南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 1545-1552.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.08.13
收稿日期:2024-05-06
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-09-06
通讯作者:
吴兴旺
E-mail:ls1603814410@163.com;duobi2004@126.com
作者简介:刘 硕,E-mail: ls1603814410@163.com
基金资助:
Shuo LIU1( ), Jing LI2,3, Xingwang WU4(
), Jing LI2,3, Xingwang WU4( )
)
Received:2024-05-06
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-09-06
Contact:
Xingwang WU
E-mail:ls1603814410@163.com;duobi2004@126.com
摘要:
目的 本研究旨在探讨Swertiamarin(STM)通过拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡改善CD样结肠炎的作用和机制。 方法 体外建立TNF-α刺激的Caco-2细胞凋亡模型,分为3组:对照组(Con)、TNF-α刺激组(TNF-α)和STM干预组(STM),通过Tunel染色、免疫印迹、免疫荧光和上皮电阻检测等方法,评估STM对细胞凋亡和屏障功能的影响。体内建立TNBS诱导的CD样结肠炎小鼠模型,分为3组:WT、TNBS和STM组,利用小鼠体质量变化、疾病活动指数评分、炎症评分和黏膜组织中炎症因子含量分析STM对结肠炎的作用;通过通透性、细菌移位率和紧密连接蛋白表达与定位观察STM对肠屏障功能的影响;使用Tunel染色和免疫印迹检测凋亡相关蛋白水平评估STM对上皮细胞凋亡的作用。体内外研究验证PI3K/AKT通路在STM抗肠上皮细胞凋亡中的调控作用。 结果 体外研究中TUNEL染色结果显示,STM显著得减少TUNEL着色的Caco-2细胞的比例(P<0.05);免疫印迹数据显示,STM组中cleavedcaspase3和Bax的表达低于TNF-α 组(P<0.05),而Bcl2的水平则增高(P<0.05);肠屏障完整性和功能检测显示,STM恢复了TEER值(P<0.05)、促进了紧密连接蛋白(ZO1和claudin 1)的定位正常化和表达水平的上调(P<0.05),以及抑制了促炎因子(IL-6和CCL3)的表达(P<0.05)。体内研究显示STM能缓解结肠炎和肠屏障功能障碍,具体表现为体重下降、疾病活动指数(DAI)评分、炎症评分和促炎因子(IL-6和CCL3)释放以及肠屏障通透性、结肠TEER、细菌移位和紧密连接蛋白(ZO1和Claudin-1)定位与表达均得到了改善(P<0.05)。机制上,STM在体和体外均抑制了p-PI3K和p-AKT的表达(P<0.05),且PI3K/AKT 通路的激活剂(740YP)阻遏了STM抗TNF-α诱导的Caco-2凋亡作用(P<0.05)。 结论 STM至少部分是通过抑制PI3K/AKT通路的激活,拮抗肠上皮细胞细胞的凋亡,进而改善肠屏障功能障碍和实验性结肠炎。
刘硕, 李静, 吴兴旺. Swertiamarin通过抑制肠上皮细胞细胞凋亡改善TNBS诱导的实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1545-1552.
Shuo LIU, Jing LI, Xingwang WU. Swertiamarin ameliorates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced colitis in mice by inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1545-1552.
