南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 853-861.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.21
• • 上一篇
张毅1,2( ), 沈昱1,2, 万志强1,2, 陶嵩1, 柳亚魁1, 王栓虎1(
), 沈昱1,2, 万志强1,2, 陶嵩1, 柳亚魁1, 王栓虎1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-26
出版日期:2025-04-20
发布日期:2025-04-28
通讯作者:
王栓虎
E-mail:2826348547@qq.com;knight01030103@126.com
作者简介:张 毅,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 2826348547@qq.com
基金资助:
Yi ZHANG1,2( ), Yu SHEN1,2, Zhiqiang WAN1,2, Song TAO1, Yakui LIU1, Shuanhu WANG1(
), Yu SHEN1,2, Zhiqiang WAN1,2, Song TAO1, Yakui LIU1, Shuanhu WANG1( )
)
Received:2024-09-26
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
Shuanhu WANG
E-mail:2826348547@qq.com;knight01030103@126.com
摘要:
目的 探究周期蛋白依赖性激酶抑制因子3(CDKN3)在胃癌中的表达情况,并分析其影响胃癌患者预后的潜在作用机制。 方法 纳入114例胃癌患者资料,分析CDKN3在胃癌组织中表达水平及其对胃癌患者术后5年生存率的影响;GO及KEGG富集分析预测CDKN3的生物学功能及可能的作用机制;通过慢病毒转染技术干预CDKN3的表达。采用Transwell、CCK-8、TUNEL染色、流式细胞术及Western blotting验证生物学功能。 结果 CDKN3在胃癌组织的表达水平显著高于癌旁组织(P<0.01),且CDKN3的表达水平与CEA、CA19-9、T分期及N分期相关(P<0.05)。单因素联合多因素分析显示,CDKN3高表达是影响胃癌患者术后5年生存率的独立风险因子(P<0.05)且CDKN3高表达对胃癌患者远期预后具有预判价值(P<0.01)。生物信息学富集分析提示CDKN3的功能可能与凋亡有关。Transwell实验结果显示,下调CDKN3可抑制胃癌细胞迁移、侵袭,上调则反之(P<0.01)。TUNEL染色结果显示,癌旁组织中细胞凋亡水平高于胃癌组织(P<0.01)。CCK-8和流式结果显示,降低CDKN3表达可抑制胃癌细胞的增殖,升高胃癌细胞凋亡率(P<0.05)。Western blotting结果显示过表达CDKN3后,p53、p21和促凋亡蛋白Bax表达降低,p-p65和抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2表达升高(P<0.05)。 结论 CDKN3在胃癌组织中高表达并影响患者预后,其可能通过p53/NF-κB信号通路调控胃癌细胞凋亡并抑制其增殖、侵袭与迁移有关。
张毅, 沈昱, 万志强, 陶嵩, 柳亚魁, 王栓虎. CDKN3高表达促进胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭:基于调控p53/NF-κB信号通路和抑制胃癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 853-861.
Yi ZHANG, Yu SHEN, Zhiqiang WAN, Song TAO, Yakui LIU, Shuanhu WANG. High expression of CDKN3 promotes migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating the p53/NF-κB signaling pathway and inhibiting cell apoptosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 853-861.
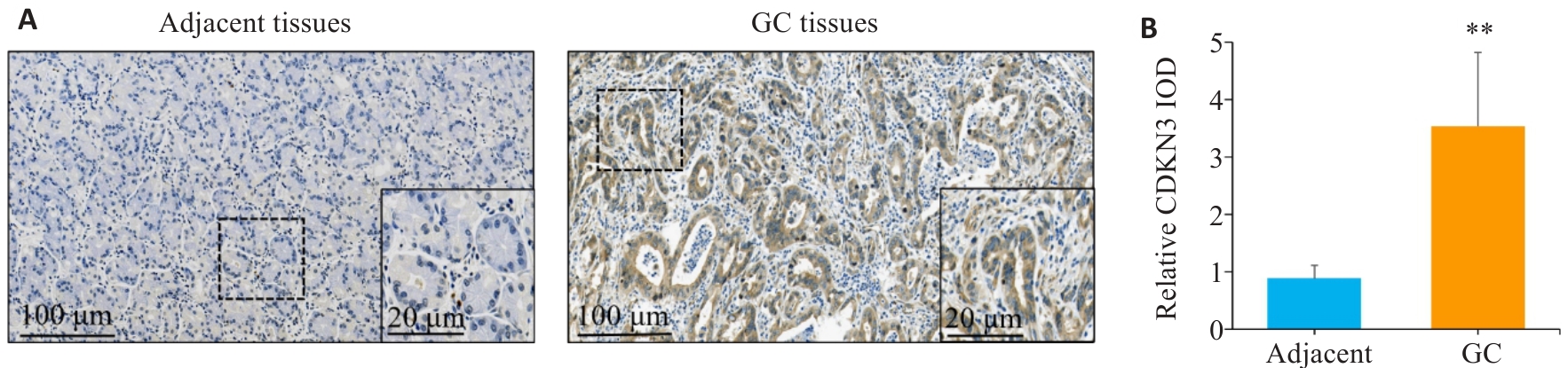
图1 CDKN3在胃癌及癌旁组织中的表达情况
Fig.1 Expression of CDKN3 in gastric cancer (GC) and adjacent tissues. A: Immunohistochemistry of CDKN3 in gastric cancer (GC) and adjacent tissues. B: Relative IOD values of CDKN3 expression. **P<0.01.
