南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 785-798.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.14
冉念东1( ), 刘杰1,2,3, 徐剑1,2,3, 张永萍1,2,3, 郭江涛1(
), 刘杰1,2,3, 徐剑1,2,3, 张永萍1,2,3, 郭江涛1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-14
出版日期:2025-04-20
发布日期:2025-04-28
通讯作者:
郭江涛
E-mail:252834816@qq.com;jtguo1987@163.com
作者简介:冉念东,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 252834816@qq.com
基金资助:
Niandong RAN1( ), Jie LIU1,2,3, Jian XU1,2,3, Yongping ZHANG1,2,3, Jiangtao GUO1(
), Jie LIU1,2,3, Jian XU1,2,3, Yongping ZHANG1,2,3, Jiangtao GUO1( )
)
Received:2024-11-14
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
Jiangtao GUO
E-mail:252834816@qq.com;jtguo1987@163.com
摘要:
目的 探讨黑骨藤正丁醇萃取部位对阿尔茨海默病(AD)的药效学研究及潜在作用机制预测。 方法 采用超高效液相-四级杆-静电场轨道阱高分辨质谱(UPLC-QE-MS)技术对黑骨藤正丁醇部位的化学成分进行分析鉴定,建立三氯化铝(AlCl3)和D-半乳糖(D-gal)联合诱导50只SPF级雄性AD大鼠模型,使用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)、苏木精-伊红染色(HE)和尼氏染色(Nissl)、免疫组化染色(ICH)、Western blotting等实验为基础,通过网络药理学及分子对接技术预测抗AD潜在作用机制。 结果 黑骨藤正丁醇萃取部位鉴定出17个化学成分,主要包括苯丙素类、黄酮类、蒽醌类、三萜类、甾体类以及挥发油类。药效学实验结果显示经过黑骨藤正丁醇萃取部位组处理后,大鼠海马中乙酰胆碱酯酶(AChE)含量降低(P<0.05),而乙酰胆碱(ACh)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-Px)的含量增加(P<0.05),在Western blotting实验中神经细胞凋亡因子B淋巴细胞瘤-2(Bcl-2)、磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶(PI3K)、蛋白激酶B(Akt)、磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶(p-PI3K)和磷酸化蛋白激酶B(p-Akt)表达上升(P<0.05),而Bax蛋白、半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶-3(Caspase-3)表达下降(P<0.01),氧化应激因子核因子红细胞系2相关因子2(Nrf-2)和血红素氧合酶1(HO-1)蛋白表达水平上调(P<0.01),氧化应激反应转录因子(Keap-1)蛋白表达水平下调(P<0.01),脑源性神经营养因子BDNF表达水平均升高(P<0.01),以及β-淀粉样蛋白Aβ、Tau蛋白表达水平均下调(P<0.01),且表现出一定的剂量依赖性。黑骨藤正丁醇萃取部位活性成分与AD共获得TNF、AKT1和ESR1等14个关键靶点。 结论 初步阐明了黑骨藤正丁醇萃取成分的药效物质基础,并证实了其具有较好的抗AD效果。预测黑骨藤正丁醇萃取部位可通过多组分、多靶点、多途径和多通路发挥抗AD作用。
冉念东, 刘杰, 徐剑, 张永萍, 郭江涛. 黑骨藤正丁醇萃取成分治疗大鼠阿尔茨海默病的药效学及作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 785-798.
Niandong RAN, Jie LIU, Jian XU, Yongping ZHANG, Jiangtao GUO. n-butanol fraction of ethanol extract of Periploca forrestii Schltr.: its active components, targets and pathways for treating Alcheimer's disease in rats[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 785-798.
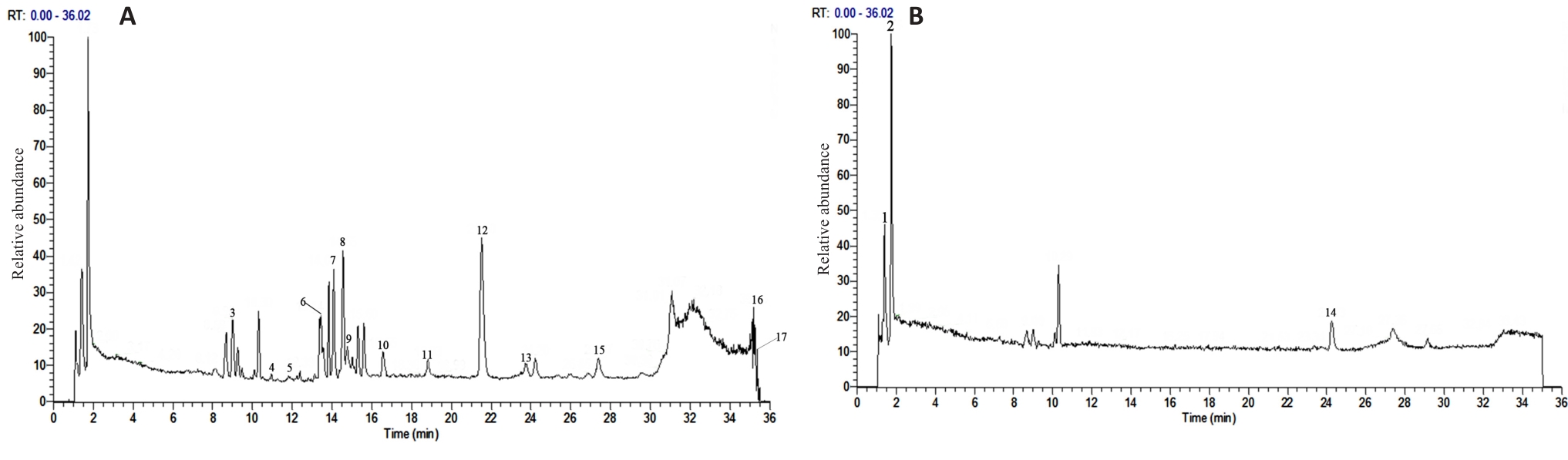
图1 黑骨藤正丁醇萃取部位的正负总离子流图
Fig.1 Positive (A) and negative (B) total ion flow diagrams of n-butanol fraction of Periploca forrestii Schltr. ethanol extract.
