南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 954-961.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.05.07
收稿日期:2024-09-23
出版日期:2025-05-20
发布日期:2025-05-23
通讯作者:
周毅波
E-mail:41274931@qq.com;boyi365@163.com
作者简介:曾玉梅,主任医师,E-mail: 41274931@qq.com
基金资助:
Yumei ZENG1( ), Jike LI2, Zhongxi HUANG2, Yibo ZHOU3(
), Jike LI2, Zhongxi HUANG2, Yibo ZHOU3( )
)
Received:2024-09-23
Online:2025-05-20
Published:2025-05-23
Contact:
Yibo ZHOU
E-mail:41274931@qq.com;boyi365@163.com
摘要:
目的 探索绒毛样蛋白VILL抑制鼻咽癌增殖的分子机制。 方法 收集136例鼻咽癌和67例鼻咽非癌组织,采用免疫共沉淀(CO-IP)、质谱、Western blotting、免疫荧光和GST pull down实验在鼻咽癌细胞株中筛查并验证VILL相互作用丰度最高蛋白。采用转基因实验,在体外(鼻咽癌细胞株)和体内(裸鼠)验证VILL与靶蛋白对鼻咽癌增殖的调控作用。采用免疫组化实验在临床组织标本中验证VILL与靶蛋白表达水平与鼻咽癌临床特征的相关性。 结果 在鼻咽癌细胞(HONE1 EBV、S18)中,VILL与E3泛素连接酶LMO7相互作用的丰度最高,二者共定位于细胞浆,直接相互作用。过表达LMO7部分逆转VILL对鼻咽癌细胞增殖的抑制作用。与67例鼻咽非癌组织比较,VILL表达在136例鼻咽癌组织中下调(P<0.0001)且与临床T分期(P=0.04)、N分期(P=0.01)和M分期(P=0.013)显著相关,而LMO7在鼻咽癌普遍高表达。 结论 VILL可能通过抑制LMO7的促癌功能而抑制鼻咽癌增殖。
曾玉梅, 李继科, 黄仲曦, 周毅波. 绒毛样蛋白VILL通过与LMO7蛋白相互作用抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 954-961.
Yumei ZENG, Jike LI, Zhongxi HUANG, Yibo ZHOU. Villin-like protein VILL suppresses proliferation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by interacting with LMO7 protein[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 954-961.