| Primers | Forward (5'-3') | Reverse (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | TCTATACCACTTCACAAGTCGGA | GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT |
| CCL3 | CTCCCAGCCAGGTGTCATTTT | CTTGGACCCAGGTCTCTTTGG |
| GAPDH | TGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTAC | GAGTTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCA |
表1 引物序列
Tab.1 Primers Sequence
| Primers | Forward (5'-3') | Reverse (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | TCTATACCACTTCACAAGTCGGA | GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT |
| CCL3 | CTCCCAGCCAGGTGTCATTTT | CTTGGACCCAGGTCTCTTTGG |
| GAPDH | TGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTAC | GAGTTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCA |
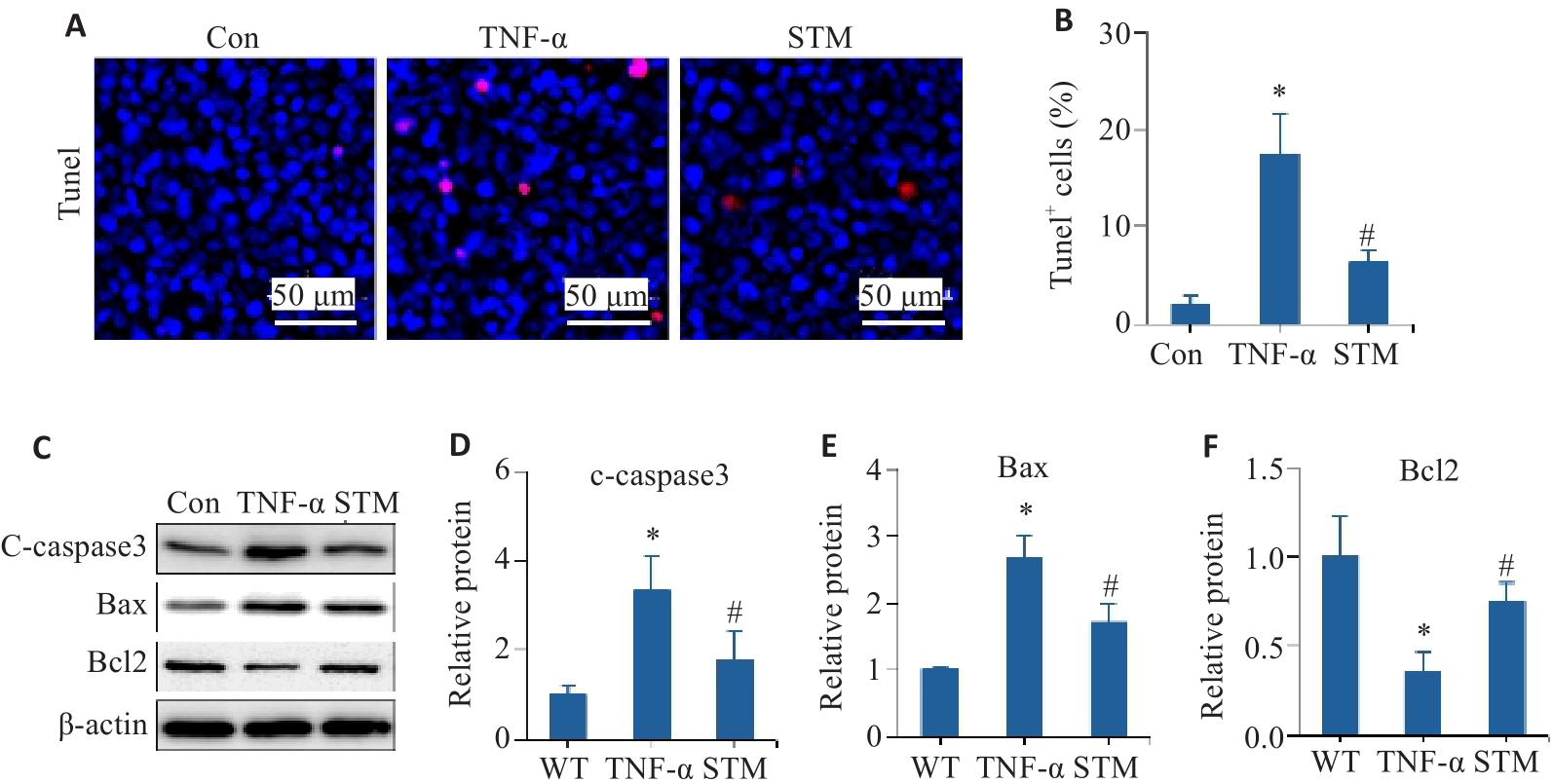
图1 STM对TNF-α诱导的Caco-2细胞凋亡的影响
Fig.1 Effect of STM on TNF-α-induced apoptosis in Caco-2 cells. A, B: Representative images of TUNEL staining and statistical analysis of the positively stained cells. C-F: Levels of c-caspase 3, Bax and Bcl2 detected by Western blotting. *P<0.05 vs Control group/WT group. #P<0.05 vs TNF-α group.
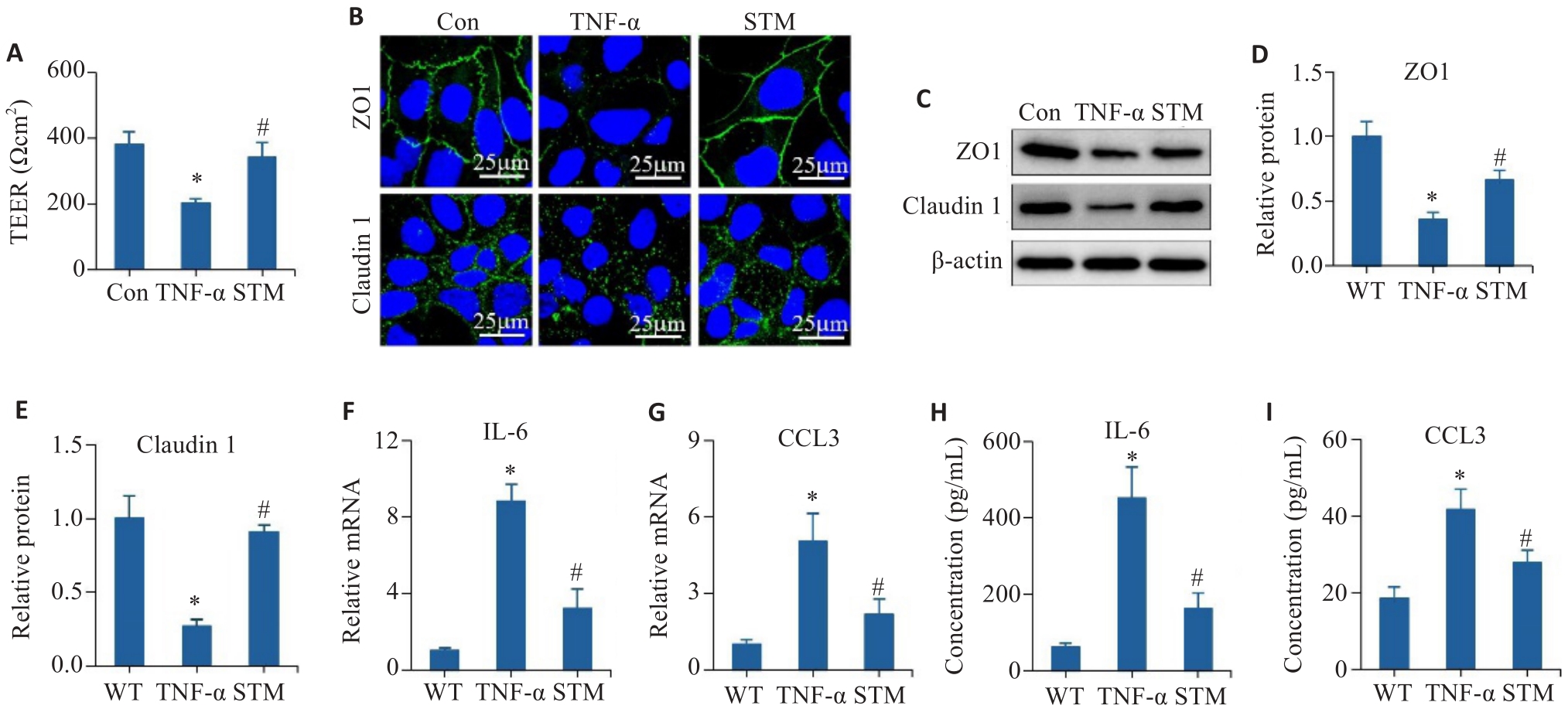
图2 STM对TNF-α诱导的Caco-2细胞的屏障和炎症反应的影响
Fig.2 Effect of STM on TNF-α-induced barrier dysfunction and inflammatory responses in Caco-2 cells. A: Detection of TEER values. B: Immunofluorescence staining of ZO1 and claudin 1. C-E: Levels of ZO1 and claudin 1 detected by Western blotting. F, G: qRT-PCR for detecting expressions of IL-6 and CCL3. H, I: Levels of IL-6 and CCL3 detected by ELISA. *P<0.05 vs Control group, WT group. #P<0.05 vs TNF-α group.
