南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 187-196.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.22
• • 上一篇
龙秀鹏1( ), 陶顺1, 阳绅1, 李素云1, 饶利兵1, 李莉1, 张哲2
), 陶顺1, 阳绅1, 李素云1, 饶利兵1, 李莉1, 张哲2
收稿日期:2024-05-15
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2025-01-20
通讯作者:
李莉,张哲
E-mail:daexiansheng@foxmail.com
作者简介:龙秀鹏,在读本科生,E-mail: daexiansheng@foxmail.com
基金资助:
Xiupeng LONG1( ), Shun TAO1, Shen YANG1, Suyun LI1, Libing RAO1, Li LI1, Zhe ZHANG2
), Shun TAO1, Shen YANG1, Suyun LI1, Libing RAO1, Li LI1, Zhe ZHANG2
Received:2024-05-15
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-20
Contact:
Li LI, Zhe ZHANG
E-mail:daexiansheng@foxmail.com
摘要:
目的 基于网络药理学探讨槲皮素治疗心力衰竭的作用机制。 方法 通过中药系统药理学数据库和Swiss ADME数据库检索槲皮素的作用靶点。利用Genecards、OMIM数据库检索心力衰竭相关靶点。使用DAVID数据库获取交集靶点的GO分析和KEGG信号通路富集分析。交集靶点使用STRING数据库和Cytoscape软件进行蛋白互作分析,并筛选核心基因。最后使用PyMOL与AutoDock Tools软件完成核心靶点与槲皮素的分子对接。以异丙肾上腺素诱导H9C2心肌细胞构建心力衰竭模型,通过细胞实验对筛选出的MAPK信号通路进行验证。 结果 经筛选共得到60个交集靶点。富集结果显示,槲皮素可能通过MAPK信号通路抑制心力衰竭。核心基因筛选出的AMPK3、BCL-2等可能是槲皮素改善心力衰竭的关键基因。细胞实验表明,不同浓度的槲皮素组呈剂量依赖性地减少异丙肾上腺素诱导心肌细胞的凋亡(P<0.01)。分子生物学实验证实,槲皮素能够降低异丙肾上腺素诱导心肌细胞的Bax/Bcl-2、caspase-3和ERK、p38表达水平(P<0.05)。 结论 槲皮素可能通过抑制MAPK信号通路抑制心肌细胞凋亡改善心力衰竭。
龙秀鹏, 陶顺, 阳绅, 李素云, 饶利兵, 李莉, 张哲. 槲皮素通过抑制MAPK信号通路改善心力衰竭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 187-196.
Xiupeng LONG, Shun TAO, Shen YANG, Suyun LI, Libing RAO, Li LI, Zhe ZHANG. Quercetin improves heart failure by inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis via suppressing the MAPK signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 187-196.
| Genes | Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| Bcl-2 | F: 5'-ATCTCCCTGTTGACGCTCT-3′ |
| R: 5'-CATCTTCTCCTTCCAGCCT-3′ | |
| Bax | F: 5'-AGCCACAAAGATGGTCACT-3′ |
