南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 90-99.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.12
刘青1( ), 刘敬1, 郑逸航1, 雷金2, 黄建华1, 刘思妤1, 刘芳1, 彭群龙1, 张远芳1, 王俊杰1, 李玉娟2(
), 刘敬1, 郑逸航1, 雷金2, 黄建华1, 刘思妤1, 刘芳1, 彭群龙1, 张远芳1, 王俊杰1, 李玉娟2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-06-27
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2025-01-20
通讯作者:
李玉娟
E-mail:liuqing@xnu.edu.cn;Li_yujuan1001@163.com
作者简介:刘 青,副教授,E-mail: liuqing@xnu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Qing LIU1( ), Jing LIU1, Yihang ZHENG1, Jin LEI2, Jianhua HUANG1, Siyu LIU1, Fang LIU1, Qunlong PENG1, Yuanfang ZHANG1, Junjie WANG1, Yujuan LI2(
), Jing LIU1, Yihang ZHENG1, Jin LEI2, Jianhua HUANG1, Siyu LIU1, Fang LIU1, Qunlong PENG1, Yuanfang ZHANG1, Junjie WANG1, Yujuan LI2( )
)
Received:2024-06-27
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-20
Contact:
Yujuan LI
E-mail:liuqing@xnu.edu.cn;Li_yujuan1001@163.com
摘要:
目的 探讨积雪草抗银屑病活性成分及其作用机制。 方法 利用TCMSP、PharmMapper等数据库获取积雪草化合物和靶点,利用GeneCards数据库筛选银屑病相关的潜在靶点,Cytoscape 3.10.0软件导入积雪草活性成分、银屑病共同靶点制作“药物-活性成分-作用靶点”网络图,使用STRING数据库构建PPI网络,借助DAVID数据库进行通路富集分析。通过网络药理学筛选得到积雪草主要活性成分槲皮素、积雪草苷、积雪草酸,并将这3种活性成分(7.5、15、30、60 μmol/L)作用于脂多糖(LPS)刺激RAW264.7小鼠巨噬细胞炎症模型,Griess法检测细胞NO水平评价抗炎活性。ELISA检测TNF-α、IL-6细胞促炎因子的表达,RT-qPCR测定细胞IL-23、IL-17A、TNF-α、IL-6 mRNA的表达,Western blotting检测细胞p-STAT3(Tyr705)、p-STAT3(Ser727)的表达变化。 结果 网络药理学研究分析获取积雪草靶点139个,银屑病靶点4604个,PPI网络图显示CASP3、EGFR、PTGS2和ESR1为治疗银屑病的关键靶点,分析得到槲皮素、积雪草苷、积雪草酸可能是积雪草抗银屑病关键活性成分。KEGG结果显示与癌症、IL-17以及MAPK信号通路相关。槲皮素、积雪草苷、积雪草酸处理细胞炎症模型,发现槲皮素表现出明显的抗炎活性,细胞NO水平降低(P<0.05)。与LPS组相比,槲皮素处理后细胞中TNF-α,IL-6促炎因子分泌减少(P<0.05),IL-23、IL-17A、TNF-α、IL-6 mRNA表达水平降低(P<0.05),STAT3磷酸化的两个位点(Tyr705、Ser727)蛋白表达均明显下调(P<0.05)。 结论 积雪草抗银屑病主要活性成分为槲皮素、积雪草苷和积雪草酸,其中关键成分槲皮素通过抑制NO产生、炎症因子TNF-α、IL-6的表达,并通过介导STAT3磷酸化调控IL-23/IL-17A炎症轴抑制炎症反应发挥抗银屑病作用。
刘青, 刘敬, 郑逸航, 雷金, 黄建华, 刘思妤, 刘芳, 彭群龙, 张远芳, 王俊杰, 李玉娟. 积雪草活性成分槲皮素通过介导STAT3磷酸化抑制IL-23/IL-17A炎症轴发挥抗银屑病作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 90-99.
Qing LIU, Jing LIU, Yihang ZHENG, Jin LEI, Jianhua HUANG, Siyu LIU, Fang LIU, Qunlong PENG, Yuanfang ZHANG, Junjie WANG, Yujuan LI. Quercetin mediates the therapeutic effect of Centella asiatica on psoriasis by regulating STAT3 phosphorylation to inhibit the IL-23/IL-17A axis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 90-99.
