Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1240-1250.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.13
Yujia YANG1( ), Lifang YANG1,2(
), Lifang YANG1,2( ), Yaling WU1, Zhaoda DUAN1, Chunze YU1, Chunyun WU1, Jianyun YU3(
), Yaling WU1, Zhaoda DUAN1, Chunze YU1, Chunyun WU1, Jianyun YU3( ), Li YANG1(
), Li YANG1( )
)
Received:2025-01-03
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-06-27
Contact:
Jianyun YU, Li YANG
E-mail:yujiayang1172@163.com;sophiay0717@163.com;jianyunyu@sina.com;yanglikm@163.com
Supported by:Yujia YANG, Lifang YANG, Yaling WU, Zhaoda DUAN, Chunze YU, Chunyun WU, Jianyun YU, Li YANG. Cannabidiol inhibits neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in rats with multiple concussions by regulating the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1240-1250.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.13
| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
PERK eIF2α CHOP | TACAGTGGACGGCGATGATG AAAGCTACTGCTGTGCTGGT CCTCGCTCTCCAGATTCCAG | CTGGGGTCCTCCTTACTGGA GTCGCAATGTAGTGCAGTGT AGCTGTGCCACTTTCCTCTC |
Tab.1 Primer sequence of qRT-PCR
| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
PERK eIF2α CHOP | TACAGTGGACGGCGATGATG AAAGCTACTGCTGTGCTGGT CCTCGCTCTCCAGATTCCAG | CTGGGGTCCTCCTTACTGGA GTCGCAATGTAGTGCAGTGT AGCTGTGCCACTTTCCTCTC |
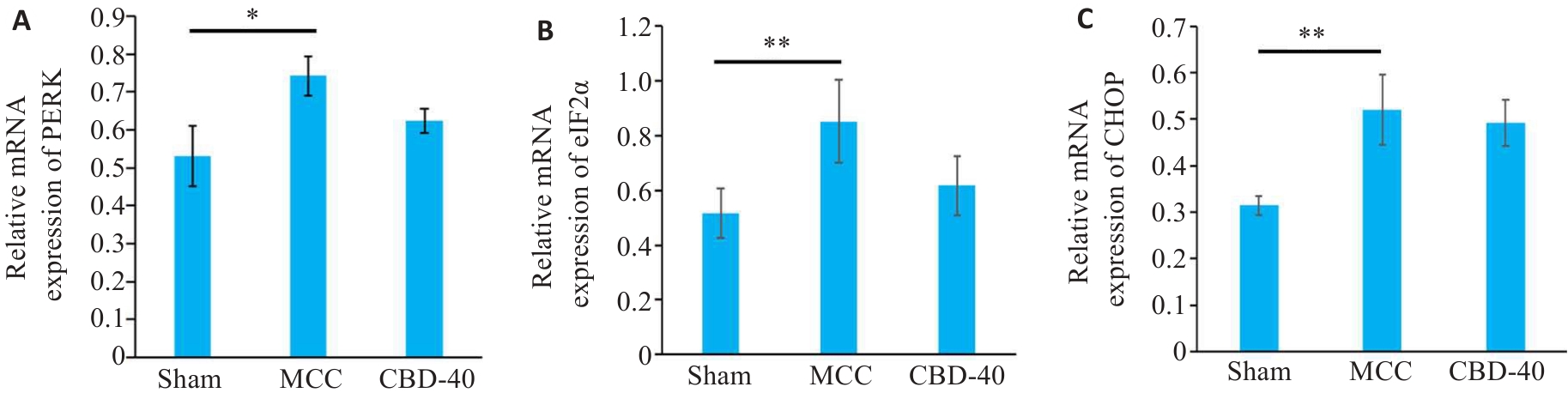
Fig.1 Changes of PERK (A), eIF2α (B) and CHOP (C) mRNA expressions levels in rat cerebral cortex after multiple concussion (MCC). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (n=3).