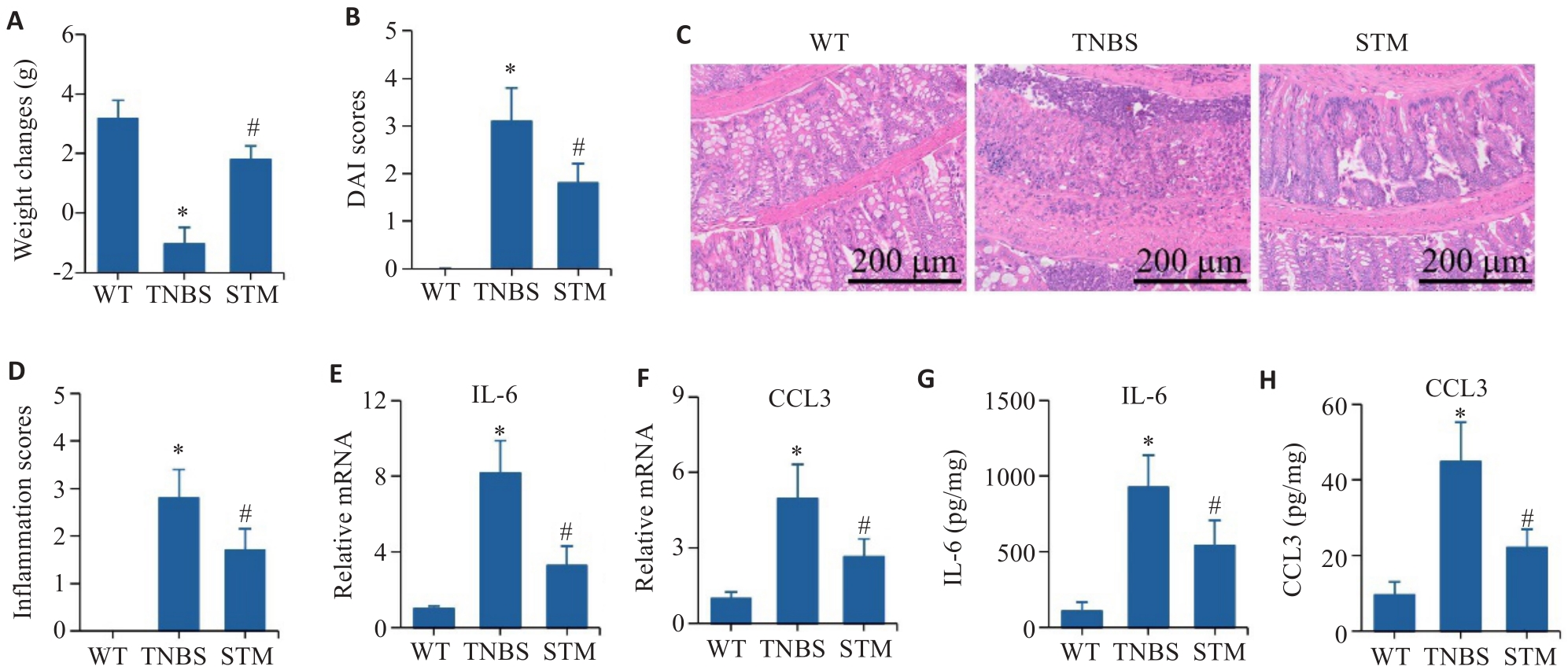
图3 STM对TNBS诱导小鼠的实验性结肠炎影响
Fig.3 Effect of STM on TNBS-induced CD-like colitis in mice. A: Body weight changes of the mice. B: DAI score. C, D: HE staining and inflammation score of the colonic tissue. E, F: qRT-PCR for detecting mRNA expressions of IL-6 and CCL3. G, H: Levels of IL-6 and CCL3 detected by ELISA. *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs TNBS group.
