南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 542-553.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.12
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-09-10
出版日期:2025-03-20
发布日期:2025-03-28
通讯作者:
沈智勇
E-mail:qingshunjie@163.com;szy2728@163.com
作者简介:庆顺杰,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: qingshunjie@163.com
基金资助:
Shunjie QING( ), Zhiyong SHEN(
), Zhiyong SHEN( )
)
Received:2024-09-10
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
Zhiyong SHEN
E-mail:qingshunjie@163.com;szy2728@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探究己糖激酶2(HK2)在结直肠癌组织中的表达,阐明其生物学功能及机制和对免疫微环境的影响。 方法 使用生物信息学方法分析HK2在结直肠癌组织中的表达水平、预后和对免疫微环境的影响。收集本院8例结直肠癌患者的肿瘤组织及配对癌旁组织,利用免疫组化、Western blotting和RT-qPCR实验验证HK2在结直肠癌中的表达水平。筛选出HK2表达量低的结直肠癌细胞系CT26及HCT116进行慢病毒转染过表达HK2,分为空白对照组和HK2过表达组;使用HK2抑制剂3-BP处理HK2表达量高的结直肠癌细胞系MC38及CACO2;使用JAK/STAT3通路抑制剂处理结直肠癌细胞HK2过表达组。采用CCK-8、平板克隆形成实验、Transwell和小鼠皮下荷瘤实验探究HK2对结直肠癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭能力的影响。通过Western blotting检测HK2过表达对JAK/STAT信号通路蛋白表达的影响。采用MCPcounter和Timer分析HK2表达与肿瘤免疫细胞浸润水平的相关性,TCGA、GEO数据库分析HK2表达与免疫检查点的相关性。 结果 癌症公共数据库显示,HK2在结直肠癌组织中的表达水平高于癌旁组织(P<0.001),并且高表达HK2的结直肠癌患者预后更差(P=0.09)。免疫组化、Western blotting和RT-qPCR结果显示结直肠癌组织的HK2表达水平高于癌旁组织(P<0.01)。相较于其他结直肠癌细胞,CT26和HCT116的HK2表达水平最低(P<0.05),HK2过表达组相较于空白对照组的HK2表达水平上调(P<0.01),且过表达组细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭能力显著提高(P<0.001)。HK2被抑制后肿瘤细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭能力明显被抑制。HK2可促进JAK/STAT信号通路中STAT3磷酸化蛋白的表达,使用JAK/STAT3通路抑制剂能够有效抑制由HK2过表达介导的肿瘤细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭能力的增强。Timer和MCP counter分析显示HK2表达与多种免疫细胞具有相关性,TCGA和GEO数据库分析显示HK2的表达水平与PDCD1等免疫检查点显著正相关(P<0.05)。 结论 HK2在结直肠癌中表达上调,可能通过激活JAK-STAT信号通路促进肿瘤细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭,并调节肿瘤免疫微环境。
庆顺杰, 沈智勇. 过表达己糖激酶2通过激活JAK/STAT途径促进结直肠癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭并调节肿瘤免疫微环境[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 542-553.
Shunjie QING, Zhiyong SHEN. High expression of hexokinase 2 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by activating the JAK/STAT pathway and regulating tumor immune microenvironment[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 542-553.
| Gene | Species | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| HK2 | Human | GAGCCACCACTCACCCTACT | CCAGGCATTCGGCAATGTG |
| Hk2 | Mouse | ATGATCGCCTGCTTATTCACG | CGCCTAGAAATCTCCAGAAGGG |
| GAPDH | Human | GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT | GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG |
| Gapdh | Mouse | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | GGGGTCGTTGATGGCAACA |
表1 引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequence for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Species | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| HK2 | Human | GAGCCACCACTCACCCTACT | CCAGGCATTCGGCAATGTG |
| Hk2 | Mouse | ATGATCGCCTGCTTATTCACG | CGCCTAGAAATCTCCAGAAGGG |
| GAPDH | Human | GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT | GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG |
| Gapdh | Mouse | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | GGGGTCGTTGATGGCAACA |
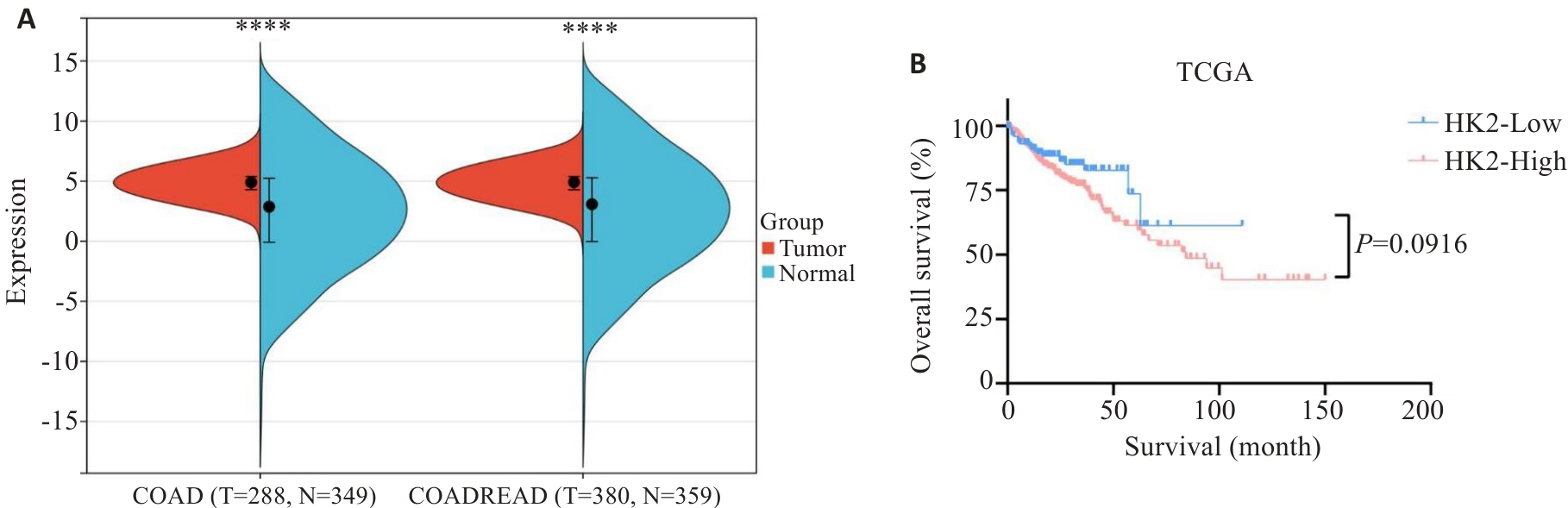
图1 HK2在结直肠癌中的表达及与预后的关系
Fig.1 Expression of HK2 in colorectal cancer and its association with patient prognosis. A: Expression levels of HK2 in colorectal cancer from TCGA databases. B: Kaplan-Meier survival curves of overall survival (OS) for CRC patients stratified by HK2 expression level. ****P<0.0001.
