南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 269-284.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.02.08
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-10-11
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2025-03-03
通讯作者:
张冬艳
E-mail:360722772@qq.com;635137884@qq.com;15013091401@163.com
作者简介:邹金华,工程师,E-mail: 360722772@qq.com基金资助:
Jinhua ZOU( ), Hui WANG(
), Hui WANG( ), Dongyan ZHANG(
), Dongyan ZHANG( )
)
Received:2024-10-11
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-03-03
Contact:
Dongyan ZHANG
E-mail:360722772@qq.com;635137884@qq.com;15013091401@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨SLC1A5高表达在泛癌种的临床意义及其促进肝癌进展的机制。 方法 利用癌症基因组图谱(TCGA)、国际肿瘤基因组协会(ICGC)等数据库探讨SLC1A5在泛癌种的表达水平及其与临床分期、淋巴结转移及生存预后的关系;利用EPIC、CIBERSORT、TIMER算法分析SLC1A5与免疫细胞浸润的关系,分析SLC1A5联合M2型巨噬细胞浸润水平与肿瘤预后的关系。利用慢病毒过表达系统构建过表达SLC1A5肝癌细胞株;利用小干扰RNA(siRNA)构建沉默SLC1A5(NC组、si-SLC1A5-1组、si-SLC1A5-2组)的肝癌细胞株;CCK-8增殖实验检测SLC1A5对肝癌细胞增殖的影响;利用过表达SLCA5稳转株(NC组,SLC1A5过表达组)构建肝癌皮下瘤模型,体内水平探讨SLC1A5对肝癌增殖的影响;利用共培养体系验证干扰和过表达SLC1A5肝癌细胞对巨噬细胞极化的影响。 结果 SLC1A5主要定位于细胞膜上,SLC1A5在大多数肿瘤中均显著高表达(P<0.05),其表达水平与临床分期及淋巴结转移呈正相关(P<0.05);SLC1A5高表达与多癌种不良预后相关(P<0.05)。在13个癌种中显示SLC1A5与免疫评分呈正相关,二者相关性在低级别胶质瘤(LGG)、肝癌(LIHC)及甲状腺癌(THCA)中最显著(P<0.05)。多癌种显示SLC1A5与巨噬细胞浸润水平呈正相关(P<0.05),该相关性在LGG及LIHC中最显著;而在包括肺鳞癌、胰腺癌、胃癌在内的5种肿瘤中,二者呈负相关(P<0.05)。生存分析发现SLC1A5高表达且M2型巨噬细胞高浸润水平的患者生存预后最差(P<0.05);SLC1A5与免疫抑制相关基因、细胞因子及细胞因子受体表达呈正相关,该相关性在LGG、LIHC中最显著(P<0.05)。不同肝癌细胞株均高表达SLC1A5,过表达SLC1A5促进肝癌细胞增殖,干扰SLC1A5则抑制肝癌细胞增殖;体内实验验证过表达SLC1A5促进肝癌增殖。SLC1A5与M2型巨噬细胞极化分子标志物表达呈正相关,过表达SLC1A5促进M2型巨噬细胞极化并抑制T细胞分泌IFN-γ。 结论 SLC1A5与多种肿瘤的临床分期、淋巴结转移、预后及免疫浸润水平相关;SLC1A5通过促进M2型巨噬细胞极化抑制T细胞功能来促进肝癌进展。
邹金华, 王惠, 张冬艳. SLC1A5通过促进M2型巨噬细胞极化促进肝癌进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 269-284.
Jinhua ZOU, Hui WANG, Dongyan ZHANG. SLC1A5 overexpression accelerates progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting M2 polarization of macrophages[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 269-284.
| Products name | Target sequence |
|---|---|
| SLC1A5(siRNA# 1) | 5'-GTACCGTCCTCAATGTAGA-3' |
| SLC1A5(siRNA# 2) | 5'- GAAGCACAGAGCCTGAGTT-3' |
表1 siRNA序列
Tab.1 siRNA sequences for SLC1A5
| Products name | Target sequence |
|---|---|
| SLC1A5(siRNA# 1) | 5'-GTACCGTCCTCAATGTAGA-3' |
| SLC1A5(siRNA# 2) | 5'- GAAGCACAGAGCCTGAGTT-3' |
| Primer | Sequence | |