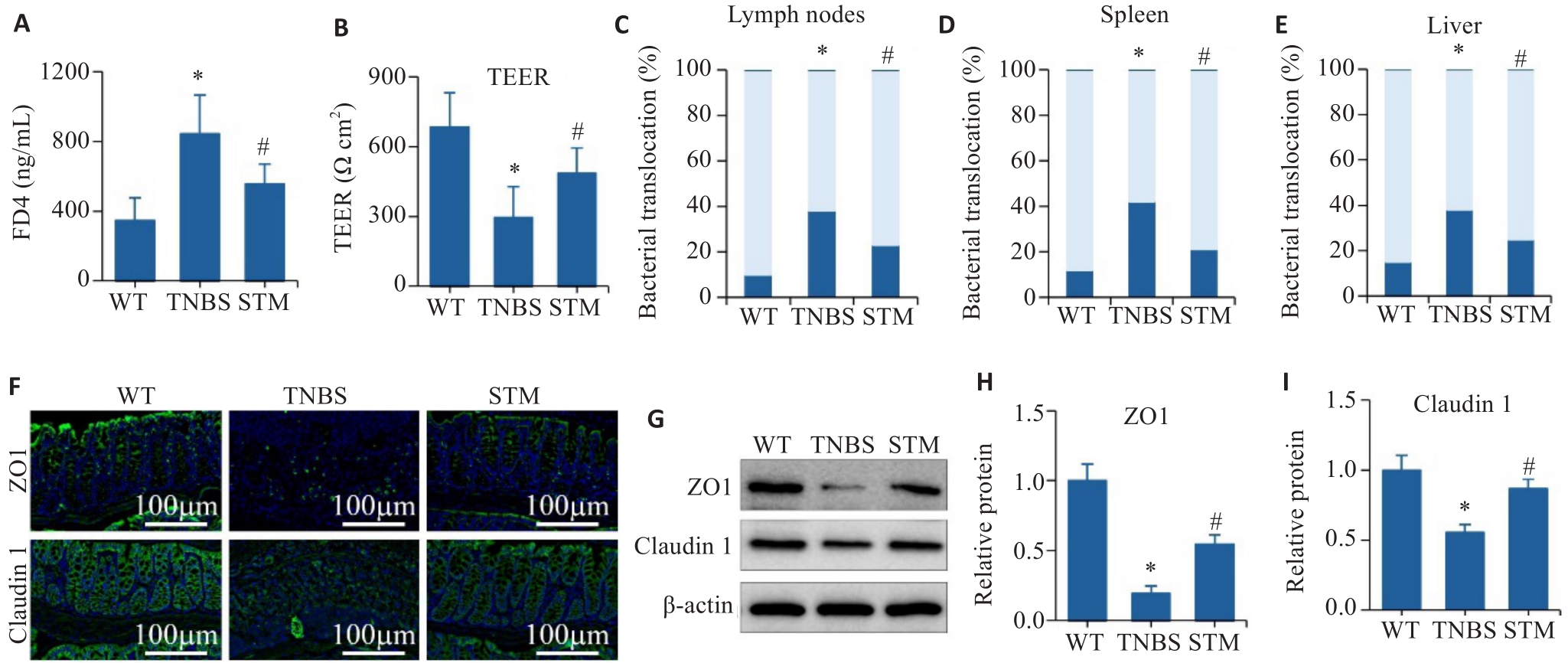
图4 STM对TNBS诱导小鼠肠屏障的影响
Fig.4 Effect of STM on intestinal barrier in TNBS-induced mice. A: Intestinal barrier permeability assay. B: TEER analysis of the colonic tissues. C-E: Assessment of the percentage of bacterial translocation in the intestinal lymph nodes, spleen and liver. F: Immunofluorescence staining of ZO1 and claudin 1. G-I: Levels of ZO1 and claudin 1 detected by Western blotting. *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs TNBS group.
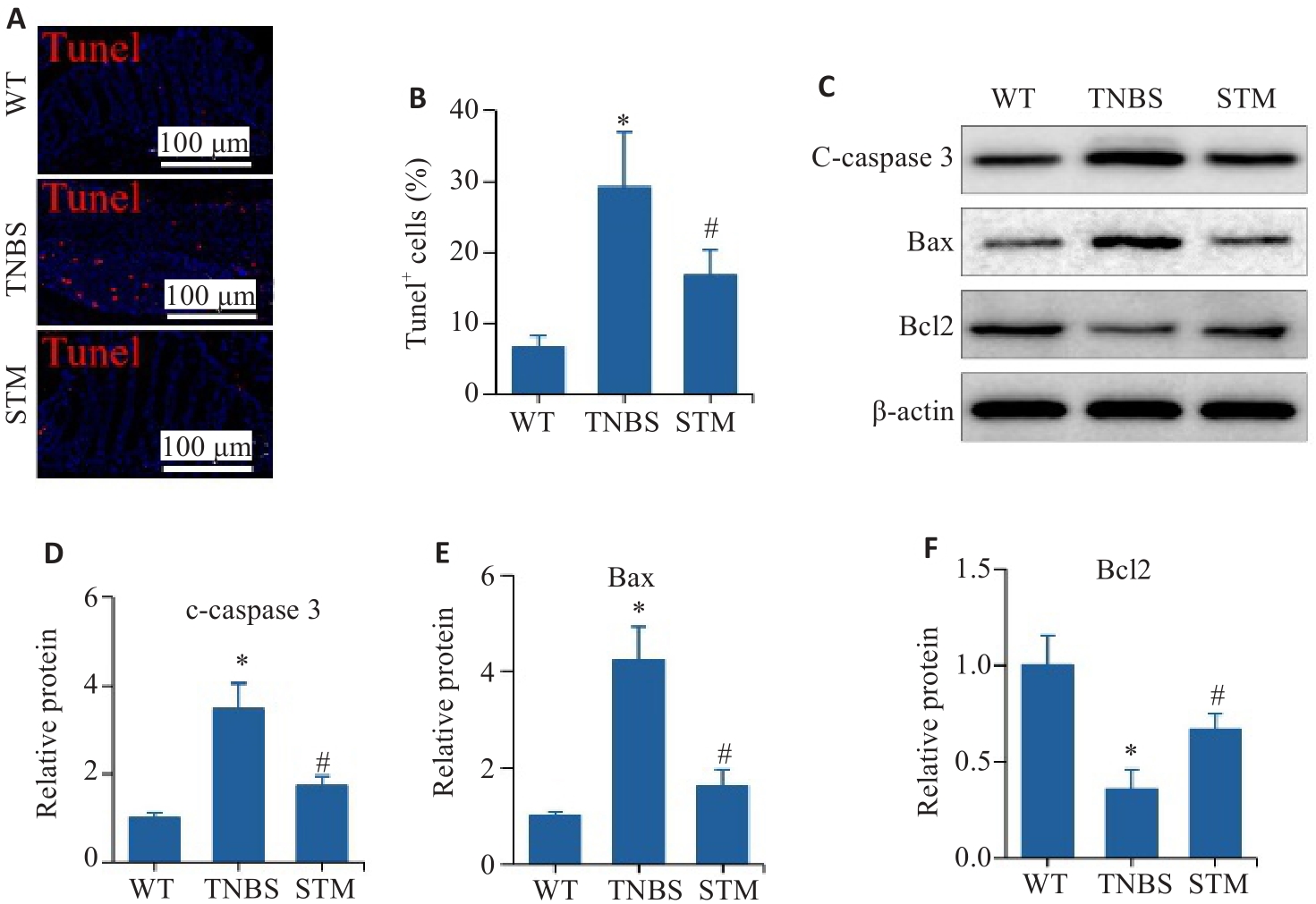
图5 STM对TNBS诱导小鼠结肠组织中肠上皮细胞凋亡的影响
Fig. 5 Effect of STM on apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells in TNBS-induced mice. A, B: Representative image