南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 531-541.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.11
孙红燕1,2( ), 卢国庆1,2, 付程文1,2, 徐梦文3, 朱小翌3, 邢国权3, 刘乐强3, 柯雨菲3, 崔乐妹3, 陈睿旸3, 王磊1,2, 康品方1,2(
), 卢国庆1,2, 付程文1,2, 徐梦文3, 朱小翌3, 邢国权3, 刘乐强3, 柯雨菲3, 崔乐妹3, 陈睿旸3, 王磊1,2, 康品方1,2( ), 唐碧1,2
), 唐碧1,2
收稿日期:2024-09-29
出版日期:2025-03-20
发布日期:2025-03-28
通讯作者:
康品方,唐碧
E-mail:1210499483@qq.com;kangpinfang.1016@163.com
作者简介:孙红燕,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 1210499483@qq.com
基金资助:
Hongyan SUN1,2( ), Guoqing LU1,2, Chengwen FU1,2, Mengwen XU3, Xiaoyi ZHU3, Guoquan XING3, Leqiang LIU3, Yufei KE3, Lemei CUI3, Ruiyang CHEN3, Lei WANG1,2, Pinfang KANG1,2(
), Guoqing LU1,2, Chengwen FU1,2, Mengwen XU3, Xiaoyi ZHU3, Guoquan XING3, Leqiang LIU3, Yufei KE3, Lemei CUI3, Ruiyang CHEN3, Lei WANG1,2, Pinfang KANG1,2( ), Bi TANG1,2
), Bi TANG1,2
Received:2024-09-29
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
Pinfang KANG, Bi TANG
E-mail:1210499483@qq.com;kangpinfang.1016@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨槲皮素对糖尿病大鼠心肌铜死亡与心肌L型钙电流的影响。 方法 动物实验:对40只SD大鼠进行对照(Con)和糖尿病模型构建,后者通过高糖高脂饲料且用STZ诱导,糖尿病模型进一步分为模型组(DM)、槲皮素组(DM+Que)和恩格列净组(DM+Empa),n=10。每2周测量大鼠血糖和体质量,通过超声心动图评估心脏功能,通过HE染色、天狼猩红染色和WGA染色观察心肌组织形态学变化,并检测血清铜离子水平和FDX1的表达情况。体外细胞(大鼠H9c2心肌细胞)实验:分别设置低糖组(Con)、高糖组(HG)、槲皮素组(HG+Que)、伊利司莫组(HG+ES)和伊利司莫+槲皮素组(HG+ES+Que),通过CK-MB和LDH评估心肌损伤,检测FDX1蛋白表达。膜片钳技术检测心肌细胞L钙电流变化。 结果 与Con组相比,DM组大鼠血糖增加(P<0.05),体质量下降(P<0.05),左心功能下降,血清铜水平和FDX1表达增加(P<0.01),心肌L钙电流减小(P<0.01),动作电位时程延长(P<0.01)。与DM组相比,药物组血糖水平降低(P<0.05)、体质量增加(P<0.05)、左心功能改善。与DM+Empa组相比,槲皮素组铜离子水平、FDX1表达减少(P<0.01),心肌L钙电流增加(P<0.05)。在体外实验中,HG组的FDX1表达水平和心肌损伤均增加,槲皮素干预后,FDX1表达降低和心肌损伤改善。HG+ES组的FDX1、CK-MB和LDH均升高(P<0.05),加入槲皮素后,这些指标与HG+ES组相比差异没有统计学意义(P>0.05)。 结论 槲皮素可以改善糖尿病大鼠心肌损伤,可能与抑制铜死亡信号通路从而恢复心肌L型钙电流有关。
孙红燕, 卢国庆, 付程文, 徐梦文, 朱小翌, 邢国权, 刘乐强, 柯雨菲, 崔乐妹, 陈睿旸, 王磊, 康品方, 唐碧. 槲皮素通过调控L型钙通道改善糖尿病大鼠心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 531-541.
