南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 1497-1507.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.08.08
• • 上一篇
庞一丹1( ), 刘雅1, 陈思嫒1, 张荆雷1, 曾今1, 潘元明2(
), 刘雅1, 陈思嫒1, 张荆雷1, 曾今1, 潘元明2( ), 安娟1(
), 安娟1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-07
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-09-06
通讯作者:
潘元明,安娟
E-mail:15546261023@163.com;peter.f.pan@hsc.pku.edu.cn;anjuan@qhu.edu.cn
作者简介:庞一丹,硕士,E-mail: 15546261023@163.com
基金资助:
Yidan PANG1( ), Ya LIU1, Siai CHEN1, Jinglei ZHANG1, Jin ZENG1, Yuanming PAN2(
), Ya LIU1, Siai CHEN1, Jinglei ZHANG1, Jin ZENG1, Yuanming PAN2( ), Juan AN1(
), Juan AN1( )
)
Received:2024-05-07
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-09-06
Contact:
Yuanming PAN, Juan AN
E-mail:15546261023@163.com;peter.f.pan@hsc.pku.edu.cn;anjuan@qhu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 在胃癌组织及癌旁组织中分析SPAG5的表达情况,通过干扰SPAG5分析其在胃癌细胞生长中的生物学作用。 方法 结合TCGA分析,免疫组织化学、免疫荧光染色分析SPAG5及MKi67在胃癌及癌旁组织中的表达模式,利用胃癌细胞AGS和MGC803进行体外细胞生物学实验,分别设置空白对照组和干扰组,采用慢病毒干扰,其中空白对照转染shCtrl,干扰组转染shSPAG5。通过Celigo、MTT和克隆形成实验、凋亡检测分析敲减SPAG5基因后对胃癌细胞生长的影响。 结果 Proteinatlas数据库、TCGA数据库分析结果发现SPAG5在胃癌中高表达,KM-plot及GEPIA数据库分析SPAG5在肺腺癌、乳腺癌、肝癌、胰腺癌、宫颈癌、膀胱癌中高表达,免疫组化发现SPAG5在胃癌中高表达(P<0.001),免疫组化和免疫荧光共聚焦证明SPAG5与MKi67存在显著相关性(R=0.393,P<0.001)。