南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 80-89.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.11
徐朦1( ), 陈丽娜2, 吴金玉3, 刘丽丽4, 施美4, 周灏4, 张国梁4(
), 陈丽娜2, 吴金玉3, 刘丽丽4, 施美4, 周灏4, 张国梁4( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-06
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2025-01-20
通讯作者:
张国梁
E-mail:1025473030@qq.com;zhangguoliang61@sina.com
作者简介:徐 朦,在读博士研究生,E-mail: 1025473030@qq.com
基金资助:
Meng XU1( ), Lina CHEN2, Jinyu WU3, Lili LIU4, Mei SHI4, Hao ZHOU4, Guoliang ZHANG4(
), Lina CHEN2, Jinyu WU3, Lili LIU4, Mei SHI4, Hao ZHOU4, Guoliang ZHANG4( )
)
Received:2024-09-06
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-20
Contact:
Guoliang ZHANG
E-mail:1025473030@qq.com;zhangguoliang61@sina.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 通过网络药理学及分子对接探究“白花蛇舌草-半枝莲”的有效成分及其作用于原发性肝癌的主要生物过程及信号通路。 方法 通过TCMSP、Uniport、Genecards、String数据库以及Cytoscape软件得出最终核心基因;通过ClueGo对药物-疾病共有基因做GO、KEGG富集分析;通过Pubcham、RCSB、Autoduck把药物有效成分与最终核心基因进行分子对接,得出结合能最高药物有效成分;再通过CCK-8、细胞凋亡、Western blotting实验研究此药物有效成分对HepG2的作用。 结果 筛选得出最终核心基因为TP53、ESR1。GO分析显示主要生物过程为BP- regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway,negative regulation of cell population proliferation;CC-membrane raft; MF-protein kinase activity等。KEGG分析显示主要信号通路为Apoptosis,Proteoglycans in cancer,PI3K-Akt signaling pathway,Hepatitis B等。分子对接结果显示,药物有效成分与最终核心基因均可以在自然条件下进行对接,其中ESR1与ursolic acid结合能最高(-4.98 kcal/mol)。CCK-8、细胞凋亡、Western blotting实验显示ursolic acid对HepG2有明显抑制作用。 结论 “白花蛇舌草-半枝莲” 通过多种有效成分与原发性肝癌紧密结合,继而对原发性肝癌起到治疗作用。
徐朦, 陈丽娜, 吴金玉, 刘丽丽, 施美, 周灏, 张国梁. “白花蛇舌草-半枝莲”治疗原发性肝癌的机制研究:基于网络药理学、分子对接及体外实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 80-89.
Meng XU, Lina CHEN, Jinyu WU, Lili LIU, Mei SHI, Hao ZHOU, Guoliang ZHANG. Mechanism of Hedyotis diffusa-Scutellaria barbata D. Don for treatment of primary liver cancer: analysis with network pharmacology, molecular docking and in vitro validation[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 80-89.
| Antibody name | Dilution ratio | Species and genus |
|---|---|---|
| JNK | 1:5000 | Mouse |