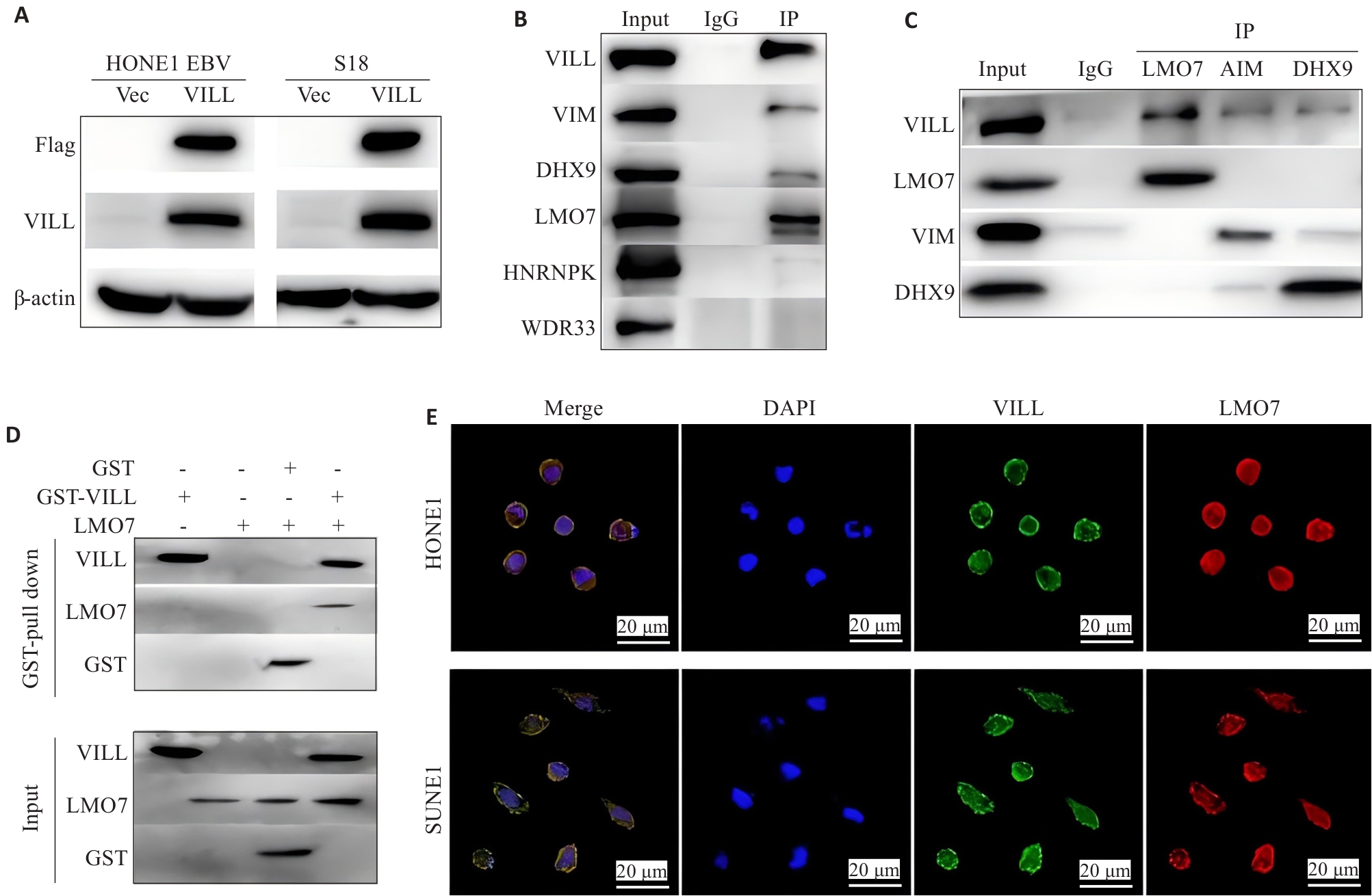
图1 LMO7与VILL蛋白直接相互作用
Fig.1 LMO7 directly interacts with VILL protein. A: Verification of successful construction of NPC cell lines (HONE1-EBV and S18) overexpressing VILL+Flag. B: CO-IP assay and Western blotting, using VILL as the bait, for verification of the proteins interacting with VILL. C: CO-IP assay and Western blotting, using LMO7, VIM and DHX9 as the decoys, for verification of the proteins interacting with VILL. D: GST-pull down experiment for verifying direct interaction between LMO7 and VILL. E: Immunofluorescence assay showing co-localization of LMO7 and VILL in NPC cell lines (HONE1 and SUNE1).
| Gene | hit_num | Score | Matches | Sequences | Cover | pi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MYH3 | 2 | 1770 | 58 | 34 | 19.5 | 5.62 |
| ACTB | 8 | 642 | 39 | 12 | 35.8 | 5.23 |
| PLEC | 13 | 524 | 23 | 23 | 5.6 | 5.74 |
| HNRNPK | 14 | 522 | 20 | 10 | 22.5 | 5.39 |
| ACTN2 | 17 | 463 | 17 | 12 | 17 | 5.31 |
| DHX9 | 19 | 419 | 25 | 20 | 16.4 | 6.41 |
| LMO7 | 21 | 398 | 21 | 10 | 16.9 | 8.73 |
| VIM | 22 | 394 | 17 | 12 | 28.5 | 5.06 |
| PABPC1 | 24 | 374 | 14 | 11 | 18.6 | 9.52 |
| RCN1 | 27 | 345 | 14 | 8 | 19.3 | 4.86 |
| DDX3X | 32 | 286 | 14 | 9 | 14.2 | 6.73 |
| DDX5 | 54 | 180 | 7 | 5 | 6.5 | 5.25 |