Real time-PCR及Western blotting结果显示SPAG5在MKN74、BGC823、MGC803、SGC7901和AGS等细胞中表达水平较高(P<0.01)。敲减SPAG5后mRNA和蛋白的表达下降,Celigo、MTT和克隆形成实验结果显示敲减SPAG5抑制胃癌细胞增殖(P<0.01),流式凋亡分析发现敲减SPAG5促进胃癌细胞凋亡(P<0.001)。 结论 SPAG5和MKi67在胃癌组织中的表达具有相关性,干扰SPAG5基因可以抑制胃癌细胞的增殖。SPAG5与患者预后相关,可能成为胃癌的潜在标志物。
庞一丹, 刘雅, 陈思嫒, 张荆雷, 曾今, 潘元明, 安娟. SPAG5在胃癌细胞恶性增殖中的生物学作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1497-1507.
Yidan PANG, Ya LIU, Siai CHEN, Jinglei ZHANG, Jin ZENG, Yuanming PAN, Juan AN. Biological role of SPAG5 in the malignant proliferation of gastric cancer cells[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1497-1507.
| Gene | Upstream primer sequences | Downstream primer sequences | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | TGACTTCAACAGCGACACCCA | CACCCTGTTGCTGTAGCCAAA | 121 |
| SPAG5 | TTGAGGCCCGTTTAGATACCA | GCTTTCCTTGGAGCAATGTAGTT | 227 |
表1 引物序列信息
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Upstream primer sequences | Downstream primer sequences | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | TGACTTCAACAGCGACACCCA | CACCCTGTTGCTGTAGCCAAA | 121 |
| SPAG5 | TTGAGGCCCGTTTAGATACCA | GCTTTCCTTGGAGCAATGTAGTT | 227 |
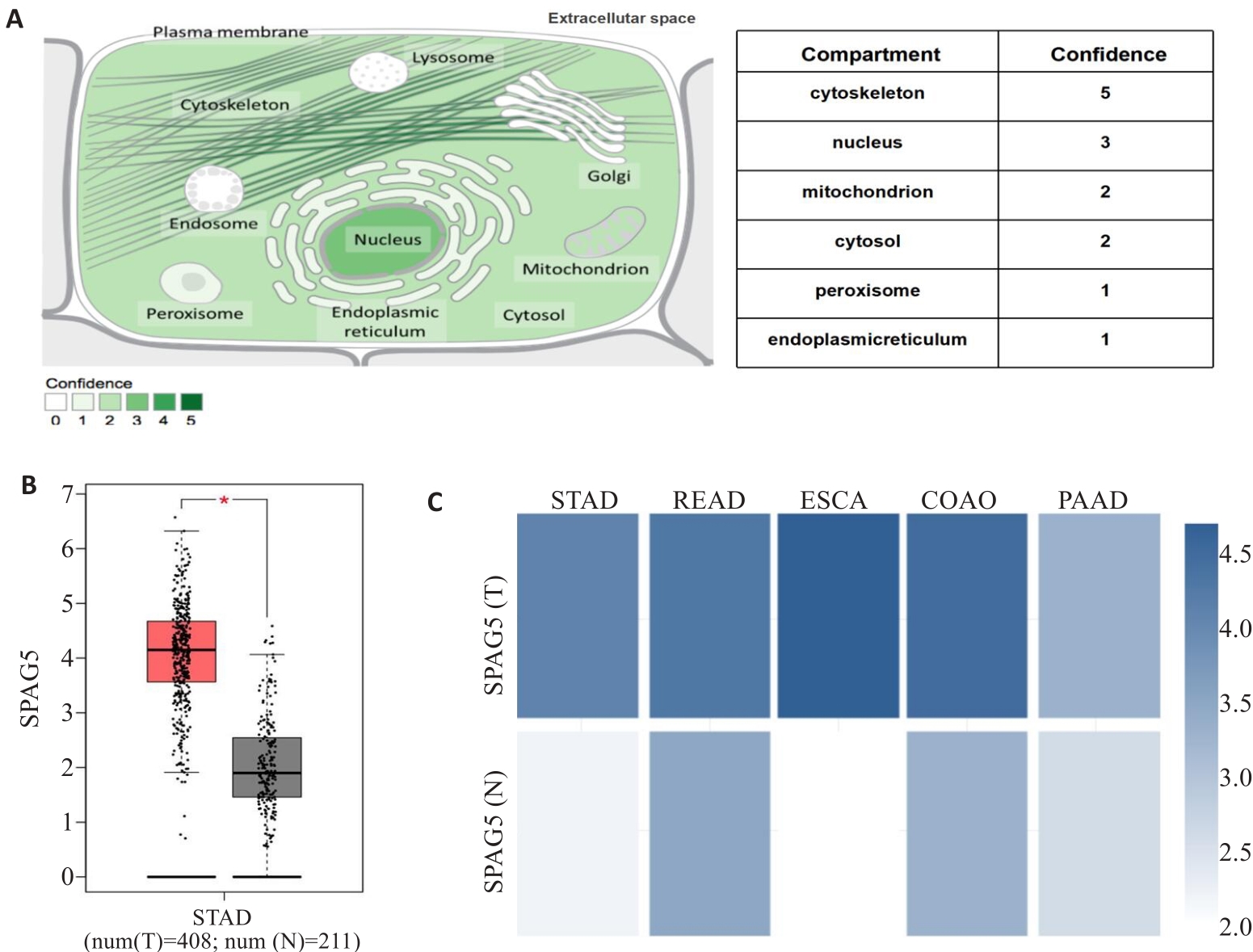