| Gene | Primer sequences (5'-3')-F | Primer sequences (5'-3')-R | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA | 123 |
| IL-23 | GTGGCATCGAGAAACTGT | GAGCCACCCAGGAAAGTA | 116 |
| IL-17A | ACTACCTCAACCGTTCCACG | TTCCTCCGCATTGACACAG | 120 |
| TNF-α | ATGAGCACAGAAAGCATGATC | GGTCTGGGCCATAGAACTGATG | 231 |
| IL-6 | TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC | TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC | 76 |
表1 实时荧光定量PCR引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequences for real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR
| Gene | Primer sequences (5'-3')-F | Primer sequences (5'-3')-R | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA | 123 |
| IL-23 | GTGGCATCGAGAAACTGT | GAGCCACCCAGGAAAGTA | 116 |
| IL-17A | ACTACCTCAACCGTTCCACG | TTCCTCCGCATTGACACAG | 120 |
| TNF-α | ATGAGCACAGAAAGCATGATC | GGTCTGGGCCATAGAACTGATG | 231 |
| IL-6 | TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC | TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC | 76 |
| Number | MOL ID | Compound Name | Oral Bioavailability | Drug Likeness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A 1 | MOL000098 | Quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 |
| A 2 | MOL007312 | Asiaticoside | 10.22 | 0.7 |
| A 3 | MOL007253 | Asiatic acid | 16.69 | 0.72 |
| A 4 | MOL000359 | Sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| A 5 | MOL007313 | Xanthanoic acid | 48.07 | 0.16 |
| A 6 | MOL007320 | 8-acetoxycentellynol | 65.94 | 0.12 |
| A 7 | MOL006370 | 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 19.61 | 0.33 |
| A 8 | MOL000008 | Qpigenin | 23.06 | 0.21 |
| A 9 | MOL007201 | Brahmic acid | 17.6 | 0.7 |
| A 10 | MOL006387 | Chlorogenic acid | 25.58 | 0.33 |
| A 11 | MOL007323 | Madasiatic acid | 18.42 | 0.72 |
| A 12 | MOL007303 | Madecassoside | 16.89 | 0.7 |
| A 13 | MOL006407 | Neochlorogenic acid | 18.05 | 0.33 |
| A 14 | MOL001434 | Quercetin 3-O-rhamnopyranosyl | 22.24 | 0.28 |
| A 15 | MOL000511 | Ursolic acid | 16.77 | 0.75 |
表2 积雪草活性成分基本信息
Tab.2 Basic information of the active components in Centella asiatica
| Number | MOL ID | Compound Name | Oral Bioavailability | Drug Likeness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A 1 | MOL000098 | Quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 |
| A 2 | MOL007312 | Asiaticoside | 10.22 | 0.7 |
| A 3 | MOL007253 | Asiatic acid | 16.69 | 0.72 |
| A 4 | MOL000359 | Sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| A 5 | MOL007313 | Xanthanoic acid | 48.07 | 0.16 |
| A 6 | MOL007320 | 8-acetoxycentellynol | 65.94 | 0.12 |
| A 7 | MOL006370 | 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 19.61 | 0.33 |
| A 8 | MOL000008 | Qpigenin | 23.06 | 0.21 |
| A 9 | MOL007201 | Brahmic acid | 17.6 | 0.7 |
| A 10 | MOL006387 | Chlorogenic acid | 25.58 | 0.33 |
| A 11 | MOL007323 | Madasiatic acid | 18.42 | 0.72 |
| A 12 | MOL007303 | Madecassoside | 16.89 | 0.7 |
| A 13 | MOL006407 | Neochlorogenic acid | 18.05 | 0.33 |
| A 14 | MOL001434 | Quercetin 3-O-rhamnopyranosyl | 22.24 | 0.28 |
| A 15 | MOL000511 | Ursolic acid | 16.77 | 0.75 |
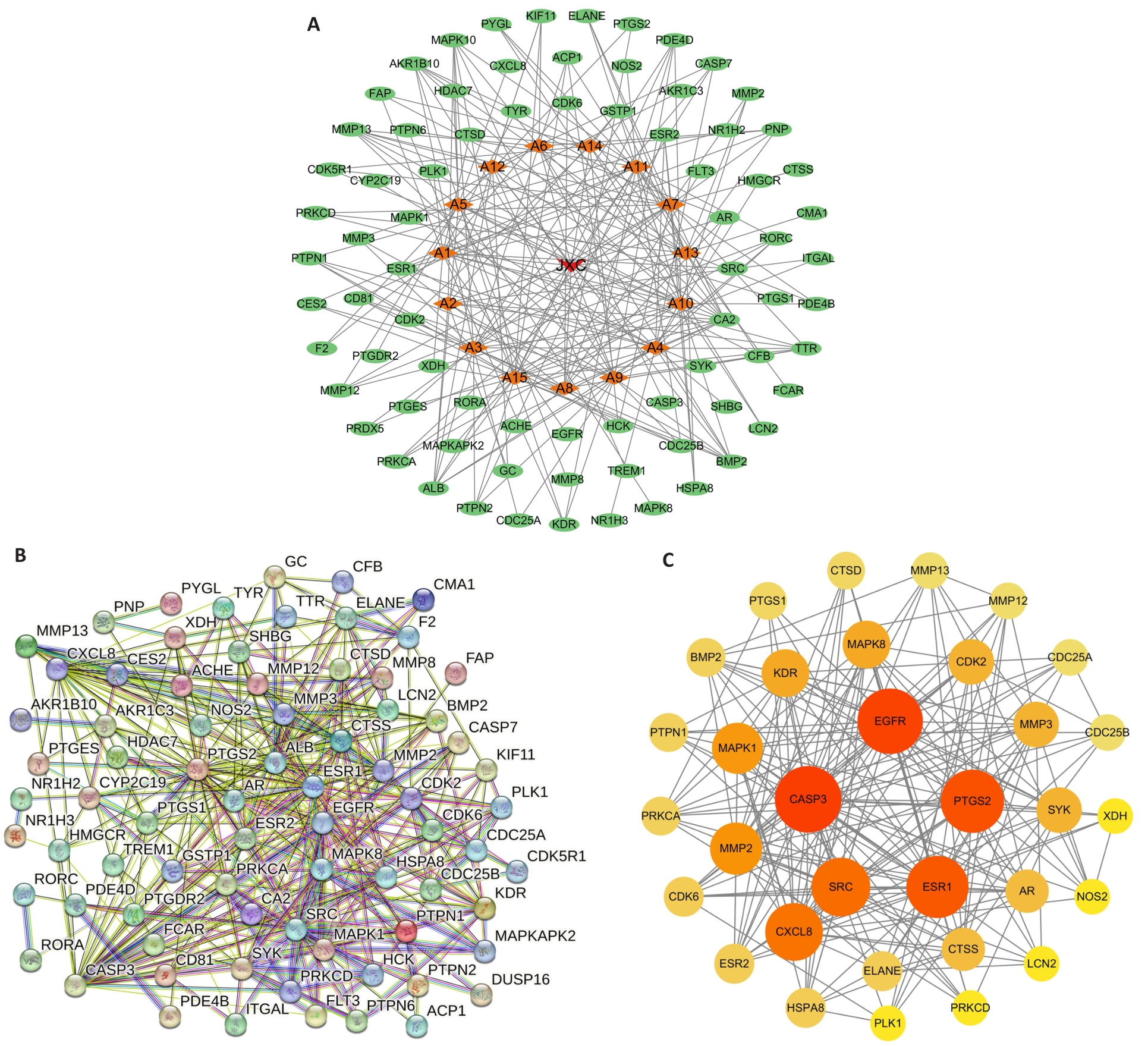
图2 "药物-活性成分-作用靶点"和PPI网络图
Fig.2 Drug-active ingredient-targets and PPI network diagram. A: Drug-active ingredient-targets network diagram. B: PPI network diagram. C: Core targets network diagram.