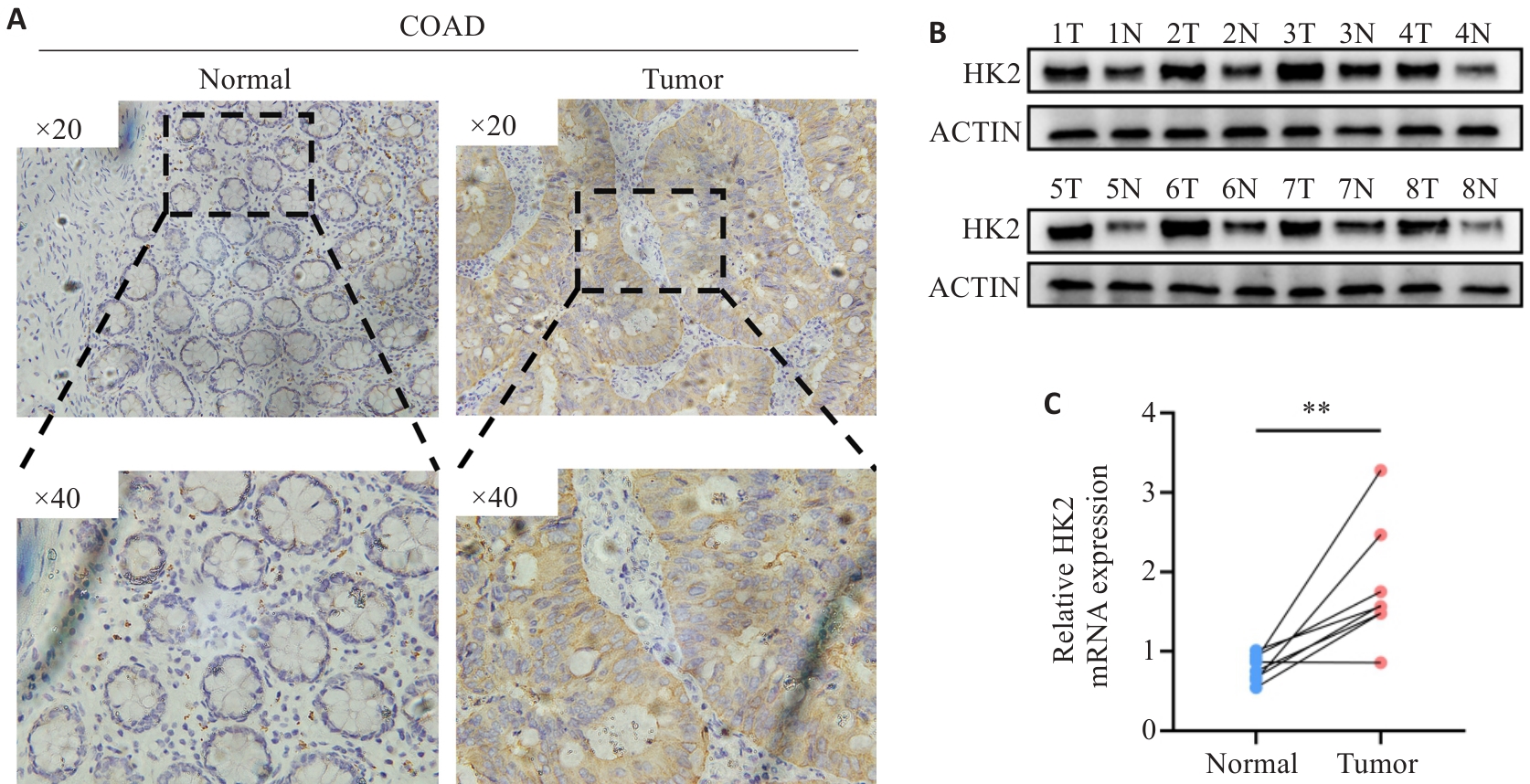
图2 HK2在临床样本组织中的表达
Fig.2 Expression of HK2 in clinical samples of CRC and adjacent tissues. A: Immunohistochemical staining for HK2 expression. B, C: HK2 protein and mRNA expression levels in cancer tissues and adjacent tissues. **P<0.01. T: Tumor; N: Normal.
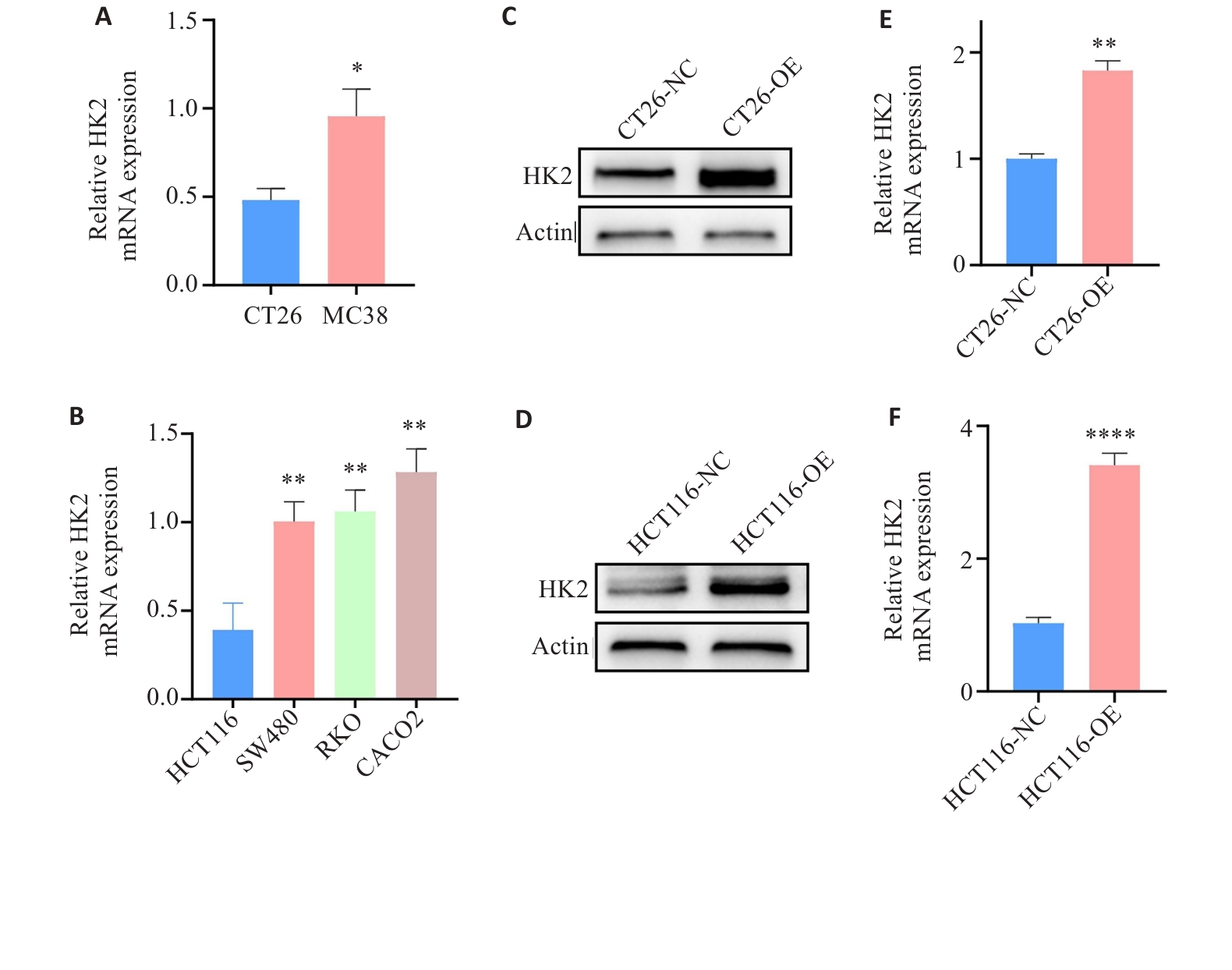
图3 HK2过表达CRC细胞的构建与验证
Fig.3 Construction and validation of HK2-overexpressing CRC cells. A, B: HK2 mRNA expression in CRC cells. C-F: Protein and mRNA expression of HK2 in CT26 and HCT116 cells after lentivirus-mediated transfection. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001.
