南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 1553-1560.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.08.14
• • 上一篇
从小凡( ), 陈腾, 李硕, 王媛媛, 周龙云, 李小龙, 张配, 孙小锦(
), 陈腾, 李硕, 王媛媛, 周龙云, 李小龙, 张配, 孙小锦( ), 赵素容(
), 赵素容( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-15
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-09-06
通讯作者:
孙小锦,赵素容
E-mail:736422754@qq.com;aijosxj@163.com;inwindangel@ qq.com
作者简介:从小凡,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 736422754@qq.com
基金资助:
Xiaofan CONG( ), Teng CHEN, Shuo LI, Yuanyuan WANG, Longyun ZHOU, Xiaolong LI, Pei ZHANG, Xiaojin SUN(
), Teng CHEN, Shuo LI, Yuanyuan WANG, Longyun ZHOU, Xiaolong LI, Pei ZHANG, Xiaojin SUN( ), Surong ZHAO(
), Surong ZHAO( )
)
Received:2024-03-15
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-09-06
Contact:
Xiaojin SUN, Surong ZHAO
E-mail:736422754@qq.com;aijosxj@163.com;inwindangel@ qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探究双氢青蒿素(DHA)与顺铂(DDP)联合应用对耐DDP鼻咽癌细胞株HNE1/DDP增殖抑制和促凋亡的作用及其机制。 方法 CCK-8法检测不同浓度DHA(0、5、10、20、40、80、160 μmol/L)和不同浓度DDP(0、4、8、16、32、64、128 μmol/L)处理24 h和48 h后HNE1/DDP细胞的存活率;采用Compusyn软件计算DHA与DDP的联合指数。将HNE1/DDP细胞分为对照组、DHA组、DDP组、DHA联合DDP组,给药处理24 h后,CCK-8、EdU和集落克隆形成实验分别检测细胞活力、细胞增殖和集落克隆形成能力;流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡情况和细胞内活性氧(ROS)水平;Western blotting检测凋亡相关蛋白Cleaved PARP、Cleaved Caspase-9、Cleaved Caspase-3表达水平。ROS抑制剂N-乙酰半胱氨酸预处理后,检测其对DHA联合DDP诱导的细胞增殖、凋亡的影响。 结果 不同浓度DHA和不同浓度DDP均能明显抑制HNE1/DDP细胞活力,DHA(5 μmol/L)联合DDP(8、16、32、64、128 μmol/L)的联合指数均小于1。与DHA或DDP单独处理组相比,DHA联合DDP组细胞活力下降(P<0.01),集落形成数和EdU阳性染色细胞减少(P<0.01),细胞凋亡率和细胞内ROS水平升高(P<0.01),细胞凋亡相关蛋白Cleaved PARP、Cleaved Caspase-9、Cleaved Caspase-3的表达水平增加(P<0.05),而N-乙酰半胱氨酸预处理可部分逆转DHA联合DDP对HNE1/DDP细胞的增殖抑制和凋亡诱导作用(P<0.01)。 结论 DHA增强DDP对HNE1/DDP细胞的增殖抑制和凋亡诱导作用,其机制可能与细胞内ROS的积累有关。
从小凡, 陈腾, 李硕, 王媛媛, 周龙云, 李小龙, 张配, 孙小锦, 赵素容. 双氢青蒿素通过促进活性氧的产生增强鼻咽癌细胞对顺铂诱导凋亡的敏感性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1553-1560.
Xiaofan CONG, Teng CHEN, Shuo LI, Yuanyuan WANG, Longyun ZHOU, Xiaolong LI, Pei ZHANG, Xiaojin SUN, Surong ZHAO. Dihydroartemisinin enhances sensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma HNE1/DDP cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by promoting ROS production[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1553-1560.