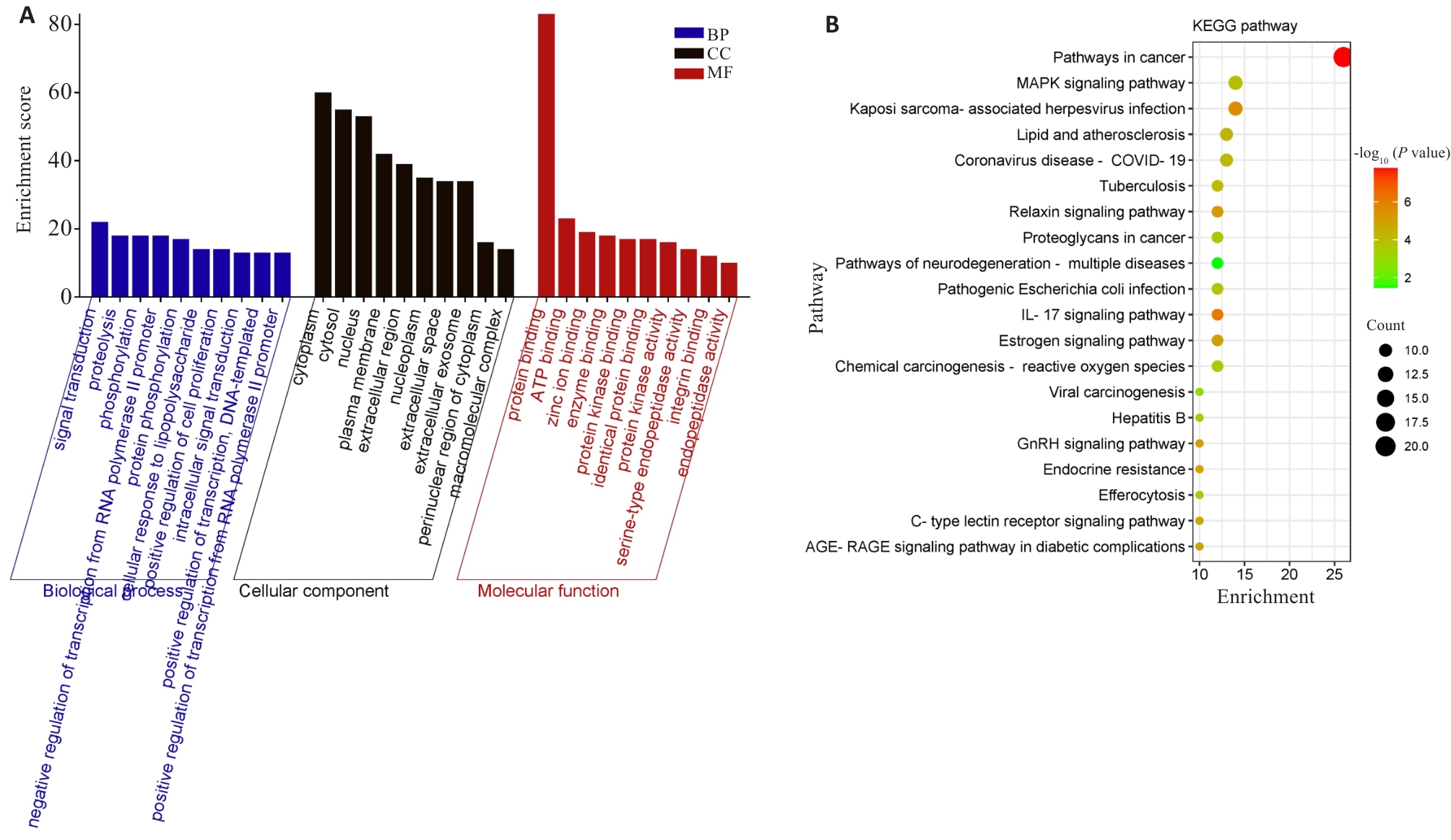
图3 积雪草抗银屑病GO功能注释与KEGG通路分析
Fig. 3 GO functional annotation and KEGG signal pathway analysis of the anti-psoriasis effect of Centella asiatica. A: GO functional annotation. B: KEGG signal pathway analysis.
