南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 1508-1517.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.08.09
• • 上一篇
陈星梅1( ), 刘琴文2,3, 李镱2,3, 钟晓宇1, 樊奇灵2,3, 马柯1, 罗柳婷1, 官道刚2,3, 朱志博1(
), 刘琴文2,3, 李镱2,3, 钟晓宇1, 樊奇灵2,3, 马柯1, 罗柳婷1, 官道刚2,3, 朱志博1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-21
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-09-06
通讯作者:
朱志博
E-mail:1842578607@qq.com;zhuzb676@smu.edu.cn
作者简介:陈星梅,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 1842578607@qq.com
基金资助:
Xingmei CHEN1( ), Qinwen LIU2,3, Yi LI2,3, Xiaoyu ZHONG1, Qiling FAN2,3, Ke MA1, Liuting LUO1, Daogang GUAN2,3, Zhibo ZHU1(
), Qinwen LIU2,3, Yi LI2,3, Xiaoyu ZHONG1, Qiling FAN2,3, Ke MA1, Liuting LUO1, Daogang GUAN2,3, Zhibo ZHU1( )
)
Received:2024-03-21
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-09-06
Contact:
Zhibo ZHU
E-mail:1842578607@qq.com;zhuzb676@smu.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 基于网络药理学和体外实验分析验证茵陈蒿汤(YCHD)治疗肝纤维化(HF)的核心功能成分群(CFCG)以及潜在通路。 方法 在DisGeNET、Genecards、CMGRN和PTHGRN提取了HF的PPI数据,使用Cytoscape 3.9.1构建权重网络。从TCMSP中收集茵陈蒿汤所有化学成分,用PreADMET Web服务器和SwissTargetPrediction选择茵陈蒿汤潜在活性成分和靶点。构建融合模型获取功能效应空间并评估有效蛋白,得到CFCG,再进一步对所有目标进行GO和KEGG通路富集分析。细胞实验:体外培养人肝星状细胞(LX-2),分别设置空白组(不加TGF-β1刺激)、对照组NC(20 ng/mL TGF-β1刺激)和化合物组(0、50、100、200 μmol/L),CCK-8实验检测药物敏感性,qPCR实验检测化合物对LX-2中Ⅰ型胶原Α1(COL1A1)的影响,Western blotting实验分析评估化合物在TGF-β1刺激下对LX-2中潜在通路的影响,验证潜在治疗机制。 结果 分析得到1005个致病基因,茵陈蒿汤潜在活性成分和靶点分别有226个和1529个,核心功能成分群有52个。根据模型计算结果,选取得分最高的乙酸苄酯、香草酸、苯甲酸甲酯、虎杖苷、月桂酸、阿魏酸进行CCK-8验证发现在200 μmol/L内无细胞毒性;在qPCR实验中,与TGF-β1组相比苯甲酸甲酯、虎杖苷、月桂酸和阿魏酸能够抑制TGF-β1诱导的LX-2活化。GO和KEGG分析及Western blotting验证发现,这4种成分在200 μmol/L浓度时对PI3K、p-PI3K、AKT、p-AKT、ERK、p-ERK、P38 MAPK、p-P38 MAPK有不同程度的抑制。 结论 茵陈蒿汤抗肝纤维化可能是其中的乙酸苄酯、香草酸、苯甲酸甲酯、虎杖苷、月桂酸、阿魏酸等成分通过抑制PI3K-AKT和MAPK通路实现的。
陈星梅, 刘琴文, 李镱, 钟晓宇, 樊奇灵, 马柯, 罗柳婷, 官道刚, 朱志博. 茵陈蒿汤治疗肝纤维化的核心功能成分群以及潜在通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1508-1517.