| R: 5'-GGAGATGAACTGGATAGCAA-3′ | |
| Caspase-3 | F: 5'-TGTTTCCCTGAGGTTTGCTG-3′ |
| R: 5'-TGCTATTGTGAGGCGGTTGT-3′ | |
| ERK | F: 5'-CGGAACTTGCAATCCTCAGT-3′ |
| R: 5'-TCGTGTGGGTCCTGAATTGG-3′ | |
| p38 | F: 5'-CTGCGAGGGCTGAAGTAT-3′ |
| R: 5'-TCCTCTTATCCGAGTCCAA-3′ | |
| GAPDH | F: 5'-GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTC-3' |
| R: 5'-GAAGATGGTGATGGGATTTC-3' |
表1 引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequence for qRT-PCR
| Genes | Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| Bcl-2 | F: 5'-ATCTCCCTGTTGACGCTCT-3′ |
| R: 5'-CATCTTCTCCTTCCAGCCT-3′ | |
| Bax | F: 5'-AGCCACAAAGATGGTCACT-3′ |
| R: 5'-GGAGATGAACTGGATAGCAA-3′ | |
| Caspase-3 | F: 5'-TGTTTCCCTGAGGTTTGCTG-3′ |
| R: 5'-TGCTATTGTGAGGCGGTTGT-3′ | |
| ERK | F: 5'-CGGAACTTGCAATCCTCAGT-3′ |
| R: 5'-TCGTGTGGGTCCTGAATTGG-3′ | |
| p38 | F: 5'-CTGCGAGGGCTGAAGTAT-3′ |
| R: 5'-TCCTCTTATCCGAGTCCAA-3′ | |
| GAPDH | F: 5'-GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTC-3' |
| R: 5'-GAAGATGGTGATGGGATTTC-3' |
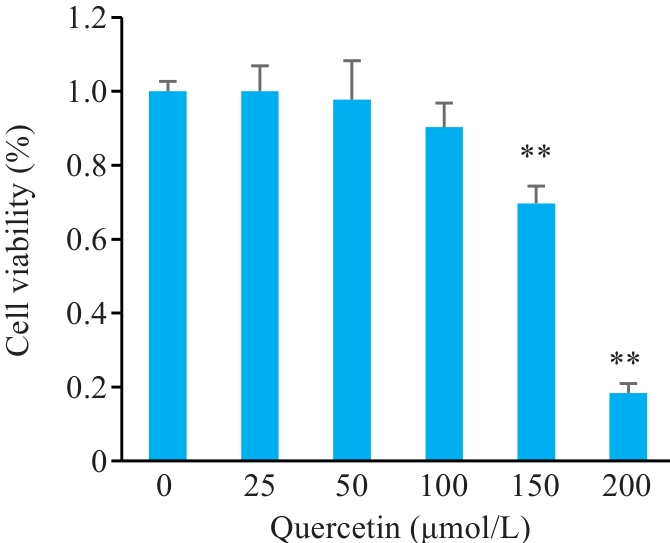
图5 不同浓度槲皮素对H9C2心肌细胞存活率的影响
Fig.5 Effects of different concentrations of quercetin on survival rate of H9C2 cardiomyocytes. **P<0.01 vs 0 μmol/L group (n=5).
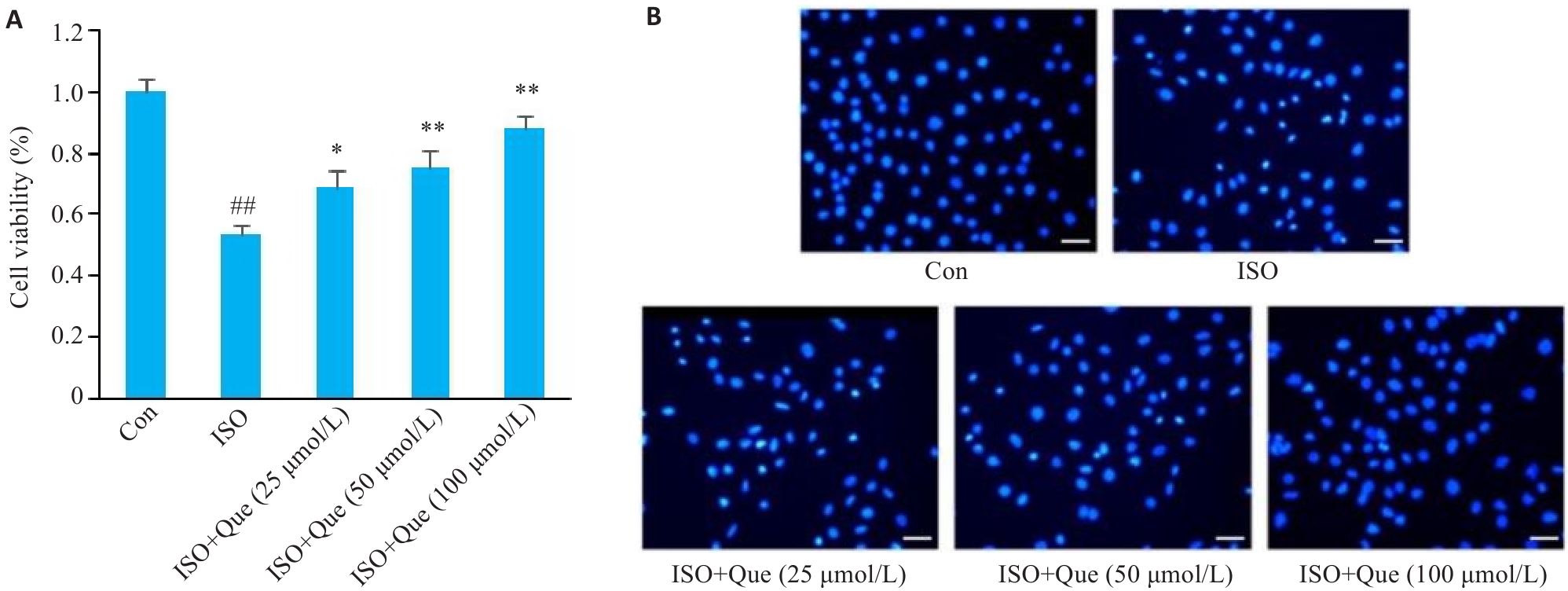
图6 不同浓度槲皮素对ISO诱导心肌细胞损伤的影响
Fig.6 Effects of different concentrations of quercetin(Que) on isoproterenol (ISO)-induced injury in mouse cardiomyocytes. A: Effects of different concentrations of quercetin on the survival rate of myocardial cells induced by ISO. B: Hoechst staining for detecting apoptosis of the injured cardiomyocytes (Original magnification:×200). ##P<0.01 vs Control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs ISO group (n=3).