表1 质谱预测与VILL发生相互作用的蛋白
Tab.1 Proteins predicted to interact with villin-like protein VILL by mass spectrometry
| Gene | hit_num | Score | Matches | Sequences | Cover | pi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MYH3 | 2 | 1770 | 58 | 34 | 19.5 | 5.62 |
| ACTB | 8 | 642 | 39 | 12 | 35.8 | 5.23 |
| PLEC | 13 | 524 | 23 | 23 | 5.6 | 5.74 |
| HNRNPK | 14 | 522 | 20 | 10 | 22.5 | 5.39 |
| ACTN2 | 17 | 463 | 17 | 12 | 17 | 5.31 |
| DHX9 | 19 | 419 | 25 | 20 | 16.4 | 6.41 |
| LMO7 | 21 | 398 | 21 | 10 | 16.9 | 8.73 |
| VIM | 22 | 394 | 17 | 12 | 28.5 | 5.06 |
| PABPC1 | 24 | 374 | 14 | 11 | 18.6 | 9.52 |
| RCN1 | 27 | 345 | 14 | 8 | 19.3 | 4.86 |
| DDX3X | 32 | 286 | 14 | 9 | 14.2 | 6.73 |
| DDX5 | 54 | 180 | 7 | 5 | 6.5 | 5.25 |
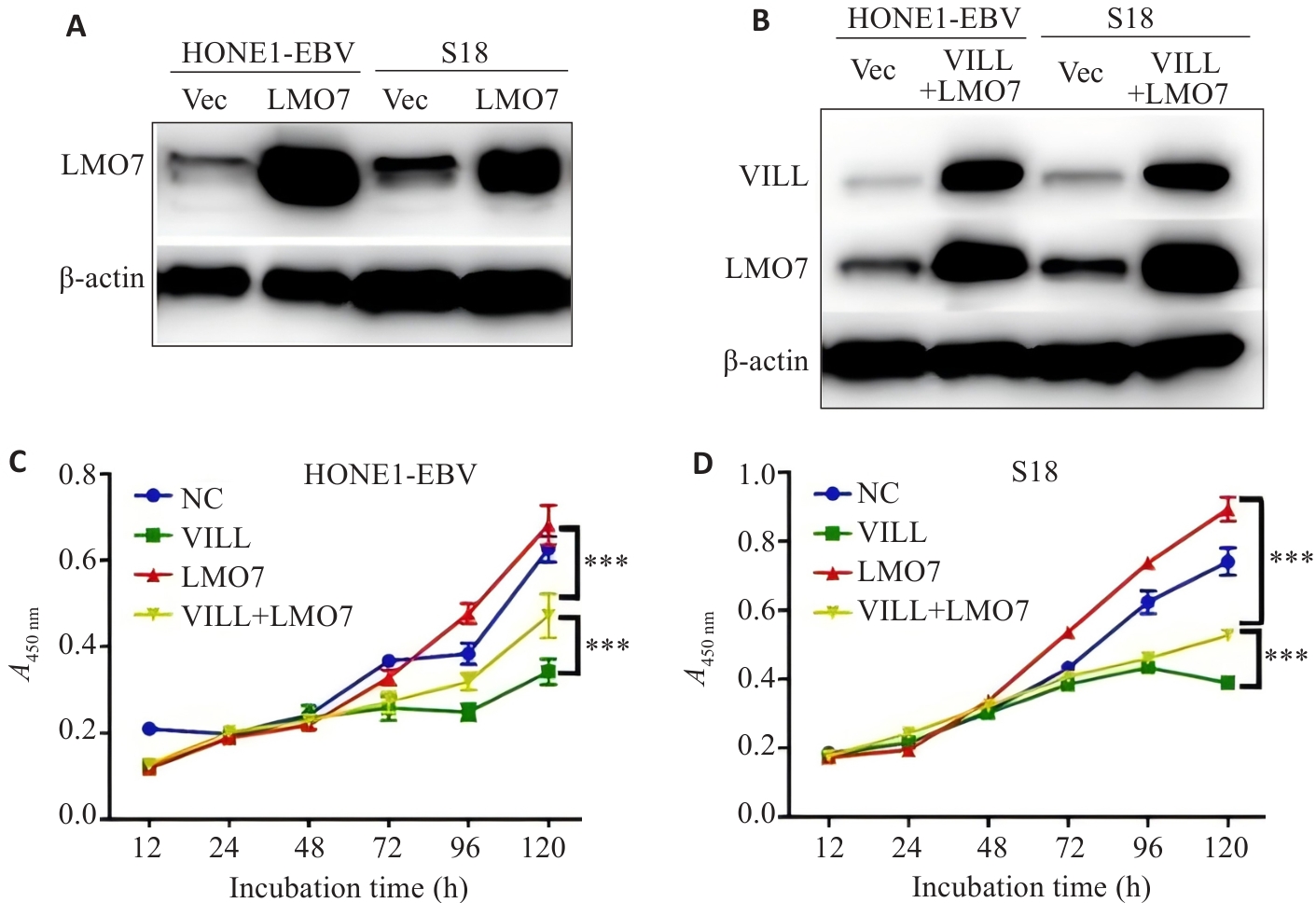
图2 CCK-8实验显示LMO7部分逆转VILL对NPC细胞增殖的抑制作用
Fig.2 CCK-8 assay showing that LMO7 partially reverses the inhibitory effect of VILL on NPC cell proliferation. A,B: Western blotting for verification of successful construction of NPC cell lines (HONE1-EBV and S18) with LMO7 overexpression (A) and VILL+LMO7 double overexpression (B). C, D: CCK-8 assay showing that LMO7 partially reverses the inhibitory effect of VILL on proliferation of NPC cell lines HONE1-EBV (C) and S18 (D). ***P<0.001.