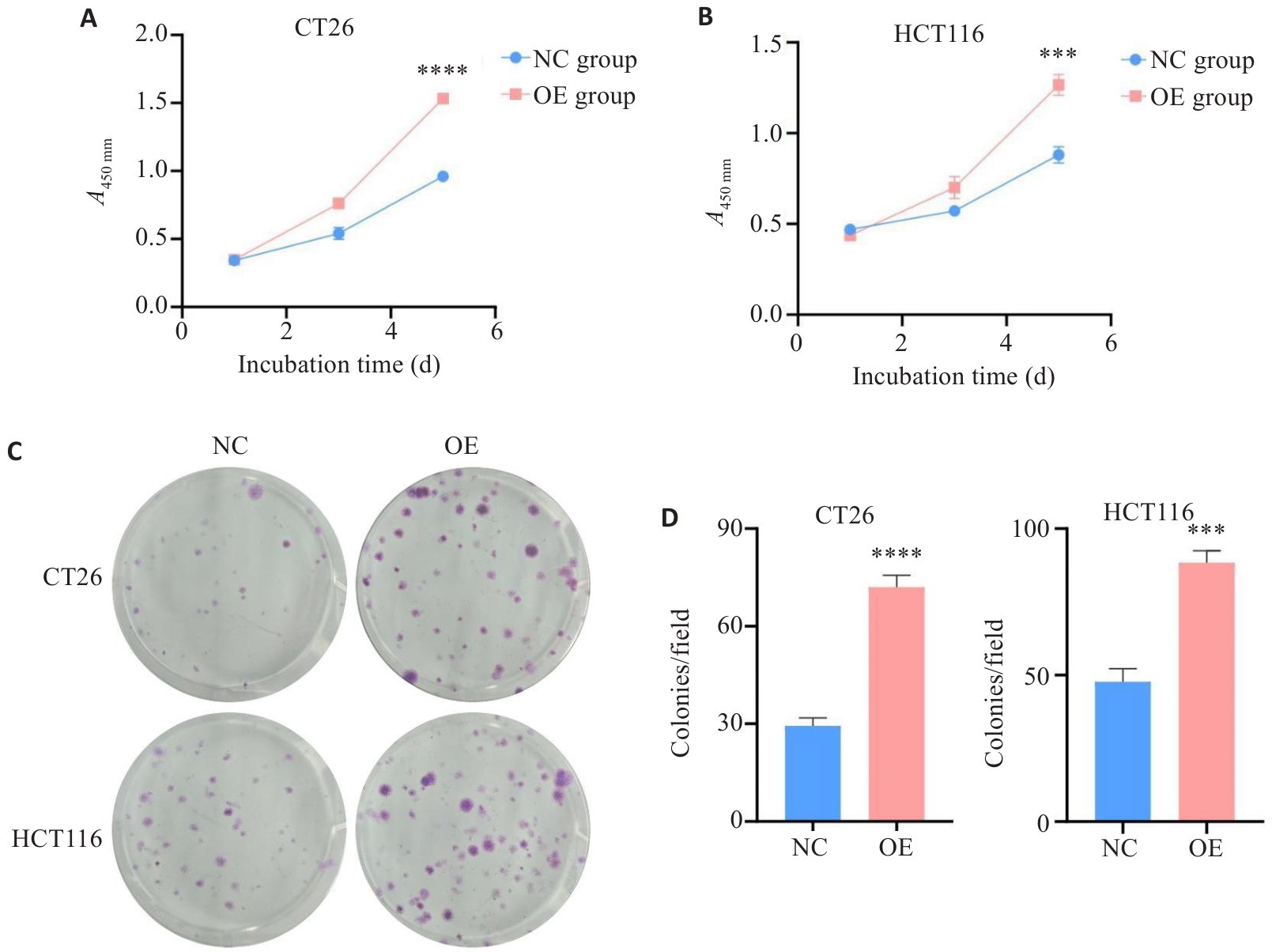
图4 HK2过表达对HCT116和CT26细胞增殖能力的影响
Fig.4 Effect of HK2 overexpression on proliferation ability of CRC cells in vitro. A-B: CCK-8. C-D: Colony-forming assay. ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
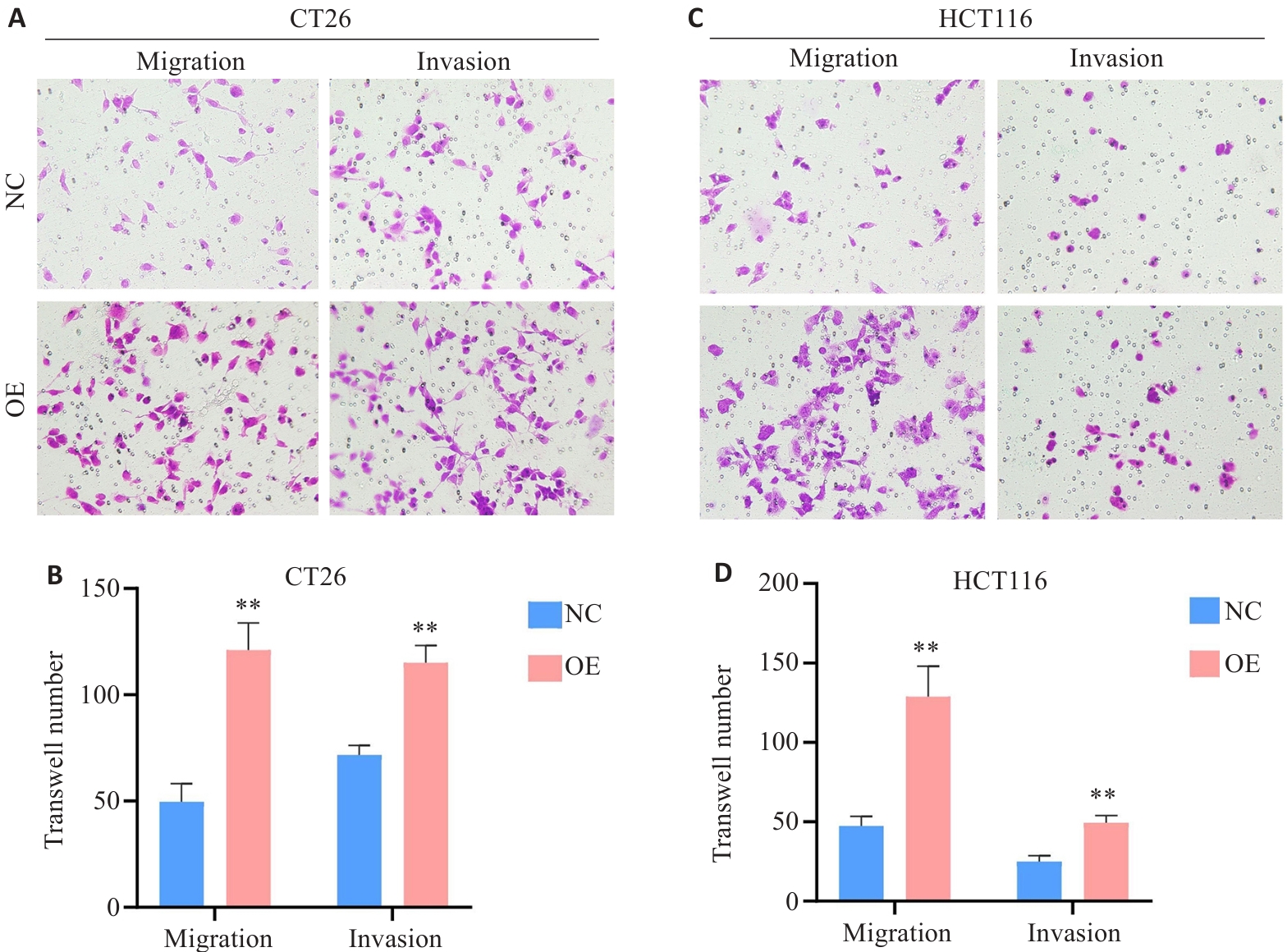
图5 HK2过表达对HCT116和CT26细胞迁移和侵袭能力的影响
Fig.5 Effect of HK2 overexpression on migration and invasion of CT26 cells (A, B) and HCT116 cells (C, D) (Original magnification: ×40). **P<0.01.