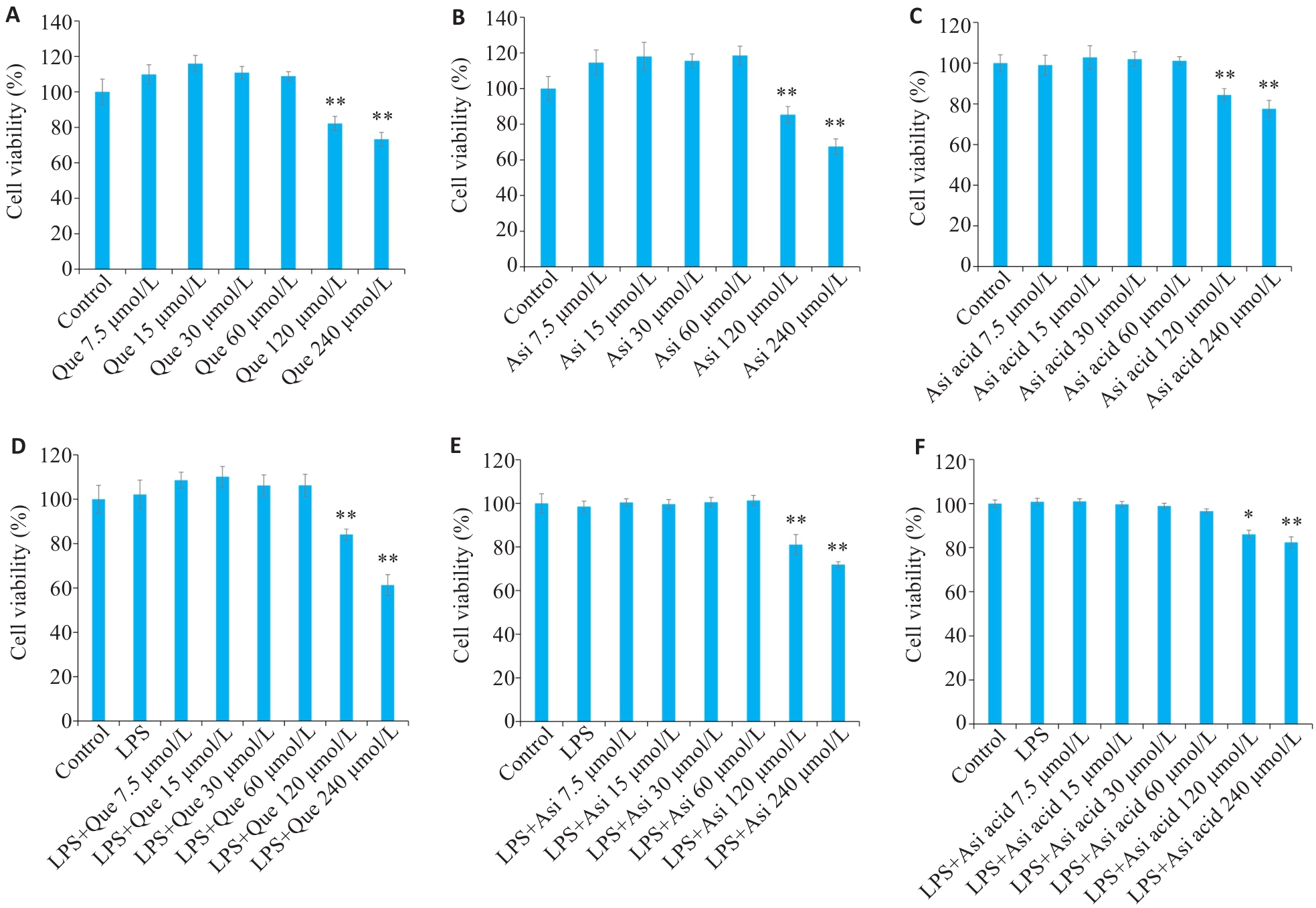
图 4 积雪草活性成分对RAW264.7细胞活力的影响
Fig.4 Effect of active components in Centella asiatica on the growth of RAW264.7 cells. A-C: Effects of Que, Asi, and Asi acid on viability of RAW264.7 cells. D-F: Effects of Que, Asi, and Asi acid on viability of RAW264.7 cells treated with LPS (100 ng/mL). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Control group.
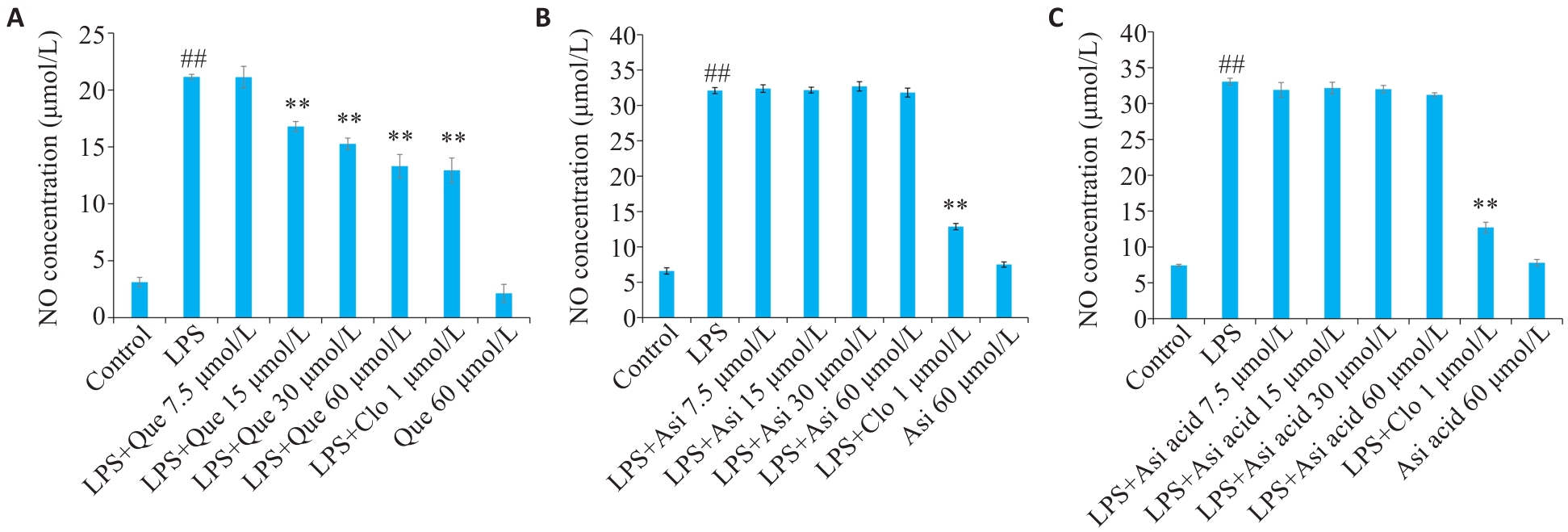
图 5 积雪草活性成分对LPS诱导的RAW264.7细胞产生NO的影响
Fig. 5 Effect of Que (A), Asi (B) and Asi acid (C) on NO levels in the cell culture media of LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells determined by Griess assay. ##P<0.01 vs Control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs LPS group.
