南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 150-161.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.18
• • 上一篇
褚乔1( ), 王小娜2, 续佳颖3, 彭荟林3, 赵裕琳3, 张静3, 陆国玉1, 王恺3(
), 王小娜2, 续佳颖3, 彭荟林3, 赵裕琳3, 张静3, 陆国玉1, 王恺3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-08-29
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2025-01-20
通讯作者:
王恺
E-mail:chuqiao670906094@163.com;wangkai@swmu.edu.cn
作者简介:褚 乔,主管护师,E-mail: chuqiao670906094@163.com
基金资助:
Qiao CHU1( ), Xiaona WANG2, Jiaying XU3, Huilin PENG3, Yulin ZHAO3, Jing ZHANG3, Guoyu LU1, Kai WANG3(
), Xiaona WANG2, Jiaying XU3, Huilin PENG3, Yulin ZHAO3, Jing ZHANG3, Guoyu LU1, Kai WANG3( )
)
Received:2024-08-29
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-20
Contact:
Kai WANG
E-mail:chuqiao670906094@163.com;wangkai@swmu.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 采用网络药理学和计算机模拟探讨白头翁皂苷D(PSD)抑制三阴性乳腺癌(TNBC)侵袭转移的作用机制,并进行实验验证。 方法 运用Super-PRED、Swiss Target Prediction、PharmMapper、STITCH和BATMAN-TCM数据库收集PSD潜在靶点,利用GeneCards和OMIM数据库获得TNBC侵袭转移靶点,将两者相交获得药物-疾病交集靶点,利用Cytoscape3.10.1软件绘制“PSD-靶点-疾病”互作网络。运用Cytoscape3.10.1中的Centiscape2.2插件设定阈值并获得核心靶点,使用String数据库进行蛋白质互作(PPI)分析,通过David数据库对核心靶点进行KEGG通路和GO功能富集分析。最后将核心靶点依次与PSD进行分子对接。通过Transwell和Western blotting法对PSD的作用及机制进行验证。 结果 网络药理学结果显示,共筛选出PSD潜在靶点285个及药物与疾病核心靶点26个。GO分析获得175个条目,涉及生物大分子(蛋白质、DNA、RNA)的结合、酶活性、基因转录调控等方面。KEGG分析获得46个条目,涉及癌症途径、化学致癌-受体活化、癌症中的微小RNA、化学致癌-活性氧、癌症中PD-L1表达和PD-1检查点通路等。分子对接显示,PSD与MTOR、HDAC2、ABL1、CDK1、TLR4、TERT、PIK3R1、NFE2L2、PTPN1有较高的结合性。Transwell和Western blotting结果显示,PSD抑制TNBC细胞侵袭迁移且降低其MMP2、MMP9、N-cadherin及关键蛋白p-mTOR、ABL1、TERT、PTPN1、HDAC2、PIK3R1、CDK1、TLR4和细胞核内NFE2L2的表达(P<0.05),PSD可通过这些靶点阻碍TNBC侵袭转移。 结论 PSD通过多靶点和多途径抑制TNBC侵袭转移,为后续深入的机制研究提供前期基础,为TNBC药物研发提供新思路。
褚乔, 王小娜, 续佳颖, 彭荟林, 赵裕琳, 张静, 陆国玉, 王恺. 白头翁皂苷D通过多靶点和多途径抑制三阴性乳腺癌侵袭转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 150-161.
Qiao CHU, Xiaona WANG, Jiaying XU, Huilin PENG, Yulin ZHAO, Jing ZHANG, Guoyu LU, Kai WANG. Pulsatilla saponin D inhibits invasion and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells through multiple targets and pathways[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 150-161.
| Compound | Target genes | Number of targets |
|---|---|---|
| PSD | BLM, PTPN1, GPR6, APEX1, KDM1A, GPR55, PTGS1, KLF5, TOP2A, TRIM24, NFKB1, SLC6A5, CLK4, ADAM10, CTSD, PDGFRA, NTRK3, NR3C2, CSNK2B, SCN2A, PTPN2, MTOR, TFPI, TLR4, SCN3A, PIK3R1, DUSP3, CYP3A4, PDE3A, GLRA1ITK, HSP90AB1, GRIA2, GRIN1, C5AR1, HSP90AA1, MMP1, FPR2, CFTR, ACACB, HDAC2, TLR8, S1PR5, SLC9A1, PSMB1, AURKB, NTSR2, HDAC7, LTA4H, F13A1, SOAT1, ATG4B, NFE2L2, CACNA1B, CHUK, NR2E3, CDK1, ADORA1, CYSLTR2, AR, CDC25B, MDM4, NR4A1, SLC40A1, SLC1A3, SCN4A, AKR1C3, CAPN1, KIF11, WDR5, TERT, PRCP, HDAC5, MAP3K14, CHRM1, TACR2, QRFPR, NR1I2, GABRA1, PSMB9, ABL1, PTGER2, CBX4, PRMT1, ABCB1, CACNA1H, DCUN1D1, FAAH, FPR1, ACACA, MC4R, RXFP1, ADK, CDK5, PDGFRB, SLC1A2, METAP2, NOX1, PROC, PRSS1, PLA2G2A, MME, PTK2B, RECQ2, PTP1B, APE, AOF2, COX1, BTEB2, TOP2, RNF82, GLYT2, KUZ, CPSD, PDGFR2, TRKC, MCR, CK2N, HBA, PTPT, FRAP, LACI, KIAA1356, GRB1, VHR, CYP3A3, EMT, HSP90B, GLUR2, NMDAR1, C5AR, HSP90A, CLG, FPRH1, ABCC7, ACC2, UNQ249/PRO286, EDG8, APNH1, PSC5, AIK2, HDAC7A, LTA4, F13A, ACACT, APG4B, NRF2, CACH5, IKKA, PNR, CDC2, CYSLT2, DHTR, CDC25HU2, MDMX, GFRP1, FPN, EAAT1, DDH1, CANPL1, EG5, BIG3, EST2, PCP, KIAA0600, NIK, NK2R, GPR103, PXR, LMP2, ABL, HMT2, MDR1, DCN1, FAAH1, ACAC, LGR7, CDKN5, PDGFR, EAAT2, MNPEP, MOX1, TRP1, PLA2B, EPN, FAK2, RECQL3, APE1, KDM1, CKLF, TIF1, NET1, MADM, RHEPDGFRA, MLR, G5A, NAC2, FRAP1, TFPI1, NAC3, LYK, HSPC2, C5R1, HSPC1, FPRL1, ACCB, NHE1, AIM1, ACACT1, AUTL1, CACNL1A5, TCF16, RNR, CDC28A, CYSLT2R, NR3C4, HMR, FPN1, GLAST, HSD17B5, PIG30, KNSL1, TCS1, NKNAR, PSMB6i, JTK7, HRMT1L2, PGY1, DCUN1L1, ACC1, PSSALRE, PDGFR1, GLT1, P67EIF2, NOH1, TRY1, PLA2L, PYK2, APEX, KIAA0601, IKLF, TIF1A, SCN2A1, FRAP2, HSPCB, HSPCA, LXA4R, AIRK2, ACAT, KIAA0943, CDKN1, PSEC0146, NAK1, IREG1, GLAST1, KIAA0119, TRIP5, TRT, TAC2R, RING12, IR1B4, RP42, ACCA, TRYP1, RASF-A, RAFTK, SCCRO, APX, LSD1, HAP1, REF1, RAPT1, SCN2A2, RAFT1, STK12, STK5, ARK2, STAT, ACAT1, P34CDC2, MSTP079, SLC11A3, PGFS, STK1, SOAT | 285 |
表1 PSD的潜在作用靶点
Tab.1 Potential targets of Pulsatilla saponin D (PSD)
| Compound | Target genes | Number of targets |
|---|---|---|
| PSD | BLM, PTPN1, GPR6, APEX1, KDM1A, GPR55, PTGS1, KLF5, TOP2A, TRIM24, NFKB1, SLC6A5, CLK4, ADAM10, CTSD, PDGFRA, NTRK3, NR3C2, CSNK2B, SCN2A, PTPN2, MTOR, TFPI, TLR4, SCN3A, PIK3R1, DUSP3, CYP3A4, PDE3A, GLRA1ITK, HSP90AB1, GRIA2, GRIN1, C5AR1, HSP90AA1, MMP1, FPR2, CFTR, ACACB, HDAC2, TLR8, S1PR5, SLC9A1, PSMB1, AURKB, NTSR2, HDAC7, LTA4H, F13A1, SOAT1, ATG4B, NFE2L2, CACNA1B, CHUK, NR2E3, CDK1, ADORA1, CYSLTR2, AR, CDC25B, MDM4, NR4A1, SLC40A1, SLC1A3, SCN4A, AKR1C3, CAPN1, KIF11, WDR5, TERT, PRCP, HDAC5, MAP3K14, CHRM1, TACR2, QRFPR, NR1I2, GABRA1, PSMB9, ABL1, PTGER2, CBX4, PRMT1, ABCB1, CACNA1H, DCUN1D1, FAAH, FPR1, ACACA, MC4R, RXFP1, ADK, CDK5, PDGFRB, SLC1A2, METAP2, NOX1, PROC, PRSS1, PLA2G2A, MME, PTK2B, RECQ2, PTP1B, APE, AOF2, COX1, BTEB2, TOP2, RNF82, GLYT2, KUZ, CPSD, PDGFR2, TRKC, MCR, CK2N, HBA, PTPT, FRAP, LACI, KIAA1356, GRB1, VHR, CYP3A3, EMT, HSP90B, GLUR2, NMDAR1, C5AR, HSP90A, CLG, FPRH1, ABCC7, ACC2, UNQ249/PRO286, EDG8, APNH1, PSC5, AIK2, HDAC7A, LTA4, F13A, ACACT, APG4B, NRF2, CACH5, IKKA, PNR, CDC2, CYSLT2, DHTR, CDC25HU2, MDMX, GFRP1, FPN, EAAT1, DDH1, CANPL1, EG5, BIG3, EST2, PCP, KIAA0600, NIK, NK2R, GPR103, PXR, LMP2, ABL, HMT2, MDR1, DCN1, FAAH1, ACAC, LGR7, CDKN5, PDGFR, EAAT2, MNPEP, MOX1, TRP1, PLA2B, EPN, FAK2, RECQL3, APE1, KDM1, CKLF, TIF1, NET1, MADM, RHEPDGFRA, MLR, G5A, NAC2, FRAP1, TFPI1, NAC3, LYK, HSPC2, C5R1, HSPC1, FPRL1, ACCB, NHE1, AIM1, ACACT1, AUTL1, CACNL1A5, TCF16, RNR, CDC28A, CYSLT2R, NR3C4, HMR, FPN1, GLAST, HSD17B5, PIG30, KNSL1, TCS1, NKNAR, PSMB6i, JTK7, HRMT1L2, PGY1, DCUN1L1, ACC1, PSSALRE, PDGFR1, GLT1, P67EIF2, NOH1, TRY1, PLA2L, PYK2, APEX, KIAA0601, IKLF, TIF1A, SCN2A1, FRAP2, HSPCB, HSPCA, LXA4R, AIRK2, ACAT, KIAA0943, CDKN1, PSEC0146, NAK1, IREG1, GLAST1, KIAA0119, TRIP5, TRT, TAC2R, RING12, IR1B4, RP42, ACCA, TRYP1, RASF-A, RAFTK, SCCRO, APX, LSD1, HAP1, REF1, RAPT1, SCN2A2, RAFT1, STK12, STK5, ARK2, STAT, ACAT1, P34CDC2, MSTP079, SLC11A3, PGFS, STK1, SOAT | 285 |
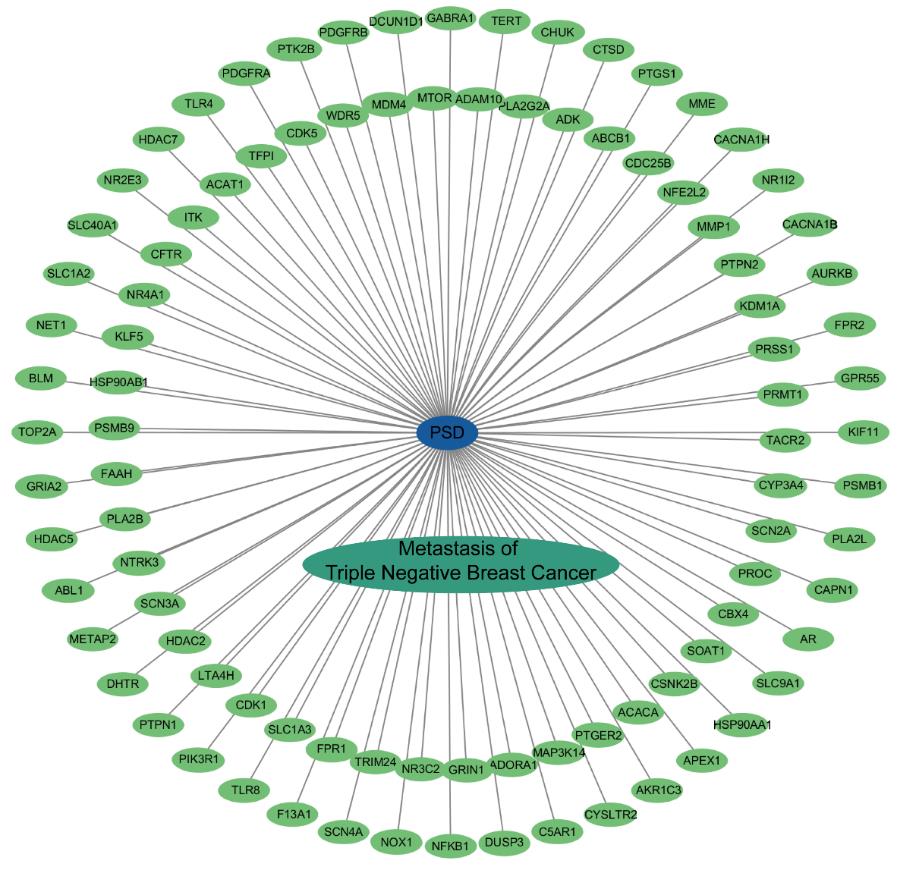
图2 “PSD-靶点-疾病”互作网络
Fig.2 "PSD-target-disease" interaction network. Blue oval nodes represent compound PSD, green oval nodes represent crossover genes, cyan oval nodes denote triple-negative breast cancer metastasis (disease), and gray lines stand for interactions.