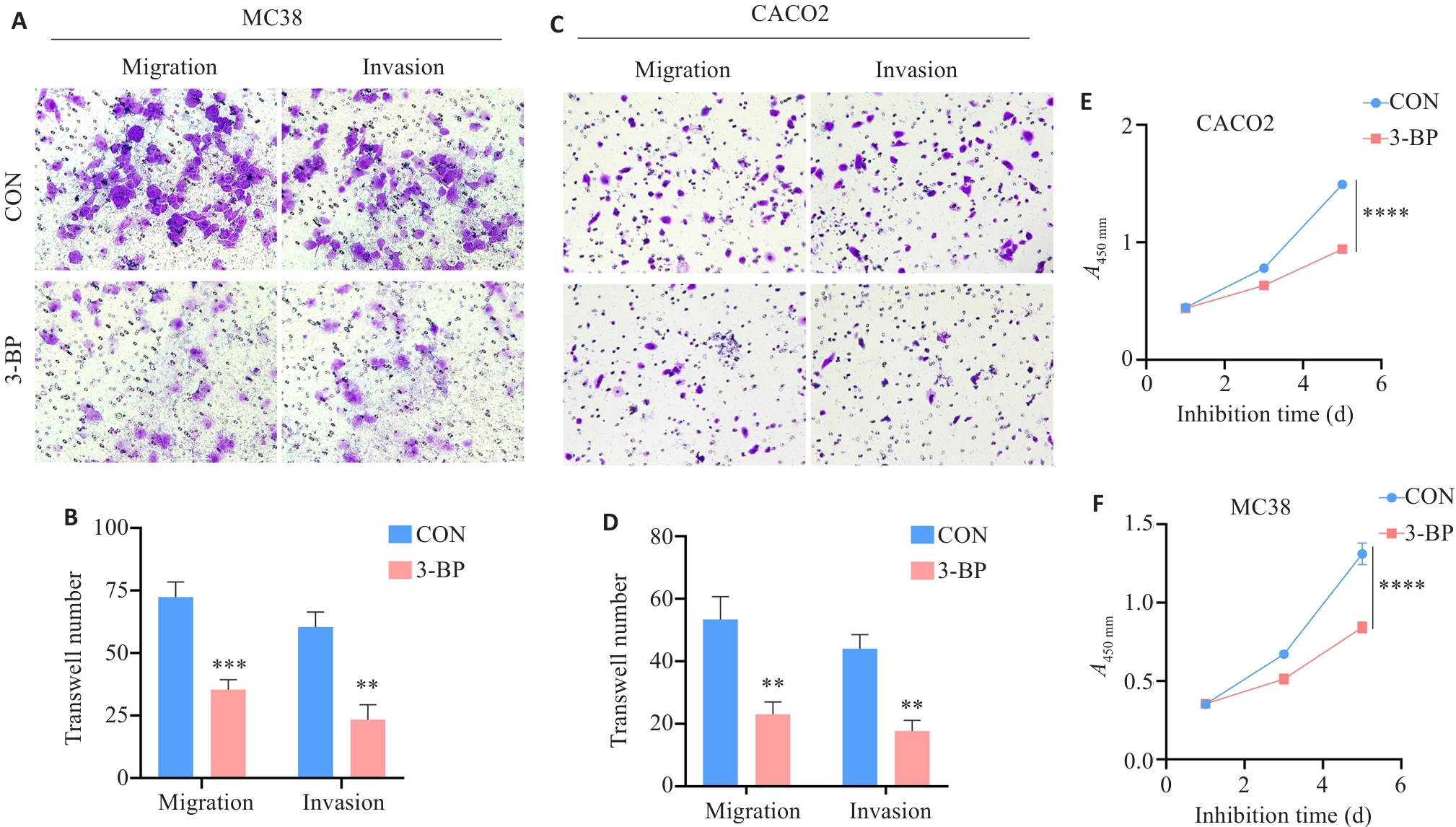
图6 HK2功能抑制对体外CRC细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭能力的影响
Fig.6 Effect of HK2 functional inhibition on the proliferation, migration, and invasion of CRC cells in vitroA-B, F: MC38. C-E: CACO2 (Original magnification: ×40). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
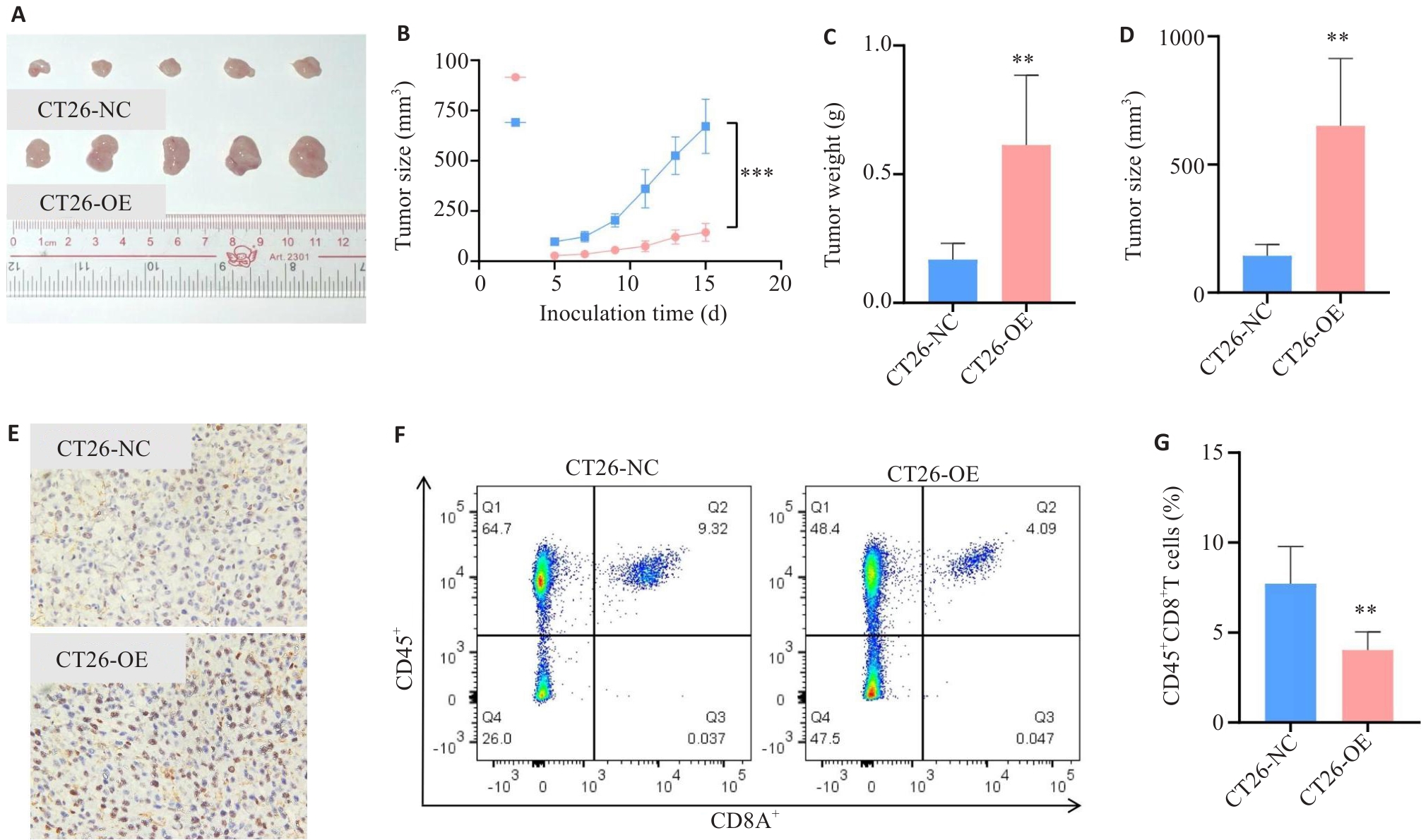
图7 HK2对体内鼠源性CRC细胞增殖能力的影响