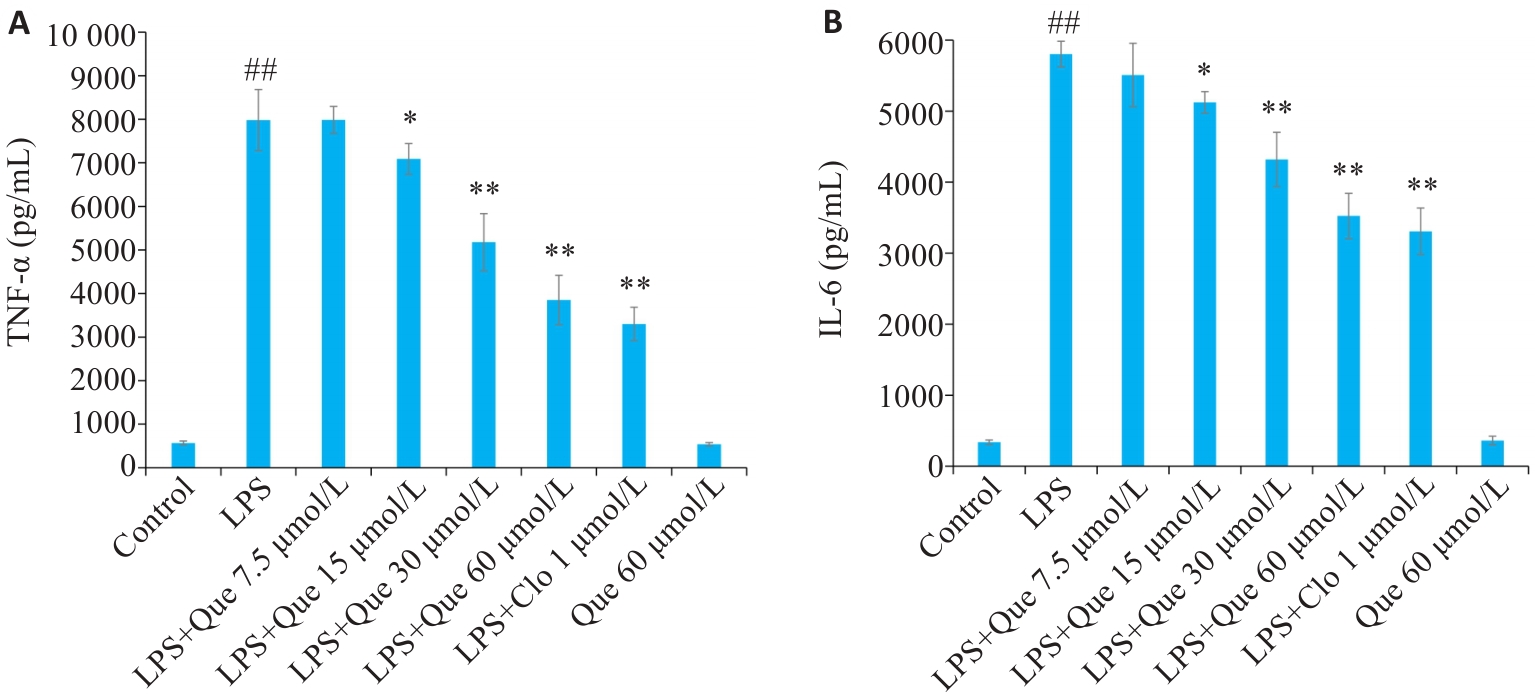
图 6 槲皮素对细胞促炎因子含量的影响
Fig. 6 Inhibitory effects of Que on secretion of TNF-α (A) and IL-6 (B) in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. ##P<0.01 vs Control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs LPS group.
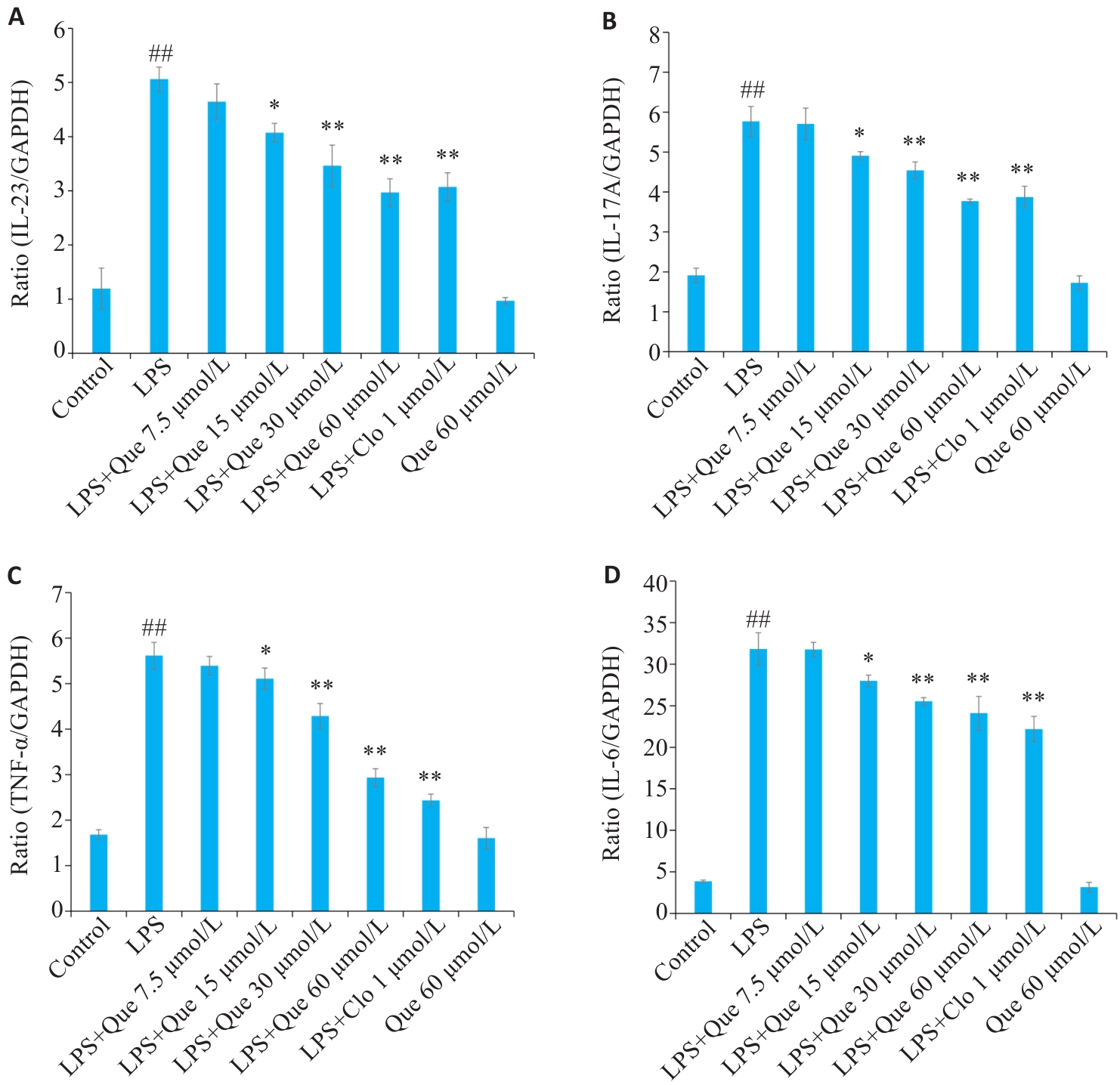
图 7 槲皮素对炎症细胞中IL-23、IL-17A、TNF-α和IL-6 mRNA表达的影响
Fig. 7 Inhibitory effects of Que on mRNA expressions of IL-23 (A), IL-17A (B), TNF-α (C), and IL-6 (D) in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. ##P<0.01 vs Control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs LPS group.
