南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (9): 1685-1695.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.09.08
纪凯1,2( ), 于冠宇2, 周乐其2, 张天帅2, 凌潜龙1, 满文江1,2, 朱冰1(
), 于冠宇2, 周乐其2, 张天帅2, 凌潜龙1, 满文江1,2, 朱冰1( ), 张卫2(
), 张卫2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-19
出版日期:2024-09-20
发布日期:2024-10-31
通讯作者:
朱冰,张卫
E-mail:1361679354@qq.com;bbmczhubing@163.com;weizhang2000cn@163.com
作者简介:纪 凯,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 1361679354@qq.com
基金资助:
Kai JI1,2( ), Guanyu YU2, Leqi ZHOU2, Tianshuai ZHANG2, Qianlong LING1, Wenjiang MAN1,2, Bing ZHU1(
), Guanyu YU2, Leqi ZHOU2, Tianshuai ZHANG2, Qianlong LING1, Wenjiang MAN1,2, Bing ZHU1( ), Wei ZHANG2(
), Wei ZHANG2( )
)
Received:2024-05-19
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-10-31
Contact:
Bing ZHU, Wei ZHANG
E-mail:1361679354@qq.com;bbmczhubing@163.com;weizhang2000cn@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 通过生物信息学和细胞实验探究HNRNP A1在结直肠癌中的临床意义及其在肿瘤组织中的表达情况。 方法 使用HPA、TIMER和GEPIA数据库,分析HNRNP A1在结直肠癌组织中的表达水平,并检验HNRNP A1与Ki-67/VEGFA在结直肠癌中表达的相关性。使用Kaplan-Meier Plotter数据库评估HNRNP A1 mRNA水平与结直肠癌患者生存率之间的联系。通过基因富集途径分析,预测HNRNP A1在结直肠癌中的潜在生物学作用。通过免疫组织化学(IHC)和Western blotting技术检测HNRNP A1在结直肠癌及其癌旁组织中的蛋白表达。利用TIMER数据库网站对HNRNP A1在免疫浸润细胞中的表达进行预测。使用慢病毒敲低RKO/Caco2细胞中HNRNP A1的表达;通过CCK-8实验检测细胞增殖,使用克隆形成实验检测HNRNP A1对细胞增殖能力的影响;利用细胞划痕实验和Transwell迁移实验评估两组细胞(RKO/Caco2-nc、RKO/Caco2-sh)的迁移能力。最后验证HNRNP A1小分子抑制剂(VPC-80051)对肿瘤细胞增殖的影响。 结果 在结直肠癌(CRC)肿瘤组织中HNRNP A1的表达显著上调并与患者的不良预后显著相关(P<0.01)。TIMER数据库的分析结果指出,HNRNP A1与肿瘤微环境中的免疫细胞之间存在一定的相关性。根据GEPIA数据库的分析,CRC组织中HNRNP A1、MKI67和VEGFA的表达均较高(P<0.05),且HNRNP A1与这两者之间存在正相关关系。通过Kaplan-Meier Plotter进行的生存分析表明,在CRC中,HNRNP A1的高表达预示着较差的总生存期(P=0.0081)和无进展生存期(P=0.012)。基因富集通路分析的数据显示,HNRNP A1可能参与到多个与CRC进展相关的生物途径中。HNRNP A1影响RKO/Caco2细胞的增殖和迁移能力,对照组(RKO/Caco2-nc)的增殖能力、克隆形成能力和迁移能力均优于实验组(RKO/Caco2-sh),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);HNRNP A1小分子抑制剂(VPC-80051)可以有效抑制结直肠癌增殖活性,并具有时间和浓度依赖性;IHC显示HNRNP A1在结直肠癌中高表达,且与肿瘤分期有密切关系(P<0.0001)。 结论 HNRNP A1基因在CRC组织中表达较高,并可调节细胞的增殖和迁移能力,与不良预后密切相关,同时HNRNP A1小分子抑制剂(VPC-80051)也可以抑制结直肠癌细胞的增殖,因而可作为CRC治疗过程中新的潜在治疗靶点。
纪凯, 于冠宇, 周乐其, 张天帅, 凌潜龙, 满文江, 朱冰, 张卫. HNRNPA1基因在结直肠癌组织中高表达及其潜在的诊断和治疗价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1685-1695.