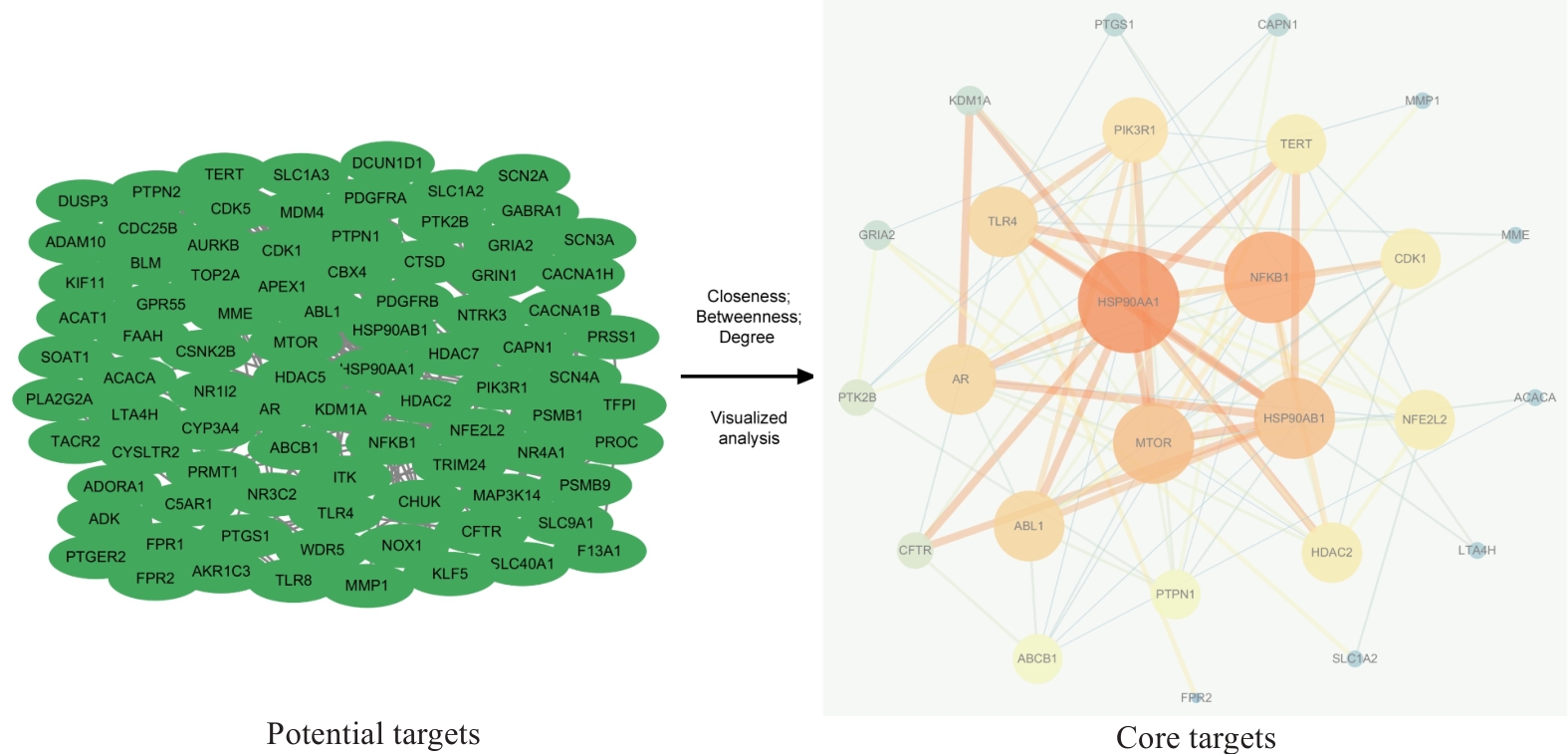
图3 PSD治疗TNBC侵袭转移的PPI网络可视化图
Fig.3 Visualization of PPI network for PSD treatment of TNBC invasion and metastasis. Green oval nodes on the left side represent 94 potential targets and the circular nodes on the right side represent 26 core targets. The size and color shades of the nodes are proportional to their importance, and the thickness and color shades of the lines are proportional to the importance between nodes.
| Core targets | Degree unDir | PDB ID |
|---|---|---|
| HSP90AA1 | 39 | 6GR5 |
| HSP90AB1 | 33 | 6N8Y |
| NFKB1 | 27 | 1SVC |
| MTOR | 24 | 4JSN |
| HDAC2 | 23 | 7JS8 |
| ABL1 | 20 | 5HU9 |
| CDK1 | 19 | 6GU2 |
| TLR4 | 18 | 2Z62 |
| TERT | 17 | 5UGW |
| AR | 17 | 8E1A |
| PIK3R1 | 17 | 7PG5 |
| NFE2L2 | 16 | 7X5G |
| ABCB1 | 12 | 7A69 |
| KDM1A | 12 | 7E0G |
| CFTR | 11 | 5TFJ |
| PTPN1 | 11 | 7MN9 |
| PTGS1 | 10 | 6Y3C |
| GRIA2 | 9 | 7F3O |
| MME | 8 | 6SUK |
| PTK2B | 7 | 3CC6 |
| ACACA | 6 | 2YL2 |
| FPR2 | 6 | 6LW5 |
| CAPN1 | 6 | 7W7O |
| SLC1A2 | 5 | 7VR7 |
| LTA4H | 4 | 3U9W |
| MMP1 | 4 | 966C |
表2 PSD治疗TNBC侵袭转移的核心靶点
Tab.2 Core targets of PSD for the treatment of TNBC invasion and metastasis
| Core targets | Degree unDir | PDB ID |
|---|---|---|
| HSP90AA1 | 39 | 6GR5 |
| HSP90AB1 | 33 | 6N8Y |
| NFKB1 | 27 | 1SVC |
| MTOR | 24 | 4JSN |
| HDAC2 | 23 | 7JS8 |
| ABL1 | 20 | 5HU9 |
| CDK1 | 19 | 6GU2 |
| TLR4 | 18 | 2Z62 |
| TERT | 17 | 5UGW |
| AR | 17 | 8E1A |
| PIK3R1 | 17 | 7PG5 |
| NFE2L2 | 16 | 7X5G |
| ABCB1 | 12 | 7A69 |
| KDM1A | 12 | 7E0G |
| CFTR | 11 | 5TFJ |
| PTPN1 | 11 | 7MN9 |
| PTGS1 | 10 | 6Y3C |
| GRIA2 | 9 | 7F3O |
| MME | 8 | 6SUK |
| PTK2B | 7 | 3CC6 |
| ACACA | 6 | 2YL2 |
| FPR2 | 6 | 6LW5 |
| CAPN1 | 6 | 7W7O |
| SLC1A2 | 5 | 7VR7 |
| LTA4H | 4 | 3U9W |
| MMP1 | 4 | 966C |
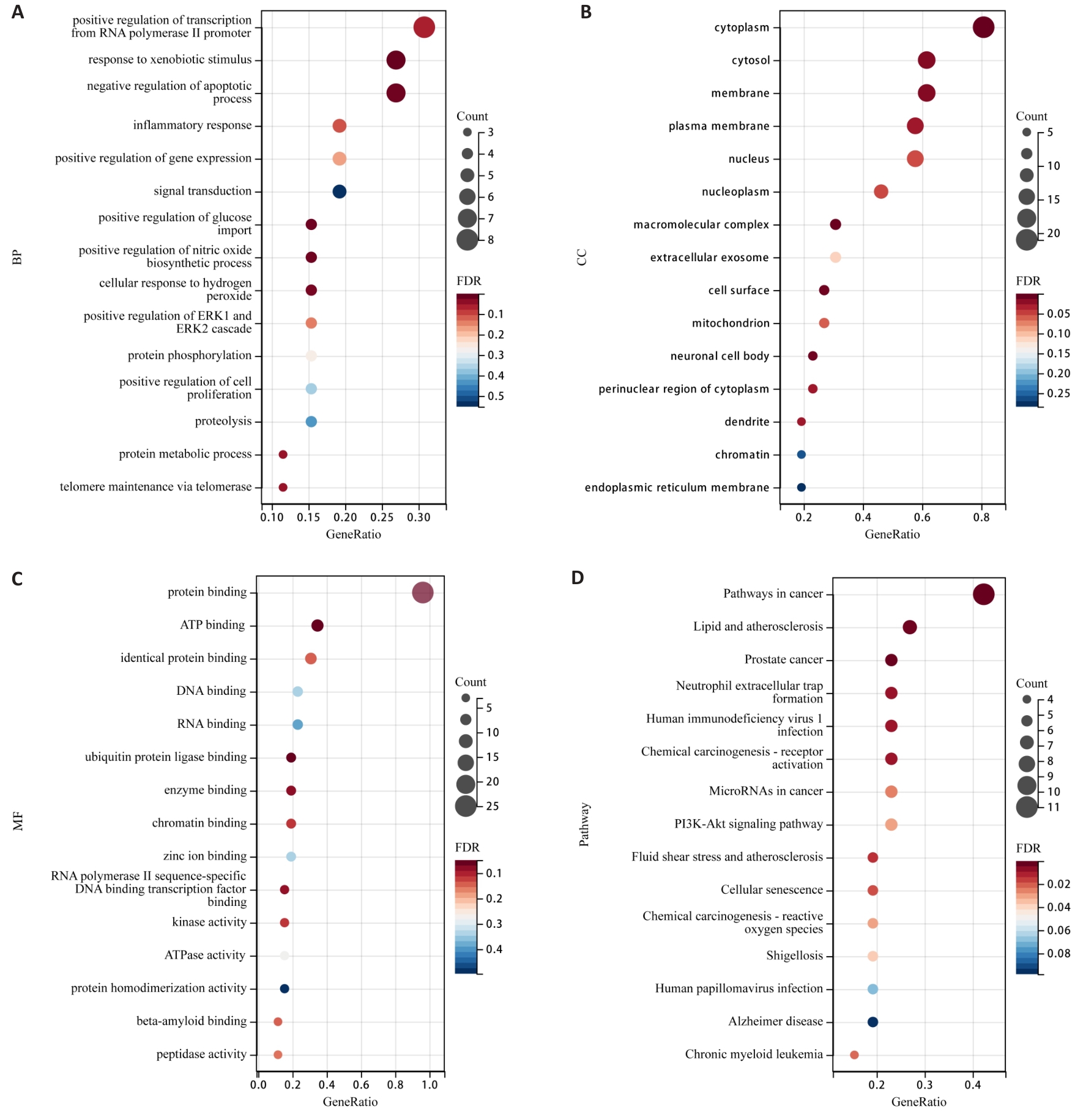
图4 PSD抑制TNBC侵袭转移的GO功能和KEGG通路富集气泡图
Fig.4 Bubble plots of GO function and KEGG pathway enrichment for PSD inhibition of TNBC invasion and metastasis. A: Enrichment analysis of BP. B: Enrichment analysis of CC. C: Enrichment analysis of MF. D: KEGG pathway enrichment analysis.
| ID | Pathways | P | Number of related genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa05200 | Pathways in cancer | 0.000000974 | 11 |
| hsa05417 | Lipid and atherosclerosis | 0.000026000 | 7 |
| hsa05215 | Prostate cancer | 0.000007060 | 6 |
| hsa04613 | Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | 0.000184000 | 6 |
| hsa05170 | Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection | 0.000298000 | 6 |
| hsa05207 | Chemical carcinogenesis - receptor activation | 0.000298000 | 6 |
| hsa05206 | MicroRNAs in cancer | 0.001673574 | 6 |
| hsa04151 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 0.003182088 | 6 |
| hsa05418 | Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis | 0.000618000 | 5 |
| hsa04218 | Cellular senescence | 0.000953000 | 5 |
| hsa05208 | Chemical carcinogenesis-reactive oxygen species | 0.003535389 | 5 |
| hsa05131 | Shigellosis | 0.005091764 | 5 |
| hsa05165 | Human papillomavirus infection | 0.014031422 | 5 |
| hsa05010 | Alzheimer disease | 0.022984313 | 5 |
| hsa05220 | Chronic myeloid leukemia | 0.001299397 | 4 |
| hsa05235 | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | 0.002047819 | 4 |