| Serial number | Retention time | Molecular formula | Measured value | Error value/ppm | Feature fragment(m/z) | Compound name | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.68 | C16H18O9 | 353.08691[M-H]- | -3.45 | 192.05919, 191.05542, 179.03412,173.04466, 93.03349 | Chlorogenic acid | [ |
| 2 | 1.73 | C16H18O9 | 353.40290[M-H]- | -2.56 | 191.05544, 179.03429, 135.04407, 91.98469,85.02808, 57.03342 | Neochlorogenic acid | [ |
| 3 | 9.18 | C17H20O9 | 369.11716[M+H]+ | 2.12 | 145.09915, 149.02530, 179.06972, 164.83426 | 3-O-Caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester | [ |
| 4 | 11.15 | C10H8O4 | 193.07759[M+H]+ | 4.73 | 178.24461, 161.94366, 150.83627 | Scopoletin | [ |
| 5 | 11.98 | C35H60O6 | 577.98993[M+H]+ | 1.98 | 413.25134, 319.17458, 295.77209 | Daucosterol | [ |
| 6 | 13.67 | C15H10O6 | 287.47942[M+H]+ | 4.34 | 164.8902, 152.63197 | Kaempferol | [ |
| 7 | 14.33 | C9H10O3 | 167.98975[M+H]+ | 1.09 | 167.10678, 165.98264, 148.96109,121.96677, 125.96402, 91.05489 | Paeonol | [ |
| 8 | 14.55 | C29H50O | 415.21033[M+H]+ | 1.21 | 119.08556, 91.05432 | Beta-Sitosterol | [ |
| 9 | 14.76 | C15H10O7 | 303.23000[M+H]+ | 3.06 | 301.29196, 257.51855, 151.59630, 107.08958 | Quercetin | [ |
| 10 | 16.55 | C30H48O3 | 457.53849[M+H]+ | 1.84 | 439.68873, 411.50410, 393.35737, 191.18426 | Ursolic Acid | [ |
| 11 | 18.87 | C21H20O11 | 449.10769[M+H]+ | 1.63 | 287.16988, 153.36526, 135.96421 | Kaempferol 3-O-β- D-glucopyranoside | [ |
| 12 | 21.57 | C15H12O4 | 257.26276[M+H]+ | 3.94 | 257.26599, 210.88354, 120.98715 | Isoliquiritigenin | [ |
| 13 | 23.67 | C16H12O5 | 285.28204[M+H]+ | 3.58 | 240.88678, 282.27838 | Questin | [ |
| 14 | 24.41 | C16H12O5 | 283.05704[M-H]- | -3.41 | 267.04141, 239.87805 | Wogonin | [ |
| 15 | 27.46 | C16H12O5 | 284.29410[M+H]+ | 1.19 | 285.29733, 238.87862, 164.61707 | Physcion | [ |
| 16 | 35.12 | C9H8O3 | 165.11798[M+H]+ | 5.85 | 165.12164, 148.08638 | Trans-4- Hydroxycinnamic acid | [ |
| 17 | 35.37 | C18H34O2 | 283.04980[M+H]+ | 2.08 | 281.04965, 265.01825 | Oleic acid | [ |
表1 黑骨藤正丁醇部位中鉴定出的17个化合物信息
Tab.1 Information of the 17 compounds identified in n-butanol fraction of Periploca forrestii Schltr. ethanol extract