Xingmei CHEN, Qinwen LIU, Yi LI, Xiaoyu ZHONG, Qiling FAN, Ke MA, Liuting LUO, Daogang GUAN, Zhibo ZHU. Analysis of core functional components in Yinchenhao Decoction and their pathways for treating liver fibrosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1508-1517.
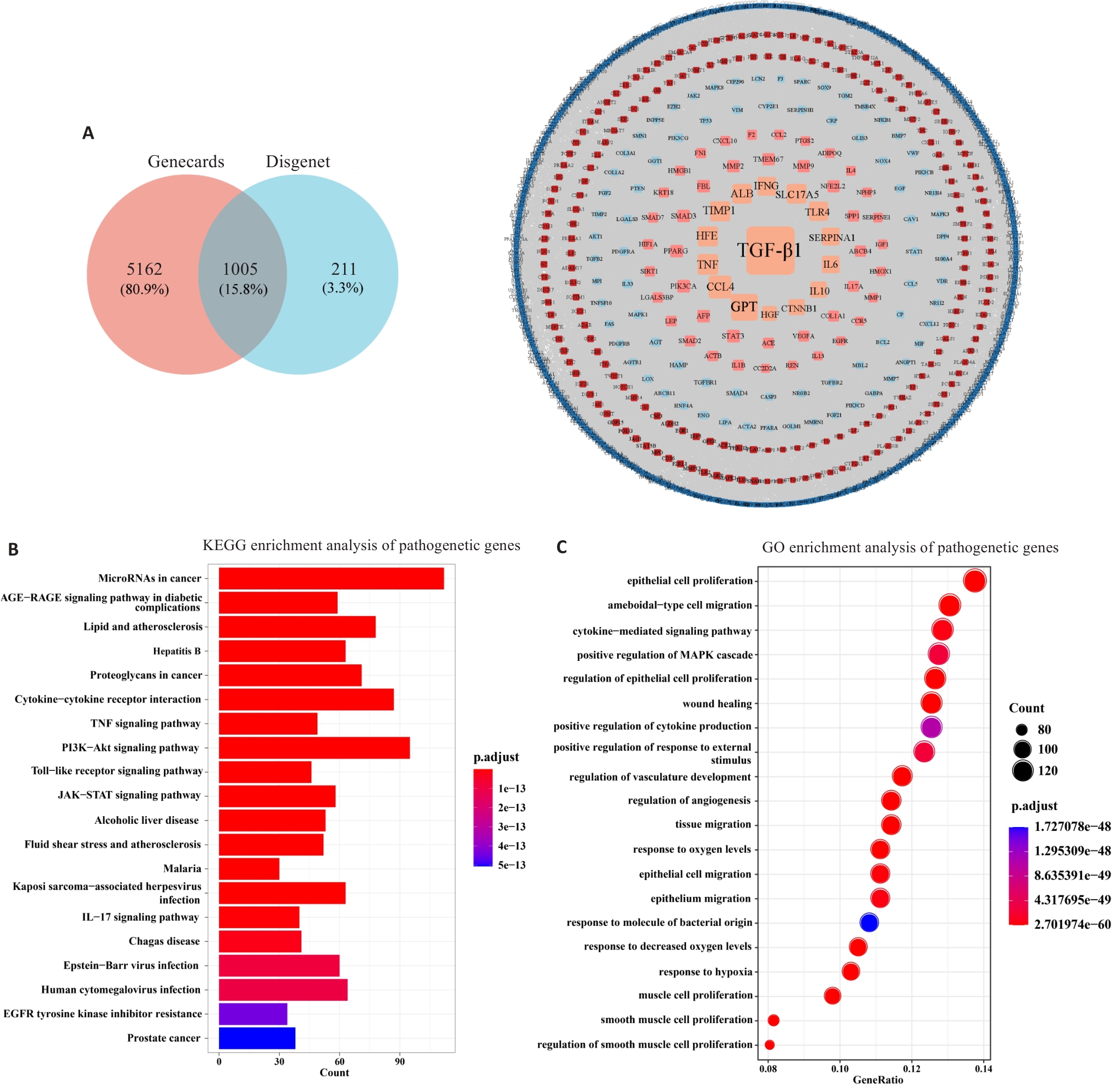
图1 致病基因的权重网络和功能分析
Fig.1 Weighted network and functional analysis of the pathogenic genes. A: Gene selection and PPI network for hepatic fibrosis (HF) based on Genescards and Disease databases. B: KEGG enrichment analysis of the pathogenic genes. C: GO enrichment analysis of the pathogenic genes.
| Formula/Herbs | Component | Content (mg/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rheum palmatumL. | Catechin | 0.015-11.66 | |
| Chrysophanol | 0.17-4.36 | ||
| (-)-epicatechin | 0.98-6.33 | ||
| Gallic acid | 0.041-4.21 | ||
| Isolindleyin | 0.056-4.37 | ||
| Lindleyin | 0.40-4.02 | ||
| Phenylbutanone-glucoside | 0.36 | ||
| Physcion | 0.09-0.15 | ||
| 4,3,5'-trihydroxystilbene-4-(6"-galloyl-glucoside) | 0.14-0.20 | ||
| Emodin | 0.058-4.15 | ||
| Rhein | 0.08-4.97 | ||
| Physcione | 0.056-1.66 | ||
| Sennoside B | 0.47-1.59 | ||
| 3,4,3',5'-tetrahydroxystilbene-3-glucoside | 0.05 | ||
| (-)-Epicatechin gallate | 0.37-0.045 | ||
| (+)-catechin | 0.07-0.79 | ||
| 1,6-digalloyl-2-cinnamoyi-glucose | 0.07-0.30 | ||
| 1-galloyl-2-cinnamoyl-glucose | 0.63-1.48 | ||
| 2-cinnamoyl-glucose | 0.13-0.42 | ||
| 4-4-HydroxyphenylButan-2-One | 0.48 | ||
| Aloe-emodin-8-glucoside | 0.31-0.46 | ||
| Chrysophanol-8-glucoside | 0.52-1.08 | ||
| Emodin-8-glucoside | 0.10-1.16 | ||
| Epicatechin | 0.28-0.70 | ||
| Musizin-glucoside | 0.06-0.82 | ||
| Physcion-8-glucoside | 0.20-0.78 | ||
| Sennosides | 0.40-2.20 | ||
| Torachrysone-8-glucoside | 0.12-0.25 | ||