Kai JI, Guanyu YU, Leqi ZHOU, Tianshuai ZHANG, Qianlong LING, Wenjiang MAN, Bing ZHU, Wei ZHANG. HNRNPA1 gene is highly expressed in colorectal cancer: its prognostic implications and potential as a therapeutic target[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1685-1695.
| Gene | Primerse quence (5'-3') | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | |
| HNRNP A1 | TCAGAGTCTCCTAAAGAGCCC | ACCTTGTGTGGCCTTGCAT |
| GAPDH | ACAACTTTGGTATCGTGGAAGG | GCCATCACGCCACAGTTTC |
表1 RT-PCR对差异表达mRNA的引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequence for qRT-PCR of HNRNP A1
| Gene | Primerse quence (5'-3') | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | |
| HNRNP A1 | TCAGAGTCTCCTAAAGAGCCC | ACCTTGTGTGGCCTTGCAT |
| GAPDH | ACAACTTTGGTATCGTGGAAGG | GCCATCACGCCACAGTTTC |
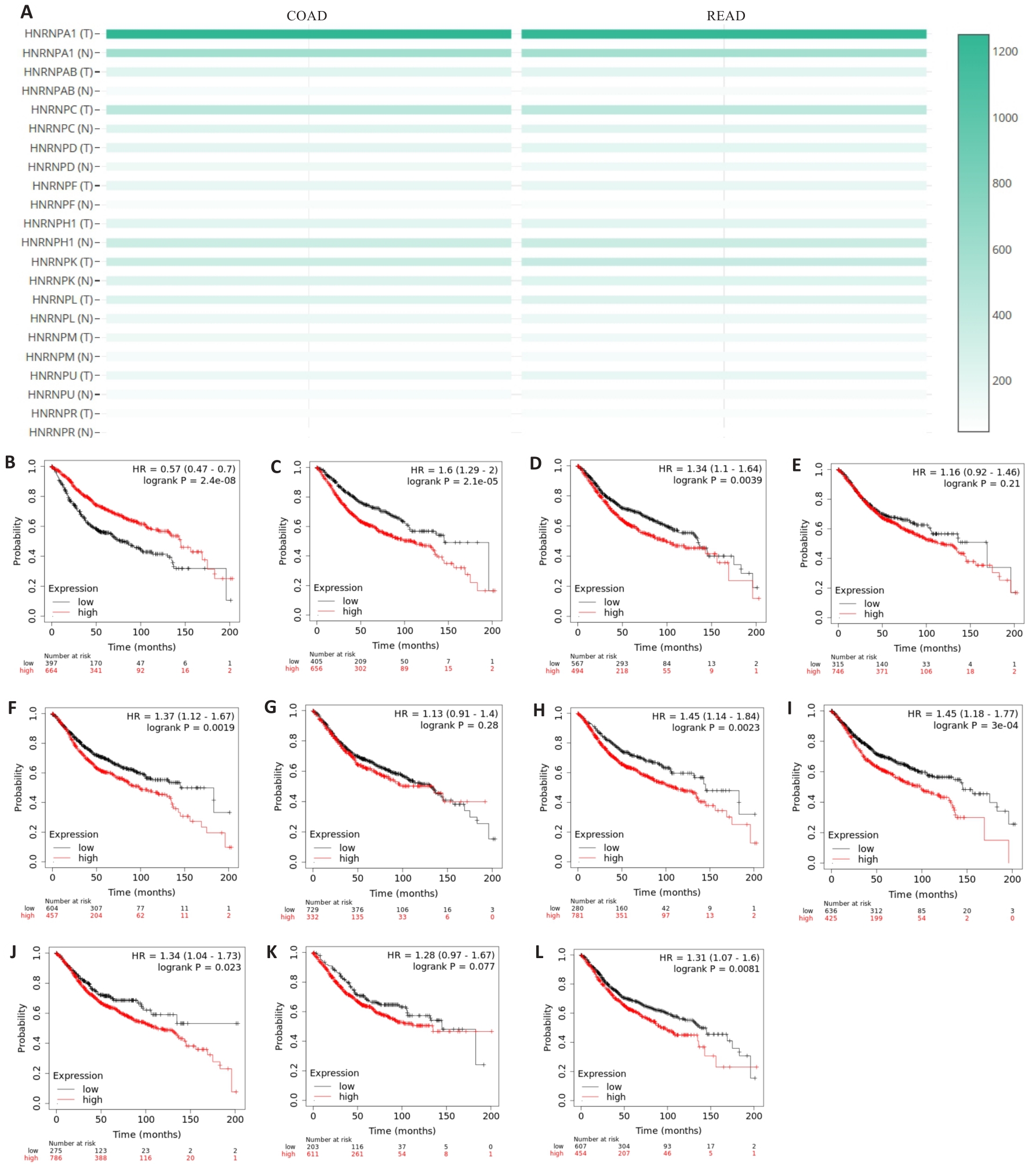
图1 HNRNP家族成员在结直肠癌中的表达及预后
Fig.1 Expression of HNRNP family members in colorectal cancer and their association with the patients' prognosis. A: Expression of HNRNP family members in colorectal cancer. B-L: Prognostic profile of HNRNP family members in colorectal cancer.

图2 HNRNP A1在细胞模型及人体细胞中的定位
Fig.2 Localization of HNRNPA1 in the cell model and human cells. A: Expression of HNRNP A1 in the cell model. B: Expression of HNRNPA1 in human cells detected using immunofluorescence assay.

图3 HNRNP A1在各种组织和免疫细胞中的表达
Fig.3 Expression of HNRNP A1 in different tissues and immune cells. A: Expression of HNRNP A1 in different tissues. B: Expression of HNRNP A1 in immune cells. C: Expression of HNRNP A1 in the core cells.

