南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 632-642.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.21
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-07-06
出版日期:2025-03-20
发布日期:2025-03-28
通讯作者:
梁淑君,张煜
E-mail:1377981055@qq.com;390611257@qq.com;yuzhang@smu.edu.cn
作者简介:刘瑨禹,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 1377981055@qq.com
基金资助:
Jinyu LIU( ), Shujun LIANG(
), Shujun LIANG( ), Yu ZHANG(
), Yu ZHANG( )
)
Received:2024-07-06
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
Shujun LIANG, Yu ZHANG
E-mail:1377981055@qq.com;390611257@qq.com;yuzhang@smu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 提出并验证一种新的基于多尺度监督与残差反馈的深度学习分割算法(DSRF),以实现对鼻咽癌患者CT图像中小器官-视交叉和视神经的精确分割。 方法 收集来自SegRap2023、StructSeg2019和HaN-Seg2023公开数据库的212例鼻咽癌患者CT图像及其真实标签。为解决传统卷积神经网络在池化过程中小器官特征丢失的问题,设计一种基于混合池化策略的解码器,利用自适应池化和平均池化技术将高级语义特征逐步细化并融合低级语义特征,使网络学习到更细小的特征信息。采用多尺度深度监督层,在深度监督下学习丰富的多尺度、多层次语义特征,以提高对视交叉和视神经边界的识别能力。针对CT图像中视交叉和视神经对比度低的挑战,设计可使网络多次迭代的残差反馈模块,该模块充分利用模糊边界和易混淆区域的信息,通过监督迭代细化分割结果,并结合每次迭代的损失优化整个分割框架,提高分割精度和边界清晰度。采用消融实验验证各组件的有效性,并与其他方法进行对比实验。 结果 引入混合池化策略、多尺度深度监督层和残差反馈模块的DSRF算法能有效提升小器官的特征表示,实现视交叉和视神经的准确分割,其平均DSC达到0.837,ASSD低至0.351。消融实验进一步验证DSRF方法中各组成部分的贡献。 结论 本文提出的基于多尺度监督及残差反馈的深度学习分割算法能有效提升特征表示能力,实现视交叉和视神经准确分割。
刘瑨禹, 梁淑君, 张煜. 基于多尺度监督与残差反馈的优化算法有效提高鼻咽癌CT图像视交叉及视神经分割精度[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 632-642.
Jinyu LIU, Shujun LIANG, Yu ZHANG. A multi-scale supervision and residual feedback optimization algorithm for improving optic chiasm and optic nerve segmentation accuracy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma CT images[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 632-642.
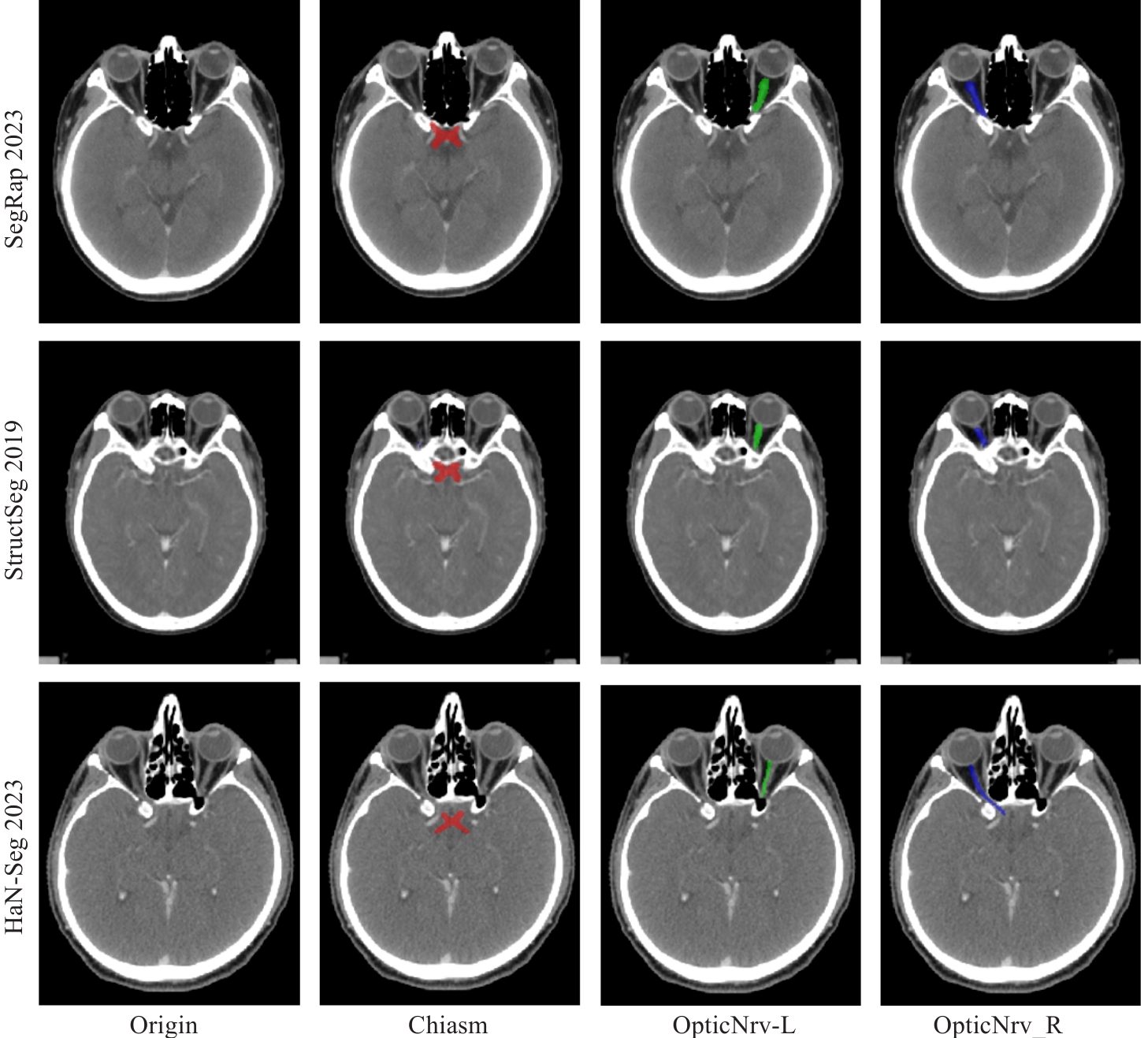
图1 3个数据集的CT图像及视交叉和视神经分割真实标签
Fig.1 CT images and ground truth labels for segmentation of the optic chiasm and optic nerve in CT images from 3 datasets. The optic chiasm is shown in red, the left optic nerve in green, and the right optic nerve in blue.
