Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 2350-2357.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.11.07
Xiaoyuan LI1( ), Yiyue ZHANG1, Yucheng GU1, Nihong CHEN2, Xinyu QIAN1, Pengjun ZHANG1, Jiaxin HAO3, Feng WANG1(
), Yiyue ZHANG1, Yucheng GU1, Nihong CHEN2, Xinyu QIAN1, Pengjun ZHANG1, Jiaxin HAO3, Feng WANG1( )
)
Received:2025-07-03
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-11-28
Contact:
Feng WANG
E-mail:xiaoyuanlee0317@foxmail.com;fengwangcn@hotmail.com
Xiaoyuan LI, Yiyue ZHANG, Yucheng GU, Nihong CHEN, Xinyu QIAN, Pengjun ZHANG, Jiaxin HAO, Feng WANG. Association between Tau protein deposition and brain metabolites: N-acetylaspartate and creatine as potential biomarkers for advanced Alzheimer's disease[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(11): 2350-2357.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.11.07
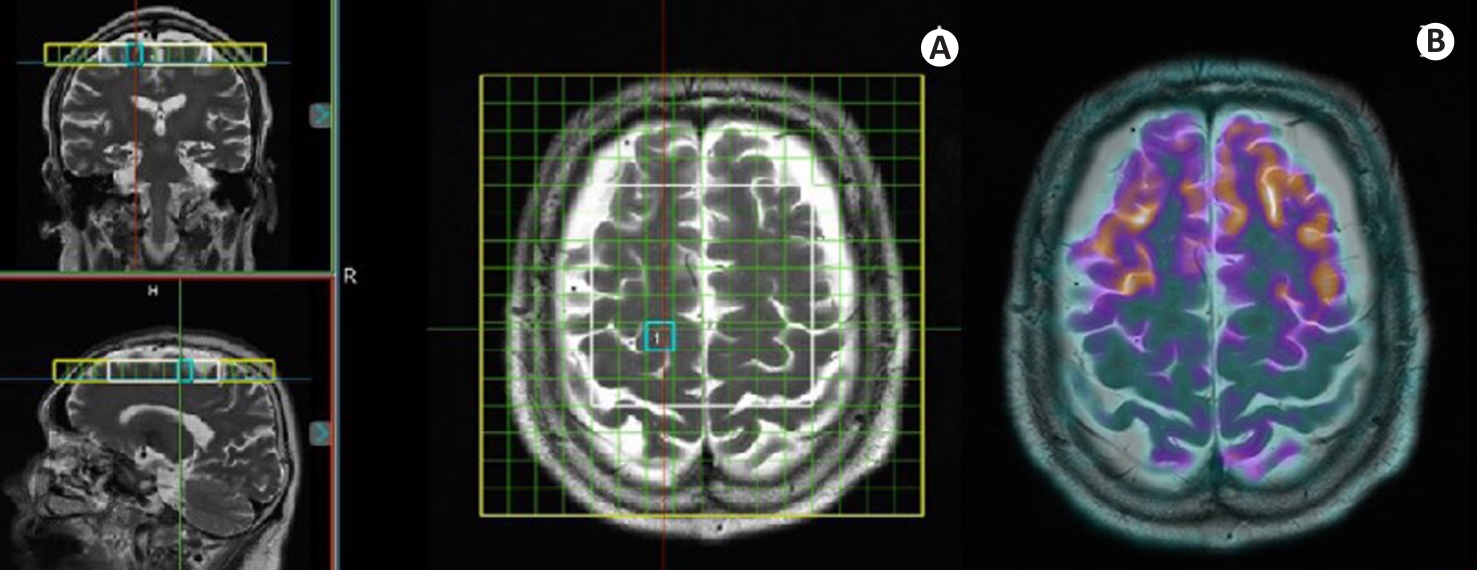
Fig.1 PET/MRS imaging of a female AD patient (76 years old, education years: 0; MMSE: 0; MoCa: 0; CDR: 3). A: Coronal, sagittal, and axial localization images of MRS acquisition site, where the yellow box indicates the homogenization region, the white box denotes the MRS acquisition area, and the blue box outlines the selected voxel. B: Co-registered PET/MR fusion image at the same level as the MRS acquisition.