|---|---|---|
| SLC1A5 | Sense Antisense | 5'-GAGGCTTTCTCTGGCTGGTAA-3' 5'-GTCTTGGACACTGAGGGCTG-3' |
TGFB1 IL-10 CSF1R CXCL1 | Sense Antisense Sense Antisense Sense Antisense Sense Antisense | 5'-CAAGTGGACATCAACGGGTTC-3' 5'-GCAGCAGTTCTTCTCCGTGG-3' 5'-GAGGAGGTGATGCCCCAAGC-3' 5'-GGGAAGAAATCGATGACAGC-3' 5'-CCTCGCTTCCAAGAATTGCA-3' 5'-CCCAATCTTGGCCACATGA-3' 5'-CTCTTCCGCTCCTCTCACAG-3' 5'-CACGGACGCTCCTGCTGC-3' |
表2 PCR引物序列
Tab.2 PCR primer sequences
| Primer | Sequence | |
|---|---|---|
| SLC1A5 | Sense Antisense | 5'-GAGGCTTTCTCTGGCTGGTAA-3' 5'-GTCTTGGACACTGAGGGCTG-3' |
TGFB1 IL-10 CSF1R CXCL1 | Sense Antisense Sense Antisense Sense Antisense Sense Antisense | 5'-CAAGTGGACATCAACGGGTTC-3' 5'-GCAGCAGTTCTTCTCCGTGG-3' 5'-GAGGAGGTGATGCCCCAAGC-3' 5'-GGGAAGAAATCGATGACAGC-3' 5'-CCTCGCTTCCAAGAATTGCA-3' 5'-CCCAATCTTGGCCACATGA-3' 5'-CTCTTCCGCTCCTCTCACAG-3' 5'-CACGGACGCTCCTGCTGC-3' |
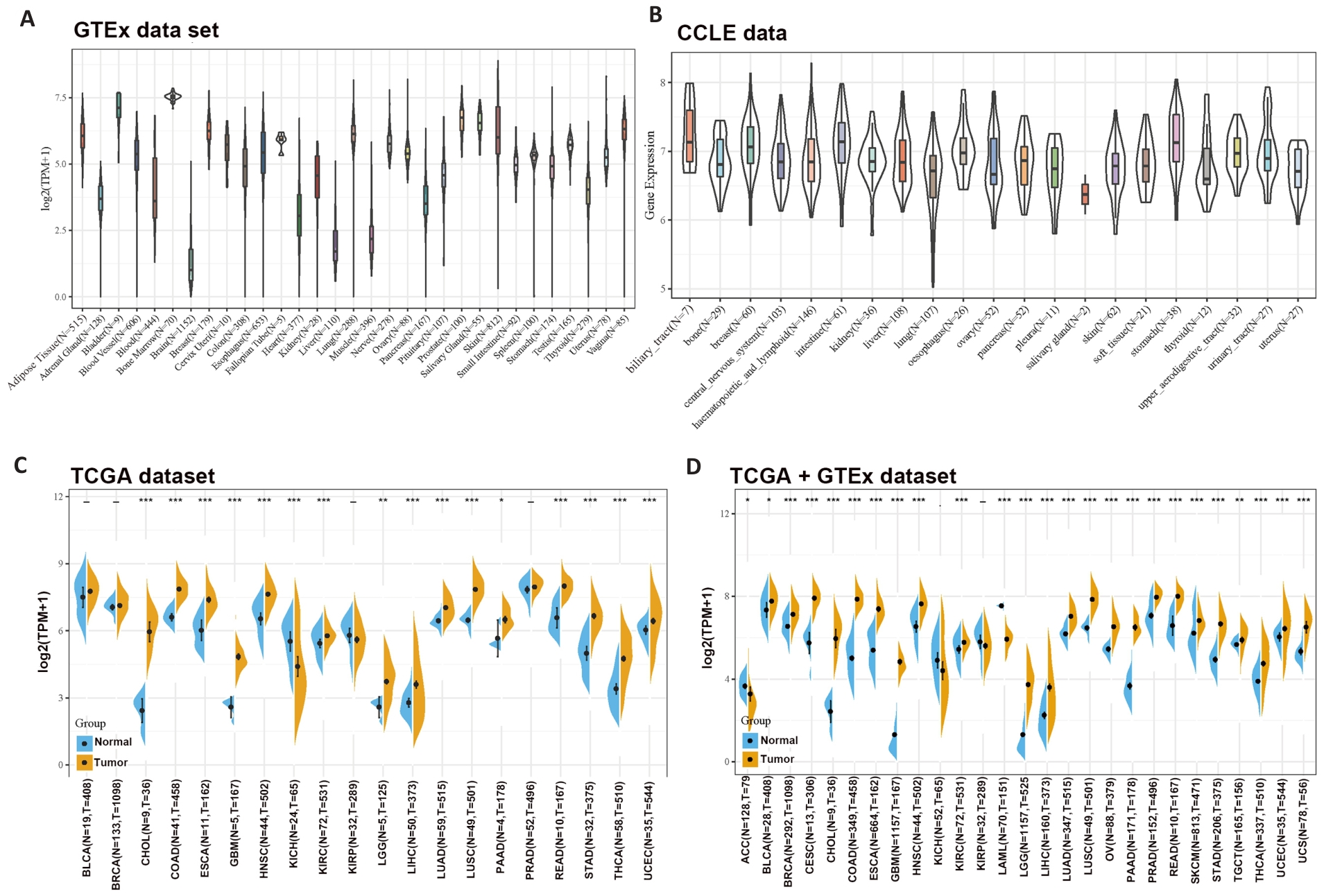
图1 泛癌种中SLC1A5的表达情况
Fig1 Differential expressions of SLC1A5 across different cancer types. A: SLC1A5 expression in normal tissues. B: SLC1A5 expression in tumor cell lines. C: Expression status of SLC1A5 gene in paired tumor and non-tumor tissues across 22 cancer types from TCGA. D: Analysis of SLC1A5 expression in 33 cancer types with their corresponding normal tissues in GTEx dataset as controls. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, *** P<0.001.
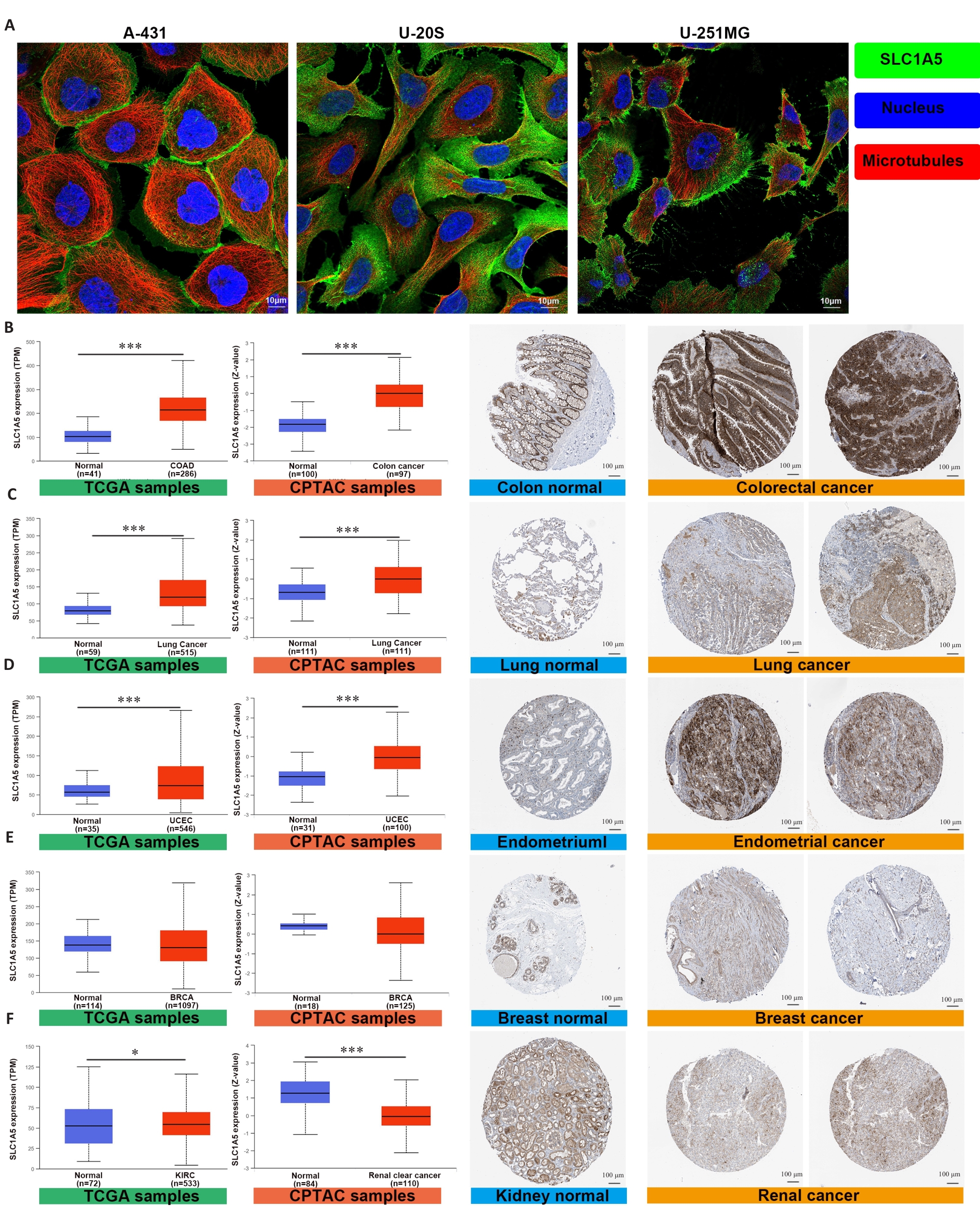
图2 SLC1A5在多种癌症中高表达
Fig.2 SLC1A5 is highly expressed in various cancers. A: Expression and distribution of SLC1A5 in different cancer cell lines (Scale bar=10 μm); B-F: Comparison of SLC1A5 gene expression between normal and tumor tissues from TCGA databases (left), SLC1A5 protein expression between normal and tumor tissues from CPTAC (middle), and immunohistochemistry images of normal and tumor tissues from HPA (right, Scale bar=100 μm). SLC1A5 expression at both the mRNA and protein levels was significantly higher in colorectal cancer (B), lung cancer (C), and endometrial cancer (D). There was no significant difference in SLC1A5 expression between tumor and non-tumor in breast cancer (E). SLC1A5 gene expression was slightly upregulated in renal cancer, but was significantly downregulated in the tumor tissues at the protein level (F). *P<0.05, ***P<0.001.