| hsa04657 | IL-17 signaling pathway | 0.002394257 | 4 |
| hsa04914 | Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | 0.003020588 | 4 |
| hsa04931 | Insulin resistance | 0.003550859 | 4 |
| hsa04659 | Th17 cell differentiation | 0.003550859 | 4 |
| hsa04066 | HIF-1 signaling pathway | 0.003644426 | 4 |
| hsa04152 | AMPK signaling pathway | 0.004886673 | 4 |
| hsa04910 | Insulin signaling pathway | 0.006900929 | 4 |
| hsa05135 | Yersinia infection | 0.006900929 | 4 |
| hsa05226 | Gastric cancer | 0.008693554 | 4 |
| hsa04217 | Necroptosis | 0.010557294 | 4 |
| hsa05161 | Hepatitis B | 0.010919274 | 4 |
| hsa05225 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | 0.012048446 | 4 |
| hsa04141 | Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | 0.012439336 | 4 |
| hsa04621 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.015830764 | 4 |
| hsa05203 | Viral carcinogenesis | 0.020215918 | 4 |
| hsa05163 | Human cytomegalovirus infection | 0.026104939 | 4 |
| hsa04024 | cAMP signaling pathway | 0.026104939 | 4 |
| hsa05171 | Coronavirus disease - COVID-19 | 0.028568364 | 4 |
| hsa05132 | Salmonella infection | 0.033858771 | 4 |
| hsa05016 | Huntington disease | 0.056576135 | 4 |
| hsa04213 | Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species | 0.013188318 | 3 |
| hsa05221 | Acute myeloid leukemia | 0.015766996 | 3 |
| hsa05212 | Pancreatic cancer | 0.020005321 | 3 |
| hsa04012 | ErbB signaling pathway | 0.02466712 | 3 |
| hsa04211 | Longevity regulating pathway | 0.026868984 | 3 |
| hsa05146 | Amoebiasis | 0.034548353 | 3 |
| hsa05142 | Chagas disease | 0.034548353 | 3 |
| hsa04620 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.038349814 | 3 |
| hsa04722 | Neurotrophin signaling pathway | 0.045714487 | 3 |
| hsa04919 | Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | 0.047106228 | 3 |
表3 KEGG通路富集
Tab.3 KEGG pathway enrichment
| ID | Pathways | P | Number of related genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa05200 | Pathways in cancer | 0.000000974 | 11 |
| hsa05417 | Lipid and atherosclerosis | 0.000026000 | 7 |
| hsa05215 | Prostate cancer | 0.000007060 | 6 |
| hsa04613 | Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | 0.000184000 | 6 |
| hsa05170 | Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection | 0.000298000 | 6 |
| hsa05207 | Chemical carcinogenesis - receptor activation | 0.000298000 | 6 |
| hsa05206 | MicroRNAs in cancer | 0.001673574 | 6 |
| hsa04151 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 0.003182088 | 6 |
| hsa05418 | Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis | 0.000618000 | 5 |
| hsa04218 | Cellular senescence | 0.000953000 | 5 |
| hsa05208 | Chemical carcinogenesis-reactive oxygen species | 0.003535389 | 5 |
| hsa05131 | Shigellosis | 0.005091764 | 5 |
| hsa05165 | Human papillomavirus infection | 0.014031422 | 5 |
| hsa05010 | Alzheimer disease | 0.022984313 | 5 |
| hsa05220 | Chronic myeloid leukemia | 0.001299397 | 4 |
| hsa05235 | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | 0.002047819 | 4 |
| hsa04657 | IL-17 signaling pathway | 0.002394257 | 4 |
| hsa04914 | Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | 0.003020588 | 4 |
| hsa04931 | Insulin resistance | 0.003550859 | 4 |