| Variables | PT group (n=64) | HC group (n=29) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (male/female, n) | 25/39 | 13/16 | 0.767 |
| Age (year) | 68.48±8.98 | 61.53±9.81 | 0.382 |
| Education years (year) | 9.46±3.56 | 11.94±3.05 | 0.440 |
| MMSE score (point) | 19.45±7.55 | 28.59±1.45 | <0.001 |
| MoCA score (point) | 15.63±7.61 | 26.66±2.83 | <0.001 |
| CDR score (point) | 0.96±0.70 | 0.02±0.09 | <0.001 |
Tab.1 Comparison of clinical information of the AD patients (PT group) and the healthy control (HC) group (Mean±SD)
| Variables | PT group (n=64) | HC group (n=29) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (male/female, n) | 25/39 | 13/16 | 0.767 |
| Age (year) | 68.48±8.98 | 61.53±9.81 | 0.382 |
| Education years (year) | 9.46±3.56 | 11.94±3.05 | 0.440 |
| MMSE score (point) | 19.45±7.55 | 28.59±1.45 | <0.001 |
| MoCA score (point) | 15.63±7.61 | 26.66±2.83 | <0.001 |
| CDR score (point) | 0.96±0.70 | 0.02±0.09 | <0.001 |
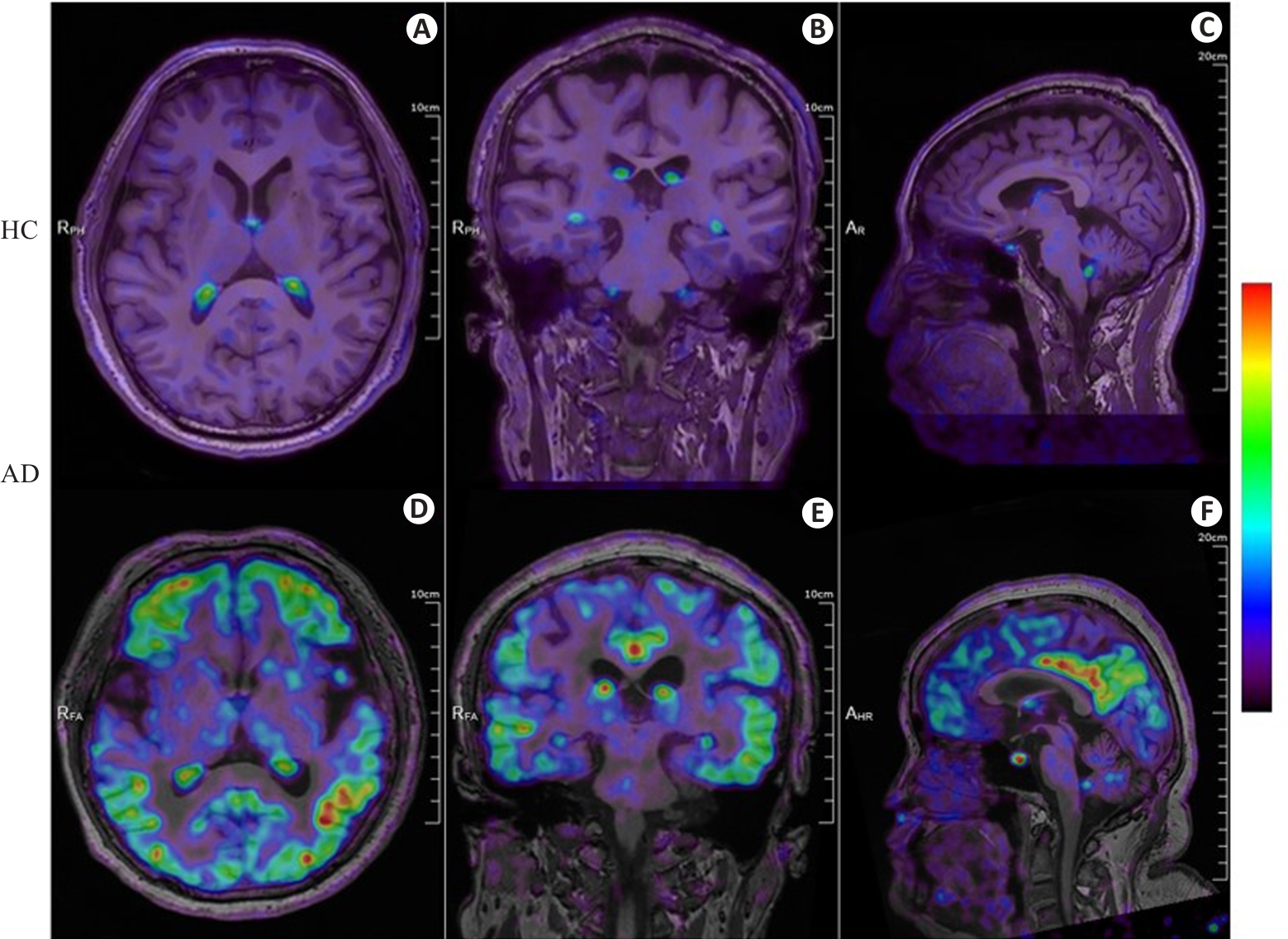
Fig.2 18F-APN-1607 PET/MR fusion imaging of a healthy control individual and an AD patient. A-C: Axial, coronal, and sagittal PET/MR fusion images of the brain of a male healthy control individual (72 years old, education years: 12; MMSE: 28, MoCa: 29; CDR: 0), showing physiological uptake in the choroid plexus without significant