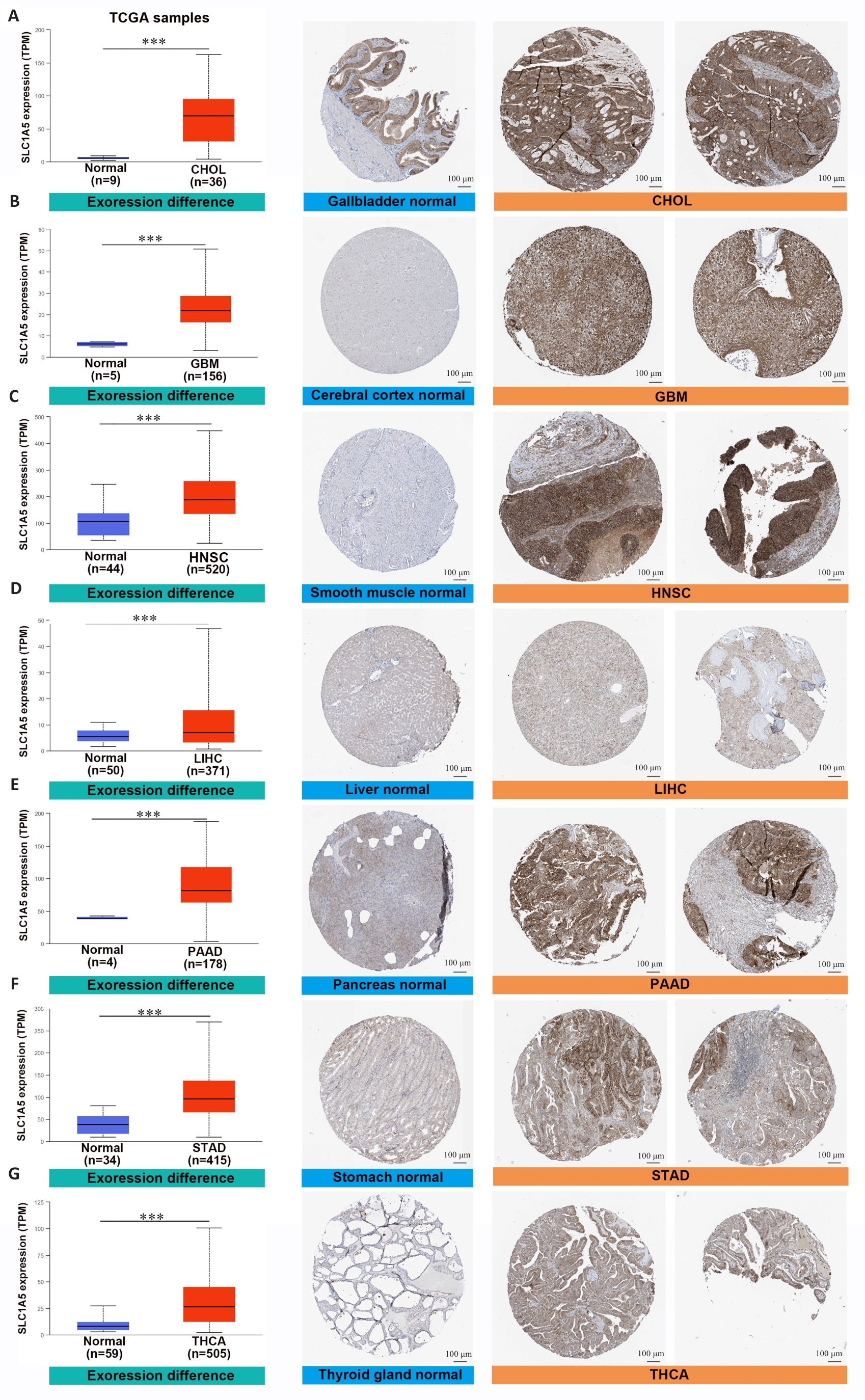
图3 SLC1A5在各种癌症类型中高表达
Fig.3 SLC1A5 is highly expressed in various cancer types. Comparison of SLC1A5 gene expression between normal and tumor tissues from TCGA databases (left), SLC1A5 protein expression between normal and tumor tissues from CPTAC (middle), and immunohistochemistry images of normal and tumor tissues from HPA (right, Scale bar=100 μm). ***P<0.001.
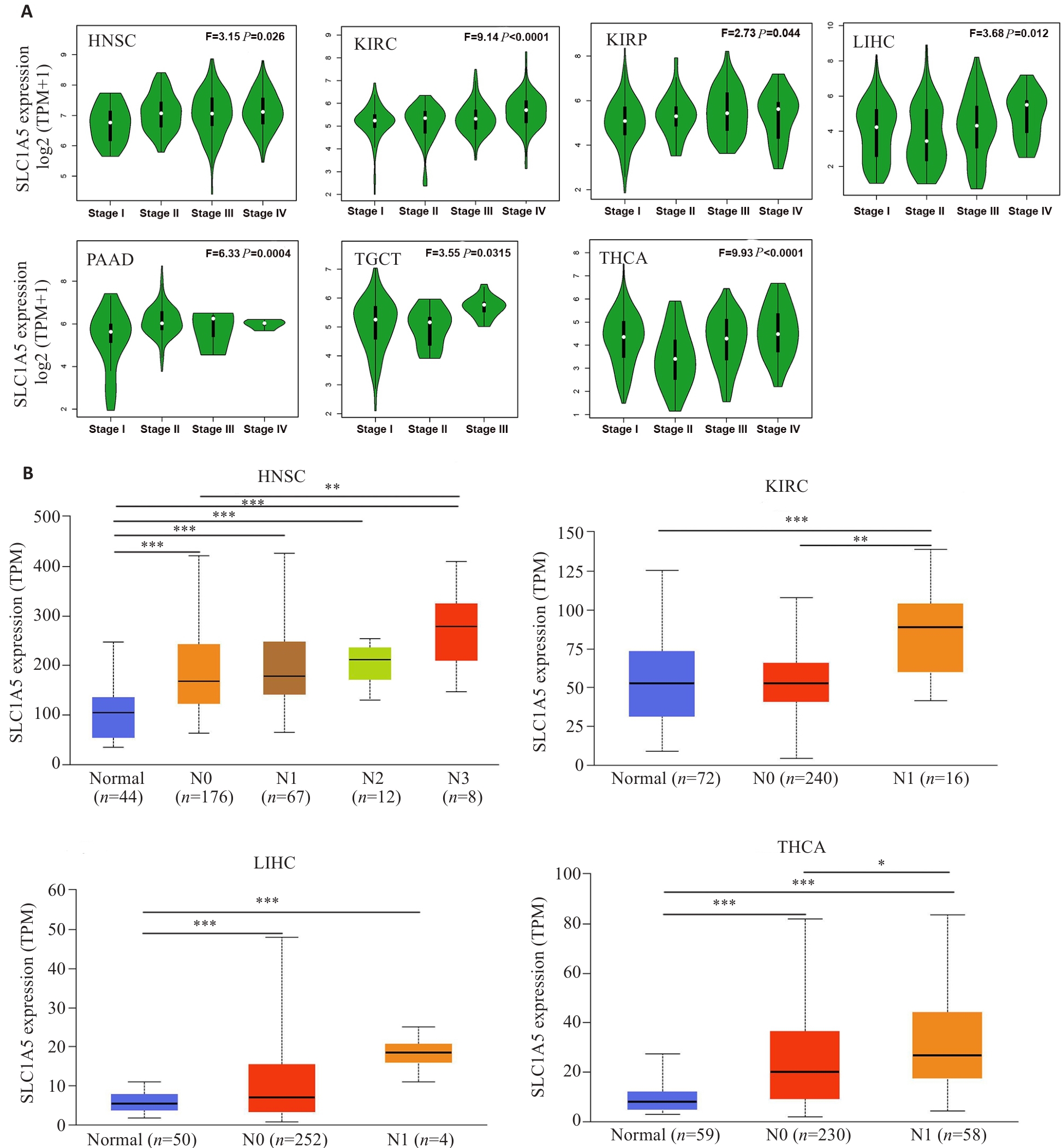
图4 SLC1A5在不同癌种不同病理分期及淋巴转移与否的肿瘤组织中的表达水平
Fig.4 Expression levels of SLC1A5 gene in cancers in realtion to pathological stages and status of lymphatic metastasis. A: Expression levels of SLC1A5 mRNA in different pathological stages of