Hongyan SUN, Guoqing LU, Chengwen FU, Mengwen XU, Xiaoyi ZHU, Guoquan XING, Leqiang LIU, Yufei KE, Lemei CUI, Ruiyang CHEN, Lei WANG, Pinfang KANG, Bi TANG. Quercetin ameliorates myocardial injury in diabetic rats by regulating L-type calcium channels[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 531-541.
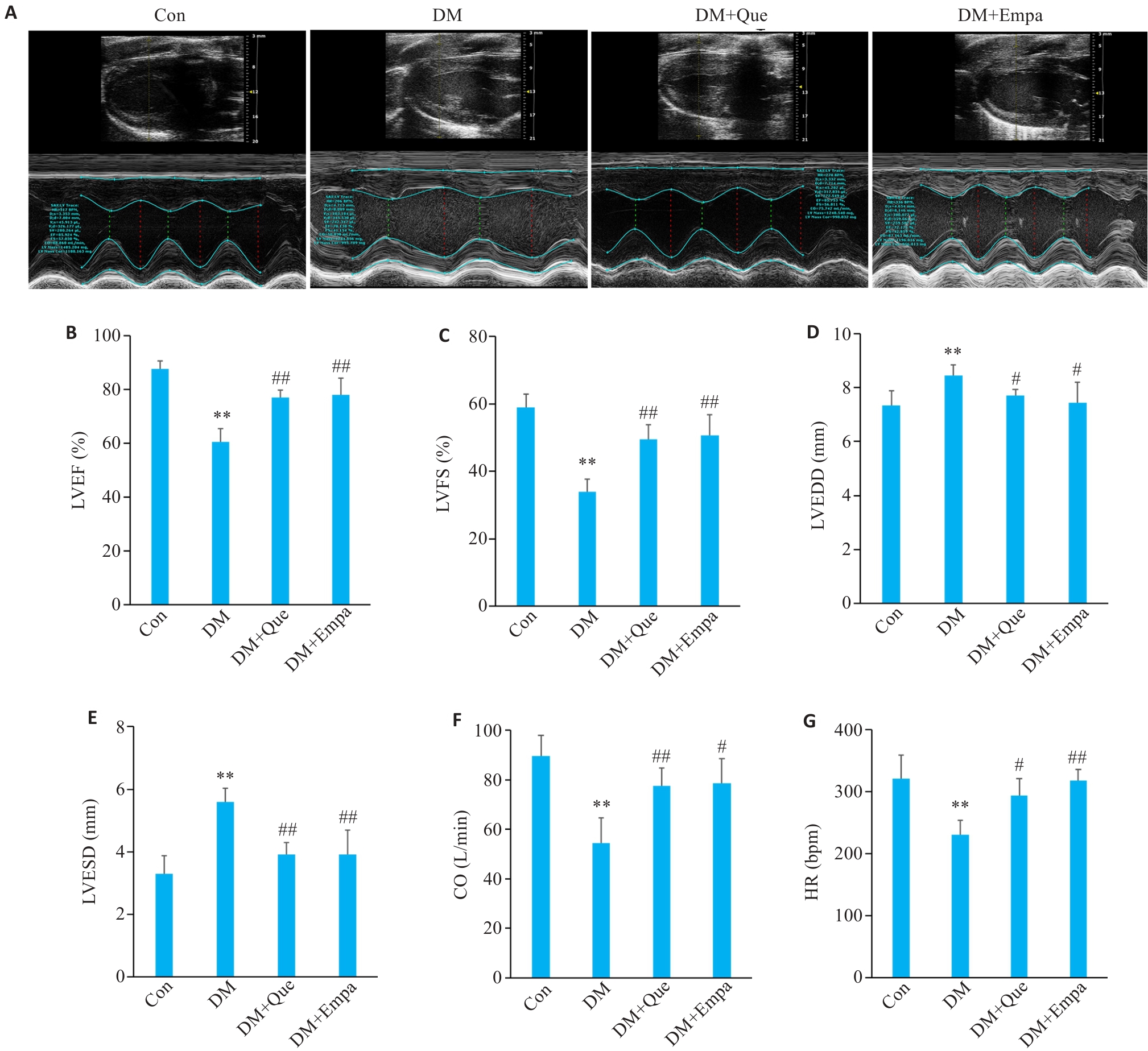
图2 槲皮素对糖尿病大鼠心功能的影响
Fig.2 Effect of quercetin on cardiac function in diabetic rats. A: Comparison of echocardiographic findings in each group. B-G: LVEF%, LVFS%, LVEDD, LVESD, CO and HR of SD rats in each group. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=6), **P<0.01 vs Con; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs DM.