| p-JNK | 1:1000 | Rabbit |
| P38 | 1:2000 | Rabbit |
| p-P38 | 1:1000 | Mouse |
| ERK1/2 | 1:1000 | Rabbit |
| P-ERK1/2 | 1:1000 | Rabbit |
表1 一抗稀释液比例
Tab.1 List of the primary antibodies used for Western blotting
| Antibody name | Dilution ratio | Species and genus |
|---|---|---|
| JNK | 1:5000 | Mouse |
| p-JNK | 1:1000 | Rabbit |
| P38 | 1:2000 | Rabbit |
| p-P38 | 1:1000 | Mouse |
| ERK1/2 | 1:1000 | Rabbit |
| P-ERK1/2 | 1:1000 | Rabbit |
| MOL | MOL name | OB% | DL |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOL000098 | quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 |
| MOL000358 | beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| MOL000449 | Stigmasterol | 43.83 | 0.76 |
表2 药物共有基因
Tab.2 Drug shared genes
| MOL | MOL name | OB% | DL |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOL000098 | quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 |
| MOL000358 | beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| MOL000449 | Stigmasterol | 43.83 | 0.76 |
| Active ingredient | Coregene | Bindingenergy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| 2-hydroxy-3-methylanthraquinone | TP53 | -4.41 |
| ESR1 | -4.34 | |
| 2-methoxy-3-methyl-9,10-anthraquinone | TP53 | -4.73 |
| ESR1 | -4.01 | |
| Quercetin | TP53 | -3.05 |
| Beta-sitosterol | TP53 | -3.79 |
| ESR1 | -4.18 | |
| Ursolic acid | TP53 | -4.49 |
| ESR1 | -4.98 | |
| Poriferasterol | TP53 | -4.7 |
| ESR1 | -4.52 | |
| Stigmasterol | TP53 | -3.97 |
| ESR1 | -4.7 | |
| Rivularin | TP53 | -3.2 |
| Chrysin-5-methylether | TP53 | -4.26 |
| 7-hydroxy-5,8-dimethoxy-2-phenyl-chromone | TP53 | -3.48 |
| ESR1 | -3.06 | |
| 5-hydroxy-7,8-dimethoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)chromone | TP53 | -3.38 |
| 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-6-methoxyflavanone | TP53 | -3.53 |
| Moslosooflavone | TP53 | -3.18 |
| eriodictyol | TP53 | -3.68 |
| Salvigenin | TP53 | -3.56 |
| ESR1 | -3.18 | |
| Baicalin | TP53 | -3.14 |
| ESR1 | -3.51 | |
| Baicalein | TP53 | -3.69 |
| Sitosteryl acetate | TP53 | -4.71 |
