南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (7): 1336-1344.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.07.13
• • 上一篇
黄燕1( ), 覃璐璐1, 管少兴2, 管宴萍2, 韦玉茹2, 操艾伶2, 李冬梅3, 韦桂宁3(
), 覃璐璐1, 管少兴2, 管宴萍2, 韦玉茹2, 操艾伶2, 李冬梅3, 韦桂宁3( ), 苏启表1(
), 苏启表1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-12-21
出版日期:2024-07-20
发布日期:2024-07-25
通讯作者:
韦桂宁,苏启表
E-mail:211214003@gdpu.edu.cn;weiguining2013@163.com;suqibiao@163.com
作者简介:黄 燕,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 211214003@gdpu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Yan HUANG1( ), Lulu QIN1, Shaoxing GUAN2, Yanping GUANG2, Yuru WEI2, Ailing CAO2, Dongmei LI3, Guining WEI3(
), Lulu QIN1, Shaoxing GUAN2, Yanping GUANG2, Yuru WEI2, Ailing CAO2, Dongmei LI3, Guining WEI3( ), Qibiao SU1(
), Qibiao SU1( )
)
Received:2023-12-21
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-07-25
Contact:
Guining WEI, Qibiao SU
E-mail:211214003@gdpu.edu.cn;weiguining2013@163.com;suqibiao@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 采用网络药理学及分子对接技术预测金缕半枫荷抗胰腺癌的关键靶点及信号通路,并通过胰腺癌细胞模型验证金缕半枫荷抗胰腺癌作用机制。 方法 通过网络药理学数据库预测药物及疾病的靶点,构建蛋白互作网络图,分析通路、功能富集和分子对接。通过CCK-8法筛选金缕半枫荷对8种癌细胞的活性,并采用侵袭、迁徙、增殖、凋亡实验方法验证金缕半枫荷对胰腺癌的作用。采用Western blotting验证网络药理学的结果。 结果 网络药理学共筛选得到金缕半枫荷活性成分18个,调控胰腺癌的潜在关键靶点21个。生物富集结果主要与蛋白质的磷酸化、信号传导、细胞凋亡等有关,通路主要与癌症信号通路、PI3K-Akt信号通路等有关。金缕半枫荷对胰腺癌细胞最敏感且显著抑制胰腺癌细胞Panc-1侵袭、迁徙和增殖,并且促进细胞凋亡(P<0.05)。Western blotting结果表明金缕半枫荷可以显著抑制PI3K和AKT的磷酸化水平(P<0.001)。 结论 金缕半枫荷通过多成分、多靶点、多通路发挥抗胰腺癌作用,其中抑制PI3K-Akt通路是其机制之一。
黄燕, 覃璐璐, 管少兴, 管宴萍, 韦玉茹, 操艾伶, 李冬梅, 韦桂宁, 苏启表. 金缕半枫荷的水提取物抑制胰腺癌的作用机制:活性成分、关键靶点和信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1336-1344.
Yan HUANG, Lulu QIN, Shaoxing GUAN, Yanping GUANG, Yuru WEI, Ailing CAO, Dongmei LI, Guining WEI, Qibiao SU. Therapeutic mechanism of aqueous extract of Semiliquidambar cathayensis Chang root for pancreatic cancer: the active components, therapeutic targets and pathways[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1336-1344.
