南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 904-912.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.05.12
王媛媛( ), 陈腾, 从小凡, 李依然, 陈蕊, 张配, 孙小锦(
), 陈腾, 从小凡, 李依然, 陈蕊, 张配, 孙小锦( ), 赵素容(
), 赵素容( )
)
收稿日期:2023-12-20
出版日期:2024-05-20
发布日期:2024-06-06
通讯作者:
孙小锦,赵素容
E-mail:wangyy0424@163.com;aijosxj@163.com;inwindangel@qq.com
作者简介:王媛媛,硕士,E-mail: wangyy0424@163.com
基金资助:
Yuanyuan WANG( ), Teng CHEN, Xiaofan CONG, Yiran LI, Rui CHEN, Pei ZHANG, Xiaojin SUN(
), Teng CHEN, Xiaofan CONG, Yiran LI, Rui CHEN, Pei ZHANG, Xiaojin SUN( ), Surong ZHAO(
), Surong ZHAO( )
)
Received:2023-12-20
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-06-06
Contact:
Xiaojin SUN, Surong ZHAO
E-mail:wangyy0424@163.com;aijosxj@163.com;inwindangel@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 观察扁蒴藤素和顺铂对鼻咽癌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响,并探讨其作用机制。 方法 CCK-8法检测不同浓度扁蒴藤素、顺铂处理24 h后HNE-1和CNE-2Z细胞的存活率,集落形成实验观察细胞集落形成能力,流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡和活性氧(ROS)水平,Western blotting检测蛋白表达。N-乙酰半胱氨酸(NAC)预处理后,检测细胞增殖、凋亡及通路的影响。 结果 CCK-8结果显示,扁蒴藤素和顺铂均可抑制HNE-1和CNE-2Z细胞的存活率(P<0.05)。