deposition of Tau protein in the remaining cerebrum and cerebellum. D-F: Axial, coronal, and sagittal PET/MR fusion images of the brain of a female AD patient (58 years old, education years: 12; MMSE: 5; MoCa: 2; CDR: 2) with diffuse and heterogeneous Tau protein deposition in the bilateral frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital cortical regions. The color bar in the figure represents SUV.
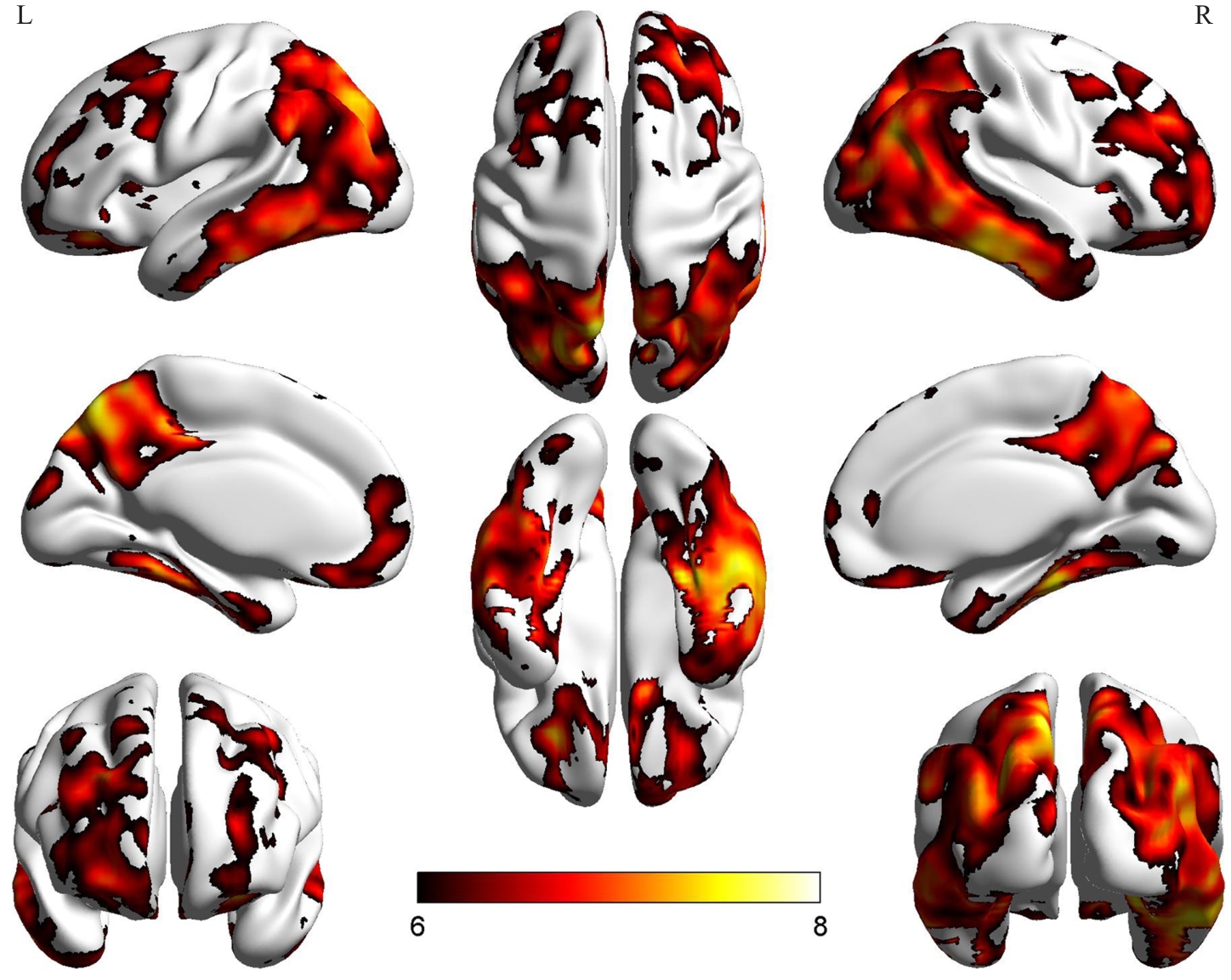
Fig.3 Regions of significantly increased Tau protein deposition in the PT group as determined by voxel-based analysis methods. The color bar in the figure represents the statistical t-values; L: Left cerebral hemisphere; R: Right cerebral hemisphere.
| Variables | PT group | HC group | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel (n) | 1422 | 814 | - |
| Cr | 29.02±12.07 | 28.97±10.71 | 0.063 |
| Cho | 24.58±11.16 | 24.47±11.40 | 0.829 |
| NAA | 45.02±20.54 | 47.03±18.84 | 0.022 |
| Cho/Cr | 0.856±0.239 | 0.864±0.219 | 0.406 |
| NAA/Cr | 1.660±0.663 | 1.742±0.564 | 0.065 |
| SUVr | 1.604±0.877 | 0.902±0.212 | <0.001 |
Tab.2 Inter-group comparison of metabolite levels (or ratios) and Tau PET standardized uptake values between PT group and HC group (Mean±SD)
| Variables | PT group | HC group | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel (n) | 1422 | 814 | - |