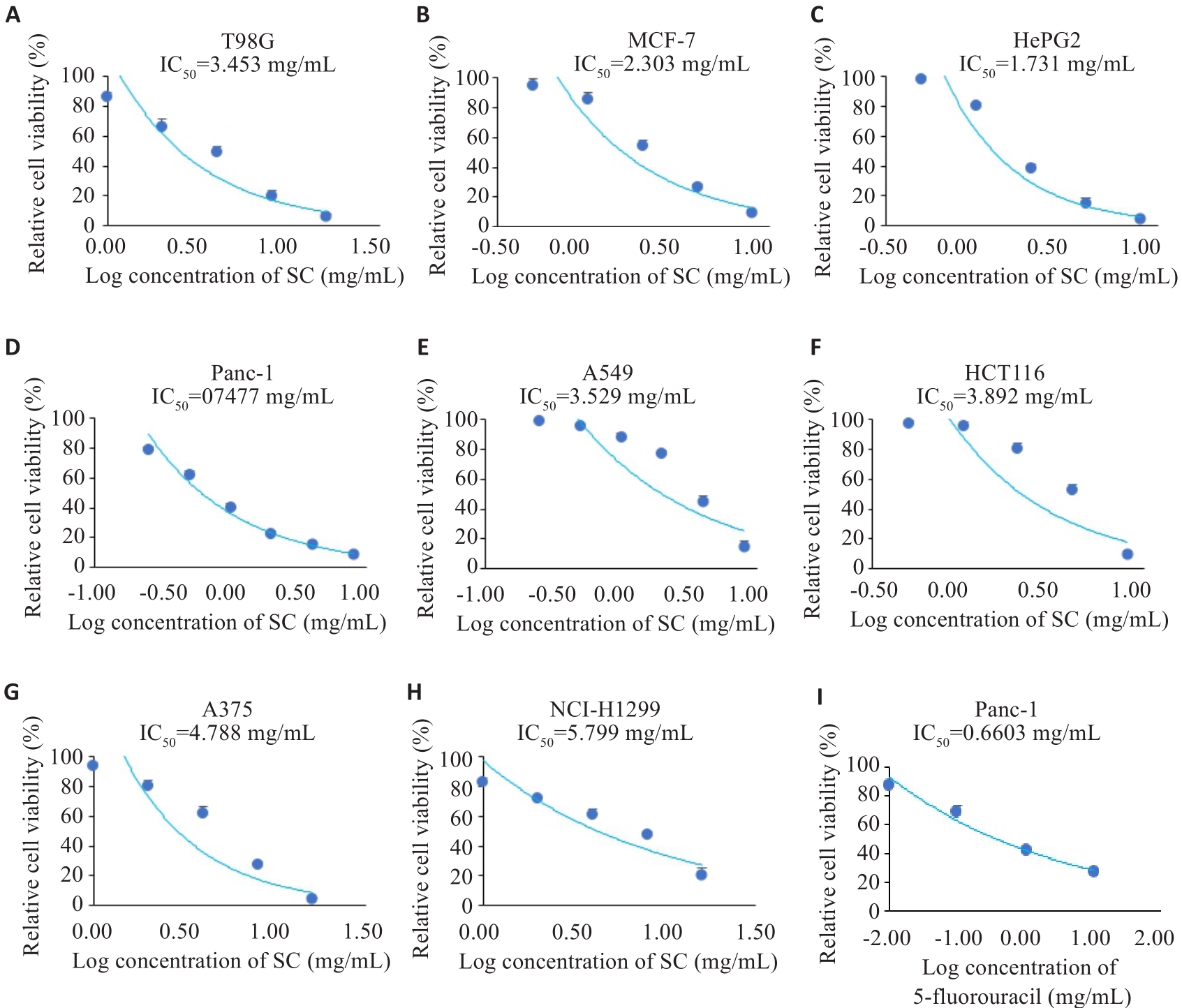
图1 金缕半枫荷和5-氟尿嘧啶对癌细胞的IC50
Fig.1 IC50 of Semiliquidambar cathayensis Chang root extract (SC) and 5-fluorouracil for different cancer cell lines. A-H: IC50 of Semiliquidambar cathayensis Chang against T98G, MCF-7, HePG2, Panc-1, A549, HCT116, A375, and NCI-H1299 cells; I: IC50 of 5-FU against Panc-1 cells.