图1 SPAG5表达模式的生物信息分析
Fig.1 Bioinformatic analysis of SPAG5 expression patterns. A:Proteinatlas database analysis showing SPAG5 distribution in both the cell nucleus and cytoplasm. B: TCGA database analysis showing significantly higher expression of SPAG5 in gastric cancer than in normal tissues (*P<0.05). C: Proteinatlas database analysis showing SPAG5 expressions in gastric, rectal adenocarcinoma, esophageal, colon adenocarcinoma, and pancreatic cancer.
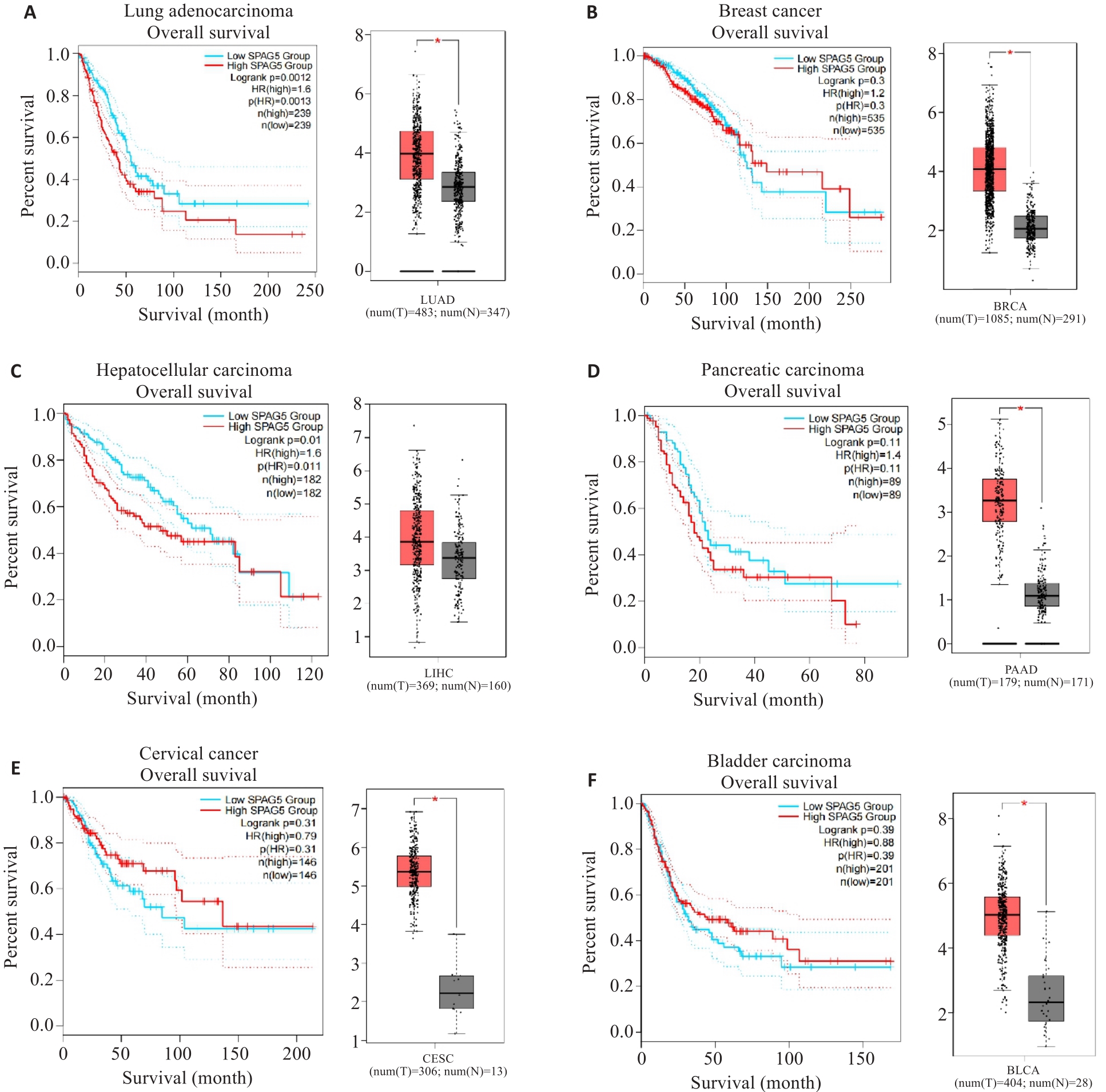
图2 KM-plot及GEPIA数据库分析SPAG5在多种实体肿瘤中的表达
Fig.2 Kaplan-Meier plots and GEPIA database analysis of SPAG5 expression in lung adenocarcinoma (A), breast cancer (B), hepatocellular carcinoma (C), pancreatic cancer (D), cervical cancer (E), and bladder cancer (F) and its association with patient survival (*P<0.05).
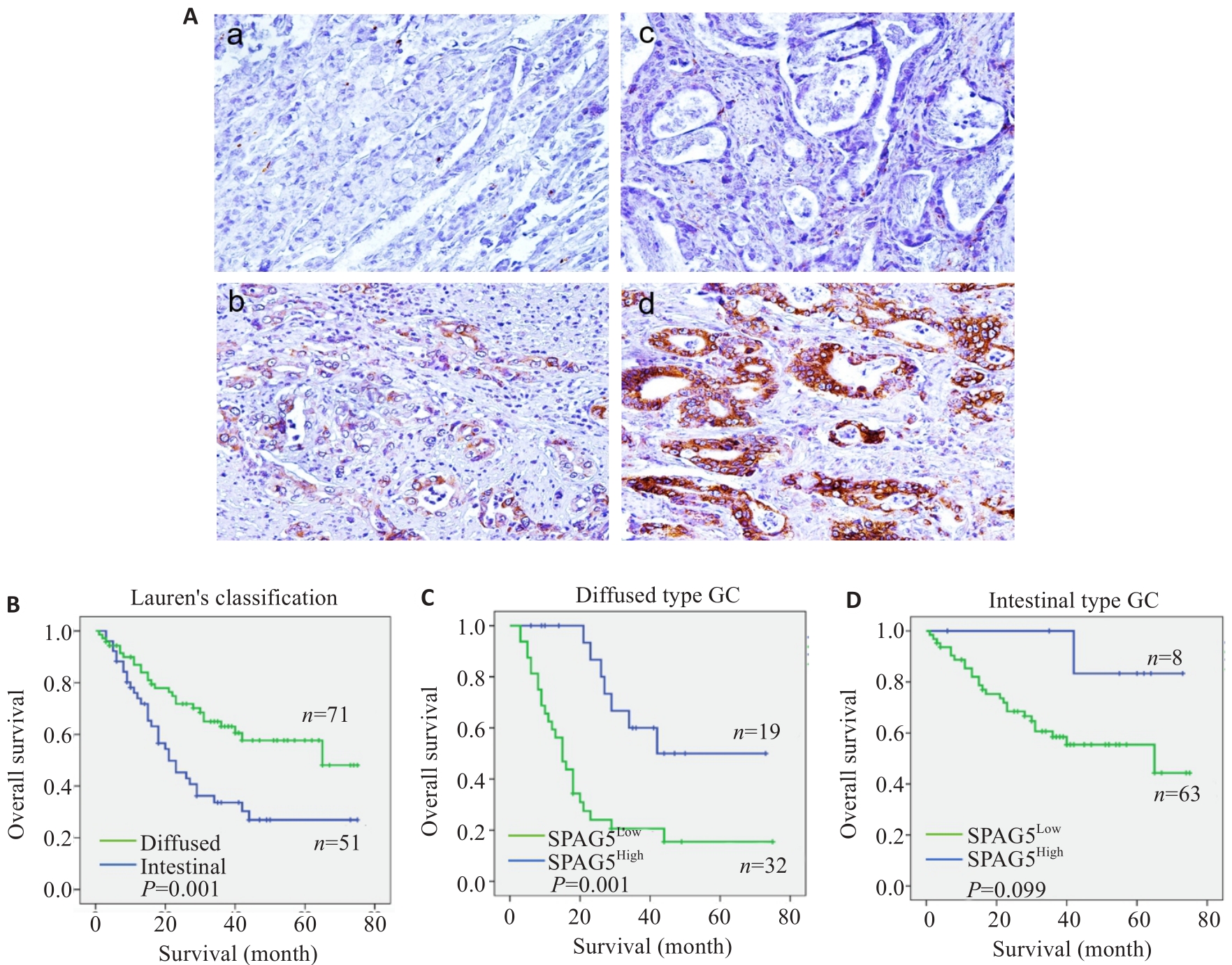
图 3 免疫组化和生存分析SPAG5
Fig.3 Immunohistochemistry for SPAG5 in gastric and adjacent tissues and survival analysis of SPAG5 expression. A: Immunohistochemistry for detecting expression of SPAG5 in gastric cancer and adjacent tissues (Original magnification: ×100). a: Normal gastric mucosal tissue Negative b: Normal gastric mucosal tissue Positive c: Gastric cancer tissue Negative