| hsa04659 | Th17 cell differentiation | 0.003550859 | 4 |
| hsa04066 | HIF-1 signaling pathway | 0.003644426 | 4 |
| hsa04152 | AMPK signaling pathway | 0.004886673 | 4 |
| hsa04910 | Insulin signaling pathway | 0.006900929 | 4 |
| hsa05135 | Yersinia infection | 0.006900929 | 4 |
| hsa05226 | Gastric cancer | 0.008693554 | 4 |
| hsa04217 | Necroptosis | 0.010557294 | 4 |
| hsa05161 | Hepatitis B | 0.010919274 | 4 |
| hsa05225 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | 0.012048446 | 4 |
| hsa04141 | Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | 0.012439336 | 4 |
| hsa04621 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.015830764 | 4 |
| hsa05203 | Viral carcinogenesis | 0.020215918 | 4 |
| hsa05163 | Human cytomegalovirus infection | 0.026104939 | 4 |
| hsa04024 | cAMP signaling pathway | 0.026104939 | 4 |
| hsa05171 | Coronavirus disease - COVID-19 | 0.028568364 | 4 |
| hsa05132 | Salmonella infection | 0.033858771 | 4 |
| hsa05016 | Huntington disease | 0.056576135 | 4 |
| hsa04213 | Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species | 0.013188318 | 3 |
| hsa05221 | Acute myeloid leukemia | 0.015766996 | 3 |
| hsa05212 | Pancreatic cancer | 0.020005321 | 3 |
| hsa04012 | ErbB signaling pathway | 0.02466712 | 3 |
| hsa04211 | Longevity regulating pathway | 0.026868984 | 3 |
| hsa05146 | Amoebiasis | 0.034548353 | 3 |
| hsa05142 | Chagas disease | 0.034548353 | 3 |
| hsa04620 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.038349814 | 3 |
| hsa04722 | Neurotrophin signaling pathway | 0.045714487 | 3 |
| hsa04919 | Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | 0.047106228 | 3 |
| Compound | Targets | PDB ID | MM-GBSA dG Bind (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSD | MTOR | 4JSN | -32.00 |
| HDAC2 | 7JS8 | -17.49 | |
| ABL1 | 5HU9 | -30.56 | |
| CDK1 | 6GU2 | -32.77 | |
| TLR4 | 2Z62 | -19.87 | |
| TERT | 5UGW | -39.09 | |
| PIK3R1 | 7PG5 | -31.43 | |
| NFE2L2 | 7X5G | -43.75 | |
| KDM1A | 7E0G | -43.68 | |
| PTPN1 | 7MN9 | -20.59 |
表4 PSD与核心靶蛋白的结合能
Tab.4 Free energy of PSD binding to the core target proteins
| Compound | Targets | PDB ID | MM-GBSA dG Bind (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSD | MTOR | 4JSN | -32.00 |
| HDAC2 | 7JS8 | -17.49 | |
| ABL1 | 5HU9 | -30.56 | |
| CDK1 | 6GU2 | -32.77 | |
| TLR4 | 2Z62 | -19.87 | |
| TERT | 5UGW | -39.09 | |
| PIK3R1 | 7PG5 | -31.43 | |
| NFE2L2 | 7X5G | -43.75 | |
| KDM1A | 7E0G | -43.68 | |
| PTPN1 | 7MN9 | -20.59 |
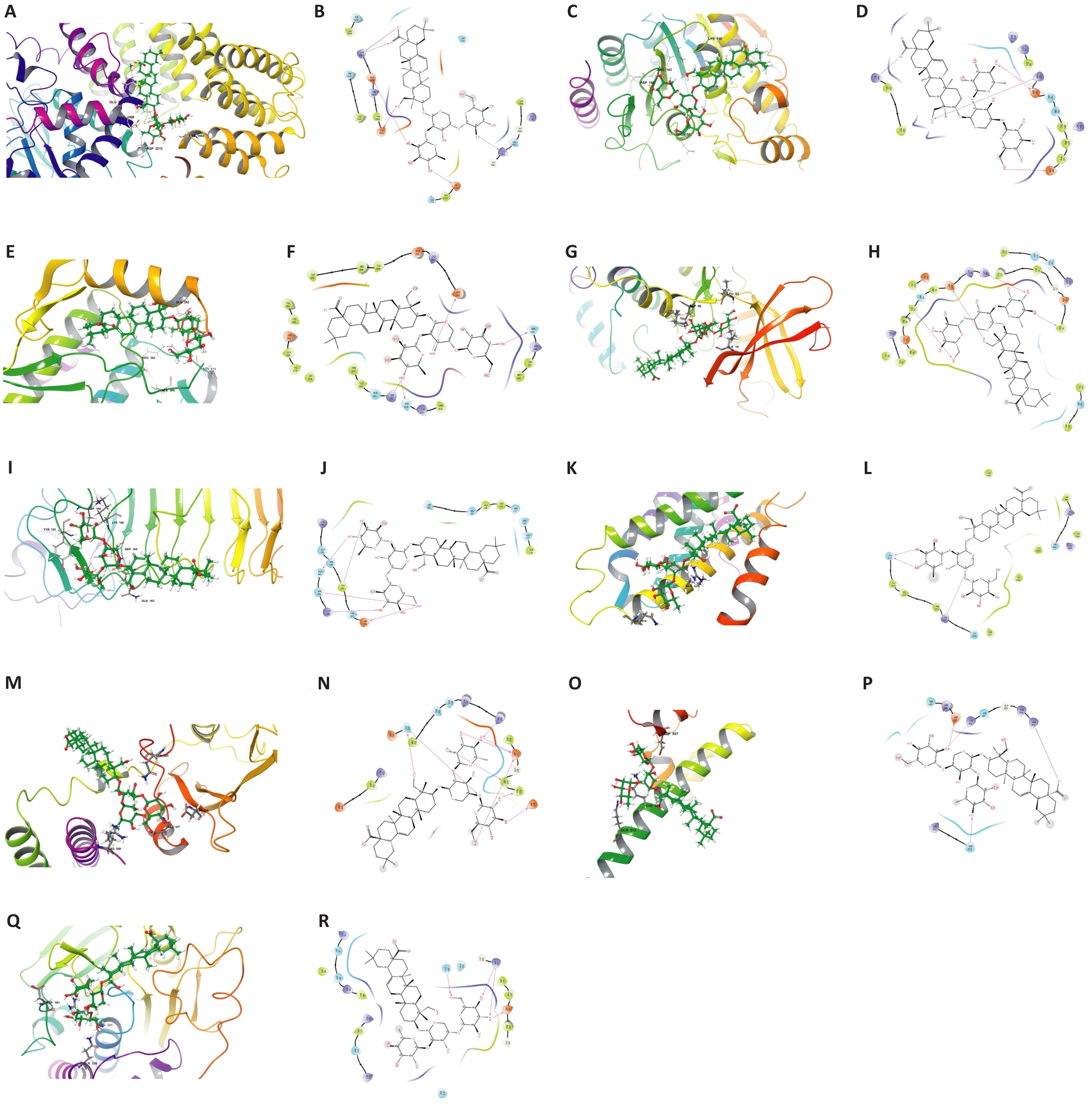
图5 PSD与关键靶蛋白的2D和3D结合模式图
Fig.5 2D and 3D binding pattern maps of PSD to the core target proteins. A: 3D binding model of PSD and MTOR. B: 2D binding model of PSD and MTOR. C: 3D binding model of PSD and HDAC2. D: 2D binding model of PSD and HDAC2. E: 3D binding model of PSD and ABL1. F: 2D binding model of PSD and ABL1. G: 3D binding model of PSD and CDK1. H: 2D binding model of PSD and CDK1. I: 3D binding model of PSD and TLR4. J: 2D binding model of PSD and TLR4. K: 3D binding model of PSD and TERT. L: 2D binding model of PSD and TERT. M: 3D binding model of PSD and PIK3R1. N: 2D binding model of PSD and PIK3R1. O: 3D binding model of PSD and NFE2L2. P: 2D binding model of PSD and NFE2L2. Q: 3D binding model of PSD and PTPN1. R: 2D binding model of PSD and PTPN1.