| Ingredient | CAS | Degree |
|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | 117-39-5 | 52 |
| Kaempferol | 520-18-3 | 51 |
| Naringenin | 480-41-1 | 50 |
| 2,3,8-Tri-O-methylellagic acid | 1617-49-8 | 31 |
| Oleanolic acid | 508-02-1 | 29 |
| Paeoniflorin | 23180-57-6 | 27 |
| Bergaptol | 486-60-2 | 26 |
| Palmitic acid | 57-10-3 | 25 |
| Fraxin | 524-30-1 | 20 |
| Beta-Sitosterol | 83-46-5 | 17 |
| Songorine | 509-24-0 | 16 |
| Atractylenolide-1 | 73069-13-3 | 14 |
| Daucosterol | 474-58-8 | 14 |
| Hyperoside | 482-36-0 | 11 |
| Gallic acid | 149-91-7 | 10 |
| Isoquercitrin | 21637-25-2 | 9 |
| Rutin | 153-18-4 | 9 |
| Acteoside(Verbascoside) | 61276-17-3 | 5 |
表1 金缕半枫荷的主要活性成分
Tab.1 Main active components in Semiliquidambar cathayensis Chang root
| Ingredient | CAS | Degree |
|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | 117-39-5 | 52 |
| Kaempferol | 520-18-3 | 51 |
| Naringenin | 480-41-1 | 50 |
| 2,3,8-Tri-O-methylellagic acid | 1617-49-8 | 31 |
| Oleanolic acid | 508-02-1 | 29 |
| Paeoniflorin | 23180-57-6 | 27 |
| Bergaptol | 486-60-2 | 26 |
| Palmitic acid | 57-10-3 | 25 |
| Fraxin | 524-30-1 | 20 |
| Beta-Sitosterol | 83-46-5 | 17 |
| Songorine | 509-24-0 | 16 |
| Atractylenolide-1 | 73069-13-3 | 14 |
| Daucosterol | 474-58-8 | 14 |
| Hyperoside | 482-36-0 | 11 |
| Gallic acid | 149-91-7 | 10 |
| Isoquercitrin | 21637-25-2 | 9 |
| Rutin | 153-18-4 | 9 |
| Acteoside(Verbascoside) | 61276-17-3 | 5 |
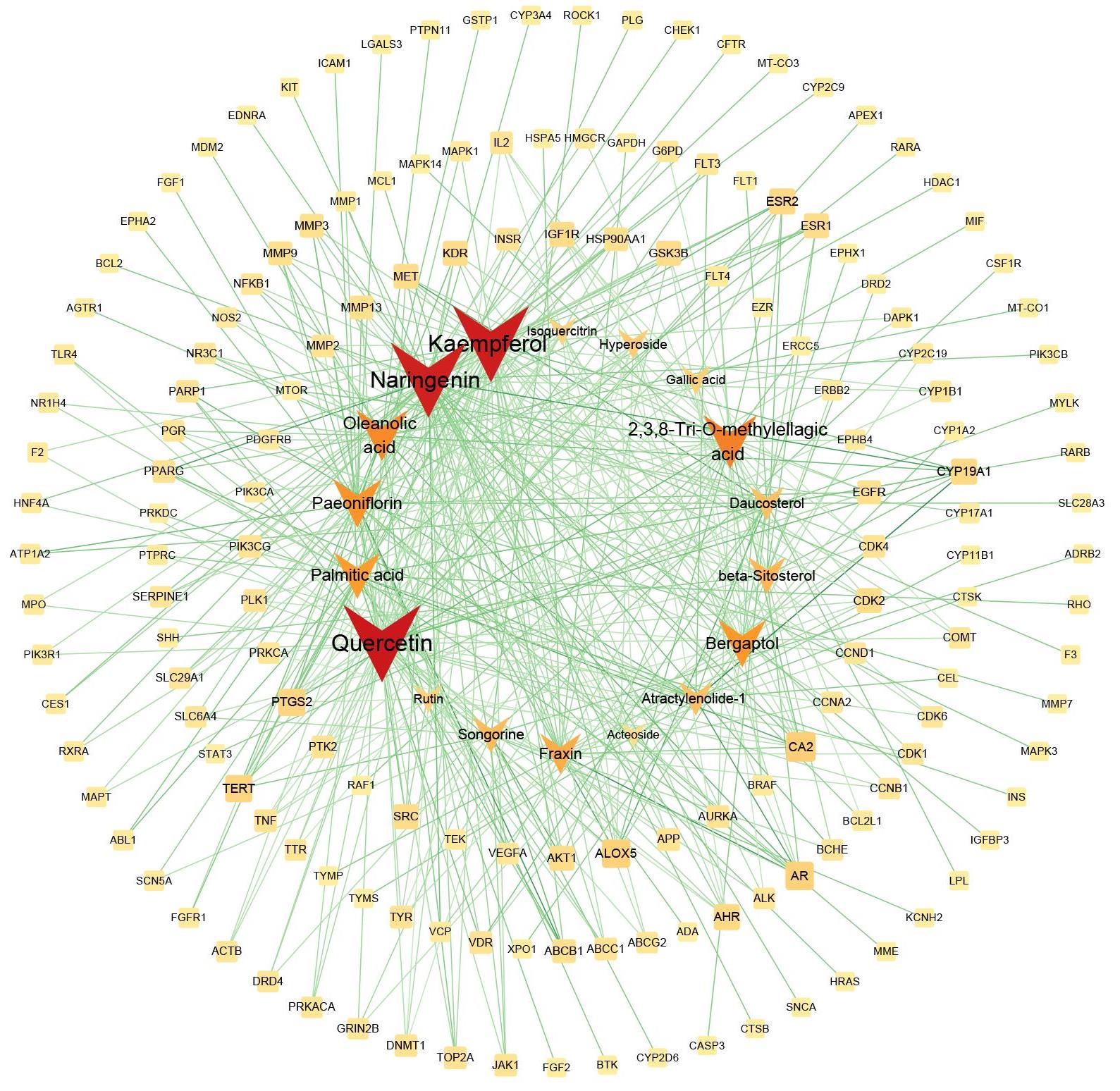
图3 金缕半枫荷关键成分预测
Fig.3 Prediction of the key components of Semiliquidambar cathayensis Chang. The circles indicate the target points of the intersection targets, and the V-shaped marks are the chemical components of Semiliquidambar cathayensis Chang. A darker color indicates a larger degree value.