| Serial number | Retention time | Molecular formula | Measured value | Error value/ppm | Feature fragment(m/z) | Compound name | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.68 | C16H18O9 | 353.08691[M-H]- | -3.45 | 192.05919, 191.05542, 179.03412,173.04466, 93.03349 | Chlorogenic acid | [ |
| 2 | 1.73 | C16H18O9 | 353.40290[M-H]- | -2.56 | 191.05544, 179.03429, 135.04407, 91.98469,85.02808, 57.03342 | Neochlorogenic acid | [ |
| 3 | 9.18 | C17H20O9 | 369.11716[M+H]+ | 2.12 | 145.09915, 149.02530, 179.06972, 164.83426 | 3-O-Caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester | [ |
| 4 | 11.15 | C10H8O4 | 193.07759[M+H]+ | 4.73 | 178.24461, 161.94366, 150.83627 | Scopoletin | [ |
| 5 | 11.98 | C35H60O6 | 577.98993[M+H]+ | 1.98 | 413.25134, 319.17458, 295.77209 | Daucosterol | [ |
| 6 | 13.67 | C15H10O6 | 287.47942[M+H]+ | 4.34 | 164.8902, 152.63197 | Kaempferol | [ |
| 7 | 14.33 | C9H10O3 | 167.98975[M+H]+ | 1.09 | 167.10678, 165.98264, 148.96109,121.96677, 125.96402, 91.05489 | Paeonol | [ |
| 8 | 14.55 | C29H50O | 415.21033[M+H]+ | 1.21 | 119.08556, 91.05432 | Beta-Sitosterol | [ |
| 9 | 14.76 | C15H10O7 | 303.23000[M+H]+ | 3.06 | 301.29196, 257.51855, 151.59630, 107.08958 | Quercetin | [ |
| 10 | 16.55 | C30H48O3 | 457.53849[M+H]+ | 1.84 | 439.68873, 411.50410, 393.35737, 191.18426 | Ursolic Acid | [ |
| 11 | 18.87 | C21H20O11 | 449.10769[M+H]+ | 1.63 | 287.16988, 153.36526, 135.96421 | Kaempferol 3-O-β- D-glucopyranoside | [ |
| 12 | 21.57 | C15H12O4 | 257.26276[M+H]+ | 3.94 | 257.26599, 210.88354, 120.98715 | Isoliquiritigenin | [ |
| 13 | 23.67 | C16H12O5 | 285.28204[M+H]+ | 3.58 | 240.88678, 282.27838 | Questin | [ |
| 14 | 24.41 | C16H12O5 | 283.05704[M-H]- | -3.41 | 267.04141, 239.87805 | Wogonin | [ |
| 15 | 27.46 | C16H12O5 | 284.29410[M+H]+ | 1.19 | 285.29733, 238.87862, 164.61707 | Physcion | [ |
| 16 | 35.12 | C9H8O3 | 165.11798[M+H]+ | 5.85 | 165.12164, 148.08638 | Trans-4- Hydroxycinnamic acid | [ |
| 17 | 35.37 | C18H34O2 | 283.04980[M+H]+ | 2.08 | 281.04965, 265.01825 | Oleic acid | [ |
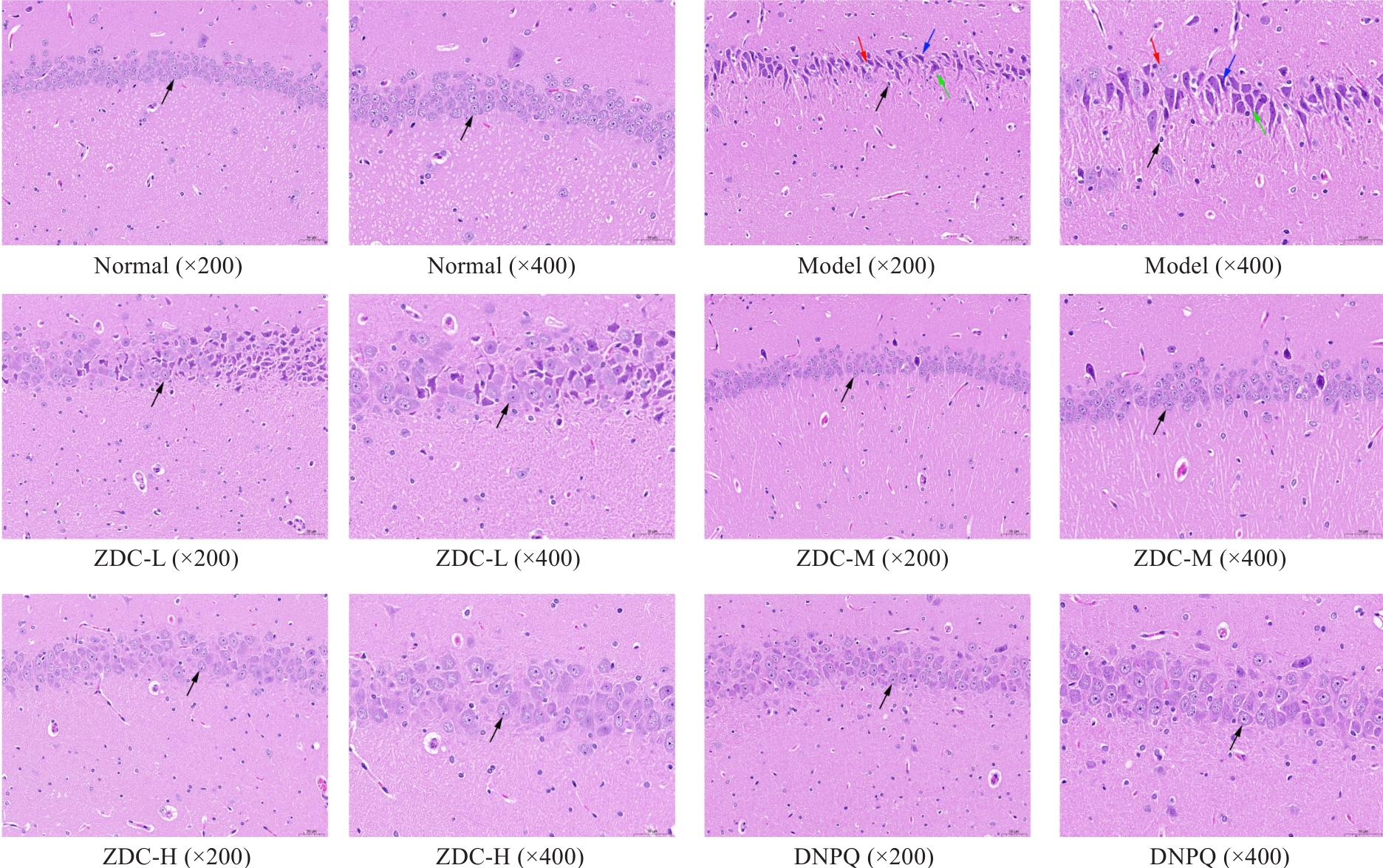
图4 各组大鼠海马HE染色显微图像
Fig.4 HE staining of rat hippocampus in each group. Nucleus (black arrow), cytoplasm (blue arrow), cell body (red arrow), irregular cell (green arrow).