Fig.7 Effect of HK2 overexpression on the proliferation of CRC cells in vivo. A-D: Effect of HK2 overexpression in CT26 cells on subcutaneous tumor proliferation. E: Ki-67 proliferative index of subcutaneous tumors (×40). F, G: Number of CD8+ T cells in subcutaneous tumors. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
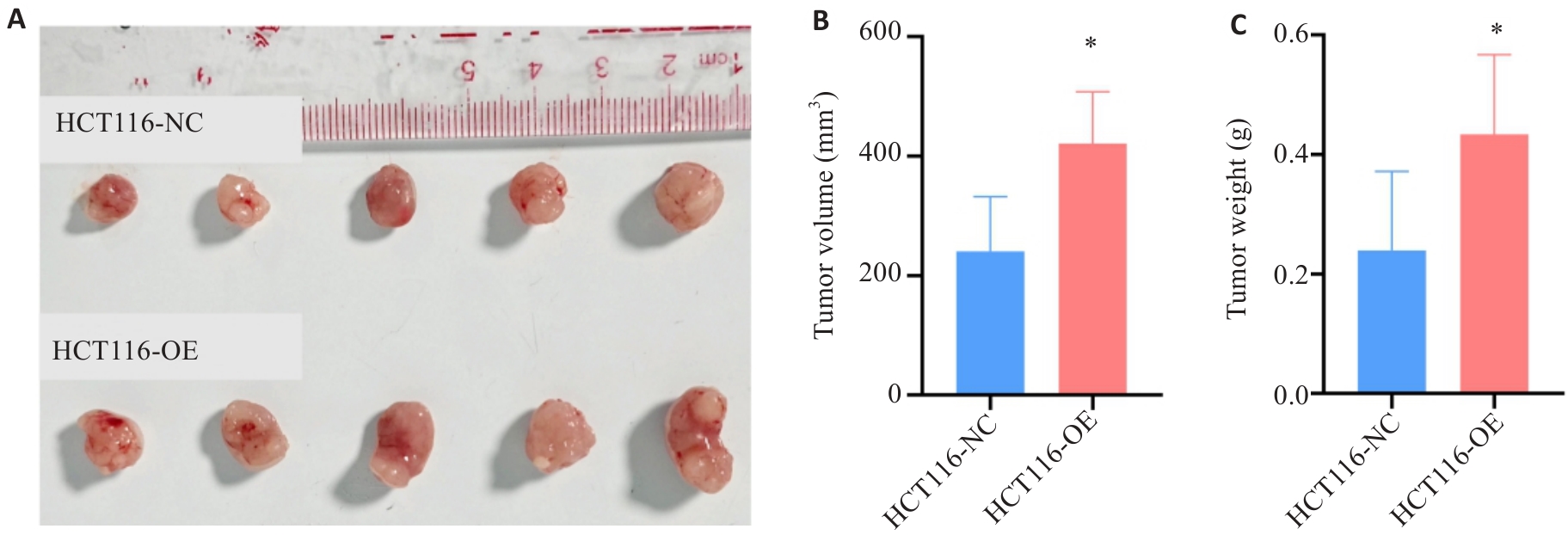
图8 HK2对体内人源性CRC细胞增殖能力的影响
Fig.8 Effect of HK2 overexpression on proliferation of HCT116 cells in nude mice. A-C: Effect of HK2 on subcutaneous tumor proliferation. *P<0.05.