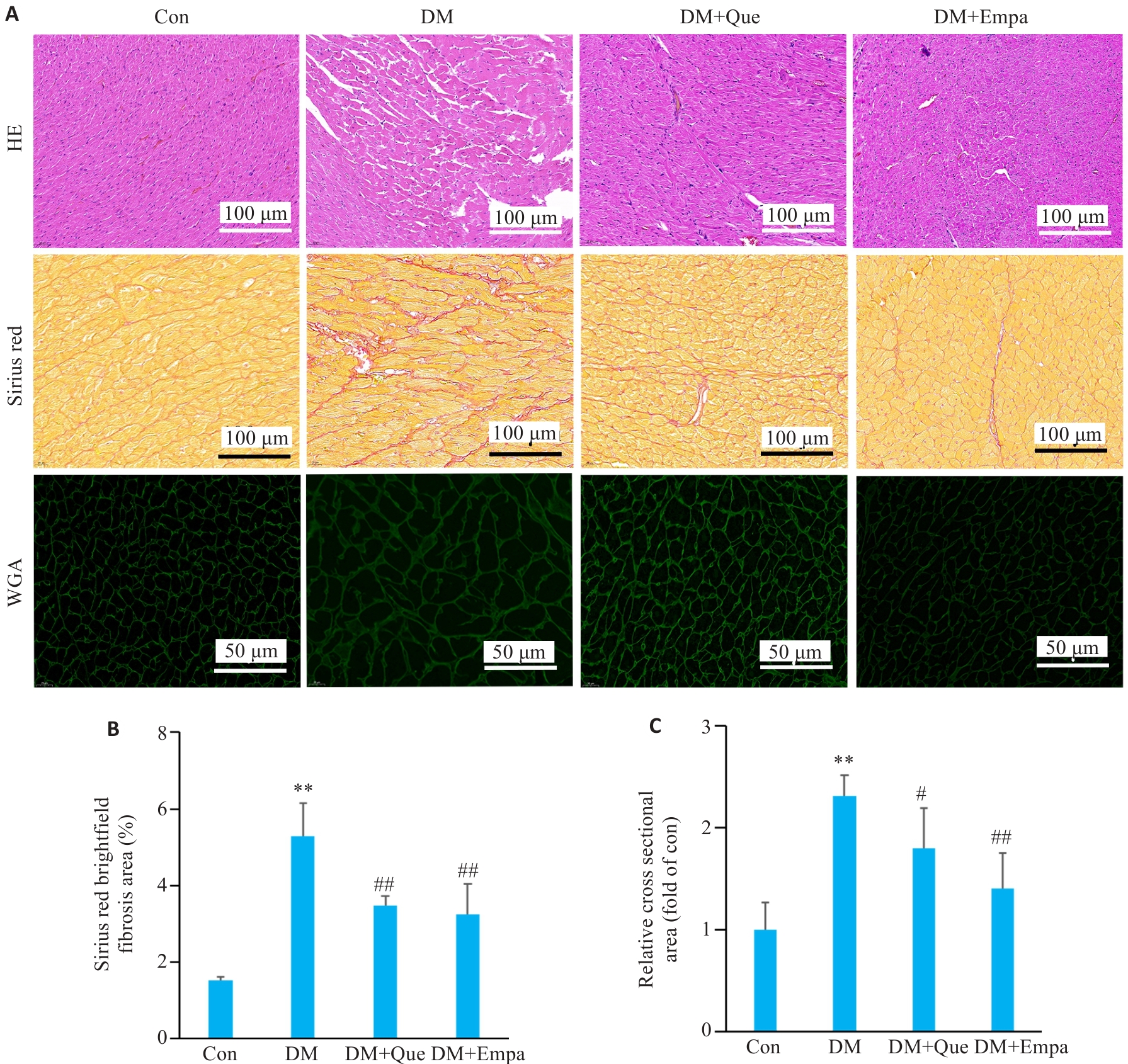
图3 槲皮素对糖尿病大鼠心肌结构的影响
Fig.3 Effect of quercetin on myocardial structure in diabetic rats. A: HE, Sirius Red, and WGA staining results of SD rats in each group. B: Analysis of the results of Sirius Red staining in each group. C: Analysis of WGA staining in each group. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=3). **P<0.01 vs Con, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs DM.