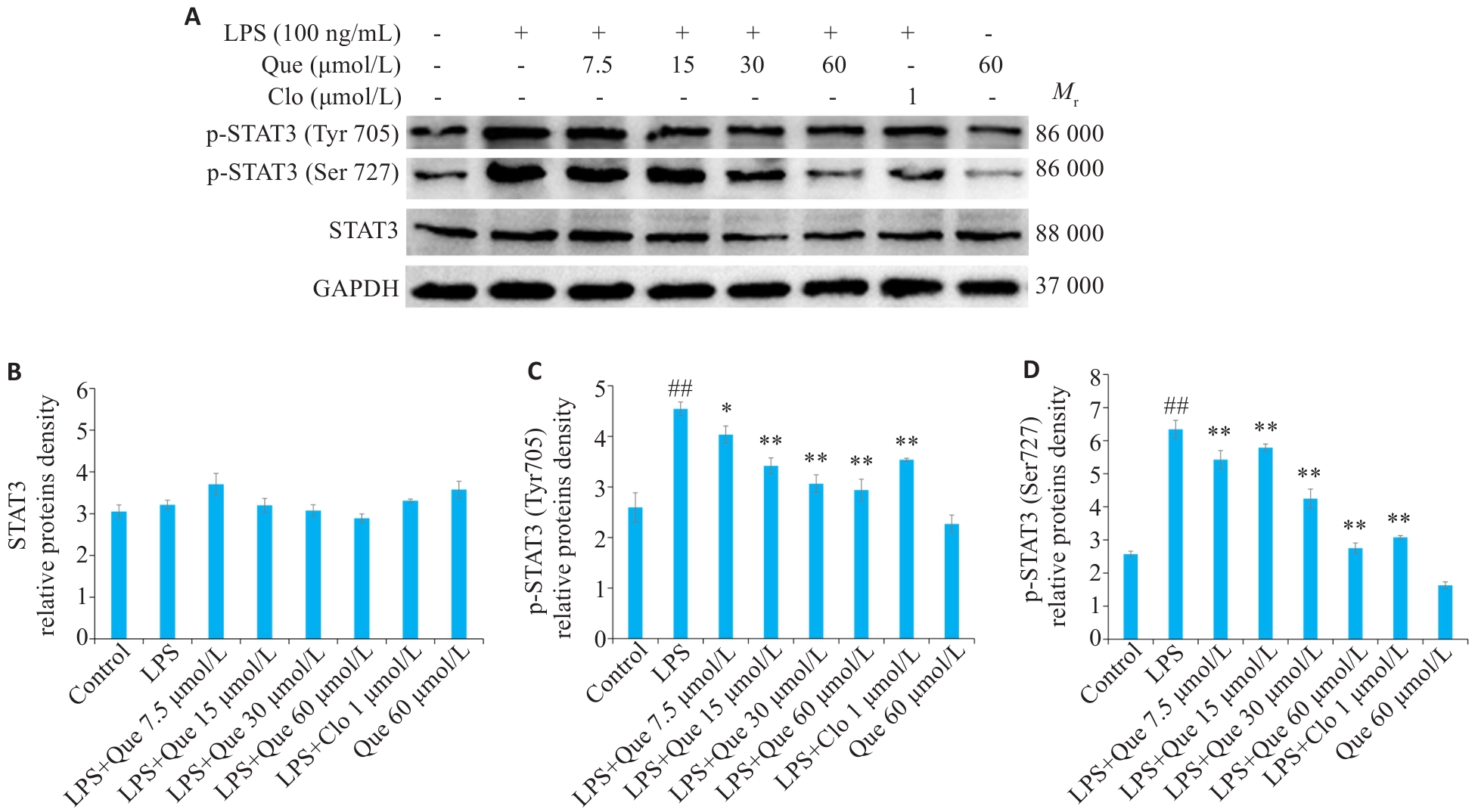
图 8 槲皮素对炎症细胞中STAT3蛋白磷酸化影响
Fig. 8 Effect of Que on STAT3 protein phosphorylation in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. A: Western blotting for detecting expressions of STAT3, p-STAT3 (Tyr705), and p-STAT3 (Ser727). B-D: Semi-quantitative analysis of STAT3, p-STAT3(Tyr705), and p-STAT3(Ser727) expression levels. ##P<0.01 vs Control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs LPS group.