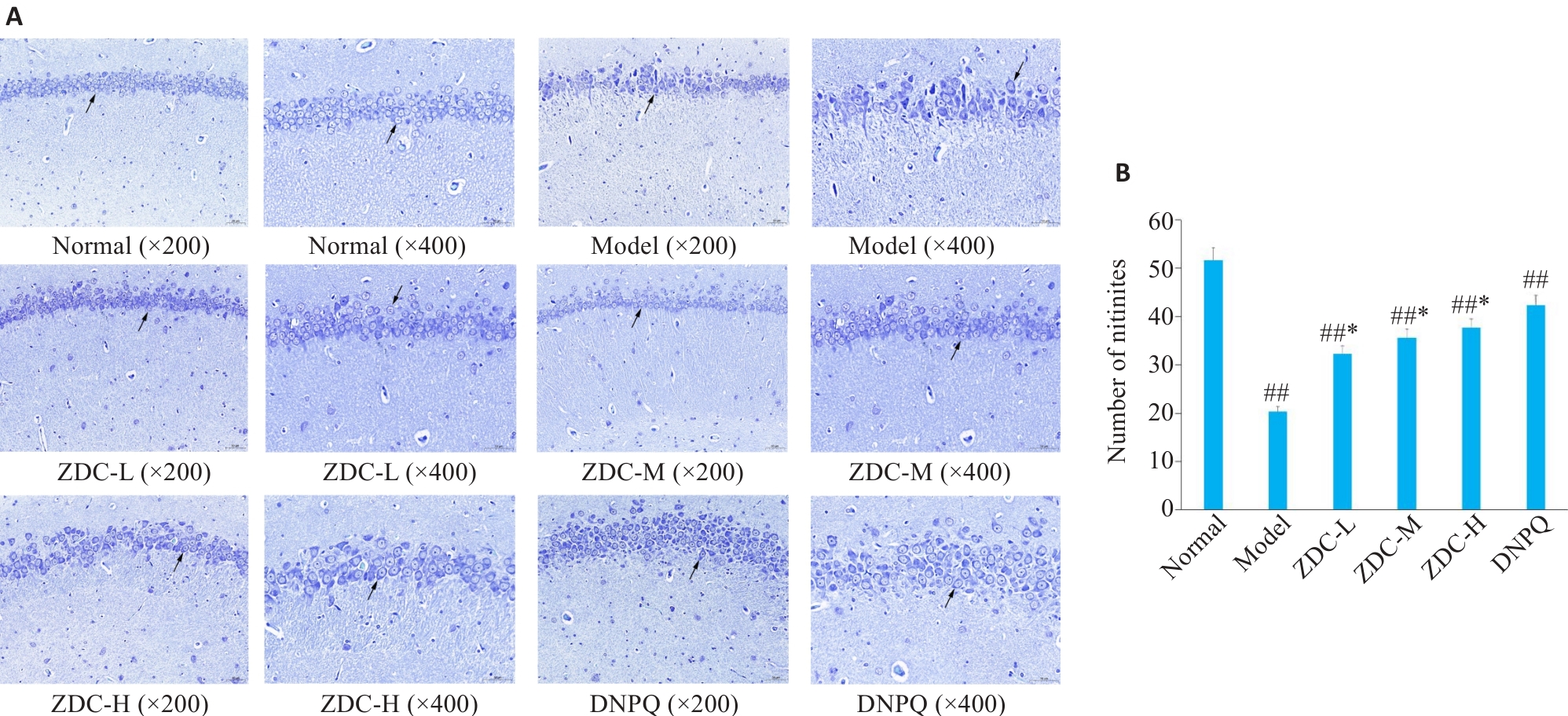
图5 各组大鼠海马组织尼氏染色结果图
Fig.5 Nissl staining of rat hippocampal tissues (A) and statistics of the number of Nissl bodies (arrows)(B) in each group. ##P<0.01 vs Normal group; *P<0.05 vs Model group.