图4 槲皮素对糖尿病大鼠心肌中FDX1及血清铜的影响
Fig.4 Effect of quercetin on myocardial FDX1 expression and serum copper level in diabetic rats. A: Immunohistochemical staining of FDX1. B: Quantitative analysis of FDX1 expression levels; C: Serum Cu levels in each group. D, E: FDX1 protein expression levels of SD rats in different groups detected by Western blotting. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=3). **P<0.01 vs Con; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs DM; △P<0.05, △△P<0.01 vs DM+Empa.

图5 槲皮素对高糖诱导的H9C2心肌细胞损伤的影响
Fig.5 Effect of quercetin on high glucose-induced injury in rat H9C2 cardiomyocytes. A, B: FDX1 protein expression levels of FDX1 protein in each group detected by Westernblotting. C, D: FDX1 expression levels in each group detected by immunofluorescence assay. E, F: CK-MB and LDH levels in each group. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=3). **P<0.01 vs Con; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs HG.
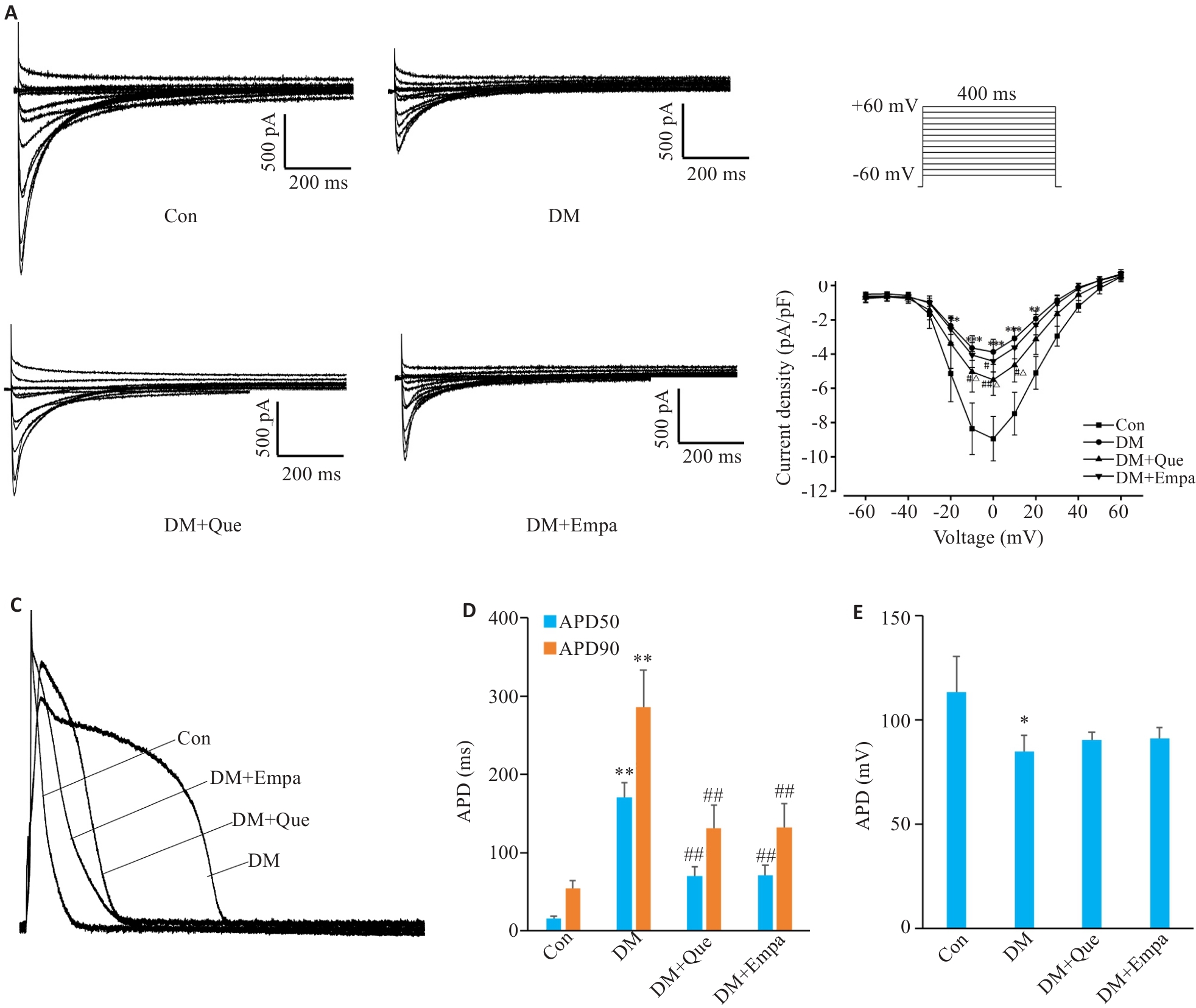
图6 槲皮素对糖尿病大鼠心肌ICa-L和动作电位(AP)的影响
Fig.6 Effects of quercetin on myocardial ICa-L and action potentials (AP) in diabetic rats. A: Representative recording traces ICa-L currents in different groups. B: Current-voltage relationship of ICa-L currents in different groups. C: Representative action potentials (AP) in APD60 and APD90 repolarization and APA recorded in different groups. D, E: APDs and APA in different groups. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=12), *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Con, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs DM, △P<0.05 vs DM+Empa.
| 1 | Kyriazis ID, Hoffman M, Gaignebet L, et al. KLF5 is induced by FOXO1 and causes oxidative stress and diabetic cardiomyopathy[J]. Circ Res, 2021, 128(3): 335-57. |
| 2 | Dillmann WH. Diabetic cardiomyopathy[J]. Circ Res, 2019, 124(8): 1160-2. |
| 3 | Jia GH, DeMarco VG, Sowers JR. Insulin resistance and hyperinsulinaemia in diabetic cardiomyopathy[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2016, 12(3): 144-53. |
| 4 | Pan GD, Munukutla S, Kar A, et al. Type-2 diabetic aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 mutant mice (ALDH 2*2) exhibiting heart failure with preserved ejection fraction phenotype can be determined by exercise stress echocardiography[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(4): e0195796. |
| 5 | Paolillo S, Marsico F, Prastaro M, et al. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: definition, diagnosis, and therapeutic implications[J]. Heart Fail Clin, 2019, 15(3): 341-7. |
| 6 | Lee TI, Trang NN, Lee TW, et al. Ketogenic diet regulates cardiac remodeling and calcium homeostasis in diabetic rat cardiomyopathy[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(22): 16142. |