与单用扁蒴藤素或顺铂相比,联合使用明显抑制细胞存活率和细胞集落形成能力(P<0.05),升高细胞凋亡率(P<0.01)和细胞内ROS水平(P<0.01),上调Bax、Cleaved caspase-3和Cleaved PARP的表达(P<0.05),下调Bcl-2、Mcl-1和PARP的表达(P<0.05),同时,下调细胞中p-PI3K和p-AKT的表达(P<0.05)。而NAC可部分逆转扁蒴藤素联合顺铂对HNE-1和CNE-2Z细胞的增殖抑制(P<0.01)和凋亡诱导作用(P<0.05),部分恢复p-PI3K和p-AKT的下调作用(P<0.05)。 结论 扁蒴藤素能增强鼻咽癌细胞对顺铂的增殖抑制和凋亡诱导作用,其机制可能与ROS介导的PI3K/AKT信号通路失活有关。
王媛媛, 陈腾, 从小凡, 李依然, 陈蕊, 张配, 孙小锦, 赵素容. 扁蒴藤素通过活性氧调控PI3K/AKT通路增强顺铂诱导鼻咽癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 904-912.
Yuanyuan WANG, Teng CHEN, Xiaofan CONG, Yiran LI, Rui CHEN, Pei ZHANG, Xiaojin SUN, Surong ZHAO. Pristimerin enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via ROS-mediated deactivation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 904-912.
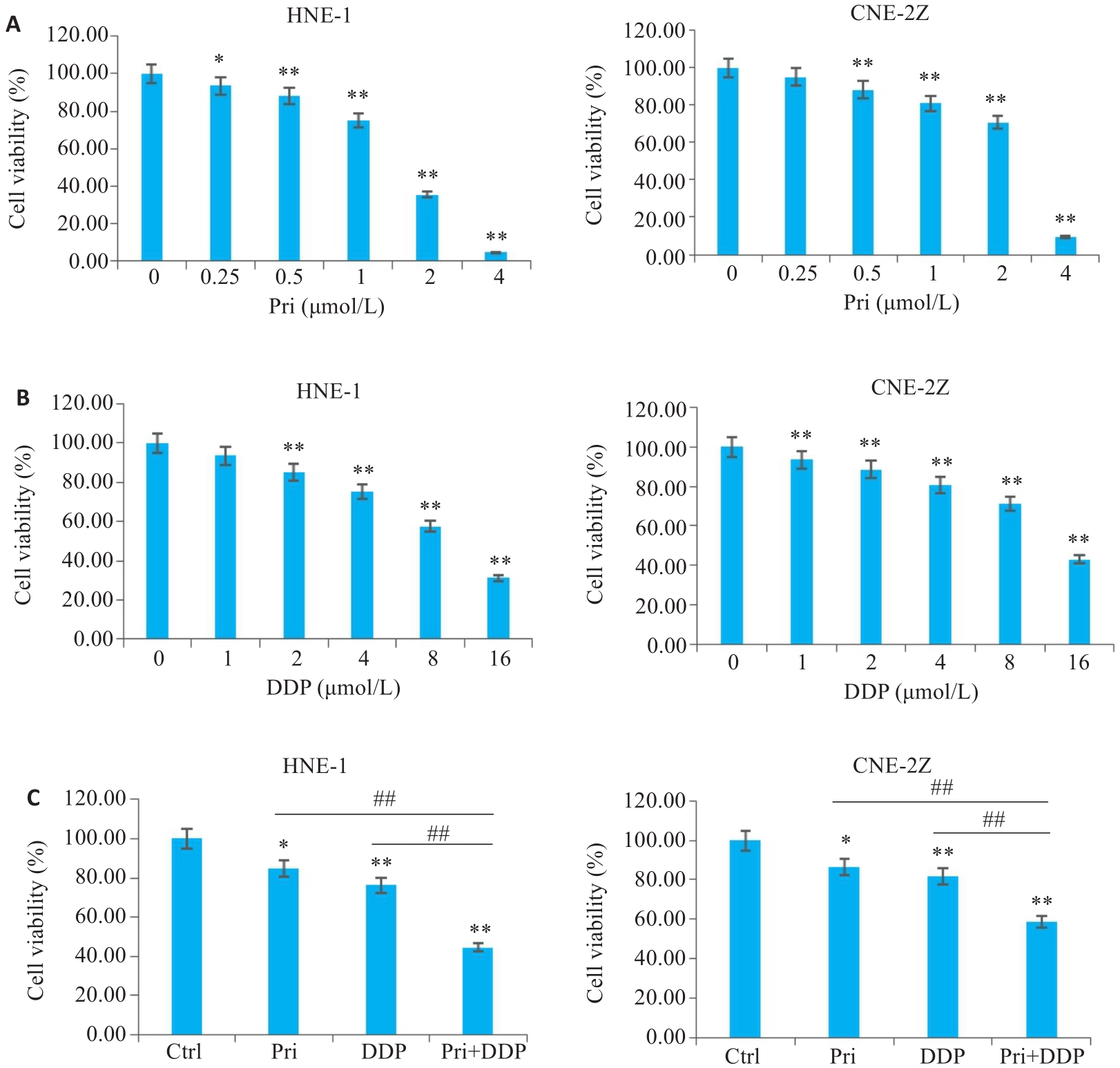
图1 扁蒴藤素和/或顺铂对鼻咽癌细胞活力的影响
Fig.1 Effect of pristimerin (Pri) and/or cisplatin (DDP) on viability of HNE-1 and CNE-2Z cells. A: CCK-8 assay for detecting viability of HNE-1 and CNE-2Z cells with Pri treatment. B: CCK-8 assay for detecting viability of HNE-1 and CNE-2Z cells with DDP treatment. C: CCK-8 assay for detecting viability of HNE-1 and CNE-2Z cells treated with Pri, DDP or their combination. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Ctrl group, ##P<0.01.