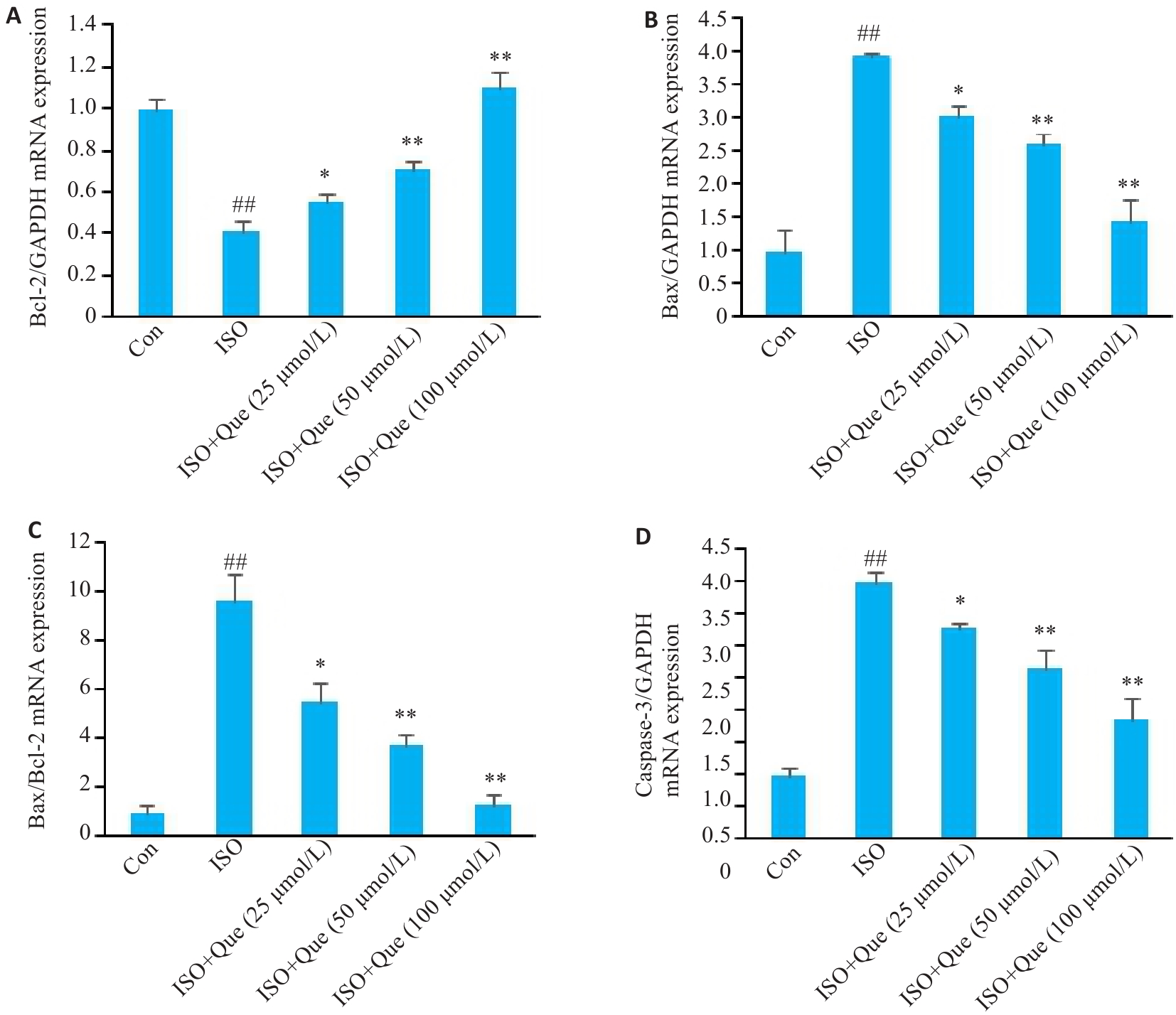
图8 不同浓度槲皮素对各组心肌细胞中Bax、Bcl-2、caspase-3 mRNA表达的影响
Fig.8 Effects of different concentrations of quercetin on mRNA expressions of Bcl-2 (A), Bax (B), Bax/Bcl-2 ratio (C) and caspase-3 (D) in the cardiomyocytes in each group. ##P<0.01 vs Control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs ISO group (n=3).