| 7 | Yuill KH, Al Kury LT, Howarth FC. Characterization of L-type calcium channel activity in atrioventricular nodal myocytes from rats with streptozotocin-induced Diabetes mellitus[J]. Physiol Rep, 2015, 3(11): e12632. |
| 8 | Korf-Klingebiel M, Reboll MR, Polten F, et al. Myeloid-derived growth factor protects against pressure overload-induced heart failure by preserving sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase expression in cardiomyocytes[J]. Circulation, 2021, 144(15): 1227-40. |
| 9 | Arow M, Waldman M, Yadin D, et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor Dapagliflozin attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2020, 19(1): 7. |
| 10 | Ozturk N, Uslu S, Ozdemir S. Diabetes-induced changes in cardiac voltage-gated ion channels[J]. World J Diabetes, 2021, 12(1): 1-18. |
| 11 | Singh RM, Waqar T, Howarth FC, et al. Hyperglycemia-induced cardiac contractile dysfunction in the diabetic heart[J]. Heart Fail Rev, 2018, 23(1): 37-54. |
| 12 | Tsvetkov P, Coy S, Petrova B, et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins[J]. Science, 2022, 375(6586): 1254-61. |
| 13 | Farrant J, Dodd S, Vaughan C, et al. Rationale and design of a randomised trial of trientine in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy[J]. Heart, 2023, 109(15): 1175-82. |
| 14 | Gong D, Lu J, Chen X, et al. A copper(II)-selective Chelator ameliorates diabetes-evoked renal fibrosis and albuminuria, and suppresses pathogenic TGF-beta activation in the kidneys of rats used as a model of diabetes[J]. Diabetologia, 2008, 51(9): 1741-51. |
| 15 | Cui XN, Wang Y, Liu H, et al. The molecular mechanisms of defective copper metabolism in diabetic cardiomyopathy[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 5418376. |
| 16 | Jia DK, Liu LL, Liu W, et al. Copper metabolism and its role in diabetic complications: a review[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2024, 206: 107264. |
| 17 | Xiao Y, Wang T, Song X, et al. Copper promotion of myocardial regeneration[J]. Exp Biol Med, 2020, 245(10): 911-21. |
| 18 | Jomova K, Valko M. Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease[J]. Toxicology, 2011, 283(2/3): 65-87. |
| 19 | Liu ZY, Liu ZY, Lin LC, et al. Redox homeostasis in cardiac fibrosis: focus on metal ion metabolism[J]. Redox Biol, 2024, 71: 103109. |
| 20 | Aggarwal NT, Makielski JC. Redox control of cardiac excitability[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2013, 18(4): 432-68. |
| 21 | Toscano CM, Filetti FM, Almenara CCP, et al. Copper exposure for 30 days at a daily dose twice the recommended increases blood pressure and cardiac contractility[J]. Life Sci, 2022, 300: 120579. |
| 22 | Zhao HJ, Wang Y, Fei DX, et al. Destruction of redox and mitochondrial dynamics co-contributes to programmed cell death in chicken kidney under arsenite or/and copper (II) exposure[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2019, 179: 167-74. |