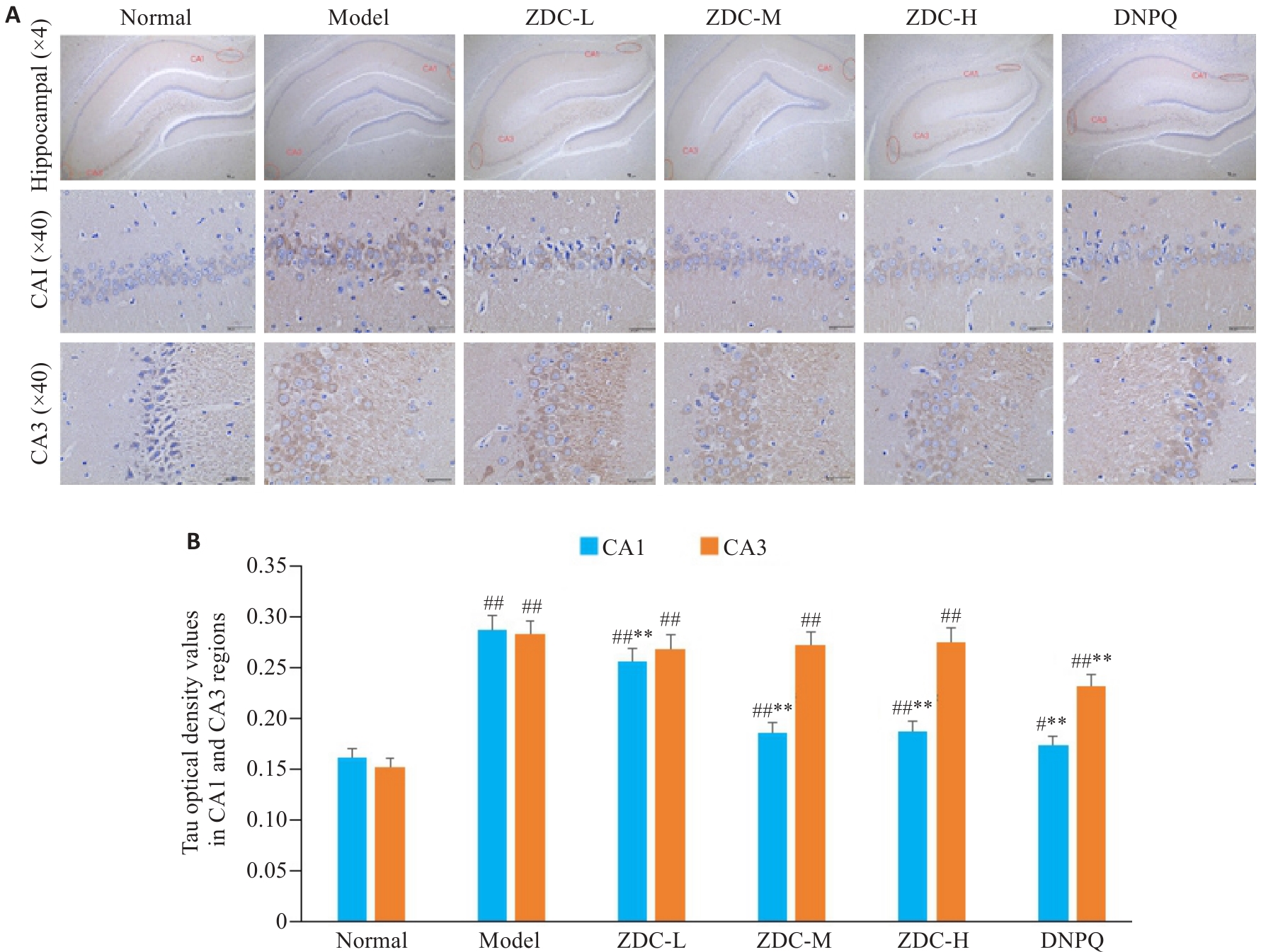
图6 各组大鼠海马内Tau蛋白结果图
Fig.6 Tau protein deposition in rat hippocampus detected by immunohistochemistry (A) and Tau optical density values in CA1 and CA3 regions (B) in each group. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs Normal group; **P<0.01 vs Model group.
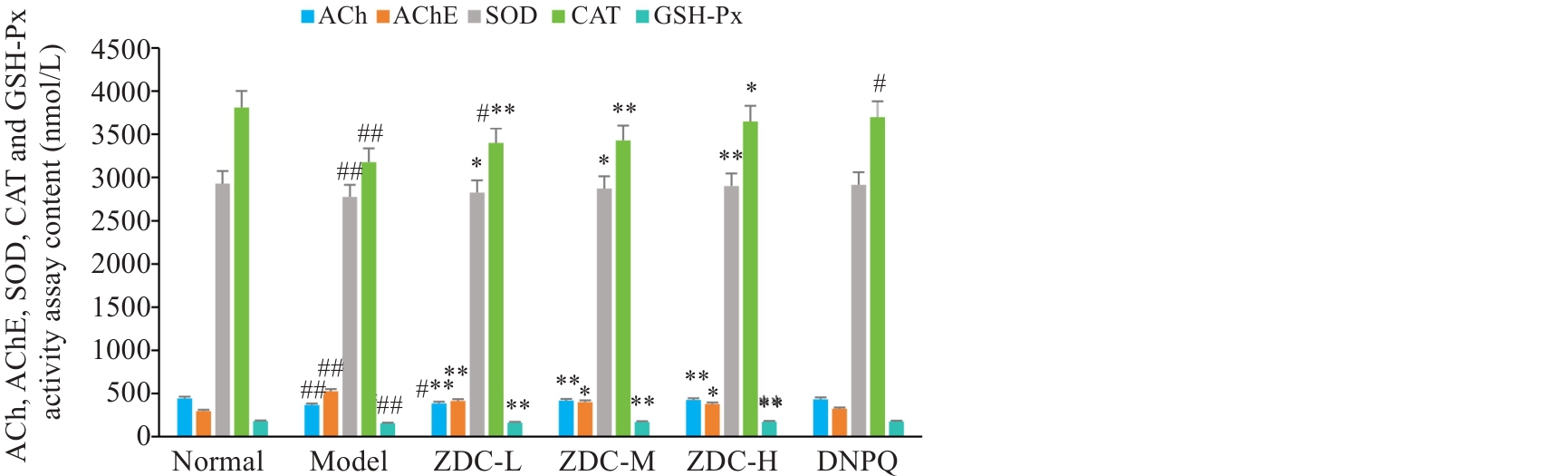
图7 ACh、AChE、SOD、CAT和GSH-Px活性检测结果
Fig.7 ACh, AChE, SOD, CAT and GSH-Px activities in rat hippocampus in each group. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs Normal group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Model group.