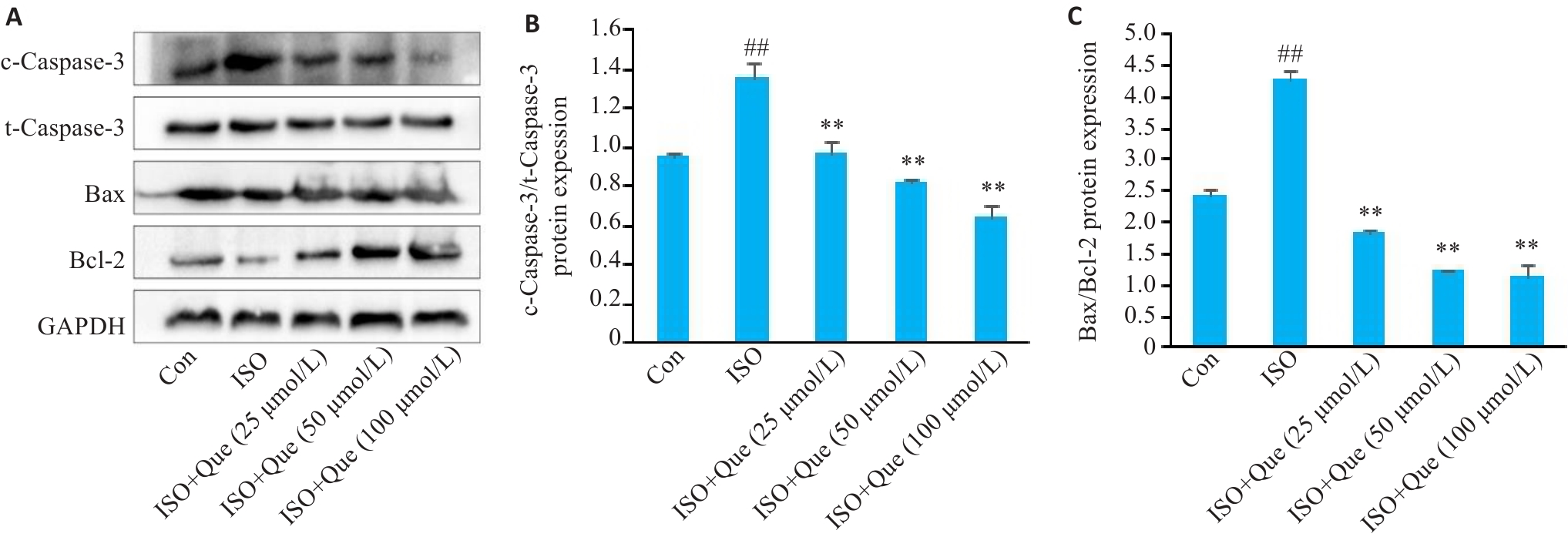
图9 不同浓度槲皮素对各组心肌细胞凋亡相关蛋白表达的影响
Fig.9 Effects of different concentrations of quercetin on the expression of apoptosis-related proteins in the cardiomyocytes in each group. A: Western blotting of c-caspase-3, t-caspase-3, Bcl-2 and Bax proteins. B: Ratio of cleaved-caspase-3/caspase-3 protein. C: Ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 protein. ##P<0.01 vs Control group, **P<0.01 vs ISO group (n=3).
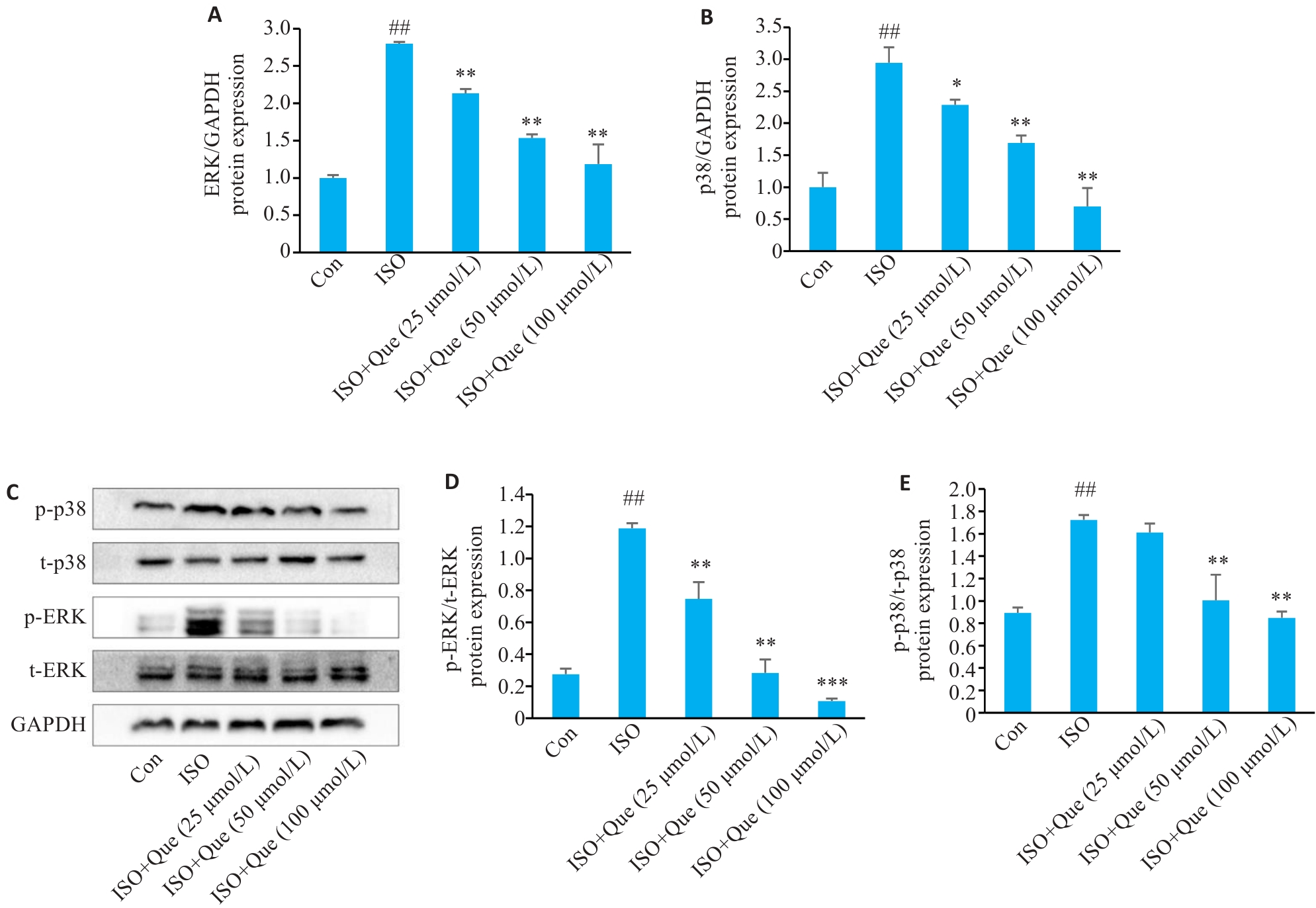
图10 不同浓度槲皮素对各组心肌细胞ERK/p38表达的影响
Fig.10 Effects of different concentrations of quercetin on ERK/p38 expression in the cardiomyocytes in each group. A, B: Effects of quercetin on expressions of ERK and p38 mRNA in the cells. C: Western blotting of p-ERK, ERK, p-p38 and p38 proteins. D, E: Expression of p-ERK/ERK and p-p38/p38 protein in the cells. ##P<0.01 vs Control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs ISO group (n=3).
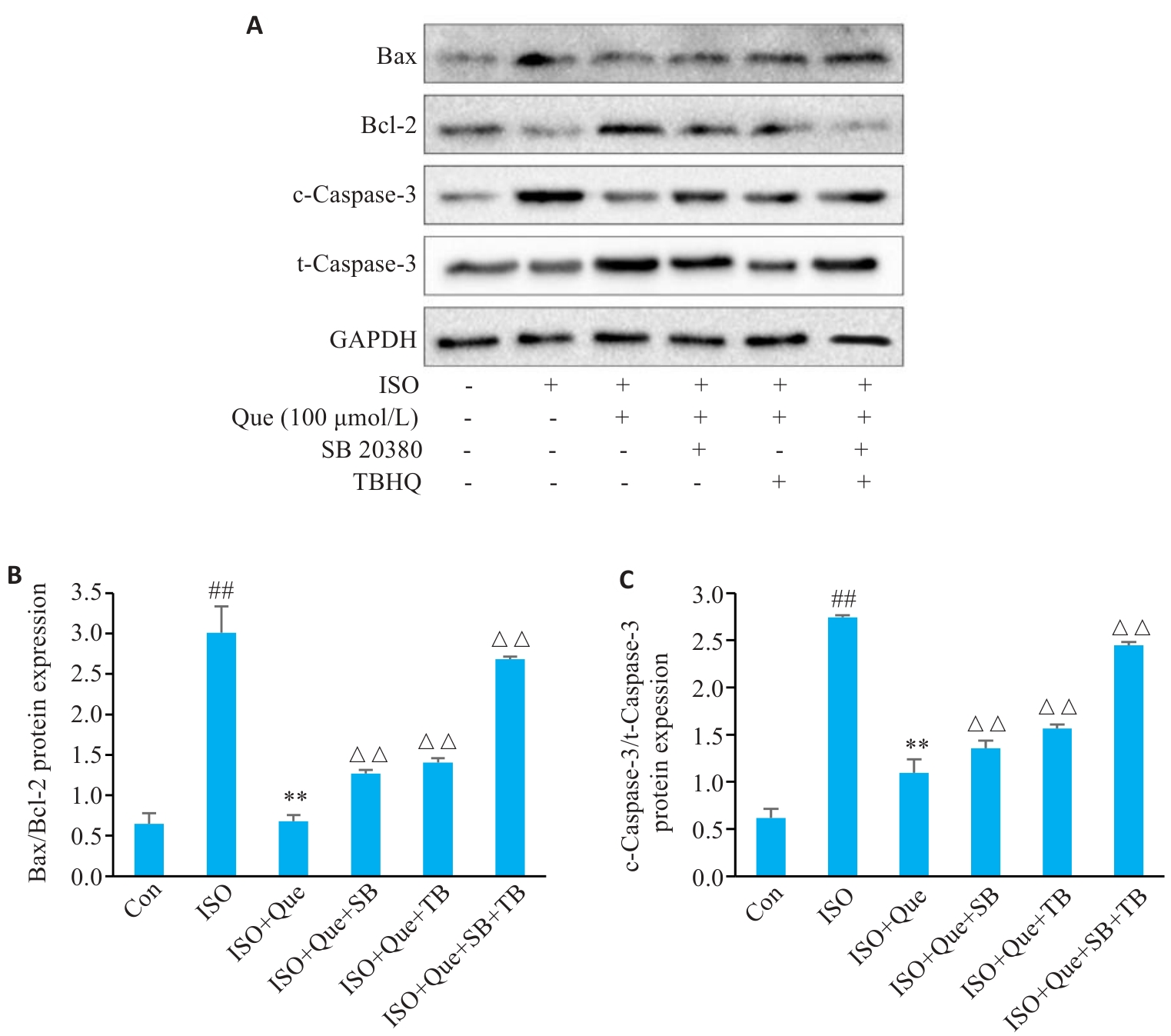
图11 不同浓度槲皮素对ERK/p38通路抑制剂介导各组心肌细胞凋亡相关蛋白的表达影响
Fig.11 Effects of different concentrations of quercetin on expressions of apoptosis-related proteins in cardiomyocytes treated with ERK/p38 pathway inhibitors. A: Effects of different concentrations of quercetin on the expression of Bax, Bcl-2 and caspase-3 in the cells after adding ERK inhibitor (TBHQ) and p38 inhibitor (SB 203580). B: Ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 protein expression. C: Ratio of cleaved-caspase-3/caspase-3 protein expression. ##P<0.01 vs Control group, **P<0.01 vs ISO group, △△P<0.01 vs ISO+Que group (n=3).
| 1 | Baman JR, Ahmad FS. Heart failure[J]. JAMA, 2020, 324(10): 1015. |
| 2 | 射血分数保留的心力衰竭诊断与治疗中国专家共识制定工作组. 射血分数保留的心力衰竭诊断与治疗中国专家共识2023[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2023, 38(4): 375-93. |
| 3 | McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure[J]. Eur Heart J, 2021, 42(36): 3599-726. |
| 4 | Mascolo A, di Mauro G, Cappetta D, et al. Current and future therapeutic perspective in chronic heart failure[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2022, 175: 106035. |
| 5 | Bai BB, Ji ZL, Wang FF, et al. CTRP12 ameliorates post-myocardial infarction heart failure through down-regulation of cardiac apo-ptosis, oxidative stress and inflammation by influencing the TAK1-p38 MAPK/JNK pathway[J]. Inflamm Res, 2023, 72(7): 1375-90. |