d: Gastric cancer tissue Positive. B-D: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of gastric cancer patients with high and low SPAG5 expression using Log-rank test and Breslow test.
| Type | Cases | SPAG5 expression [n (%)] | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | Low | |||
| Nomal | 50 | 11 (22.0) | 39 (78.0) | <0.01 |
| Tumor | 122 | 95 (78.0) | 27 (22.0) | |
表2-1 SPAG5在胃癌及癌旁组织中的表达
Tab.2-1 Expression of SPAG5 in gastric cancer and adjacent tissues
| Type | Cases | SPAG5 expression [n (%)] | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | Low | |||
| Nomal | 50 | 11 (22.0) | 39 (78.0) | <0.01 |
| Tumor | 122 | 95 (78.0) | 27 (22.0) | |
| Type | Cases | MKi67 expression [n (%)] | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | Low | |||
| Nomal | 50 | 27 (54.0) | 23 (46.0) | <0.01 |
| Tumor | 122 | 75 (61.5) | 47 (38.5) | |
表2-2 MKi67在胃癌及癌旁组织中的表达
Tab.2-2 Expression of MKi67 in gastric cancer and adjacent tissues
| Type | Cases | MKi67 expression [n (%)] | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | Low | |||
| Nomal | 50 | 27 (54.0) | 23 (46.0) | <0.01 |
| Tumor | 122 | 75 (61.5) | 47 (38.5) | |