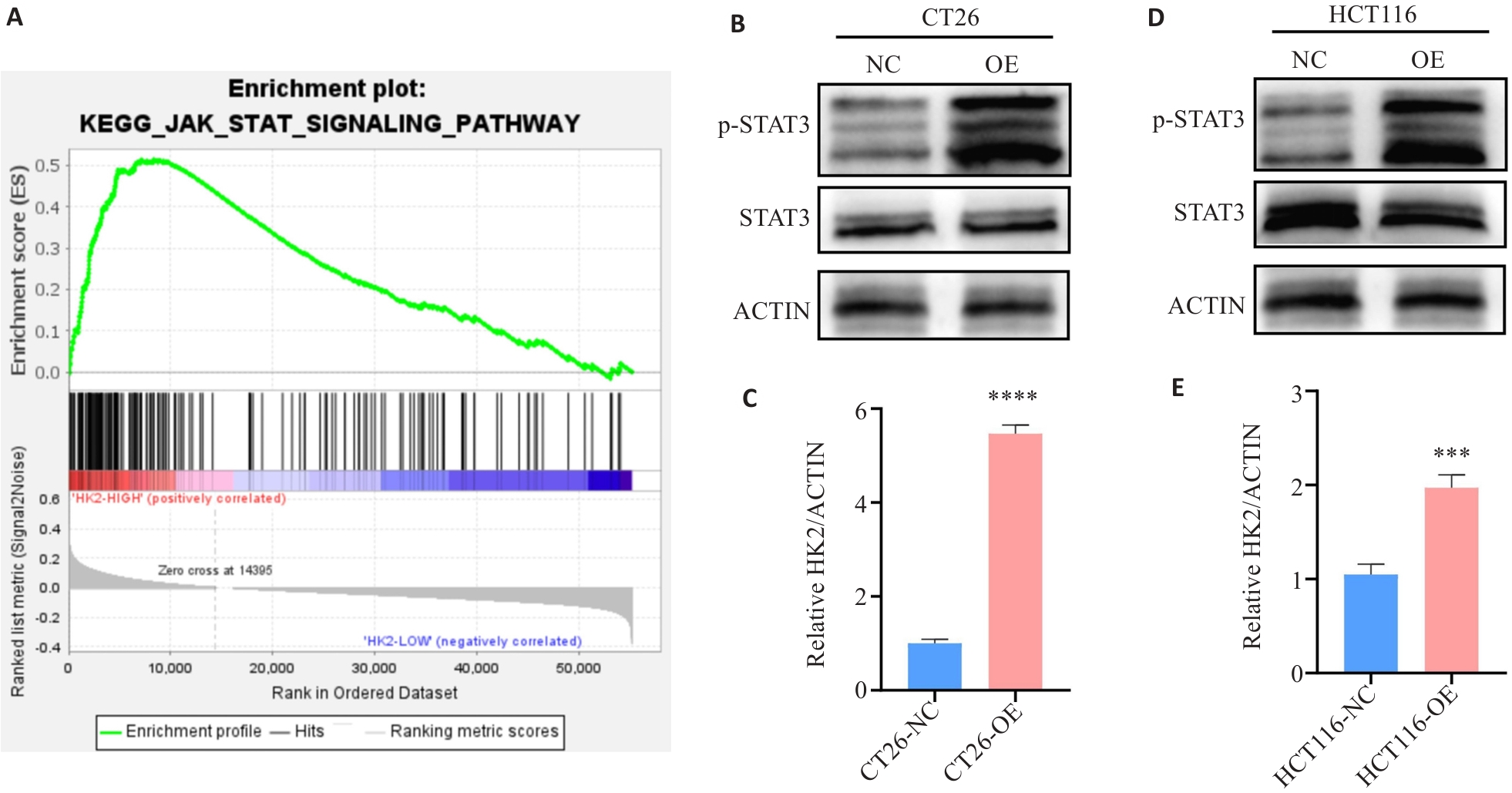
图9 HK2调控JAK/STAT信号通路
Fig.9 HK2 regulates the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. A: GSEA confirms that the JAK/STAT signaling pathway is significantly enriched in CRC with high HK2 expression based on CRC data from TCGA. B-E: Western blotting showing expression levels of STAT and p-STAT after HK2 overexpression. ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
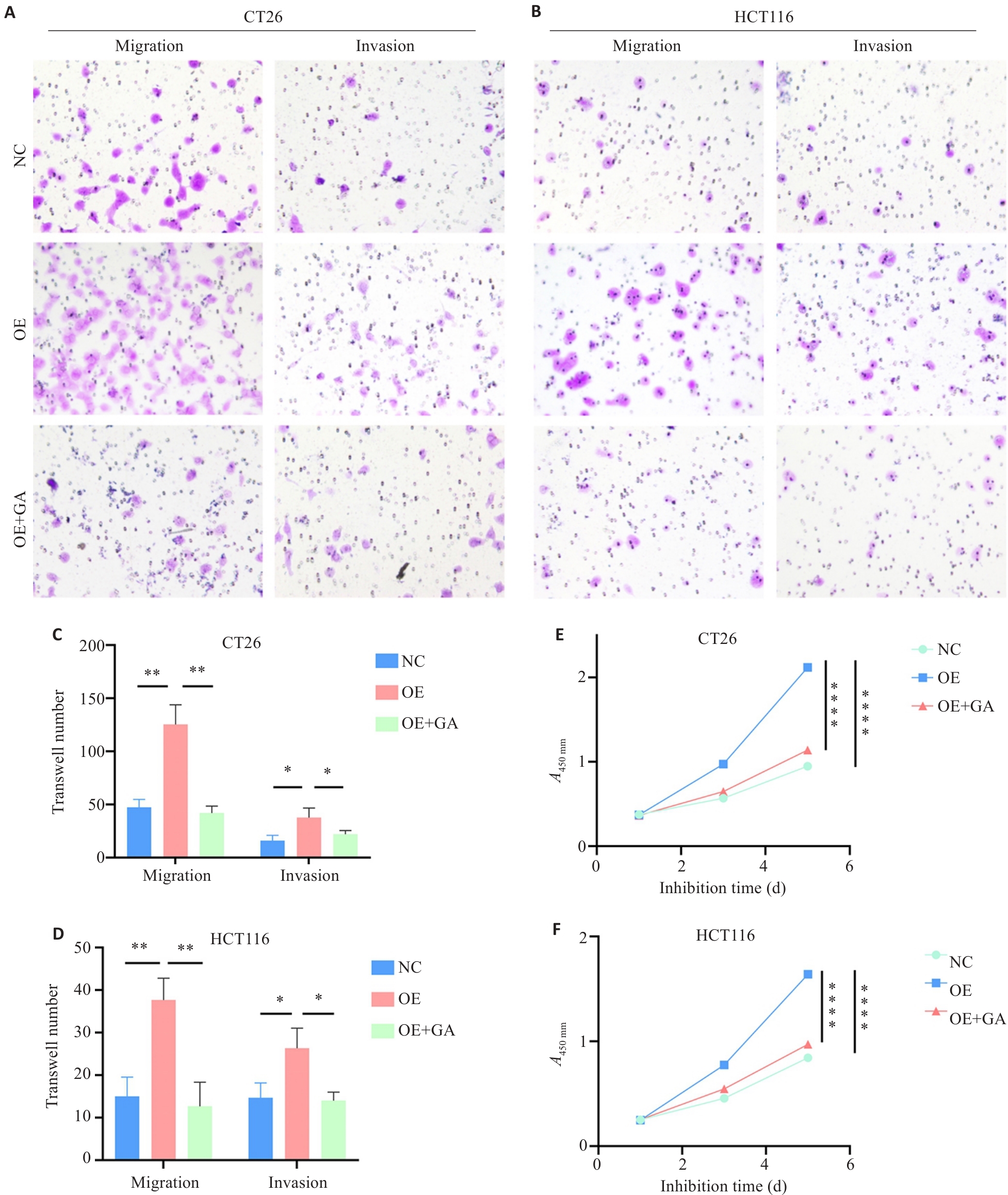
图10 HK2通过JAK/STAT影响结直肠癌细胞生物学行为
Fig.10 HK2 affects biological behaviors of CRC cells through the JAK/STAT pathway. A, B: Transwell assay showing migration and invasion of CT26 (A) and HCT116 (B) cells in the NC, OE and OE+GA groups (×40). C, D: Quantification of numbers of migrating and invading cells in CT26 (C) and HCT116 (D) from the Transwell assays. E, F: Cell proliferation assessed by CCK-8 assay in CT26 (E) and HCT116 (F) cells in different groups. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001.