| ESR1 | -4.34 | |
| 24-Ethylcholest-4-en-3-one | TP53 | -4.26 |
| ESR1 | -3.89 | |
| Dinatin | TP53 | -3.39 |
| (2R)-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)chroman-4-one | TP53 | -3.38 |
| ESR1 | -3.21 | |
| CLR | TP53 | -4.45 |
| ESR1 | -4.63 | |
| Sitosterol | TP53 | -3.83 |
| ESR1 | -4.25 | |
| Wogonin | TP53 | -3.61 |
表3 药物有效成分与最终核心基因对接的结合能(部分)
Tab.3 Binding energy of drug active ingredients and final core gene docking (part)
| Active ingredient | Coregene | Bindingenergy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| 2-hydroxy-3-methylanthraquinone | TP53 | -4.41 |
| ESR1 | -4.34 | |
| 2-methoxy-3-methyl-9,10-anthraquinone | TP53 | -4.73 |
| ESR1 | -4.01 | |
| Quercetin | TP53 | -3.05 |
| Beta-sitosterol | TP53 | -3.79 |
| ESR1 | -4.18 | |
| Ursolic acid | TP53 | -4.49 |
| ESR1 | -4.98 | |
| Poriferasterol | TP53 | -4.7 |
| ESR1 | -4.52 | |
| Stigmasterol | TP53 | -3.97 |
| ESR1 | -4.7 | |
| Rivularin | TP53 | -3.2 |
| Chrysin-5-methylether | TP53 | -4.26 |
| 7-hydroxy-5,8-dimethoxy-2-phenyl-chromone | TP53 | -3.48 |
| ESR1 | -3.06 | |
| 5-hydroxy-7,8-dimethoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)chromone | TP53 | -3.38 |
| 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-6-methoxyflavanone | TP53 | -3.53 |
| Moslosooflavone | TP53 | -3.18 |
| eriodictyol | TP53 | -3.68 |
| Salvigenin | TP53 | -3.56 |
| ESR1 | -3.18 | |
| Baicalin | TP53 | -3.14 |
| ESR1 | -3.51 | |
| Baicalein | TP53 | -3.69 |
| Sitosteryl acetate | TP53 | -4.71 |
| ESR1 | -4.34 | |
| 24-Ethylcholest-4-en-3-one | TP53 | -4.26 |
| ESR1 | -3.89 | |
| Dinatin | TP53 | -3.39 |
| (2R)-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)chroman-4-one | TP53 | -3.38 |
| ESR1 | -3.21 | |
| CLR | TP53 | -4.45 |
| ESR1 | -4.63 | |
| Sitosterol | TP53 | -3.83 |
| ESR1 | -4.25 | |
| Wogonin | TP53 | -3.61 |
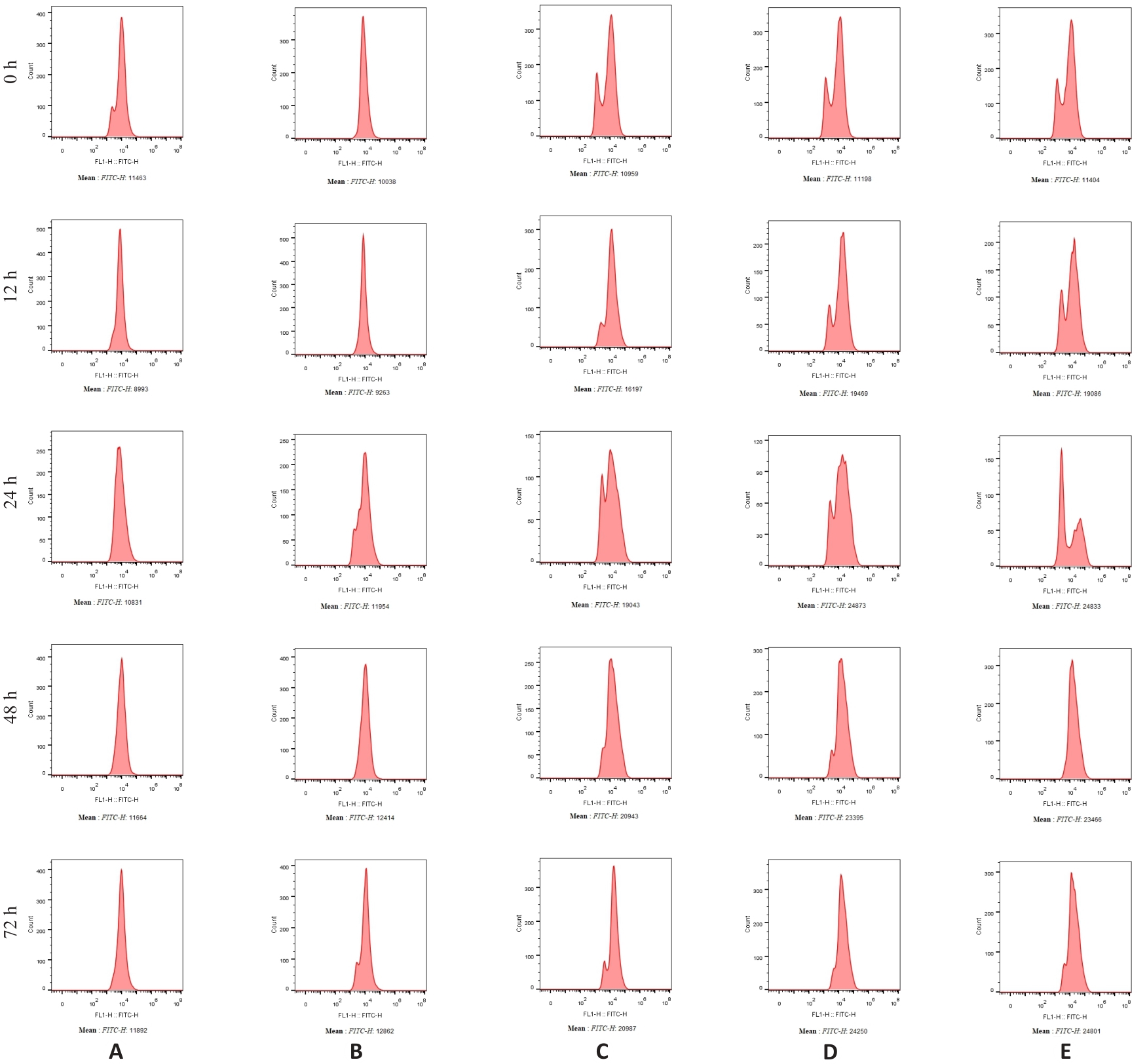
图8 ROS流式检测图
Fig.8 ROS flow cytometry analysis. A: HepG2. B: 0 µmol/L ursolic acid. C: 20 µmol/L ursolic acid. D: 40 µmol/L ursolic acid. E: 80 µmol/L ursolic acid.