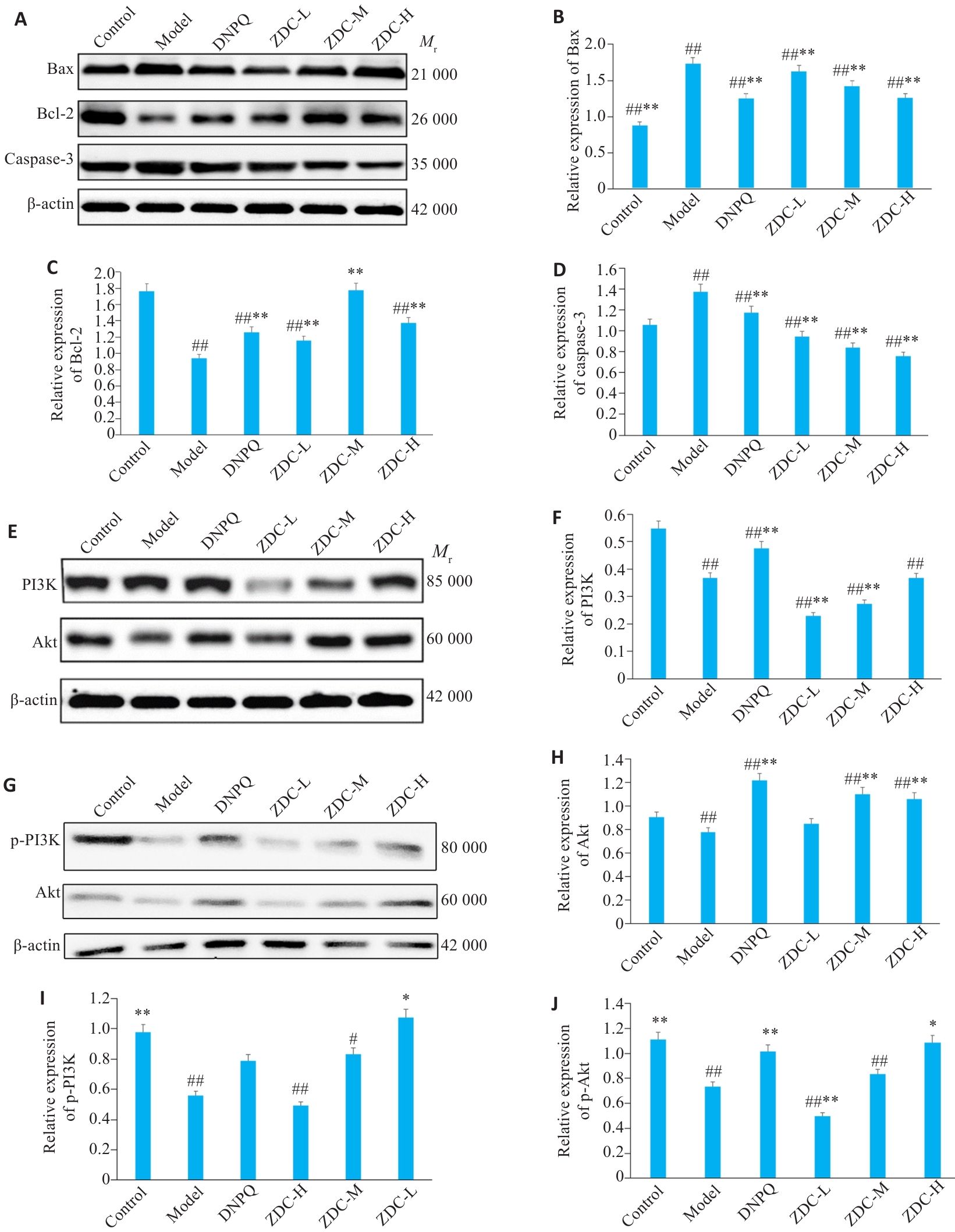
图8 黑骨藤正丁醇部位各蛋白相对表达量及蛋白条带示意图
Fig.8 Western blotting for detecting protein expression levels in the hippocampus in each group. A-D: Bcl-2, Bax and caspase-3 protein bands and their relative expression levels. E-J: PI3K, Akt, p-PI3K and p-Akt protein bands and their relative expression levels. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs Control group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Model group.
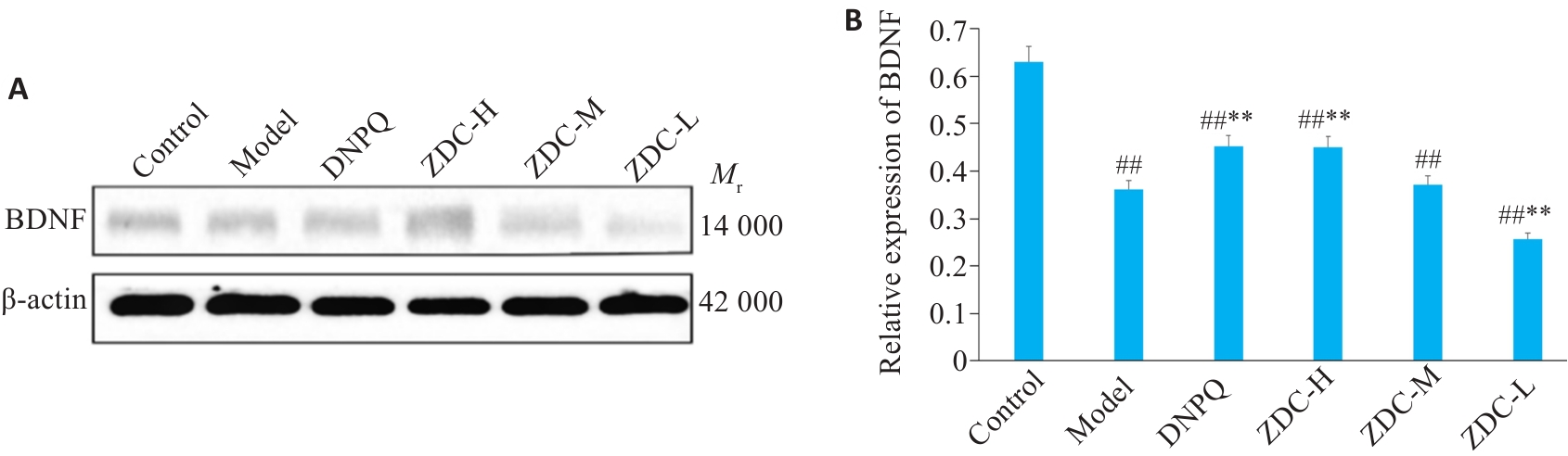
图9 黑骨藤正丁醇部位的BDNF蛋白条带示意图及相对表达量
Fig.9 Expression levels of BDNF protein in the hippocampus in each group detected by Western blotting. ##P<0.01 vs Control group; **P<0.01 vs Model group.