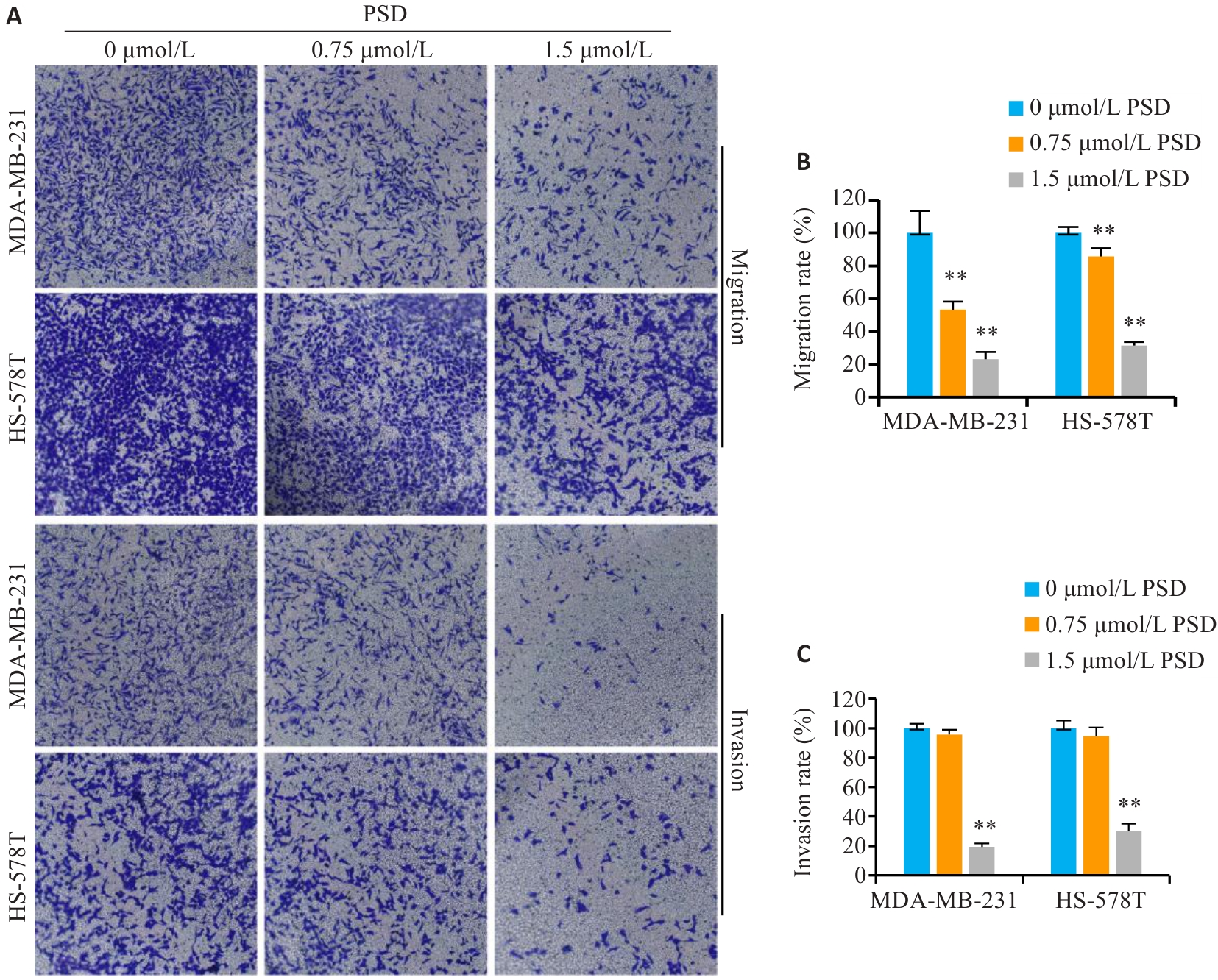
图6 PSD抑制TNBC细胞侵袭和迁移
Fig.6 PSD inhibits invasion and migration of TNBC cells. A: Crystal violet staining for detecting migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 and HS-578T cells (Original magnification: ×200). B, C: Quantitative analysis of the results. **P<0.01 vs 0 μmol/L PSD group.