| Clinicopatholological parameters | n | CDKN3 | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low expression (n=57) | High expression (n=57) | ||||
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 81 | 43 (53.09%) | 38 (46.91%) | 1.066 | 0.302 |
| Female | 33 | 14 (42.42%) | 19 (57.58%) | ||
| Age (year) | |||||
| <60 | 46 | 22 (47.83%) | 24 (52.17%) | 0.146 | 0.703 |
| ≥60 | 68 | 35 (51.47%) | 33 (48.53%) | ||
| CEA (μg/L) | |||||
| <5 | 69 | 46 (66.67%) | 23 (33.33%) | 19.422 | <0.001 |
| ≥5 | 45 | 11 (24.44%) | 34 (75.56%) | ||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | |||||
| <37 | 86 | 53 (61.63%) | 33 (38.37%) | 18.937 | <0.001 |
| ≥37 | 28 | 4 (14.29%) | 24 (85.71%) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | |||||
| <5 | 67 | 38 (56.72%) | 29 (43.28%) | 2.932 | 0.087 |
| ≥5 | 47 | 19 (40.43%) | 28 (59.57%) | ||
| Histological type | |||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 104 | 53 (50.96%) | 51 (49.04%) | 0.438 | 0.508 |
| Other | 10 | 4 (40.00%) | 6 (60.00%) | ||
| Grade of differentiation | |||||
| Well | 10 | 4 (40.00%) | 6 (60.00%) | 4.001 | 0.135 |
| Moderate | 38 | 24 (63.16%) | 14 (36.84%) | ||
| Poor | 66 | 29 (43.94%) | 37 (56.06%) | ||
| T Stage | |||||
| T1-T2 | 37 | 24 (64.86%) | 13 (35.14%) | 4.842 | 0.028 |
| T3-T4 | 77 | 33 (42.86%) | 44 (57.14%) | ||
| N Stage | |||||
| N0-N1 | 71 | 41 (57.75%) | 30 (42.25%) | 4.518 | 0.034 |
| N2-N3 | 43 | 16 (37.21%) | 27 (62.79%) | ||
表1 CDKN3表达量与胃癌患者临床病理参数间的关系
Tab.1 Relationship between the expression level of CDKN3 in GC tissues and clinicopathological parameters of the patients
