南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (7): 1327-1335.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.07.12
陈芊伊1,2( ), 尚书涵1,2,3, 鲁欢1,2, 李思思1,2,4, 孙志勉1,2,3, 范喜瑞1,2(
), 尚书涵1,2,3, 鲁欢1,2, 李思思1,2,4, 孙志勉1,2,3, 范喜瑞1,2( ), 戚之琳1,2(
), 戚之琳1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-14
出版日期:2024-07-20
发布日期:2024-07-25
通讯作者:
范喜瑞,戚之琳
E-mail:937441097@qq.com;20210006@wnmc.edu.cn;20010012@wnmc.edu.cn
作者简介:陈芊伊,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 937441097@qq.com
基金资助:
Qianyi CHEN1,2( ), Shuhan SHANG1,2,3, Huan LU1,2, Sisi LI1,2,4, Zhimian SUN1,2,3, Xirui FAN1,2(
), Shuhan SHANG1,2,3, Huan LU1,2, Sisi LI1,2,4, Zhimian SUN1,2,3, Xirui FAN1,2( ), Zhilin QI1,2(
), Zhilin QI1,2( )
)
Received:2024-05-14
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-07-25
Contact:
Xirui FAN, Zhilin QI
E-mail:937441097@qq.com;20210006@wnmc.edu.cn;20010012@wnmc.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 探讨金盏花苷E抑制肝癌细胞增殖和迁移的分子机制。 方法 金盏花苷E处理肝癌细胞,CCK-8检测细胞活力;Western blotting检测GPX4、SLC7A11、LC3、P62的表达以及Akt/mTOR的磷酸化。自噬抑制剂LY294002和激活剂Rapamycin与金盏花苷E联合处理肝癌细胞,EdU和Transwell实验分别检测肝癌细胞的增殖和迁移能力。TCGA数据库分析GPX4和SLC7A11在肝癌及正常肝组织中的表达水平,以及与肝癌患者存活之间的关系。Western blotting和qPCR分别检测GPX4和SLC7A11在肝癌细胞和正常肝细胞中的表达水平。 结果 金盏花苷E能够显著抑制肝癌细胞的存活(P<0.05);GPX4和SLC7A11在肝癌组织和肝癌细胞中均显著高表达;GPX4和SLC7A11的表达与肝癌患者存活呈显著负相关(P<0.001);金盏花苷E显著抑制GPX4和SLC7A11蛋白的表达,激活Akt-mTOR通路,增强LC3 Ⅱ的表达(P<0.01);自噬激活剂Rapamycin显著增强金盏花苷E对GPX4和SLC7A11的抑制作用,而自噬抑制剂LY294002则明显逆转了金盏花苷E对GPX4和SLC7A11的抑制作用(P<0.05);抑制自噬途径能够逆转金盏花苷E对肝癌细胞增殖和迁移的抑制作用,增强自噬途径则发生相反的变化(P<0.01)。 结论 金盏花苷E经自噬途径下调GPX4和SLC7A11抑制肝癌细胞的增殖和迁移。