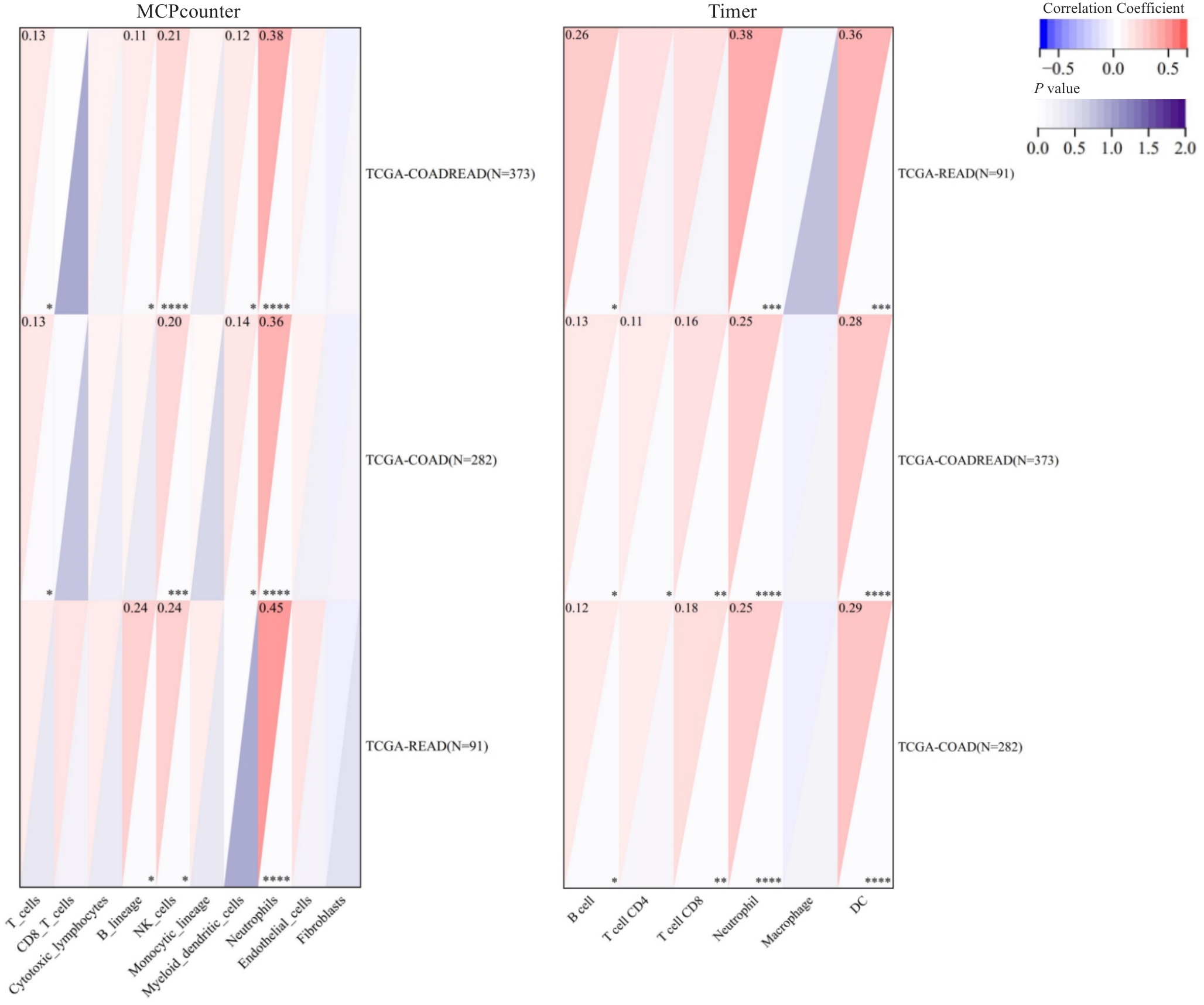
图11 HK2与肿瘤免疫细胞浸润的相关性
Fig.11 Correlation between HK2 expression and immune infiltration analyzed using MCPcounter and TIMER. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
| 1 | Kim S, Koh J, Song SG, et al. High tumor hexokinase-2 expression promotes a pro-tumorigenic immune microenvironment by modulating CD8+/regulatory T-cell infiltration[J]. BMC Cancer, 2022, 22(1): 1120. |
| 2 | Ciscato F, Ferrone L, Masgras I, et al. Hexokinase 2 in cancer: a Prima donna playing multiple characters[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(9): 4716. |
| 3 | Yu Q, Wang Y, Dong L, et al. Regulations of glycolytic activities on macrophages functions in tumor and infectious inflammation[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2020, 10: 287. |
| 4 | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-49. |
| 5 | Li Y, Shen Z, Chai Z, et al. Targeting MS4A4A on tumour-associated macrophages restores CD8+ T-cell-mediated antitumour immunity[J]. Gut, 2023, 72(12): 2307-20. |
| 6 | Zou Y, Wang S, Zhang H, et al. The triangular relationship between traditional Chinese medicines, intestinal flora, and colorectal cancer[J]. Med Res Rev, 2024, 44(2): 539-67. |
| 7 | Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Zeng HM, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2016[J]. J Natl Cancer Cent, 2022, 2(1): 1-9. |
| 8 | Rumpold H, Niedersüß-Beke D, Heiler C, et al. Prediction of mortality in metastatic colorectal cancer in a real-life population: a multicenter explorative analysis[J]. BMC Cancer, 2020, 20(1): 1149. |
| 9 | Zygowiec J. Virtually grounded[J]. JAMA, 2023, 329(12): 977. |
| 10 | Zhu J, Cai H, Xu C, et al. Acidity-responsive nanoreactors destructed “Warburg effect” for toxic-acidosis and starvation synergistic therapy[J]. Small, 2023, 19(46): e2304058. |
| 11 | Zhou Y, Guo Y, Tam KY. Targeting glucose metabolism to develop anticancer treatments and therapeutic patents[J]. Expert Opin Ther Pat, 2022, 32(4): 441-53. |
| 12 | DeWaal D, Nogueira V, Terry AR, et al. Author Correction: Hexokinase-2 depletion inhibits glycolysis and induces oxidative phosphorylation in hepatocellular carcinoma and sensitizes to metformin[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9: 2539. |
| 13 | Zhuang W, Liu X, Liu G, et al. Purinergic receptor P2Y12 boosts autoimmune hepatitis through hexokinase 2-dependent glycolysis in T cells[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2023, 19(11): 3576-94. |
| 14 | Zhong J, Lu S, Jia X, et al. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in apoptosis induced by HK2 inhibitor and its potential as a new drug combination strategy[J]. Cell Stress Chaperones, 2022, 27(3): 273-83. |
| 15 | Zhang Y, Zhu JH, Zhou Y, et al. Activation of HIF-1α C-terminal transactivation domain promotes tubulointerstitial fibrosis through hexokinase 2-mediated metabolic reprogramming[J]. Cell Signal, 2024, 127: 111531. |
| 16 | Shangguan X, He J, Ma Z, et al. SUMOylation controls the binding of hexokinase 2 to mitochondria and protects against prostate cancer tumorigenesis[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 1812. |
| 17 | Wang J, Shao F, Yang Y, et al. A non-metabolic function of hexokinase 2 in small cell lung cancer: promotes cancer cell stemness by increasing USP11-mediated CD133 stability[J]. Cancer Commun: Lond, 2022, 42(10): 1008-27. |
| 18 | Zheng Y, Zhan Y, Zhang Y, et al. Hexokinase 2 confers radio-resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting autophagy-dependent degradation of AIMP2[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(8): 488. |
| 19 | Esposito M, Ganesan S, Kang Y. Emerging strategies for treating metastasis[J]. Nat Cancer, 2021, 2(3): 258-70. |
| 20 | Sleeboom JJF, van Tienderen GS, Schenke-Layland K, et al. The extracellular matrix as hallmark of cancer and metastasis: From biomechanics to therapeutic targets[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2024, 16(728): eadg3840. |
| 21 | Tian Y, Wang Y, Wen N, et al. Prognostic factors associated with early recurrence following liver resection for colorectal liver metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BMC Cancer, 2024, 24(1): 426. |