图4 HNRNP A1在结直肠癌和癌旁组织中的表达情况
Fig. 4 Expression of HNRNP A1 in colorectal cancer and adjacent tissues. A: Expression of HNRNP A1 in different tumors in TIMER 2.0 database. B: Expression of HNRNP A1 in colorectal cancer in GEPIA database. C: Immunohistochemical analysis of SPHK1 expression in colorectal cancer tissue and adjacent tissue.

图5 HNRNP A1与MKI67/VEGFA相关性与患者预后的关系
Fig.5 Correlation of HNRNP A1 with MKI67 and VEGFA expressions and prognosis of colorectal cancer patients. A: Correlation between HNRNP A1 and MKI67 expression. B: Correlation between HNRNP A1 and VEGFA expression. C: Expression of MKI67 in CRC tissue. D: Expression of VEGFA in colorectal cancer tissue. E: Expression of HNRNPA1 in COAD based on individual cancer stages. F: Expression of HNRNPA1 in READ based on individual cancer stages. G: Overall survival of colorectal cancer patients. H: Post progression survival in colorectal cancer patients.

图6 结直肠癌中HNRNP A1与免疫浸润水平的相关性
Fig.6 Correlation between HNRNP A1 and immune infiltration level in colorectal cancer. A: Expression of HNRNP A1 correlates with immune cell infiltration in colon cancer microenvironment. B: Expression of HNRNP A1 correlates with immune cell infiltration in rectal cancer microenvironment.

图7 HNRNP A1的通路富集结果
Fig.7 Enrichment analysis of HNRNP A1 pathways. A: GOterm analysis of BP. B: GOterm analysis of CC. C: GOterm analysis of MF. D: KEGGterm analysis result.