of TUNEL staining and statistical analysis of the positively stained intestinal epithelial cells. C-F: Levels of c-caspase 3, Bax and Bcl2 detected by Western blotting. *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs TNBS group.
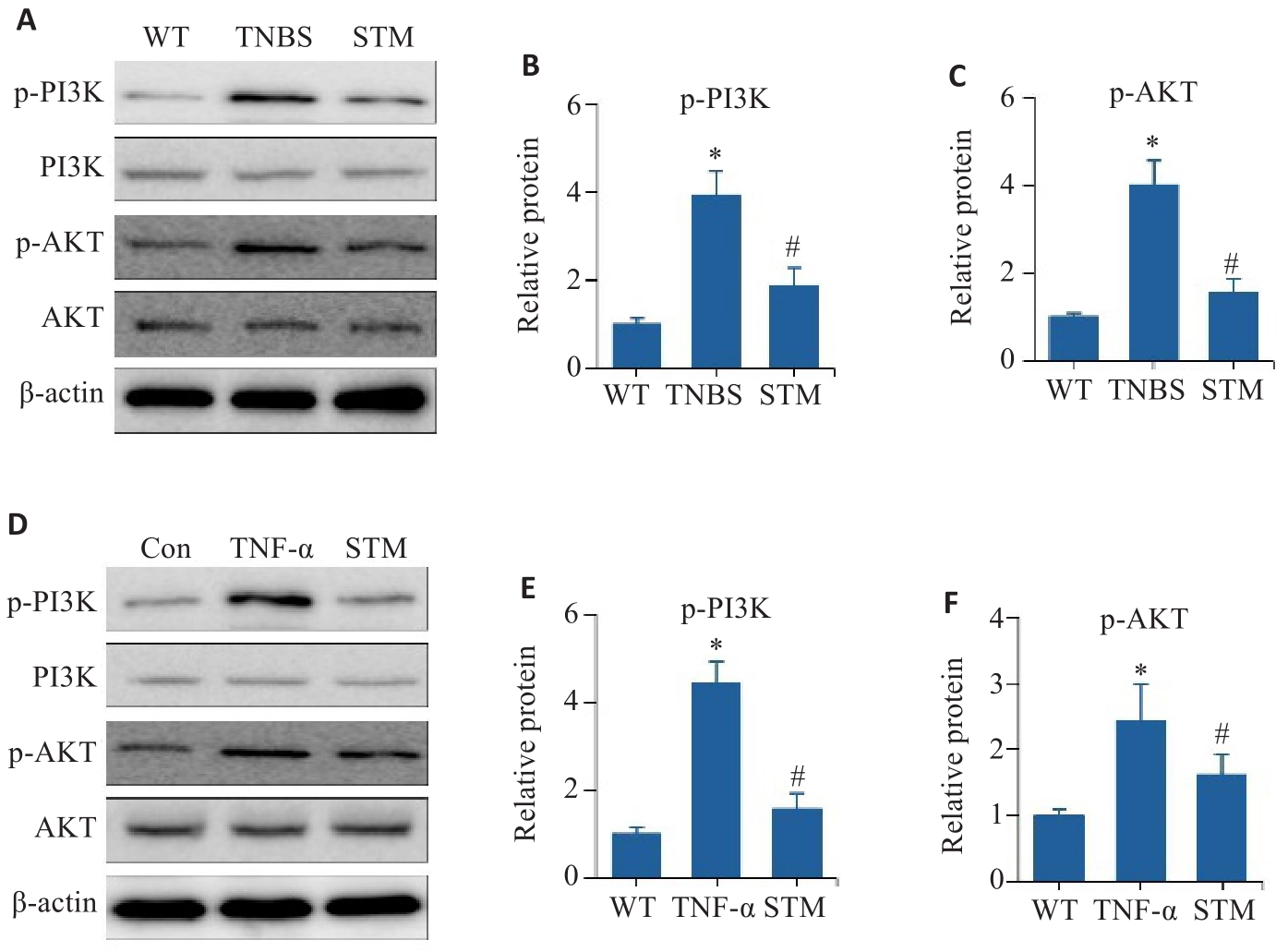
图6 体内外验证STM对PI3K/AKT通路的影响
Fig. 6 In vitro and in vivo experiments for validating the effect of STM on the PI3K/AKT pathway. A-C: Levels of p-PI3K, PI3K, p-AKT and AKT detected in TNF-α-induced Caco-2 cells by Western blotting. D-F: Western blotting for detecting expression levels of p-PI3K, PI3K, p-AKT and AKT in the intestinal mucosal tissues of TNBS-induced mice. *P<0.05 vs WT or Con group. #P<0.05 vs TNBS or TNF-α group.