| Characteristics | Nomal-SPAG5 expression | Characteristics | Tumor-SPAG5 expression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | Low | High | ||
| Nomal-MKi67[High] | 17 | 10 | Tumor-MKi67[High] | 6 | 109 |
| Nomal-MKi67[Low] | 22 | 1 | Tumor-MKi67[Low] | 27 | 30 |
| P | 0.006 | P | <0.01 | ||
| Pearson's R | 0.393 | Pearson's R | 0.504 | ||
表3 结合临床病理学资料分析SPAG5与MKi67在胃癌组织中的表达相关性
Tab.3 Analysis of the correlation between SPAG5 and MKi67 expressions in gastric cancer tissues
| Characteristics | Nomal-SPAG5 expression | Characteristics | Tumor-SPAG5 expression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | Low | High | ||
| Nomal-MKi67[High] | 17 | 10 | Tumor-MKi67[High] | 6 | 109 |
| Nomal-MKi67[Low] | 22 | 1 | Tumor-MKi67[Low] | 27 | 30 |
| P | 0.006 | P | <0.01 | ||
| Pearson's R | 0.393 | Pearson's R | 0.504 | ||
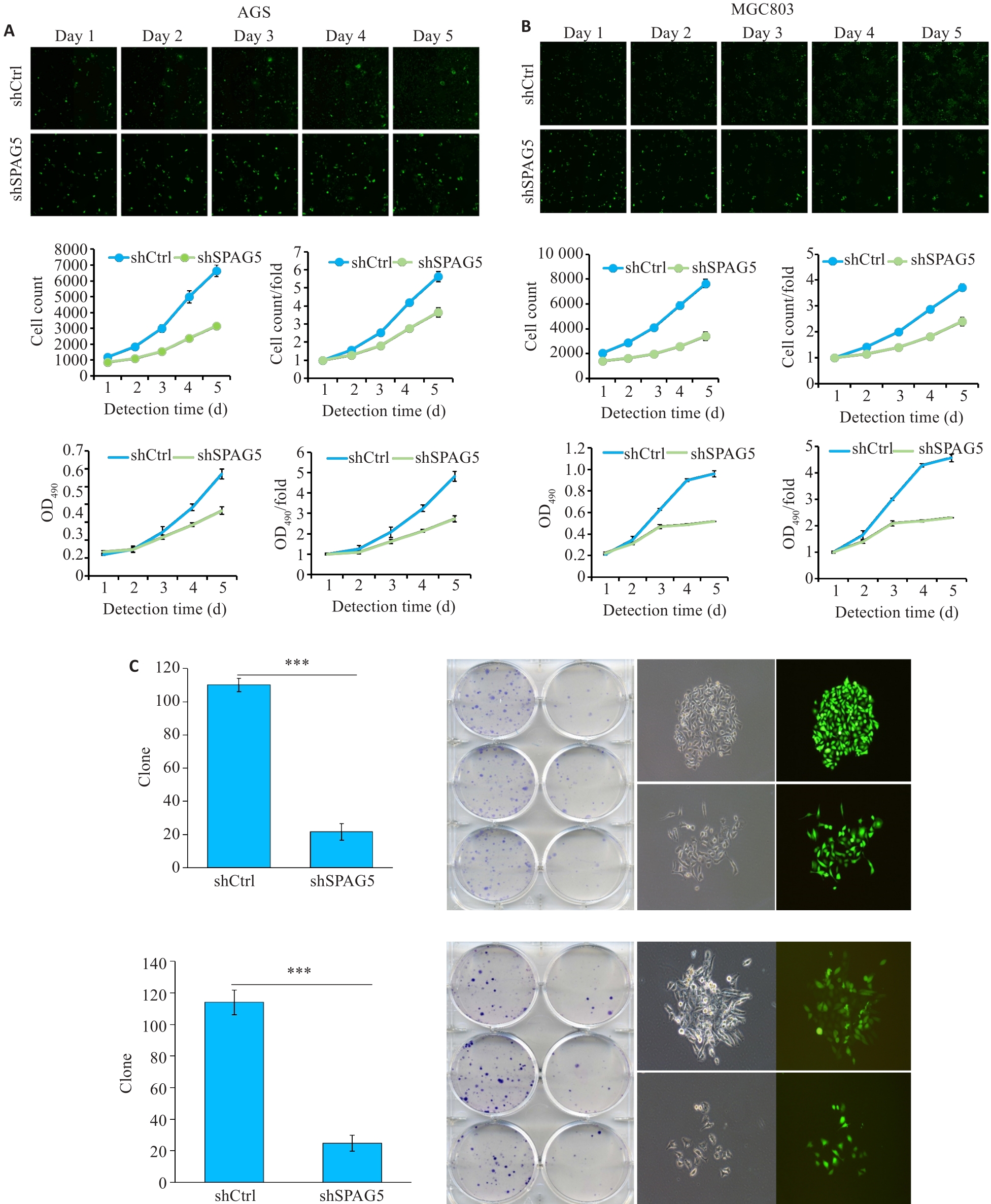
图7 干扰SPAG5后AGS和MGC803细胞的增殖受到显著抑制
Fig.7 Lentivirus-mediated SPAG5 interference inhibits proliferation of AGS and MGC803 cells. A, B: Celigo assay and MTT assays showing inhibition of proliferation of AGS and MGC-803 cells 3 days after lentivirus infection in the experimental group was significantly inhibited. C: Number of clones formed by AGS and MGC-803 cells with SPAG5 knockdown (×100). ***P<0.001.