| Clinicopatholological parameters | n | CDKN3 | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low expression (n=57) | High expression (n=57) | ||||
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 81 | 43 (53.09%) | 38 (46.91%) | 1.066 | 0.302 |
| Female | 33 | 14 (42.42%) | 19 (57.58%) | ||
| Age (year) | |||||
| <60 | 46 | 22 (47.83%) | 24 (52.17%) | 0.146 | 0.703 |
| ≥60 | 68 | 35 (51.47%) | 33 (48.53%) | ||
| CEA (μg/L) | |||||
| <5 | 69 | 46 (66.67%) | 23 (33.33%) | 19.422 | <0.001 |
| ≥5 | 45 | 11 (24.44%) | 34 (75.56%) | ||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | |||||
| <37 | 86 | 53 (61.63%) | 33 (38.37%) | 18.937 | <0.001 |
| ≥37 | 28 | 4 (14.29%) | 24 (85.71%) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | |||||
| <5 | 67 | 38 (56.72%) | 29 (43.28%) | 2.932 | 0.087 |
| ≥5 | 47 | 19 (40.43%) | 28 (59.57%) | ||
| Histological type | |||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 104 | 53 (50.96%) | 51 (49.04%) | 0.438 | 0.508 |
| Other | 10 | 4 (40.00%) | 6 (60.00%) | ||
| Grade of differentiation | |||||
| Well | 10 | 4 (40.00%) | 6 (60.00%) | 4.001 | 0.135 |
| Moderate | 38 | 24 (63.16%) | 14 (36.84%) | ||
| Poor | 66 | 29 (43.94%) | 37 (56.06%) | ||
| T Stage | |||||
| T1-T2 | 37 | 24 (64.86%) | 13 (35.14%) | 4.842 | 0.028 |
| T3-T4 | 77 | 33 (42.86%) | 44 (57.14%) | ||
| N Stage | |||||
| N0-N1 | 71 | 41 (57.75%) | 30 (42.25%) | 4.518 | 0.034 |
| N2-N3 | 43 | 16 (37.21%) | 27 (62.79%) | ||
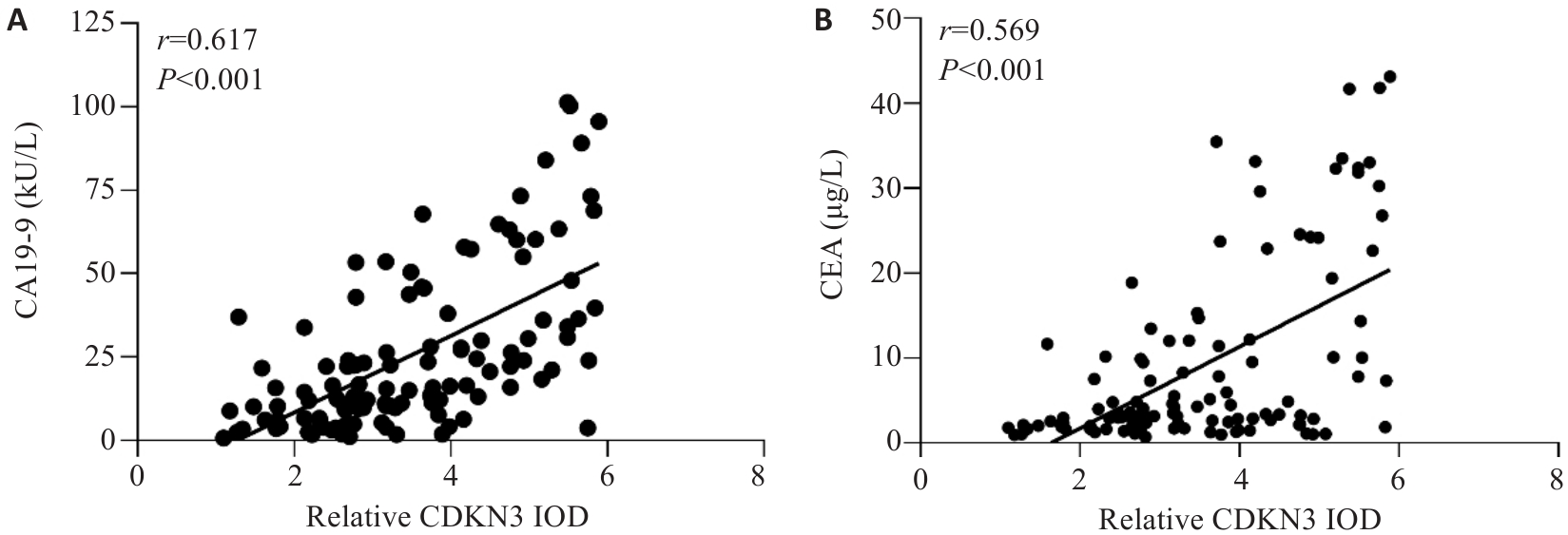
图2 胃癌组织中CDKN3表达水平与CA19-9及CEA的相关性分析