| Trans-cinnamic acid | 1.05 | ||
| Artemisia capillaris Thunb. | Caffeic acid | 0.31 | |
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.49-25.09 | ||
| P-hydroxyacetophenone | 0.03 | ||
| Oleanolic acid | 4.03 | ||
| Rutin | 0.045 | ||
| Isoquercitrin | 0.0094 | ||
| 4,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid | 0.92 | ||
| Hyperin | 0.0129 | ||
| Isorhamnetin-3-o-glucoside | 0.0039 | ||
| 3, 5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid | 4.21 | ||
| 4,5-O-dicaffeoyl quinic acid | 4.55 | ||
| Hyperoside | 0.52-7.81 | ||
| Yinchenhao Decoction | Catechin | 0.09-1.29 | |
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.43-18.12 | ||
| Gallic acid | 0.58 | ||
| Genipin | 0.0053 | ||
| Geniposide | 0.033-23.07 | ||
| p-Hydroxyacetophenone | 0.69 | ||
| Physcion | 0.004-1.20 | ||
| Quercetin | 0.041 | ||
| Scoparone | 0.15 | ||
| Scopoletin | 0.0087 | ||
| Emodin | 0.0083-1.39 | ||
| Crocin I | 1.38 | ||
| Crocin II | 0.15 | ||
| Rhein | 0.15-13.04 | ||
| Esculetin | 0.024 | ||
| Aloe-emodin | 0.041-6.26 | ||
| Aloe-emodin-8-O-β-D-glucoside | 0.20 | ||
| Chrysophanol-1-O-β-D-glucoside | 0.17 | ||
| deacetyl asperulosidic acid methylester | 0.67 | ||
| Hyperoside | 0.065 | ||
| Gardenia jasminoides Ellis | Chlorogenic acid | 0.12-0.27 | |
| Geniposide | 2.13-74.65 | ||
| Geniposidic acid | 1.04-1.99 | ||
| Neochlorogenic acid | 0.43 | ||
| Picrocrocin | 1.30 | ||
| Crocin I | 1.27-19.16 | ||
| Crocin II | 0.96-1.18 | ||
| 4-Dicaffeoylquinic Acid | 2.14 | ||
| Crocin III | 0.44 | ||
| Deacetyl asperulosidic acid methylester | 0.44-3.36 | ||
| Genipin 1-gentiobioside | 0.56-17.94 | ||
| Rutinum | 1.03 |
表1 实验验证的方剂关键成分的收集
Tab.1 Collection of experimentally validated key components of the formula by HPLC
| Formula/Herbs | Component | Content (mg/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rheum palmatumL. | Catechin | 0.015-11.66 | |