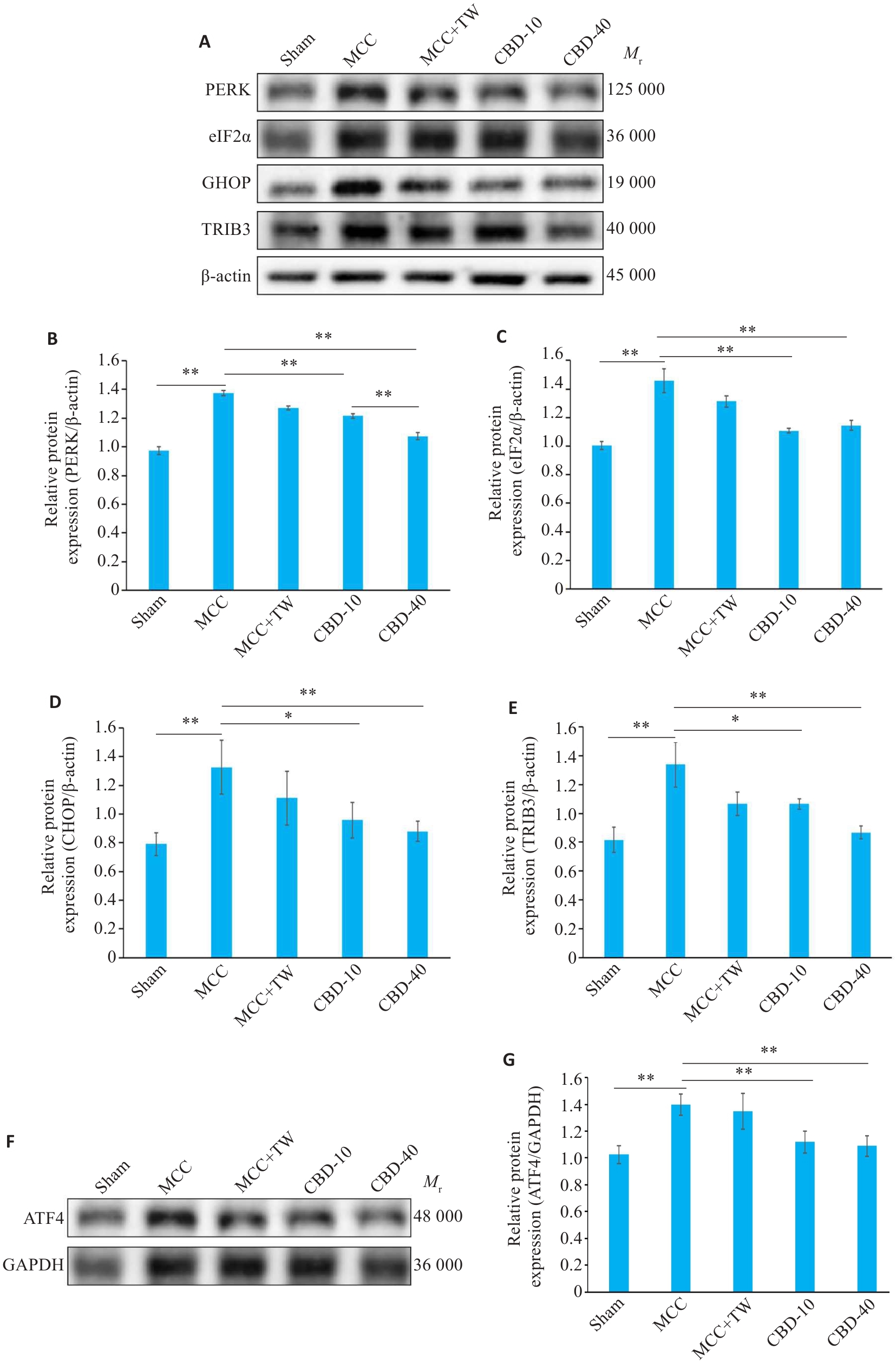
Fig.2 Protein expressions of PERK, eIF2α, CHOP, TRIB3 and ATF4 in the cerebral cortex of rats after MCC. A, F: Western blotting for detecting the taget proteins. B, C, D, E, G: Quantitative analysis of the expression levels of PERK, eIF2α, CHOP, TRIB3 and ATF4. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