| 6 | Zhang SY, Liu HB, Fang QQ, et al. Shexiang Tongxin dropping pill protects against chronic heart failure in mice via inhibiting the ERK/MAPK and TGF‑β signaling pathways[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 796354. |
| 7 | Wan CR, Han DD, Xu JQ, et al. Jujuboside A attenuates norepinephrine-induced apoptosis of H9c2 cardiomyocytes by modulating MAPK and AKT signaling pathways[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 17(1): 1132-40. |
| 8 | Hu QC, Qu CY, Xiao XL, et al. Flavonoids on diabetic nephropathy: advances and therapeutic opportunities[J]. Chin Med, 2021, 16(1): 74. |
| 9 | Zhang WW, Zheng Y, Yan F, et al. Research progress of quercetin in cardiovascular disease[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2023, 10: 1203713. |
| 10 | Wang SH, Tsai KL, Chou WC, et al. Quercetin mitigates cisplatin-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes through Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2022, 50(5): 1281-98. |
| 11 | 李 霞, 程贝贝, 谭骏岚, 等. 黄芪主成分槲皮素通过MAPK通路调控PASMCs铁死亡抗低氧性肺动脉高压的研究(英文)[J]. 中国药学(英文版), 2024, 33(8): 714-29. |
| 12 | 谭 鑫, 鲜 维, 陈永锋, 等. 槲皮素治疗心力衰竭的分子机制:基于网络药理学与分子对接方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(8): 1198-206. |
| 13 | Nogales C, Mamdouh ZM, List M, et al. Network pharmacology: curing causal mechanisms instead of treating symptoms[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2022, 43(2): 136-50. |
| 14 | Shi TT, Hou CQ, Duan YZ, et al. Mechanism of Smilax China L. in the treatment of intrauterine adhesions based on network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental validation[J]. BMC Complement Med Ther, 2024, 24(1): 150. |
| 15 | Li X, Wei SZ, Niu SQ, et al. Network pharmacology prediction and molecular docking-based strategy to explore the potential mechanism of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction against sepsis[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2022, 144: 105389. |
| 16 | Sauer AJ, Cole R, Jensen BC, et al. Practical guidance on the use of sacubitril/valsartan for heart failure[J]. Heart Fail Rev, 2019, 24(2): 167-76. |