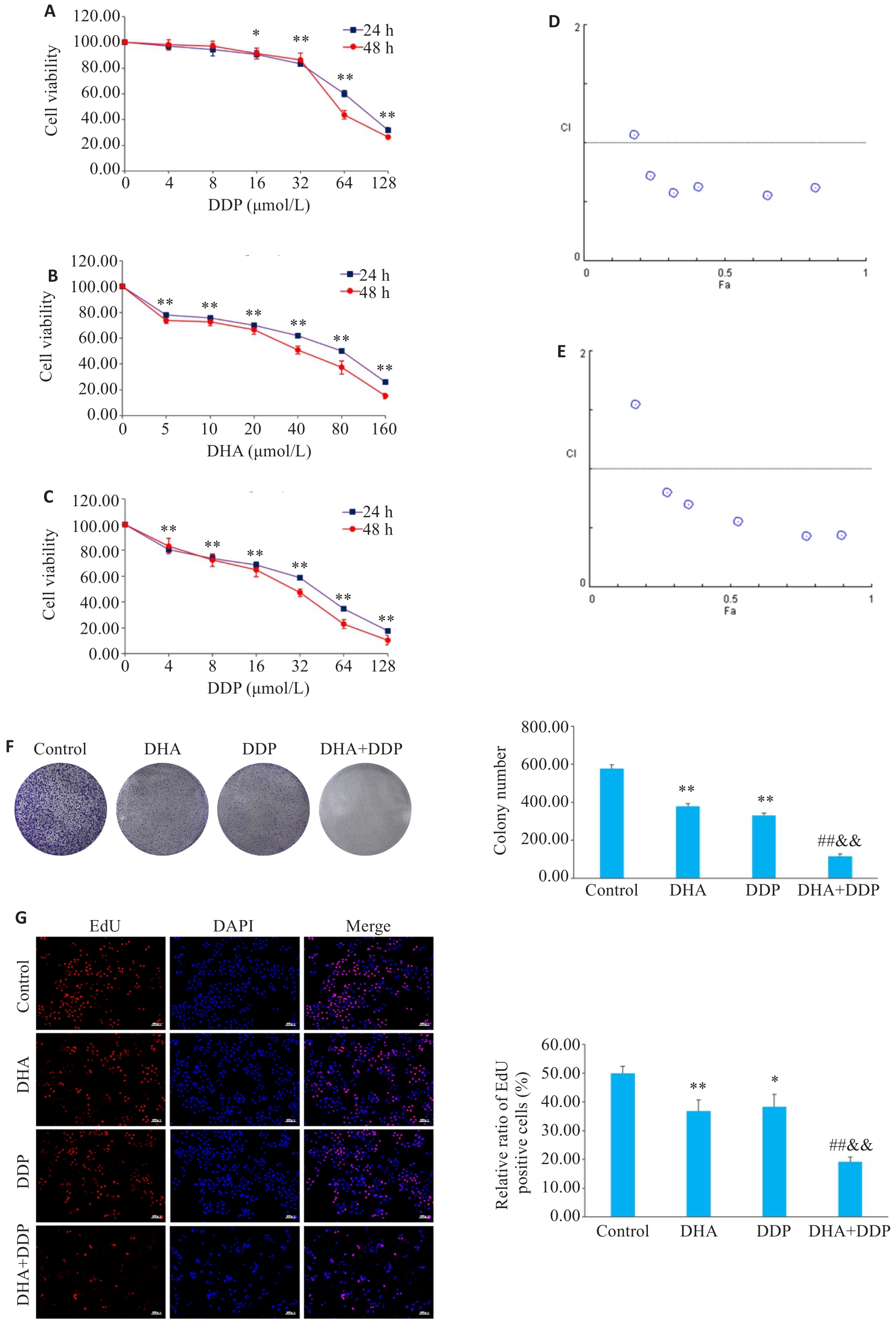
图2 DHA或/和DDP抑制HNE1/DDP细胞活力和增殖
Fig.2 Inhibitory effects of DHA, DDP, and their combination on viability and proliferation of HNE1/DDP cells. A, B: CCK-8 assay for detecting viability of HNE1/DDP cells treated with DHA and DDP for 24 and 48 h. C: CCK-8 assay for detecting viability of HNE1/DDP cells treated with DHA (5 μmol/L) combined with DDP (0, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128 μmol/L) for 24 and 48 h. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs 0 μmol/L. D, E: Combination index (CI) of combination treatment with DHA and DDP for 24, 48 h. F: Colony formation ability of cells treated with DHA or/and DDP for 24 h. G: EdU test for detecting proliferation of HNE1/DDP cells treated with DHA or/and DDP for 24 h (Original magnification: ×10). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Control group; ##P<0.01 vs DHA group; &&P<0.01 vs DDP group.