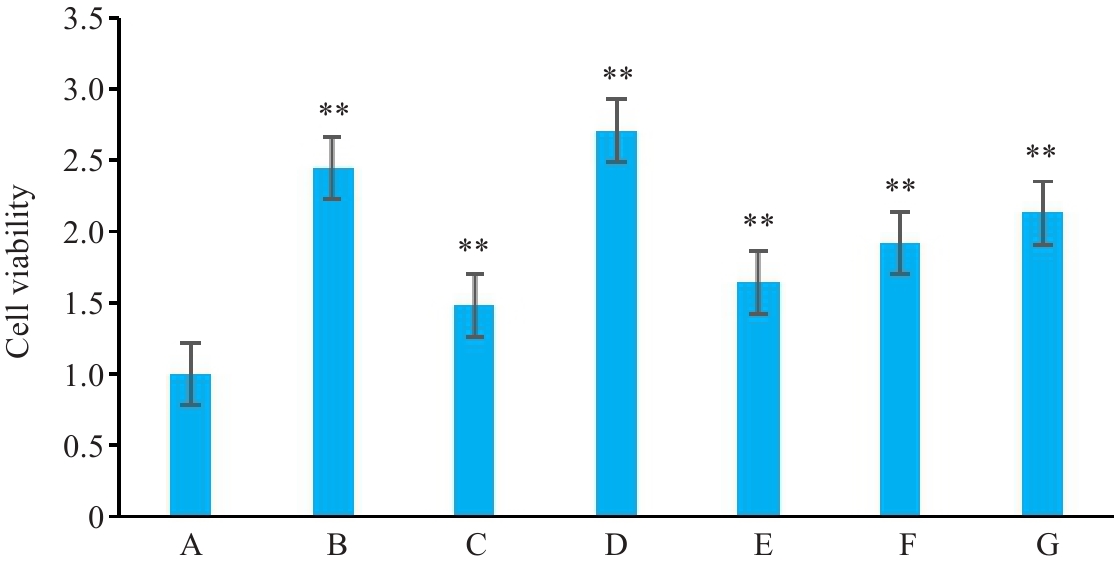
图10 Ursolic acid及索拉非尼对HepG2细胞活力的影响
Fig.10 Effects of usolic acid and sorafenib on viability of HepG2 cells. A: LO-2. B: HepG2+blank serum. C: HepG2+40 µmol/L ursolic acid. D: HepG2+1.5 µmol/L JNK inhibitor. E: HepG2+sorafenib (10 µmol/L, cultured for 24 hours). F: HepG2+40 µmol/L ursolic acid+1.5 µmol/L JNK inhibitor. G: HepG2+sorafenib (10 µmol/L, cultured for 24 hours)+1.5 µmol/L JNK inhibitor. **P<0.01 vs A.
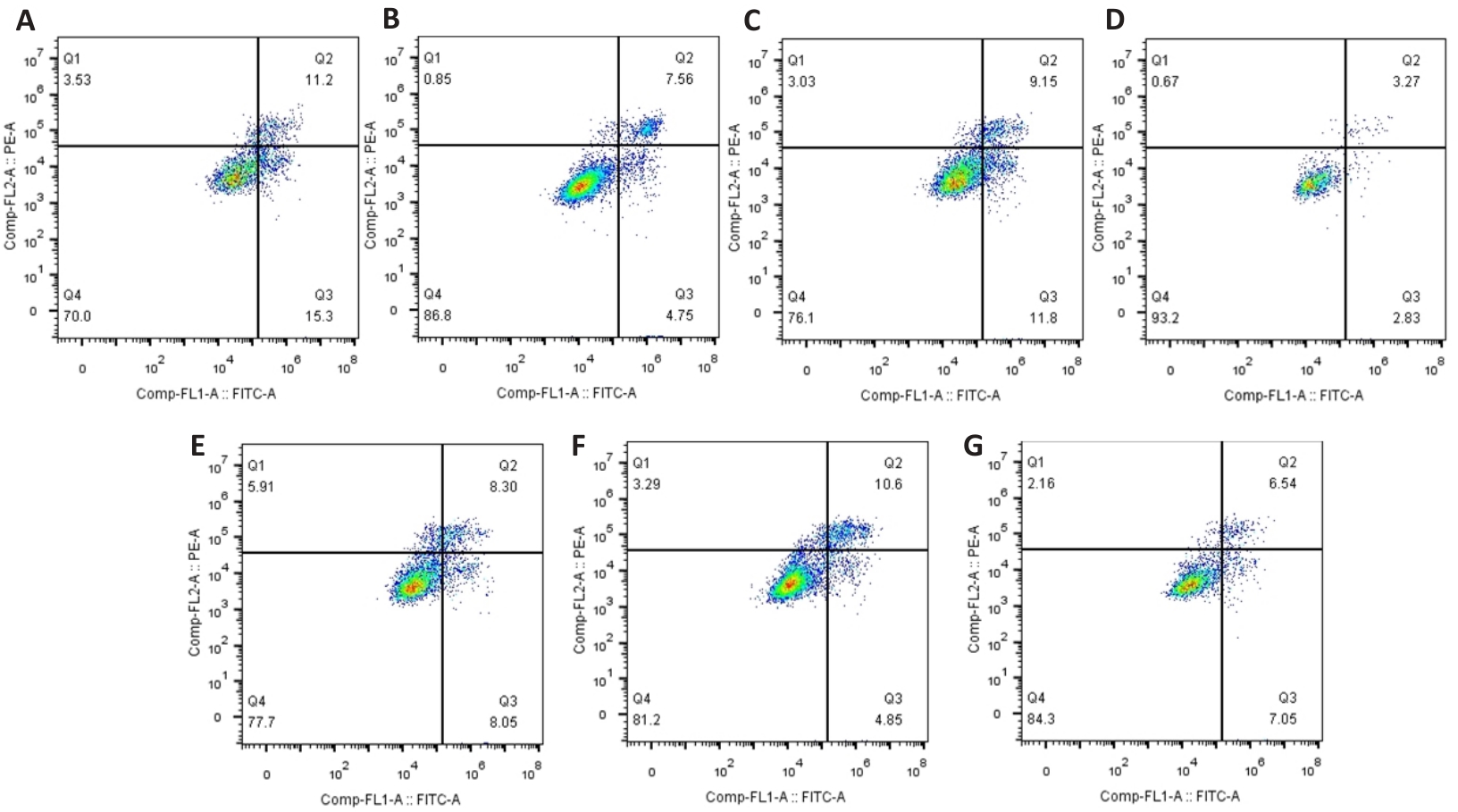
图11 HepG2细胞凋亡率
Fig.11 Apoptosis rate of HepG2 cells with different treatments. A: LO-2. B: HepG2. C: HepG2+optimal concentration of ursolic acid. D: HepG2+optimal concentration of JNK inhibitor. E: HepG2+sorafenib (10 µmol/L, cultured