| Chrysophanol | 0.17-4.36 | ||
| (-)-epicatechin | 0.98-6.33 | ||
| Gallic acid | 0.041-4.21 | ||
| Isolindleyin | 0.056-4.37 | ||
| Lindleyin | 0.40-4.02 | ||
| Phenylbutanone-glucoside | 0.36 | ||
| Physcion | 0.09-0.15 | ||
| 4,3,5'-trihydroxystilbene-4-(6"-galloyl-glucoside) | 0.14-0.20 | ||
| Emodin | 0.058-4.15 | ||
| Rhein | 0.08-4.97 | ||
| Physcione | 0.056-1.66 | ||
| Sennoside B | 0.47-1.59 | ||
| 3,4,3',5'-tetrahydroxystilbene-3-glucoside | 0.05 | ||
| (-)-Epicatechin gallate | 0.37-0.045 | ||
| (+)-catechin | 0.07-0.79 | ||
| 1,6-digalloyl-2-cinnamoyi-glucose | 0.07-0.30 | ||
| 1-galloyl-2-cinnamoyl-glucose | 0.63-1.48 | ||
| 2-cinnamoyl-glucose | 0.13-0.42 | ||
| 4-4-HydroxyphenylButan-2-One | 0.48 | ||
| Aloe-emodin-8-glucoside | 0.31-0.46 | ||
| Chrysophanol-8-glucoside | 0.52-1.08 | ||
| Emodin-8-glucoside | 0.10-1.16 | ||
| Epicatechin | 0.28-0.70 | ||
| Musizin-glucoside | 0.06-0.82 | ||
| Physcion-8-glucoside | 0.20-0.78 | ||
| Sennosides | 0.40-2.20 | ||
| Torachrysone-8-glucoside | 0.12-0.25 | ||
| Trans-cinnamic acid | 1.05 | ||
| Artemisia capillaris Thunb. | Caffeic acid | 0.31 | |
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.49-25.09 | ||
| P-hydroxyacetophenone | 0.03 | ||
| Oleanolic acid | 4.03 | ||
| Rutin | 0.045 | ||
| Isoquercitrin | 0.0094 | ||
| 4,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid | 0.92 | ||
| Hyperin | 0.0129 | ||
| Isorhamnetin-3-o-glucoside | 0.0039 | ||
| 3, 5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid | 4.21 | ||
| 4,5-O-dicaffeoyl quinic acid | 4.55 | ||
| Hyperoside | 0.52-7.81 | ||
| Yinchenhao Decoction | Catechin | 0.09-1.29 | |
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.43-18.12 | ||
| Gallic acid | 0.58 | ||
| Genipin | 0.0053 | ||