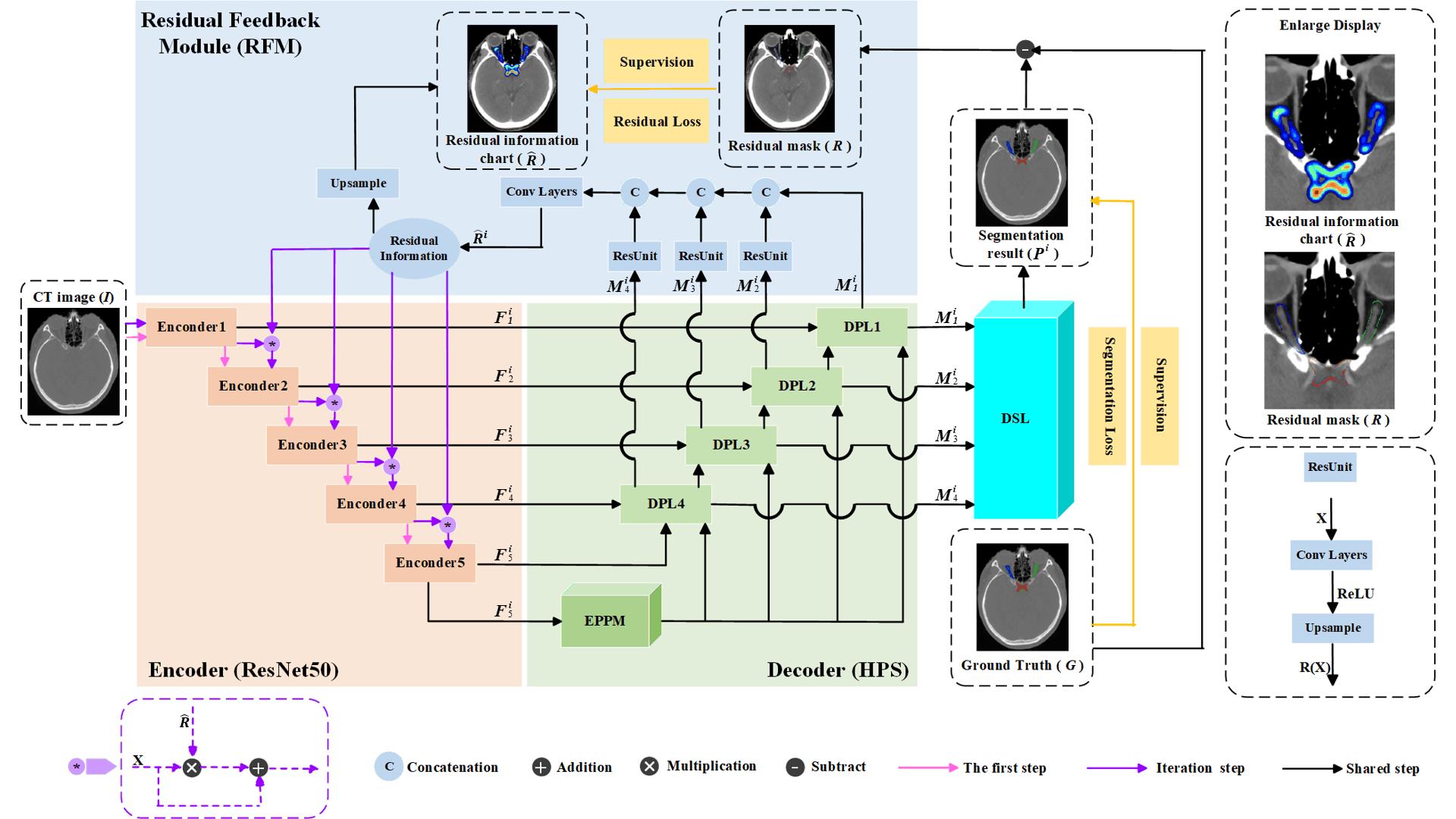
图2 DSRF网络框架
Fig.2 Deep supervision residual feedback network framework. The orange components represent the encoder, the green components represent the decoder based on the Hybrid Pooling Strategy (HPS), the blue components represent the Residual Feedback Module (RFM), and the cyan components represent the Multi-scale Deep Supervision Layers (DSL). The top-right corner shows a magnified view of the residual information map and residual mask. The bottom-right corner illustrates the structure of the residual unit.