HNSC, KIRC, KIRP, LIHC, PAAD, TGCT, and THCA. B: Expression levels of SLC1A5 mRNA analyzed in relation to lymphatic metastasis in HNSC, KIRC, LIHC, and THCA. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
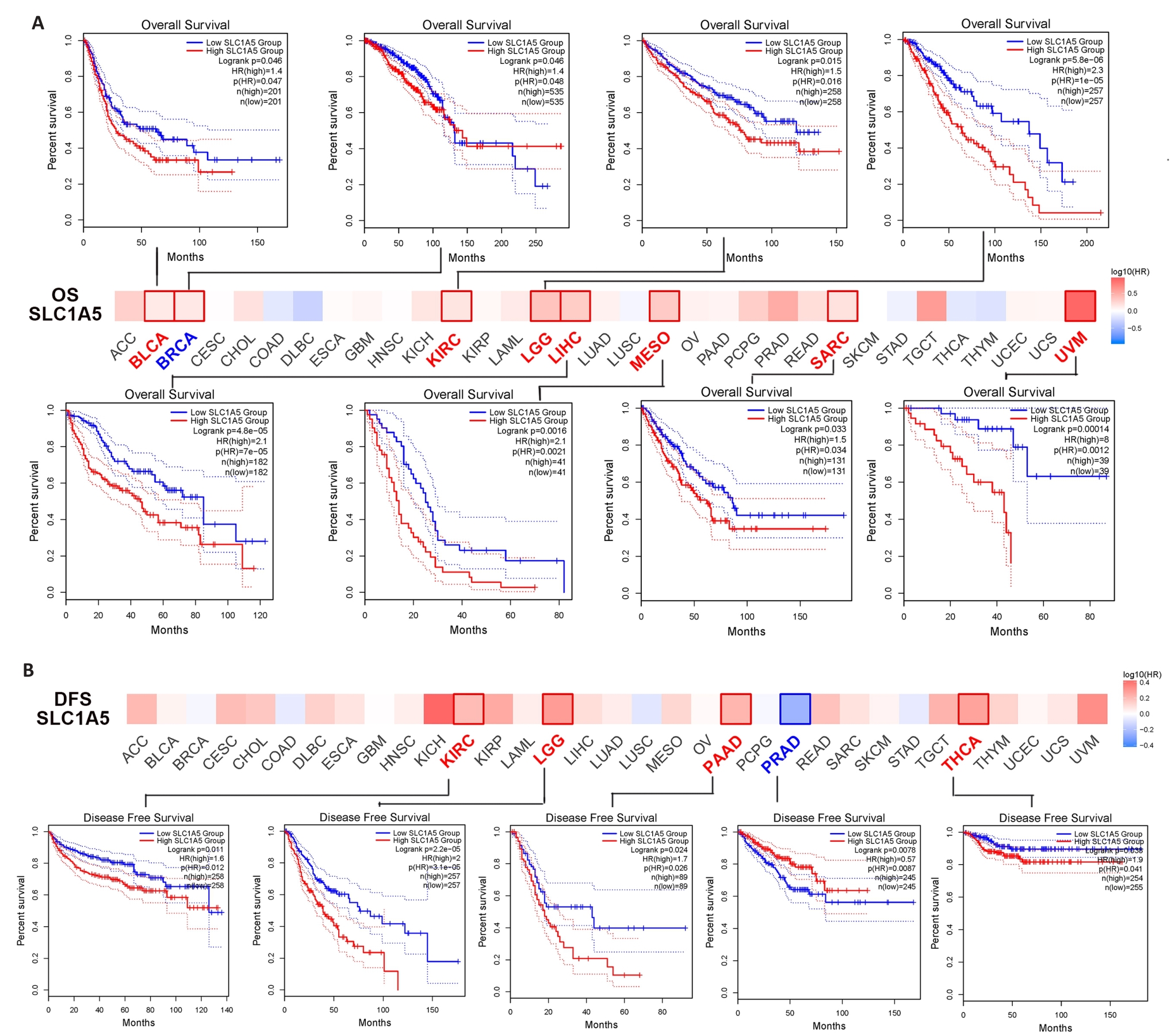
图5 SLC1A5表达与不同肿瘤生存预后的关系
Fig.5 Correlation between SLC1A5 expression and survival outcomes of different cancers. A: GEPIA2 tool was used for analysis of overall survival (A) and disease-survival (B) for 33 cancers in TCGA in relation to SLC1A5 expression. The survival map and survival curves with statistical significance are shown.
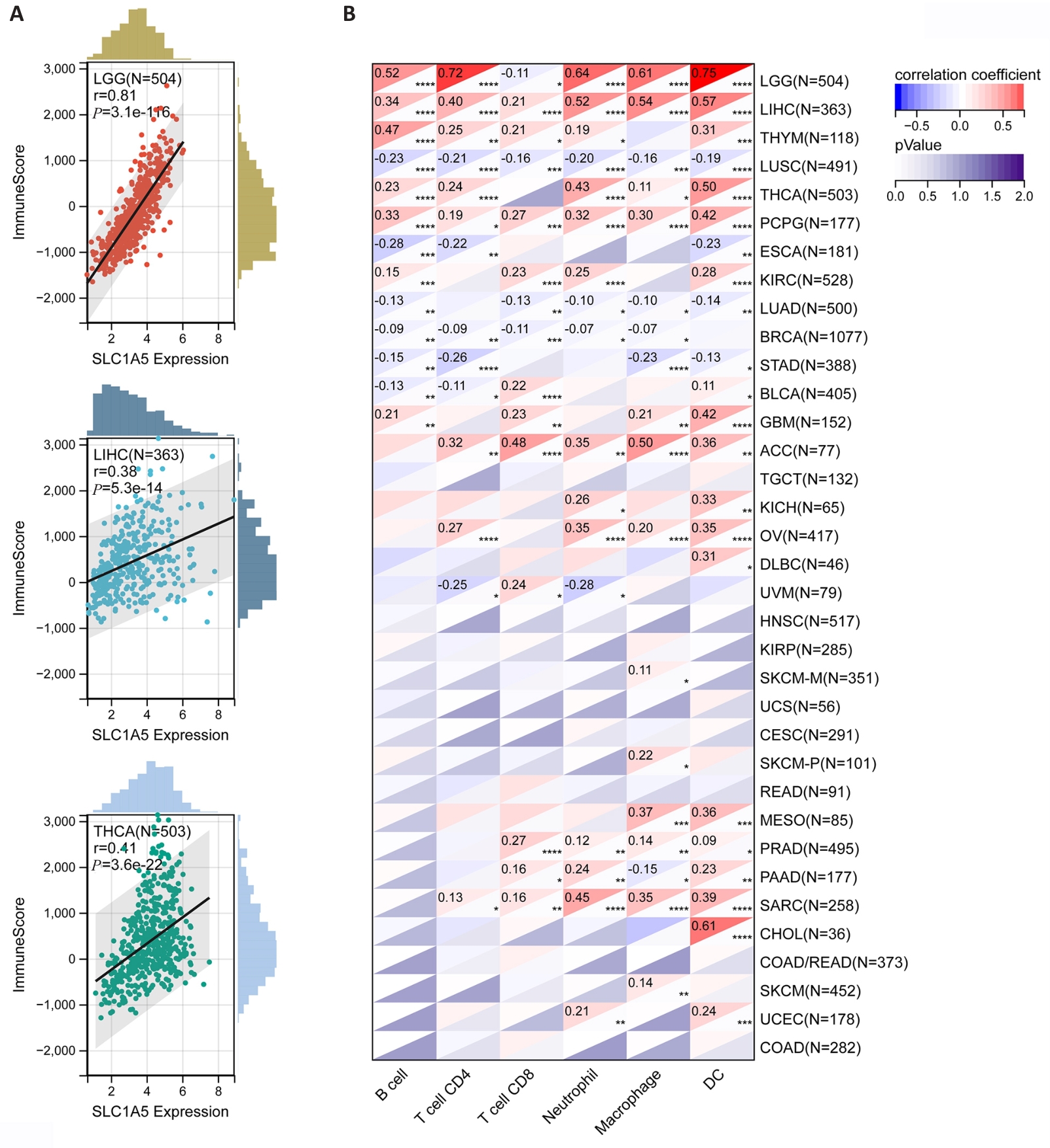
图6 SLC1A5表达水平与肿瘤微环境及肿瘤免疫细胞浸润水平的相关性