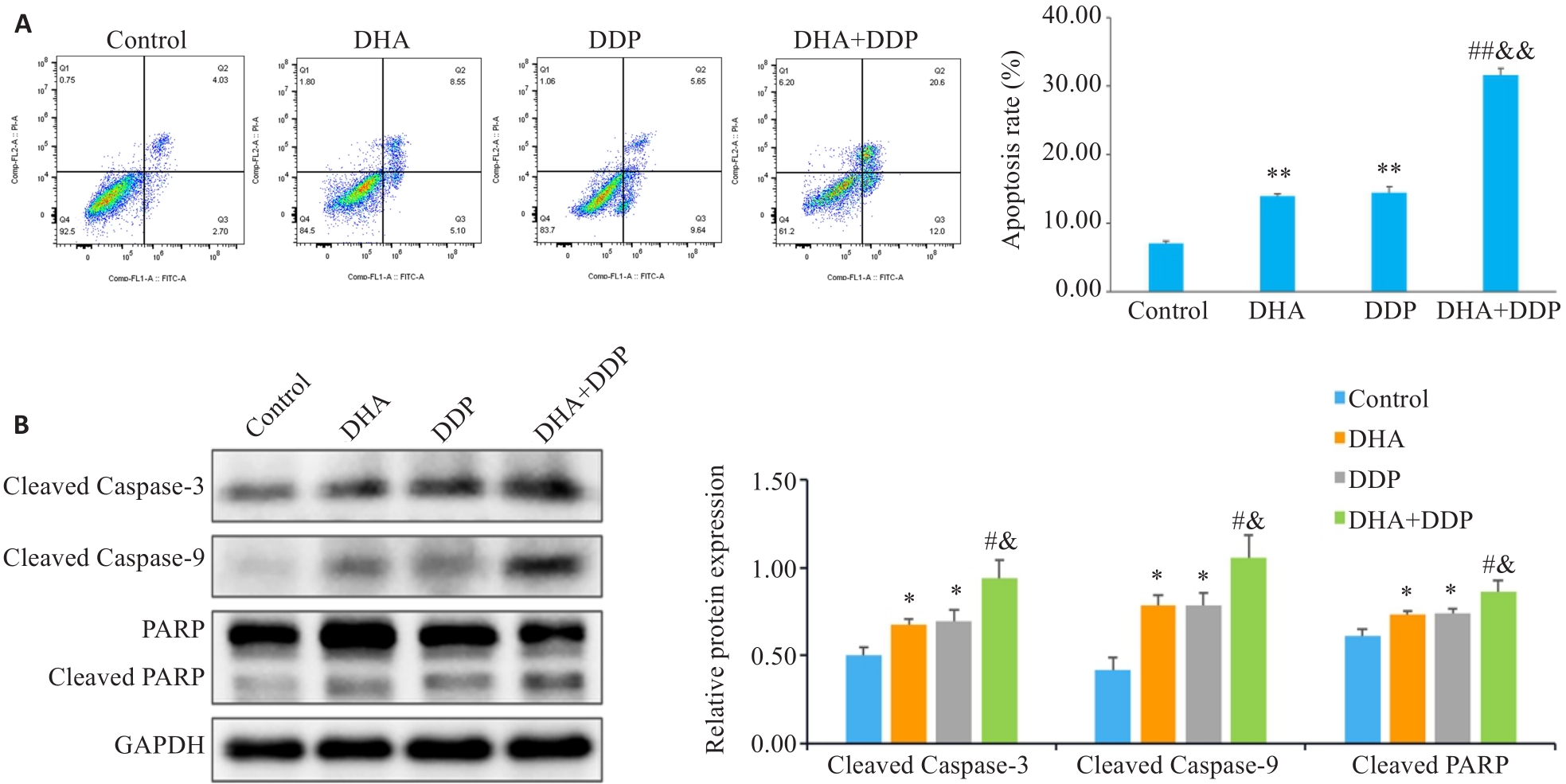
图3 DHA联合DDP诱导HNE1/DDP细胞凋亡
Fig.3 DHA combined with DDP more potently induces apoptosis in HNE1/DDP cells. A: Apoptosis of HNE1/DDP cells treated with DHA or/and DDP for 24 h detected by flow cytometry. B: Protein levels of cleaved PARP, cleaved caspase-9, and cleaved caspase-3 in HNE1/DDP cells detected by Western blotting. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs DHA group; &P<0.05, &&P<0.01 vs DDP group.