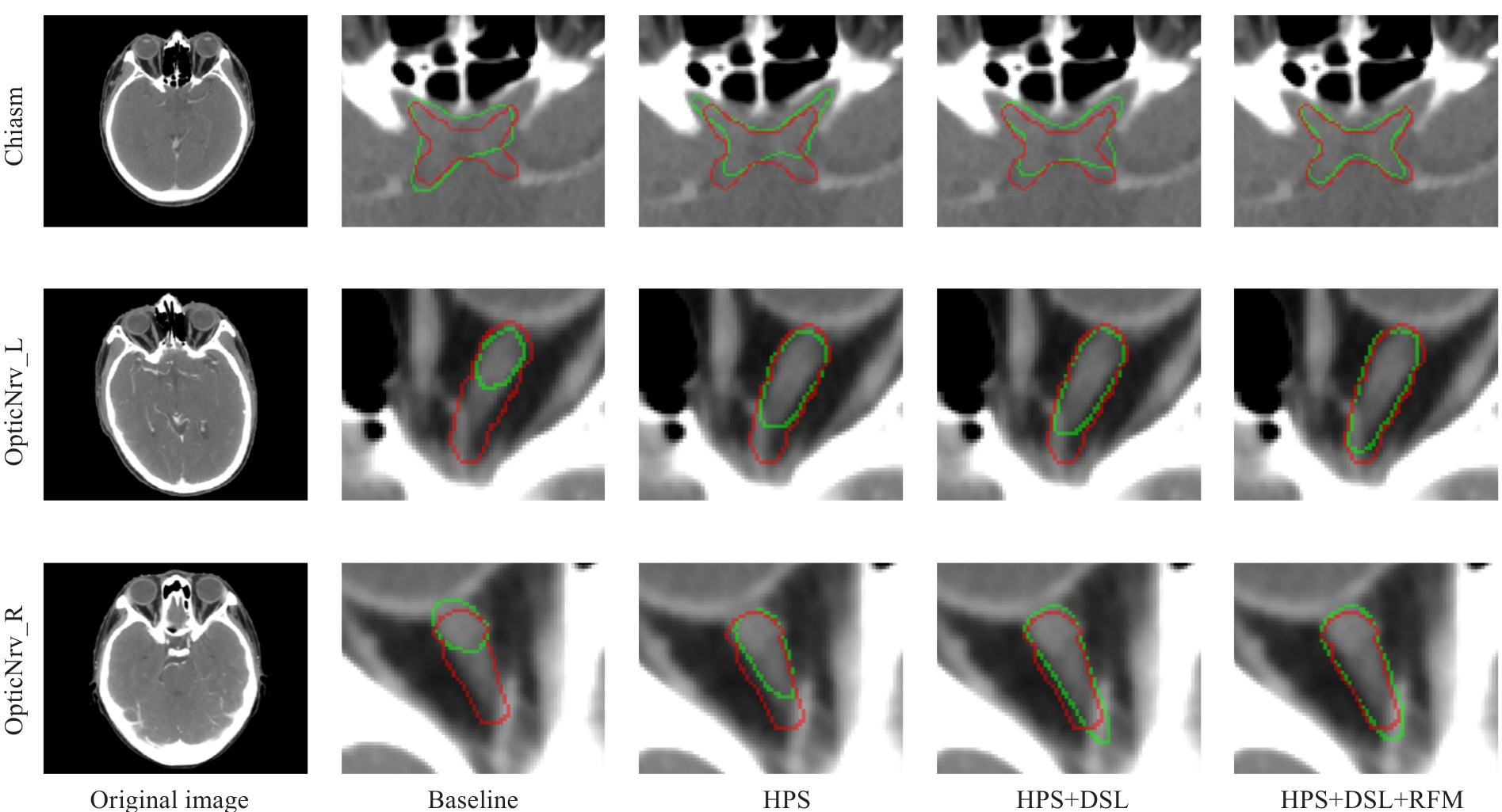
图5 DSRF在内部测试集上进行消融实验的可视化结果
Fig.5 Visualized results of the ablation experiments on the internal test set for DSRF. The ground truth labels are shown in red, and the segmentation results of the model are shown in green.