| Cr | 29.02±12.07 | 28.97±10.71 | 0.063 |
| Cho | 24.58±11.16 | 24.47±11.40 | 0.829 |
| NAA | 45.02±20.54 | 47.03±18.84 | 0.022 |
| Cho/Cr | 0.856±0.239 | 0.864±0.219 | 0.406 |
| NAA/Cr | 1.660±0.663 | 1.742±0.564 | 0.065 |
| SUVr | 1.604±0.877 | 0.902±0.212 | <0.001 |
| Variables | Tau+voxel | Tau-voxel | HC voxel | P | P1 | P2 | P3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel (n) | 994 | 428 | 814 | - | - | - | |
| Cr | 27.11±11.92 | 29.84±12.05 | 28.97±10.71 | <0.001 | 0.004 | 0.495 | <0.001 |
| Cho | 24.90±10.92 | 23.82±11.66 | 24.47±11.40 | 0.242 | - | - | - |
| NAA | 45.82±20.17 | 43.17±21.28 | 47.03±18.84 | 0.005 | 0.596 | 0.004 | 0.065 |
| Cho/Cr | 0.844±0.246 | 0.882±0.209 | 0.864±0.219 | 0.014 | 0.212 | 0.592 | 0.015 |
| NAA/Cr | 1.676±1.380 | 1.622±0.588 | 1.742±0.564 | 0.119 | - | - | - |
| SUVr | 1.921±0.871 | 0.870±0.149 | 0.902±0.212 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.999 | <0.001 |
Tab.3 Inter-group comparison of metabolite levels (or ratios) and Tau PET SUVr following subgrouping of PT group voxels (Mean±SD)
| Variables | Tau+voxel | Tau-voxel | HC voxel | P | P1 | P2 | P3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel (n) | 994 | 428 | 814 | - | - | - | |
| Cr | 27.11±11.92 | 29.84±12.05 | 28.97±10.71 | <0.001 | 0.004 | 0.495 | <0.001 |