| Geniposide | 0.033-23.07 | ||
| p-Hydroxyacetophenone | 0.69 | ||
| Physcion | 0.004-1.20 | ||
| Quercetin | 0.041 | ||
| Scoparone | 0.15 | ||
| Scopoletin | 0.0087 | ||
| Emodin | 0.0083-1.39 | ||
| Crocin I | 1.38 | ||
| Crocin II | 0.15 | ||
| Rhein | 0.15-13.04 | ||
| Esculetin | 0.024 | ||
| Aloe-emodin | 0.041-6.26 | ||
| Aloe-emodin-8-O-β-D-glucoside | 0.20 | ||
| Chrysophanol-1-O-β-D-glucoside | 0.17 | ||
| deacetyl asperulosidic acid methylester | 0.67 | ||
| Hyperoside | 0.065 | ||
| Gardenia jasminoides Ellis | Chlorogenic acid | 0.12-0.27 | |
| Geniposide | 2.13-74.65 | ||
| Geniposidic acid | 1.04-1.99 | ||
| Neochlorogenic acid | 0.43 | ||
| Picrocrocin | 1.30 | ||
| Crocin I | 1.27-19.16 | ||
| Crocin II | 0.96-1.18 | ||
| 4-Dicaffeoylquinic Acid | 2.14 | ||
| Crocin III | 0.44 | ||
| Deacetyl asperulosidic acid methylester | 0.44-3.36 | ||
| Genipin 1-gentiobioside | 0.56-17.94 | ||
| Rutinum | 1.03 |
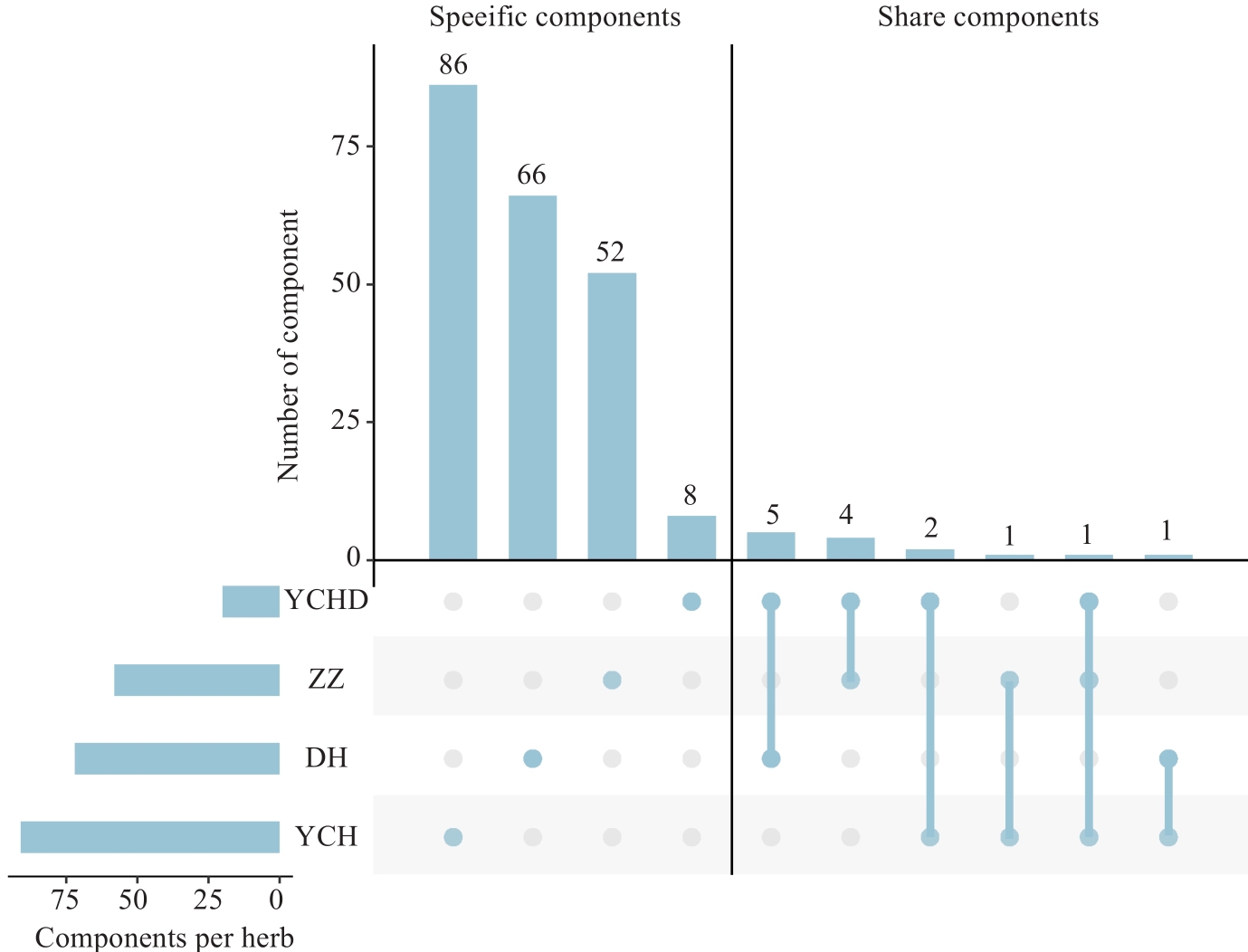
图2 茵陈蒿汤中3种药用植物和方剂中化学成分的交集情况
Fig.2 Distribution of sepecific and common chemical components in 3 medicinal plants and prescriptions in YCHD (ZZ, DH and YCH refer to Zhizi, Dahuang and Yinchenhao).
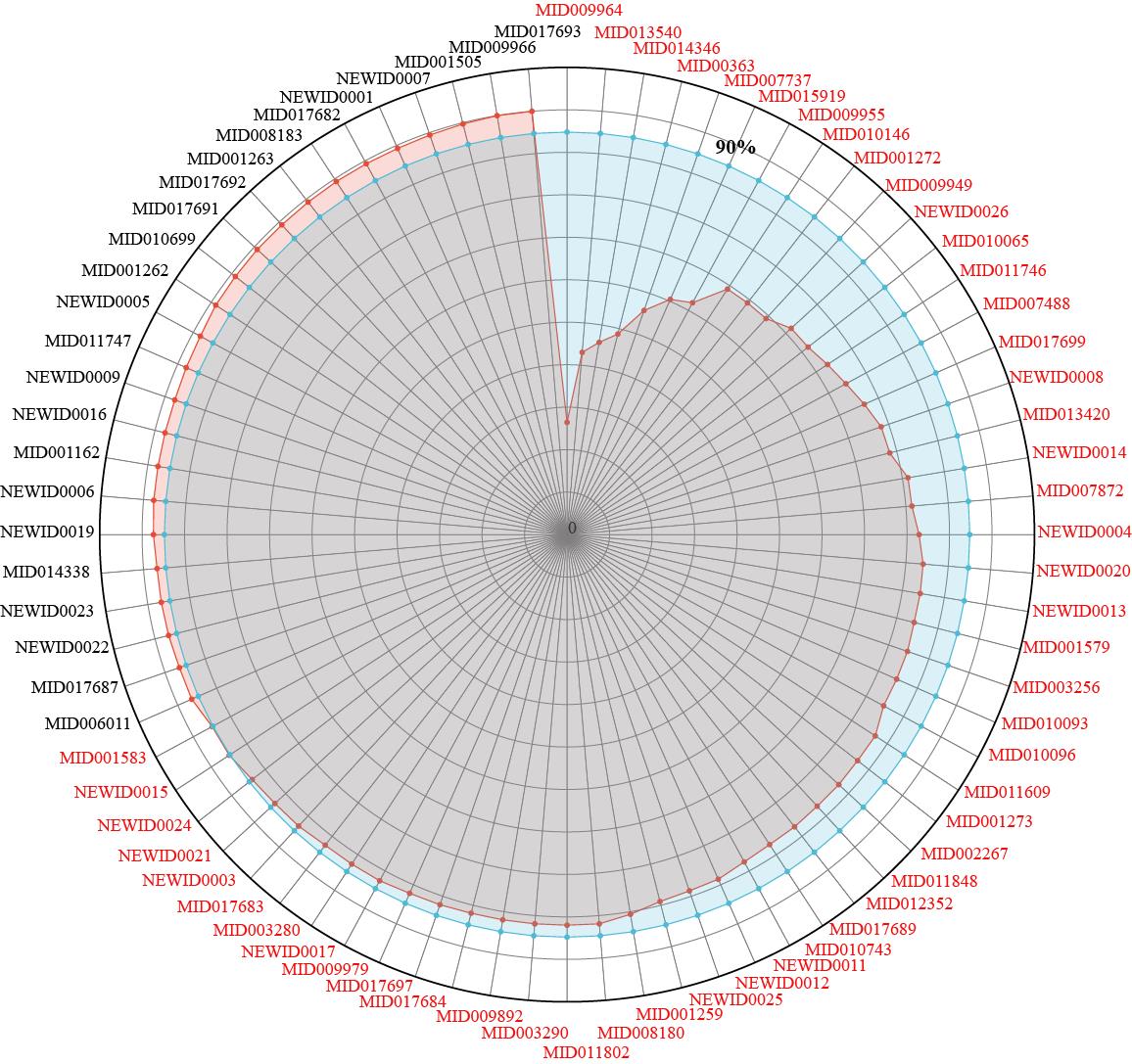
图3 茵陈蒿汤中核心功能成分群及其贡献率
Fig.3 Core functional component groups (CFCG) in YCHD and its distribution rate. MID and NEWID represent the ID of the active ingredients; the red line represents the coverage of active ingredients from 0 to 100%; the blue line represents 90% coverage; the contribution rate of 52 components of labeled red was less than 90%, which was defined as the CFCG of YCHD.
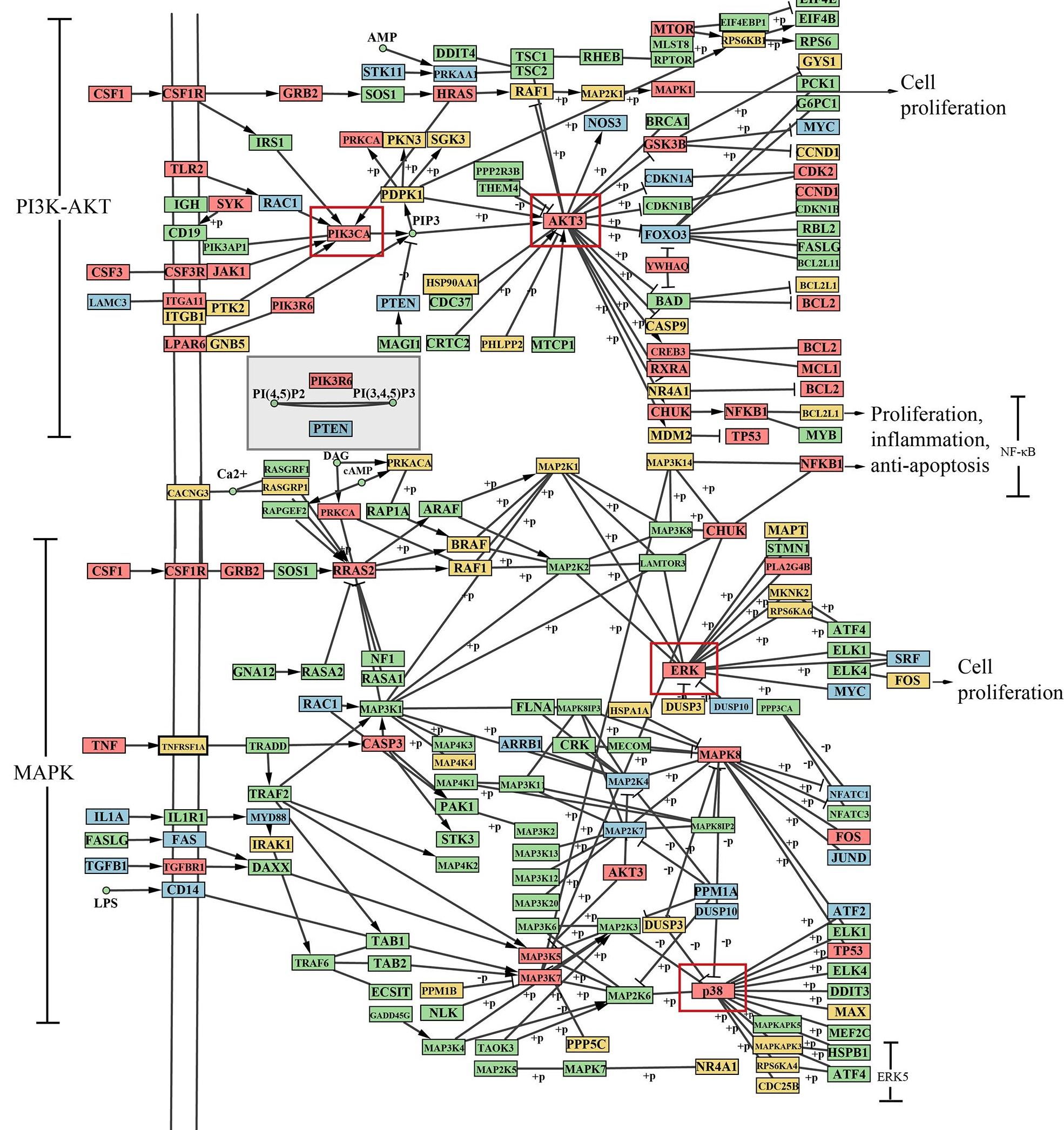
图5 核心功能成分群靶点在综合途径中的分布
Fig.5 Distribution of CFCG targets and pathogenic genes in the integrated pathway. The blue, orange and pink frames represent pathogenic genes, CFCG targets and their common genes, respectively.