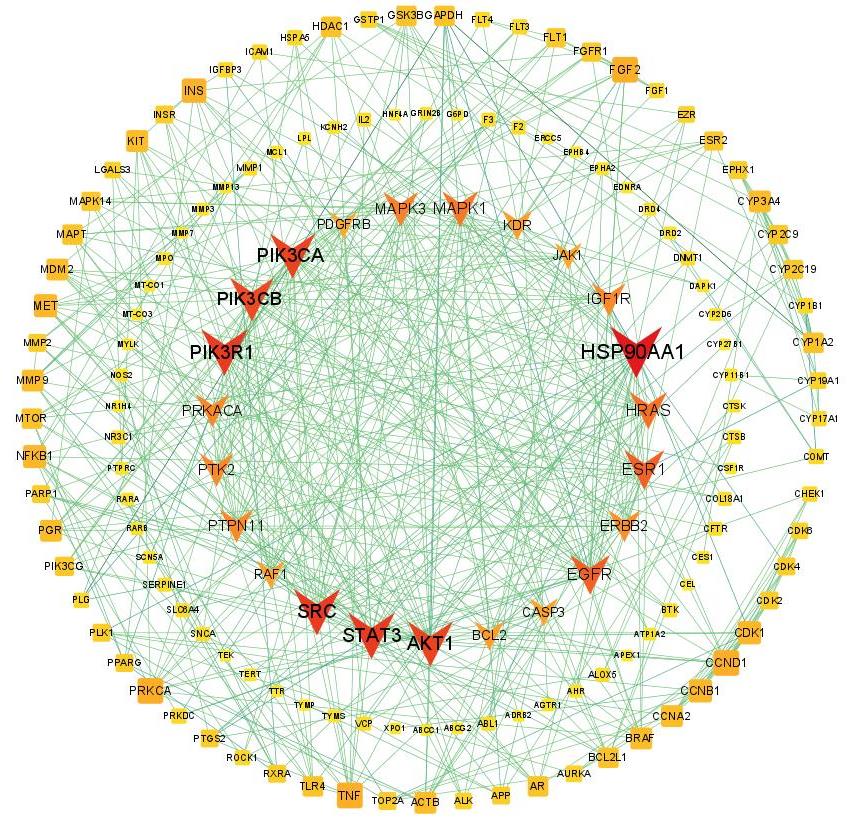
图4 金缕半枫荷与胰腺癌关键靶点预测
Fig.4 Prediction of the key targets of Semiliquidambar cathayensis Chang and pancreatic cancer. The V-shaped marks indicate the key targets of Semiliquidambar cathayensis Chang, and the circles are other target points. A darker color indicates a larger degree value.