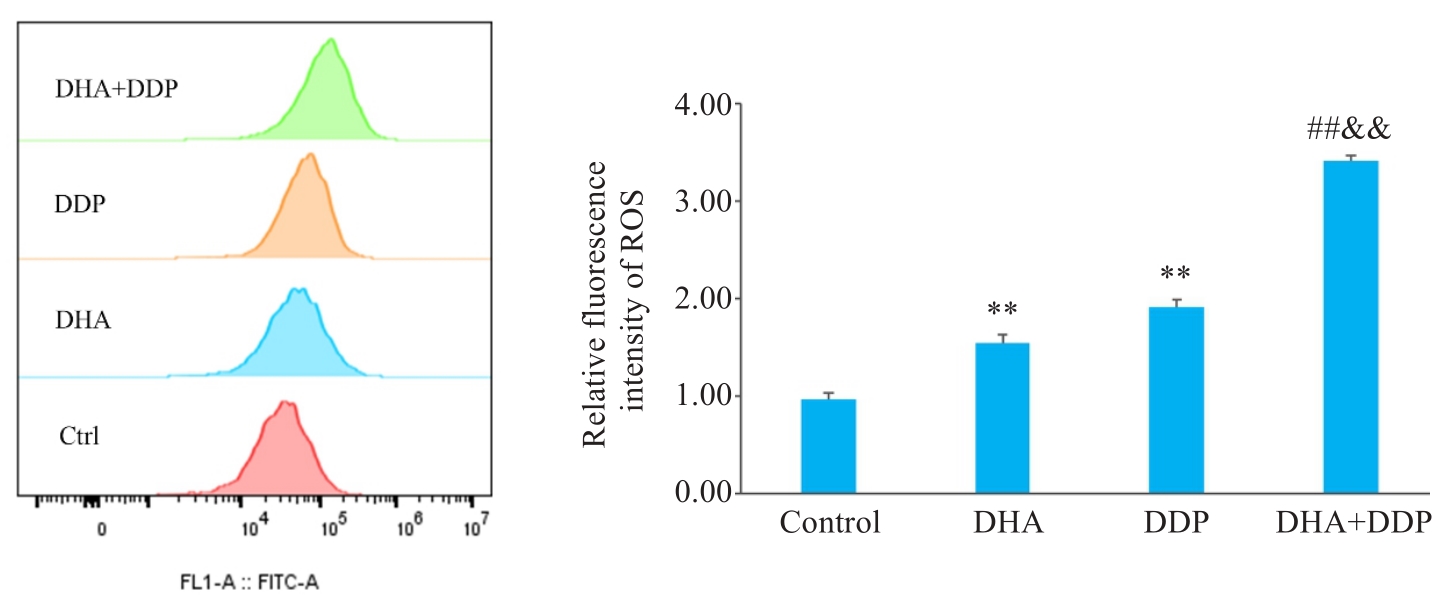
图4 DHA联合DDP促进HNE1/DDP细胞内ROS的产生
Fig.4 DHA combined with DDP enhances ROS production in HNE1/DDP cells. **P<0.01 vs Control group; ##P<0.01 vs DHA group; &&P<0.01 vs DDP group.
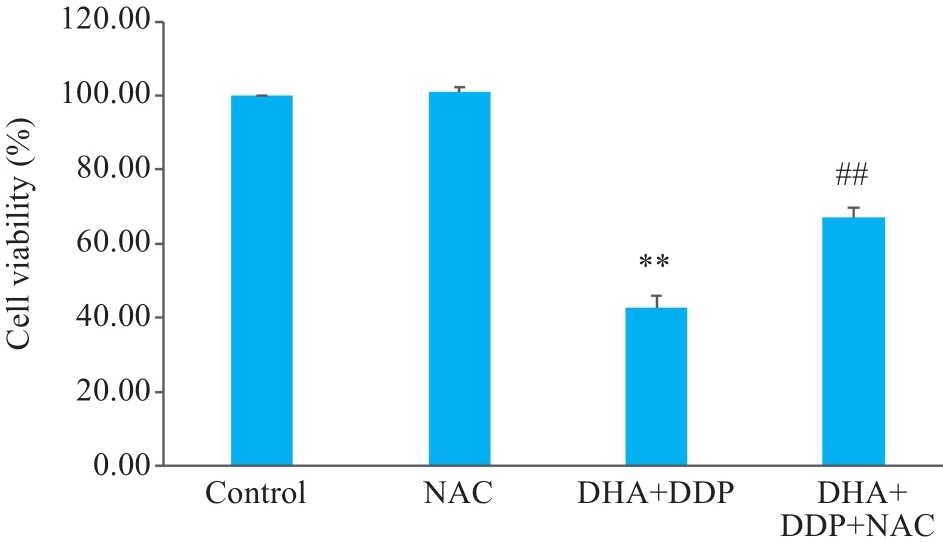
图5 DHA联合DDP抑制HNE1/DDP细胞增殖作用依赖于ROS的积累
Fig.5 DHA combined with DDP more strongly inhibits proliferation of HNE1/DDP cells by promoting ROS accumulation. **P<0.01 vs Control group; ##P<0.01 vs DHA+DDP group.