| 22 | Liu QL, Zhou H, Zhou ZG, et al. Colorectal cancer liver metastasis: genomic evolution and crosstalk with the liver microenvironment[J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2023, 42(2): 575-87. |
| 23 | Fang Q, Ni CD, Cai Z, et al. Prognostic significance of hsa_circ_0048122 to predict liver metastasis in early-stage colorectal cancer[J]. Clinical Laboratory Analysis, 2022, 36(8): e24577. |
| 24 | Johnson DE, O’Keefe RA, Grandis JR. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2018, 15(4): 234-48. |
| 25 | Zhou QL, Ren Q, Jiao LH, et al. The potential roles of JAK/STAT signaling in the progression of osteoarthritis[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2022, 13: 1069057. |
| 26 | Zalpoor H, Nabi-Afjadi M, Forghaniesfidvajani R, et al. Quercetin as a JAK-STAT inhibitor: a potential role in solid tumors and neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 2022, 27(1): 60. |
| 27 | Xue C, Yao Q, Gu X, et al. Evolving cognition of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway: autoimmune disorders and cancer[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 204. |
| 28 | Sun YC, Gong WP, Zhang S. METTL3 promotes colorectal cancer progression through activating JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(11): 765. |
| 29 | Wang J, Zhang Y, Song H, et al. The circular RNA circSPARC enhances the migration and proliferation of colorectal cancer by regulating the JAK/STAT pathway[J]. Mol Cancer, 2021, 20(1): 81. |
| 30 | Guo D, Tong YY, Jiang XM, et al. Aerobic glycolysis promotes tumor immune evasion by hexokinase2-mediated phosphorylation of IκBα[J]. Cell Metab, 2022, 34(9): 1312-24.e6. |
| 31 | Gu MD, Zhou XF, Sohn JH, et al. NF-κB-inducing kinase maintains T cell metabolic fitness in antitumor immunity[J]. Nat Immunol, 2021, 22(2): 193-204. |
| 32 | Cao YN, Yi YN, Han CX, et al. NF-κB signaling pathway in tumor microenvironment[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1476030. |
| [1] | 纪凯, 于冠宇, 周乐其, 张天帅, 凌潜龙, 满文江, 朱冰, 张卫. HNRNPA1基因在结直肠癌组织中高表达及其潜在的诊断和治疗价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1685-1695. |
| [2] | 张银亮, 骆泽谭, 赵睿, 赵娜, 徐志东, 奥迪, 丛古一, 刘新宇, 郑海伦. 血根碱通过调控STUB1/GPX4诱导直肠癌细胞发生铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1537-1544. |
| [3] | 何欣容, 熊斯丽, 朱真如, 孙景苑, 曹传辉, 王惠. UBE2T通过调节性T细胞诱导肝细胞癌的放疗抵抗[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1149-1158. |
| [4] | 高志强, 林 洁, 洪 鹏, 胡再宏, 董军君, 石秦林, 田小毛, 刘 丰, 魏光辉. 基于高通量 RNA 测序分析 Wilms 瘤中关键基因对预后及免疫应答的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 727-738. |
| [5] | 陈守峰, 张舒超, 樊伟林, 孙 巍, 刘贝贝, 刘建民, 郭园园. 吡非尼酮联合PD-L1抑制剂抑制小鼠异位膀胱肿瘤的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 210-216. |
| [6] | 郗雪艳, 邓婷, 杜伯雨. 结直肠成纤维细胞通过激活ERK信号通路促进结直肠癌细胞的恶性生物学行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(10): 1866-1873. |
| [7] | 姚倚钠, 刘 佳, 周想军, 刘泽宇, 邱士珍, 何颖政, 周雪琼. TTC9A在泛癌中的表达水平与多种癌症的预后和免疫微环境相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 70-82. |
| [8] | 颜 畅, 刘 爽, 宋庆志, 胡艺冰. 二甲双胍通过抑制线粒体氧化磷酸化降低结直肠癌干细胞的自我更新能力[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1279-1286. |
| [9] | 魏 可, 石纪雯, 肖雨寒, 王文锐, 杨清玲, 陈昌杰. miR-30e-5p过表达促进结直肠癌细胞的增殖和迁移:基于下调PTEN激活CXCL12轴[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1081-1092. |
| [10] | 张雪芳, 陈延华, 李宗恒, 尚 靖, 袁泽婷, 邓皖利, 骆 莺, 韩 娜, 殷佩浩, 殷 军. 六神丸治疗小鼠结肠炎相关性结直肠癌的作用机制:基于网络药理学和体内验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1051-1062. |
| [11] | 邓 婷, 杜伯雨, 郗雪艳. 结直肠癌细胞通过激活成纤维细胞的ERK通路诱导癌症相关成纤维细胞的形成[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 943-951. |
| [12] | 马振南, 赵雪峰, 张晓微, 许广大, 刘福全. DTX2通过Notch2/Akt轴促进结直肠癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 340-348. |
| [13] | 王旋成, 朱一帆, 周海琳, 黄宗声, 陈鸿炜, 张嘉豪, 杨珊伊, 陈广辉, 张淇淞. 血清非靶向代谢组学联合靶向胆汁酸代谢组学筛查结直肠癌的潜在生物标志物[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 443-453. |
| [14] | 赵欢灵, 凌羽晓, 宓 帅, 朱家豪, 范佳耀, 杨 叶, 王 晶, 李迎君. Leptin循环水平与结直肠腺瘤及结直肠癌的关联性:一项病例对照和孟德尔随机化研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(12): 1989-1997. |
| [15] | 邓金海, 潘 腾, 周广林, 高 悦, 彭伟雄, 魏 玮, 吕纯鑫. 高表达分泌颗粒蛋白II增加结直肠癌细胞对奥沙利铂的耐药性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1657-1664. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||