南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 930-940.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.05.15
收稿日期:2024-01-17
出版日期:2024-05-20
发布日期:2024-06-04
通讯作者:
谢曦,罗海彬
E-mail:21211007000005@hainanu.edu.cn;xiexi@hainanu.edu.cn;hbluo@hainanu.edu.cn
作者简介:李睿镈,硕士,E-mail: 21211007000005@hainanu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Ruibo LI( ), Ge GAO, Xi XIE(
), Ge GAO, Xi XIE( ), Haibin LUO(
), Haibin LUO( )
)
Received:2024-01-17
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-06-04
Contact:
Xi XIE, Haibin LUO
E-mail:21211007000005@hainanu.edu.cn;xiexi@hainanu.edu.cn;hbluo@hainanu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探究槟榔的成分及其促进口腔黏膜下纤维化的机制。 方法 采用Thermo QE plus液相色谱串联高分辨质谱仪和Compound discover 3.2数据处理软件进行槟榔中药化学成分分析,将检测到的化合物以质谱响应值排序,分析排名前20化合物的活性。化合物活性来源根据《中国药典(2015版)》汇总,数据查询基于PubChem、Chemical book 以及Scifinder数据库。借助网络药理学方法分析槟榔影响口腔黏膜下纤维化(OSF)的潜在活性成分、核心靶点及主要影响的生物功能、信号通路。通过整合人类基因数据库(Genecards)、基因组百科全书数据库(KEGG)等数据库获取OSF的作用靶点。以OB≥30%为条件,在中药系统药理学技术平台(TCMSP)中筛选出槟榔可作用于靶点的化合物,并构建靶点-化合物、化合物-中药、靶点-化合物-中药网络。运用MOE软件的分子对接技术,分析成分-靶点结合的可能性,再利用Pymol软件进行分子对接可视化。最后通过免疫组化在临床样本中验证槟榔是否影响PI3K-Akt、MAPK两条通路涉及的主要蛋白,初步验证槟榔诱导OSF的潜在作用机制。 结果 基于网络药理学和槟榔粗提物中筛选出前10的化合物与OSF核心靶点中核心交集基因,确定了槟榔可能通过调控PI3K-Akt与MAPK通路。通过免疫组化在临床样本中验证,细胞膜上的PI3K蛋白表达量在OSF患者组中表达下降(P=0.0002),p-PI3K(P=0.0002)表达量上升,进一步激活下游的AKT1蛋白表达增加(P=0.0006),加剧磷酸化蛋白p-AKT蛋白的表达及堆积(P=0.0013);而在MAPK通路中,OSF患者组对比正常组,通过上调JNK蛋白(P=0.0130),诱导下游AP-1复合蛋白c-jun及c-fos转录因子的活性增加,促使其向细胞核聚集;且OSF患者组较正常组血浆的IL-6(P<0.0001)与IL-8(P=0.0095)含量均上升。 结论 槟榔碱、槟榔次碱、异去甲槟榔碱等槟榔中的主要活性成分可能通过刺激PI3K-Akt与MAPK信号通路,促进炎症介质IL-6及IL-8的表达,诱导胶原增生,导致口腔黏膜下纤维化病变。
李睿镈, 高歌, 谢曦, 罗海彬. 槟榔活性成分诱导口腔黏膜下纤维化的机制:基于网络药理学结合临床样本验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 930-940.
Ruibo LI, Ge GAO, Xi XIE, Haibin LUO. Oral submucosal fibrosis induced by active components in areca nut: a network pharmacology-based analysis and validation of the mechanism[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 930-940.