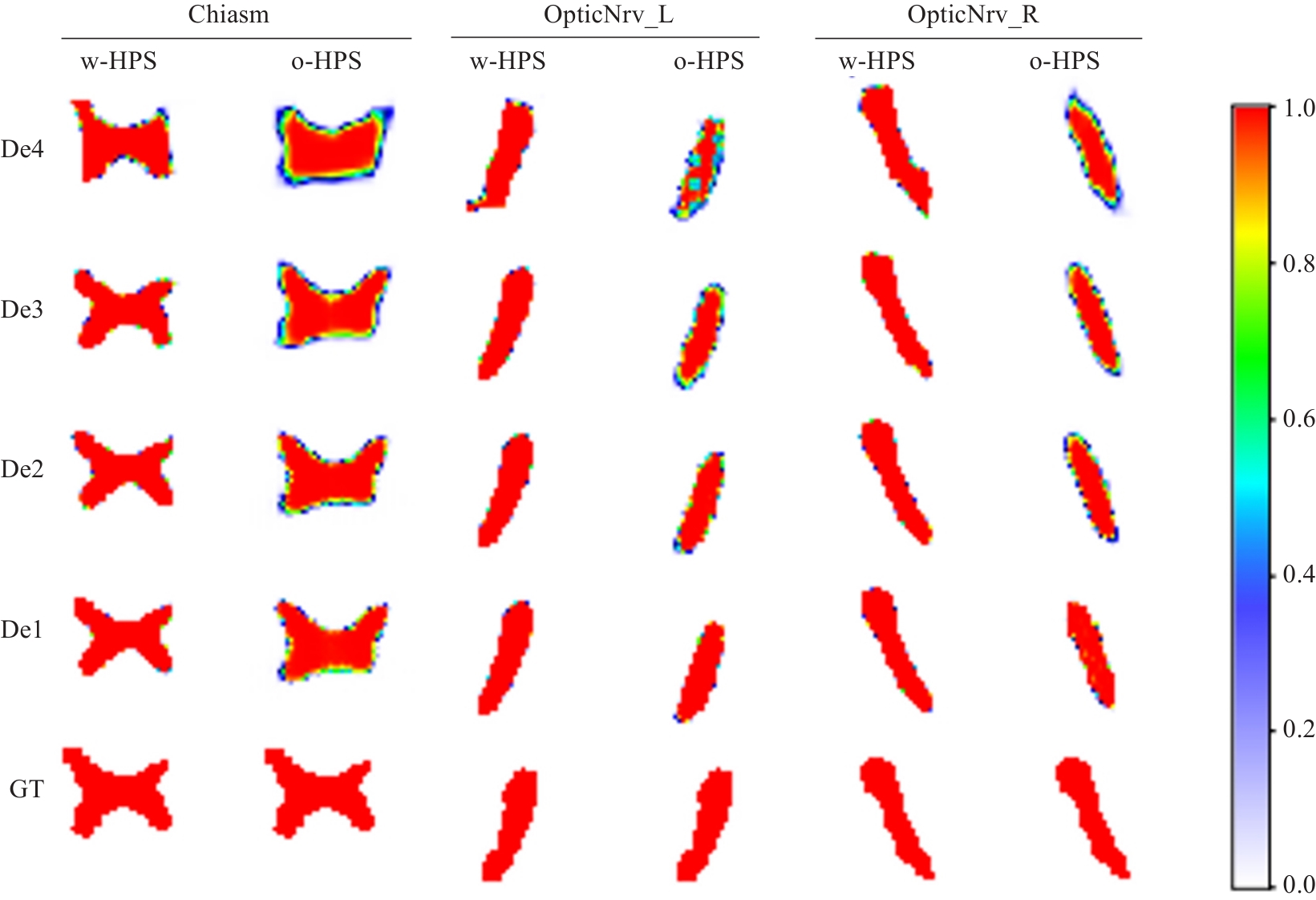
图6 解码器块语义特征热图示例
Fig.6 Examples of semantic feature heatmaps in the decoder blocks. w-HPS represents the DSRF model, o-HPS represents the DSL+RFM model, and De4 to De1 correspond to decoder blocks from deep to shallow layers. GT denotes the ground truth labels. The heatmap colors range from white to red, indicating semantic feature values from low probability to high probability.
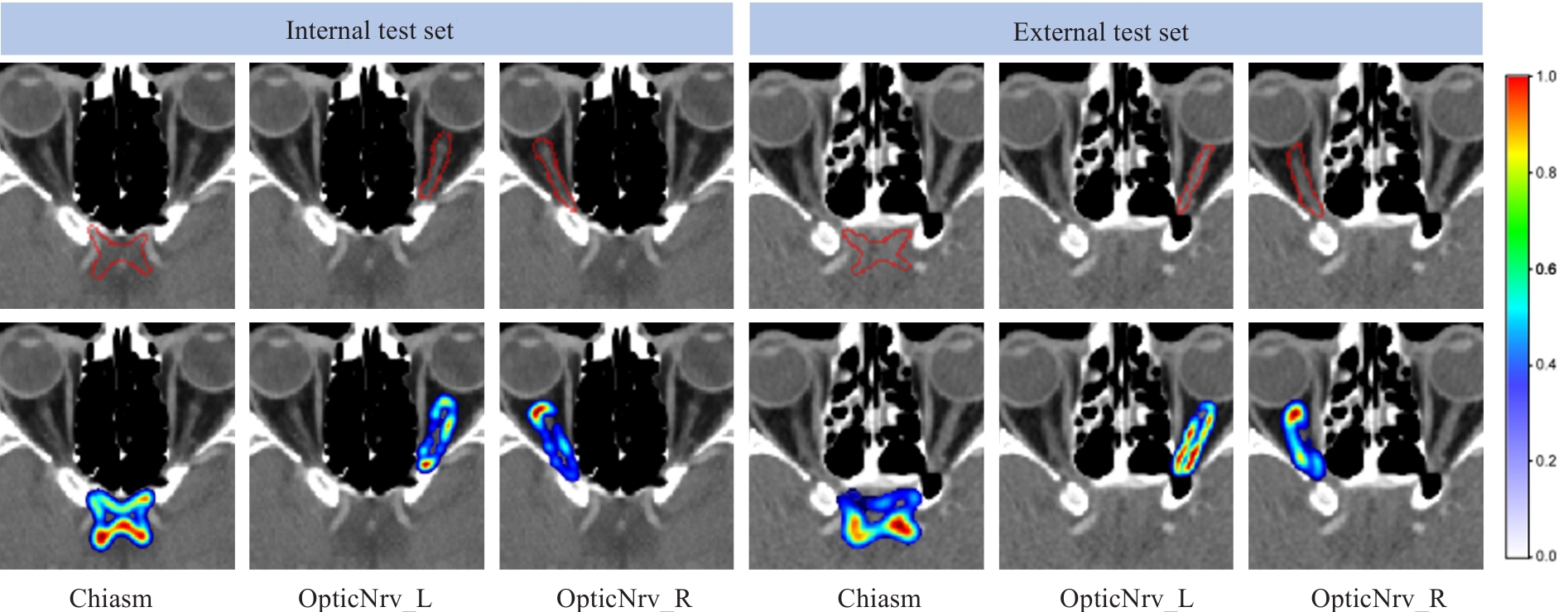
图7 残差表达的示例
Fig.7 Two examples of residual expression. The red contour in the first row represents the edge of the ground truth label. In the second row, the residual information color changes (from blue to red) indicate low to high probabilities.