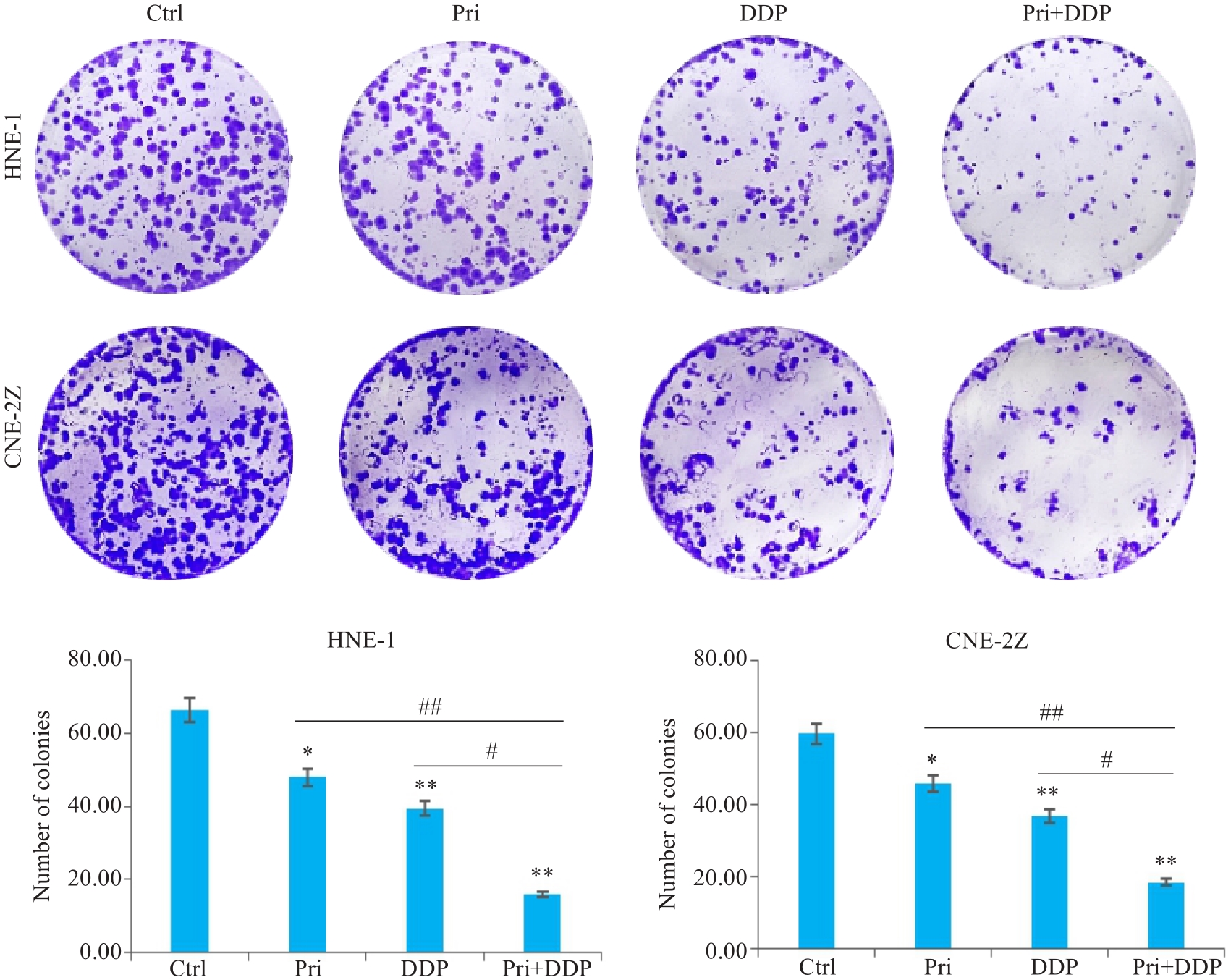
图2 扁蒴藤素联合顺铂对鼻咽癌细胞集落形成的影响
Fig.2 Effect of Pri combined with DDP on colony formation in HNE-1 and CNE-2Z cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Ctrl group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs Pri or DDP group.
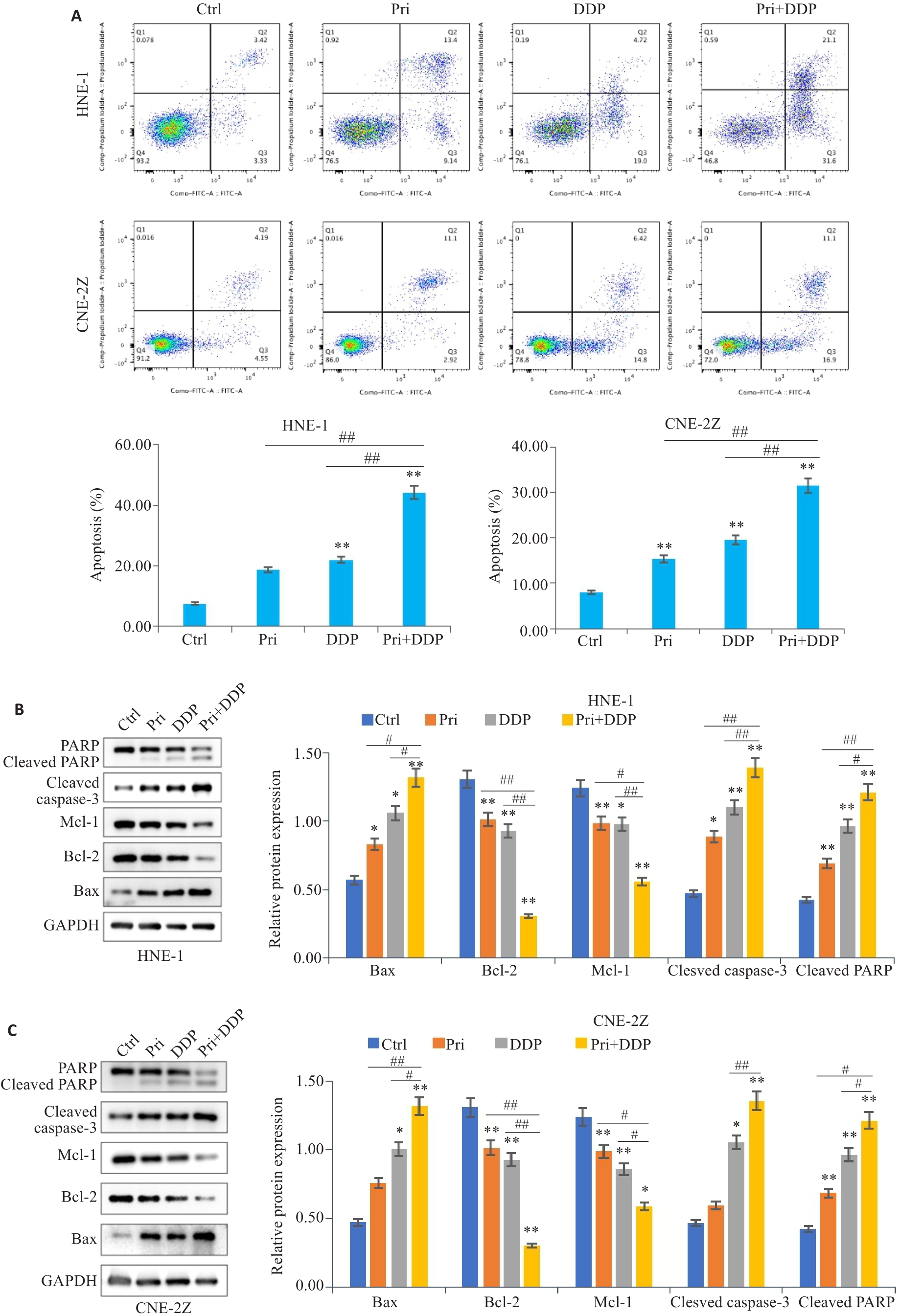
图3 扁蒴藤素联合顺铂对鼻咽癌细胞凋亡的影响
Fig.3 Effect of Pri combined with DDP on apoptosis of HNE-1 and CNE-2Z cells. A: Apoptosis of HNE-1 and CNE-2Z cells treated with Pri and/or DDP for 24 h detected by flow cytometry. B: Expressions of Bax, Bcl-2, Mcl-1, cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved PARP in HNE-1 cells detected by Western blotting. C: Expressions of Bax, Bcl-2, Mcl-1, cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved PARP in CNE-2Z cells detected by Western blotting. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Ctrl group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs Pri or DDP group.