| Cho | 24.90±10.92 | 23.82±11.66 | 24.47±11.40 | 0.242 | - | - | - |
| NAA | 45.82±20.17 | 43.17±21.28 | 47.03±18.84 | 0.005 | 0.596 | 0.004 | 0.065 |
| Cho/Cr | 0.844±0.246 | 0.882±0.209 | 0.864±0.219 | 0.014 | 0.212 | 0.592 | 0.015 |
| NAA/Cr | 1.676±1.380 | 1.622±0.588 | 1.742±0.564 | 0.119 | - | - | - |
| SUVr | 1.921±0.871 | 0.870±0.149 | 0.902±0.212 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.999 | <0.001 |
| Variables | r | P |
|---|---|---|
| Cr | -0.161 | <0.001 |
| Cho | -0.176 | <0.001 |
| NAA | -0.200 | <0.001 |
| Cho/Cr | -0.058 | 0.787 |
| NAA/Cr | -0.009 | 0.069 |
Tab.4 Correlation analysis of metabolite levels (or ratios) and Tau PET SUVr in Tau+ voxel
| Variables | r | P |
|---|---|---|
| Cr | -0.161 | <0.001 |
| Cho | -0.176 | <0.001 |
| NAA | -0.200 | <0.001 |
| Cho/Cr | -0.058 | 0.787 |
| NAA/Cr | -0.009 | 0.069 |

Fig.4 1H-MRS metabolite heatmap and 18F-APN-1607 PET/MR fusion image of an AD patient. A-E: Heat maps of NAA, Cho, Cr, NAA/Cr, and Cho/Cr, respectively. F:18F-APN-1607 PET/MR fusion image of the AD patient (female, 58 years old, education years: 12; MMSE: 5; MoCa: 2; CDR: 2). NAA, Cho and Cr are lower in the Tau protein deposition area, while NAA/Cr and Cho/Cr showed no significant differences between the Tau protein deposition area and the non-Tau protein deposition area.