Fig.2 Correlation analysis between the expression level of CDKN3 in GC and the levels of CA19-9 and CEA in peripheral blood. A: Correlation analysis between CDKN3 and CA19-9. B: Correlation analysis between CDKN3 and CEA.
| Factors | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log-rank χ2 | P | HR | 95% CI | P | ||
| Gender (female vs male) | 0.108 | 0.742 | - | - | - | |
| Age (≥60 years vs <60 years) | 0.162 | 0.687 | - | - | - | |
| CDKN3 expression (high vs low) | 34.036 | <0.001 | 2.819 | 1.396-5.692 | 0.004 | |
| CEA(≥5 μg/L vs <5 μg/L) | 20.961 | <0.001 | 1.954 | 1.084-3.522 | 0.026 | |
| CA19-9 (≥37 kU/L vs <37 kU/L) | 22.695 | <0.001 | 1.847 | 1.048-3.257 | 0.034 | |
| Tumor size (≥5 cm vs <5 cm) | 6.139 | 0.013 | 0.978 | 0.552-1.730 | 0.938 | |
| Histological type (other vs adenocarcinoma) | 0.309 | 0.578 | - | - | - | |
| Grade of differentiation (well vs moderate vs poor) | 5.623 | 0.060 | - | - | - | |
| T Stage (T3-T4vs T1-T2) | 13.586 | <0.001 | 2.438 | 1.160-5.120 | 0.019 | |
| N Stage (N2-N3vs N0-N1) | 20.178 | <0.001 | 2.099 | 1.177-3.744 | 0.012 | |
表2 影响胃癌根治术后5年生存率的单因素及多因素分析
Tab.2 Univariate and multivariate analyses of the factors affecting the 5-year survival rate after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer patients
| Factors | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log-rank χ2 | P | HR | 95% CI | P | ||
| Gender (female vs male) | 0.108 | 0.742 | - | - | - | |
| Age (≥60 years vs <60 years) | 0.162 | 0.687 | - | - | - | |
| CDKN3 expression (high vs low) | 34.036 | <0.001 | 2.819 | 1.396-5.692 | 0.004 | |