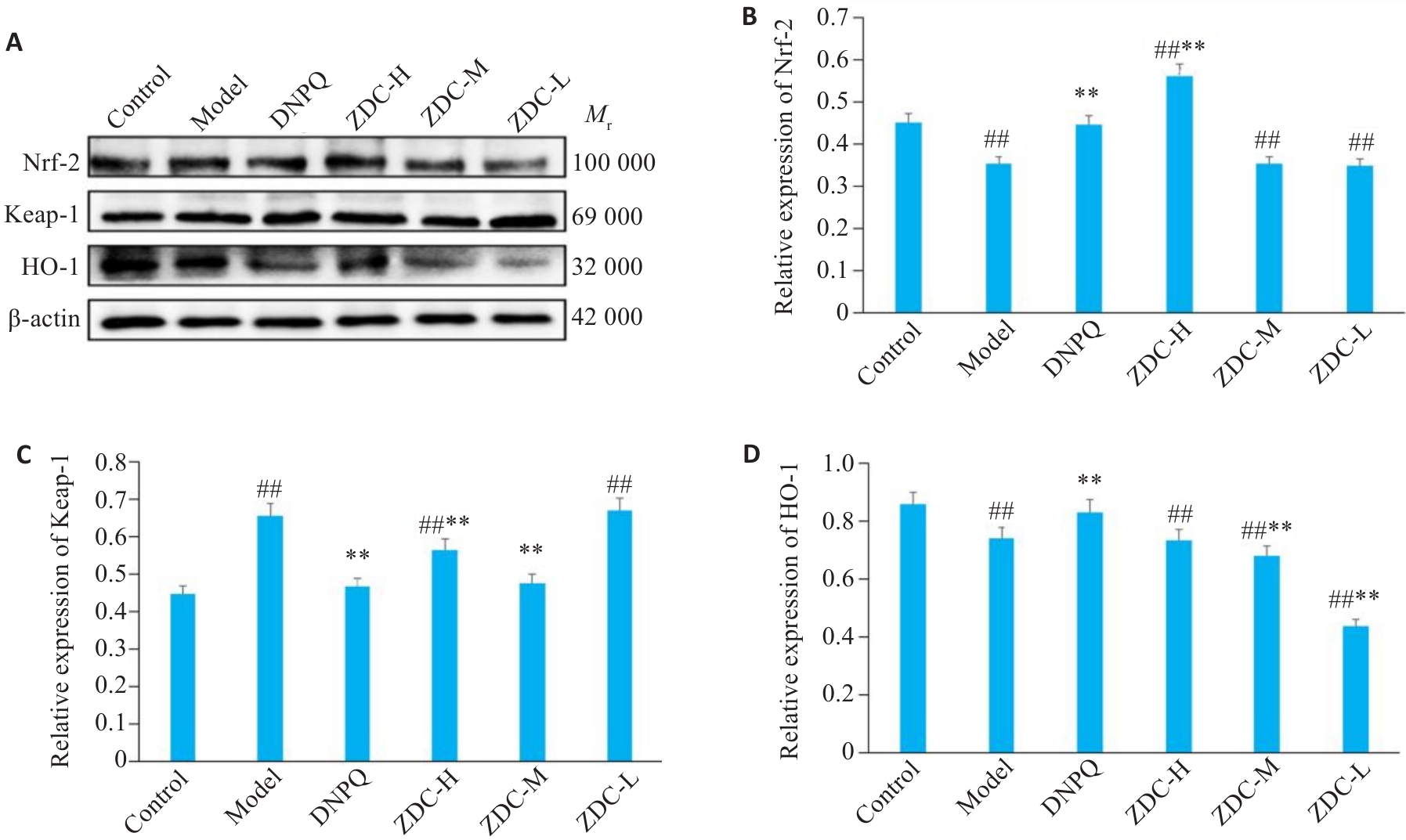
图10 黑骨藤正丁醇部位的Nrf-2、Keap-1、HO-1蛋白条带示意图及相对表达量
Fig.10 Expression levels of Nrf-2, Keap-1, and HO-1 in the hippocampus in each group detected by Western blotting. ##P<0.01 vs Control group; **P<0.01 vs Model group.