陈芊伊, 尚书涵, 鲁欢, 李思思, 孙志勉, 范喜瑞, 戚之琳. 金盏花苷E通过自噬途径下调GPX4和SLC7A11抑制肝癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1327-1335.
Qianyi CHEN, Shuhan SHANG, Huan LU, Sisi LI, Zhimian SUN, Xirui FAN, Zhilin QI. Calenduloside E inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration by down-regulating GPX4 and SLC7A11 expression through the autophagy pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1327-1335.
| Primers | Sequence of primer | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward (form 5′ to 3′) | Reverse (from 5′ to 3′) | |
| SLC7A11 | TCTCCAAAGGAGGTTACCTGC | AGACTCCCCTCAGTAAAGTGAC |
| GPX4 | GAGGCAAGACCGAAGTAAACTAC | CCGAACTGGTTACACGGGAA |
| GAPDH | AAAGCCTGCCGGTGACTAA | AGAGTTAAAAGCAGCCCTGG |
表1 SLC7A11、GPX4以及GAPDH引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR of SLC7A11, GPX4 and GAPDH
| Primers | Sequence of primer | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward (form 5′ to 3′) | Reverse (from 5′ to 3′) | |
| SLC7A11 | TCTCCAAAGGAGGTTACCTGC | AGACTCCCCTCAGTAAAGTGAC |
| GPX4 | GAGGCAAGACCGAAGTAAACTAC | CCGAACTGGTTACACGGGAA |
| GAPDH | AAAGCCTGCCGGTGACTAA | AGAGTTAAAAGCAGCCCTGG |
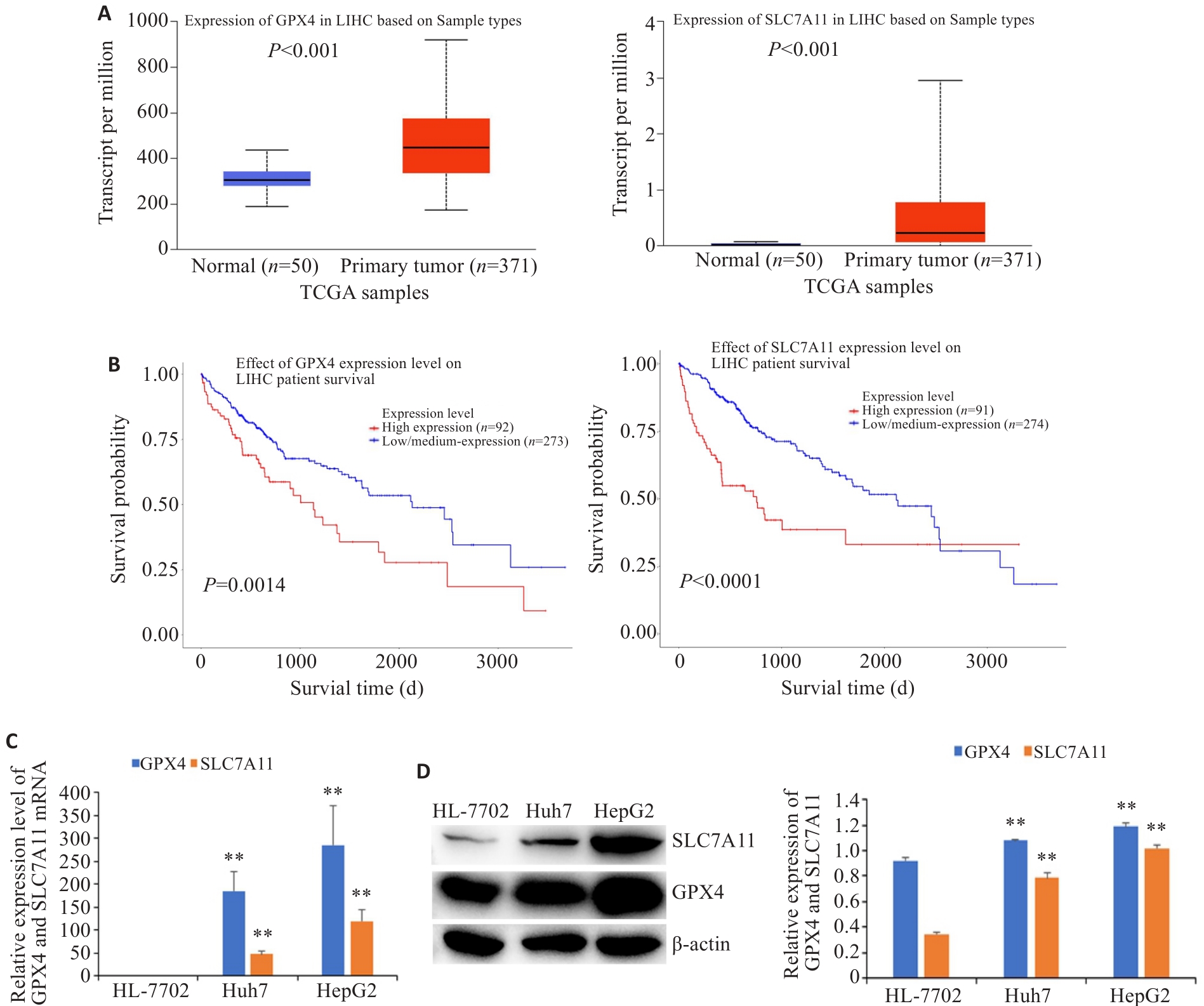
图2 GPX4和SLC7A11在肝癌组织和细胞中的表达及其与患者存活的相关性
Fig.2 Expression levels of GPX4 and SLC7A11 in HCC tissues and cells and their correlation with the patients' survival (Mean±SD). A: Expression of GPX4 and SLC7A11 in HCC tissues and normal liver tissues. B: Correlation of GPX4 and SLC7A11 expressions with the patients' survival. The expressions of GPX4 and SLC7A11 mRNA (C) and protein (D) in HCC cells and normal liver cells. **P<0.01 vs HL-7702.