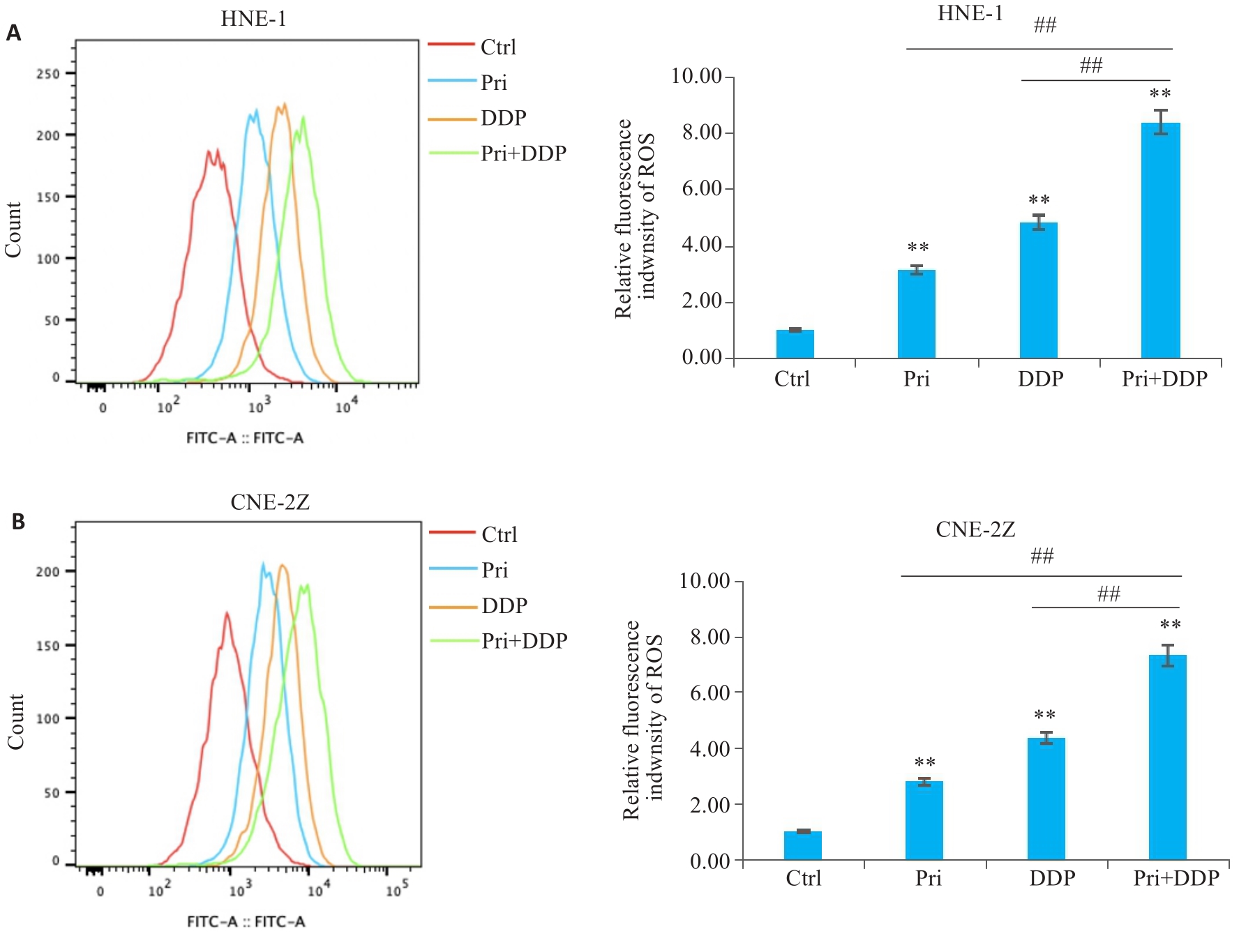
图4 扁蒴藤素联合顺铂对鼻咽癌细胞ROS水平的影响
Fig.4 Effect of Pri combined with DDP on ROS levels in HNE-1 and CNE-2Z cells. A: ROS level of HNE-1 cells treated with Pri or DDP or their combination for 24 h detected by flow cytometry. B: ROS level in CNE-2Z cells treated with Pri or DDP or their combination for 24 h detected by flow cytometry. **P<0.01 vs Ctrl group; ##P<0.01.