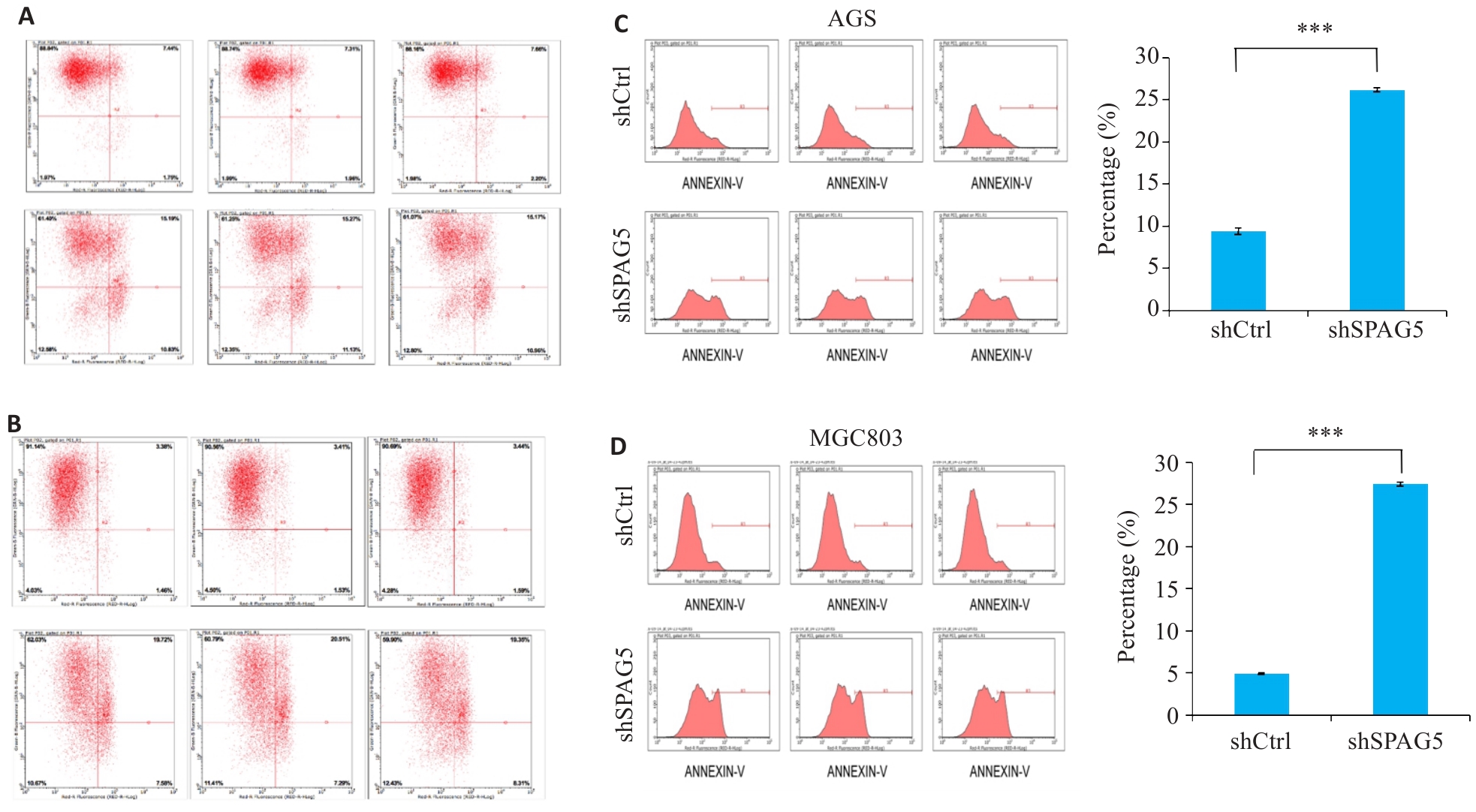
图8 干扰SPAG5促进AGS和MGC803细胞的细胞凋亡
Fig.8 SPAG5 interference promotes apoptosis in AGS and MGC803 cells. A, B: Scatter plot of flow cytometry after SPAG5 interference in AGS cells and MGC803 cells. C, D: Apoptosis rates in AGS cells and MGC803 cells 5 days after SPAG5 interference (***P<0.001).
| 1 | Chen WQ, Zheng RS, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA A Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(2): 115-32. |
| 2 | Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, et al. Gastric cancer[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10251): 635-48. |
| 3 | Guan WL, He Y, Xu RH. Gastric cancer treatment: recent progress and future perspectives[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2023, 16(1): 57. |
| 4 | Zeng XY, Xu WB, Tong JJ, et al. SPAG5 as a novel biomarker and potential therapeutic target via regulating AKT pathway in multiple myeloma[J]. Leuk Lymphoma, 2022, 63(11): 2565-72. |
| 5 | Xiao G, Xu X, Chen ZB, et al. SPAG5 expression predicts poor prognosis and is associated with adverse immune infiltration in lung adenocarcinomas[J]. Clin Med Insights Oncol, 2023, 17: 11795549231199915. |
| 6 | Gao XF, Bu HT, Gao XZ, et al. Pan-cancer analysis: SPAG5 is an immunological and prognostic biomarker for multiple cancers[J]. FASEB J, 2023, 37(10): e23159. |
| 7 | 葛柯乐, 方 成, 燕海娇, 等. 胃癌组织中SPAG5的表达及意义[J]. 山东医药, 2020, 60(10): 55-9. |
| 8 | Liu GD, Liu S, Cao GY, et al. SPAG5 contributes to the progression of gastric cancer by upregulation of Survivin depend on activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2019, 379(1): 83-91. |
| 9 | Chang MS, Huang CJ, Chen ML, et al. Cloning and characterization of hMAP126, a new member of mitotic spindle-associated proteins[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2001, 287(1): 116-21. |
| 10 | Yang YC, Hsu YT, Wu CC, et al. Silencing of astrin induces the p53-dependent apoptosis by suppression of HPV18 E6 expression and sensitizes cells to paclitaxel treatment in HeLa cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2006, 343(2): 428-34. |
| 11 | Kodani A, Yu TW, Johnson JR, et al. Centriolar satellites assemble centrosomal microcephaly proteins to recruit CDK2 and promote centriole duplication[J]. Elife, 2015, 4: e07519. |
| 12 | Gruber J, Harborth J, Schnabel J, et al. The mitotic-spindle-associated protein astrin is essential for progression through mitosis[J]. J Cell Sci, 2002, 115(Pt 21): 4053-9. |
| 13 | Chen W, Chen X, Li SJ, et al. Expression, immune infiltration and clinical significance of SPAG5 in hepatocellular carcinoma: a gene expression-based study[J]. J Gene Med, 2020, 22(4): e3155. |
| 14 | Wang CH, Su HY, Cheng R, et al. SPAG5 is involved in human gliomagenesis through the regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 673780. |
| 15 | He J, Green AR, Li Y, et al. SPAG5: an emerging oncogene[J]. Trends Cancer, 2020, 6(7): 543-7. |
| 16 | Liu P, Li H, Liao CF, et al. Identification of key genes and biological pathways in Chinese lung cancer population using bioinformatics analysis[J]. PeerJ, 2022, 10: e12731. |
| 17 | Xu J, Deng YJ, Wang Y, et al. SPAG5-AS1 inhibited autophagy and aggravated apoptosis of podocytes via SPAG5/AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. Cell Prolif, 2020, 53(2): e12738. |