图8 HNRNP A1对CRC细胞的增殖、迁移的影响
Fig.8 HNRNP A1 promotes proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells. A, B, G, H: Relative expression level of HNRNPA1 in RKO cells. C, I: CCK-8 assay for assessing cell proliferation. D, J: Clone formation assay. E, K: Wound-healing assay for assessing cell migration (Scale bar: 200 μm). F, L: Transwell assay for assessing cell migration (Scale bar: 50 μm). M, N: Effect of VPC-80051 at different concentrations on cell proliferation. O: Viability of the cells treated with 10 μmol/L VPC-80051 at different time points. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001
| Parameters | Clinical case characteristics | |
|---|---|---|
| Case | Rate (%) | |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 29 | 59.2 |
| Female | 20 | 40.8 |
| Age (year) | ||
| ≥60 | 32 | 65.3 |
| <60 | 17 | 34.7 |
| Pathologic stage | ||
| Tis | 2 | 4.08 |
| Ⅰ+Ⅱ | 25 | 51.02 |
| Ⅲ+Ⅳ | 22 | 44.9 |
| T stage | ||
| T1+T2 | 14 | 29.79 |
| T3+T4 | 33 | 70.21 |
| N stage | ||
| N0 | 25 | 53.19 |
| N1+N2 | 22 | 46.81 |
表 2 HNRNP A1表达与临床病例特点的关系
Tab.2 Relationship between HNRNP A1 expression and clinical characteristics of the patients
| Parameters | Clinical case characteristics | |
|---|---|---|
| Case | Rate (%) | |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 29 | 59.2 |
| Female | 20 | 40.8 |
| Age (year) | ||
| ≥60 | 32 | 65.3 |
| <60 | 17 | 34.7 |
| Pathologic stage | ||
| Tis | 2 | 4.08 |
| Ⅰ+Ⅱ | 25 | 51.02 |
| Ⅲ+Ⅳ | 22 | 44.9 |
| T stage | ||
| T1+T2 | 14 | 29.79 |
| T3+T4 | 33 | 70.21 |
| N stage | ||
| N0 | 25 | 53.19 |
| N1+N2 | 22 | 46.81 |
| 1 | Xi Y, Xu PF. Global colorectal cancer burden in 2020 and projections to 2040[J]. Transl Oncol, 2021, 14(10): 101174. |
| 2 | Ahmad R, Singh JK, Wunnava A, et al. Emerging trends in colorectal cancer: Dysregulated signaling pathways (Review)[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2021, 47(3): 14. |
| 3 | Klimeck L, Heisser T, Hoffmeister M, et al. Colorectal cancer: a health and economic problem[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol, 2023, 66: 101839. |
| 4 | Li QY, Zhao HX, Dong WW, et al. RAB27A promotes the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 19359. |
| 5 | Siculella L, Giannotti L, Di Chiara Stanca B, et al. A comprehensive understanding of hnRNP A1 role in cancer: new perspectives on binding with noncoding RNA[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2023, 30(3): 394-403. |
| 6 | 杨宏广, 童春梅, 邓惠敏. hnRNP A1的功能研究进展[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2021, 48(10): 1146-56. |
| 7 | Liu X, Ishizuka T, Bao HL, et al. Structure-dependent binding of hnRNPA1 to telomere RNA[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2017, 139(22): 7533-9. |
| 8 | Li YX, Yang Y, Ma Q, et al. HNRNPK/CLCN3 axis facilitates the progression of LUAD through CAF-tumor interaction[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2022, 18(16): 6084-101. |
| 9 | Li MY, Yang XJ, Zhang GX, et al. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K promotes the progression of lung cancer by inhibiting the p53-dependent signaling pathway[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2022, 13(9): 1311-21. |
| 10 | Jiang RQ, Su GF, Chen X, et al. Esculetin inhibits endometrial cancer proliferation and promotes apoptosis via hnRNPA1 to down-regulate BCLXL and XIAP[J]. Cancer Lett, 2021, 521: 308-21. |
| 11 | Xu HR, Li P, Wang XY, et al. Emerging roles of hnRNP A2B1 in cancer and inflammation[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2022, 221: 1077-92. |