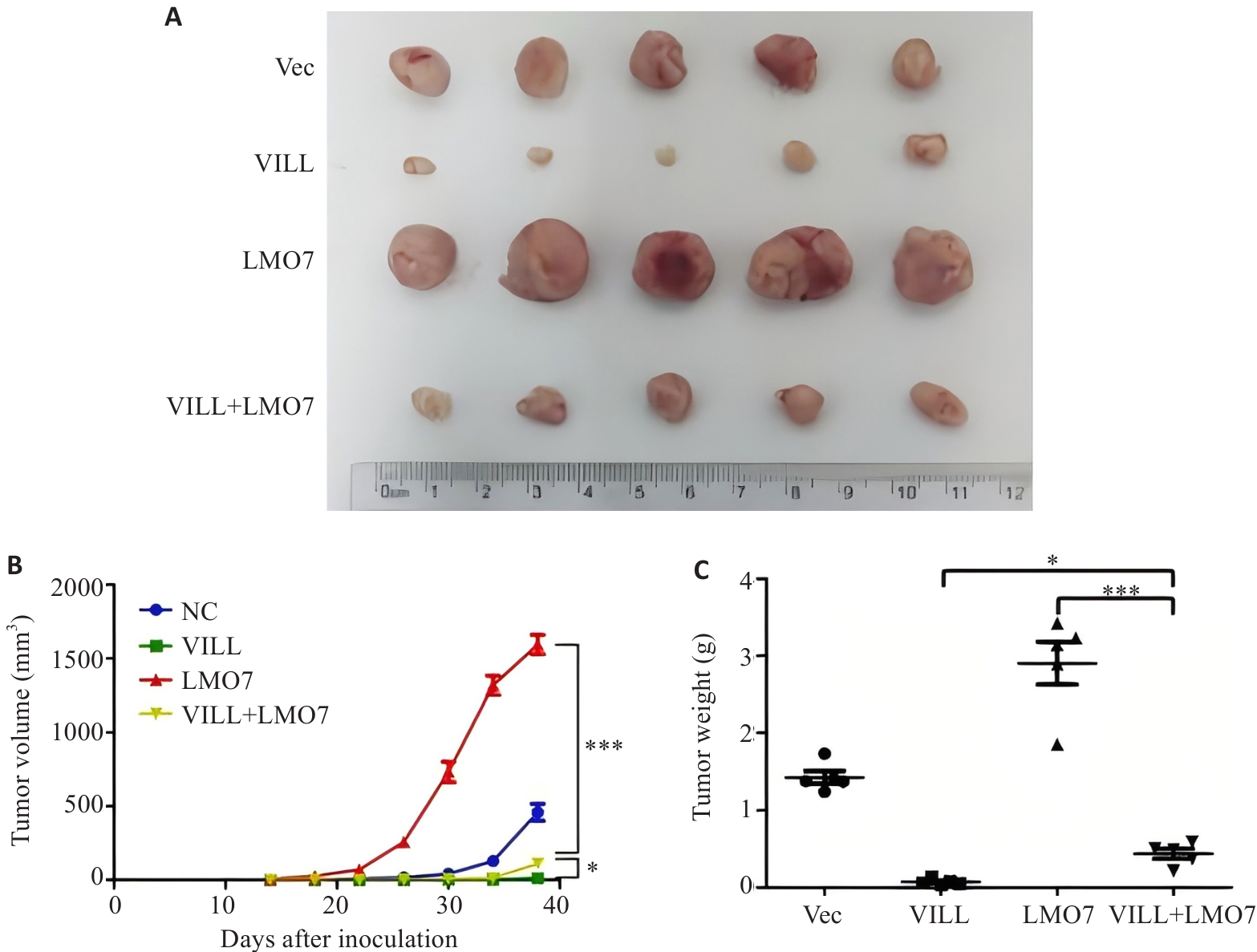
图3 裸鼠皮下成瘤实验显示LMO7部分逆转VILL对NPC细胞增殖的抑制作用
Fig.3 Subcutaneous tumor formation in nude mice showing that LMO7 partially reverses the inhibitory effect of VILL on NPC cell proliferation in vivo. A: Tumors dissected 40 days after subcutaneous implantation of NPC cells (S18) in nude mice. B: Time curve of subcutaneous tumor growth in nude mice. C: Tumor weight 40 days after subcutaneous implantation of NPC cells (S18) in nude mice. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001.