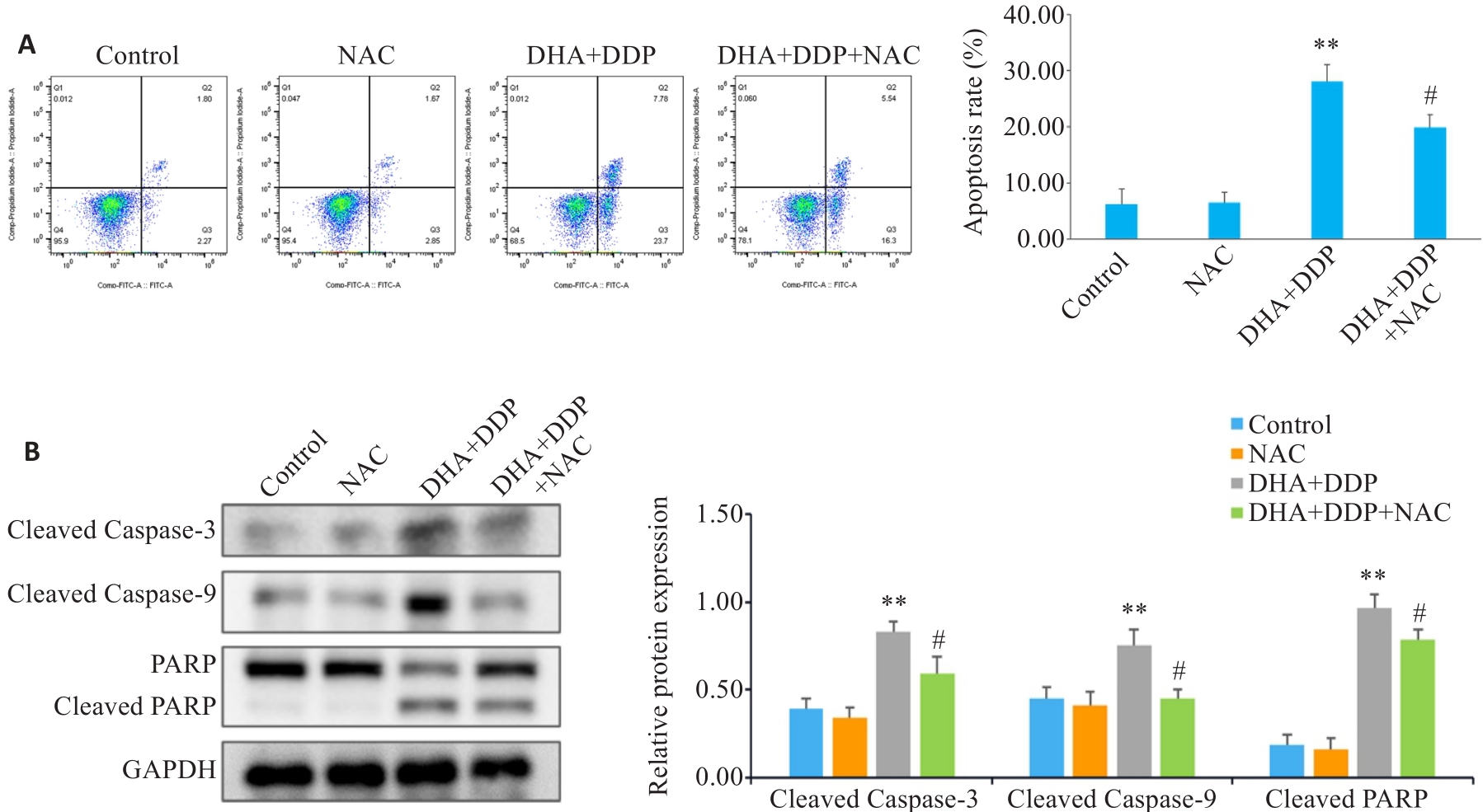
图6 抑制ROS生成对HNE1/DDP细胞凋亡和凋亡相关蛋白表达水平的影响
Fig.6 Effects of inhibiting ROS production on apoptosis and expression of apoptosis-related proteins in HNE1/DDP cells following combined treatment with DHA and DDP for 24 h. A: Apoptosis of HNE1/DDP cells treated with NAC (5 mmol/L) followed by combined treatment with DHA and DDP for 24 h was detected by flow cytometry. B: Protein levels of cleaved PARP, cleaved caspase-9, and cleaved caspase-3 in HNE1/DDP cells detected by Western blotting. **P<0.01 vs Control group; #P<0.05 vs DHA+DDP group.