| NO. | Molecule | Molecular formula | QD (ppm) | Mw | RT (min) | Matching score | Peak area | Relative content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Arecoline | C8H13NO2 | -5.75 | 155.09374 | 3.758 | 90.9 | 68518632210 | 45.473 |
| 2 | Quinic acid | C7H12O6 | -2.88 | 192.06283 | 1.539 | 92.6 | 22692914797 | 15.060 |
| 3 | Epicatechin | C15H14O6 | -3.42 | 290.07805 | 18.93 | 94.7 | 14748028849 | 9.788 |
| 4 | Trigonelline HCl | C7H7NO2 | -5.85 | 137.04688 | 1.547 | 87.3 | 12273994597 | 8.146 |
| 5 | Citric acid | C6H8O7 | -2.05 | 192.02661 | 1.672 | 85.3 | 11231967076 | 7.454 |
| 6 | Procyanidin B1 | C30H26O12 | -4.2 | 578.14 | 18.324 | 92.4 | 7264204843 | 4.821 |
| 7 | p-Coumaric acid | C9H8O3 | -5.71 | 164.04641 | 4.772 | 85 | 3213100960 | 2.132 |
| 8 | (+)-Catechin hydrate | C15H14O6 | -3.73 | 290.07796 | 19.914 | 95.2 | 857006365.1 | 0.569 |
| 9 | Uridine | C9H12N2O6 | -2.72 | 244.06887 | 4.959 | 93.6 | 835052793.2 | 0.566 |
| 10 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-nehesperidine | C28H32O16 | -3.49 | 624.16686 | 22.33 | 92.2 | 760984003.5 | 0.505 |
| 11 | Sucrose | C12H22O11 | -3.26 | 342.1151 | 1.575 | 93.4 | 721956624 | 0.479 |
| 12 | 4'-O-Glucosylvitexin | C27H30O15 | -4.08 | 594.15604 | 20.961 | 87 | 608955062.8 | 0.404 |
| 13 | Procyanidin B2 | C30H28O10 | -5.78 | 578.13909 | 19.473 | 90.1 | 563763212.9 | 0.374 |
| 14 | Rosarin | C20H28O10 | -2.75 | 428.16707 | 22.833 | 79.7 | 480609598 | 0319 |
| 15 | Isoguanosine | C10H13N5O5 | -2.41 | 283.09099 | 10.894 | 83.8 | 44491969.7 | 0.295 |
| 16 | Nicotinic acid | C6H5NO2 | -4.82 | 123.03143 | 2.533 | 78 | 432658200.9 | 0.287 |
| 17 | 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural | C6H6O3 | -5.63 | 126.03098 | 1.912 | 73.9 | 431787858.3 | 0.287 |
| 18 | 2-Pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid | C5H9NO2 | -5.99 | 115.06264 | 1.547 | 74.7 | 397002912.3 | 0.263 |
| 19 | L-Tyrosine | C9H11NO3 | -2.26 | 181.07348 | 4.815 | 88.5 | 373792777.1 | 0.248 |
| 20 | Benzoic acid | C7H6O2 | -6.16 | 122.03603 | 18.932 | 88.4 | 277514777.6 | 0.184 |
表1 海南槟榔提取物前20成分鉴定
Tab.1 Identification of the top 20 components of areca extract from Hainan areca nut