| 17 | Hyman DA, Siebert VR, Birnbaum GD, et al. A modern history RAAS inhibition and beta blockade for heart failure to underscore the non-equivalency of ACEIs and ARBs[J]. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther, 2020, 34(2): 215-21. |
| 18 | Romero-Becerra R, Santamans AM, Folgueira C, et al. p38 MAPK pathway in the heart: new insights in health and disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(19): 7412. |
| 19 | Zhang M, Li YC, Wang YQ, et al. Quercetin inhibition of myocardial fibrosis through regulating MAPK signaling pathway via ROS[J]. Pak J Pharm Sci, 2019, 32(3 Special): 1355-9. |
| 20 | Tan X, Xian W, Li XR, et al. Mechanisms of Quercetin against atrial fibrillation explored by network pharmacology combined with molecular docking and experimental validation[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 9777. |
| 21 | Bass-Stringer S, Tai CMK, McMullen JR. IGF1-PI3K-induced physiological cardiac hypertrophy: implications for new heart failure therapies, biomarkers, and predicting cardiotoxicity[J]. J Sport Health Sci, 2021, 10(6): 637-47. |
| 22 | Gao JY, Feng WJ, Lv W, et al. HIF-1/AKT signaling-activated PFKFB2 alleviates cardiac dysfunction and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in response to hypoxia[J]. Int Heart J, 2021, 62(2): 350-8. |
| 23 | Al-Rasheed NM, Fadda LM, Attia HA, et al. Quercetin inhibits sodium nitrite-induced inflammation and apoptosis in different rats organs by suppressing Ba x, HIF1‑α, TGF‑β, Smad-2, and AKT pathways[J]. J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2017, 31(5). doi: 10.1002/jbt.21883 . |
| 24 | Fang Z, Yushanjiang F, Wang GJ, et al. Germacrone mitigates cardiac remodeling by regulating PI3K/AKT-mediated oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 124(Pt A): 110876. |
| 25 | Fu C, Yao YYY, Li LB, et al. P4239Bradykinin inhibits High Glucose-Induced Senescence of c-kit Positive Cardiac Stem Cells via B2R/PI3K/AKT/mTOR/P53 signal pathway[J]. Eur Heart J, 2017, 38(): ehx504.P4239. |
| 26 | Tang XY, Jiang HL, Lin PY, et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 regulates HIF-1α degradation to inhibit apoptosis in hypoxic cardiomyocytes[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2021, 7(1): 242. |