| 1 | Boehncke WH, Schön MP. Psoriasis[J]. Lancet (London, England), 2015, 386(9997): 983-94. |
| 2 | Raharja A, Mahil SK, Barker JN. Psoriasis: a brief overview[J]. Clin Med, 2021, 21(3): 170-3. |
| 3 | Takuathung MN, Potikanond S, Sookkhee S, et al. Anti-psoriatic and anti-inflammatory effects of Kaempferia parviflora in keratinocytes and macrophage cells[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2021, 143: 112229. |
| 4 | Kim SY, Han SD, Kim M, et al. Mentha arvensis essential oil exerts anti-inflammatory in LPS-stimulated inflammatory responses via inhibition of ERK/NF‑κB signaling pathway and anti-atopic dermatitis-like effects in 2, 4-dinitrochlorobezene-induced BALB/c mice[J]. Antioxidants, 2021, 10(12): 1941. |
| 5 | Li PH, Li YL, Jiang H, et al. Glabridin, an isoflavan from licorice root, ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like inflammation of BALB/c mice[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2018, 59: 243-51. |
| 6 | Tan RZ, Zhong X, Han RY, et al. Macrophages mediate psoriasis via Mincle-dependent mechanism in mice[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2023, 9(1): 140. |
| 7 | Kamata M, Tada Y. Dendritic cells and macrophages in the pathogenesis of psoriasis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 941071. |
| 8 | Tokuyama M, Mabuchi T. New treatment addressing the pathogenesis of psoriasis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(20): 7488. |
| 9 | Silvagni E, Missiroli S, Perrone M, et al. From bed to bench and back: TNF‑α, IL-23/IL-17A, and JAK-dependent inflammation in the pathogenesis of psoriatic synovitis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 672515. |
| 10 | Brembilla NC, Senra L, Boehncke WH. The IL-17 family of cytokines in psoriasis: IL-17A and beyond[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 1682. |
| 11 | Sharma A, Upadhyay DK, Gupta GD, et al. IL-23/Th17 axis: a potential therapeutic target of psoriasis[J]. Curr Drug Res Rev, 2022, 14(1): 24-36. |
| 12 | Di Cesare A, Di Meglio P, Nestle FO. The IL-23/Th17 axis in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2009, 129(6): 1339-50. |
| 13 | Reid C, Griffiths CEM. Psoriasis and treatment: past, present and future aspects[J]. Acta Derm Venereol, 2020, 100(3): adv00032. |
| 14 | Bakshi H, Nagpal M, Singh M, et al. Treatment of psoriasis: a comprehensive review of entire therapies[J]. Curr Drug Saf, 2020, 15(2): 82-104. |
| 15 | Gohil KJ, Patel JA, Gajjar AK. Pharmacological review on Centella asiatica: a potential herbal cure-all[J]. Indian J Pharm Sci, 2010, 72(5): 546-56. |
| 16 | Lin P, Shi HY, Lu YY, et al. Centella asiatica alleviates psoriasis through JAK/STAT3-mediated inflammation: an in vitro and in vivo study[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 317: 116746. |
| 17 | Dagar N, Kale A, Jadhav HR, et al. Nutraceuticals and network pharmacology approach for acute kidney injury: a review from the drug discovery aspect[J]. Fitoterapia, 2023, 168: 105563. |
| 18 | Su YY, Bai Q, Tao HX, et al. Prospects for the application of traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology in food science research[J]. J Sci Food Agric, 2023, 103(11): 5183-200. |
| 19 | Dai HB, Shan Y, Yu MS, et al. Network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental verification of the mechanism of huangqi-jixuecao herb pair in treatment of peritoneal fibrosis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 318(Pt A): 116874. |
| 20 | Bhoir SS, Vishwapathi V, Singh KK. Antipsoriatic potential of Annona squamosa seed oil: an in vitro and in vivo evaluation[J]. Phytomedicine, 2019, 54: 265-77. |
| 21 | Ayoub R, Jilani J, Jarrar Q, et al. Synthesis and In-vivo evaluation of benzoxazole derivatives as promising anti-psoriatic drugs for clinical use[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(9): 3023. |
| 22 | Liu Q, Xiao XH, Hu LB, et al. Anhuienoside C ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis through inhibition of MAPK and NF‑κB signaling pathways[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2017, 8: 299. |
| 23 | Rendon A, Schäkel K. Psoriasis pathogenesis and treatment[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(6): 1475. |
| 24 | Guo J, Zhang HY, Lin WR, et al. Signaling pathways and targeted therapies for psoriasis[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 437. |
| 25 | Wu MJ, Dai C, Zeng FF. Cellular mechanisms of psoriasis pathogenesis: a systemic review[J]. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol, 2023, 16: 2503-15. |
| 26 | Armstrong AW, Read C. Pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis: a review[J]. JAMA, 2020, 323(19): 1945-60. |
| 27 | Lee HJ, Kim M. Challenges and future trends in the treatment of psoriasis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(17): 13313. |
| 28 | Li TT, Gao S, Han W, et al. Potential effects and mechanisms of Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of psoriasis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 294: 115275. |