| 12 | Möller K, Wecker AL, Höflmayer D, et al. Upregulation of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein hnRNPA1 is an independent predictor of early biochemical recurrence in TMPRSS2: ERG fusion-negative prostate cancers[J]. Virchows Arch, 2020, 477(5): 625-36. |
| 13 | Ma YL, Peng JY, Zhang P, et al. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 is identified as a potential biomarker for colorectal cancer based on differential proteomics technology[J]. J Proteome Res, 2009, 8(10): 4525-35. |
| 14 | Ghosh M, Singh M. RGG-box in hnRNPA1 specifically recognizes the telomere G-quadruplex DNA and enhances the G-quadruplex unfolding ability of UP1 domain[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018, 46(19): 10246-61. |
| 15 | Biller LH, Schrag D. Diagnosis and treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: a review[J]. JAMA, 2021, 325(7): 669-85. |
| 16 | Liu Y, Shi SL. The roles of hnRNP A2/B1 in RNA biology and disease[J]. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA, 2021, 12(2): e1612. |
| 17 | Xie W, Zhu HC, Zhao M, et al. Crucial roles of different RNA-binding hnRNP proteins in Stem Cells[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2021, 17(3): 807-17. |
| 18 | Dutta K, Kravtsov V, Oleynikova K, et al. Analyzing the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms on hnRNPA2/B1 protein stability and function: insights for anticancer therapeutic design[J]. ACS Omega, 2024, 9(5): 5485-95. |
| 19 | Low YH, Asi Y, Foti SC, et al. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins: implications in neurological diseases[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2021, 58(2): 631-46. |
| 20 | Kim HJ, Kim NC, Wang YD, et al. Mutations in prion-like domains in hnRNPA2B1 and hnRNPA1 cause multisystem proteinopathy and ALS[J]. Nature, 2013, 495(7442): 467-73. |
| 21 | Xia AL, Yuan WW, Wang Q, et al. The cancer-testis lncRNA lnc-CTHCC promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis by binding hnRNP K and activating YAP1 transcription[J]. Nat Cancer, 2022, 3(2): 203-18. |
| 22 | Gao R, Yu Y, Inoue A, et al. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP-K) promotes tumor metastasis by induction of genes involved in extracellular matrix, cell movement, and angiogenesis[J]. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(21): 15046-56. |
| 23 | Zhu HE, Li T, Shi SN, et al. ESCO2 promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression by regulating hnRNPA1 acetylation[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2021, 40(1): 64. |
| 24 | Zhou JM, Jiang H, Yuan T, et al. High hnRNP AB expression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer[J]. Oncol Lett, 2019, 18(6): 6459-68. |
| 25 | Li H, Liu JW, Shen SX, et al. Pan-cancer analysis of alternative splicing regulator heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) family and their prognostic potential[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2020, 24(19): 11111-9. |
| 26 | Shi X, Ran L, Liu Y, et al. Knockdown of hnRNP A2/B1 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and cell cycle triggering apoptosis in cervical cancer via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Oncol Rep, 2018, 39(3): 939-50. |
| 27 | Zhang PS, Ji DH, Hu XH, et al. Oncogenic heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D-like promotes the growth of human colon cancer SW620 cells via its regulation of cell-cycle[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin, 2018, 50(9): 880-7. |