| NO. | Molecule | Molecular formula | QD (ppm) | Mw | RT (min) | Matching score | Peak area | Relative content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Arecoline | C8H13NO2 | -5.75 | 155.09374 | 3.758 | 90.9 | 68518632210 | 45.473 |
| 2 | Quinic acid | C7H12O6 | -2.88 | 192.06283 | 1.539 | 92.6 | 22692914797 | 15.060 |
| 3 | Epicatechin | C15H14O6 | -3.42 | 290.07805 | 18.93 | 94.7 | 14748028849 | 9.788 |
| 4 | Trigonelline HCl | C7H7NO2 | -5.85 | 137.04688 | 1.547 | 87.3 | 12273994597 | 8.146 |
| 5 | Citric acid | C6H8O7 | -2.05 | 192.02661 | 1.672 | 85.3 | 11231967076 | 7.454 |
| 6 | Procyanidin B1 | C30H26O12 | -4.2 | 578.14 | 18.324 | 92.4 | 7264204843 | 4.821 |
| 7 | p-Coumaric acid | C9H8O3 | -5.71 | 164.04641 | 4.772 | 85 | 3213100960 | 2.132 |
| 8 | (+)-Catechin hydrate | C15H14O6 | -3.73 | 290.07796 | 19.914 | 95.2 | 857006365.1 | 0.569 |
| 9 | Uridine | C9H12N2O6 | -2.72 | 244.06887 | 4.959 | 93.6 | 835052793.2 | 0.566 |
| 10 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-nehesperidine | C28H32O16 | -3.49 | 624.16686 | 22.33 | 92.2 | 760984003.5 | 0.505 |
| 11 | Sucrose | C12H22O11 | -3.26 | 342.1151 | 1.575 | 93.4 | 721956624 | 0.479 |
| 12 | 4'-O-Glucosylvitexin | C27H30O15 | -4.08 | 594.15604 | 20.961 | 87 | 608955062.8 | 0.404 |
| 13 | Procyanidin B2 | C30H28O10 | -5.78 | 578.13909 | 19.473 | 90.1 | 563763212.9 | 0.374 |
| 14 | Rosarin | C20H28O10 | -2.75 | 428.16707 | 22.833 | 79.7 | 480609598 | 0319 |
| 15 | Isoguanosine | C10H13N5O5 | -2.41 | 283.09099 | 10.894 | 83.8 | 44491969.7 | 0.295 |
| 16 | Nicotinic acid | C6H5NO2 | -4.82 | 123.03143 | 2.533 | 78 | 432658200.9 | 0.287 |
| 17 | 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural | C6H6O3 | -5.63 | 126.03098 | 1.912 | 73.9 | 431787858.3 | 0.287 |
| 18 | 2-Pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid | C5H9NO2 | -5.99 | 115.06264 | 1.547 | 74.7 | 397002912.3 | 0.263 |
| 19 | L-Tyrosine | C9H11NO3 | -2.26 | 181.07348 | 4.815 | 88.5 | 373792777.1 | 0.248 |
| 20 | Benzoic acid | C7H6O2 | -6.16 | 122.03603 | 18.932 | 88.4 | 277514777.6 | 0.184 |

图2 槟榔成分网络药理学分析