| CEA(≥5 μg/L vs <5 μg/L) | 20.961 | <0.001 | 1.954 | 1.084-3.522 | 0.026 | |
| CA19-9 (≥37 kU/L vs <37 kU/L) | 22.695 | <0.001 | 1.847 | 1.048-3.257 | 0.034 | |
| Tumor size (≥5 cm vs <5 cm) | 6.139 | 0.013 | 0.978 | 0.552-1.730 | 0.938 | |
| Histological type (other vs adenocarcinoma) | 0.309 | 0.578 | - | - | - | |
| Grade of differentiation (well vs moderate vs poor) | 5.623 | 0.060 | - | - | - | |
| T Stage (T3-T4vs T1-T2) | 13.586 | <0.001 | 2.438 | 1.160-5.120 | 0.019 | |
| N Stage (N2-N3vs N0-N1) | 20.178 | <0.001 | 2.099 | 1.177-3.744 | 0.012 | |
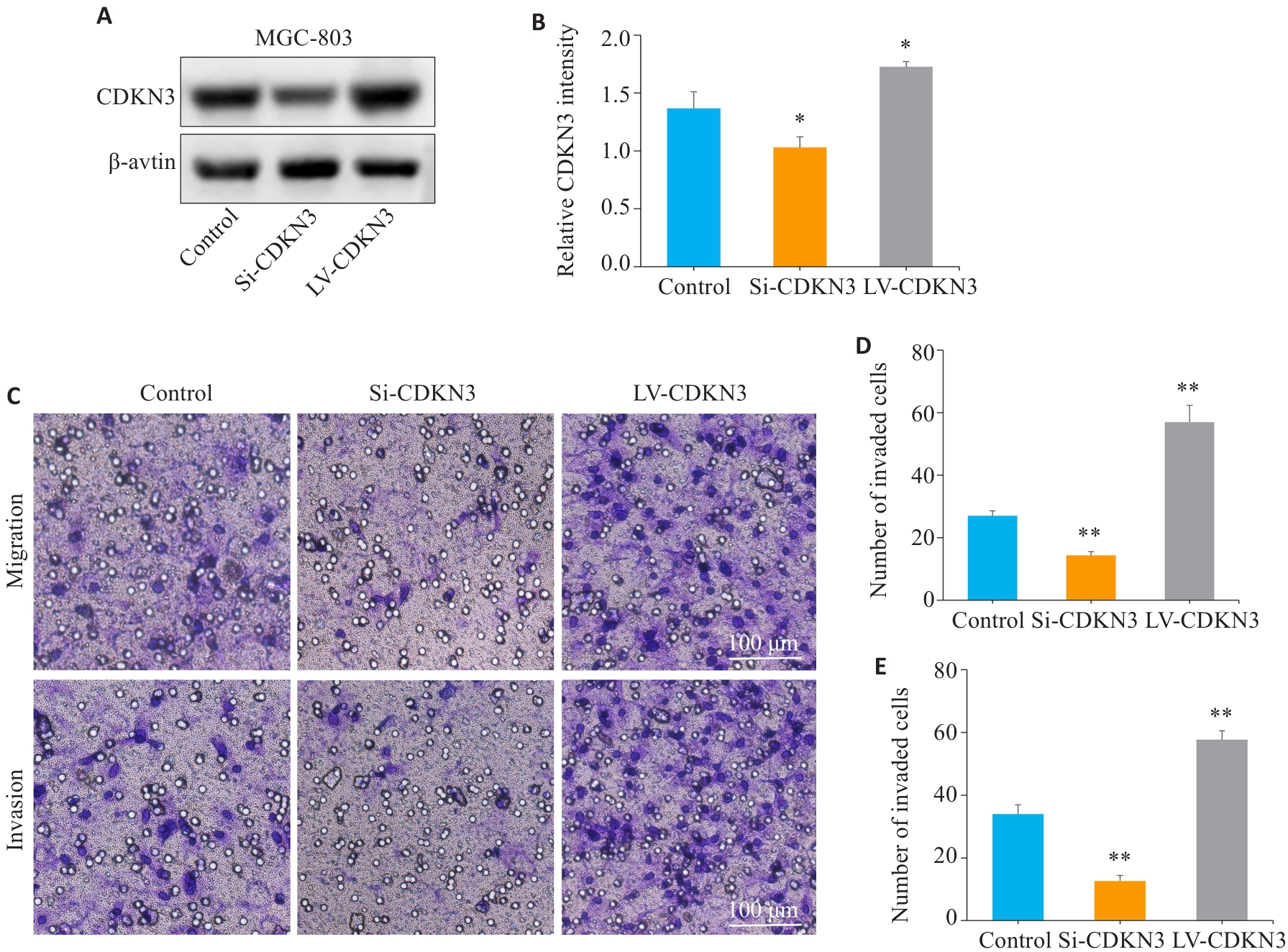
图5 CDKN3促进胃癌细胞的迁移与侵袭
Fig.5 CDKN3 overexpression promotes gastric cancer cell migration and invasion. A,B: The expression of CDKN3 protein after lentivirus transfection was detected by Western blotting. C:Transwell experiment for analyzing the impact of CDKN3 on the migration and invasion abilities of MGC803 cells. D: Quantitative analysis of the number of migrated cells. E: Quantitative analysis of the number of invaded cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs control.
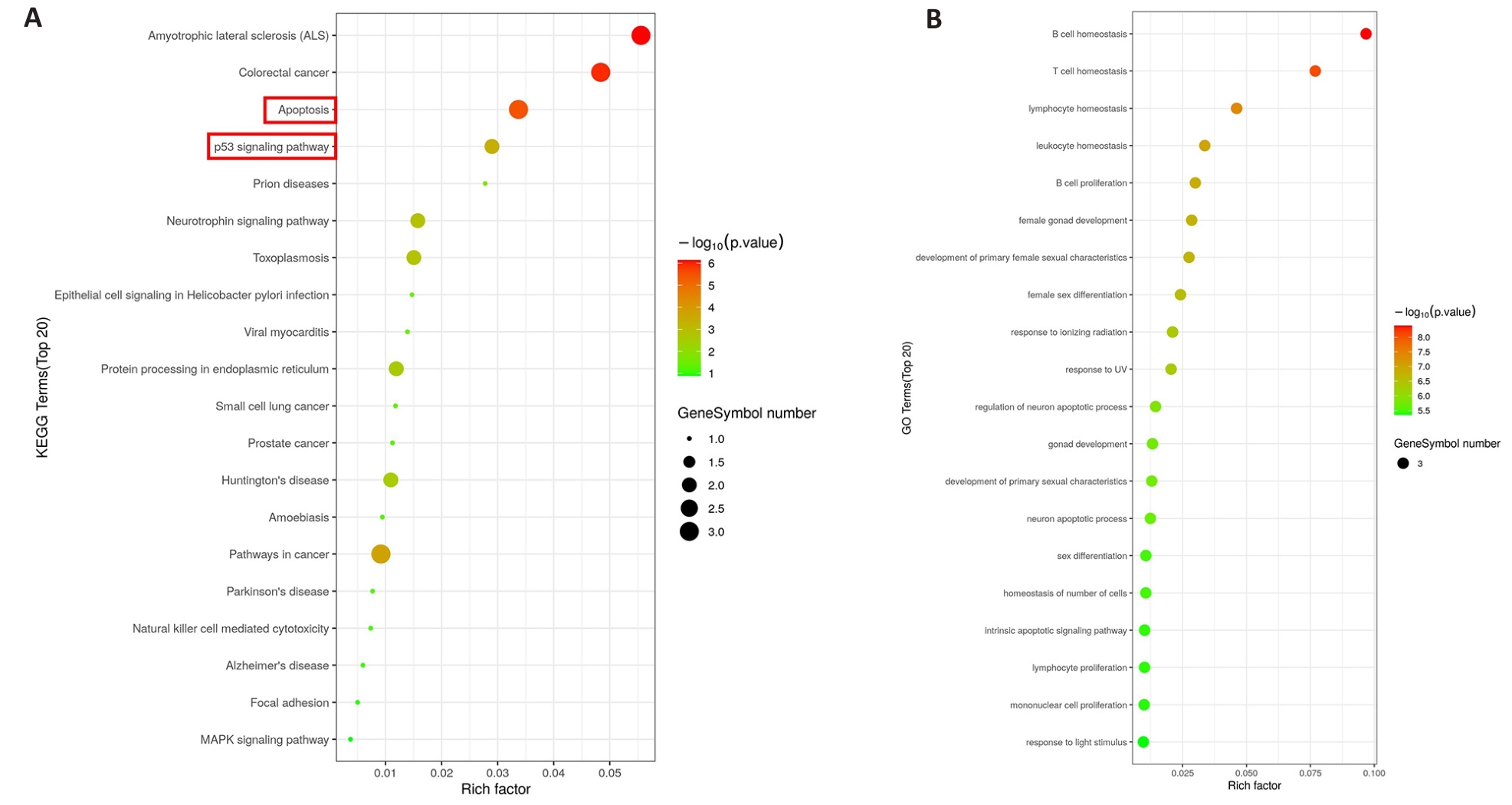
图6 CDKN3的KEGG和GO富集分析
Fig.6 KEGG and GO enrichment analysis of CDKN3. A: KEGG analysis of CDKN3 in gastric cancer. B: GO analysis of CDKN3 in gastric cancer.
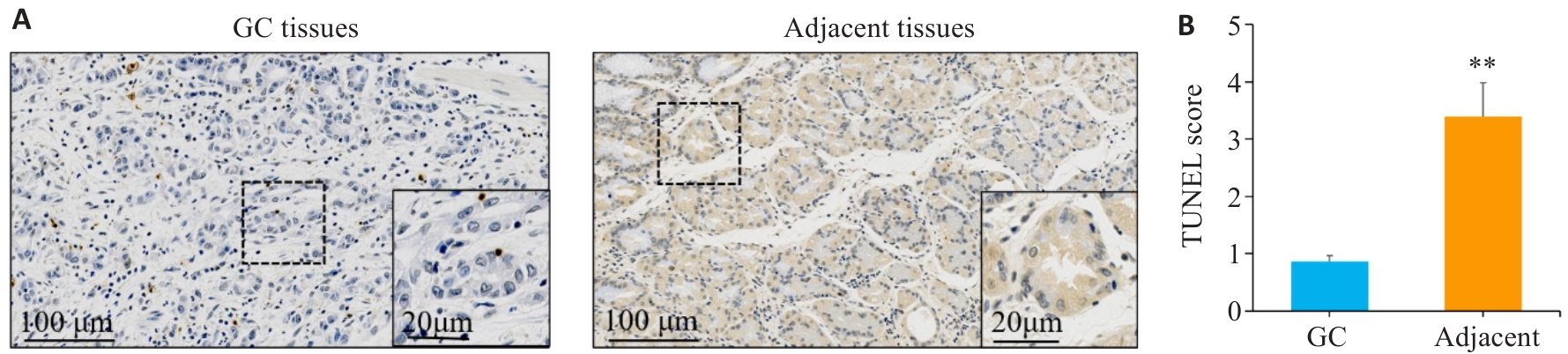
图7 TUNEL染色检测胃癌及癌旁组织中细胞凋亡情况
Fig.7 TUNEL staining was used to detect cell apoptosis in gastric cancer and adjacent tissues. A,B: TUNEL staining and scoring of apoptosis in gastric cancer tissues sections and adjacent tissues sections. **P<0.01vs gastric cancer. GC: Gastric cancer.