for 24 hours). F: HepG2+optimal concentration of ursolic acid+optimal concentration of JNK inhibitor. G: HepG2+sorafenib (10 µmol/L, cultured for 24 hours)+optimal concentration of JNK inhibitor.
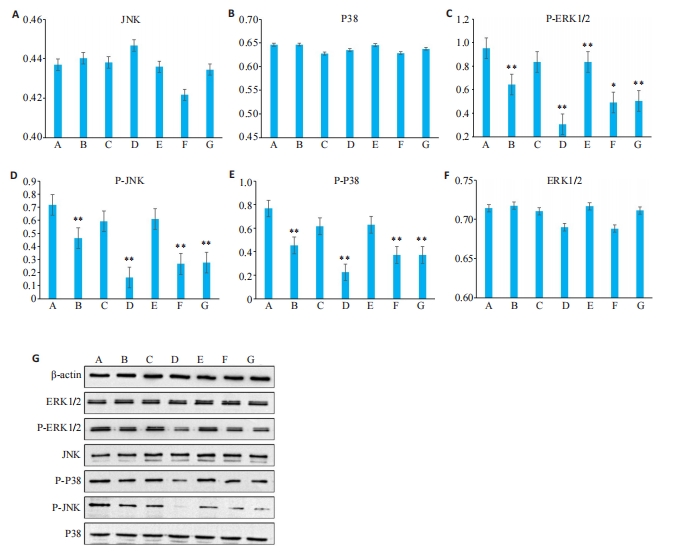
图12 各组HepG2中蛋白的相对表达量
Fig.12 Relative expression levels of proteins in HepG2 cells with different treatments. A: LO-2. B: HepG2. C: HepG2+optimal concentration of ursolic acid. D: HepG2+optimal concentration of JNK inhibitor. E: HepG2+sorafenib (10 µmol/L, cultured for 24 hours). F:HepG2+optimal concentration of ursolic acid+optimal concentration of JNK inhibitor. G: HepG2+sorafenib (10 µmol/L, cultured for 24hours)+optimal concentration of JNK inhibitor *P<0.05, **P<0.01vs A.