| [1] | Gin A, Nguyen PD, Serrano G, et al. Towards early diagnosis and screening of Alzheimer's disease using frequency locked whispering gallery mode microtoroid biosensors[J]. Res Sq, 2024: rs.3.rs-4355995. doi:10.1038/s44328-024-00009-8 |
| [2] | Peretti DE, Boccalini C, Ribaldi F, et al. Association of glial fibrillary acid protein, Alzheimer's disease pathology and cognitive decline[J]. Brain, 2024, 147(12): 4094-104. doi:10.1093/brain/awae211 |
| [3] | CliffordJr Jack, , Andrews JS, Beach TG, et al. Revised criteria for diagnosis and staging of Alzheimer's disease: Alzheimer's Association Workgroup[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2024, 20(8): 5143-69. doi:10.1002/alz.13859 |
| [4] | Lu JY, Wang J, Wu J, et al. Pilot implementation of the revised criteria for staging of Alzheimer's disease by the Alzheimer's Association Workgroup in a tertiary memory clinic[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2024, 20(11): 7831-46. doi:10.1002/alz.14245 |
| [5] | Tahami Monfared AA, Byrnes MJ, White LA, et al. Alzheimer's disease: epidemiology and clinical progression[J]. Neurol Ther, 2022, 11(2): 553-69. doi:10.1007/s40120-022-00338-8 |
| [6] | Scheltens P, De Strooper B, Kivipelto M, et al. Alzheimer's disease[J]. Lancet, 2021, 397(10284): 1577-90. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)32205-4 |
| [7] | Stelzl LS, Pietrek LM, Holla A, et al. Global structure of the intrinsically disordered protein tau emerges from its local structure[J]. JACS Au, 2022, 2(3): 673-86. doi:10.1021/jacsau.1c00536 |
| [8] | Zhao LH, Teng JL, Mai W, et al. A pilot study on the cutoff value of related brain metabolite in Chinese elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment using MRS[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2021, 13: 617611. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2021.617611 |
| [9] | Valatkevičienė K, Levin O, Šarkinaitė M, et al. N-acetyl-aspartate and myo-inositol as markers of white matter microstructural organization in mild cognitive impairment: evidence from a DTI-1H-MRS pilot study[J]. Diagnostics (Basel), 2023, 13(4): 654. doi:10.3390/diagnostics13040654 |
| [10] | Kara F, Joers JM, Deelchand DK, et al. 1H MR spectroscopy biomarkers of neuronal and synaptic function are associated with tau deposition in cognitively unimpaired older adults[J]. Neurobiol Aging, 2022, 112: 16-26. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2021.12.010 |
| [11] | Li L, Liu FT, Li M, et al. Clinical utility of 18F-APN-1607 tau PET imaging in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy[J]. Mov Disord, 2021, 36(10): 2314-23. doi:10.1002/mds.28672 |
| [12] | Krix S, Wilczynski E, Falgàs N, et al. Towards early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: advances in immune-related blood biomarkers and computational approaches[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1343900. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1343900 |
| [13] | Chang Y, Liu JJ, Xu XD, et al. Subcortical tau deposition and plasma glial fibrillary acidic protein as predictors of cognitive decline in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2025, 52(4): 1496-509. doi:10.1007/s00259-024-07016-x |
| [14] | 鲁佳荧, 蒋皆恢, 王 敏, 等. 阿尔茨海默病患者脑内tau蛋白分布与认知组分相关性的PET显像研究[J]. 中国临床神经科学, 2020, 28(4): 396-404. |
| [15] | Qiao Z, Wang GH, Zhao XB, et al. Neuropsychological performance is correlated with tau protein deposition and glucose metabolism in patients with Alzheimer's disease[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2022, 14: 841942. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2022.841942 |
| [16] | Xu XJ, Ruan WW, Liu F, et al. 18F-APN-1607 tau positron emission tomography imaging for evaluating disease progression in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2022, 13: 789054. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2021.789054 |
| [17] | Matthews DC, Kinney JW, Ritter A, et al. Relationships between plasma biomarkers, tau PET, FDG PET, and volumetric MRI in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease patients[J]. Alzheimers Dement (N Y), 2024, 10(3): e12490. doi:10.1002/trc2.12490 |
| [18] | Ye JW, Wan HL, Chen SH, et al. Targeting tau in Alzheimer's disease: from mechanisms to clinical therapy[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2024, 19(7): 1489-98. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.385847 |
| [19] | Waheed Z, Choudhary J, Jatala FH, et al. The role of tau proteoforms in health and disease[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2023, 60(9): 5155-66. doi:10.1007/s12035-023-03387-8 |