| 23 | Hung Y, Chen YC, Huang SY, et al. Klotho modulates electrical activity and calcium homeostasis in pulmonary vein cardiomyocytes via PI3K/Akt signalling[J]. Europace, 2020, 22(7): 1132-41. |
| 24 | Chu SJ, Wang WJ, Zhang N, et al. Protective effects of 18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid against myocardial infarction: Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway activation and inhibiting Ca2+ influx via L-type Ca2+ channels[J]. Food Sci Nutr, 2021, 9(12): 6831-43. |
| 25 | Clark JL, Zahradka P, Taylor CG. Efficacy of flavonoids in the management of high blood pressure[J]. Nutr Rev, 2015, 73(12): 799-822. |
| 26 | Islam MT, Tuday E, Allen S, et al. Senolytic drugs, dasatinib and quercetin, attenuate adipose tissue inflammation, and ameliorate metabolic function in old age[J]. Aging Cell, 2023, 22(2): e13767. |
| 27 | Oyedemi SO, Nwaogu G, Chukwuma CI, et al. Quercetin modulates hyperglycemia by improving the pancreatic antioxidant status and enzymes activities linked with glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes model of rats: in silico studies of molecular interaction of quercetin with hexokinase and catalase[J]. J Food Biochem, 2020, 44(2): e13127. |
| 28 | Lazuardi M, Anjani QK, Budiatin AS, et al. Efficacy of quercetin-like compounds from the mistletoe plant of Dendrophthoe pentandra L. Miq, as oral random blood sugar lowering treatment in diabetic rats[J]. Vet Q, 2024, 44(1): 1-14. |
| 29 | Song XL, Wang YL, Gao LG. Mechanism of antioxidant properties of quercetin and quercetin-DNA complex[J]. J Mol Model, 2020, 26(6): 133. |
| 30 | Pham TND, Stempel S, Shields MA, et al. Quercetin enhances the anti-tumor effects of BET inhibitors by suppressing hnRNPA1[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(17): 4293. |
| 31 | Xu HY, Li SF, Liu JY, et al. Bioactive compounds from Huashi Baidu decoction possess both antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects against COVID-19[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2023, 120(18): e2301775120. |
| 32 | Hosseini A, Razavi BM, Banach M, et al. Quercetin and metabolic syndrome: a review[J]. Phytother Res, 2021, 35(10): 5352-64. |
| 33 | Hayamizu K, Morimoto S, Nonaka M, et al. Cardiotonic actions of quercetin and its metabolite tamarixetin through a Digitalis-like enhancement of Ca2+ transients[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2018, 637: 40-7. |
| 34 | Chen YF, Qiu Q, Wang L, et al. Quercetin ameliorates myocardial injury in diabetic rats by regulating autophagy and apoptosis through AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2024, 52(3): 841-64. |
| 35 | Trang NN, Chung CC, Lee TW, et al. Empagliflozin and liraglutide differentially modulate cardiac metabolism in diabetic cardiom-yopathy in rats[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(3): 1177. |