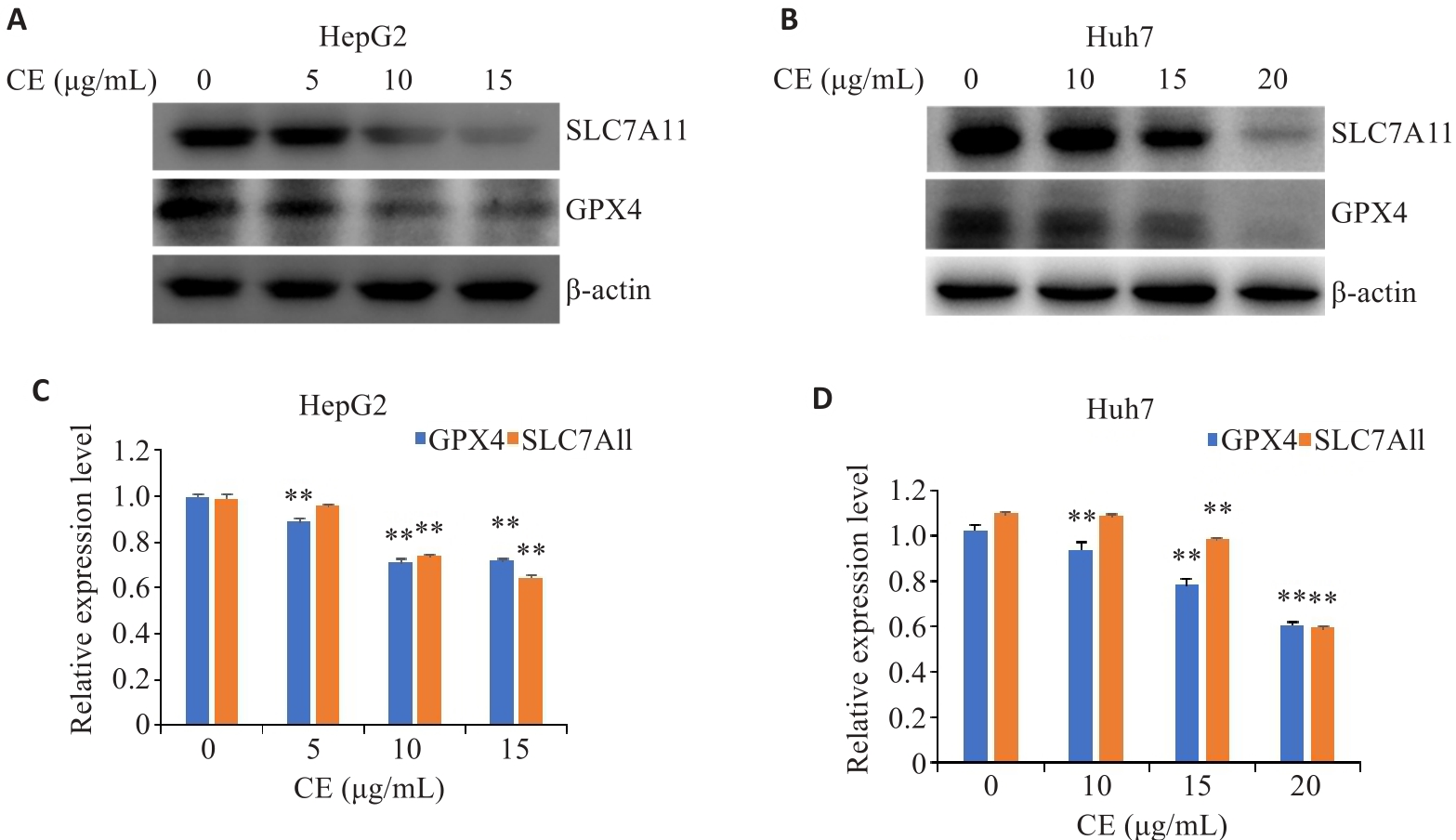
图3 金盏花苷E对GPX4和SLC7A11表达的影响
Fig.3 Effects of CE on GPX4 and SLC7A11 expressions in HepG2 (A, B) and Huh7 cells (C, D). Data are presented as Mean±SD. **P<0.01 vs 0 µg/mL. CE: Calenduloside E.
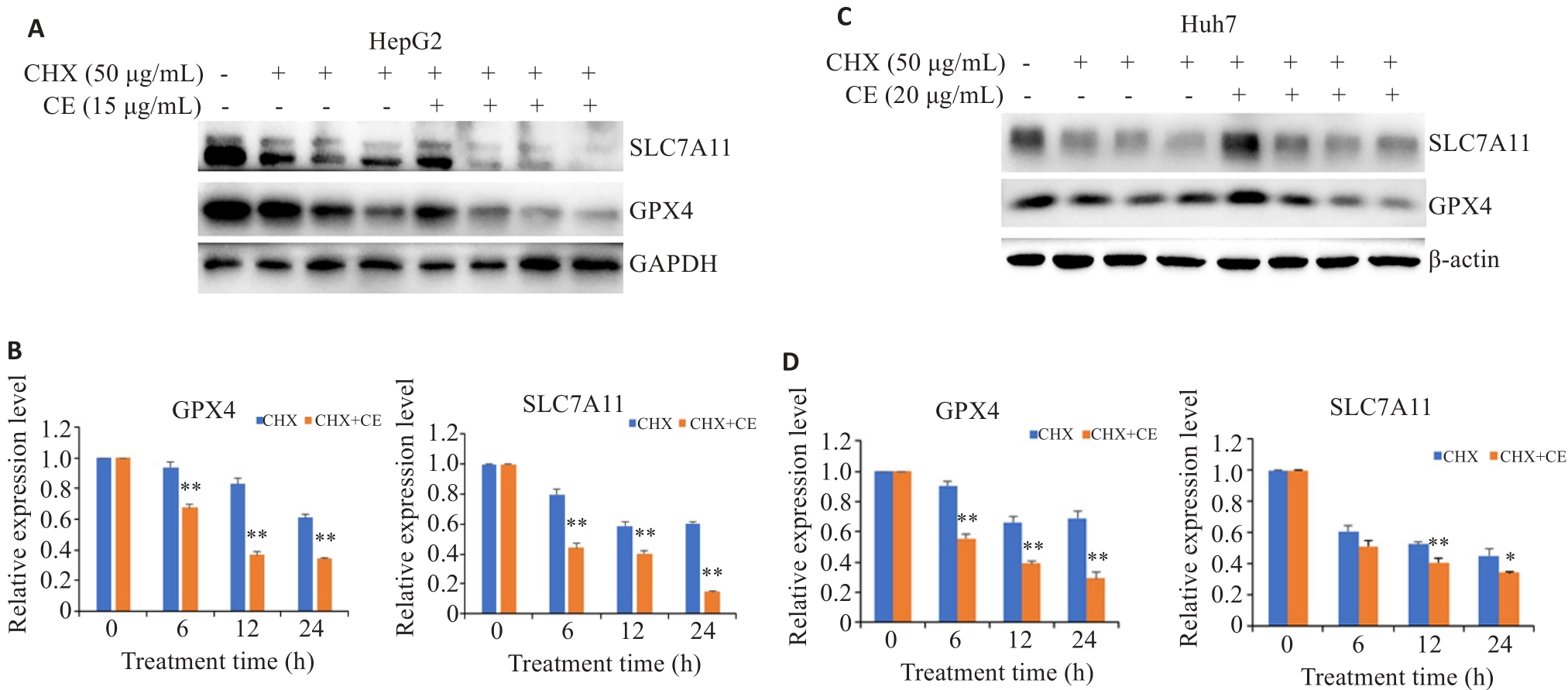
图4 金盏花苷E对GPX4和SLC7A11降解的影响
Fig.4 Effects of CE on GPX4 and SLC7A11 protein degradation in