Fig.2 Network pharmacological analysis of the components of areca nut. A: Network pharmacology technology flow chart. B: Areca nut active ingredient-disease target for oral submucous fibrosis (OSF). C: Protein-protein interaction. D: Core target acquisition map. E: Intersection of the core target genes of the active ingredients of areca nut and OSF. F: Areca nut-component-target-OSF target interaction map. G: Effect of areca nut active ingredients on GO enrichment of OSF targets. H: KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of the effects of areca nut active ingredients on OSF targets. I: KEGG pathway secondary classification analysis. J: Molecular docking binding energy heat map.
| NO. | Molecule ID | Molecule name | OB/% | PubChem ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | MOL005835 | Guvacine | 98.35 | 40468028 |
| A2 | MOL005833 | Arecaine | 84.34 | 6971195 |
| A3 | MOL005838 | isoguvacine | 72.17 | 7059534 |
| A4 | MOL010481 | WLN: GR DSWR DG | 70.57 | 6625 |
| A5 | MOL000004 | Procyanidin B1 | 67.87 | 11250133 |
| A6 | MOL000676 | DBP | 64.54 | 3026 |
| A7 | MOL004544 | Quinic acid | 63.53 | 37439 |
| A8 | MOL001456 | citric acid | 56.22 | 19782904 |
| A9 | MOL004365 | Isomenthol | 55.30 | 19244 |
| A10 | MOL000492 | Catechin | 54.83 | 9064 |
| A11 | MOL002095 | DEP | 52.19 | 6781 |
| A12 | MOL000555 | Homoarecoline | 52.03 | 34167 |
| A13 | MOL010483 | dehydeoacetic acid | 52.02 | 1712264 |
| A14 | MOL000635 | vanilline | 52.00 | 1183 |
| A15 | MOL000073 | ent-Epicatechin | 48.96 | 1822932 |
| A16 | MOL010485 | EPA | 45.66 | 446284 |
| A17 | MOL010482 | WLN: 6OVR BVO6 | 43.74 | 6786 |
| A18 | MOL001749 | ZINC03860434 | 43.59 | 7057921 |
| A19 | MOL000131 | EIC | 41.90 | 5280450 |
| A20 | MOL004454 | ODD | 41.70 | 5282800 |
| A21 | MOL000041 | PHA | 41.62 | 6925665 |
| A22 | MOL010492 | Arecoline | 40.70 | 2230 |
| A23 | MOL002032 | DNOP | 40.59 | 8346 |
| A24 | MOL002850 | butylated hydroxytoluene | 40.02 | 31404 |
| A25 | MOL000198 | (R)-linalool | 39.80 | 443158 |
| A26 | MOL000234 | L-Limonen | 38.09 | 439250 |
| A27 | MOL001739 | zoomaric acid | 35.78 | 445638 |
| A28 | MOL010488 | 10Z-heptadecenoic acid | 34.42 | 5312435 |
| A29 | MOL002372 | (6Z,10E,14E,18E)-2,6,10,15,19,23-hexamethyltetracosa-2,6,10,14,18,22-hexaene | 33.55 | 11975273 |
| A30 | MOL000675 | oleic acid | 33.13 | 445639 |
| A31 | MOL010487 | Guvacoline | 32.67 | 160492 |
| A32 | MOL000301 | 2-lauroleic acid | 31.42 | 5282729 |