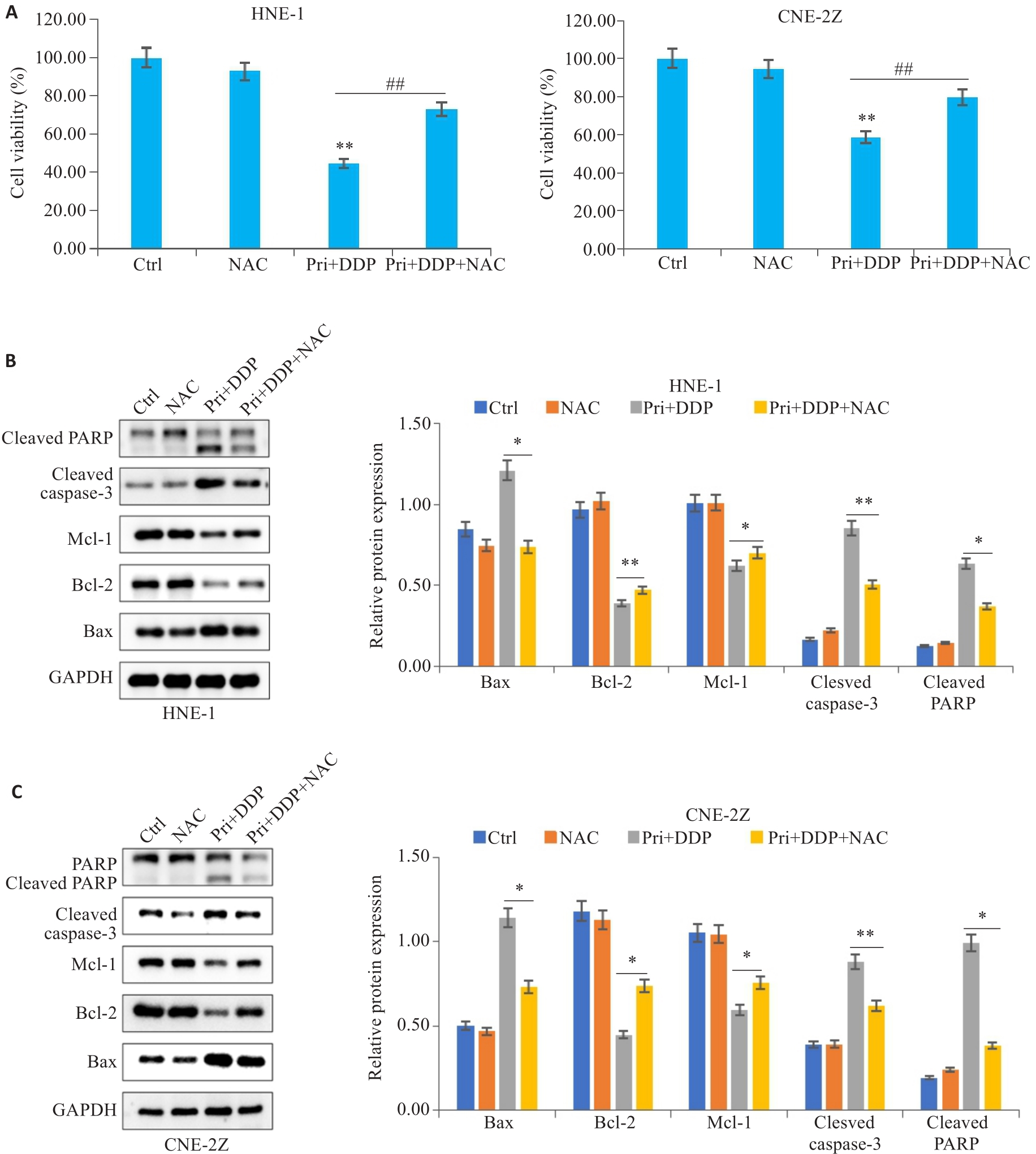
图5 ROS参与扁蒴藤素联合顺铂对鼻咽癌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响
Fig.5 ROS was involved in mediating the effect of Pri combined with DDP on proliferation and apoptosis in HNE-1 and CNE-2Z cells. A: CCK-8 assay for detecting viability of HNE-1 and CNE-2Z cells treated with NAC followed by Pri combined with DDP. **P<0.01vs Ctrl group, ##P<0.01 vs Pri+DDP group. B, C: Protein levels of Bax, Bcl-2, Mcl-1, cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved PARP in HNE-1 cells and CNE-2Z cells detected by Western blotting. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Pri+DDP group.