| Affinity | Naringenin | 2, 3, 8-Tri-O-methylellagic acid | Quercetin | Kaempferol | Oleanolic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSP90AA1 | -8.9 | -9.3 | -9.3 | -9.4 | -7.0 |
| SRC | -8.3 | -7.9 | -8.8 | -8.6 | -9.1 |
| STAT3 | -7.7 | -7.2 | -8.1 | -7.8 | -6.9 |
| PIK3R1 | -8.3 | -6.1 | -8.6 | -8.7 | -9.7 |
| AKTI | -8.7 | -8.5 | -7.9 | -7.9 | -8.1 |
表2 关键成分与关键靶点的对接分数
Tab.2 Molecular docking score of the key components against the key targets
| Affinity | Naringenin | 2, 3, 8-Tri-O-methylellagic acid | Quercetin | Kaempferol | Oleanolic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSP90AA1 | -8.9 | -9.3 | -9.3 | -9.4 | -7.0 |
| SRC | -8.3 | -7.9 | -8.8 | -8.6 | -9.1 |
| STAT3 | -7.7 | -7.2 | -8.1 | -7.8 | -6.9 |
| PIK3R1 | -8.3 | -6.1 | -8.6 | -8.7 | -9.7 |
| AKTI | -8.7 | -8.5 | -7.9 | -7.9 | -8.1 |
| 1 | Huang JJ, Lok V, Ngai CH, et al. Worldwide burden of, risk factors for, and trends in pancreatic cancer[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 160(3): 744-54. |
| 2 | Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(1): 7-30. |
| 3 | Park W, Chawla A, O’Reilly EM. Pancreatic cancer: a review[J]. JAMA, 2021, 326(9): 851-62. |
| 4 | Lin WF, Lu JY, Cheng BB, et al. Progress in research on the effects of traditional Chinese medicine on the tumor microenvironment[J]. J Integr Med, 2017, 15(4): 282-7. |
| 5 | 苏玉平, 刘 宇, 马晓琴, 等. 贵州黔东南地区半枫荷的研究进展[J]. 中央民族大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 31(1): 92-6. |
| 6 | 唐 娟, 刘晓龙, 胡成刚, 等. 半枫荷化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 广州化工, 2022, 50(21): 7-10, 35. |
| 7 | 田晓明, 颜立红, 蒋利媛, 等. 半枫荷抗炎镇痛活性部位筛选及其成分分析[J]. 陕西中医药大学学报, 2021, 44(5): 63-8. |
| 8 | Shadhu K, Xi CH. Inflammation and pancreatic cancer: an updated review[J]. Saudi J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(1): 3-13. |
| 9 | Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation[J]. Cell, 2011, 144(5): 646-74. |
| 10 | Stone ML, Beatty GL. Cellular determinants and therapeutic implications of inflammation in pancreatic cancer[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 201: 202-13. |
| 11 | Farajzadeh Valilou S, Keshavarz-Fathi M, Silvestris N, et al. The role of inflammatory cytokines and tumor associated macrophages (TAMs) in microenvironment of pancreatic cancer[J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2018, 39: 46-61. |
| 12 | Florean C, Dicato M, Diederich M. Immune-modulating and anti-inflammatory marine compounds against cancer[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 80: 58-72. |
| 13 | 韩东波, 何俊慧, 贾春莲, 等. 基于NF-κB/TNF-α/IL-6通路探讨拟黑多刺蚁活性组分对脂多糖诱导抑郁小鼠神经炎症的影响[J]. 中药材, 2023, 46(10): 2551-7. |
| 14 | 何 飞, 李冬梅, 苏启表, 等. 拟黑多刺蚁活性组分治疗小鼠皮肤瘙痒的实验研究[J]. 中药材, 2018, 41(5): 1200-3. |
| 15 | Pu XY, Tian K, Sun JX, et al. Anti-inflammatory monoterpene esters from the stems of Illigera aromatica [J]. Nat Prod Res, 2021, 35(6): 960-6. |
| 16 | Su QB, Su H, Nong ZH, et al. Hypouricemic and nephroprotective effects of an active fraction from Polyrhachis vicina Roger on potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemia in rats[J]. Kidney Blood Press Res, 2018, 43(1): 220-33. |
| 17 | 韦 洁, 李冬梅, 何俊慧, 等. 香青藤提取物通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制胶质瘤U87细胞的间质转化[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2023, 39(7): 1431-6. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2023.07.016 |