| Variable | n | VILL expression | P (Fisher's Exact Test) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | |||
| Nasopharyngeal tissues | 67 | 0 (0.0) | 67 (100.0) | P<0.001 |
| NPC | 136 | 99 (72.8) | 37 (27.2) | |
表2 VILL在67例鼻咽非癌组织标本和136例 NPC组织标本中的表达谱
Tab.2 Expression profiles of VILL in 67 non-cancerous naso-pharyngeal tissues and 136 NPC tissues (n, %)
| Variable | n | VILL expression | P (Fisher's Exact Test) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | |||
| Nasopharyngeal tissues | 67 | 0 (0.0) | 67 (100.0) | P<0.001 |
| NPC | 136 | 99 (72.8) | 37 (27.2) | |
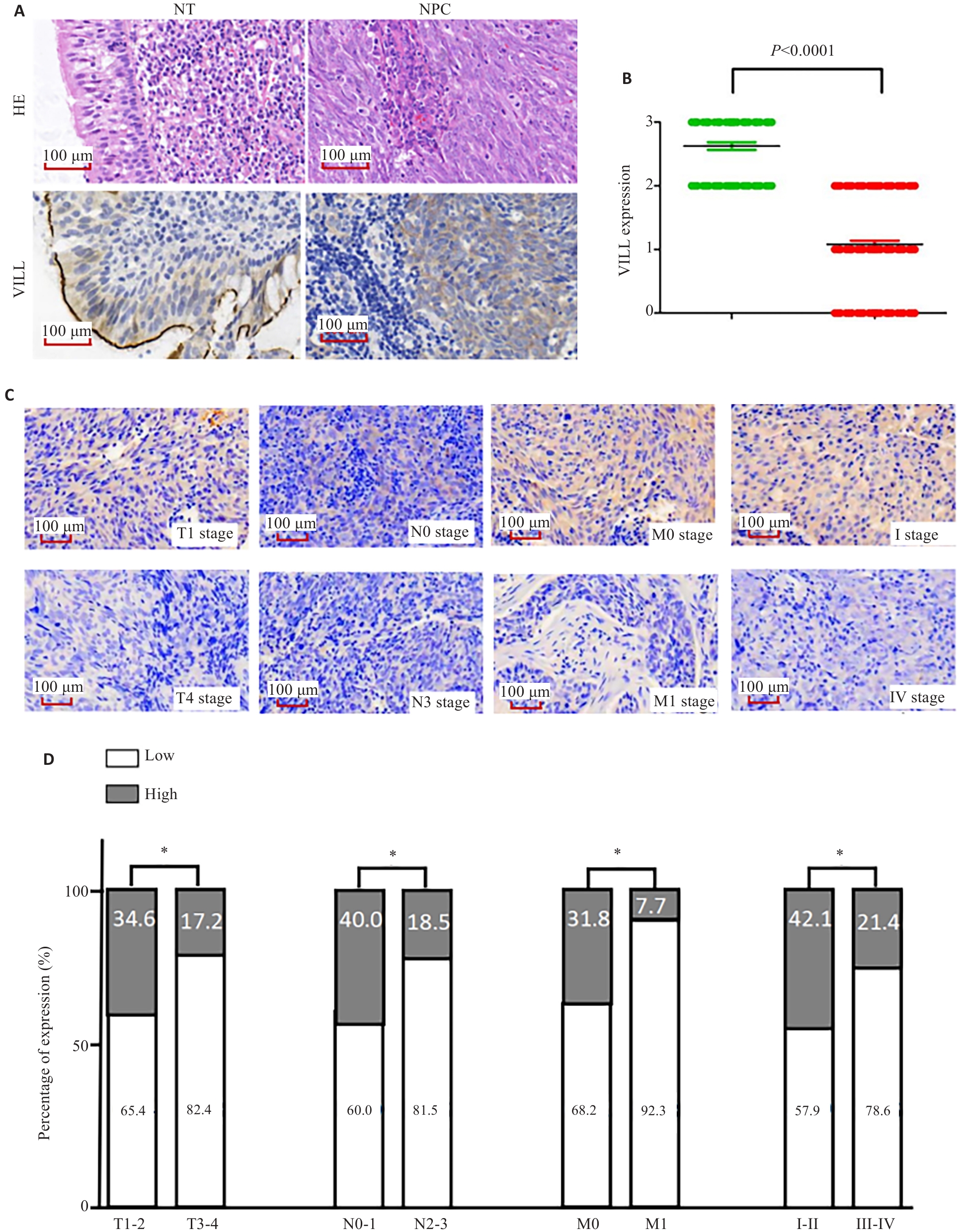
图4 VILL在NPC组织标本上的表达谱及与临床病理特征的相关性
Fig.4 Expression profile of VILL in NPC tissue specimens and its correlation with clinicopathological features of the patients. A, B: Immunohistochemistry showing significant down-regulation of VILL expression in NPC tissues. C: Representative maps of VILL expression in NPC tissues in different TNM stages. D: Positivity rate of VILL in NPC tissues in different TNM stages. *P<0.05.