| HPS | DSL | RFM | Internal Test | External Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpticNrv_L | OpticNrv_R | OpticNrv_L | OpticNrv_R | |||||
| 0.689 | 0.789 | 0.793 | 0.537 | 0.711 | 0.706 | |||
| √ | 0.729 | 0.836 | 0.838 | 0.659 | 0.768 | 0.773 | ||
| √ | 0.706 | 0.808 | 0.801 | 0.594 | 0.730 | 0.736 | ||
| √ | 0.701 | 0.796 | 0.796 | 0.564 | 0.718 | 0.717 | ||
| √ | √ | 0.712 | 0.818 | 0.821 | 0.601 | 0.747 | 0.751 | |
| √ | √ | 0.743 | 0.852 | 0.858 | 0.672 | 0.788 | 0.789 | |
| √ | √ | 0.752 | 0.858 | 0.857 | 0.688 | 0.801 | 0.813 | |
| √ | √ | √ | 0.764 | 0.872 | 0.874 | 0.708 | 0.819 | 0.828 |
表1 DSRF在内部测试集和外部测试集上进行消融实验的平均DSC结果
Tab.1 Average dice similarity coefficient of DSRF in ablation experiments on the internal and external test sets
| HPS | DSL | RFM | Internal Test | External Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpticNrv_L | OpticNrv_R | OpticNrv_L | OpticNrv_R | |||||
| 0.689 | 0.789 | 0.793 | 0.537 | 0.711 | 0.706 | |||
| √ | 0.729 | 0.836 | 0.838 | 0.659 | 0.768 | 0.773 | ||
| √ | 0.706 | 0.808 | 0.801 | 0.594 | 0.730 | 0.736 | ||
| √ | 0.701 | 0.796 | 0.796 | 0.564 | 0.718 | 0.717 | ||
| √ | √ | 0.712 | 0.818 | 0.821 | 0.601 | 0.747 | 0.751 | |
| √ | √ | 0.743 | 0.852 | 0.858 | 0.672 | 0.788 | 0.789 | |
| √ | √ | 0.752 | 0.858 | 0.857 | 0.688 | 0.801 | 0.813 | |
| √ | √ | √ | 0.764 | 0.872 | 0.874 | 0.708 | 0.819 | 0.828 |
| HPS | DSL | RFM | Internal Test | External Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpticNrv_L | OpticNrv_R | OpticNrv_L | OpticNrv_R | |||||
| 0.875 | 0.450 | 0.451 | 1.386 | 0.728 | 0.783 | |||
| √ | 0.668 | 0.326 | 0.343 | 0.925 | 0.537 | 0.541 | ||
| √ | 0.838 | 0.437 | 0.447 | 1.168 | 0.626 | 0.646 | ||
| √ | 0.867 | 0.448 | 0.452 | 1.327 | 0.658 | 0.679 | ||
| √ | √ | 0.768 | 0.366 | 0.414 | 1.068 | 0.568 | 0.614 | |
| √ | √ | 0.657 | 0.279 | 0.270 | 0.859 | 0.447 | 0.440 | |
| √ | √ | 0.640 | 0.247 | 0.270 | 0.690 | 0.374 | 0.388 | |
| √ | √ | √ | 0.601 | 0.220 | 0.232 | 0.615 | 0.334 | 0.333 |
表2 DSRF在内部测试集和外部测试集上进行消融实验的平均ASSD结果
Tab.2 Average symmetric surface distance of DSRF in ablation experiments on the internal and external test sets
| HPS | DSL | RFM | Internal Test | External Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpticNrv_L | OpticNrv_R | OpticNrv_L | OpticNrv_R | |||||
| 0.875 | 0.450 | 0.451 | 1.386 | 0.728 | 0.783 | |||
| √ | 0.668 | 0.326 | 0.343 | 0.925 | 0.537 | 0.541 | ||