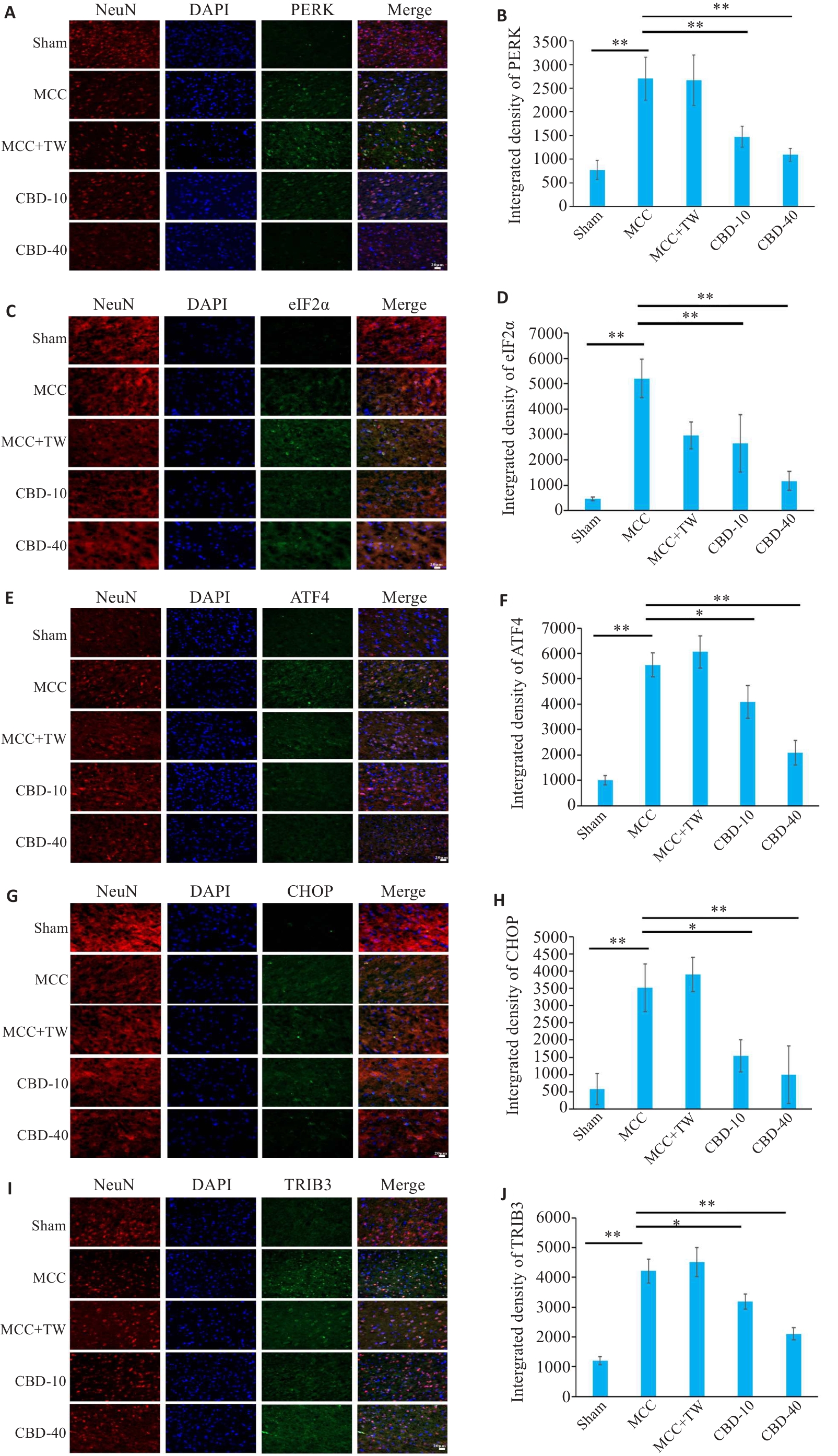
Fig.3 Immunofluorescence staining of PERK, eIF2α, ATF4, CHOP and TRIB3 in the cerebral cortex of rats after MCC. A, C, E, G, I: Immunofluorescence staining images of PERK, eIF2α, ATF4, CHOP and TRIB3, respectively (Original magnification: ×400). B, D, F, H, J: Quantitative analysis of PERK, eIF2α, ATF4, CHOP and TRIB3 