| Characteristics | Case | VILL expression | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | ||||
| Gender | |||||
| Female | 39 | 27 (69.2) | 12 (30.8) | 0.144 | 0.705 |
| Male | 97 | 72 (74.2) | 25 (25.8) | ||
| Age (years) | |||||
| <50 | 62 | 44 (71.0) | 18 (29.0) | 0.060 | 0.807 |
| ≥50 | 74 | 55 (74.3) | 19 (25.7) | ||
| T classification | |||||
| T1-T2 | 78 | 51 (65.4) | 27 (34.6) | 4.231 | 0.040 |
| T3-T4 | 58 | 48 (82.8) | 10 (17.2) | ||
| N classification | |||||
| N0-N1 | 55 | 33 (60.0) | 22 (40.0) | 6.587 | 0.010 |
| N2-N3 | 81 | 66 (81.5) | 15 (18.5) | ||
| M classification | |||||
| M0 | 110 | 75 (68.2) | 35 (31.8) | 5.023 | 0.013 |
| M1 | 26 | 24 (92.3) | 2 (7.7) | ||
| Clinical stage | |||||
| Ⅰ-Ⅱ | 38 | 22 (57.9) | 16 (42.1) | 4.913 | 0.027 |
| III-IV | 98 | 77 (78.6) | 21 (21.4) | ||
表3 VILL表达与NPC临床病理特征的相关性
Tab.3 Correlation between VILL expression level and clinico-pathological features of NPC patients (n, %)
| Characteristics | Case | VILL expression | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | ||||
| Gender | |||||
| Female | 39 | 27 (69.2) | 12 (30.8) | 0.144 | 0.705 |
| Male | 97 | 72 (74.2) | 25 (25.8) | ||
| Age (years) | |||||
| <50 | 62 | 44 (71.0) | 18 (29.0) | 0.060 | 0.807 |
| ≥50 | 74 | 55 (74.3) | 19 (25.7) | ||
| T classification | |||||
| T1-T2 | 78 | 51 (65.4) | 27 (34.6) | 4.231 | 0.040 |
| T3-T4 | 58 | 48 (82.8) | 10 (17.2) | ||
| N classification | |||||
| N0-N1 | 55 | 33 (60.0) | 22 (40.0) | 6.587 | 0.010 |
| N2-N3 | 81 | 66 (81.5) | 15 (18.5) | ||
| M classification | |||||
| M0 | 110 | 75 (68.2) | 35 (31.8) | 5.023 | 0.013 |
| M1 | 26 | 24 (92.3) | 2 (7.7) | ||
| Clinical stage | |||||
| Ⅰ-Ⅱ | 38 | 22 (57.9) | 16 (42.1) | 4.913 | 0.027 |
| III-IV | 98 | 77 (78.6) | 21 (21.4) | ||
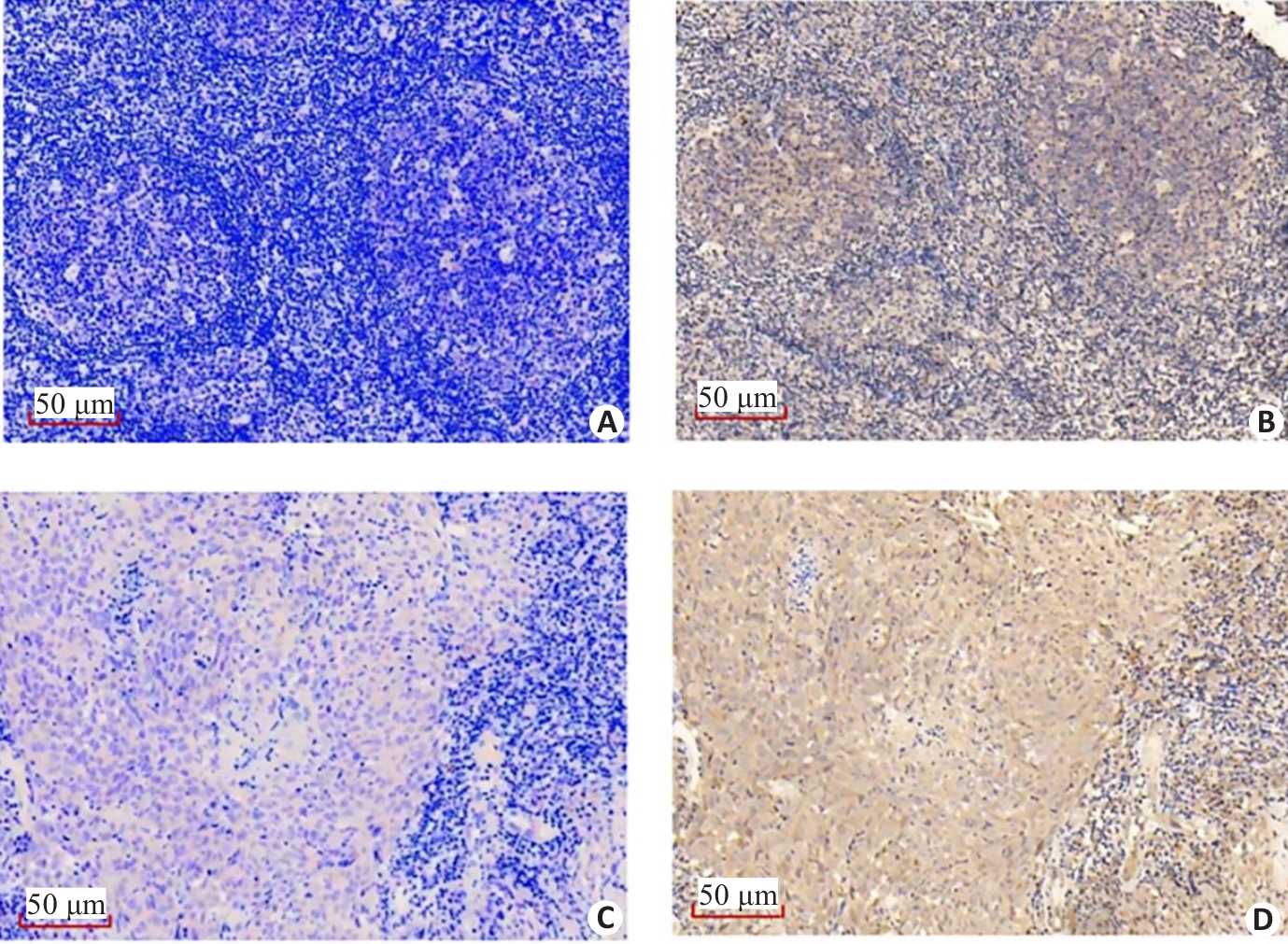
图5 免疫组化显示VILL和LMO7在NPC组织标本上的表达相关性
Fig.5 Immunohistochemistry showing the correlation between the expressions of VILL and LMO7 in NPC tissue specimens. VILL is lowly expressed (A) while LMO7 is highly expressed (B) in a NPC tissue specimen. VILL (C) and LMO7 (D) are both highly expressed in a NPC tissue specimen.