| A33 | MOL010489 | Resivit | 30.84 | 71629 |
| A34 | MOL003505 | Panosorb | 30.82 | 643460 |
表2 槟榔活性成分筛选
Tab.2 Screening of active ingredients in areca nut
| NO. | Molecule ID | Molecule name | OB/% | PubChem ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | MOL005835 | Guvacine | 98.35 | 40468028 |
| A2 | MOL005833 | Arecaine | 84.34 | 6971195 |
| A3 | MOL005838 | isoguvacine | 72.17 | 7059534 |
| A4 | MOL010481 | WLN: GR DSWR DG | 70.57 | 6625 |
| A5 | MOL000004 | Procyanidin B1 | 67.87 | 11250133 |
| A6 | MOL000676 | DBP | 64.54 | 3026 |
| A7 | MOL004544 | Quinic acid | 63.53 | 37439 |
| A8 | MOL001456 | citric acid | 56.22 | 19782904 |
| A9 | MOL004365 | Isomenthol | 55.30 | 19244 |
| A10 | MOL000492 | Catechin | 54.83 | 9064 |
| A11 | MOL002095 | DEP | 52.19 | 6781 |
| A12 | MOL000555 | Homoarecoline | 52.03 | 34167 |
| A13 | MOL010483 | dehydeoacetic acid | 52.02 | 1712264 |
| A14 | MOL000635 | vanilline | 52.00 | 1183 |
| A15 | MOL000073 | ent-Epicatechin | 48.96 | 1822932 |
| A16 | MOL010485 | EPA | 45.66 | 446284 |
| A17 | MOL010482 | WLN: 6OVR BVO6 | 43.74 | 6786 |
| A18 | MOL001749 | ZINC03860434 | 43.59 | 7057921 |
| A19 | MOL000131 | EIC | 41.90 | 5280450 |
| A20 | MOL004454 | ODD | 41.70 | 5282800 |
| A21 | MOL000041 | PHA | 41.62 | 6925665 |
| A22 | MOL010492 | Arecoline | 40.70 | 2230 |
| A23 | MOL002032 | DNOP | 40.59 | 8346 |
| A24 | MOL002850 | butylated hydroxytoluene | 40.02 | 31404 |
| A25 | MOL000198 | (R)-linalool | 39.80 | 443158 |
| A26 | MOL000234 | L-Limonen | 38.09 | 439250 |
| A27 | MOL001739 | zoomaric acid | 35.78 | 445638 |
| A28 | MOL010488 | 10Z-heptadecenoic acid | 34.42 | 5312435 |
| A29 | MOL002372 | (6Z,10E,14E,18E)-2,6,10,15,19,23-hexamethyltetracosa-2,6,10,14,18,22-hexaene | 33.55 | 11975273 |
| A30 | MOL000675 | oleic acid | 33.13 | 445639 |
| A31 | MOL010487 | Guvacoline | 32.67 | 160492 |
| A32 | MOL000301 | 2-lauroleic acid | 31.42 | 5282729 |
| A33 | MOL010489 | Resivit | 30.84 | 71629 |
| A34 | MOL003505 | Panosorb | 30.82 | 643460 |
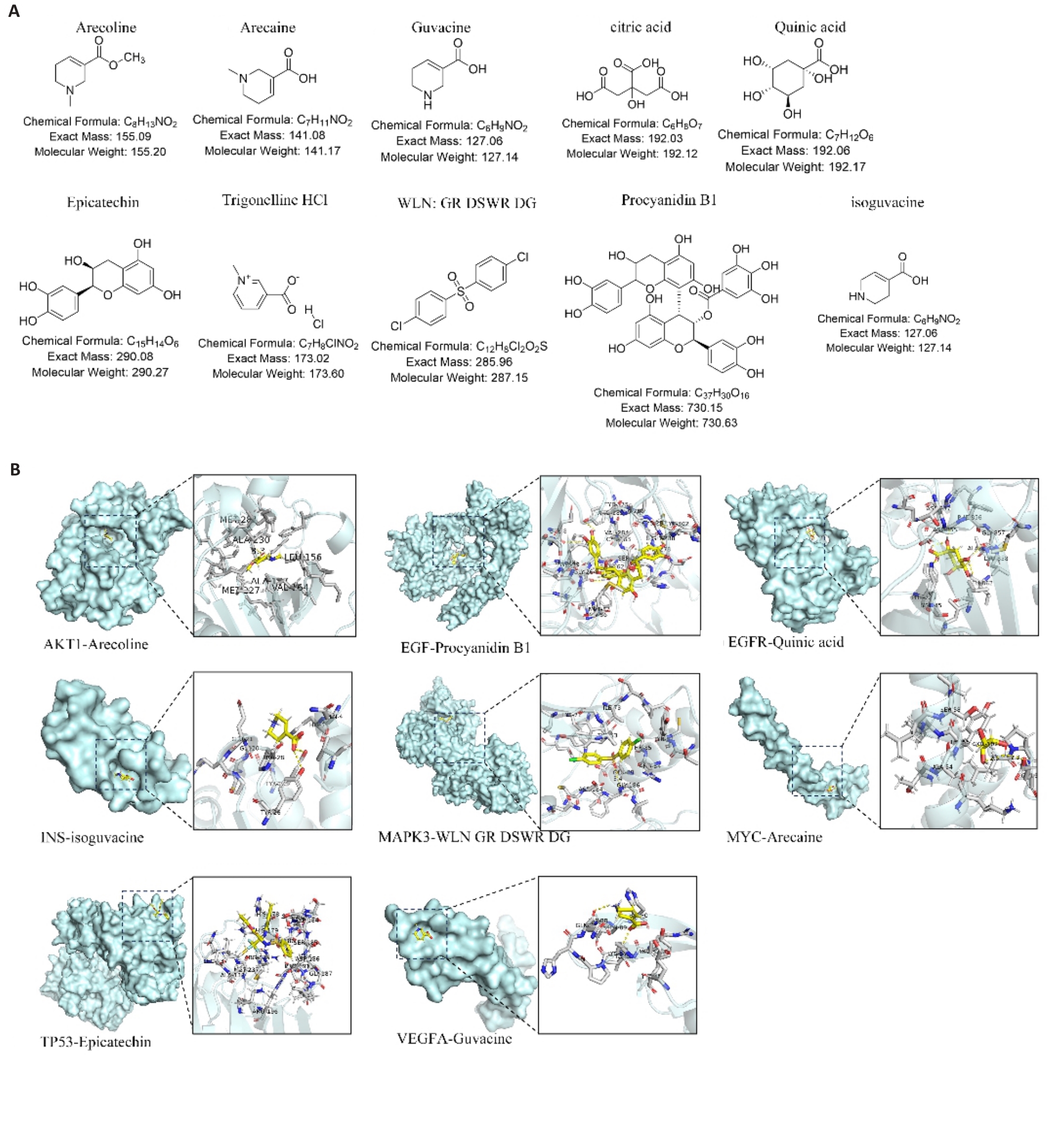
图3 槟榔成分分子对接
Fig.3 Molecular docking of areca nut components. A: Chemical structures of 10 areca nut active ingredients. B: Visualization of molecular docking of some active ingredients of areca nut with the core targets.