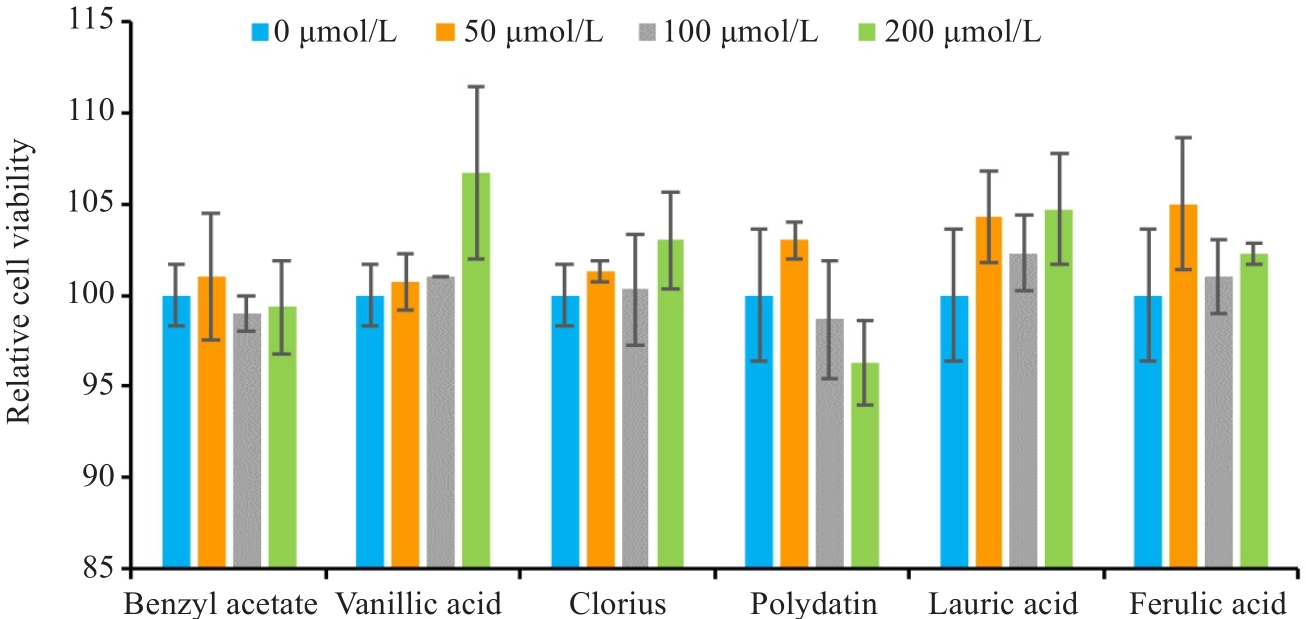
图6 CCK-8实验结果
Fig.6 CCK-8 assay of LX-2 cells treated with benzyl acetate, vanillic acid, clorius, polydatin, lauric acid or ferulic acid (drug concentration: 0-200 μmol/L).
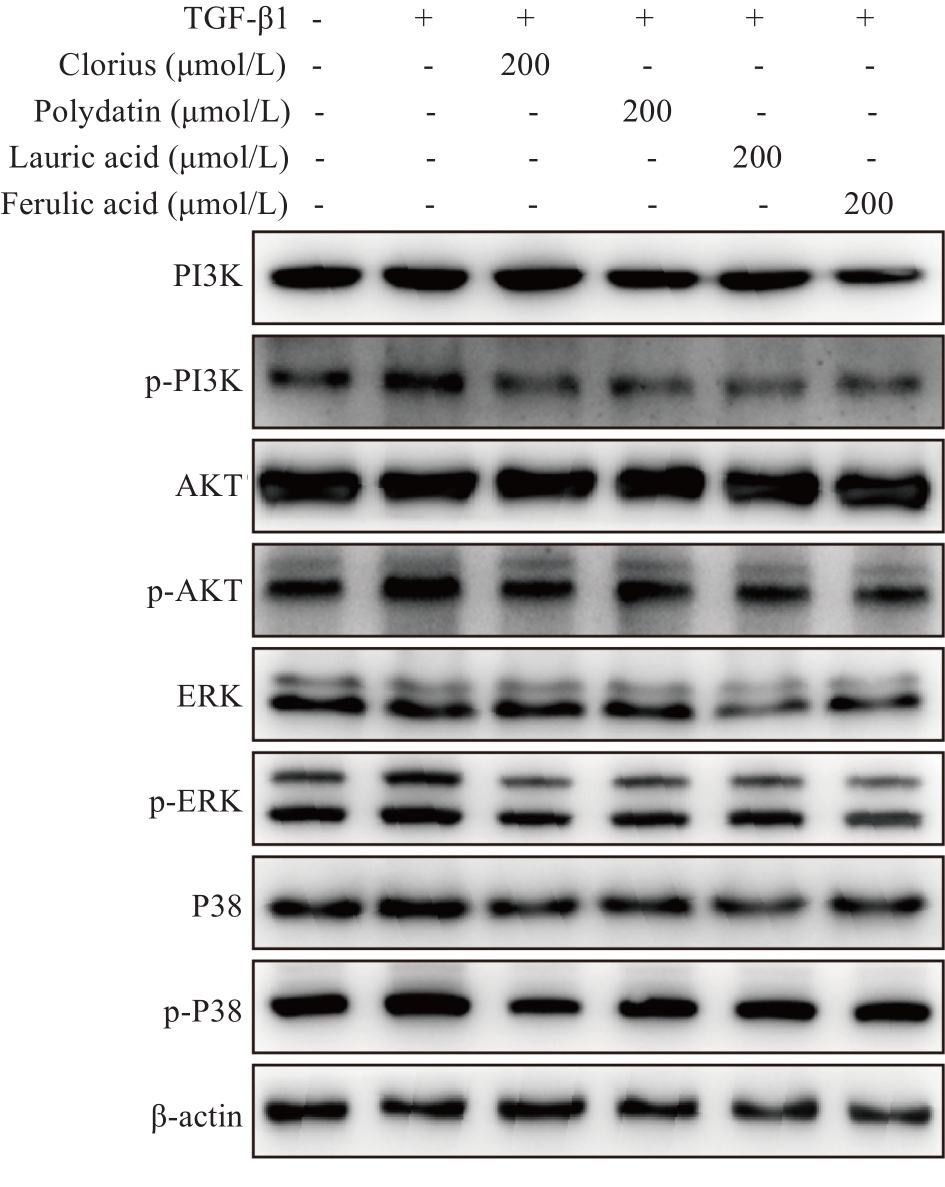
图8 核心功能成分群的Western blotting结果
Fig.8 Western blotting of PI3K, AKT and MAPK expressions in TGF‑β1-induced LX-2 cells treated with clorius, polydatin, lauric acid and ferulic acid (Mean±SD, n=3).
| 1 | Caligiuri A, Gentilini A, Pastore M, et al. Cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying liver fibrosis regression[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(10): 2759. |
| 2 | Li Z, Zhu JF, Ouyang H. Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine in improving hepatic fibrosis based on inhibiting pathological angiogenesis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1303012. |
| 3 | Li H. Advances in anti hepatic fibrotic therapy with Traditional Chinese Medicine herbal formula[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2020, 251: 112442. |
| 4 | Xu FP, Zhang H, Chen JM, et al. Recent progress on the application of compound formulas of traditional Chinese medicine in clinical trials and basic research in vivo for chronic liver disease[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 321: 117514. |
| 5 | Ma Z, Zhang B, Fan YQ, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine combined with hepatic targeted drug delivery systems: a new strategy for the treatment of liver diseases[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2019, 117: 109128. |
| 6 | He ZW, Chen SY, Pan TT, et al. Ginsenoside Rg2 ameliorating CDAHFD-induced hepatic fibrosis by regulating AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2022, 70(6): 1911-22. |
| 7 | Cai YJ, Zheng Q, Sun R, et al. Recent progress in the study of Artemisiae Scopariae Herba (Yin Chen), a promising medicinal herb for liver diseases[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 130: 110513. |
| 8 | Wei CL, Qiu J, Wu YY, et al. Promising traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of cholestatic liver disease process (cholestasis, hepatitis, liver fibrosis, liver cirrhosis)[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 297: 115550. |
| 9 | Liu JJ, Xu Y, Chen S, et al. The mechanism of Yinchenhao Decoction in treating obstructive-jaundice-induced liver injury based on Nrf2 signaling pathway[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2022, 28(32): 4635-48. |
| 10 | Xu L, Xie T, Shen T, et al. Yinchenhao decoction for chronic hepatitis B: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Medicine, 2019, 98(8): e14648. |
| 11 | Zhang P, Zhang DF, Zhou WA, et al. Network pharmacology: towards the artificial intelligence-based precision traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Brief Bioinform, 2023, 25(1): bbad518. |
| 12 | Nogales C, Mamdouh ZM, List M, et al. Network pharmacology: curing causal mechanisms instead of treating symptoms[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2022, 43(2): 136-50. |