HepG2 (A, B) and Huh7 cells (C, D). Data are presented as Mean±SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs CHX group.
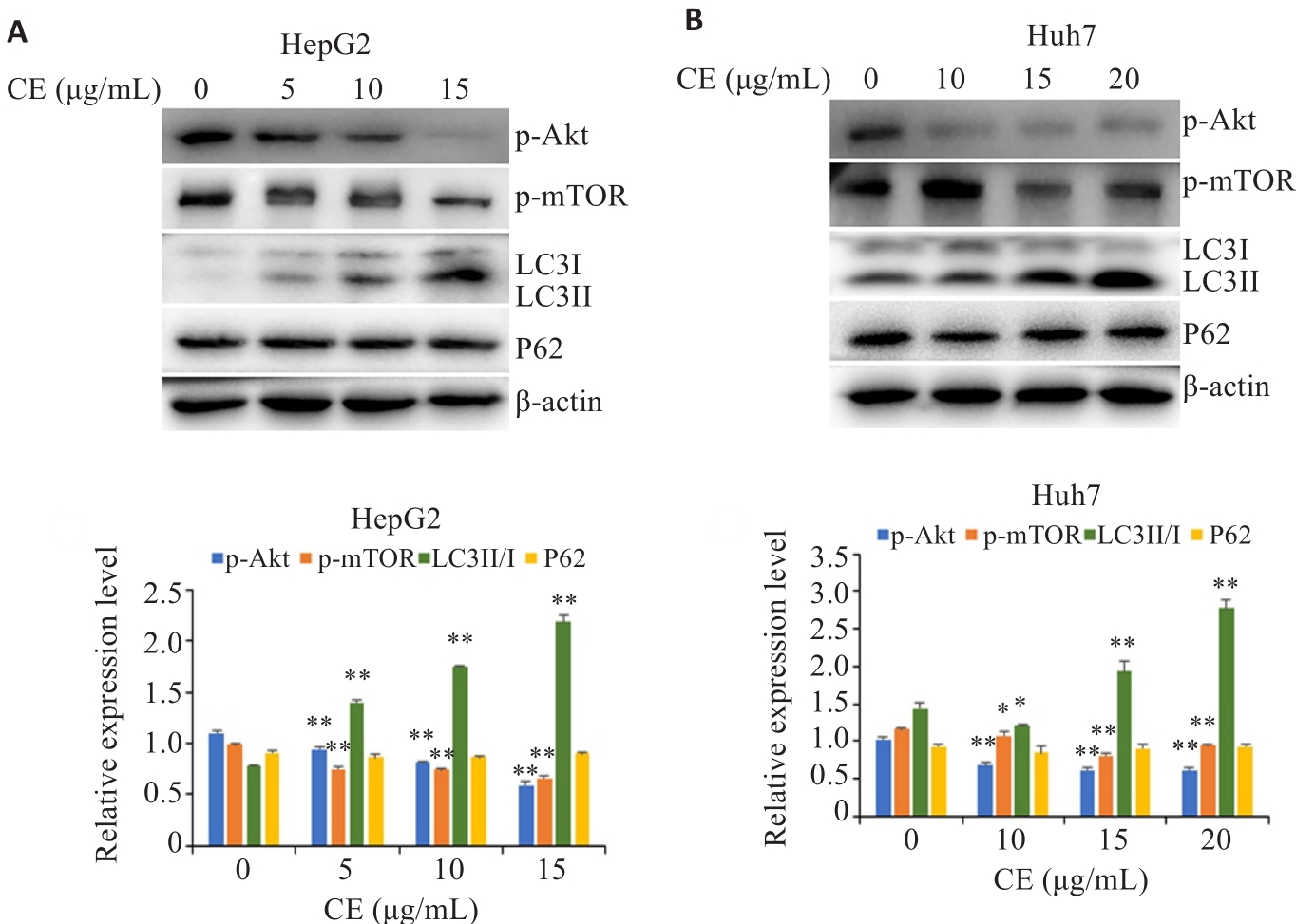
图5 金盏花苷E对肝癌细胞自噬途径的影响
Fig.5 Effects of CE on the autophagy pathway in HepG2 (A) and Huh7 cells (B). Data are presented as Mean±SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs 0 µg/mL.