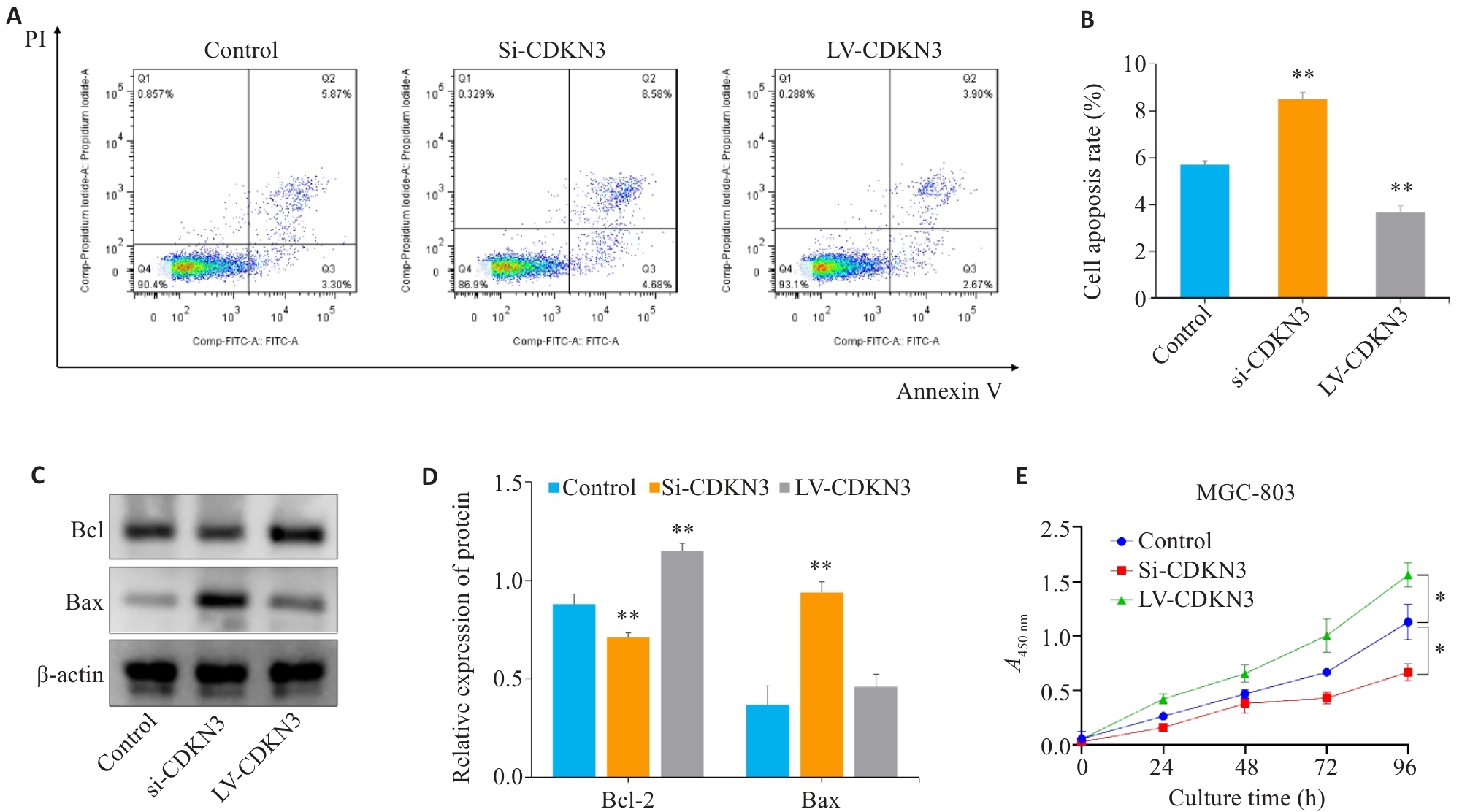
图8 CDKN3对胃癌细胞凋亡和增殖的影响
Fig.8 Effect of CDKN3 on apoptosis and proliferation of MGC803 cells. A,B: Cell apoptosis rate detected by flow cytometry after lentivirus transfection. C: Expression of Bcl-2 and Bax in MGC803 cells. D: Quantitative analysis of Bcl-2/Bax ratio. E: Effect of CDKN3 on proliferation of MGC-803 cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs control.
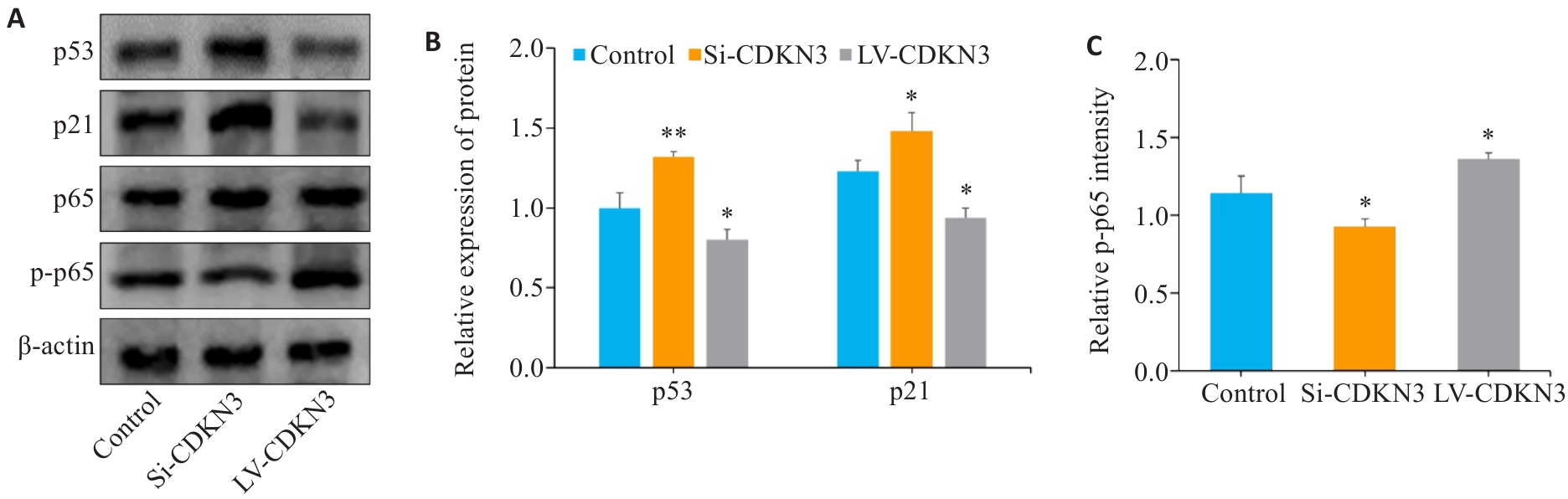
图9 CDKN3对胃癌细胞p53/NF-κB信号通路的影响
Fig.9 Effect of CDKN3 on p53/NF-κB signaling in MGC803 cells. A: Expression of p53, p21, p65 and p-p65 in MGC803 cells. B, C: Quantitative analysis of p53, p21, p65 and p-p65 ratio. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs control.