expressions, respectively; *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
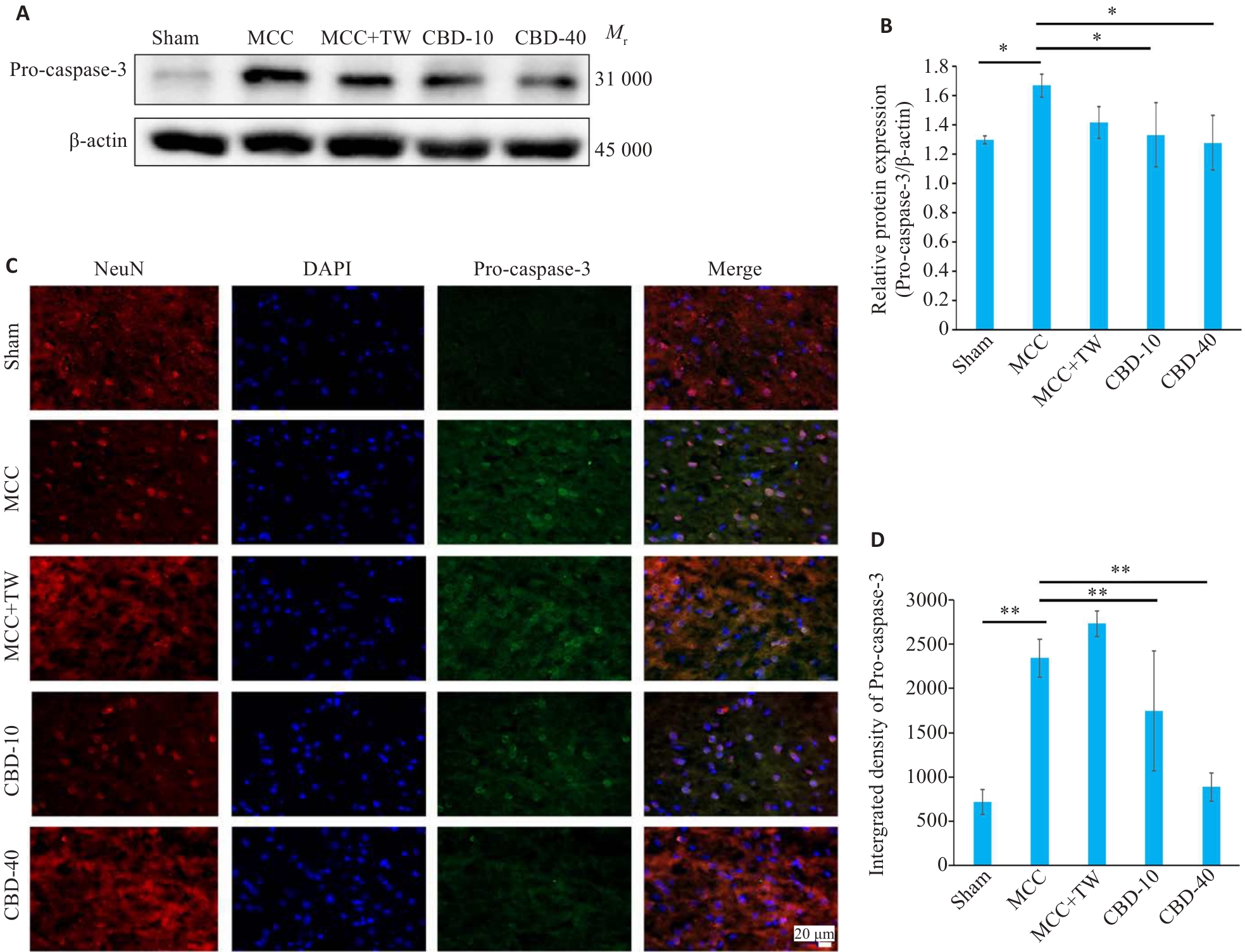
Fig.4 Expression of pro-caspase-3 in rat brain after MCC. A, B: Western blotting for analyzing pro-caspase-3 expression levels. C, D: Immunofluorescence double-label staining for detecting Pro-caspase-3 expression levels (scale bar=20 µm). *P<0.05, **P<0.01.