| 36 | Kang PF, Wang JH, Fang D, et al. Activation of ALDH2 attenuates high glucose induced rat cardiomyocyte fibrosis and necroptosis[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2020, 146: 198-210. |
| 37 | Huang XP, Shi ZH, Ming GF, et al. S-Allyl-L-cysteine (SAC) inhibits copper-induced apoptosis and cuproptosis to alleviate cardiomyocyte injury[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2024, 730: 150341. |
| 38 | Nakamura K, Miyoshi T, Yoshida M, et al. Pathophysiology and treatment of diabetic cardiomyopathy and heart failure in patients with diabetes mellitus[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(7): 3587. |
| 39 | Huo SQ, Wang Q, Shi W, et al. ATF3/SPI1/SLC31A1 signaling promotes cuproptosis induced by advanced glycosylation end products in diabetic myocardial injury[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(2): 1667. |
| 40 | Zhang L, Ward ML, Phillips ARJ, et al. Protection of the heart by treatment with a divalent-copper-selective Chelator reveals a novel mechanism underlying cardiomyopathy in diabetic rats[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2013, 12: 123. |
| 41 | Coskun O, Kanter M, Korkmaz A, et al. Quercetin, a flavonoid antioxidant, prevents and protects streptozotocin-induced oxidative stress and beta-cell damage in rat pancreas[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2005, 51(2): 117-23. |
| 42 | Chang X, Zhang T, Wang JY, et al. SIRT5-related desuccinylation modification contributes to quercetin-induced protection against heart failure and high-glucose-prompted cardiomyocytes injured through regulation of mitochondrial quality surveillance[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021, 2021: 5876841. |
| 43 | 王盼盼, 杨 赞, 刘冬兰, 等. 槲皮素对心肌缺血后线粒体能量代谢功能的影响[J]. 中国药房, 2024, 35(4): 401-6. |
| 44 | Liang YR, Zhang YY, Liu MM, et al. Protective effect of quercetin against myocardial ischemia as a Ca2+ channel inhibitor: involvement of inhibiting contractility and Ca2+ influx via L-type Ca2+ channels[J]. Arch Pharm Res, 2020, 43(8): 808-20. |
| 45 | Zhang YM, Zhang ZY, Wang RX. Protective mechanisms of quercetin against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury[J]. Front Physiol, 2020, 11: 956. |
| 46 | Zhong DY, Li L, Cheng H, et al. Study on computer screening and drug properties of herbs intervening in copper death[J]. Comput Math Methods Med, 2023, 2023: 3311834. |
| 47 | Schulz V, Basu S, Freibert SA, et al. Functional spectrum and specificity of mitochondrial ferredoxins FDX1 and FDX2[J]. Nat Chem Biol, 2023, 19(2): 206-17. |
| 48 | Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 373(22): 2117-28. |
| 49 | Preda A, Montecucco F, Carbone F, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors: from glucose-lowering to cardiovascular benefits[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2024, 120(5): 443-60. |