| 18 | Liu HL, Hu JW, Wei R, et al. SPAG5 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by downregulating SCARA5 through modifying β-catenin degradation[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 37(1): 229. |
| 19 | Li M, Li AQ, Zhou SL, et al. SPAG5 upregulation contributes to enhanced c-MYC transcriptional activity via interaction with c-MYC binding protein in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2019, 12(1): 14. |
| 20 | Li YW, Diao YC, Wang ZX, et al. The splicing factor SF3B4 drives proliferation and invasion in cervical cancer by regulating SPAG5[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2022, 8(1): 326. |
| 21 | Dang L, Shi CP, Zhang QQ, et al. Downregulation of sperm-associated antigen 5 inhibits melanoma progression by regulating forkhead box protein M1/a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17/NOTCH1 signaling[J]. Bioengineered, 2022, 13(3): 4744-56. |
| 22 | Buechler S. Low expression of a few genes indicates good prognosis in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer[J]. BMC Cancer, 2009, 9: 243. |
| 23 | Abdel-Fatah TMA, Agarwal D, Liu DX, et al. SPAG5 as a prognostic biomarker and chemotherapy sensitivity predictor in breast cancer: a retrospective, integrated genomic, transcriptomic, and protein analysis[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2016, 17(7): 1004-18. |
| 24 | Du Q, Xiao RD, Luo RG, et al. Construction of long non-coding RNA- and microRNA-mediated competing endogenous RNA networks in alcohol-related esophageal cancer[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(6): e0269742. |
| 25 | Huang RJ, Li AL. SPAG5 is associated with unfavorable prognosis in patients with lung adenocarcinoma and promotes proliferation, motility and autophagy in A549 cells[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2020, 20(5): 77. |
| 26 | Li HY, Qin YF, Huang YR, et al. SPAG5, the upstream protein of Wnt and the target of curcumin, inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncol Rep, 2023, 50(3): 172. |
| 27 | Zhang WW, Xiao YH, Zhou Q, et al. KNSTRN is a prognostic biomarker that is correlated with immune infiltration in breast cancer and promotes cell cycle and proliferation[J]. Biochem Genet, 2024: Online ahead of print.. |
| 28 | An J, Yang L, Pan YM, et al. SPAG5 activates PI3K/AKT pathway and promotes the tumor progression and chemo-resistance in gastric cancer[J]. DNA Cell Biol, 2022, 41(10): 893-902. |
| 29 | Hashmi AA, Hashmi KA, Irfan M, et al. Ki67 index in intrinsic breast cancer subtypes and its association with prognostic parameters[J]. BMC Res Notes, 2019, 12(1): 605. |
| 30 | Uxa S, Castillo-Binder P, Kohler R, et al. Ki-67 gene expression[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2021, 28(12): 3357-70. |
| 31 | Luo ZW, Zhu MG, Zhang ZQ, et al. Increased expression of Ki-67 is a poor prognostic marker for colorectal cancer patients: a meta analysis[J]. BMC Cancer, 2019, 19(1): 123. |
| 32 | Faragalla H, Plotkin A, Barnes P, et al. Ki67 in breast cancer assay: an ad hoc testing recommendation from the Canadian association of pathologists task force[J]. Curr Oncol, 2023, 30(3): 3079-90. |