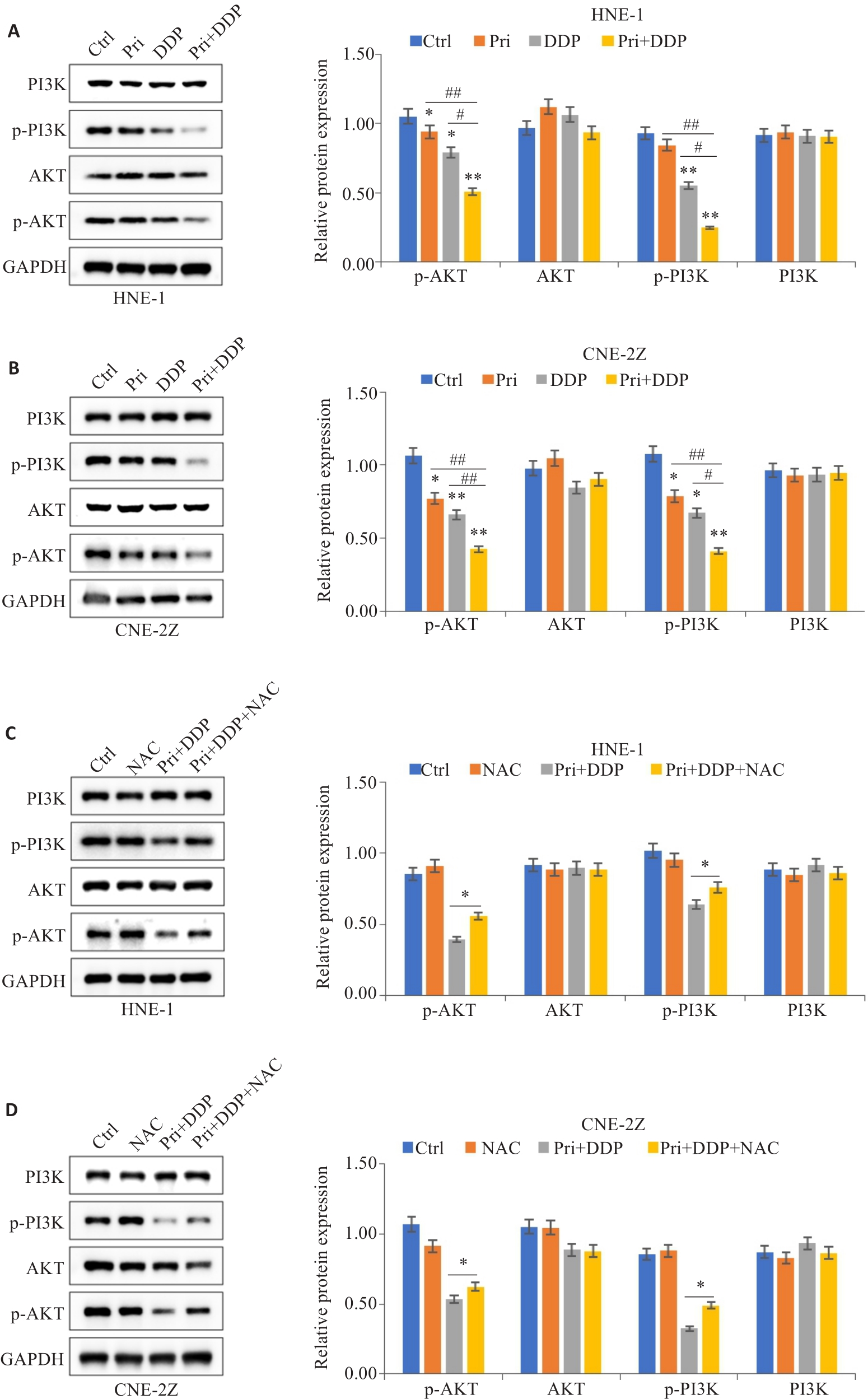
图6 扁蒴藤素联合顺铂对PI3K/AKT信号通路相关蛋白表达的影响
Fig.6 Effect of Pri combined with DDP on expression of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway-related proteins in HNE-1 and CNE-2Z cells. A, B: Protein expression levels of PI3K, AKT, p-PI3K and p-AKT in HNE-1 cells and CNE-2Z cells detected by Western blotting. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Ctrl group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs Pri or DDP group. C, D: Western blotting of protein expression levels of PI3K, AKT, p-PI3K and p-AKT in HNE-1 cells and CNE-2Z cells with NAC pretreatment. *P<0.05 vs Pri+DDP group.