| 1 | Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2002[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2005, 55(2):74-108. |
| 2 | El-Serag, Hashem B. Hepatocellular Carcinoma[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2002,35(5):72-8. |
| 3 | Ananthakrishnan A, Gogineni V, Saeian K. Epidemiology of primary and secondary liver cancers[J]. Semin Intervent Radiol, 2006, 23(1): 47-63. |
| 4 | Donato F, Boffetta P, Puoti M. A meta-analysis of epidemiological studies on the combined effect of hepatitis B and C virus infections in causing hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Cancer, 1998, 75(3): 347-54. |
| 5 | Kew MC, dos Santos HA, Sherlock S. Diagnosis of primary cancer of the liver[J]. Br Med J, 1971, 4(5784): 408-11. |
| 6 | Li ZQ. Traditional Chinese medicine for primary liver cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 1998, 4(4): 360. |
| 7 | Hu CJ, He J, Li GZ, et al. Analyzing hedyotis diffusa mechanisms of action from the genomics perspective[J]. Comput Meth Programs Biomed, 2019, 174: 1-8. |
| 8 | Qian K, Fu D, Jiang BR, et al. Mechanism of Hedyotis diffusa in the treatment of cervical cancer[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 808144. |
| 9 | Wang TS, Wang SQ, Xiao DL. A review of phytochemistry and antitumor activity of a valuable medicinal species: Scutellaria barbata[J]. J Med Plant Res, 2012,6(26):4259-75. |
| 10 | 杨培伟, 朱金霞, 陈欣菊, 等.半枝莲-白花蛇舌草调控Wnt/β-catenin轴对肝癌迁移和侵袭的作用机制研究[J/OL].中药药理与临床,2024,11:1-18. |
| 11 | Xu TF, Li SZ, Sun YF, et al. Systematically characterize the absorbed effective substances of Wutou Decoction and their metabolic pathways in rat plasma using UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS combined with a target network pharmacological analysis[J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2017, 141: 95-107. |
| 12 | Ru JL, Li P, Wang JN, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines[J]. J Cheminform, 2014, 6: 13. |
| 13 | Wang JH, Zhao LF, Lin P, et al. GenCLiP 2.0: a web server for functional clustering of genes and construction of molecular networks based on free terms[J]. Bioinformatics, 2014, 30(17): 2534-6. |
| 14 | Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks[J]. Genome Res, 2003, 13(11): 2498-504. |
| 15 | Safran M, Dalah I, Alexander J, et al. GeneCards Version 3: the human gene integrator[J]. Database, 2010, 2010: baq020. |
| 16 | Luo WJ, Brouwer C. Pathview: an R/Bioconductor package for pathway-based data integration and visualization[J]. Bioinformatics, 2013, 29(14): 1830-1. |
| 17 | Martucci D, Masseroli M, Pinciroli F. Gene ontology application to genomic functional annotation, statistical analysis and knowledge mining[J]. Stud Health Technol Inform, 2004, 102: 108-31. |
| 18 | 王 宇, 范璐璐. BET蛋白抑制剂JQ1增强索拉非尼对肝癌细胞的增殖抑制研究[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2020, 55(8): 1185-8. |
| 19 | Bykov VJN, Eriksson SE, Bianchi, et al. Targeting mutant p53 for efficient cancer therapy[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2018, 18(2): 89-102. |
| 20 | Zhang YY, Cheng JX, Zhong C, et al. ESR1 regulates the obesity- and metabolism-differential gene MMAA to inhibit the occurrence and development of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 899969. |
| 21 | Elsherbiny NM, Eisa NH, El-Sherbiny M, et al. Chemo-preventive effect of crocin against experimentally-induced hepatocarcinogenesis via regulation of apoptotic and Nrf2 signaling pathways[J]. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol, 2020, 80: 103494. |