| √ | 0.838 | 0.437 | 0.447 | 1.168 | 0.626 | 0.646 | ||
| √ | 0.867 | 0.448 | 0.452 | 1.327 | 0.658 | 0.679 | ||
| √ | √ | 0.768 | 0.366 | 0.414 | 1.068 | 0.568 | 0.614 | |
| √ | √ | 0.657 | 0.279 | 0.270 | 0.859 | 0.447 | 0.440 | |
| √ | √ | 0.640 | 0.247 | 0.270 | 0.690 | 0.374 | 0.388 | |
| √ | √ | √ | 0.601 | 0.220 | 0.232 | 0.615 | 0.334 | 0.333 |
| Method | DSC | ASSD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpticNrv_L | OpticNrv_R | OpticNrv_L | OpticNrv_R | |||
| DSRF0 | 0.752 | 0.858 | 0.857 | 0.640 | 0.247 | 0.270 |
| DSRF1 | 0.764 | 0.872 | 0.874 | 0.601 | 0.220 | 0.232 |
| DSRF2 | 0.759 | 0.875 | 0.876 | 0.598 | 0.214 | 0.220 |
表3 DSRF不同迭代次数的量化结果
Tab.3 Quantitative results of different iteration counts for DSRF
| Method | DSC | ASSD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpticNrv_L | OpticNrv_R | OpticNrv_L | OpticNrv_R | |||
| DSRF0 | 0.752 | 0.858 | 0.857 | 0.640 | 0.247 | 0.270 |
| DSRF1 | 0.764 | 0.872 | 0.874 | 0.601 | 0.220 | 0.232 |
| DSRF2 | 0.759 | 0.875 | 0.876 | 0.598 | 0.214 | 0.220 |
| Method | DSC | ASSD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpticNrv_L | OpticNrv_R | OpticNrv_L | OpticNrv_R | |||
| nnU-Net[ | 0.721 | 0.809 | 0.824 | 0.632 | 0.354 | 0.363 |
| PoolNet[ | 0.722 | 0.838 | 0.834 | 0.676 | 0.330 | 0.353 |
| STU-Net[ | 0.732 | 0.802 | 0.828 | 0.640 | 0.422 | 0.368 |
| UMamba[ | 0.733 | 0.816 | 0.814 | 0.769 | 0.371 | 0.409 |
| RF-Net[ | 0.735 | 0.863 | 0.869 | 0.807 | 0.246 | 0.242 |
| DSRF | 0.764 | 0.872 | 0.874 | 0.601 | 0.220 | 0.232 |
表4 DSRF与其他办法在内部测试集上的分割结果
Tab.4 Segmentation results of DSRF and other methods on the internal test set
| Method | DSC | ASSD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpticNrv_L | OpticNrv_R | OpticNrv_L | OpticNrv_R | |||
| nnU-Net[ | 0.721 | 0.809 | 0.824 | 0.632 | 0.354 | 0.363 |
| PoolNet[ | 0.722 | 0.838 | 0.834 | 0.676 | 0.330 | 0.353 |
| STU-Net[ | 0.732 | 0.802 | 0.828 | 0.640 | 0.422 | 0.368 |
| UMamba[ | 0.733 | 0.816 | 0.814 | 0.769 | 0.371 | 0.409 |
| RF-Net[ | 0.735 | 0.863 | 0.869 | 0.807 | 0.246 | 0.242 |
| DSRF | 0.764 | 0.872 | 0.874 | 0.601 | 0.220 | 0.232 |
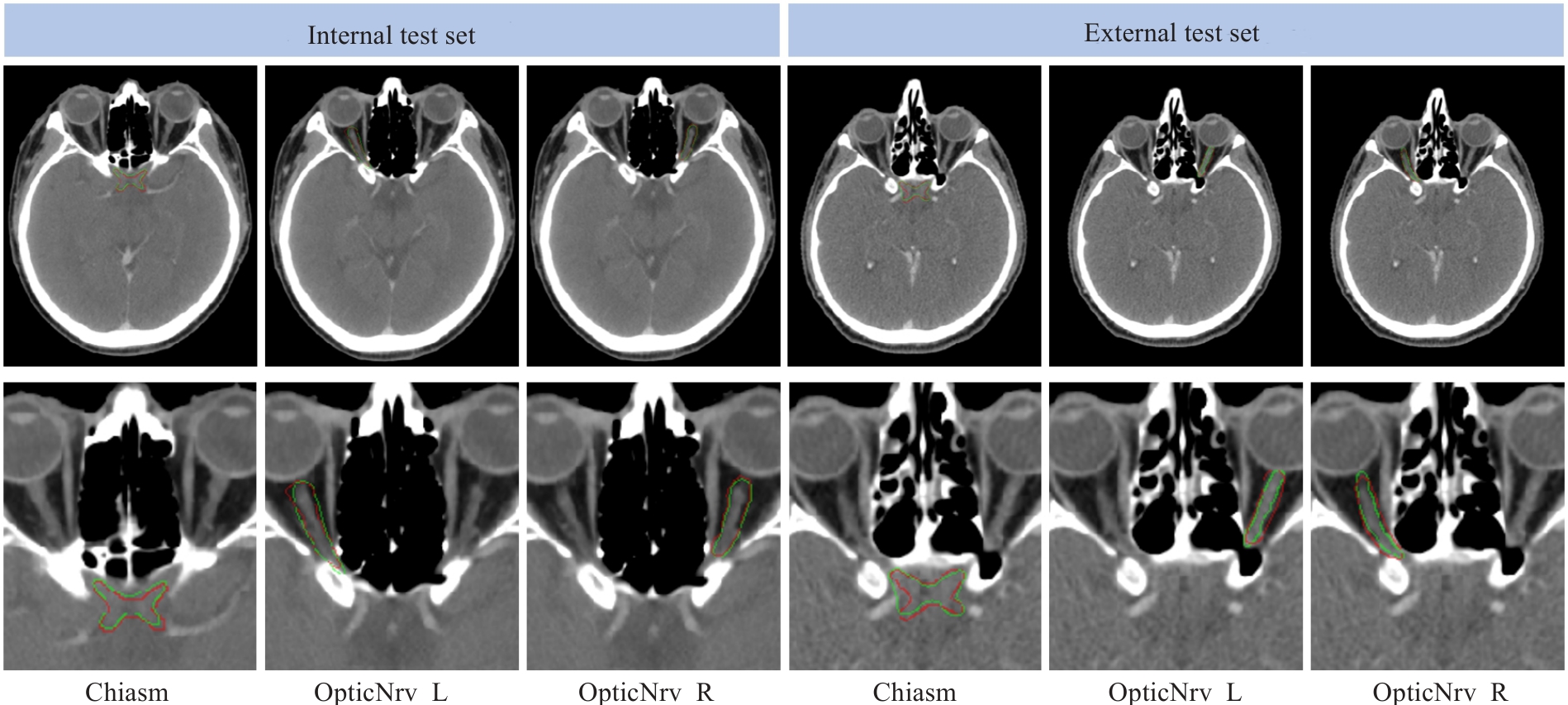
图8 两个分别从内部测试集和外部测试集中随机选择的测试对象的真实标签(红色)和我们提出的框架(绿色)的分割结果的视觉比较
Fig.8 Visual comparison of the segmentation results between the ground truth (red) and the proposed framework (green) for two randomly selected testing subjects from the internal and external test sets.