Fig.5 Expression of p-AKT in rat brain after MCC. A, B: Expression of p-AKT detected by Western blotting. C, D: Expression of p-AKT detected by immunofluorescence double-label staining (scale bar=20 µm). *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
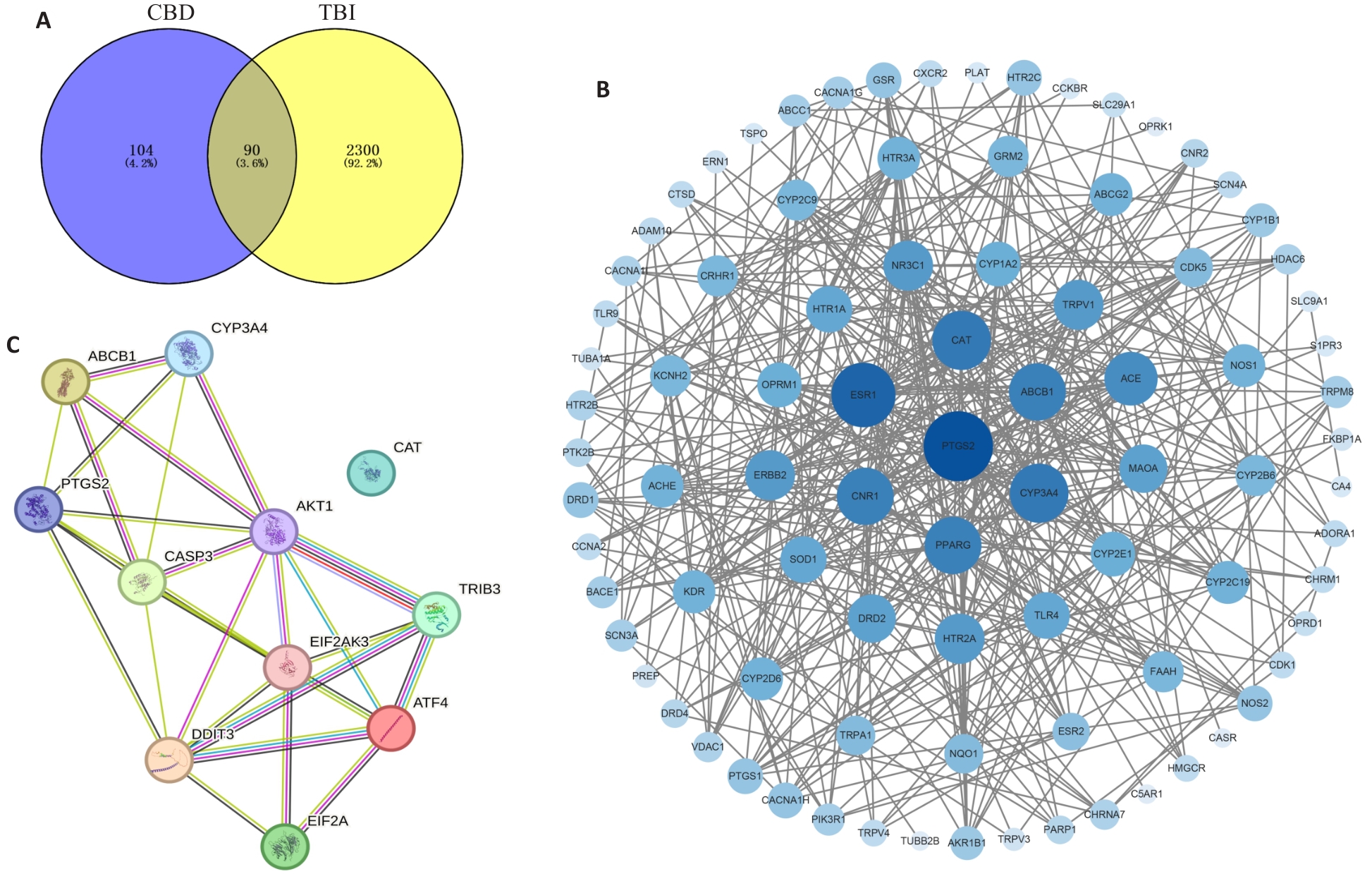
Fig.6 Venn map of network pharmacology analysis of CBD for treatment of traumatic brain injury (TBI) and the protein-protein interaction network. A: Venn diagram of CBD targets and TBI disease targets. B: Visualization of interactions between CBD and TBI intersection target proteins. C: Protein-protein interactions of the core targets of cannabidiol in treatment of TBI diseases with PERK, eIF2α, ATF4, CHOP, TRIB3, AKT, and caspase-3.