| 1 | Wang SM, Claret FX, Wu WY. MicroRNAs as therapeutic targets in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2019, 9: 756. |
| 2 | Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. |
| 3 | Chen YP, Chan ATC, Le QT, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Lancet, 2019, 394(10192): 64-80. |
| 4 | Pfister DG, Spencer S, Adelstein D, et al. Head and neck cancers, version 2.2020, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2020, 18(7): 873-98. |
| 5 | Blanchard P, Lee A, Marguet S, et al. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an update of the MAC-NPC meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2015, 16(6): 645-55. |
| 6 | Perri F, Bosso D, Buonerba C, et al. Locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: current and emerging treatment strategies[J]. World J Clin Oncol, 2011, 2(12): 377-83. |
| 7 | Perri F, Della Vittoria Scarpati G, Caponigro F, et al. Management of recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: current perspectives[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12: 1583-91. |
| 8 | Cui ZQ, Pu T, Zhang YJ, et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC00346 contributes to cisplatin resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by repressing miR-342-5p[J]. Open Biol, 2020, 10(5): 190286. |
| 9 | Dutta S, Mahalanobish S, Saha S, et al. Natural products: an upcoming therapeutic approach to cancer[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2019, 128: 240-55. |
| 10 | Zhang J, Li Y, Wang JG, et al. Dihydroartemisinin affects STAT3/DDA1 signaling pathway and reverses breast cancer resistance to cisplatin[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2023, 51(2): 445-59. |
| 11 | Malami I, Bunza AM, Alhassan AM, et al. Dihydroartemisinin as a potential drug candidate for cancer therapy: a structural-based virtual screening for multitarget profiling[J]. J Biomol Struct Dyn, 2022, 40(3): 1347-62. |
| 12 | Liu YM, Gao SJ, Zhu J, et al. Dihydroartemisinin induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion in epithelial ovarian cancer via inhibition of the hedgehog signaling pathway[J]. Cancer Med, 2018, 7(11): 5704-15. |
| 13 | Hu H, Wang ZD, Tan CL, et al. Dihydroartemisinin/miR-29b combination therapy increases the pro-apoptotic effect of dihydroartemisinin on cholangiocarcinoma cell lines by regulating Mcl-1 expression[J]. Adv Clin Exp Med, 2020, 29(8): 911-9. |
| 14 | Lu YY, Chen TS, Wang XP, et al. Single-cell analysis of dihydroartemisinin-induced apoptosis through reactive oxygen species-mediated caspase-8 activation and mitochondrial pathway in ASTC-a-1 cells using fluorescence imaging techniques[J]. J Biomed Opt, 2010, 15(4): 046028. |
| 15 | Li PC, Yang S, Dou MM, et al. Synergic effects of artemisinin and resveratrol in cancer cells[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2014, 140(12): 2065-75. |
| 16 | Ni LL, Zhu XP, Zhao Q, et al. Dihydroartemisinin, a potential PTGS1 inhibitor, potentiated cisplatin-induced cell death in non-small cell lung cancer through activating ROS-mediated multiple signaling pathways[J]. Neoplasia, 2024, 51: 100991. |
| 17 | 刘艳艳, 安 倩, 海 波, 等. 双氢青蒿素联合顺铂对人神经母细胞瘤细胞增殖及凋亡的影响[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2023, 31(22): 4129-35. |
| 18 | Cao SM, Simons MJ, Qian CN. The prevalence and prevention of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in China[J]. Chin J Cancer, 2011, 30(2): 114-9. |