| 1 | Chen YP, Chan ATC, Le QT, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Lancet, 2019, 394(10192): 64-80. |
| 2 | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-49. |
| 3 | Han BF, Zheng RS, Zeng HM, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022[J]. J Natl Cancer Cent, 2024, 4(1): 47-53. |
| 4 | Liang YY, Deng XB, Lin XT, et al. RASSF1A inhibits PDGFB-driven malignant phenotypes of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in a YAP1-dependent manner[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(10): 855. |
| 5 | Zhao Y, Hong XH, Li K, et al. ZNF582 hypermethylation promotes metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating the transcription of adhesion molecules Nectin-3 and NRXN3[J]. Cancer Commun: Lond, 2020, 40(12): 721-37. |
| 6 | Chen Y, Zhao Y, Yang X, et al. USP44 regulates irradiation-induced DNA double-strand break repair and suppresses tumorigenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 501. |
| 7 | Wang YQ, Wu DH, Wei D, et al. TEAD4 is a master regulator of high-risk nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Sci Adv, 2023, 9(1): eadd0960. |
| 8 | Li ZX, Zheng ZQ, Yang PY, et al. WTAP-mediated m6A modification of lncRNA DIAPH1-AS1 enhances its stability to facilitate nasopharyngeal carcinoma growth and metastasis[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2022, 29(6): 1137-51. |
| 9 | Chen B, Huang R, Xia T, et al. The m6A reader IGF2BP3 preserves NOTCH3 mRNA stability to sustain Notch3 signaling and promote tumor metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Oncogene, 2023, 42(48): 3564-74. |
| 10 | Zhang B, Li J, Wang Y, et al. Deubiquitinase USP7 stabilizes KDM5B and promotes tumor progression and cisplatin resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through the ZBTB16/TOP2A axis[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2024, 31(3): 309-21. |
| 11 | Sun XS, Zhang K, Peng XZ, et al. HDAC4 mediated LHPP deacetylation enhances its destabilization and promotes the proliferation and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Cancer Lett, 2023, 562: 216158. |
| 12 | Luo SD, Tsai HT, Hwang CF, et al. Aberrant miR-874-3p/leptin/EGFR/c-Myc signaling contributes to nasopharyngeal carcinoma pathogenesis[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 41(1): 215. |
| 13 | Wu P, Hou X, Peng M, et al. Circular RNA circRILPL1 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma malignant progression by activating the Hippo-YAP signaling pathway[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2023, 30(7): 1679-94. |
| 14 | Bruce JP, To KF, Lui VWY, et al. Whole-genome profiling of nasopharyngeal carcinoma reveals viral-host co-operation in inflammatory NF-κB activation and immune escape[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 4193. |
| 15 | Patel SA, Hirosue S, Rodrigues P, et al. The renal lineage factor PAX8 controls oncogenic signalling in kidney cancer[J]. Nature, 2022, 606(7916): 999-1006. |
| 16 | Schrag D, Beer TM, McDonnell CH, et al. Blood-based tests for multicancer early detection (PATHFINDER): a prospective cohort study[J]. Lancet, 2023, 402(10409): 1251-60. |
| 17 | Huang H, Liu A, Liang Y, et al. A urinary assay for mutation and methylation biomarkers in the diagnosis and recurrence prediction of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer patients[J]. BMC Med, 2023, 21(1): 357. |
| 18 | Jiang W, Liu N, Chen XZ, et al. Genome-wide identification of a methylation gene panel as a prognostic biomarker in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2015, 14(12): 2864-73. |
| 19 | Guo S, Diep D, Plongthongkum N, et al. Identification of methylation haplotype blocks aids in deconvolution of heterogeneous tissue samples and tumor tissue-of-origin mapping from plasma DNA[J]. Nat Genet, 2017, 49(4): 635-42. |