| 1 | Yang L, Ying X, Liu S, et al. Gastric cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors and prevention strategies[J]. Chin J Cancer Res, 2020, 32(6): 695-704. |
| 2 | Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(3): 229-63. |
| 3 | Machlowska J, Baj J, Sitarz M, et al. Gastric cancer: epidemiology, risk factors, classification, genomic characteristics and treatment strategies[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(11): E4012. |
| 4 | Thrift AP, Wenker TN, El-Serag HB. Global burden of gastric cancer: epidemiological trends, risk factors, screening and prevention[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2023, 20(5): 338-49. |
| 5 | Li WH, Zhang L, Wu YH. CDKN3 regulates cisplatin resistance to colorectal cancer through TIPE1[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(7): 3614-23. |
| 6 | Dai W, Miao H, Fang S, et al. CDKN3 expression is negatively associated with pathological tumor stage and CDKN3 inhibition promotes cell survival in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2016, 14(2): 1509-14. |
| 7 | Dai W, Fang S, Cai G, et al. CDKN3 expression predicates poor prognosis and regulates adriamycin sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro [J]. J Int Med Res, 2020, 48(7): 300060520936879. |
| 8 | Chang SL, Chen TJ, Lee YE, et al. CDKN3 expression is an independent prognostic factor and associated with advanced tumor stage in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2018, 15(10): 992-8. |
| 9 | Wang J, Che W, Wang W, et al. CDKN3 promotes tumor progression and confers cisplatin resistance via RAD51 in esophageal cancer[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2019, 11: 3253-64. |
| 10 | 李苗苗, 王海啸, 陶国全. CDKN3基因在肝癌中的表达及其对肝癌细胞生长、细胞周期的影响[J]. 山西医科大学学报, 2016, 47(6): 496-501. |
| 11 | 朱 慧, 陆欢平, 李天佑, 等. CDKN3在口腔鳞状细胞癌中的预后价值及免疫细胞浸润分析[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2024, 45(11): 1302-1307. |
| 12 | 胡 赞, 孙 锐, 程方雄, 等. 胰腺癌中细胞周期依赖激酶抑制剂3的表达及意义[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2018, 34(20): 3403-5. |
| 13 | de Visser KE, Joyce JA. The evolving tumor microenvironment: From cancer initiation to metastatic outgrowth[J]. Cancer Cell, 2023, 41(3): 374-403. |
| 14 | Ma J, Zhou W, Yuan Y, et al. PSMD12 interacts with CDKN3 and facilitates pancreatic cancer progression[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2023, 30(8): 1072-83. |
| 15 | Srinivas V, Kitagawa M, Wong J, et al. The tumor suppressor Cdkn3 is required for maintaining the proper number of centrosomes by regulating the centrosomal stability of Mps1[J]. Cell Rep, 2015, 13(8): 1569-77. |
| 16 | Zhang CL, Shen Q, Gao MQ, et al. The role of Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 3 (CDKN3) in promoting human tumors: Literature review and pan-cancer analysis[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(4): e26061. |
| 17 | Li Y, Ji S, Fu LY, et al. Knockdown of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 3 inhibits proliferation and invasion in human gastric cancer cells[J]. Oncol Res, 2017, 25(5): 721-31. |
| 18 | Zhou Y, Bian S, Zhou X, et al. Single-cell multiomics sequencing reveals prevalent genomic alterations in tumor stromal cells of human colorectal cancer[J]. Cancer Cell, 2020, 38(6): 818-28. e5. |
| 19 | Cooper J, Giancotti FG. Integrin signaling in cancer: mechanotransduction, stemness, epithelial plasticity, and therapeutic resistance[J]. Cancer Cell, 2019, 35(3): 347-67. |
| 20 | Yan CS, Zheng L, Jiang ST, et al. Exhaustion-associated cholesterol deficiency dampens the cytotoxic arm of antitumor immunity[J]. Cancer Cell, 2023, 41(7): 1276-93.e11. |
| 21 | 米贤良, 魏子白, 杨长青. 基于生物信息学分析胃癌与癌旁组织中差异基因的表达[J]. 现代消化及介入诊疗, 2022, 27(11): 1419-23. |
| 22 | Ucaryilmaz Metin C, Ozcan G. Comprehensive bioinformatic analysis reveals a cancer-associated fibroblast gene signature as a poor prognostic factor and potential therapeutic target in gastric cancer[J]. BMC Cancer, 2022, 22(1): 692. |
| 23 | Pistritto G, Trisciuoglio D, Ceci C, et al. Apoptosis as anticancer mechanism: function and dysfunction of its modulators and targeted therapeutic strategies[J]. Aging: Albany NY, 2016, 8(4): 603-19. |