| 18 | 韦 贤, 李冬梅, 何俊慧, 等. 拟黑多刺蚁活性组分通过miR-186-5p/Cx43促进结直肠癌SW116细胞凋亡的作用[J]. 中成药, 2022, 44(6): 1783-91. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2022.06.011 |
| 19 | Li DM, Zhong M, Su QB, et al. Active fraction of Polyrhachis vicina Rogers (AFPR) suppressed breast cancer growth and progression via regulating EGR1/lncRNA-NKILA/NF-κB axis[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2020, 123: 109616. |
| 20 | Li DM, Zhu FC, Wei J, et al. The Active Fraction of Polyrhachis vicina Roger (AFPR) activates ERK to cause necroptosis in colorectal cancer[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 312: 116454. |
| 21 | 何俊慧, 韦 洁, 李冬梅, 等. 基于网络药理学、分子对接和动物实验探究壮药金缕半枫荷对抑郁症炎症的作用机制[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2023, 39(7): 1362-70. |
| 22 | 卢海啸, 吕思颖, 姚水莲, 等. 金缕半枫荷甲醇部位化学成分研究[J]. 中药材, 2022, 45(3): 606-10. |
| 23 | 裘 硕, 陈月圆, 颜小捷, 等. 金缕半枫荷叶化学成分研究[J]. 中药材, 2020, 43(5): 1134-7. |
| 24 | Yang L, Liu RH, He JW. Rapid analysis of the chemical compositions in Semiliquidambar cathayensis roots by ultra high-performance liquid chromatography and quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(22): 4098. |
| 25 | Zhu D, Qu XC, Sun XM, et al. Comparative authentication of Semiliquidambar cathayensis and its substituted species via macroscopic and microscopic features[J]. Chin Herb Med, 2022, 14(4): 535-42. |
| 26 | Hsin KY, Ghosh S, Kitano H. Combining machine learning systems and multiple docking simulation packages to improve docking prediction reliability for network pharmacology[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(12): e83922. |
| 27 | Zhao L, Zhang H, Li N, et al. Network pharmacology, a promising approach to reveal the pharmacology mechanism of Chinese medicine formula[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 309: 116306. |
| 28 | Mortazavi M, Moosavi F, Martini M, et al. Prospects of targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in pancreatic cancer[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2022, 176: 103749. |
| 29 | Kong Y, Li YT, Luo YM, et al. circNFIB1 inhibits lymphan-giogenesis and lymphatic metastasis via the miR-486-5p/PIK3R1/VEGF-C axis in pancreatic cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2020, 19(1): 82. |
| 30 | Xu RY, Song JL, Ruze R, et al. SQLE promotes pancreatic cancer growth by attenuating ER stress and activating lipid rafts-regulated Src/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(8): 497. |
| 31 | Nwaeburu CC, Abukiwan A, Zhao ZF, et al. Quercetin-induced miR-200b-3p regulates the mode of self-renewing divisions in pancreatic cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2017, 16(1): 23. |
| 32 | Lee J, Kim DH, Kim JH. Combined administration of naringenin and hesperetin with optimal ratio maximizes the anti-cancer effect in human pancreatic cancer via down regulation of FAK and p38 signaling pathway[J]. Phytomedicine, 2019, 58: 152762. |
| 33 | Wang FJ, Wang L, Qu C, et al. Kaempferol induces ROS-dependent apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells via TGM2-mediated Akt/mTOR signaling[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 396. |
| 34 | Shopit A, Li XD, Tang ZY, et al. MiR-421 up-regulation by the oleanolic acid derivative K73-03 regulates epigenetically SPINK1 transcription in pancreatic cancer cells leading to metabolic changes and enhanced apoptosis[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2020, 161: 105130. |