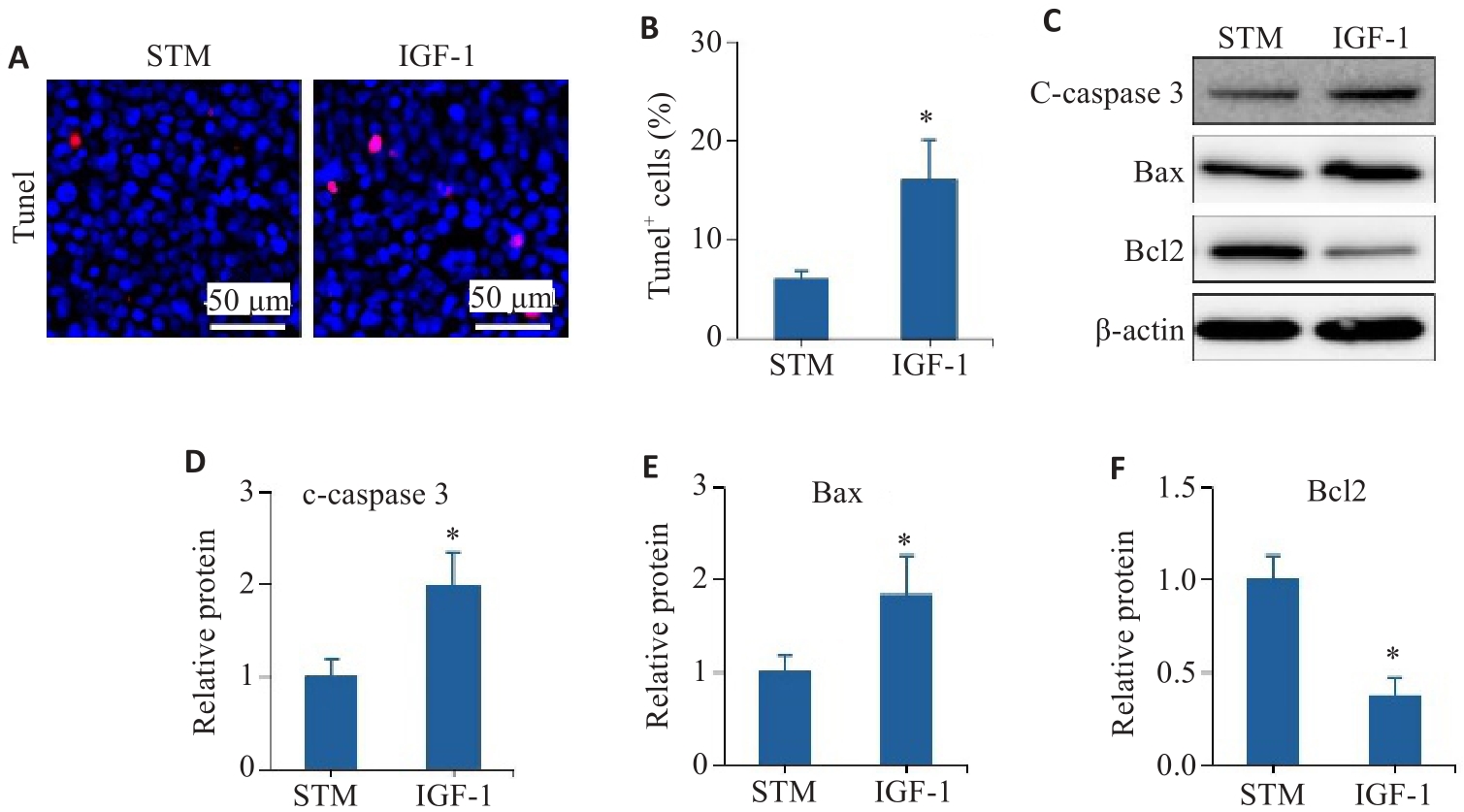
图7 PI3K/AKT通路参与STM抗肠上皮细胞凋亡
Fig.7 The PI3K/AKT pathway is involved in STM-mediated inhibition of intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis. A, B: TUNEL staining and statistical analysis of the positively stained intestinal epithelial cells. C-F: Levels of c-caspase 3, Bax and Bcl2 detected by Western blotting. *P<0.05 vs STM group.