| 19 | Hong Y, Che SM, Hui BN, et al. Combination therapy of lung cancer using layer-by-layer cisplatin prodrug and curcumin co-encapsulated nanomedicine[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2020, 14: 2263-74. |
| 20 | Yang ML, Li HR, Li YR, et al. Identification of genes and pathways associated with MDR in MCF-7/MDR breast cancer cells by RNA-seq analysis[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 17(5): 6211-26. |
| 21 | Kadioglu O, Elbadawi M, Fleischer E, et al. Identification of novel anthracycline resistance genes and their inhibitors[J]. Pharmaceuticals, 2021, 14(10): 1051. |
| 22 | Dama S, Niangaly H, Djimde M, et al. A randomized trial of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine versus artemether-lumefantrine for treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Mali[J]. Malar J, 2018, 17(1): 347. |
| 23 | Slezakova S, Ruda-Kucerova J. Anticancer activity of artemisinin and its derivatives[J]. Anticancer Res, 2017, 37(11): 5995-6003. |
| 24 | Zhang CZ, Zhang HT, Yun JP, et al. Dihydroartemisinin exhibits antitumor activity toward hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo [J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2012, 83(9): 1278-89. |
| 25 | Qin GQ, Zhao CB, Zhang LL, et al. Dihydroartemisinin induces apoptosis preferentially via a Bim-mediated intrinsic pathway in hepatocarcinoma cells[J]. Apoptosis, 2015, 20(8): 1072-86. |
| 26 | Im E, Yeo C, Lee HJ, et al. Dihydroartemisinin induced caspase-dependent apoptosis through inhibiting the specificity protein 1 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma SK-Hep-1 cells[J]. Life Sci, 2018, 192: 286-92. |
| 27 | Dong J, Yang WH, Han JQ, et al. Effect of dihydroartemisinin on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in canine mammary tumour cells[J]. Res Vet Sci, 2019, 124: 240-7. |
| 28 | Li N, Zhang SY, Luo Q, et al. The effect of dihydroartemisinin on the malignancy and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer cells[J]. Curr Pharm Biotechnol, 2019, 20(9): 719-26. |
| 29 | Yao YY, Guo QL, Cao Y, et al. Artemisinin derivatives inactivate cancer-associated fibroblasts through suppressing TGF‑β signaling in breast cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 37(1): 282. |
| 30 | Chen HH, Zhou HJ, Fang X. Inhibition of human cancer cell line growth and human umbilical vein endothelial cell angiogenesis by artemisinin derivatives in vitro [J]. Pharmacol Res, 2003, 48(3): 231-6. |
| 31 | Lu JJ, Chen SM, Zhang XW, et al. The anti-cancer activity of dihydroartemisinin is associated with induction of iron-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress in colorectal carcinoma HCT116 cells[J]. Invest New Drugs, 2011, 29(6): 1276-83. |
| 32 | Feng X, Li L, Jiang H, et al. Dihydroartemisinin potentiates the anticancer effect of cisplatin via mTOR inhibition in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells: involvement of apoptosis and autophagy[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2014, 444(3): 376-81. |
| 33 | Dai XS, Chen W, Qiao Y, et al. Dihydroartemisinin inhibits the development of colorectal cancer by GSK-3β/TCF7/MMP9 pathway and synergies with capecitabine[J]. Cancer Lett, 2024, 582: 216596. |
| 34 | Li XM, Hou YN, Zhao JT, et al. Combination of chemotherapy and oxidative stress to enhance cancer cell apoptosis[J]. Chem Sci, 2020, 11(12): 3215-22. |
| 35 | Tian YZ, Liu YP, Tian SC, et al. Antitumor activity of ginsenoside Rd in gastric cancer via up-regulation of Caspase-3 and Caspase-9[J]. Pharmazie, 2020, 75(4): 147-50. |