Fig.6 Correlation of SLC1A5 expression levels with tumor microenvironment and levels of tumor immune cell infiltration. A: Three tumors with the highest correlation coefficients between SLC1A5 expression and the tumor microenvironment. B: Correlation coefficients between SLC1A5 expression and tumor infiltration level of different immune cells in 33 cancer types. *P<0.05; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
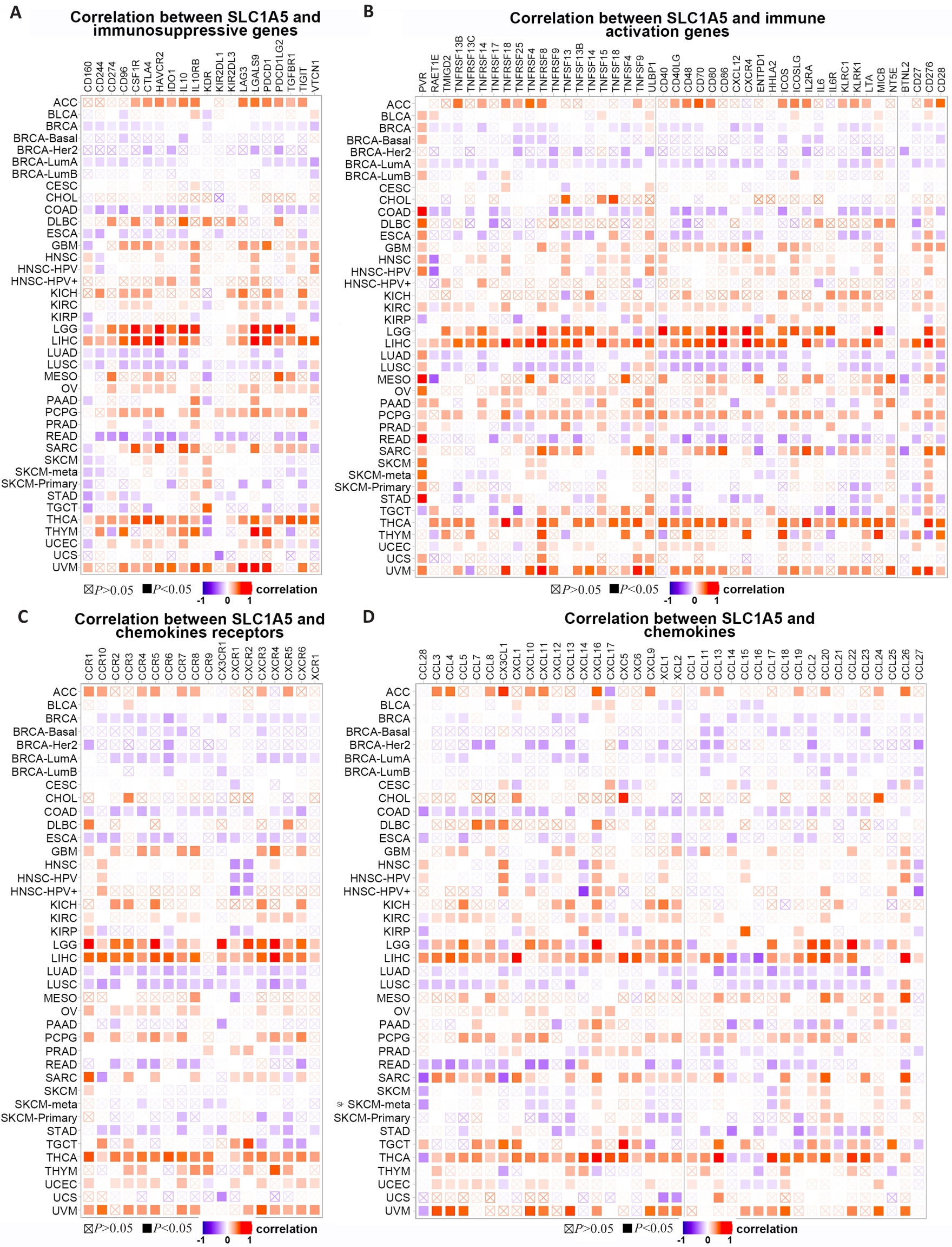
图7 SLC1A5表达与免疫相关基因的共表达
Fig.7 Co-expression of SLC1A5 expression and immune-related genes. Correlations of SLC1A5 expression with immunosuppressive genes (A), immune activation genes (B), chemokines receptor (C), and chemokines (D) are presented.