| 1 | Roda G, Chien Ng S, Kotze PG, et al. Crohn’s disease[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2020, 6(1): 22. |
| 2 | Ananthakrishnan AN, Bernstein CN, Iliopoulos D, et al. Environmental triggers in IBD: a review of progress and evidence[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 15(1): 39-49. |
| 3 | Lo BC, Shin SB, Canals Hernaez D, et al. IL-22 preserves gut epithelial integrity and promotes disease remission during chronic Salmonella infection[J]. J Immunol, 2019, 202(3): 956-65. |
| 4 | Deng FH, Peng L, Li ZJ, et al. YAP triggers the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway and promotes enterocyte self-renewal, regeneration and tumorigenesis after DSS-induced injury[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(2): 153. |
| 5 | Stremmel W, Staffer S, Schneider MJ, et al. Genetic mouse models with intestinal-specific tight junction deletion resemble an ulcerative colitis phenotype[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2017, 11(10): 1247-57. |
| 6 | Woznicki JA, Saini, Flood P, et al. TNF-α synergises with IFN-γ to induce caspase-8-JAK1/2-STAT1-dependent death of intestinal epithelial cells[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(10): 864. |
| 7 | Dotti I, Mora-Buch R, Ferrer-Picón E, et al. Alterations in the epithelial stem cell compartment could contribute to permanent changes in the mucosa of patients with ulcerative colitis[J]. Gut, 2017, 66(12): 2069-79. |
| 8 | Zhang J, Cen L, Zhang XF, et al. MPST deficiency promotes intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis and aggravates inflammatory bowel disease via AKT[J]. Redox Biol, 2022, 56: 102469. |
| 9 | Lei H, Yang L, Xu HZ, et al. Ubiquitin-specific protease 47 regulates intestinal inflammation through deubiquitination of TRAF6 in epithelial cells[J]. Sci China Life Sci, 2022, 65(8): 1624-35. |
| 10 | Zhao S, Dejanovic D, Yao P, et al. Selective deletion of MyD88 signaling in α‑SMA positive cells ameliorates experimental intestinal fibrosis via post-transcriptional regulation[J]. Mucosal Immunol, 2020, 13(4): 665-78. |
| 11 | Mao R, Doyon G, Gordon IO, et al. Activated intestinal muscle cells promote preadipocyte migration: a novel mechanism for creeping fat formation in Crohn's disease[J]. Gut, 2022, 71(1): 55-67. |
| 12 | Zhang QR, Chen K, Wu T, et al. Swertiamarin ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic apoptosis via blocking the PI3K/Akt pathway in rats[J]. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol, 2019, 23(1): 21-8. |
| 13 | Saravanan S, Islam VI, Thirugnanasambantham K, et al. Swertiamarin ameliorates inflammation and osteoclastogenesis intermediates in IL-1β induced rat fibroblast-like synoviocytes[J]. Inflamm Res, 2014, 63(6): 451-62. |
| 14 | Yang WJ, Han FH, Gu YP, et al. TGR5 agonist inhibits intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis via cAMP/PKA/c-FLIP/JNK signaling pathway and ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2023, 44(8): 1649-64. |
| 15 | Li R, Shi CR, Wei CT, et al. Fufang Shenhua Tablet inhibits renal fibrosis by inhibiting PI3K/AKT[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 116: 154873. |
| 16 | Zuo LG, Geng ZJ, Song X, et al. Browning of mesenteric white adipose tissue in Crohn's disease: a new pathological change and therapeutic target[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2023, 17(8): 1179-92. |
| 17 | Huang LY, Qian WW, Xu YH, et al. Mesenteric adipose tissue contributes to intestinal fibrosis in Crohn's disease through the ATX-LPA axis[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2022, 16(7): 1124-39. |
| 18 | Shi YJ, Sheng WJ, Xue MT, et al. Effect of morroniside on the transcriptome profiles of rat in injured spinal cords[J]. Gene, 2022, 823: 146338. |
| 19 | Kucharzik T, Ellul P, Greuter T, et al. ECCO guidelines on the prevention, diagnosis, and management of infections in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2021, 15(6): 879-913. |
| 20 | Wang T, Wu SB, Ibrahim IAA, et al. Cardioprotective role of swertiamarin, a plant glycoside against experimentally induced myocardial infarction via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functions[J]. Appl Biochem Biotechnol, 2023, 195(9): 5394-408. |
| 21 | Wang GW, Quan J, Su NR, et al. Proteomic analysis of swertiamarin-treated BV-2 cells and possible implications in neuroinflammation[J]. J Oleo Sci, 2022, 71(3): 395-400. |
| 22 | Patel N, Zinzuvadia A, Prajapati M, et al. Swertiamarin-mediated immune modulation/adaptation confers protection against Plasmodium berghei [J]. Future Microbiol, 2022, 17: 931-41. |
| 23 | Okayasu I, Hatakeyama S, Yamada M, et al. A novel method in the induction of reliable experimental acute and chronic ulcerative colitis in mice[J]. Gastroenterology, 1990, 98(3): 694-702. |
| 24 | Gäbele E, Dostert K, Hofmann C, et al. DSS induced colitis increases portal LPS levels and enhances hepatic inflammation and fibrogenesis in experimental NASH[J]. J Hepatol, 2011, 55(6): 1391-9. |