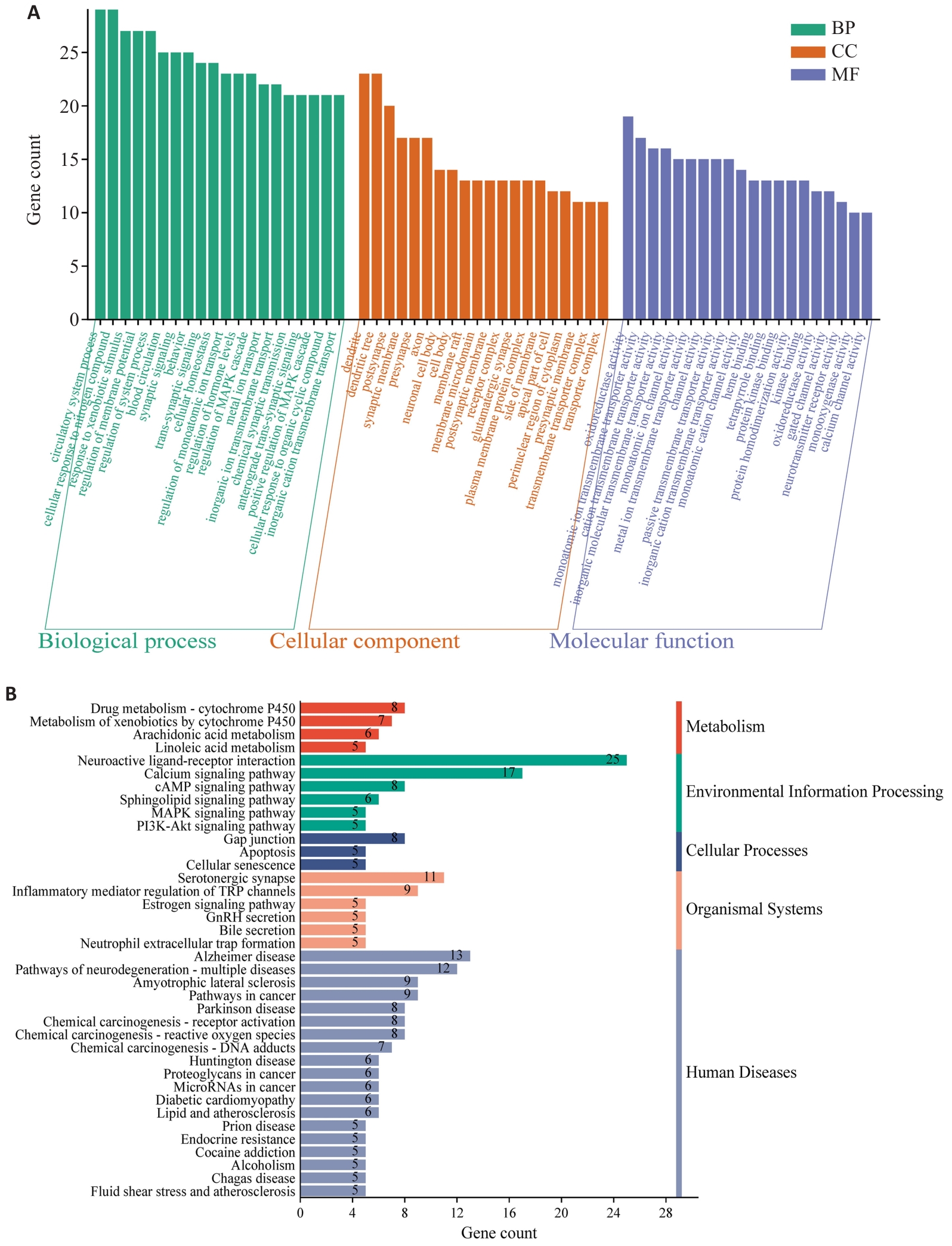
Fig.7 GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses of the potential targets of CBD in modulating TBI. A: GO enrichment analysis bubble chart. B: KEGG enrichment analysis bar chart.