| 50 | Landstrom AP, Dobrev D, Wehrens XHT. Calcium signaling and cardiac arrhythmias[J]. Circ Res, 2017, 120(12): 1969-93. |
| 51 | Liu CH, Chang HK, Lee SP, et al. Activation of the Ca2+-sensing receptors increases currents through inward rectifier K+ channels via activation of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase[J]. Pflugers Arch, 2016, 468(11/12): 1931-43. |
| 52 | Liu ZL, Shan ZM, Yang HY, et al. Quercetin, main active ingredient of moutan cortex, alleviates chronic orofacial pain via block of voltage-gated sodium channel[J]. Anesth Analg, 2024, 138(6): 1324-36. |
| 53 | Saponara S, Fusi F, Iovinelli D, et al. Flavonoids and hERG channels: friends or foes[J]? Eur J Pharmacol, 2021, 899: 174030. |
| [1] | 黄鹏伟, 陈洁, 邹金虎, 高雪锋, 曹虹. 槲皮素促进应激颗粒G3BP1解聚改善HIV-1 gp120诱导的星形胶质细胞神经毒性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 304-312. |
| [2] | 高俊杰, 叶开, 吴竞. 槲皮素通过调控TP53基因抑制肾透明细胞癌的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [3] | 龙秀鹏, 陶顺, 阳绅, 李素云, 饶利兵, 李莉, 张哲. 槲皮素通过抑制MAPK信号通路改善心力衰竭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 187-196. |
| [4] | 刘青, 刘敬, 郑逸航, 雷金, 黄建华, 刘思妤, 刘芳, 彭群龙, 张远芳, 王俊杰, 李玉娟. 积雪草活性成分槲皮素通过介导STAT3磷酸化抑制IL-23/IL-17A炎症轴发挥抗银屑病作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 90-99. |
| [5] | 姜一凡, 李小荣, 耿嘉逸, 陈永锋, 唐碧, 康品方. 槲皮素通过抑制HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB信号通路减轻糖尿病引起的大鼠肾脏损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1769-1775. |
| [6] | 张文祥, 顾惠贤, 陈鹏德, 吴思宇, 马洪艳, 姚蓝. 复方玉液汤通过调控PI3K/Akt信号通路抑制糖尿病大鼠心肌细胞凋亡和炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1306-1314. |
| [7] | 舒萍, 袁孟珂, 杨珂, 何伟志, 刘丽. 槲皮素通过抑制NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD信号通路抑制小鼠成纤维细胞焦亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(10): 1874-1880. |
| [8] | 叶红伟, 张钰明, 云 琦, 杜若丽, 李 璐, 李玉萍, 高 琴. 白藜芦醇可减轻高糖诱导的心肌细胞肥大:基于促进SIRT1表达维持线粒体稳态[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 45-51. |
| [9] | 张宁宁, 邱 奇, 陈永锋, 孙正宇, 卢国庆, 王 磊, 康品方, 王洪巨. 槲皮素可改善大鼠肺动脉高压:基于调控 HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1606-1612. |
| [10] | 刘丽兰, 邓儒雅, 周稳进, 林 敏, 夏玲姿, 高海涛. 槲皮素降低邻苯二甲酸酯类混合物暴露致大鼠睾丸组织的氧化损伤的机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(4): 577-584. |
| [11] | 高晓阳, 赵晓璐, 张春艳, 颜羽昕, 金 蓉, 马月宏. 槲皮素诱导肝星状细胞凋亡:基于调控miR-146影响PI3K/Akt信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1725-1733. |
| [12] | 郑冬晓, 陈琳琳, 韦其慧, 朱梓然, 刘子略, 金 琳, 杨观玉, 谢 曦. 褐藻素通过调控Nrf2/Keap1通路缓解糖尿病大鼠心肌肥大[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(5): 752-759. |
| [13] | 谭 鑫, 鲜 维, 陈永锋, 李小荣, 王其一, 康品方, 王洪巨. 槲皮素治疗心力衰竭的分子机制:基于网络药理学与分子对接方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(8): 1198-1206. |
| [14] | 谭继翔,何进,秦文熠,赵林. 槲皮素通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB通路缓解脂多糖诱导的急性肾损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(05): 598-. |
| [15] | 梁青春,陈燕亭,李传翔,陆立鹤. 槲皮素调节ROS/TLR4信号通路抑制Ox-LDL诱导的血管平滑肌细胞钙化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(08): 980-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||