| 33 | Gerdes J, Li L, Schlueter C, et al. Immunobiochemical and molecular biologic characterization of the cell proliferation-associated nuclear antigen that is defined by monoclonal antibody Ki-67[J]. Am J Pathol, 1991, 138(4): 867-73. |
| 34 | van Ree JH, Jeganathan KB, Malureanu L, et al. Overexpression of the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UbcH10 causes chromosome missegregation and tumor formation[J]. J Cell Biol, 2010, 188(1): 83-100. |
| 35 | Chen Z, Zhang CP, Wu DY, et al. Phospho-MED1-enhanced UBE2C locus looping drives castration-resistant prostate cancer growth[J]. EMBO J, 2011, 30(12): 2405-19. |
| 36 | Ramos-Santillan V, Oshi M, Nelson E, et al. High Ki67 gene expression is associated with aggressive phenotype in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. World J Oncol, 2024, 15(2): 257-67. |
| 37 | Li B, Severson E, Pignon JC, et al. Comprehensive analyses of tumor immunity: implications for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Genome Biol, 2016, 17(1): 174. |
| [1] | 耿志军, 杨晶晶, 牛民主, 刘馨悦, 施金冉, 刘亦珂, 姚新宇, 张雨路, 张小凤, 胡建国. 桑黄酮G通过调控PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路抑制胃癌细胞的生长、迁移和侵袭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1476-1484. |
| [2] | 何华星, 刘璐琳, 刘颖茵, 陈纳川, 孙素霞. 丁酸钠与索拉非尼可能通过YAP诱导铁死亡协同抑制肝癌细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1425-1430. |
| [3] | 夏勇生, 王炼, 陈孝华, 张雨路, 孙奥飞, 陈德利. 过表达TSR2通过下调PI3K/AKT信号通路抑制胃癌细胞的增殖和侵袭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 913-919. |
| [4] | 杨晶晶, 殷丽霞, 段婷, 牛民主, 何震东, 陈心蕊, 张小凤, 李静, 耿志军, 左芦根. 胃癌组织中高表达ATP5A1与患者术后的不良预后和肿瘤细胞的糖代谢有关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 974-980. |
| [5] | 梁一豪, 赖颖君, 袁燕文, 袁 炜, 张锡波, 张拔山, 卢志锋. 基于GEO数据库筛选胃癌差异表达基因及其功能和通路富集分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 605-616. |
| [6] | 沈梦迪, 赵 娜, 邓晓晶, 邓 敏. COX6B2在胃癌组织中高表达并影响患者的远期预后:基于抑制p53信号调控胃癌细胞的增殖及细胞周期[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 289-297. |
| [7] | 张 诺, 张 震, 张雨路, 宋 雪, 张小凤, 李 静, 左芦根, 胡建国. PCID2在胃癌组织中高表达并通过调控细胞周期进程和增殖影响患者预后[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 324-332. |
| [8] | 张文静, 张 诺, 杨 子, 张小凤, 孙奥飞, 王 炼, 宋 雪, 耿志军, 李 静, 胡建国. BZW1 高表达促进胃癌细胞的侵袭和转移:基于调控Wnt//β-catenin通路和促进上皮间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 354-362. |
| [9] | 段 婷, 张 震, 施金冉, 肖林雨, 杨晶晶, 殷丽霞, 张小凤, 耿志军, 陆国玉. CPNE3在胃癌中高表达并与患者的预后不良相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 129-137. |
| [10] | 冯 雯, 赖跃兴, 王 静, 徐 萍. 长链非编码RNA ABHD11-AS1促进胃癌细胞糖酵解并加速肿瘤恶性进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1485-1492. |
| [11] | 王 炼, 夏勇生, 张 震, 刘馨悦, 施金冉, 王月月, 李 静, 张小凤, 耿志军, 宋 雪, 左芦根. 高表达MRPL13促进胃癌细胞增殖并影响患者预后:基于抑制p53信号[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1558-1566. |
| [12] | 左芦根, 王 炼, 杨 子, 李骏杰, 王文锋, 李 静, 王月月, 宋 雪, 张小凤, 耿志军. 高表达CAMSAP2通过上调TGF-β信号促进胃癌细胞的侵袭和转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1460-1468. |
| [13] | 王秋生, 张 震, 王 炼, 汪 煜, 姚新宇, 王月月, 张小凤, 葛思堂, 左芦根. 高表达DAP5促进胃癌细胞的糖代谢并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1063-1070. |
| [14] | 张 浩, 张 震, 王秋生, 王 炼, 杨 子, 耿志军, 王月月, 李 静, 左芦根. FJX1在胃癌组织中高表达并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 975-984. |
| [15] | 葛 菲, 万梦琪, 程振宇, 陈雪雷, 陈芊伊, 戚之琳. 芦荟苷可抑制胃癌细胞的增殖和迁移:基于下调STAT3/HMGB1信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 702-709. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||