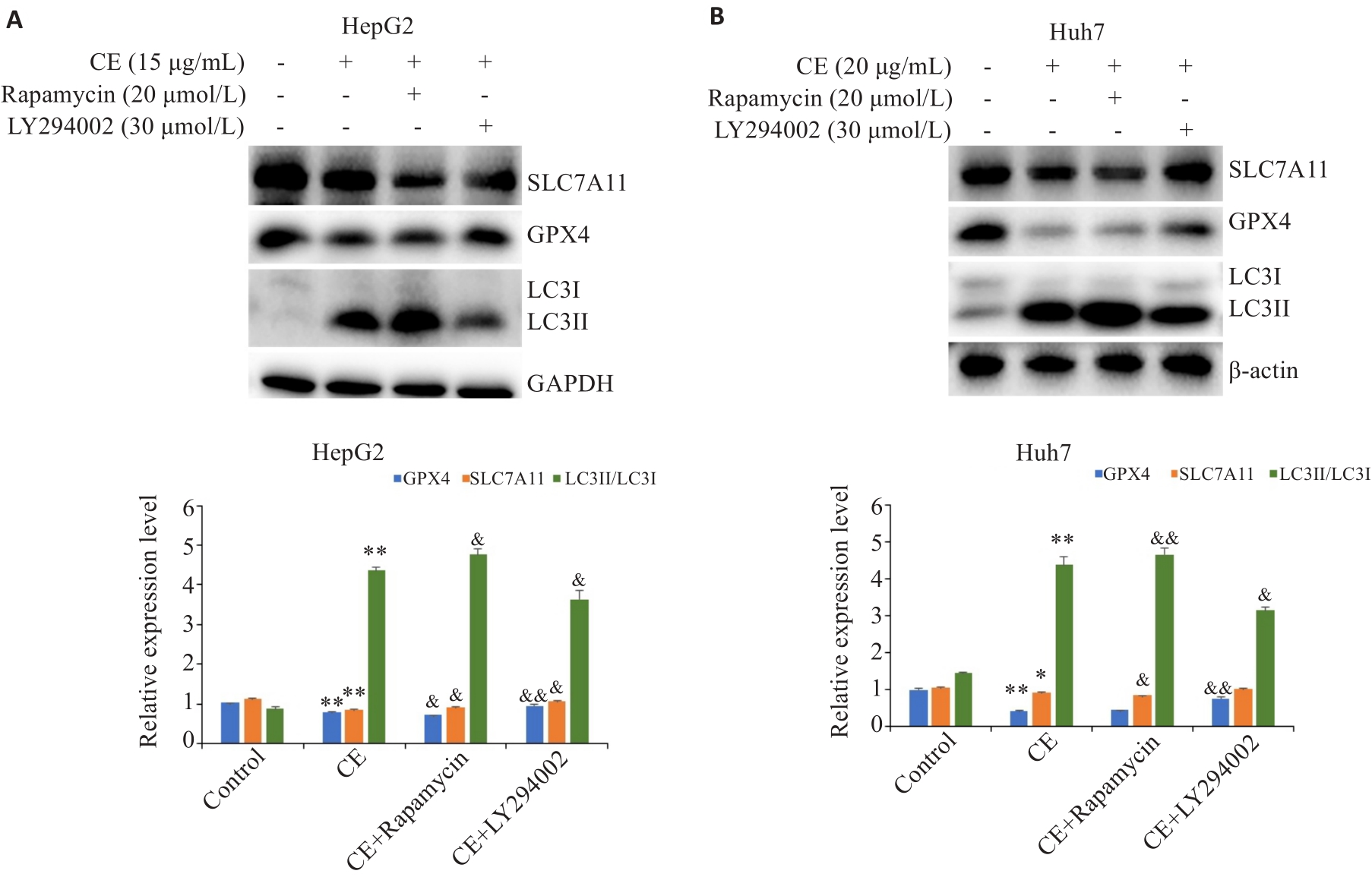
图7 自噬抑制剂或激活剂对金盏花苷E下调GPX4和SLC7A11的影响
Fig.7 Effects of autophagy inhibitor or activator on CE-induced GPX4 and SLC7A11 down-regulation in HepG2 (A) and Huh7 (B) cells (Mean±SD). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Control; &P<0.05, &&P<0.01 vs CE.