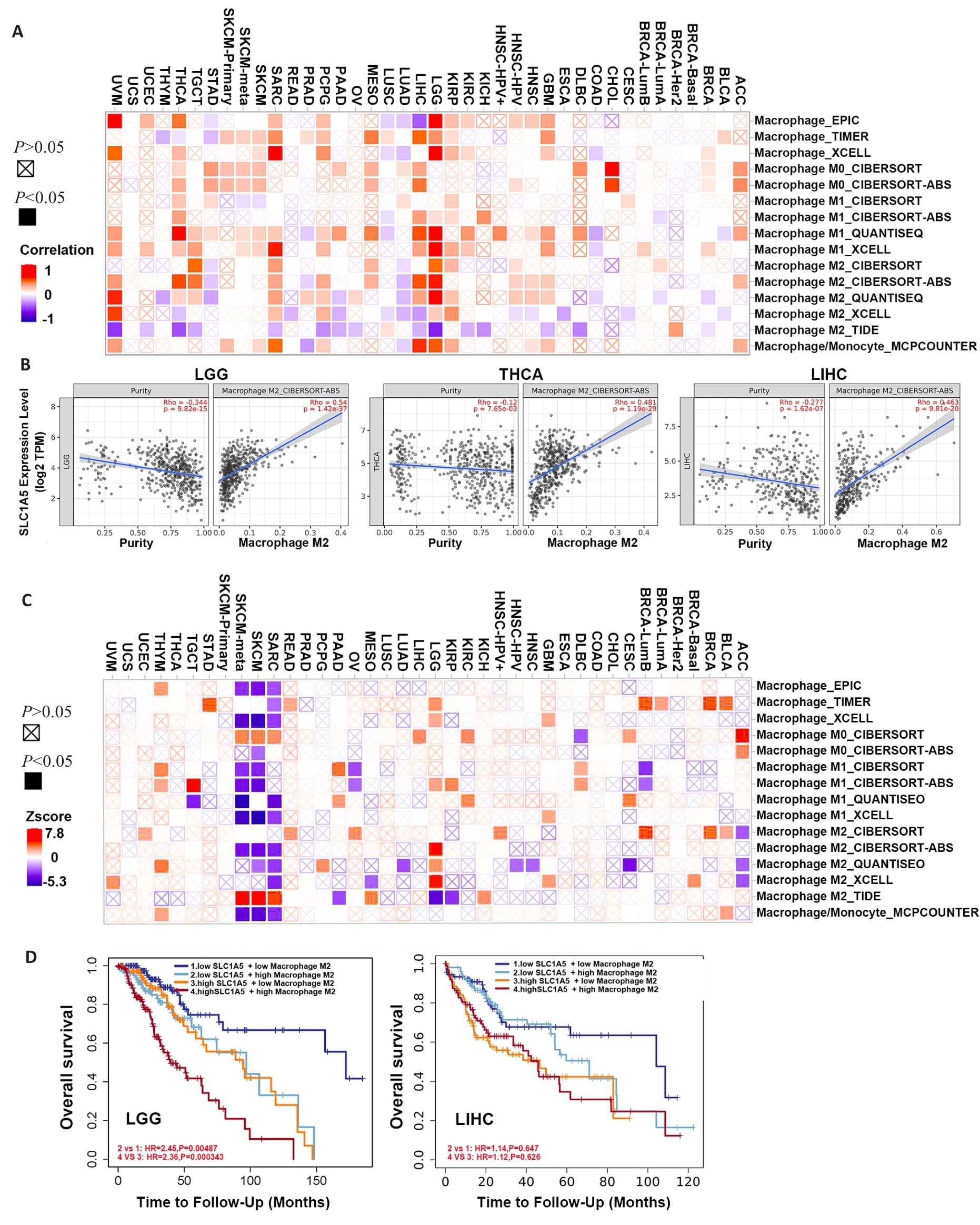
图8 SLC1A5表达与不同亚型巨噬细胞的相关性
Fig.8 Correlation between SLC1A5 expression and different subtypes of macrophage. A: Relationship between SLC1A5 expression and different subtypes of macrophage. B: Three tumors with the highest correlation coefficients between SLC1A5 expression and M2 macrophages. C: Survival map illustrating the correlation between different subtypes of macrophage and overall survival in different cancers. D: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of LGG (left) and LIHC (right) patients with different SLC1A5 expression levels stratified by levels of infiltrating M2 macrophages.
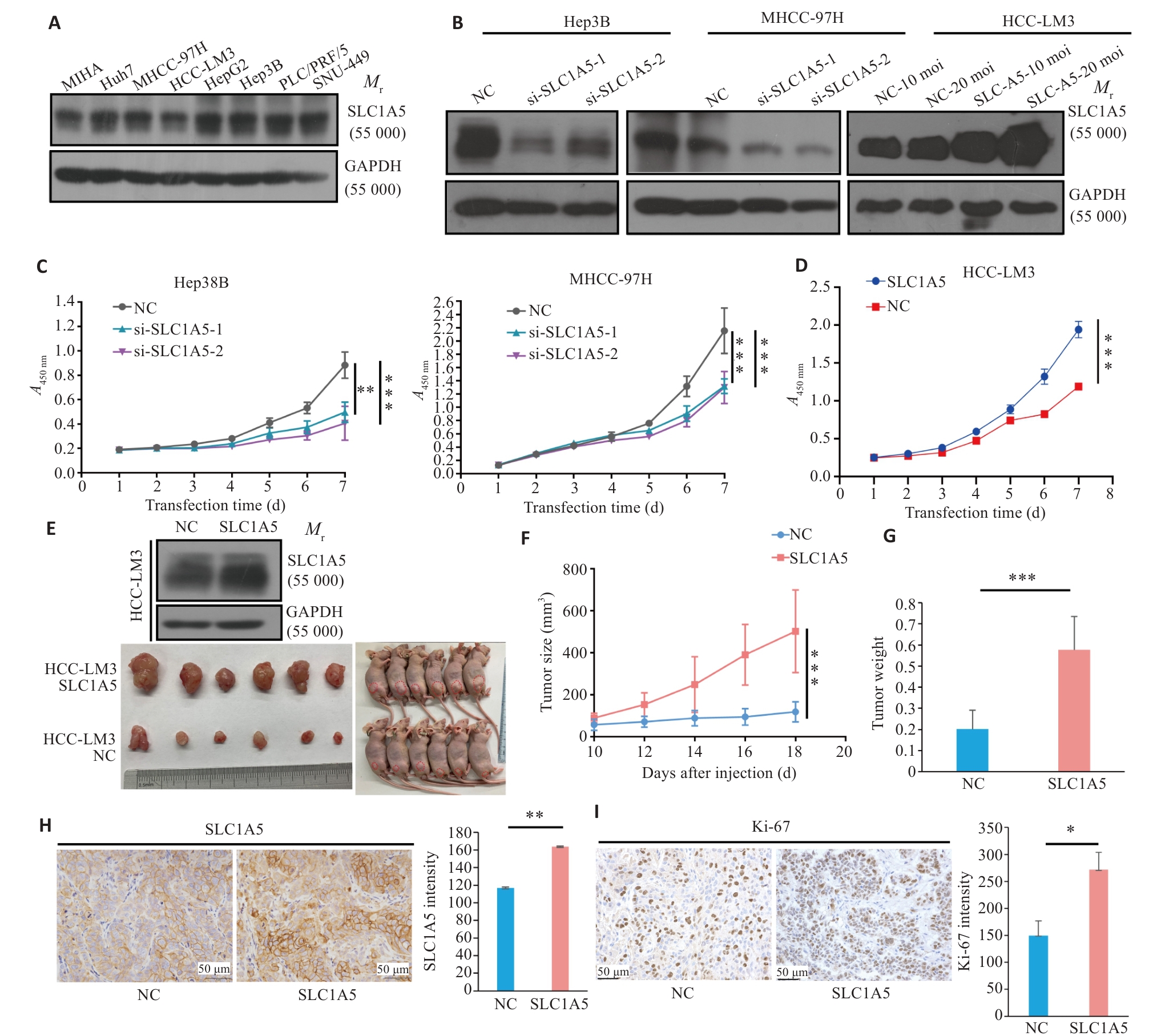
图9 过表达SLC1A5促进肝癌增殖
Fig.9 Overexpression of SLC1A5 promotes proliferation of HCC cells. A: Expression of SLC1A5 in HCC cell lines detected by Western blotting. LE: Long exposure; SE: Short exposure. B: Verification of SLC1A5 knockout and overexpression efficiency in different HCC cell lines using Western blotting. C: Effect of RNA interference of SLC1A5 on HCC cell proliferation assessed using CCK-8 assay. D: Effect of SLC1A5 overexpression on HCC cell proliferation assessed using by CCK-8 assay. E: Overexpression efficiency of SLC1A5 in HCC-LM3 cells examined by Western blotting (upper). Examination of subcutaneous tumors in nude mice (bottom). F, G: Proliferation curve of subcutaneous tumor (F) and tumor weight (G) in nude mice. H, I: Expressions of SLC1A5 and Ki-67 in subcutaneous tumors detected by immunohistochemistry. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
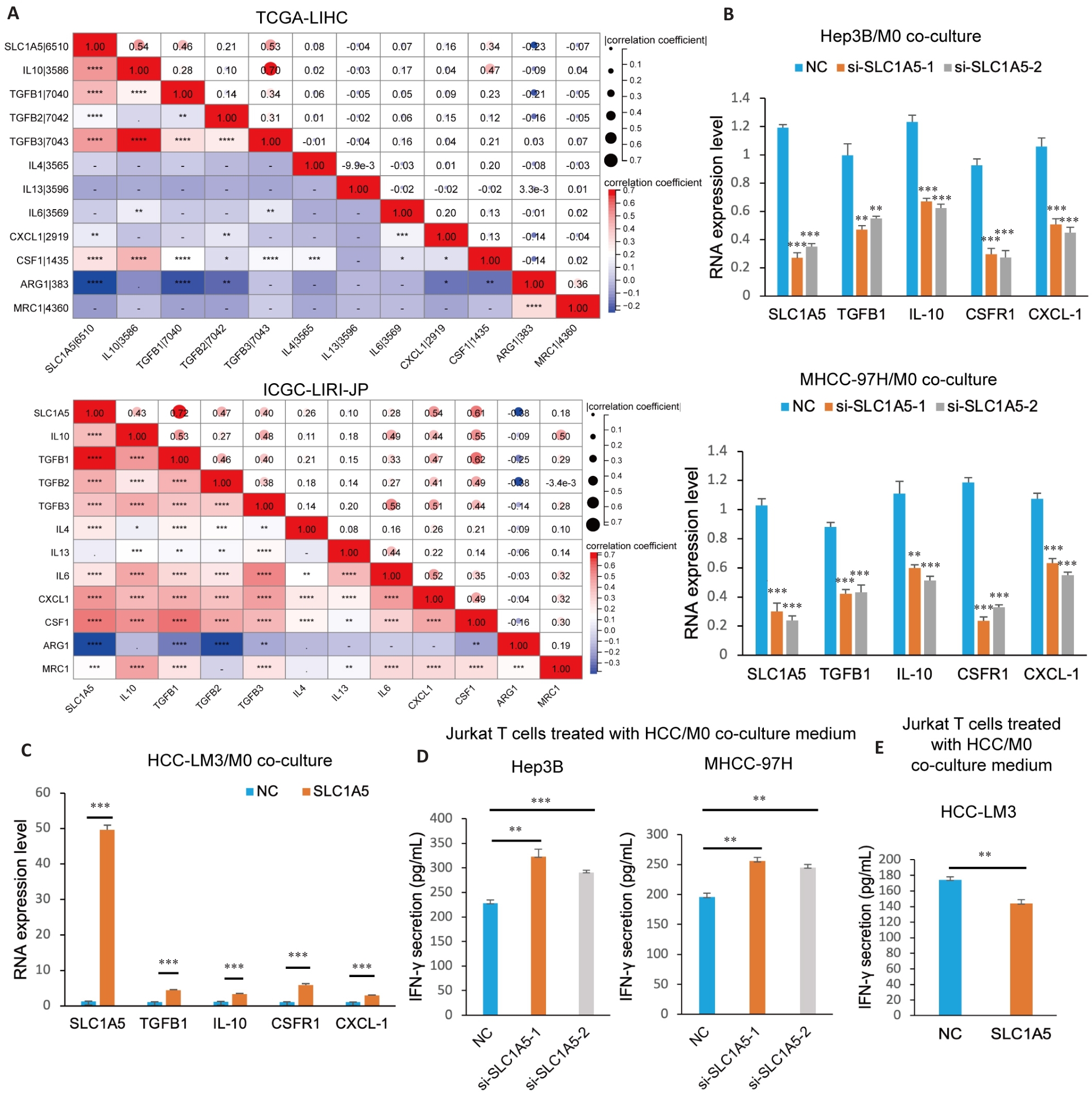
图10 SLC1A5促进M2型巨噬细胞极化并抑制T细胞功能
Fig.10 SLC1A5 promotes M2 polarization of macrophages and induces CD8+ T cell dysfunction. A: Correlation analysis between SLC1A5 expression and molecular markers of M2 macrophages. B: M0 cells co-cultured with HCC cells transfected with SLC1A5-specific siRNA or negative control siRNA and induced to polarize into M2 phenotype using IL-4 (20 ng/mL). Interference efficiency of SLC1A5 and expressions of M2 markers (IL-10, TGFB1, CSF1R and CXCL-1) detected using qRT-PCR. C: M0 cells co-cultured with SLC1A5-overpressing HCC-LM3 cells and induced to polarize into M2 phenotype using IL-4 (20 ng/mL). The overpression efficiency of SLC1A5 and the expression of M2 markers (IL-10, TGFB1, CSF1R and CXCL-1) were detected using qRT-PCR. D, E: M0 cells co-cultured with HCC cells with SLC1A5 knockdown (D) and overexpression (E) and induced into the M2 phenotype using IL-4 (20 ng/mL). The culture medium was used to treat activated Jurkat T cells for 48 h, and IFN-γ secretion was detected by ELISA. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
| 1 | Sasidharan Nair V, Elkord E. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer therapy: a focus on T-regulatory cells[J]. Immunol Cell Biol, 2018, 96(1): 21-33. |
| 2 | Sharma P, Goswami S, Raychaudhuri D, et al. Immune checkpoint therapy-current perspectives and future directions[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(8): 1652-69. |
| 3 | Wang QY, Shen XF, Chen G, et al. How to overcome resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in colorectal cancer: from mechanisms to translation[J]. Int J Cancer, 2023, 153(4): 709-22. |
| 4 | Bou-Dargham MJ, Sha LL, Sarker DB, et al. TCGA RNA-seq and tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte imaging data reveal cold tumor signatures of invasive ductal carcinomas and estrogen receptor-positive human breast tumors[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(11): 9355. |
| 5 | He Y, Wang XS. Identifying biomarkers associated with immunotherapy response in melanoma by multi-omics analysis[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2023, 167: 107591. |