| Main active ingredients | Binding energy with target (kcal/mol) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule name | PubChem ID | AKT1 (4GV1) | INS (1TYL) | EGF (1NQL) | EGFR (3W2S) | VEGFA (4KZN) | TP53 (3Q01) | MAPK3 (4QTB) | MYC (5I4Z) |
| Guvacine | 40468028 | -4.35 | -4.16 | 0.00 | -4.41 | -3.82 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -4.17 |
| Arecaine | 6971195 | -4.25 | -4.43 | 0.00 | -4.27 | -3.74 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -4.46 |
| isoguvacine | 7059534 | -4.38 | -4.06 | 0.00 | -4.01 | -3.78 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -3.85 |
| WLN: GR DSWR DG | 6625 | -5.66 | -4.89 | -5.32 | -4.73 | -4.38 | -4.76 | -5.71 | -4.54 |
| Procyanidin B1 | 11250133 | -6.86 | -6.42 | -6.70 | -6.68 | -5.45 | -6.02 | -6.60 | -5.94 |
| Quinic acid | 37439 | -4.78 | -4.45 | 0.00 | -5.28 | -4.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -4.14 |
| ent-Epicatechin | 1822932 | -6.54 | -5.61 | -5.72 | -6.15 | -4.91 | -5.51 | -6.54 | -5.16 |
| Arecoline | 2230 | -5.28 | -4.69 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -4.47 | -4.03 | 0.00 | -4.48 |
表3 分子对接打分一览表
Tab.3 Molecular docking scoring list
| Main active ingredients | Binding energy with target (kcal/mol) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule name | PubChem ID | AKT1 (4GV1) | INS (1TYL) | EGF (1NQL) | EGFR (3W2S) | VEGFA (4KZN) | TP53 (3Q01) | MAPK3 (4QTB) | MYC (5I4Z) |
| Guvacine | 40468028 | -4.35 | -4.16 | 0.00 | -4.41 | -3.82 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -4.17 |
| Arecaine | 6971195 | -4.25 | -4.43 | 0.00 | -4.27 | -3.74 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -4.46 |
| isoguvacine | 7059534 | -4.38 | -4.06 | 0.00 | -4.01 | -3.78 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -3.85 |
| WLN: GR DSWR DG | 6625 | -5.66 | -4.89 | -5.32 | -4.73 | -4.38 | -4.76 | -5.71 | -4.54 |
| Procyanidin B1 | 11250133 | -6.86 | -6.42 | -6.70 | -6.68 | -5.45 | -6.02 | -6.60 | -5.94 |
| Quinic acid | 37439 | -4.78 | -4.45 | 0.00 | -5.28 | -4.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -4.14 |
| ent-Epicatechin | 1822932 | -6.54 | -5.61 | -5.72 | -6.15 | -4.91 | -5.51 | -6.54 | -5.16 |
| Arecoline | 2230 | -5.28 | -4.69 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -4.47 | -4.03 | 0.00 | -4.48 |

图4 临床验证
Fig.4 Clinical validation. A: HE staining, Masson, SR staining (Original magnification: ×100 or ×200). B: Fibronectin immunohistochemistry and H-score semi-quantitative analysis (×100 or ×200; n≥5). C: SR staining and differentiation of COL I and COL III under polarized light (×100). Orange and red fluorescence indicate Col I. Green fluorescence indicates COL III. D: Immunohistochemical staining of PI3K-Akt pathway proteins (×100 or ×200; n≥5). E: Immunohistochemistry and H-score semi-quantitative analysis of PI3K-Akt pathway proteins (n≥5). F: Immunohistochemical staining of MAPK pathway protein (×100, ×200 or ×400; n≥5). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
| 1 | Mehrtash H, Duncan K, Parascandola M, et al. Defining a global research and policy agenda for betel quid and areca nut[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2017, 18(12): e767-75. DOI: 10.1016/s1470-2045(17)30460-6 |
| 2 | 周明玺, 郭亦晨, 李 珂, 等. 槟榔活性成分及药理毒理作用研究进展[J]. 中成药, 2022, 44(3): 878-83. |
| 3 | 周思安, 刘斯薇, 金力行, 等. 槟榔碱对生殖与泌尿系统的影响[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2019, 38(5): 413-7. |
| 4 | Kondaiah P, Pant I, Khan I. Molecular pathways regulated by areca nut in the etiopathogenesis of oral submucous fibrosis[J]. Periodontol 2000, 2019, 80(1): 213-24. DOI: 10.1111/prd.12266 |
| 5 | 中华口腔医学会, 口腔黏膜下纤维性变诊断与临床管理指南:T/ [S]. 2022. |
| 6 | Arakeri G, Rai KK, Hunasgi S, et al. Oral submucous fibrosis: an update on current theories of pathogenesis[J]. J Oral Pathology Medicine, 2017, 46(6): 406-12. DOI: 10.1111/jop.12581 |
| 7 | Gupta S, Jawanda MK. Oral submucous fibrosis: an overview of a challenging entity[J]. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol, 2021, 87: 768-77. DOI: 10.25259/ijdvl_371_20 |