| 22 | Xiao SF, Tang HR, Bai Y, et al. Swertiamarin suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via negative regulation of FRAT1[J]. Eur J Histochem, 2020, 64(4): 3169. |
| 23 | Ripa I, Andreu S, López-Guerrero JA, et al. Membrane rafts: portals for viral entry[J]. Front Microbiol, 2021, 12: 631274. |
| 24 | Brábek J, Hanks SK. Assaying protein kinase activity. In: Dickson, R.C., Mendenhall, M.D. (eds) signal transduction protocols[J]. Methods Molecul Biol, 2020,284: 1302-9. |
| 25 | Roques M, Tirard A, DeGroot LJ. Liver protein kinase activity and triiodothyronine[J]. Endocrinology, 1977, 100(4): 967-73. |
| 26 | Arbuthnot P, Kew M. Hepatitis B virus and hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Exp Pathol, 2001, 82(2): 77-100. |
| 27 | Martini M, De Santis MC, Braccini L, et al. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: an updated review[J]. Ann Med, 2014, 46(6): 372-83. |
| 28 | Baghy K, Tátrai P, Regős E, et al. Proteoglycans in liver cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22(1):379-93. |
| 29 | Guicciardi ME, Gores GJ. Apoptosis: a mechanism of acute and chronic liver injury[J]. Gut, 2005, 54(7): 1024-33. |
| [1] | 褚乔, 王小娜, 续佳颖, 彭荟林, 赵裕琳, 张静, 陆国玉, 王恺. 白头翁皂苷D通过多靶点和多途径抑制三阴性乳腺癌侵袭转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [2] | 龙秀鹏, 陶顺, 阳绅, 李素云, 饶利兵, 李莉, 张哲. 槲皮素通过抑制MAPK信号通路改善心力衰竭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 187-196. |
| [3] | 陈星梅, 刘琴文, 李镱, 钟晓宇, 樊奇灵, 马柯, 罗柳婷, 官道刚, 朱志博. 茵陈蒿汤治疗肝纤维化的核心功能成分群以及潜在通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1508-1517. |
| [4] | 张珊苑, 蔡巧燕, 祁江晗, 殷恺馨, 何晨晨, 高铸烨, 张铃, 褚剑锋. 清心解瘀颗粒抗动脉粥样硬化的药效学及调控机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1518-1528. |
| [5] | 张钰明, 夏士程, 张淋淋, 陈梦茜, 刘晓婧, 高琴, 叶红伟. 金银花提取物对小鼠阿霉素肝脏损伤的保护作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1571-1581. |
| [6] | 王瑾瑾, 崔文飞, 窦雪伟, 尹冰磊, 牛钰琪, 牛羚, 闫国立. 鬼箭羽通过调节EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂耐药信号通路延缓糖尿病肾病的进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1243-1255. |
| [7] | 王琳月, 戚文月, 高记华, 田茂生, 许建成. 痛痒消洗剂可促进大鼠肛瘘术后的创面愈合[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1256-1265. |
| [8] | 张文祥, 顾惠贤, 陈鹏德, 吴思宇, 马洪艳, 姚蓝. 复方玉液汤通过调控PI3K/Akt信号通路抑制糖尿病大鼠心肌细胞凋亡和炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1306-1314. |
| [9] | 黄燕, 覃璐璐, 管少兴, 管宴萍, 韦玉茹, 操艾伶, 李冬梅, 韦桂宁, 苏启表. 金缕半枫荷的水提取物抑制胰腺癌的作用机制:活性成分、关键靶点和信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1336-1344. |
| [10] | 任志军, 刁建新, 王奕婷. 芎归汤通过抑制氧化应激诱导的心肌凋亡减轻小鼠心梗后心衰引起的心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1416-1424. |
| [11] | 李睿镈, 高歌, 谢曦, 罗海彬. 槟榔活性成分诱导口腔黏膜下纤维化的机制:基于网络药理学结合临床样本验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 930-940. |
| [12] | 李云飞, 杨婧怡, 张 颖, 张财霞, 韦宇翔, 王怡颖, 吴 宁, 孙见飞, 吴遵秋. 苗药四大血减轻大鼠的类风湿性关节炎:基于下调基质金属蛋白表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 739-747. |
| [13] | 陈君洁, 黄传兵, 李 明. 健脾滋肾方抑制系统性红斑狼疮患者的足细胞自噬:基于网络药理学和临床研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 465-473. |
| [14] | 崔艺馨, 王德财, 谢东晴, 王海明, 徐睿鑫, 唐潇然, 张 印. 健脾温阳凝胶剂脐疗治疗脾胃虚弱型慢性腹泻的疗效及机制:一项临床随机对照试验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 217-225. |
| [15] | 蔡华俊, 陈致岐, 胡文婷, 谭伟, 吴昊, 王超. 鼠曲草总黄酮通过激活Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX-4信号通路抑制肝细胞铁死亡缓解对乙酰氨基酚诱导的小鼠急性肝损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2201-2208. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||