| 29 | Wang JY, Zhang CS, Zhang AL, et al. Chinese herbal medicine bath therapy for psoriasis vulgaris using topical calcipotriol as the comparator: a systematic review with meta-analysis and association rule analysis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 330: 118166. |
| 30 | Lee Y, Choi HK, N'Deh KPU, et al. Inhibitory effect of Centella asiatica extract on DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis in HaCaT cells and BALB/c mice[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(2): 411. |
| 31 | Ghoreschi K, Balato A, Enerback C, et al. Therapeutics targeting the IL-23 and IL-17 pathway in psoriasis[J]. Lancet, 2021, 397(10275): 754-66. |
| 32 | Hawkes JE, Yan BY, Chan TC, et al. Discovery of the IL-23/IL-17 signaling pathway and the treatment of psoriasis[J]. J Immunol, 2018, 201(6): 1605-13. |
| 33 | Kukula O, Kırmızıkan S, Tiryaki ES, et al. Asiatic acid exerts an anti-psoriatic effect in the imiquimod-induced psoriasis model in mice[J]. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol, 2022, 44(3): 367-72. |
| 34 | Wang HL, Peters T, Sindrilaru A, et al. Key role of macrophages in the pathogenesis of CD18 hypomorphic murine model of psoriasis[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2009, 129(5): 1100-14. |
| 35 | Stratis A, Pasparakis M, Rupec RA, et al. Pathogenic role for skin macrophages in a mouse model of keratinocyte-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation[J]. J Clin Invest, 2006, 116(8): 2094-104. |
| 36 | Zhou W, Hu MM, Zang XH, et al. Luteolin attenuates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in BALB/c mice via suppression of inflammation response[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2020, 131: 110696. |
| 37 | Calautti E, Avalle L, Poli V. Psoriasis: a STAT3-centric view[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(1): 171. |
| 38 | Kanda N. Psoriasis: pathogenesis, comorbidities, and therapy updated[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(6): 2979. |
| 39 | Kanemaru K, Matsuyuki A, Nakamura Y, et al. Obesity exacerbates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like epidermal hyperplasia and interleukin-17 and interleukin-22 production in mice[J]. Exp Dermatol, 2015, 24(6): 436-42. |
| 40 | Cai L, Jiang CJ, Zhang GQ, et al. A multicentre randomized double-blind placebo-controlled phase III study of the efficacy andsafety ofxeligekimab (GR1501) in patients withmoderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis[J]. Br J Dermatol, 2024, 191(3): 336-43. |
| 41 | Dong WL, Nie XY, Wang JX, et al. Randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase Ⅰ/Ⅱ dose escalation and expansion trial of GR1501 in patients with plaque psoriasis: study protocol[J]. BMJ Open, 2020, 10(11): e039067. |
| [1] | 褚乔, 王小娜, 续佳颖, 彭荟林, 赵裕琳, 张静, 陆国玉, 王恺. 白头翁皂苷D通过多靶点和多途径抑制三阴性乳腺癌侵袭转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [2] | 龙秀鹏, 陶顺, 阳绅, 李素云, 饶利兵, 李莉, 张哲. 槲皮素通过抑制MAPK信号通路改善心力衰竭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 187-196. |
| [3] | 徐朦, 陈丽娜, 吴金玉, 刘丽丽, 施美, 周灏, 张国梁. “白花蛇舌草-半枝莲”治疗原发性肝癌的机制研究:基于网络药理学、分子对接及体外实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 80-89. |
| [4] | 姜一凡, 李小荣, 耿嘉逸, 陈永锋, 唐碧, 康品方. 槲皮素通过抑制HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB信号通路减轻糖尿病引起的大鼠肾脏损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1769-1775. |
| [5] | 陈星梅, 刘琴文, 李镱, 钟晓宇, 樊奇灵, 马柯, 罗柳婷, 官道刚, 朱志博. 茵陈蒿汤治疗肝纤维化的核心功能成分群以及潜在通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1508-1517. |
| [6] | 张珊苑, 蔡巧燕, 祁江晗, 殷恺馨, 何晨晨, 高铸烨, 张铃, 褚剑锋. 清心解瘀颗粒抗动脉粥样硬化的药效学及调控机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1518-1528. |
| [7] | 张钰明, 夏士程, 张淋淋, 陈梦茜, 刘晓婧, 高琴, 叶红伟. 金银花提取物对小鼠阿霉素肝脏损伤的保护作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1571-1581. |
| [8] | 王瑾瑾, 崔文飞, 窦雪伟, 尹冰磊, 牛钰琪, 牛羚, 闫国立. 鬼箭羽通过调节EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂耐药信号通路延缓糖尿病肾病的进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1243-1255. |
| [9] | 王琳月, 戚文月, 高记华, 田茂生, 许建成. 痛痒消洗剂可促进大鼠肛瘘术后的创面愈合[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1256-1265. |
| [10] | 张文祥, 顾惠贤, 陈鹏德, 吴思宇, 马洪艳, 姚蓝. 复方玉液汤通过调控PI3K/Akt信号通路抑制糖尿病大鼠心肌细胞凋亡和炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1306-1314. |
| [11] | 黄燕, 覃璐璐, 管少兴, 管宴萍, 韦玉茹, 操艾伶, 李冬梅, 韦桂宁, 苏启表. 金缕半枫荷的水提取物抑制胰腺癌的作用机制:活性成分、关键靶点和信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1336-1344. |
| [12] | 任志军, 刁建新, 王奕婷. 芎归汤通过抑制氧化应激诱导的心肌凋亡减轻小鼠心梗后心衰引起的心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1416-1424. |
| [13] | 李睿镈, 高歌, 谢曦, 罗海彬. 槟榔活性成分诱导口腔黏膜下纤维化的机制:基于网络药理学结合临床样本验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 930-940. |
| [14] | 李云飞, 杨婧怡, 张 颖, 张财霞, 韦宇翔, 王怡颖, 吴 宁, 孙见飞, 吴遵秋. 苗药四大血减轻大鼠的类风湿性关节炎:基于下调基质金属蛋白表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 739-747. |
| [15] | 陈君洁, 黄传兵, 李 明. 健脾滋肾方抑制系统性红斑狼疮患者的足细胞自噬:基于网络药理学和临床研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 465-473. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||