| 6 | Osman I, He XQ, Liu JH, et al. TEAD1 (TEA domain transcription factor 1) promotes smooth muscle cell proliferation through upregulating SLC1A5 (solute carrier family 1 member 5)-mediated glutamine uptake[J]. Circ Res, 2019, 124(9): 1309-22. |
| 7 | Hassanein M, Hoeksema MD, Shiota M, et al. SLC1A5 mediates glutamine transport required for lung cancer cell growth and survival[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2013, 19(3): 560-70. |
| 8 | Huang F, Zhao YC, Zhao JZ, et al. Upregulated SLC1A5 promotes cell growth and survival in colorectal cancer[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2014, 7(9): 6006-14. |
| 9 | van Geldermalsen M, Wang Q, Nagarajah R, et al. ASCT2/SLC1A5 controls glutamine uptake and tumour growth in triple-negative basal-like breast cancer[J]. Oncogene, 2016, 35(24): 3201-8. |
| 10 | Wang Q, Hardie RA, Hoy AJ, et al. Targeting ASCT2-mediated glutamine uptake blocks prostate cancer growth and tumour development[J]. J Pathol, 2015, 236(3): 278-89. |
| 11 | Hinshaw DC, Shevde LA. The tumor microenvironment innately modulates cancer progression[J]. Cancer Res, 2019, 79(18): 4557-66. |
| 12 | Hui LL, Chen Y. Tumor microenvironment: sanctuary of the devil[J]. Cancer Lett, 2015, 368(1): 7-13. |
| 13 | Jin MZ, Jin WL. The updated landscape of tumor microenvironment and drug repurposing[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2020, 5(1): 166. |
| 14 | Nakaya M, Xiao YC, Zhou XF, et al. Inflammatory T cell responses rely on amino acid transporter ASCT2 facilitation of glutamine uptake and mTORC1 kinase activation[J]. Immunity, 2014, 40(5): 692-705. |
| 15 | Masle-Farquhar E, Bröer A, Yabas M, et al. ASCT2 (SLC1A5)-deficient mice have normal B-cell development, proliferation, and antibody production[J]. Front Immunol, 2017, 8: 549. |
| 16 | Ansari RE, Craze ML, Althobiti M, et al. Enhanced glutamine uptake influences composition of immune cell infiltrates in breast cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2020, 122(1): 94-101. |
| 17 | Han LY, Zhou JP, Li LY, et al. SLC1A5 enhances malignant phenotypes through modulating ferroptosis status and immune microenvironment in glioma[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(12): 1071. |
| 18 | Zheng ST, Liu T, Li L, et al. SLC1A5, unrelated to prognosis, was associated with CD8+ T-cell exclusion in the tumor micro-environment of squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(3): e14571. |
| 19 | Siemers NO, Holloway JL, Chang H, et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies genetic correlates of immune infiltrates in solid tumors[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(7): e0179726. |
| 20 | Zhou R, Zhang JW, Zeng DQ, et al. Immune cell infiltration as a biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of stage I-III colon cancer[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2019, 68(3): 433-42. |
| 21 | Csanadi A, Oser A, Aumann K, et al. Overexpression of SLC1a5 in lymph node metastases outperforms assessment in the primary as a negative prognosticator in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Pathology, 2018, 50(3): 269-75. |
| 22 | Liu YD, Yang L, An HM, et al. High expression of Solute Carrier Family 1, member 5 (SLC1A5) is associated with poor prognosis in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 16954. |
| 23 | Sun HW, Yu XJ, Wu WC, et al. GLUT1 and ASCT2 as predictors for prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(12): e0168907. |
| 24 | Kaira K, Sunose Y, Arakawa K, et al. Clinicopathological significance of ASC amino acid transporter-2 expression in panc-reatic ductal carcinoma[J]. Histopathology, 2015, 66(2): 234-43. |