| 1 | Chen YP, Chan ATC, Le QT, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Lancet, 2019, 394(10192): 64-80. |
| 2 | Wong KCW, Hui EP, Lo KW, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an evolving paradigm[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2021, 18(11): 679-95. |
| 3 | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-49. |
| 4 | Huang HG, Yao YY, Deng XY, et al. Immunotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: current status and prospects (Review)[J]. Int J Oncol, 2023, 63(2): 97. |
| 5 | Chen L, Zhang Y, Lai SZ, et al. 10-year results of therapeutic ratio by intensity-modulated radiotherapy versus two-dimensional radiotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Oncologist, 2019, 24(1): e38-45. |
| 6 | 许艳芳, 王振国, 王倩倩. 局部晚期鼻咽癌的治疗研究进展[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2022, 30(14): 2642-6. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2022.14.035 |
| 7 | Guan SZ, Wei JR, Huang LK, et al. Chemotherapy and chemo-resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2020, 207: 112758. |
| 8 | Hong XH, Li Q, Li JY, et al. CircIPO7 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis and cisplatin chemoresistance by facilitating YBX1 nuclear localization[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 28(20): 4521-35. |
| 9 | Wang YZ, Feng WK, Wang XZ, et al. The multifaceted mechanisms of pristimerin in the treatment of tumors state-of-the-art[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2022, 154: 113575. |
| 10 | Zhao Q, Bi Y, Zhong J, et al. Pristimerin suppresses colorectal cancer through inhibiting inflammatory responses and Wnt/β-catenin signaling[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2020, 386: 114813. |
| 11 | Li JJ, Yan YY, Sun HM, et al. Anti-cancer effects of pristimerin and the mechanisms: a critical review[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 746. |
| 12 | Li JJ, Guo QR, Lei XP, et al. Pristimerin induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation, migration in H1299 Lung Cancer Cells[J]. J Cancer, 2020, 11(21): 6348-55. |
| 13 | Zhao Q, Liu YX, Zhong J, et al. Pristimerin induces apoptosis and autophagy via activation of ROS/ASK1/JNK pathway in human breast cancer in vitro and in vivo [J]. Cell Death Discov, 2019, 5: 125. |
| 14 | Yousef BA, Hassan HM, Guerram M, et al. Pristimerin inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion, and induces apoptosis in HCT-116 colorectal cancer cells[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2016, 79: 112-9. |
| 15 | Jiang ZZ, Zhao Y, Zhao Y, et al. Pristimerin synergizes with gemcitabine through abrogating Chk1/53BP1-mediated DNA repair in pancreatic cancer cells[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2021, 147: 111919. |
| 16 | Tang YB, Chen J, Li JQ, et al. Pristimerin synergistically sensitizes conditionally reprogrammed patient derived-primary hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib through endoplasmic reticulum stress and ROS generation by modulating Akt/FoxO1/p27kip1 signaling pathway[J]. Phytomedicine, 2021, 86: 153563. |
| 17 | Zhang YB, Wang JQ, Hui BN, et al. Pristimerin enhances the effect of cisplatin by inhibiting the miR-23a/Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway and suppressing autophagy in lung cancer cells[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2019, 43(3): 1382-94. |
| 18 | Cheung EC, Vousden KH. The role of ROS in tumour development and progression[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2022, 22(5): 280-97. |
| 19 | Aggarwal V, Tuli HS, Varol A, et al. Role of reactive oxygen species in cancer progression: molecular mechanisms and recent advancements[J]. Biomolecules, 2019, 9(11): 735. |
| 20 | Wang CC, Guo J, Wu ZA. Combinative treatment of Curdione and docetaxel triggers reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated intrinsic apoptosis of triple-negative breast cancer cells[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12(2): 10037-48. |
| 21 | Li BQ, Shao HL, Gao L, et al. Nano-drug co-delivery system of natural active ingredients and chemotherapy drugs for cancer treatment: a review[J]. Drug Deliv, 2022, 29(1): 2130-61. |
| 22 | Sahoo BM, Banik BK, Borah P, et al. Reactive oxygen species (ROS): key components in cancer therapies[J]. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 2022, 22(2): 215-22. |