| 13 | Wu Q, Yin CH, Li Y, et al. Detecting critical functional ingredients group and mechanism of xuebijing injection in treating sepsis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 769190. |
| 14 | Cai FF, Bian YQ, Wu R, et al. Yinchenhao decoction suppresses rat liver fibrosis involved in an apoptosis regulation mechanism based on network pharmacology and transcriptomic analysis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 114: 108863. |
| 15 | Huang L, Xie DL, Yu YR, et al. TCMID 2.0: a comprehensive resource for TCM[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018, 46(D1): D1117-D1120. |
| 16 | Wu Y, Zhang FL, Yang K, et al. SymMap: an integrative database of traditional Chinese medicine enhanced by symptom mapping[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47(D1): D1110-D1117. |
| 17 | Xu HY, Zhang YQ, Liu ZM, et al. ETCM: an encyclopaedia of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47(D1): D976-D982. |
| 18 | Khan HU, Aamir K, Jusuf PR, et al. Lauric acid ameliorates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced liver inflammation by mediating TLR4/MyD88 pathway in Sprague Dawley (SD) rats[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 265: 118750. |
| 19 | Shan L, Wang FL, Xue WJ, et al. New insights into fibrotic signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1196298. |
| 20 | Mu M, Zuo S, Wu RM, et al. Ferulic acid attenuates liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation via inhibition of TGF‑β/Smad signaling pathway[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2018, 12: 4107-15. |
| 21 | Zhao XM, Zhang J, Liang YN, et al. Astragaloside IV synergizes with ferulic acid to alleviate hepatic fibrosis in bile duct-ligated cirrhotic rats[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2020, 65(10): 2925-36. |
| 22 | Tang DD, Zhang Q, Duan H, et al. Polydatin: a critical promising natural agent for liver protection via antioxidative stress[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 9218738. |
| 23 | Cheng K, Niu JY, Zheng XT, et al. Aflatoxin-B1-exposure-induced hepatic injury could be alleviated by polydatin through reducing oxidative stress, inhibiting inflammation and improving mitophagy[J]. Toxics, 2023, 11(4): 309. |
| 24 | Peng RQ, Wang SZ, Wang R, et al. Antifibrotic effects of tanshinol in experimental hepatic fibrosis by targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K1 signaling pathways[J]. Discov Med, 2017, 23(125): 81-94. |
| 25 | Lei Y, Wang QL, Shen L, et al. MicroRNA-101 suppresses liver fibrosis by downregulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2019, 43(5): 575-84. |
| 26 | Xiao Q, Yu HB, Zhu X. The associations of hub gene polymorphisms in PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and Schistosomiasis Japonica infection and hepatic fibrosis[J]. Infect Genet Evol, 2020, 85: 104423. |