| 24 | Patriarca C, Pini GM, Conti G. Invasion and metastasis: a historical perspective[J]. Pathologica, 2020, 112(4): 229-33. |
| 25 | Park W, Wei S, Kim BS, et al. Diversity and complexity of cell death: a historical review[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2023, 55(8): 1573-94. |
| 26 | Bedoui S, Herold MJ, Strasser A. Emerging connectivity of programmed cell death pathways and its physiological implications[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2020, 21(11): 678-95. |
| 27 | Vaghari-Tabari M, Ferns GA, Qujeq D, et al. Signaling, metabolism, and cancer: an important relationship for therapeutic intervention[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236(8): 5512-32. |
| 28 | Herriage HC, Huang YT, Calvi BR. The antagonistic relationship between apoptosis and polyploidy in development and cancer[J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2024, 156: 35-43. |
| 29 | Hadian K, Stockwell BR. The therapeutic potential of targeting regulated non-apoptotic cell death[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2023, 22(9): 723-42. |
| 30 | Kumar S, Dorstyn L, Lim Y. The role of caspases as executioners of apoptosis[J]. Biochem Soc Trans, 2022, 50(1): 33-45. |
| 31 | Li MM, Yang JY, Li J, et al. Epiberberine induced p53/p21-dependent G2/M cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis in gastric cancer cells by activating γ‑aminobutyric acid receptor‑β3[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 123: 155198. |
| 32 | 艾亚楠, 赵唯含. NF-κB信号通路在胃癌前病变中的发病机制及中西医治疗的研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28(24): 237-43. |
| 33 | Schäfer C, Göder A, Beyer M, et al. Class I histone deacetylases regulate p53/NF-κB crosstalk in cancer cells[J]. Cell Signal, 2017, 29: 218-25. |
| [1] | 陈悦, 肖林雨, 任侣, 宋雪, 李静, 胡建国. 水晶兰苷通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路减少神经元凋亡改善脊髓损伤后小鼠的运动功能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 774-784. |
| [2] | 储菲, 陈孝华, 宋博文, 杨晶晶, 左芦根. 苏荠宁黄酮通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡改善小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 819-828. |
| [3] | 岳雅清, 牟召霞, 王希波, 刘艳. Aurora-A过表达通过激活NF-κBp65/ARPC4信号轴促进宫颈癌细胞的侵袭和转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 837-843. |
| [4] | 庆顺杰, 沈智勇. 过表达己糖激酶2通过激活JAK/STAT途径促进结直肠癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭并调节肿瘤免疫微环境[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 542-553. |
| [5] | 黄晴晴, 张文静, 张小凤, 王炼, 宋雪, 耿志军, 左芦根, 王月月, 李静, 胡建国. 高表达MYO1B促进胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭并与患者的不良预后有关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 622-631. |
| [6] | 李华莉, 宋婷, 刘嘉雯, 李永宝, 姜兆静, 窦文, 周凌宏. 预后导向的肺癌调强放疗计划优化新方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 643-649. |
| [7] | 宋雪, 陈悦, 张敏, 张诺, 左芦根, 李静, 耿志军, 张小凤, 王月月, 王炼, 胡建国. GPSM2在胃癌组织中高表达并通过促进肿瘤细胞的增殖影响患者预后[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 229-238. |
| [8] | 陈镝, 吕莹, 郭怡欣, 张怡荣, 王蕊璇, 周小若, 陈雨欣, 武晓慧. 双氢青蒿素可显著增强阿霉素诱导的三阴性乳腺癌细胞凋亡:基于负向调控STAT3/HIF-1α通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 254-260. |
| [9] | 邹金华, 王惠, 张冬艳. SLC1A5通过促进M2型巨噬细胞极化促进肝癌进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 269-284. |
| [10] | 宾禹, 李子雯, 左素微, 孙思诺, 李敏, 宋佳茵, 林旭, 薛刚, 吴靖芳. 载脂蛋白C1高表达通过激活JAK2/STAT3信号通路促进甲状腺乳头状癌细胞的增殖并抑制凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 359-370. |
| [11] | 曹周芳, 汪元, 王梦娜, 孙玥, 刘菲菲. LINC00837/miR-671-5p/SERPINE2功能轴促进类风湿关节炎成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞的恶性病理学过程[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 371-378. |
| [12] | 唐天威, 李路安, 陈源汉, 张丽, 徐丽霞, 李志莲, 冯仲林, 张辉林, 华瑞芳, 叶智明, 梁馨苓, 李锐钊. 高血清胱抑素C水平是IgA肾病不良预后的独立危险因素[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 379-386. |
| [13] | 陈晓睿, 魏青政, 张宗亮, 原江水, 宋卫青. 过表达带电多泡体蛋白2B基因抑制肾透明细胞癌细胞的增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 126-136. |
| [14] | 王耀彬, 陈柳燕, 罗伊凌, 申继清, 周素芳. NUF2对泛癌的预后和免疫治疗效果的预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 137-149. |
| [15] | 周超, 张晶晶, 唐巧, 付双楠, 张宁, 何召云, 张瑾, 张田义, 刘鹏程, 宫嫚. 血清色氨酸用于乙肝相关慢加急性肝衰竭90 d死亡风险分层管理的潜在价值:一项多中心回顾性研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 59-64. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||