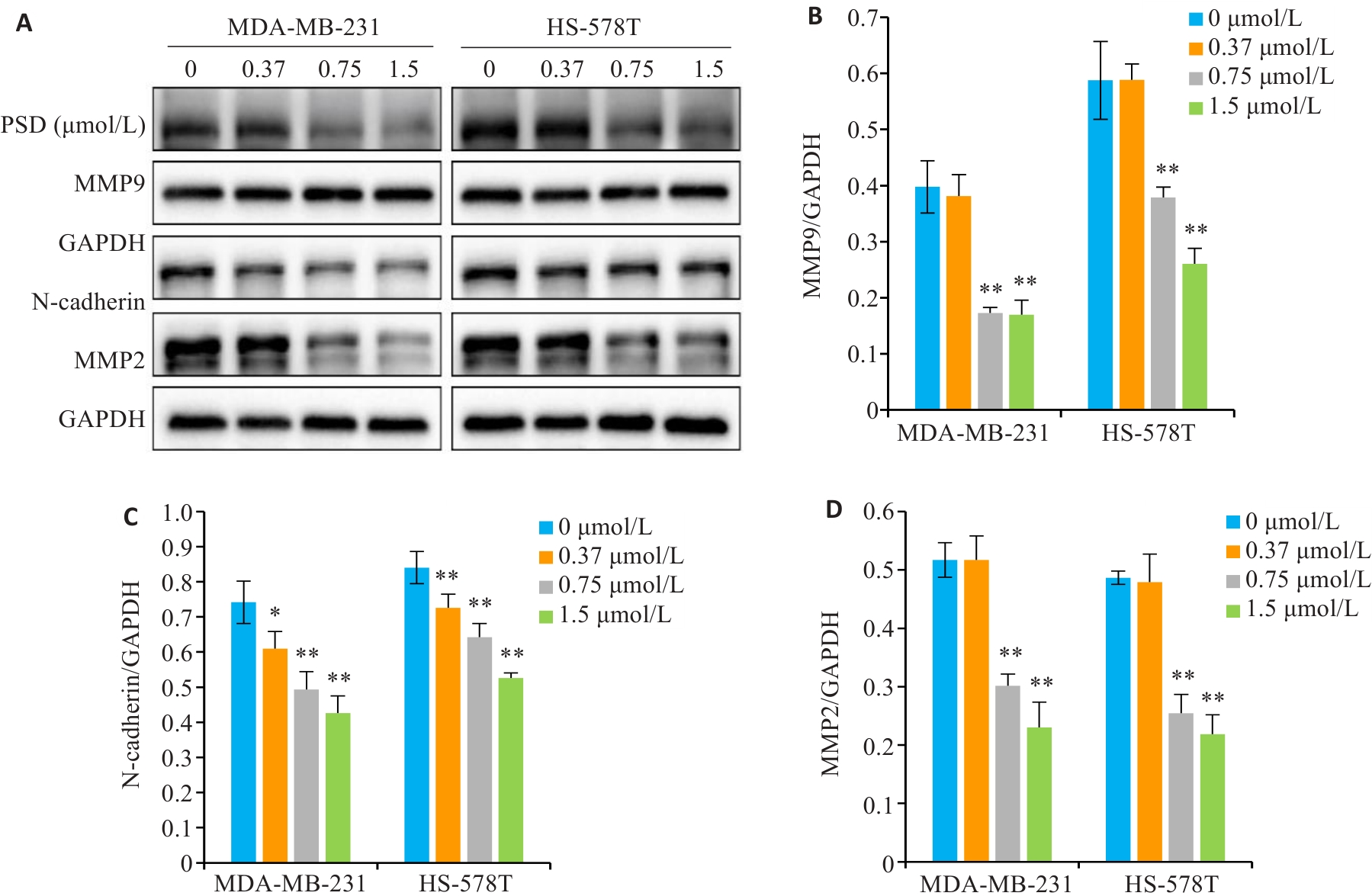
图7 PSD抑制侵袭迁移相关蛋白表达
Fig.7 PSD inhibits the expression of invasion and migration related proteins. A: MMP9, N-cadherin, and MMP2 protein levels were detected by Western blotting. B-D: Quantitative analysis of the results. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs 0 μmol/L group.

图8 PSD抑制TNBC细胞中9种核心靶蛋白表达
Fig.8 PSD inhibits the expression of 9 core target proteins in TNBC cells. A: p-mTOR, mTOR, CDK1, ABL1, TERT, PTPN1, HDAC2, PIK3R1, TLR4 and nuclear NRF2 protein levels detected by Western blotting. B-J: Quantitative analysis of the results. NRF2: NFE2L2. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs 0 μmol/L PSD group.
| 1 | Adrada BE, Moseley TW, Kapoor MM, et al. Triple-negative breast cancer: histopathologic features, genomics, and treatment[J]. Radiographics, 2023, 43(10): e230034. |
| 2 | Lin SY, Mo HN, Li YQ, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and survival outcomes in patients with synchronous lung metastases upon initial metastatic breast cancer diagnosis in Han population[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 1330. |
| 3 | 尹海庆, 苏 莉, 陈万贞, 等. 术后首发肺转移的三阴性乳腺癌临床病理特点及预后因素分析[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2019, 27(16): 2872-6. |
| 4 | Yang R, Shi YY, Han XH, et al. The impact of platinum-containing chemotherapies in advanced triple-negative breast cancer: meta-analytical approach to evaluating its efficacy and safety[J]. Oncol Res Treat, 2021, 44(6): 333-43. |
| 5 | Mason SR, Willson ML, Egger SJ, et al. Platinum-based chemotherapy for early triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2023, 9(9): CD014805. |
| 6 | McGuinness JE, Kalinsky K. Antibody-drug conjugates in metastatic triple negative breast cancer: a spotlight on sacituzumab govitecan, ladiratuzumab vedotin, and trastuzumab deruxtecan[J]. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2021, 21(7): 903-13. |
| 7 | Mediratta K, El-Sahli S, D’Costa V, et al. Current progresses and challenges of immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Cancers, 2020, 12(12): 3529. |
| 8 | Li LY, Zhang F, Liu ZY, et al. Immunotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer: combination strategies to improve outcome[J]. Cancers, 2023, 15(1): 321. |
| 9 | Ye F, Dewanjee S, Li YH, et al. Advancements in clinical aspects of targeted therapy and immunotherapy in breast cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2023, 22(1): 105. |
| 10 | Lev S. Targeted therapy and drug resistance in triple-negative breast cancer: the EGFR axis[J]. Biochem Soc Trans, 2020, 48(2): 657-65. |
| 11 | Li YH, Zou M, Han Q, et al. Therapeutic potential of triterpenoid saponin anemoside B4 from Pulsatilla chinensis [J]. Pharmacol Res, 2020, 160: 105079. |
| 12 | Fang YY, Hu DY, Li HL, et al. Synthesis, biological evaluation, and mode of action of Pulsatilla saponin D derivatives as promising anticancer agents[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 1208. |
| 13 | Zhang YL, Bao JL, Wang K, et al. Pulsatilla saponin D inhibits autophagic flux and synergistically enhances the anticancer activity of chemotherapeutic agents against HeLa cells[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2015, 43(8): 1657-70. |
| 14 | Hong SW, Jung KH, Lee HS, et al. SB365, Pulsatilla saponin D, targets c-Met and exerts antiangiogenic and antitumor activities[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2013, 34(9): 2156-69. |
| 15 | Lu YY, He WB, Huang XX, et al. Pulsatilla saponin D regulates ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 3 (RAC3) to overcome resistance to paclitaxel in lung adenocarcinoma cells[J]. BMC Cancer, 2024, 24(1): 55. |
| 16 | Lim JH, Jung KH, Kim MS, et al. SB365 induces apoptosis and suppresses proliferation of glioblastoma cells[J]. Indian J Pharmacol, 2020, 52(2): 102-7. |
| 17 | Wang K, Tu YB, Wan JB, et al. Synergistic anti-breast cancer effect of pulsatilla saponin D and camptothecin through interrupting autophagic-lysosomal function and promoting p62-mediated ubiquitinated protein aggregation[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2020, 41(6): 804-16. |
| 18 | Zhong JM, Tan LH, Chen MW, et al. Pharmacological activities and molecular mechanisms of Pulsatilla saponins[J]. Chin Med, 2022, 17(1): 59. |
| 19 | Bryan S, Witzel I, Borgmann K, et al. Molecular mechanisms associated with brain metastases in HER2-positive and triple negative breast cancers[J]. Cancers, 2021, 13(16): 4137. |
| 20 | 江远玲, 冯 楠, 邵欣宇, 等. 黄芪的现代药理作用研究进展[J]. 西南医科大学学报, 2023, 46(5): 456-60, 封3. |
| 21 | Tewari D, Patni P, Bishayee A, et al. Natural products targeting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in cancer: a novel therapeutic strategy[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 80: 1-17. |
| 22 | Zheng YY, Dai MR, Dong Y, et al. ZEB2/TWIST1/PRMT5/NuRD Multi complex Contributes to the Epigenetic Regulation of EMT and Metastasis in Colorectal Carcinoma[J]. Cancers, 2022, 14(14): 3426. |
| 23 | Bradley WD, Koleske AJ. Regulation of cell migration and morphogenesis by Abl-family kinases: emerging mechanisms and physiological contexts[J]. J Cell Sci, 2009, 122(Pt 19): 3441-54. |