| 36 | NavaneethaKrishnan S, Rosales JL, Lee KY. Loss of Cdk5 in breast cancer cells promotes ROS-mediated cell death through dysregulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore[J]. Oncogene, 2018, 37(13): 1788-804. |
| 37 | Olliaro PL, Haynes RK, Meunier B, et al. Possible modes of action of the artemisinin-type compounds[J]. Trends Parasitol, 2001, 17(3): 122-6. |
| 38 | Li X, Liu CQ, Zhang X, et al. Bruceine A: Suppressing metastasis via MEK/ERK pathway and invoking mitochondrial apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2023, 168: 115784. |
| 39 | Zhu JW, Sun Y, Lu Y, et al. Glaucocalyxin A exerts anticancer effect on osteosarcoma by inhibiting GLI1 nuclear translocation via regulating PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(6): 708. |
| 40 | Perillo B, di Donato M, Pezone A, et al. ROS in cancer therapy: the bright side of the moon[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2020, 52(2): 192-203. |
| 41 | Zhou Q, Ye FF, Qiu JX, et al. Dihydroartemisinin induces ER stress-mediated apoptosis in human tongue squamous carcinoma by regulating ROS production[J]. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 2022, 22(16): 2902-8. |
| 42 | Liu ZY, Huang ML, Hong Y, et al. Isovalerylspiramycin I suppresses non-small cell lung carcinoma growth through ROS-mediated inhibition of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2022, 18(9): 3714-30. |
| [1] | 庞一丹, 刘雅, 陈思嫒, 张荆雷, 曾今, 潘元明, 安娟. SPAG5在胃癌细胞恶性增殖中的生物学作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1497-1507. |
| [2] | 刘硕, 李静, 吴兴旺. Swertiamarin通过抑制肠上皮细胞细胞凋亡改善TNBS诱导的实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1545-1552. |
| [3] | 郑孟冬, 刘妍, 刘娇娇, 康巧珍, 王婷. 蛋白4.1R对肝细胞HL-7702增殖、凋亡以及糖酵解的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1355-1360. |
| [4] | 王元国, 张鹏. 铁死亡抑制基因在食管癌中的高表达分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1389-1396. |
| [5] | 任志军, 刁建新, 王奕婷. 芎归汤通过抑制氧化应激诱导的心肌凋亡减轻小鼠心梗后心衰引起的心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1416-1424. |
| [6] | 何华星, 刘璐琳, 刘颖茵, 陈纳川, 孙素霞. 丁酸钠与索拉非尼可能通过YAP诱导铁死亡协同抑制肝癌细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1425-1430. |
| [7] | 陈桂玲, 廖晓凤, 孙鹏涛, 岑欢, 舒盛春, 李碧晶, 黎金华. 澳洲茄碱通过调控Bcl-2/Bax/caspase-3信号通路促进非小细胞肺癌发生凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1109-1116. |
| [8] | 房锦存, 刘立威, 林俊豪, 陈逢生. CDHR2过表达通过抑制PI3K/Akt通路抑制乳腺癌细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1117-1125. |
| [9] | 王媛媛, 陈腾, 从小凡, 李依然, 陈蕊, 张配, 孙小锦, 赵素容. 扁蒴藤素通过活性氧调控PI3K/AKT通路增强顺铂诱导鼻咽癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 904-912. |
| [10] | 夏勇生, 王炼, 陈孝华, 张雨路, 孙奥飞, 陈德利. 过表达TSR2通过下调PI3K/AKT信号通路抑制胃癌细胞的增殖和侵袭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 913-919. |
| [11] | 黄秋虎, 周 建, 王子珍, 杨 堃, 陈政纲. miR-26b-3p 靶向 CREB1 调控神经胶质瘤细胞的增殖、迁移及侵袭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 578-584. |
| [12] | 朱 瑾, 欧阳欣, 刘 屿, 钱叶梅, 夏 斌, 施延安, 俞力夫. miR-132-3p/CAMTA1对I-125粒子处理的面神经损伤大鼠施万细胞的调控作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 571-577. |
| [13] | 沈梦迪, 赵 娜, 邓晓晶, 邓 敏. COX6B2在胃癌组织中高表达并影响患者的远期预后:基于抑制p53信号调控胃癌细胞的增殖及细胞周期[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 289-297. |
| [14] | 王 娟, 杨雯钦, 刘 进, 石金凤, 肖 萍, 李美香. 脂联素通过上调PPARα/HOXA10通路改善多囊卵巢综合征大鼠的子宫内膜容受性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 298-307. |
| [15] | 张 诺, 张 震, 张雨路, 宋 雪, 张小凤, 李 静, 左芦根, 胡建国. PCID2在胃癌组织中高表达并通过调控细胞周期进程和增殖影响患者预后[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 324-332. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||