| Protein | PDB ID | Ligands | Affinity (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
AKT PERK CHOP eIF2α caspase-3 TRIB3 ATF4 | 3oiw 4g31 2zfy 4v0x 3gjt 3gj0 4ut3 | CBD CBD CBD CBD CBD CBD CBD | -7.1 -6.91 -6.68 -6.2 -5.38 -4.68 -4.46 |
Tab.2 Moleculare docking binding energy of CBD with endoplasmic reticulum stress- and apoptosis-related proteins
| Protein | PDB ID | Ligands | Affinity (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
AKT PERK CHOP eIF2α caspase-3 TRIB3 ATF4 | 3oiw 4g31 2zfy 4v0x 3gjt 3gj0 4ut3 | CBD CBD CBD CBD CBD CBD CBD | -7.1 -6.91 -6.68 -6.2 -5.38 -4.68 -4.46 |

Fig.8 Molecular docking of CBD and endoplasmic reticulum stress- and apoptosis-related proteins AKT (A), PERK (B), CHOP (C), eIF2α (D), caspase-3 (E), TRIB3 (F) and ATF4 (G).
| 1 | Howell DR, Southard J. The molecular pathophysiology of concussion[J]. Clin Sports Med, 2021, 40(1): 39-51. doi:10.1016/j.csm.2020.08.001 |
| 2 | McGuire JL, Ngwenya LB, McCullumsmith RE. Neurotransmitter changes after traumatic brain injury: an update for new treatment strategies[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2019, 24(7): 995-1012. doi:10.1038/s41380-018-0239-6 |
| 3 | Galgano M, Toshkezi G, Qiu XC, et al. Traumatic brain injury: current treatment strategies and future endeavors[J]. Cell Transplant, 2017, 26(7): 1118-30. doi:10.1177/0963689717714102 |
| 4 | Kang X, Wang J, Yan LY. Endoplasmic reticulum in oocytes: spatiotemporal distribution and function[J]. J Assist Reprod Genet, 2023, 40(6): 1255-63. doi:10.1007/s10815-023-02782-3 |
| 5 | Ajoolabady A, Kaplowitz N, Lebeaupin C, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77(2): 619-39. doi:10.1002/hep.32562 |
| 6 | Di Conza G, Ho PC. ER stress responses: an emerging modulator for innate immunity[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(3): 695. doi:10.3390/cells9030695 |
| 7 | Chen S, Li X, Zhang XW, et al. PCV2 and PRV coinfection induces endoplasmic reticulum stress via PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP and IRE1-XBP1-EDEM pathways[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(9): 4479. doi:10.3390/ijms23094479 |
| 8 | Xia SH, Wu JW, Zhou WD, et al. HRC promotes anoikis resistance and metastasis by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2021, 18(14): 3112-24. doi:10.7150/ijms.60610 |
| 9 | Paccosi E, Balzerano A, Proietti-De-Santis L. Interfering with the ubiquitin-mediated regulation of Akt as a strategy for cancer treatment[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(3): 2809. doi:10.3390/ijms24032809 |
| 10 | Khezri MR, Ghasemnejad-Berenji M, Moloodsouri D. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and Caspase-3 in alzheimer's disease: Which one Is the beginner[J]? J Alzheimers Dis, 2023, 92(2): 391-3. doi:10.3233/jad-221157 |
| 11 | 曹珍珍, 于建云, 李娟娟, 等. 一重和三重脑震荡大鼠脑固缩的神经细胞定量变化研究[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2013, 34(7): 12-6. |
| 12 | Zhang H, Zhang ZG, Wang Z, et al. Research on the changes in balance motion behavior and learning, as well as memory abilities of rats with multiple cerebral concussion-induced chronic traumatic encephalopathy and the underlying mechanism[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2018, 16(3): 2295-302. doi:10.3892/etm.2018.6474 |
| 13 | Wang L, Wu XH, Yang G, et al. Cannabidiol alleviates the damage to dopaminergic neurons in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydro-pyridine-induced Parkinson's disease mice via regulating neuronal apoptosis and neuroinflammation[J]. Neuroscience, 2022, 498: 64-72. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.06.036 |
| 14 | Castillo-Arellano J, Canseco-Alba A, Cutler SJ, et al. The polypharmacological effects of cannabidiol[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(7): 3271. doi:10.3390/molecules28073271 |