| 24 | Ren LW, Yang YH, Li W, et al. CDK1 serves as a therapeutic target of adrenocortical carcinoma via regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition, G2/M phase transition, and PANoptosis[J]. J Transl Med, 2022, 20(1): 444. |
| 25 | Kashani B, Zandi Z, Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi A, et al. The role of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in cancer progression: a possible therapeutic target[J]? J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236(6): 4121-37. |
| 26 | Zhou Q, Xue CQ, Man JW, et al. Correlation of tumor-associated macrophage infiltration in glioblastoma with magnetic resonance imaging characteristics: a retrospective cross-sectional study[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2023, 13(9): 5958-73. |
| 27 | Lin L, Wu Q, Lu FF, et al. Nrf2 signaling pathway: current status and potential therapeutic targetable role in human cancers[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1184079. |
| 28 | Sivaganesh V, Sivaganesh V, Scanlon C, et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: mechanisms in cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(23): 12865. |
| 29 | Liu Q, Guan CC, Liu C, et al. Targeting hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha: a new strategy for triple-negative breast cancer therapy[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2022, 156: 113861. |
| 30 | Xu ZW, Goel HL, Burkart C, et al. Inhibition of VEGF binding to neuropilin-2 enhances chemosensitivity and inhibits metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2023, 15(694): eadf1128. |
| 31 | Wu TQ, Song HM, Xie D, et al. Silencing of ASPP2 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Int J Oncol, 2018, 52(6): 2001-10. |
| 32 | Liu X, Adorno-Cruz V, Chang YF, et al. EGFR inhibition blocks cancer stem cell clustering and lung metastasis of triple negative breast cancer[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(13): 6632-43. |
| 33 | Liu T, Li KD, Zhang ZX, et al. Tetrandrine inhibits cancer stem cell characteristics and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in triple-negative breast cancer via SOD1/ROS signaling pathway[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2023, 51(2): 425-44. |
| 34 | Fang H, Xie JP, Zhang M, et al. miRNA-21 promotes proliferation and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells through targeting PTEN[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2017, 9(3): 953-61. |
| 35 | Xu JH, Zhao JX, Jiang MY, et al. MiR-193 promotes cell proliferation and invasion by ING5/PI3K/AKT pathway of triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(6): 3122-9. |
| 36 | Chen CH, Li SH, Xue JL, et al. PD-L1 tumor-intrinsic signaling and its therapeutic implication in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. JCI Insight, 2021, 6(8): e131458. |
| 37 | Bacci M, Lorito N, Ippolito L, et al. Reprogramming of amino acid transporters to support aspartate and glutamate dependency sustains endocrine resistance in breast cancer[J]. Cell Rep, 2019, 28(1): 104-18.e8. |
| [1] | 陈孝华, 鲁辉, 王子良, 王炼, 夏勇生, 耿志军, 张小凤, 宋雪, 王月月, 李静, 胡建国, 左芦根. ABI2在胃癌进展和预后中的作用及其调控机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1653-1661. |
| [2] | 纪凯, 于冠宇, 周乐其, 张天帅, 凌潜龙, 满文江, 朱冰, 张卫. HNRNPA1基因在结直肠癌组织中高表达及其潜在的诊断和治疗价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1685-1695. |
| [3] | 陈星梅, 刘琴文, 李镱, 钟晓宇, 樊奇灵, 马柯, 罗柳婷, 官道刚, 朱志博. 茵陈蒿汤治疗肝纤维化的核心功能成分群以及潜在通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1508-1517. |
| [4] | 张珊苑, 蔡巧燕, 祁江晗, 殷恺馨, 何晨晨, 高铸烨, 张铃, 褚剑锋. 清心解瘀颗粒抗动脉粥样硬化的药效学及调控机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1518-1528. |
| [5] | 张钰明, 夏士程, 张淋淋, 陈梦茜, 刘晓婧, 高琴, 叶红伟. 金银花提取物对小鼠阿霉素肝脏损伤的保护作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1571-1581. |
| [6] | 王瑾瑾, 崔文飞, 窦雪伟, 尹冰磊, 牛钰琪, 牛羚, 闫国立. 鬼箭羽通过调节EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂耐药信号通路延缓糖尿病肾病的进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1243-1255. |
| [7] | 王琳月, 戚文月, 高记华, 田茂生, 许建成. 痛痒消洗剂可促进大鼠肛瘘术后的创面愈合[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1256-1265. |
| [8] | 张文祥, 顾惠贤, 陈鹏德, 吴思宇, 马洪艳, 姚蓝. 复方玉液汤通过调控PI3K/Akt信号通路抑制糖尿病大鼠心肌细胞凋亡和炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1306-1314. |
| [9] | 黄燕, 覃璐璐, 管少兴, 管宴萍, 韦玉茹, 操艾伶, 李冬梅, 韦桂宁, 苏启表. 金缕半枫荷的水提取物抑制胰腺癌的作用机制:活性成分、关键靶点和信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1336-1344. |
| [10] | 任志军, 刁建新, 王奕婷. 芎归汤通过抑制氧化应激诱导的心肌凋亡减轻小鼠心梗后心衰引起的心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1416-1424. |
| [11] | 赵倩, 张振, 周星琦, 荣翔宇, 刘雪柔, 赵新丽, 王豪杰, 庞金龙, 李姗姗, 李娴. 川芎增强替莫唑胺对小鼠脑转移黑色素瘤脑的抑制作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1088-1097. |
| [12] | 孙畅, 郑士耀, 李梅, 杨铭, 秦梦园, 徐媛, 梁伟华, 胡建明, 王良海, 李锋, 周虹, 杨兰. 干性相关分子Nanog在食管鳞状细胞癌组织中高表达并促进食管鳞癌细胞的侵袭转移:基于激活TGF-β信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1209-1216. |
| [13] | 崔芝, 马萃娇, 王倩茹, 陈金豪, 严子阳, 杨建林, 吕亚丰, 曹春雨. 表达 TGF-βⅡ受体的腺相关病毒载体抑制小鼠三阴性乳腺癌4T1细胞的增殖和肺转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 818-826. |
| [14] | 李睿镈, 高歌, 谢曦, 罗海彬. 槟榔活性成分诱导口腔黏膜下纤维化的机制:基于网络药理学结合临床样本验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 930-940. |
| [15] | 夏勇生, 王炼, 陈孝华, 张雨路, 孙奥飞, 陈德利. 过表达TSR2通过下调PI3K/AKT信号通路抑制胃癌细胞的增殖和侵袭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 913-919. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||