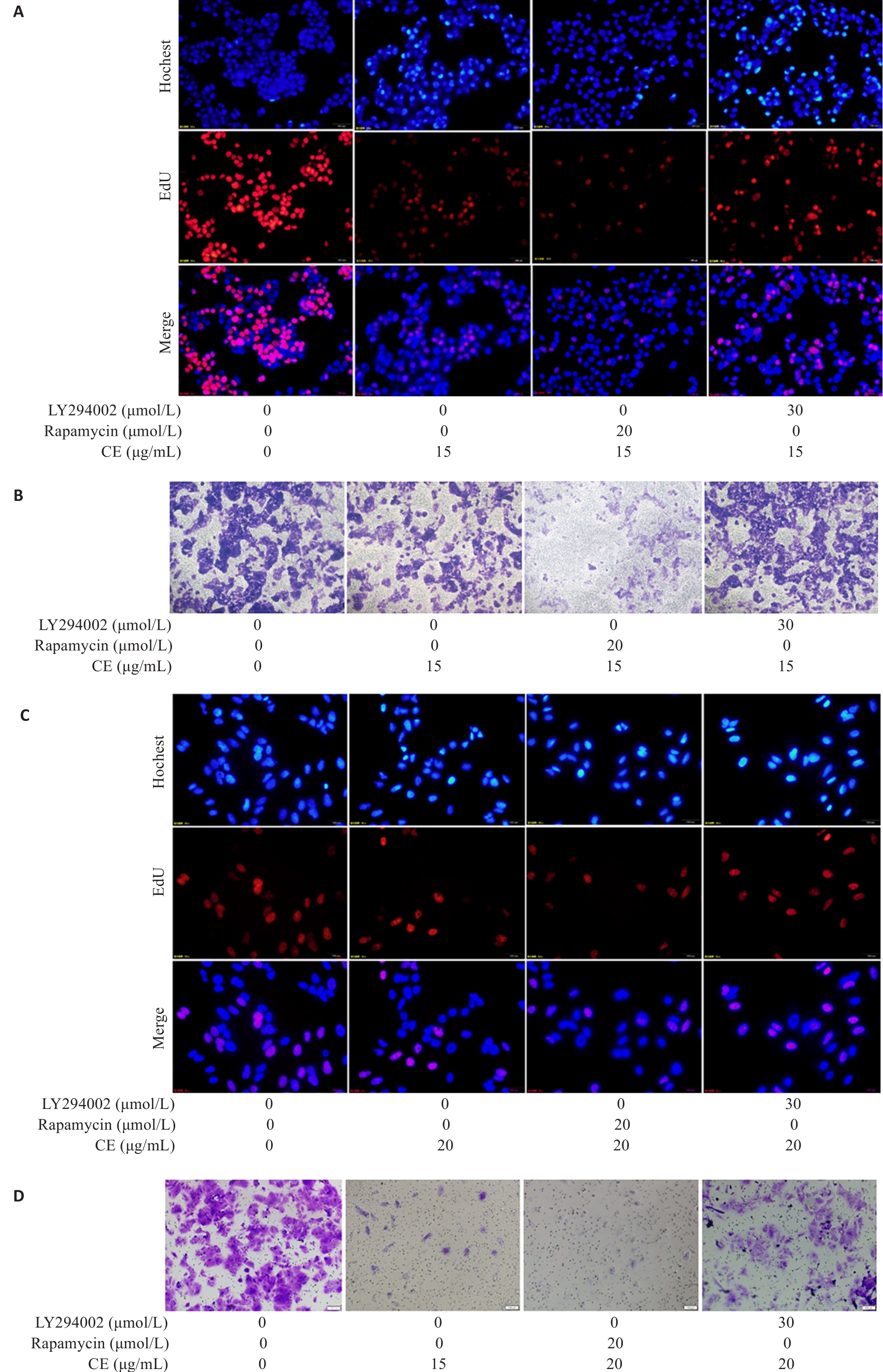
图8 自噬抑制剂或激活剂对金盏花苷E抑制肝癌细胞增殖和迁移的影响
Fig.8 Effects of autophagy inhibitor or activator on proliferation and migration of CE-treated HepG2 (A, B) and Huh7 (C, D) cells (×100).