| 1 | Du XJ, Wang GY, Zhu XD, et al. Refining the 8th edition TNM classification for EBV related nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Cancer Cell, 2024, 42(3): 464-73.e3. |
| 2 | 陈美宁, 刘懿梅, 彭应林, 等. 不同级别肿瘤中心医师对鼻咽癌调强放疗靶区和危及器官勾画差异比较[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志, 2024, 41(3): 265-72. |
| 3 | Guo DZ, Jin DK, Zhu Z, et al. Organ at risk segmentation for head and neck cancer using stratified learning and neural architecture search[C]//2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, 2020: 4223-32. |
| 4 | Guo H, Wang J, Xia X, et al. The dosimetric impact of deep learning-based auto-segmentation of organs at risk on nasopharyngeal and rectal cancer[J]. Radiat Oncol, 2021, 16(1): 113. |
| 5 | Costea M, Zlate A, Durand M, et al. Comparison of atlas-based and deep learning methods for organs at risk delineation on head-and-neck CT images using an automated treatment planning system[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2022, 177: 61-70. |
| 6 | Peng YL, Liu YM, Shen GZ, et al. Improved accuracy of auto-segmentation of organs at risk in radiotherapy planning for nasopharyngeal carcinoma based on fully convolutional neural network deep learning[J]. Oral Oncol, 2023, 136: 106261. |
| 7 | Luan S, Wei C, Ding Y, et al. PCG-net: feature adaptive deep learning for automated head and neck organs-at-risk segmentation[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1177788. |
| 8 | Liu P, Sun Y, Zhao X, et al. Deep learning algorithm performance in contouring head and neck organs at risk: a systematic review and single-arm meta-analysis[J]. Biomed Eng Online, 2023, 22(1): 104. |
| 9 | Wang K, Liang SJ, Zhang Y. Residual feedback network for breast lesion segmentation in ultrasound image[M]//Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2021. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2021: 471-81. |
| 10 | Luo XD, Fu J, Zhong YX, et al. SegRap2023: a benchmark of organs-at-risk and gross tumor volume Segmentation for Radiotherapy Planning of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma[J]. Med Image Anal, 2025, 101: 103447. |
| 11 | Automatic Structure Segmentation for Radiotherapy Planning Challenge 2019. The MICCAI 2019 Challenge[OL]. Retrieved from |
| 12 | Podobnik G, Strojan P, Peterlin P, et al. HaN-Seg: The head and neck organ-at-risk CT and MR segmentation dataset[J]. Med Phys, 2023, 50(3): 1917-27. |
| 13 | Isensee F, Jaeger PF, Kohl SAA, et al. nnU-Net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation[J]. Nat Meth, 2021, 18: 203-11. |
| 14 | He KM, Zhang XY, Ren SQ, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). June 27-30, 2016. Las Vegas, NV, USA. IEEE, 2016: 770-778. |
| 15 | Kingma DP, Ba J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization [J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:, 2014. |
| 16 | Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Commun ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. |
| 17 | Liu JJ, Hou QB, Cheng MM, et al. A simple pooling-based design for real-time salient object detection[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). June 15-20, 2019. Long Beach, CA, USA. IEEE, 2019: 3917-3926. |
| 18 | Huang ZY, Ye J, Wang HY, et al. Evaluating STU-net for brain tumor segmentation[M]//Brain Tumor Segmentation, and Cross-Modality Domain Adaptation for Medical Image Segmentation. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2024: 140-51. |
| 19 | Ma J, Li FF, Wang B. U-mamba: enhancing long-range dependency for biomedical image segmentation[EB/OL]. 2024: 2401.04722. . |
| 20 | Wenderott K, Krups J, Zaruchas F, et al. Effects of artificial intelligence implementation on efficiency in medical imaging: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis[J]. NPJ Digit Med, 2024, 7: 265. |
| 21 | 赖建军, 陈丽婷, 胡海丽, 等. 基于深度学习自动勾画在鼻咽癌调强放射治疗计划中的系统性评价研究[J]. 中国现代医药杂志, 2023, 25(10): 24-30. |
| 22 | 黄 新, 王新卓, 薛 涛, 等. 鼻咽癌放射治疗危及器官自动勾画的几何和剂量学分析[J]. 生物医学工程与临床, 2024, 28(1): 26-34. |