| 28 | Yao P, Wu JB, Lindner D, et al. Interplay between miR-574-3p and hnRNP L regulates VEGFA mRNA translation and tumorigenesis[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45(13): 7950-64. |
| 29 | Bilotta MT, Antignani A, Fitzgerald DJ. Managing the TME to improve the efficacy of cancer therapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 954992. |
| 30 | Khan S, Kwak YT, Peng L, et al. NLRP12 downregulates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway via interaction with STK38 to suppress colorectal cancer[J]. J Clin Invest, 2023, 133(19): e166295. |
| 31 | Bradley RK, Anczuków O. RNA splicing dysregulation and the hallmarks of cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2023, 23(3): 135-55. |
| 32 | Wan LD, Yu WY, Shen EH, et al. SRSF6-regulated alternative splicing that promotes tumour progression offers a therapy target for colorectal cancer[J]. Gut, 2019, 68(1): 118-29. |
| 33 | Wen ZL, Lian LY, Ding H, et al. LncRNA ANCR promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through upregulating HNRNPA1 expression[J]. RNA Biol, 2020, 17(3): 381-94. |
| 34 | Carabet LA, Leblanc E, Lallous N, et al. Computer-aided discovery of small molecules targeting the RNA splicing activity of hnRNP A1 in castration-resistant prostate cancer[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(4): 763. |
| [1] | 陈孝华, 鲁辉, 王子良, 王炼, 夏勇生, 耿志军, 张小凤, 宋雪, 王月月, 李静, 胡建国, 左芦根. ABI2在胃癌进展和预后中的作用及其调控机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1653-1661. |
| [2] | 叶梦楠, 武鸿美, 梅琰, 张庆玲. CREM在胃癌中高表达并与患者的不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1776-1782. |
| [3] | 张银亮, 骆泽谭, 赵睿, 赵娜, 徐志东, 奥迪, 丛古一, 刘新宇, 郑海伦. 血根碱通过调控STUB1/GPX4诱导直肠癌细胞发生铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1537-1544. |
| [4] | 陈莉莉, 吴天宇, 张铭, 丁子夏, 张妍, 杨依清, 郑佳倩, 张小楠. 类风湿关节炎的潜在生物标志物及其免疫调控机制:基于GEO数据库[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1098-1108. |
| [5] | 刘鹏程, 娄丽娟, 刘霞, 王建, 姜颖. M2巨噬细胞特征基因风险评分能准确预测HBV相关肝细胞癌患者的预后[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 827-840. |
| [6] | 周伟, 聂军, 胡佳, 蒋艺枝, 张大发. 内质网应激相关基因在主动脉夹层疾病中的差异性表达及与免疫浸润的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 859-866. |
| [7] | 裴蓓, 张艺, 魏思源, 梅语, 宋标, 董港, 温子昂, 李学军. 基于转录组学测序及生物信息学方法鉴定肠上皮化生的潜在致病基因[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 941-949. |
| [8] | 杨晶晶, 殷丽霞, 段婷, 牛民主, 何震东, 陈心蕊, 张小凤, 李静, 耿志军, 左芦根. 胃癌组织中高表达ATP5A1与患者术后的不良预后和肿瘤细胞的糖代谢有关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 974-980. |
| [9] | 王沁智, 宋冰, 郝诗睿, 肖志远, 金连辉, 郑通, 柴芳. 基于生物信息学分析CCND2在甲状腺乳头状癌中的表达及其对免疫浸润的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 981-988. |
| [10] | 高志强, 林 洁, 洪 鹏, 胡再宏, 董军君, 石秦林, 田小毛, 刘 丰, 魏光辉. 基于高通量 RNA 测序分析 Wilms 瘤中关键基因对预后及免疫应答的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 727-738. |
| [11] | 梁一豪, 赖颖君, 袁燕文, 袁 炜, 张锡波, 张拔山, 卢志锋. 基于GEO数据库筛选胃癌差异表达基因及其功能和通路富集分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 605-616. |
| [12] | 沈梦迪, 赵 娜, 邓晓晶, 邓 敏. COX6B2在胃癌组织中高表达并影响患者的远期预后:基于抑制p53信号调控胃癌细胞的增殖及细胞周期[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 289-297. |
| [13] | 张 诺, 张 震, 张雨路, 宋 雪, 张小凤, 李 静, 左芦根, 胡建国. PCID2在胃癌组织中高表达并通过调控细胞周期进程和增殖影响患者预后[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 324-332. |
| [14] | 张文静, 张 诺, 杨 子, 张小凤, 孙奥飞, 王 炼, 宋 雪, 耿志军, 李 静, 胡建国. BZW1 高表达促进胃癌细胞的侵袭和转移:基于调控Wnt//β-catenin通路和促进上皮间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 354-362. |
| [15] | 成佳聪, 李智慧, 刘 鳐, 李 成, 黄 鑫, 田颖鑫, 沈富兵. 早幼粒细胞白血病蛋白与TAK1结合蛋白相互作用的生物信息学分析与验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 179-186. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||