| 1 | Xia CF, Dong XS, Li H, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants[J]. Chin Med J, 2022, 135(5): 584-90. |
| 2 | Wang SN, Wu XW, Wu XM, et al. Systematic analysis of the role of LDHs subtype in pan-cancer demonstrates the importance of LDHD in the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients[J]. BMC Cancer, 2024, 24(1): 156. |
| 3 | 谢思雨, 李淼生, 江峰乐, 等. EHHADH是肝细胞癌脂肪酸代谢通路的关键基因: 基于转录组分分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 680-93. DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.05.02 |
| 4 | Metur SP, Lei YC, Zhang ZH, et al. Regulation of autophagy gene expression and its implications in cancer[J]. J Cell Sci, 2023, 136(10): jcs260631. |
| 5 | Jain V, Singh MP, Amaravadi RK. Recent advances in targeting autophagy in cancer[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2023, 44(5): 290-302. |
| 6 | Chow AK, Yau SW, Ng L. Novel molecular targets in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. World J Clin Oncol, 2020, 11(8): 589-605. |
| 7 | Wang Y, Deng BC. Hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular mechanism, targeted therapy, and biomarkers[J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2023, 42(3): 629-52. |
| 8 | Glaviano A, Foo ASC, Lam HY, et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies in cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2023, 22(1): 138. |
| 9 | He PZ, He Y, Ma JJ, et al. Thymoquinone induces apoptosis and protective autophagy in gastric cancer cells by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway[J]. Phytother Res, 2023, 37(8): 3467-80. |
| 10 | Lee J, Roh JL. SLC7A11 as a gateway of metabolic perturbation and ferroptosis vulnerability in cancer[J]. Antioxidants, 2022, 11(12): 2444. |
| 11 | Liu JY, Xia XJ, Huang P. xCT: a critical molecule that links cancer metabolism to redox signaling[J]. Mol Ther, 2020, 28(11): 2358-66. |
| 12 | Huang Y, Dai ZY, Barbacioru C, et al. Cystine-glutamate transporter SLC7A11 in cancer chemosensitivity and chemoresistance[J]. Cancer Res, 2005, 65(16): 7446-54. |
| 13 | Li SJ, Lu ZY, Sun RB, et al. The role of SLC7A11 in cancer: friend or foe[J]? Cancers, 2022, 14(13): 3059. |
| 14 | Zhang W, Liu Y, Liao Y, et al. GPX4, ferroptosis, and diseases[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2024, 174: 116512. |
| 15 | Jia CX, Zhang X, Qu TT, et al. Depletion of PSMD14 suppresses bladder cancer proliferation by regulating GPX4[J]. PeerJ, 2023, 11: e14654. |
| 16 | Tang X, Ding H, Liang ML, et al. Curcumin induces ferroptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer via activating autophagy[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2021, 12(8): 1219-30. |
| 17 | Le YF, Guo JN, Liu ZJ, et al. Calenduloside E ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via modulating a pyroptosis-dependent pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 319(Pt 2): 117239. |
| 18 | Li JX, Bu YJ, Li B, et al. Calenduloside E alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by preserving mitochondrial function[J]. J Mol Histol, 2022, 53(4): 713-27. |
| 19 | 汤 托, 王胜男, 蔡田雨, 等. 金盏花苷E通过ROS介导的JAK1-stat3信号途径抑制LPS诱发的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(8): 904-10. DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.08.05 |
| 20 | Wang SN, Chen XL, Cheng J, et al. Calunduloside E inhibits HepG2 cell proliferation and migration via p38/JNK-HMGB1 signalling axis[J]. J Pharmacol Sci, 2021, 147(1): 18-26. |
| 21 | Zhang W, Jiang BP, Liu YX, et al. Bufotalin induces ferroptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by facilitating the ubiquitination and degradation of GPX4[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2022, 180: 75-84. |
| 22 | Li DB, Wang YH, Dong C, et al. CST1 inhibits ferroptosis and promotes gastric cancer metastasis by regulating GPX4 protein stability via OTUB1[J]. Oncogene, 2023, 42(2): 83-98. |
| 23 | Wang XB, Chen YQ, Wang XD, et al. Stem cell factor SOX2 confers ferroptosis resistance in lung cancer via upregulation of SLC7A11[J]. Cancer Res, 2021, 81(20): 5217-29. |
| 24 | Hanzl A, Winter GE. Targeted protein degradation: current and future challenges[J]. Curr Opin Chem Biol, 2020, 56: 35-41. |
| 25 | Wang Y, Le WD. Autophagy and ubiquitin-proteasome system[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019, 1206: 527-50. |