| 23 | Su ZY, Siak PY, Lwin YY, et al. Epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: current insights and future outlook[J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2024, 43(3): 919-39. |
| 24 | Azad R, Aghdam EK, Rauland A, et al. Medical image segmentation review: the success of U-net[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2024, 46(12): 10076-95. |
| 25 | Liu JJ, Hou Q, Liu ZA, et al. PoolNet+: exploring the potential of pooling for salient object detection[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2023, 45(1): 887-904. |
| 26 | Hu K, Chen W, Sun Y, et al. PPNet: Pyramid pooling based network for polyp segmentation[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2023, 160: 107028. |
| 27 | Wu YH, Liu Y, Zhan X, et al. P2T: pyramid pooling transformer for scene understanding[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2023, 45(11): 12760-71. |
| 28 | Wang LW, Lee CY, Tu ZW, et al. Training deeper convolutional networks with deep supervision[EB/OL]. 2015: 1505.02496. . |
| 29 | Zhang LF, Chen X, Zhang JB, et al. Contrastive deep supervision[M]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2022. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2022: 1-19. |
| 30 | Ahmad S, Ullah Z, Gwak J. Multi-teacher cross-modal distillation with cooperative deep supervision fusion learning for unimodal segmentation[J]. Knowl Based Syst, 2024, 297: 111854. |
| 31 | Umer MJ, Sharif MI, Kim J. Breast cancer segmentation from ultrasound images using multiscale cascaded convolution with residual attention-based double decoder network[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 107888-902. |
| 32 | Wang J, Liang J, Xiao Y, et al. TaiChiNet: negative-positive cross-attention network for breast lesion segmentation in ultrasound images[J]. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 2024, 28(3): 1516-27. |
| [1] | 陶露, 韦卓利, 王月月, 项平. CEACAM6通过调控上皮间质转化抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 566-576. |
| [2] | 从小凡, 陈腾, 李硕, 王媛媛, 周龙云, 李小龙, 张配, 孙小锦, 赵素容. 双氢青蒿素通过促进活性氧的产生增强鼻咽癌细胞对顺铂诱导凋亡的敏感性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1553-1560. |
| [3] | 王媛媛, 陈腾, 从小凡, 李依然, 陈蕊, 张配, 孙小锦, 赵素容. 扁蒴藤素通过活性氧调控PI3K/AKT通路增强顺铂诱导鼻咽癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 904-912. |
| [4] | 胡玥, 曾玉, 王琳婧, 廖志伟, 谭剑明, 邝燕好, 龚攀, 齐斌, 甄鑫. 多模态多分类器融合模型预测放射性口腔黏膜炎的性能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2434-2442. |
| [5] | 张浩轩, 陆 进, 蒋成义, 方美芳. 基于人工智能技术的鼻咽癌风险预测模型的构建与评价[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 271-279. |
| [6] | 胡 桐, 勾文峰, 任中昊, 刘改廷, 李祎亮, 左代英, 侯文彬. 淫羊藿素通过调控铁死亡增加鼻咽癌细胞的放射敏感性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1665-1673. |
| [7] | 张恒毅, 庞金龙, 张语涵, 马 月, 范方田, 刘 浩. AZD9291通过抑制PI3K-AKT-mTOR通路抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(9): 1403-1409. |
| [8] | 周兰柱, 吴 俊, 张明洁 , 赵 报 , 马士崟. PRMT1通过促进RRM2表达抑制鼻咽癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(12): 1783-1790. |
| [9] | 高莉莉, 张 雄, 窦思雨, 岳小丁, 杨捷玲. 干扰长链编码RNA FOXCUT能抑制鼻咽癌细胞上皮间质转化及诱导线粒体损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(9): 1334-1341. |
| [10] | 王文忠, 周兰柱, 孙 哲, 吴 俊, 崔忆旋. TRIM59靶向调控PPM1B对鼻咽癌侵袭和迁移的作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(7): 1030-1036. |
| [11] | 陈星睿, 李登科, 黄仲曦, 钟水生, 蔡林波. EBV 阳性人鼻咽癌细胞外泌体促进淋巴管新生与鼻咽癌淋巴结转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(12): 1776-1783. |
| [12] | 时宗芬,张配,鲁星月,朱晨露,陈长江,赵素容,刘浩. 下调miR-205-5p增强3-溴丙酮酸对人鼻咽癌CNE2Z细胞的凋亡诱导作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(10): 1166-. |
| [13] | 曾玉梅,王思思,封慕茵,邵钟铭,袁建玲,申志华,揭伟. SETD2基因敲除前后鼻咽癌细胞中定量蛋白组学研究及差异信号富集[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(10): 1191-. |
| [14] | 周雅青,杨蓉,马刚. 沉默YAP1 可抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖、迁移及侵袭能力[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(03): 286-. |
| [15] | 王浩,李维,谭国林. 长片段非编码RNA XIST可改变人鼻咽癌HNE1 细胞对顺铂的耐药性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(03): 357-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||