| 15 | Song H, Xu LC, Zhang RP, et al. Rosemary extract improves cognitive deficits in a rats model of repetitive mild traumatic brain injury associated with reduction of astrocytosis and neuronal degeneration in hippocampus[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2016, 622: 95-101. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2016.04.048 |
| 16 | Sun DD, Wang JH, Liu XL, et al. Dexmedetomidine attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and improves neuronal function after traumatic brain injury in mice[J]. Brain Res, 2020, 1732: 146682. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2020.146682 |
| 17 | Ruan Z, Lu Q, Wang JE, et al. MIF promotes neurodegeneration and cell death via its nuclease activity following traumatic brain injury[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2021, 79(1): 39. doi:10.1007/s00018-021-04037-9 |
| 18 | Yang YY, Lu DF, Wang MH, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response: emerging regulators in progression of traumatic brain injury[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2024, 15(2): 156. doi:10.1038/s41419-024-06515-x |
| 19 | Davis CK, Bathula S, Hsu M, et al. An antioxidant and anti-ER stress combo therapy decreases inflammation, secondary brain damage and promotes neurological recovery following traumatic brain injury in mice[J]. J Neurosci, 2022, 42(35): 6810-21. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.0212-22.2022 |
| 20 | Ghemrawi R, Khair M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and unfolded protein response in neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(17): 6127. doi:10.3390/ijms21176127 |
| 21 | 陈乃洁, 林 瑶, 许 茜, 等. 基于PERK-eIF2α通路探讨苁蓉舒痉颗粒对帕金森病模型大鼠黑质纹状体内质网应激的调节作用 [J]. 福建中医药, 2023, 54(8): 18-22. |
| 22 | Jiang W, Dong W, Li M, et al. Nitric oxide induces immunogenic cell death and potentiates cancer immunotherapy[J]. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(3): 3881-94. doi:10.1021/acsnano.1c09048 |
| 23 | 费慧芝. CTRP1改善脑缺血再灌注致神经元损伤及机制研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆医科大学, 2021. |
| 24 | Meng Y, Xu XJ, Niu D, et al. Organophosphate flame retardants induce oxidative stress and Chop/Caspase 3-related apoptosis via Sod1/p53/Map3k6/Fkbp5 in NCI-1975 cells[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2022, 819: 153160. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153160 |
| 25 | 刘殿雷, 龙景培, 卜贺启, 等. 冬凌草甲素通过内质网应激诱导胰腺癌细胞凋亡的研究[J]. 中草药, 2022, 53(15): 4773-80. |
| 26 | 朱 宝, 李 国, 王兰清. 米索前列醇抑制内质网应激减轻脊髓损伤小鼠神经细胞凋亡[J]. 解剖科学进展, 2023, 29(4): 337-40. |
| 27 | Song MQ, Bode AM, Dong ZG, et al. AKT as a therapeutic target for cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2019, 79(6): 1019-31. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-18-2738 |
| 28 | Fan J, Du JX, Zhang ZW, et al. The protective effects of hydrogen sulfide new donor methyl S-(4-fluorobenzyl)- N-(3, 4, 5-trimethoxybenzoyl)-l-cysteinate on the ischemic stroke[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(5): 1554. doi:10.3390/molecules27051554 |
| 29 | Zhao Y, Han Y, Bu DF, et al. Reduced AKT phosphorylation contributes to endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated hippocampal neuronal apoptosis in rat recurrent febrile seizure[J]. Life Sci, 2016, 153: 153-62. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2016.04.008 |
| 30 | Blaskovich MAT, Kavanagh AM, Elliott AG, et al. The antimicrobial potential of cannabidiol[J]. Commun Biol, 2021, 4(1): 7. doi:10.1038/s42003-020-01530-y |
| 31 | Patel V, Abu-Hijleh F, Rigg N, et al. Cannabidiol protects striatal neurons by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res, 2023, 8(2): 299-308. |
| 32 | 杨丽芳, 于春泽, 张先俊, 等. 大麻二酚对大鼠多重脑震荡炎症反应的抑制作用 [J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志, 2024, 42(3): 278-83. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||