| 26 | Xu ZR, Han X, Ou DM, et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy for tumor therapy[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2020, 104(2): 575-87. |
| 27 | Zhang M, Liu SH, Chua MS, et al. SOCS5 inhibition induces autophagy to impair metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10(8): 612. |
| 28 | Li H, Zhao SF, Shen LW, et al. E2F2 inhibition induces autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in gastric cancer[J]. Aging, 2021, 13(10): 13626-43. |
| 29 | Zhang JH, Fan JJ, Zeng X, et al. Targeting the autophagy promoted antitumor effect of T-DM1 on HER2-positive gastric cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(4): 288. |
| 30 | Yi H, Wang K, Du BY, et al. Aleuritolic acid impaired autophagic flux and induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells[J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(6): 1338. |
| 31 | Li JK, Zhu PL, Wang Y, et al. Gracillin exerts anti-melanoma effects in vitro and in vivo: role of DNA damage, apoptosis and autophagy[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 108: 154526. |
| 32 | Yu WX, Lu C, Wang B, et al. Effects of rapamycin on osteosarcoma cell proliferation and apoptosis by inducing autophagy[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(2): 915-21. |
| 33 | Chen WS, Xian GY, Gu MH, et al. Autophagy inhibitors 3-MA and LY294002 repress osteoclastogenesis and titanium particle-stimulated osteolysis[J]. Biomater Sci, 2021, 9(14): 4922-35. |
| 34 | Ouyang SM, Li HX, Lou LL, et al. Inhibition of STAT3-ferroptosis negative regulatory axis suppresses tumor growth and alleviates chemoresistance in gastric cancer[J]. Redox Biol, 2022, 52: 102317. |
| 35 | Zeng C, Lin J, Zhang KT, et al. SHARPIN promotes cell proliferation of cholangiocarcinoma and inhibits ferroptosis via p53/SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling[J]. Cancer Sci, 2022, 113(11): 3766-75. |
| 36 | Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death[J]. Cell, 2012, 149(5): 1060-72. |
| 37 | Mou YH, Wang J, Wu JC, et al. Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: opportunities and challenges in cancer[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2019, 12(1): 34. |
| [1] | 李玮怡, 江露, 张宗星, 陈丹, 包卓玛, 黄丽, 袁林. 强骨康疏方通过抑制HIF-1α/BNIP3自噬信号通路减少类风湿性关节炎大鼠的破骨细胞分化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1389-1396. |
| [2] | 王心恒, 邵小涵, 李童童, 张璐, 杨勤军, 叶卫东, 童佳兵, 李泽庚, 方向明. 平喘宁方通过调控HMGB1/Beclin-1轴介导的自噬改善患寒哮证大鼠的气道炎症[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1153-1162. |
| [3] | 董妍妍, 张可敬, 储俊, 储全根. 抵当汤含药血清通过PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路增强高糖诱导的大鼠肾小球内皮细胞自噬[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 461-469. |
| [4] | 廖茗, 钟文华, 张冉, 梁娟, 徐文陶睿, 万文珺, 吴超, 李曙. 源自蛇毒的蛋白C激活剂通过调控HIF-1α抑制BNIP3活性氧生成保护人脐静脉内皮细胞免受缺氧-复氧损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 614-621. |
| [5] | 郭克磊, 李颖利, 宣晨光, 侯紫君, 叶松山, 李林运, 陈丽平, 韩立, 卞华. 益气养阴化浊通络方通过调控miR-21a-5p/FoxO1/PINK1介导的线粒体自噬减轻糖尿病肾病小鼠的足细胞损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 27-34. |
| [6] | 展俊平, 黄硕, 孟庆良, 范围, 谷慧敏, 崔家康, 王慧莲. 缺氧微环境下补阳还五汤通过抑制BNIP3-PI3K/Akt通路抑制类风湿关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞的线粒体自噬[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 35-42. |
| [7] | 陈志亮, 杨永刚, 黄霞, 成彦, 瞿媛, 衡琪琪, 符羽佳, 李可薇, 顾宁. 外泌体miRNA差异表达可作为诊断慢性心力衰竭合并高尿酸血症患者新型分子标志物及靶基因功能分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 43-51. |
| [8] | 程瑶, 王远迎, 姚飞扬, 胡盼, 陈铭勰, 吴宁. 黄芩苷通过调控PI3K/AKT信号通路抑制登革病毒感染诱导的人静脉内皮细胞的自噬[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1272-1283. |
| [9] | 张叶明, 张袁祥, 沈学彬, 王国栋, 朱磊. 在抑郁症大鼠模型中MiRNA-103-3p调控Rab10促进神经细胞自噬[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1315-1326. |
| [10] | 何欣容, 熊斯丽, 朱真如, 孙景苑, 曹传辉, 王惠. UBE2T通过调节性T细胞诱导肝细胞癌的放疗抵抗[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1149-1158. |
| [11] | 刘鹏程, 娄丽娟, 刘霞, 王建, 姜颖. M2巨噬细胞特征基因风险评分能准确预测HBV相关肝细胞癌患者的预后[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 827-840. |
| [12] | 周凤敏, 郭艳菊, 陈 宁. 运动诱导的Irisin表达改善2型糖尿病大鼠的肾脏损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 675-681. |
| [13] | 陈君洁, 黄传兵, 李 明. 健脾滋肾方抑制系统性红斑狼疮患者的足细胞自噬:基于网络药理学和临床研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 465-473. |
| [14] | 肖红敏, 韩保松, 郭家成, 吴 超, 吴敬医. HTD4010 可减轻脓毒症心肌病小鼠的心肌损伤:基于促进AMPK/mTOR信号通路介导的自噬[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 507-514. |
| [15] | 钟伟雄, 梁芳蓉, 杨蕊梦, 甄 鑫. 基于多期动态增强CT影像组学特征和多分类器分层融合模型预测肝细胞癌的微血管侵犯[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 260-269. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||