| 20 | Silacci P, Mazzolai L, Gauci C, et al. Gelsolin superfamily proteins: key regulators of cellular functions[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS, 2004, 61(19): 2614-23. |
| 21 | Uhlén M, Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, et al. Proteomics. tissue-based map of the human proteome[J]. Science, 2015, 347(6220): 1260419. |
| 22 | Mahajan-Miklos S, Cooley L. The villin-like protein encoded by the Drosophila quail gene is required for actin bundle assembly during oogenesis[J]. Cell, 1994, 78(2): 291-301. |
| 23 | Kang CK, Lee TH. Medaka villin 1-like protein (VILL) is associated with the formation of microvilli induced by decreasing salinities in the absorptive ionocytes[J]. Front Zool, 2014, 11(1): 2. |
| 24 | Zeng Q, Jiang T, Wang J. Role of LMO7 in cancer (review)[J]. Oncol Rep, 2024, 52(3): 117. |
| 25 | Karlsson T, Kvarnbrink S, Holmlund C, et al. LMO7 and LIMCH1 interact with LRIG proteins in lung cancer, with prognostic implications for early-stage disease[J]. Lung Cancer, 2018, 125: 174-84. |
| 26 | Liu X, Yuan H, Zhou J, et al. LMO7 as an unrecognized factor promoting pancreatic cancer progression and metastasis[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 647387. |
| 27 | Takahashi M, Lio CJ, Campeau A, et al. The tumor suppressor kinase DAPK3 drives tumor-intrinsic immunity through the STING-IFN-β pathway[J]. Nat Immunol, 2021, 22(4): 485-96. |
| 28 | Dai S, Peng Y, Wang G, et al. LIM domain only 7: a novel driver of immune evasion through regulatory T cell differentiation and chemotaxis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2025, 32(2): 271-90. |
| [1] | 谢婷, 王云云, 郭婷, 袁春华. 雷氏大疣蛛多肽毒素组分通过激活促凋亡通路和协同作用抑制癌细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1460-1470. |
| [2] | 岳雅清, 牟召霞, 王希波, 刘艳. Aurora-A过表达通过激活NF-κBp65/ARPC4信号轴促进宫颈癌细胞的侵袭和转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 837-843. |
| [3] | 张毅, 沈昱, 万志强, 陶嵩, 柳亚魁, 王栓虎. CDKN3高表达促进胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭:基于调控p53/NF-κB信号通路和抑制胃癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [4] | 庆顺杰, 沈智勇. 过表达己糖激酶2通过激活JAK/STAT途径促进结直肠癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭并调节肿瘤免疫微环境[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 542-553. |
| [5] | 陶露, 韦卓利, 王月月, 项平. CEACAM6通过调控上皮间质转化抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 566-576. |
| [6] | 黄晴晴, 张文静, 张小凤, 王炼, 宋雪, 耿志军, 左芦根, 王月月, 李静, 胡建国. 高表达MYO1B促进胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭并与患者的不良预后有关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 622-631. |
| [7] | 刘瑨禹, 梁淑君, 张煜. 基于多尺度监督与残差反馈的优化算法有效提高鼻咽癌CT图像视交叉及视神经分割精度[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 632-642. |
| [8] | 邹金华, 王惠, 张冬艳. SLC1A5通过促进M2型巨噬细胞极化促进肝癌进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 269-284. |
| [9] | 宾禹, 李子雯, 左素微, 孙思诺, 李敏, 宋佳茵, 林旭, 薛刚, 吴靖芳. 载脂蛋白C1高表达通过激活JAK2/STAT3信号通路促进甲状腺乳头状癌细胞的增殖并抑制凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 359-370. |
| [10] | 曹周芳, 汪元, 王梦娜, 孙玥, 刘菲菲. LINC00837/miR-671-5p/SERPINE2功能轴促进类风湿关节炎成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞的恶性病理学过程[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 371-378. |
| [11] | 陈孝华, 鲁辉, 王子良, 王炼, 夏勇生, 耿志军, 张小凤, 宋雪, 王月月, 李静, 胡建国, 左芦根. ABI2在胃癌进展和预后中的作用及其调控机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1653-1661. |
| [12] | 薛良军, 谈秋瑜, 许静文, 冯璐, 李文锦, 颜亮, 李玉磊. MiR-6838-5p过表达下调DDR1基因表达抑制乳腺癌MCF-7细胞的增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1677-1684. |
| [13] | 纪凯, 于冠宇, 周乐其, 张天帅, 凌潜龙, 满文江, 朱冰, 张卫. HNRNPA1基因在结直肠癌组织中高表达及其潜在的诊断和治疗价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1685-1695. |
| [14] | 庞一丹, 刘雅, 陈思嫒, 张荆雷, 曾今, 潘元明, 安娟. SPAG5在胃癌细胞恶性增殖中的生物学作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1497-1507. |
| [15] | 从小凡, 陈腾, 李硕, 王媛媛, 周龙云, 李小龙, 张配, 孙小锦, 赵素容. 双氢青蒿素通过促进活性氧的产生增强鼻咽癌细胞对顺铂诱导凋亡的敏感性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1553-1560. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||