| 23 | Wei F, Nian Q, Zhao MY, et al. Natural products and mitochondrial allies in colorectal cancer therapy[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2023, 167: 115473-8. |
| 24 | Park C, Cha HJ, Lee H, et al. Induction of G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by genistein in human bladder cancer T24 cells through inhibition of the ROS-dependent PI3k/akt signal transduction pathway[J]. Antioxidants, 2019, 8(9): 327-33. |
| 25 | Yang C, Song J, Hwang S, et al. Apigenin enhances apoptosis induction by 5-fluorouracil through regulation of thymidylate synthase in colorectal cancer cells[J]. Redox Biol, 2021, 47: 102144-9. |
| 26 | Xu BQ, Li JD, Chen XL, et al. Puerarin attenuates cisplatin-induced apoptosis of hair cells through the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res, 2022, 1869(4): 119208-16. |
| 27 | Geng YD, Liu P, Xie YB, et al. Xanthatin suppresses pancreatic cancer cell growth via the ROS/RBL1 signaling pathway: in vitro and in vivo insights[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 119: 155004-13. |
| 28 | Fan XQ, Xie XN, Yang M, et al. YBX3 mediates the metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via PI3K/AKT signaling[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 617621-7. |
| 29 | Bo S, Lai J, Lin H, et al. Purpurin, a anthraquinone induces ROS-mediated A549 lung cancer cell apoptosis via inhibition of PI3K/AKT and proliferation[J]. J Pharm Pharmacol, 2021, 73(8): 1101-8. |
| 30 | Liao XZ, Tao LT, Liu JH, et al. Matrine combined with cisplatin synergistically inhibited urothelial bladder cancer cells via down-regulating VEGF/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2017, 17: 124-32. |
| 31 | Liu YH, Shi CJ, He Z, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT signaling via ROS regulation is involved in Rhein-induced apoptosis and enhancement of oxaliplatin sensitivity in pancreatic cancer cells[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2021, 17(2): 589-602. |
| 32 | Zhang P, Zhao SR, Lu XY, et al. Metformin enhances the sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to cisplatin through ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Gene, 2020, 745: 144623-9. |
| [1] | 梁梓琛, 余常辉, 梁世秀, 周梓聪, 周子丽, 孟晓静, 邹 飞, 蔡绍曦. 桔梗素D通过下调成纤维细胞TRPC6表达改善小鼠肺纤维化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 60-69. |
| [2] | 朱 权, 黄柏胜, 位磊艳, 罗奇志. 过表达LncRNA MEG3通过促进铁死亡增强肝癌细胞对顺铂的化疗敏感性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 17-24. |
| [3] | 刘 芳, 彭岚竹, 席菁乐. 高表达MYH9通过激活AKT/c-Myc通路抑制非小细胞肺癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(4): 527-536. |
| [4] | 张浩轩, 陆 进, 蒋成义, 方美芳. 基于人工智能技术的鼻咽癌风险预测模型的构建与评价[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 271-279. |
| [5] | 高晓阳, 赵晓璐, 张春艳, 颜羽昕, 金 蓉, 马月宏. 槲皮素诱导肝星状细胞凋亡:基于调控miR-146影响PI3K/Akt信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1725-1733. |
| [6] | 胡 桐, 勾文峰, 任中昊, 刘改廷, 李祎亮, 左代英, 侯文彬. 淫羊藿素通过调控铁死亡增加鼻咽癌细胞的放射敏感性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1665-1673. |
| [7] | 范晓丽, 王 娟, 王梨明. 甘草查尔酮A通过调控PI3K/AKT信号通路诱导肺鳞癌细胞周期阻滞[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(1): 111-116. |
| [8] | 张恒毅, 庞金龙, 张语涵, 马 月, 范方田, 刘 浩. AZD9291通过抑制PI3K-AKT-mTOR通路抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(9): 1403-1409. |
| [9] | 周兰柱, 吴 俊, 张明洁 , 赵 报 , 马士崟. PRMT1通过促进RRM2表达抑制鼻咽癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(12): 1783-1790. |
| [10] | 梁小芳, 杨 越, 徐帅帅, 刘 映, 褚晗玉, 唐 艳, 杨 飞. 微囊藻毒素-LR长期低剂量暴露诱导小鼠肾脏结构和功能损伤:基于激活PI3K/AKT信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(10): 1486-1494. |
| [11] | 刘见荣, 沈卫星, 程海波, 范旻旻, 肖 君, 徐长亮, 谭佳妮, 赖岳阳, 余成涛, 孙东东, 李 柳. 参白解毒方显著抑制小鼠结直肠腺瘤的形成及癌变: 基于PTEN/PI3K/AKT通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(10): 1452-1461. |
| [12] | 冯苑仪, 羊冬梅, 智喜梅, 邓海鸥, 张伟杰, 王瑞雪, 吴 文. 活性氧与铁死亡通路相互作用在丙酮醛引起的小鼠胚胎成骨细胞损伤中起重要作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(1): 108-115. |
| [13] | 高莉莉, 张 雄, 窦思雨, 岳小丁, 杨捷玲. 干扰长链编码RNA FOXCUT能抑制鼻咽癌细胞上皮间质转化及诱导线粒体损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(9): 1334-1341. |
| [14] | 王文忠, 周兰柱, 孙 哲, 吴 俊, 崔忆旋. TRIM59靶向调控PPM1B对鼻咽癌侵袭和迁移的作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(7): 1030-1036. |
| [15] | 吴胜男, 张 露, 樊红莲, 黄艳平, 宗巧凤, 高 琴, 李正红. PI3K/Akt通路在内吗啡肽-1后处理减轻大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤中的作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(6): 870-875. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||