| [20] | Zhang SM, Crossley CA, Yuan Q. Neuronal vulnerability of the entorhinal cortex to tau pathology in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Br J Biomed Sci, 2024, 81: 13169. doi:10.3389/bjbs.2024.13169 |
| [21] | Hu JX, Sha WC, Yuan SS, et al. Aggregation, transmission, and toxicity of the microtubule-associated protein tau: a complex comprehension[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(19): 15023. doi:10.3390/ijms241915023 |
| [22] | Wang M, Wei M, Wang LY, et al. Tau protein accumulation trajectory-based brain age prediction in the Alzheimer's disease continuum[J]. Brain Sci, 2024, 14(6): 575. doi:10.3390/brainsci14060575 |
| [23] | Stouffer KM, Chen C, Kulason S, et al. Early amygdala and ERC atrophy linked to 3D reconstruction of rostral neurofibrillary tau tangle pathology in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Neuroimage Clin, 2023, 38: 103374. doi:10.1016/j.nicl.2023.103374 |
| [24] | Ma D, Fetahu IS, Wang M, et al. The fusiform gyrus exhibits an epigenetic signature for Alzheimer's disease[J]. Clin Epigenetics, 2020, 12(1): 129. doi:10.1186/s13148-020-00916-3 |
| [25] | Hu JL, Zhang M, Zhang YY, et al. Neurometabolic topography and associations with cognition in Alzheimer's disease: a whole-brain high-resolution 3D MRSI study[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2024, 20(9): 6407-22. doi:10.1002/alz.14137 |
| [26] | Zhang M, Hu JL, Zhang YY, et al. Associations between Aβ deposition and neurometabolic alterations in Alzheimer's disease: Insights from hybrid 3D MRSI-PET imaging[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2025, 21(6): e70332. doi:10.1002/alz.70332 |
| [27] | Sheikh-Bahaei N, Chen M, Pappas I. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2024, 2785: 115-42. doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-3774-6_9 |
| [28] | Kara F, Kantarci K. Understanding proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy neurochemical changes using Alzheimer's disease biofluid, PET, postmortem pathology biomarkers, and APOE genotype[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(18): 10064. doi:10.3390/ijms251810064 |
| [29] | Muñoz-Castro C, Serrano-Pozo A. Astrocyte-neuron interactions in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Adv Neurobiol, 2024, 39: 345-82. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-64839-7_14 |
| [30] | Singh S, Khan S, Shahid M, et al. Targeting tau in Alzheimer's and beyond: insights into pathology and therapeutic strategies[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2025, 104: 102639. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2024.102639 |
| [31] | Olešová D, Dobešová D, Majerová P, et al. Changes in lipid metabolism track with the progression of neurofibrillary pathology in tauopathies[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2024, 21(1): 78. doi:10.1186/s12974-024-03060-4 |
| [32] | Živanović M, Aracki Trenkić A, Milošević V, et al. The role of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis and prognosis of dementia[J]. Biomol Biomed, 2023, 23(2): 209-24. doi:10.17305/bjbms.2022.8085 |
| [33] | Abbaspour F, Mohammadi N, Amiri H, et al. Applications of magnetic resonance spectroscopy in diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases: a systematic review[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(9): e30521. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30521 |
| [34] | Matsuoka K, Hirata K, Kokubo N, et al. Investigating neural dysfunction with abnormal protein deposition in Alzheimer's disease through magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging, plasma biomarkers, and positron emission tomography[J]. Neuroimage Clin, 2024, 41: 103560. doi:10.1016/j.nicl.2023.103560 |
| [1] | ZHONG Lei1,2, TAN Jie2, OUYANG Shi1, XU Jiang-ping1 1Department of Neurology, Wuhan General Hospital of Guangzhou Command, Wuhan 430070, China; 2Department of Pharmacology, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China; 3Third Department of Internal Medicine, 94 Hospital of PLA, Nanchang 330002, China. Effects of Saponin B from Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bunge on tau hyperphosphorylation induced by beta-amyloid peptide (25-35) in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2006, 26(08): 1106-1109. |
| [2] | CHU Wen-zheng, QIAN Cai-yun. Expressions of Aβ1-40, Aβ1-42, tau202, tau396 and tau404 after intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2005, 25(02): 168-170,173. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||