| 8 | Hsieh PL, Yu CC. Oral fibrosis and oral cancer: from molecular targets to therapeutics[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(11): 6110. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23116110 |
| 9 | Shih YH, Wang TH, Shieh TM, et al. Oral submucous fibrosis: a review on etiopathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(12): 2940. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20122940 |
| 10 | Warnakulasuriya S, Tilakaratne WM, Kerr A. Oral submucous fibrosis[M]//Contemporary Oral Oncology. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 329-53. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-14911-0_8 |
| 11 | Wang LP, Tang ZG. Immunopathogenesis of oral submucous fibrosis by chewing the areca nut[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2022, 111(2): 469-76. DOI: 10.1002/jlb.3mr0521-763rr |
| 12 | Zhou BL, Zhu W, Ren CP. First steps to regulate advertising of areca nut in China[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2019, 20(5): 615-6. DOI: 10.1016/s1470-2045(19)30231-1 |
| 13 | Zhou LH, Tan J, Dai YZ, et al. Jiawei Danxuan Koukang alleviates arecoline induced oral mucosal lesions: network pharmacology and the combined ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) and mass spectrometry (MS)[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2023, 17: 3085-101. DOI: 10.2147/dddt.s413897 |
| 14 | Luo WF, Deng J, He JC, et al. Integration of molecular docking, molecular dynamics and network pharmacology to explore the multi-target pharmacology of fenugreek against diabetes[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2023, 27(14): 1959-74. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17787 |
| 15 | 欧海亚,叶小鹏,李舒 等.基于网络药理学及数据挖掘探讨中药调节铁死亡的用药规律研究[J]. 中国现代应用药,2019,36(18):2317-24 |
| 16 | Hou FF, Yu ZY, Cheng Y, et al. Deciphering the pharmacological mechanisms of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi on oral leukoplakia by combining network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental evaluations[J]. Phytomedicine, 2022, 103: 154195. DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154195 |
| 17 | Zhao JL, Lin FZ, Liang GH, et al. Exploration of the molecular mechanism of polygonati rhizoma in the treatment of osteoporosis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2022, 12: 815891. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.815891 |
| 18 | Gao P, Chang K, Yuan S, et al. Exploring the mechanism of hepatotoxicity induced by Dictamnus dasycarpus based on network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental pharmacology[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(13): 5045. DOI: 10.3390/molecules28135045 |
| 19 | Luo WF, Deng J, He JC, et al. Integration of molecular docking, molecular dynamics and network pharmacology to explore the multi-target pharmacology of fenugreek against diabetes[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2023, 27(14): 1959-74. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17787 |
| 20 | He JH, Han DB, Jia CL, et al. Integrating network pharmacology, molecular docking and pharmacological evaluation for exploring the Polyrhachis vicina Rogers in ameliorating depression[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2023, 17: 717-35. DOI: 10.2147/dddt.s399183 |
| 21 | Zhan QX, Zhao JN, Liu L, et al. Integrated network pharmacology and molecular docking analyses of the mechanisms underlying the antihypertensive effects of lotusine[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2023, 945: 175622. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175622 |
| 22 | Torres PHM, Sodero ACR, Jofily P, et al. Key topics in molecular docking for drug design[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(18): 4574. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20184574 |
| 23 | Liao F, Yousif M, Huang RY, et al. Network pharmacology- and molecular docking-based analyses of the antihypertensive mechanism of Ilex kudingcha [J]. Front Endocrinol, 2023, 14: 1216086. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1216086 |