| 27 | Wang L, Wu HW, Xiong L, et al. Quercetin downregulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression and HIF-1α/VEGF signaling-related angiogenesis in a mouse model of abdominal aortic aneurysm[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 9485398. |
| 28 | Meijles DN, Cull JJ, Markou T, et al. Redox regulation of cardiac ASK1 (apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1) controls p38-MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) and orchestrates cardiac remodeling to hypertension[J]. Hypertension, 2020, 76(4): 1208-18. |
| 29 | Cheng J, Huang Y, Zhang XH, et al. TRIM21 and PHLDA3 negatively regulate the crosstalk between the PI3K/AKT pathway and PPP metabolism[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 1880. |
| 30 | Moulin S, Thomas A, Wagner S, et al. Intermittent hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte death is mediated by HIF-1 dependent MAM disruption[J]. Antioxidants, 2022, 11(8): 1462. |
| 31 | Fleisher TA. Apoptosis[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 1997, 78(3): 245-50. |
| 32 | Lin XY, Ouyang SY, Zhi CX, et al. Focus on ferroptosis, pyroptosis, apoptosis and autophagy of vascular endothelial cells to the strategic targets for the treatment of atherosclerosis[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2022, 715: 109098. |
| 33 | Liu YL, Yang LQ, Yin JM, et al. MicroRNA-15b deteriorates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by down-regulating bcl-2 and MAPK3[J]. J Investig Med, 2018, 66(1): 39-45. |
| 34 | Chen SN, Lombardi R, Karmouch J, et al. DNA damage response/TP53 pathway is activated and contributes to the pathogenesis of dilated cardiomyopathy associated with LMNA (lamin A/C) mutations[J]. Circ Res, 2019, 124(6): 856-73. |
| 35 | Chen YF, Qiu Q, Wang L, et al. Quercetin ameliorates myocardial injury in diabetic rats by regulating autophagy and apoptosis through AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2024, 52(3): 841-64. |
| 36 | de Lacerda Alexandre JV, Viana YIP, David CEB, et al. Quercetin treatment increases H2O2 removal by restoration of endogenous antioxidant activity and blocks isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy[J]. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 2021, 394(2): 217-26. |