| 35 | Zhong B, Shen JX, Zhang CY, et al. Plasma heat shock protein 90 alpha: a valuable predictor of early chemotherapy effectiveness in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2021, 27: e924778. |
| 36 | Bardelli A, Siena S. Molecular mechanisms of resistance to cetuximab and panitumumab in colorectal cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2010, 28(7): 1254-61. |
| 37 | Higginbotham JN, Demory Beckler M, Gephart JD, et al. Amphiregulin exosomes increase cancer cell invasion[J]. Curr Biol, 2011, 21(9): 779-86. |
| 38 | Yotsumoto F, Fukami T, Yagi H, et al. Amphiregulin regulates the activation of ERK and Akt through epidermal growth factor receptor and HER3 signals involved in the progression of pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Sci, 2010, 101(11): 2351-60. |
| 39 | Albury TM, Pandey V, Gitto SB, et al. Constitutively active Akt1 cooperates with KRas(G12D) to accelerate in vivo pancreatic tumor onset and progression[J]. Neoplasia, 2015, 17(2): 175-82. |
| 40 | Kong Y, Luo YM, Zheng SY, et al. Mutant KRAS mediates circARFGEF2 biogenesis to promote lymphatic metastasis of panc-reatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Cancer Res, 2023, 83(18): 3077-94. |
| [1] | 王瑾瑾, 崔文飞, 窦雪伟, 尹冰磊, 牛钰琪, 牛羚, 闫国立. 鬼箭羽通过调节EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂耐药信号通路延缓糖尿病肾病的进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1243-1255. |
| [2] | 王琳月, 戚文月, 高记华, 田茂生, 许建成. 痛痒消洗剂可促进大鼠肛瘘术后的创面愈合[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1256-1265. |
| [3] | 张文祥, 顾惠贤, 陈鹏德, 吴思宇, 马洪艳, 姚蓝. 复方玉液汤通过调控PI3K/Akt信号通路抑制糖尿病大鼠心肌细胞凋亡和炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1306-1314. |
| [4] | 李睿镈, 高歌, 谢曦, 罗海彬. 槟榔活性成分诱导口腔黏膜下纤维化的机制:基于网络药理学结合临床样本验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 930-940. |
| [5] | 李云飞, 杨婧怡, 张 颖, 张财霞, 韦宇翔, 王怡颖, 吴 宁, 孙见飞, 吴遵秋. 苗药四大血减轻大鼠的类风湿性关节炎:基于下调基质金属蛋白表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 739-747. |
| [6] | 陈君洁, 黄传兵, 李 明. 健脾滋肾方抑制系统性红斑狼疮患者的足细胞自噬:基于网络药理学和临床研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 465-473. |
| [7] | 崔艺馨, 王德财, 谢东晴, 王海明, 徐睿鑫, 唐潇然, 张 印. 健脾温阳凝胶剂脐疗治疗脾胃虚弱型慢性腹泻的疗效及机制:一项临床随机对照试验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 217-225. |
| [8] | 孙敬杰, 卢 鹏, 管莎莎, 刘淞淞. 胰腺癌细胞的异质性和肿瘤细胞分子亚型鉴定:基于CEACAM5、LGALS1和CENPF基因表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1567-1576. |
| [9] | 张 倩, 张梅奎, 刘颖璐, 王 妍, 吕菲菲, 王毓国. 六味酸枣汤治疗围绝经期失眠的作用机制:基于网络药理学与动物实验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1536-1547. |
| [10] | 张雪芳, 陈延华, 李宗恒, 尚 靖, 袁泽婷, 邓皖利, 骆 莺, 韩 娜, 殷佩浩, 殷 军. 六神丸治疗小鼠结肠炎相关性结直肠癌的作用机制:基于网络药理学和体内验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1051-1062. |
| [11] | 刘 芳, 张远芳, 刘 鹏, 刘佳敏, 刘思妤, 王俊杰. 东革阿里抗炎的物质基础及其作用机制:基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS和网络药理学方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 879-888. |
| [12] | 罗冠峰, 刘华熙, 谢 钡, 邓伊健, 谢鹏辉, 赵晓山, 孙晓敏. 肾病III号方治疗慢性肾脏病大鼠肾脏纤维化的作用机制:基于网络药理学和分子对接技术[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 924-934. |
| [13] | 孙 洋, 许轶博, 肖林雨, 朱国庆, 李 静, 宋 雪, 徐 磊, 胡建国. 乙酰紫堇灵促进大鼠脊髓损伤后的功能恢复:基于调控EGFR/MAPK信号通路抑制小胶质细胞活化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 915-923. |
| [14] | 梁利渡, 张浩杰, 鲁 倩, 周陈杰, 李淑龙. aFaster RCNN:一种基于平扫 CT 的多疾病阶段胰腺病灶检测模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 755-763. |
| [15] | 赵宇曦, 赵 旭, 朱清楠, 朱炳睿, 张震彬, 陈 静. 桂枝甘草汤通过多靶点、多通路治疗心力衰竭:基于网络药理学方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 772-782. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||