| 25 | Dong LJ, Xie JW, Wang YY, et al. Mannose ameliorates experimental colitis by protecting intestinal barrier integrity[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 4804. |
| 26 | Kinchen J, Chen HH, Parikh K, et al. Structural remodeling of the human colonic mesenchyme in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Cell, 2018, 175(2): 372-86.e17. |
| 27 | Varani J, McClintock SD, Aslam MN. Cell-matrix interactions contribute to barrier function in human colon organoids[J]. Front Med, 2022, 9: 838975. |
| 28 | Jelinsky SA, Derksen M, Bauman E, et al. Molecular and functional characterization of human intestinal organoids and monolayers for modeling epithelial barrier[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2023, 29(2): 195-206. |
| 29 | Chen SB, Liu HB, Li ZJ, et al. Epithelial PBLD attenuates intestinal inflammatory response and improves intestinal barrier function by inhibiting NF-κB signaling[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(6): 563. |
| 30 | Kuo WT, Shen L, Zuo L, et al. Inflammation-induced occludin downregulation limits epithelial apoptosis by suppressing caspase-3 expression[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 157(5): 1323-37. |
| 31 | Li CC, Gong LQ, Jiang Y, et al. Sanguisorba officinalis ethyl acetate extract attenuates ulcerative colitis through inhibiting PI3K-AKT/NF‑κB/STAT3 pathway uncovered by single-cell RNA sequencing[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 120: 155052. |
| 32 | Kim SM, Park S, Hwang SH, et al. Secreted Akkermansia muciniphila threonyl-tRNA synthetase functions to monitor and modulate immune homeostasis[J]. Cell Host Microbe, 2023, 31(6): 1021-37.e10. |
| 33 | Ma WJ, Long JL, Dong LJ, et al. Uncovering the key pharmacodynamic material basis and possible molecular mechanism of Xiaoke formulation improve insulin resistant through a comprehensive investigation[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 323: 117752. |
| 34 | Stein J, Aksan A, Farrag K, et al. Management of inflammatory bowel disease-related anemia and iron deficiency with specific reference to the role of intravenous iron in current practice[J]. Expert Opin Pharmacother, 2017, 18(16): 1721-37. |
| 35 | Guo BJ, Bian ZX, Qiu HC, et al. Biological and clinical implications of herbal medicine and natural products for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2017, 1401(1): 37-48. |
| 36 | Wan P, Zhu XD, Liu XP, et al. Inhibition of neddylation ameliorates DSS-induced colitis[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2018, 15(6): 649-50. |
| 37 | Mizuta Y, Isomoto H, Takahashi T. Impaired nitrergic innervation in rat colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium[J]. Gastroenterology, 2000, 118(4): 714-23. |
| [1] | 牛民主, 殷丽霞, 乔通, 尹林, 张可妮, 胡建国, 宋传旺, 耿志军, 李静. 旱莲苷A通过调控JAK2/STAT3通路抑制M1型巨噬细胞极化改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1297-1306. |
| [2] | 储菲, 陈孝华, 宋博文, 杨晶晶, 左芦根. 苏荠宁黄酮通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡改善小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 819-828. |
| [3] | 殷丽霞, 牛民主, 张可妮, 耿志军, 胡建国, 李江艳, 李静. 升麻素抑制MAPK通路调节辅助性T细胞免疫平衡改善小鼠克罗恩病样结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 595-602. |
| [4] | 黄菊, 殷丽霞, 牛民主, 耿志军, 左芦根, 李静, 胡建国. 紫花前胡苷通过抑制肠上皮细胞焦亡改善2,4,6-三硝基苯磺酸诱导的小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 261-268. |
| [5] | 周雪利, 李华, 陈青宇, 靳美娜, 李海波, 白炜, 贾楚璇, 魏翠英. 慢性间歇低氧和复氧对大鼠胰岛素抵抗及骨骼肌miR-27a-3p/PPARγ/IRS1/PI3K/AKT表达的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1729-1737. |
| [6] | 房锦存, 刘立威, 林俊豪, 陈逢生. CDHR2过表达通过抑制PI3K/Akt通路抑制乳腺癌细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1117-1125. |
| [7] | 王妍, 阮毓卿, 崔璨, 王秀. 交泰丸通过激活PI3K/AKT信号通路改善阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠大脑的葡萄糖代谢[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 894-903. |
| [8] | 席 进, 张 敏, 张永玉, 张 晨, 张雨路, 王 锐, 申 林, 李 静, 宋 雪. 上调KLF11可改善结肠炎模型小鼠的肠道炎症:基于抑制JAK2/STAT3信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 765-772. |
| [9] | 牛民主, 殷丽霞, 段婷, 黄菊, 李静, 耿志军, 胡建国, 宋传旺. 川续断皂苷VI通过抑制PI3K/AKT/NF-κB通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡缓解TNBS诱导的小鼠克罗恩病样结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2335-2346. |
| [10] | 邵荣瑢, 杨 子, 张文静, 张 诺, 赵雅静, 张小凤, 左芦根, 葛思堂. 茯苓酸缓解小鼠克罗恩病:基于抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 935-942. |
| [11] | 徐文琴, 叶静静, 王 飞, 陈天兵. 吡罗克酮乙醇胺盐通过PI3K/AKT通路破坏胶质瘤细胞的线粒体动力学[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 764-771. |
| [12] | 杨 子, 赵天豪, 程 阳, 周约青, 李岳彤, 王欣茹, 张小凤, 左芦根, 葛思堂. 香叶木素通过调节小鼠的肠道免疫平衡减轻克罗恩病样结肠炎:基于抑制PI3K/AKT通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 474-482. |
| [13] | 王 冰, 黄启林, 李 帅, 吴 俊, 原小惠, 孙红玉, 汤礼军. 鸟苷酸环化酶C在重症急性胰腺炎大鼠相关性肠损伤中的变化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(3): 376-383. |
| [14] | 高 倩,董红霞,李 瑾. 52周英夫利西疗程中第14周中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值可预测克罗恩患者是否对治疗产生失应答[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(04): 453-458. |
| [15] | 姜从桥,朱平胜,时依,项武军,葛思堂,张宗兵,左芦根. 原花青素B2 对三硝基苯磺酸结肠炎模型小鼠肠炎及肠屏障的保护作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(07): 778-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||