| 25 | Lu J, Chen M, Tao ZH, et al. Effects of targeting SLC1A5 on inhibiting gastric cancer growth and tumor development in vitro and in vivo [J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(44): 76458-67. |
| 26 | Liao ZX, Hsu SH, Tang SC, et al. Potential targeting of the tumor microenvironment to improve cancer virotherapy[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2023, 250: 108521. |
| 27 | Wang CX, Zheng XC, Zhang JL, et al. CD300ld on neutrophils is required for tumour-driven immune suppression[J]. Nature, 2023, 621(7980): 830-9. |
| 28 | Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, et al. Cancer statistics, 2023 [J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2023, 73(1): 17-48. |
| 29 | Xia CF, Dong XS, Li H, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants[J]. Chin Med J, 2022, 135(5): 584-90. |
| 30 | Li YM, Liu F. The extracellular vesicles targeting tumor microenvironment: a promising therapeutic strategy for melanoma[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1200249. |
| 31 | Vitale I, Manic G, Coussens LM, et al. Macrophages and metabolism in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Cell Metab, 2019, 30(1): 36-50. |
| 32 | Guilliams M, Scott CL. Liver macrophages in health and disease[J]. Immunity, 2022, 55(9): 1515-29. |
| 33 | Chen YN, Hu MR, Wang L, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2020, 877: 173090. |
| 34 | Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, et al. Macrophage polarization: tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes[J]. Trends Immunol, 2002, 23(11): 549-55. |
| [1] | 王耀彬, 陈柳燕, 罗伊凌, 申继清, 周素芳. NUF2对泛癌的预后和免疫治疗效果的预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 137-149. |
| [2] | 徐朦, 陈丽娜, 吴金玉, 刘丽丽, 施美, 周灏, 张国梁. “白花蛇舌草-半枝莲”治疗原发性肝癌的机制研究:基于网络药理学、分子对接及体外实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 80-89. |
| [3] | 陈孝华, 鲁辉, 王子良, 王炼, 夏勇生, 耿志军, 张小凤, 宋雪, 王月月, 李静, 胡建国, 左芦根. ABI2在胃癌进展和预后中的作用及其调控机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1653-1661. |
| [4] | 薛良军, 谈秋瑜, 许静文, 冯璐, 李文锦, 颜亮, 李玉磊. MiR-6838-5p过表达下调DDR1基因表达抑制乳腺癌MCF-7细胞的增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1677-1684. |
| [5] | 张力苹, 刘喜娟, 胡潇, 王嘉丽, 余锡贺, 栗国梁, 游海敏, 张启周, 张海波. 经动脉化疗栓塞续贯肝动脉灌注化疗联合TKI和PD-1单抗在晚期肝癌一线治疗中的疗效观察[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1831-1838. |
| [6] | 纪凯, 于冠宇, 周乐其, 张天帅, 凌潜龙, 满文江, 朱冰, 张卫. HNRNPA1基因在结直肠癌组织中高表达及其潜在的诊断和治疗价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1685-1695. |
| [7] | 庞一丹, 刘雅, 陈思嫒, 张荆雷, 曾今, 潘元明, 安娟. SPAG5在胃癌细胞恶性增殖中的生物学作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1497-1507. |
| [8] | 从小凡, 陈腾, 李硕, 王媛媛, 周龙云, 李小龙, 张配, 孙小锦, 赵素容. 双氢青蒿素通过促进活性氧的产生增强鼻咽癌细胞对顺铂诱导凋亡的敏感性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1553-1560. |
| [9] | 郑孟冬, 刘妍, 刘娇娇, 康巧珍, 王婷. 蛋白4.1R对肝细胞HL-7702增殖、凋亡以及糖酵解的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1355-1360. |
| [10] | 何华星, 刘璐琳, 刘颖茵, 陈纳川, 孙素霞. 丁酸钠与索拉非尼可能通过YAP诱导铁死亡协同抑制肝癌细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1425-1430. |
| [11] | 房锦存, 刘立威, 林俊豪, 陈逢生. CDHR2过表达通过抑制PI3K/Akt通路抑制乳腺癌细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1117-1125. |
| [12] | 夏勇生, 王炼, 陈孝华, 张雨路, 孙奥飞, 陈德利. 过表达TSR2通过下调PI3K/AKT信号通路抑制胃癌细胞的增殖和侵袭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 913-919. |
| [13] | 陈 浩, 李振汉, 王明婷, 卢林明, 唐乾利, 罗良平. 高表达UBE2S通过增加癌细胞干性促进肝癌的进程机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 455-464. |
| [14] | 黄秋虎, 周 建, 王子珍, 杨 堃, 陈政纲. miR-26b-3p 靶向 CREB1 调控神经胶质瘤细胞的增殖、迁移及侵袭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 578-584. |
| [15] | 朱 瑾, 欧阳欣, 刘 屿, 钱叶梅, 夏 斌, 施延安, 俞力夫. miR-132-3p/CAMTA1对I-125粒子处理的面神经损伤大鼠施万细胞的调控作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 571-577. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||