| [1] | 褚乔, 王小娜, 续佳颖, 彭荟林, 赵裕琳, 张静, 陆国玉, 王恺. 白头翁皂苷D通过多靶点和多途径抑制三阴性乳腺癌侵袭转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [2] | 姜一凡, 李小荣, 耿嘉逸, 陈永锋, 唐碧, 康品方. 槲皮素通过抑制HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB信号通路减轻糖尿病引起的大鼠肾脏损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1769-1775. |
| [3] | 陈星梅, 刘琴文, 李镱, 钟晓宇, 樊奇灵, 马柯, 罗柳婷, 官道刚, 朱志博. 茵陈蒿汤治疗肝纤维化的核心功能成分群以及潜在通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1508-1517. |
| [4] | 张珊苑, 蔡巧燕, 祁江晗, 殷恺馨, 何晨晨, 高铸烨, 张铃, 褚剑锋. 清心解瘀颗粒抗动脉粥样硬化的药效学及调控机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1518-1528. |
| [5] | 张钰明, 夏士程, 张淋淋, 陈梦茜, 刘晓婧, 高琴, 叶红伟. 金银花提取物对小鼠阿霉素肝脏损伤的保护作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1571-1581. |
| [6] | 王瑾瑾, 崔文飞, 窦雪伟, 尹冰磊, 牛钰琪, 牛羚, 闫国立. 鬼箭羽通过调节EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂耐药信号通路延缓糖尿病肾病的进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1243-1255. |
| [7] | 王琳月, 戚文月, 高记华, 田茂生, 许建成. 痛痒消洗剂可促进大鼠肛瘘术后的创面愈合[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1256-1265. |
| [8] | 张文祥, 顾惠贤, 陈鹏德, 吴思宇, 马洪艳, 姚蓝. 复方玉液汤通过调控PI3K/Akt信号通路抑制糖尿病大鼠心肌细胞凋亡和炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1306-1314. |
| [9] | 黄燕, 覃璐璐, 管少兴, 管宴萍, 韦玉茹, 操艾伶, 李冬梅, 韦桂宁, 苏启表. 金缕半枫荷的水提取物抑制胰腺癌的作用机制:活性成分、关键靶点和信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1336-1344. |
| [10] | 任志军, 刁建新, 王奕婷. 芎归汤通过抑制氧化应激诱导的心肌凋亡减轻小鼠心梗后心衰引起的心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1416-1424. |
| [11] | 申采玉, 王帅, 周锐盈, 汪雨贺, 高琴, 陈兴智, 杨枢. 慢性心力衰竭合并肺部感染患者院内死亡风险预测:基于可解释性机器学习方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1141-1148. |
| [12] | 李睿镈, 高歌, 谢曦, 罗海彬. 槟榔活性成分诱导口腔黏膜下纤维化的机制:基于网络药理学结合临床样本验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 930-940. |
| [13] | 李云飞, 杨婧怡, 张 颖, 张财霞, 韦宇翔, 王怡颖, 吴 宁, 孙见飞, 吴遵秋. 苗药四大血减轻大鼠的类风湿性关节炎:基于下调基质金属蛋白表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 739-747. |
| [14] | 陈君洁, 黄传兵, 李 明. 健脾滋肾方抑制系统性红斑狼疮患者的足细胞自噬:基于网络药理学和临床研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 465-473. |
| [15] | 崔艺馨, 王德财, 谢东晴, 王海明, 徐睿鑫, 唐潇然, 张 印. 健脾温阳凝胶剂脐疗治疗脾胃虚弱型慢性腹泻的疗效及机制:一项临床随机对照试验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 217-225. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||