| 24 | Di-Luoffo M, Ben-Meriem Z, Lefebvre P, et al. PI3K functions as a hub in mechanotransduction[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2021, 46(11): 878-88. DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.05.005 |
| 25 | Fruman DA, Chiu H, Hopkins BD, et al. The PI3K pathway in human disease[J]. Cell, 2017, 170(4): 605-35. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.029 |
| 26 | Wang JC, Hu KL, Cai XY, et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT signaling for treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2022, 12(1): 18-32. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.07.023 |
| 27 | de Oliveira RP, de Andrade JS, Spina M, et al. Clozapine prevented social interaction deficits and reduced c-Fos immunoreactivity expression in several brain areas of rats exposed to acute restraint stress[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(3): e0262728. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262728 |
| 28 | Yang Y, Gong WY, Jin CX, et al. Naringin ameliorates experimental diabetic renal fibrosis by inhibiting the ERK1/2 and JNK MAPK signaling pathways[J]. J Funct Foods, 2018, 50: 53-62. DOI: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.09.020 |
| 29 | Pant I, Rao SG, Kondaiah P. Role of areca nut induced JNK/ATF2/Jun axis in the activation of TGF-β pathway in precancerous Oral Submucous Fibrosis[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 34314. DOI: 10.1038/srep34314 |
| 30 | Carleton M, Zhou M, De Henau O, et al. Serum interleukin 8 (IL-8) may serve as a biomarker of response to immuno-oncology (I-O) therapy[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2018, 36(): 3025. DOI: 10.1200/jco.2018.36.15_suppl.3025 |
| 31 | Bucur M, Dinca O, Vladan C, et al. Variation in expression of inflammation-related signaling molecules with profibrotic and antifibrotic effects in cutaneous and oral mucosa scars[J]. J Immunol Res, 2018, 2018: 5196023. DOI: 10.1155/2018/5196023 |
| [1] | 李云飞, 杨婧怡, 张 颖, 张财霞, 韦宇翔, 王怡颖, 吴 宁, 孙见飞, 吴遵秋. 苗药四大血减轻大鼠的类风湿性关节炎:基于下调基质金属蛋白表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 739-747. |
| [2] | 陈君洁, 黄传兵, 李 明. 健脾滋肾方抑制系统性红斑狼疮患者的足细胞自噬:基于网络药理学和临床研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 465-473. |
| [3] | 崔艺馨, 王德财, 谢东晴, 王海明, 徐睿鑫, 唐潇然, 张 印. 健脾温阳凝胶剂脐疗治疗脾胃虚弱型慢性腹泻的疗效及机制:一项临床随机对照试验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 217-225. |
| [4] | 张 倩, 张梅奎, 刘颖璐, 王 妍, 吕菲菲, 王毓国. 六味酸枣汤治疗围绝经期失眠的作用机制:基于网络药理学与动物实验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1536-1547. |
| [5] | 张雪芳, 陈延华, 李宗恒, 尚 靖, 袁泽婷, 邓皖利, 骆 莺, 韩 娜, 殷佩浩, 殷 军. 六神丸治疗小鼠结肠炎相关性结直肠癌的作用机制:基于网络药理学和体内验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1051-1062. |
| [6] | 刘 芳, 张远芳, 刘 鹏, 刘佳敏, 刘思妤, 王俊杰. 东革阿里抗炎的物质基础及其作用机制:基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS和网络药理学方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 879-888. |
| [7] | 罗冠峰, 刘华熙, 谢 钡, 邓伊健, 谢鹏辉, 赵晓山, 孙晓敏. 肾病III号方治疗慢性肾脏病大鼠肾脏纤维化的作用机制:基于网络药理学和分子对接技术[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 924-934. |
| [8] | 孙 洋, 许轶博, 肖林雨, 朱国庆, 李 静, 宋 雪, 徐 磊, 胡建国. 乙酰紫堇灵促进大鼠脊髓损伤后的功能恢复:基于调控EGFR/MAPK信号通路抑制小胶质细胞活化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 915-923. |
| [9] | 赵宇曦, 赵 旭, 朱清楠, 朱炳睿, 张震彬, 陈 静. 桂枝甘草汤通过多靶点、多通路治疗心力衰竭:基于网络药理学方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 772-782. |
| [10] | 张 钰, 涂 星, 张 燕, 文德鉴, 赵方毓, 袁 林, 李文慧. 文王一支笔的抗炎作用机制:基于网络药理学、分子对接及实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 383-392. |
| [11] | 黄永祺, 喻 伟, 游月华. 槟榔碱通过促进巨噬细胞分泌含miR-155-5p外泌体诱导人口腔成纤维细胞的活化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(1): 60-67. |
| [12] | 徐 朦, 张 鹏, 张国梁. 益气解毒方治疗原发性肝癌的作用机制:基于网络药理学及分子对接方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(6): 805-814. |
| [13] | 崔艺馨, 米继伟, 冯 宇, 李灵生, 王雨佳, 呼 健, 王海明. 黄芪四君子汤治疗乳腺癌癌因性疲乏的疗效及机制:基于94例临床随机对照试验和网络药理学[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(5): 649-657. |
| [14] | 邢 磊, 邢文文, 郭宏敏. 龙杞方治疗糖尿病肾脏病的作用机制:基于网络药理学和大鼠验证实验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(2): 171-180. |
| [15] | 赵 石, 刘珂娣, 段佳林, 陶星茹, 李伟红, 白 杨, 卫培峰, 奚苗苗, 杨红莲. 单味中药治疗心肌梗死的药效物质及作用机制:基于网络药理学和多靶标分子对接方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(1): 13-25. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||