheng WANG, Xiaohan SHAO, Tongtong LI, Lu ZHANG, Qinjun YANG, Weidong YE, Jiabing TONG, Zegeng LI, Xiangming FANG. Pingchuanning Formula suppresses airway inflammation in a rat model of asthmatic cold syndrome by regulating the HMGB1/Beclin-1 axis-mediated autophagy [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1153-1162. |
| [4] | Yujia YANG, Lifang YANG, Yaling WU, Zhaoda DUAN, Chunze YU, Chunyun WU, Jianyun YU, Li YANG. Cannabidiol inhibits neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in rats with multiple concussions by regulating the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1240-1250. |
| [5] | Minzhu NIU, Lixia YIN, Tong QIAO, Lin YIN, Keni ZHANG, Jianguo HU, Chuanwang SONG, Zhijun GENG, Jing LI. Ecliptasaponin A ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice by suppressing M1 macrophage polarization via inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1297-1306. |
| [6] | Yue CHEN, Linyu XIAO, Lü REN, Xue SONG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. Monotropein improves motor function of mice with spinal cord injury by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to suppress neuronal apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 774-784. |
| [7] | Fei CHU, Xiaohua CHEN, Bowen SONG, Jingjing YANG, Lugen ZUO. Moslosooflavone ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by suppressing intestinal epithelium apoptosis via inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 819-828. |
| [8] | Yi ZHANG, Yu SHEN, Zhiqiang WAN, Song TAO, Yakui LIU, Shuanhu WANG. High expression of CDKN3 promotes migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating the p53/NF-κB signaling pathway and inhibiting cell apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [9] | Yanyan DONG, Kejing ZHANG, Jun CHU, Quangen CHU. Didang Decoction-medicated serum enhances autophagy in high glucose-induced rat glomerular endothelial cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 461-469. |
| [10] | Lixia YIN, Minzhu NIU, Keni ZHANG, Zhijun GENG, Jianguo HU, Jiangyan LI, Jing LI. Cimifugin ameliorates Crohn's disease-like colitis in mice by modulating Th-cell immune balance via inhibiting the MAPK pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 595-602. |
| [11] | Ming LIAO, Wenhua ZHONG, Ran ZHANG, Juan LIANG, Wentaorui XU, Wenjun WAN, Chao LI Shu WU. Protein C activator derived from snake venom protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells against hypoxia-reoxygenation injury by suppressing ROS via upregulating HIF-1α and BNIP3 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 614-621. |
| [12] | Di CHEN, Ying LÜ, Yixin GUO, Yirong ZHANG, Ruixuan WANG, Xiaoruo ZHOU, Yuxin CHEN, Xiaohui WU. Dihydroartemisinin enhances doxorubicin-induced apoptosis of triple negative breast cancer cells by negatively regulating the STAT3/HIF-1α pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 254-260. |
| [13] | Yu BIN, Ziwen LI, Suwei ZUO, Sinuo SUN, Min LI, Jiayin SONG, Xu LIN, Gang XUE, Jingfang WU. High expression of apolipoprotein C1 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells by activating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 359-370. |
| [14] | Jinzhi XIA, Yue CHEN, Lü REN, Jing LI, Xue SONG, Lu TAO, Jianguo HU. Kahweol improves motor function of mice with spinal cord injury by inhibiting microglial activation via regulating the IκBα/NF-κB pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2561-2572. |
| [15] | Siyu MA, Meiqing CHEN, Tianyu WU, Wenhong ZHAO. Dietary secoisolariciresinol diglucoside alleviates chronic kidney disease in offspring rats caused by maternal trans-fatty acid exposure by regulating the Bcl-2/Bax/caspase-3 signaling axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2658-2666. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||