| 27 | Su GY, Li ZY, Wang R, et al. Signaling pathways involved in p38-ERK and inflammatory factors mediated the anti-fibrosis effect of AD-2 on thioacetamide-induced liver injury in mice[J]. Food Funct, 2019, 10(7): 3992-4000. |
| 28 | Wang Y, Song JY, Bian HY, et al. Apelin promotes hepatic fibrosis through ERK signaling in LX-2 cells[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2019, 460(1/2): 205-15. |
| 29 | Huang Y, Wang ZL, He Y, et al. Jiawei Taohe Chengqi Decoction attenuates hepatic fibrosis by preventing activation of HSCs through regulating Src/ERK/Smad3 signal pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 305: 116059. |
| 30 | Wang R, Zhang H, Wang YY, et al. Inhibitory effects of quercetin on the progression of liver fibrosis through the regulation of NF-кB/IкBα, p38 MAPK, and Bcl-2/Bax signaling[J]. Int Immuno-pharmacol, 2017, 47: 126-33. |
| [1] | 王瑾瑾, 崔文飞, 窦雪伟, 尹冰磊, 牛钰琪, 牛羚, 闫国立. 鬼箭羽通过调节EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂耐药信号通路延缓糖尿病肾病的进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1243-1255. |
| [2] | 王琳月, 戚文月, 高记华, 田茂生, 许建成. 痛痒消洗剂可促进大鼠肛瘘术后的创面愈合[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1256-1265. |
| [3] | 张文祥, 顾惠贤, 陈鹏德, 吴思宇, 马洪艳, 姚蓝. 复方玉液汤通过调控PI3K/Akt信号通路抑制糖尿病大鼠心肌细胞凋亡和炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1306-1314. |
| [4] | 黄燕, 覃璐璐, 管少兴, 管宴萍, 韦玉茹, 操艾伶, 李冬梅, 韦桂宁, 苏启表. 金缕半枫荷的水提取物抑制胰腺癌的作用机制:活性成分、关键靶点和信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1336-1344. |
| [5] | 任志军, 刁建新, 王奕婷. 芎归汤通过抑制氧化应激诱导的心肌凋亡减轻小鼠心梗后心衰引起的心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1416-1424. |
| [6] | 李睿镈, 高歌, 谢曦, 罗海彬. 槟榔活性成分诱导口腔黏膜下纤维化的机制:基于网络药理学结合临床样本验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 930-940. |
| [7] | 曹家樊, 孙 跃, 丁 鑫, 李盛文, 陈 博, 兰 天. 熊果苷通过抑制巨噬细胞募集并调控Akt/NF-κB和Smad信号通路改善小鼠肝纤维化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 652-659. |
| [8] | 李云飞, 杨婧怡, 张 颖, 张财霞, 韦宇翔, 王怡颖, 吴 宁, 孙见飞, 吴遵秋. 苗药四大血减轻大鼠的类风湿性关节炎:基于下调基质金属蛋白表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 739-747. |
| [9] | 陈君洁, 黄传兵, 李 明. 健脾滋肾方抑制系统性红斑狼疮患者的足细胞自噬:基于网络药理学和临床研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 465-473. |
| [10] | 崔艺馨, 王德财, 谢东晴, 王海明, 徐睿鑫, 唐潇然, 张 印. 健脾温阳凝胶剂脐疗治疗脾胃虚弱型慢性腹泻的疗效及机制:一项临床随机对照试验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 217-225. |
| [11] | 徐小惠, 冯金梅, 罗 颖, 何昕觎, 臧金宝, 黄道超. NDUFA13过表达可减轻CCl4诱导的小鼠肝纤维化:基于抑制NLRP3活化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 201-209. |
| [12] | 张 倩, 张梅奎, 刘颖璐, 王 妍, 吕菲菲, 王毓国. 六味酸枣汤治疗围绝经期失眠的作用机制:基于网络药理学与动物实验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1536-1547. |
| [13] | 张雪芳, 陈延华, 李宗恒, 尚 靖, 袁泽婷, 邓皖利, 骆 莺, 韩 娜, 殷佩浩, 殷 军. 六神丸治疗小鼠结肠炎相关性结直肠癌的作用机制:基于网络药理学和体内验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1051-1062. |
| [14] | 林嘉宜, 娄安妮, 李 旭. 脂多糖刺激巨噬细胞分泌含miR-155-5p的外泌体促进肝星状细胞的活化及迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 994-1001. |
| [15] | 刘 芳, 张远芳, 刘 鹏, 刘佳敏, 刘思妤, 王俊杰. 东革阿里抗炎的物质基础及其作用机制:基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS和网络药理学方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 879-888. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||