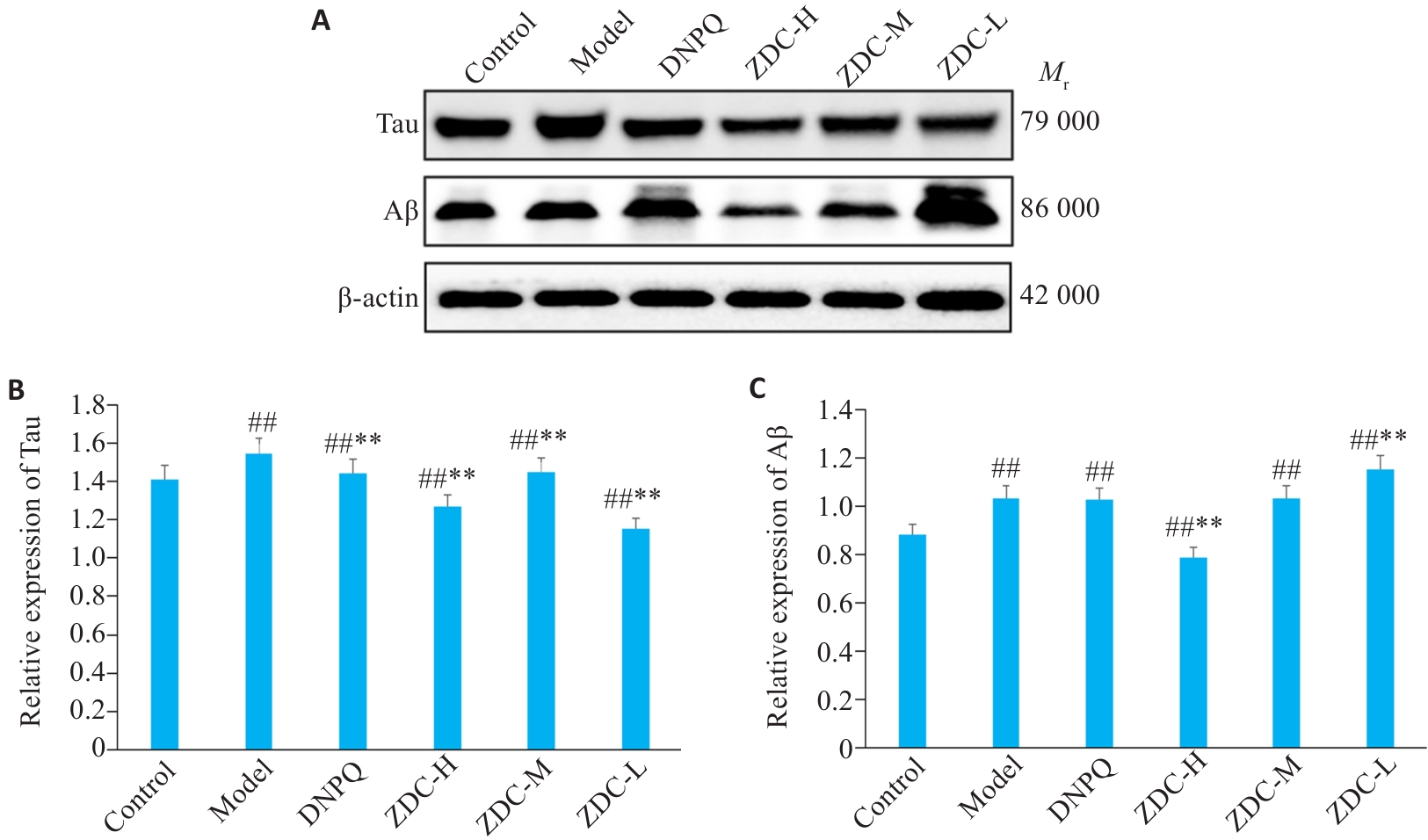
图11 黑骨藤正丁醇部位的Tau、Aβ蛋白条带示意图及相对表达量
Fig.11 Expression levels of Tau and Aβ protein bands in the hippocampus in each group detected by Western blotting. ##P<0.01 vs Control group; **P<0.01 vs Model group.
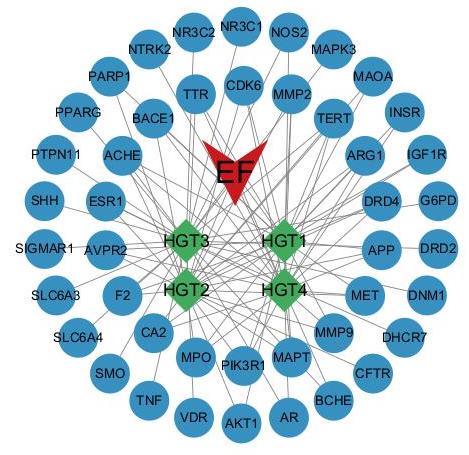
图13 药物-成分-交集靶点图
Fig.13 Drug-component-intersection target map. Red "V" shape: n-butanol fraction; Green rhombus: Active components; Blue circle: Targets of the components.
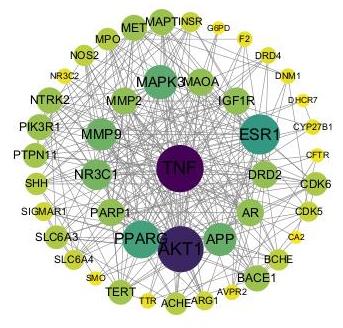
图14 黑骨藤抗AD潜在靶点PPI网络图
Fig.14 PPI network of the potential targets of n-butanol fraction of Periploca forrestii Schltr. ethanol extract for treating AD.
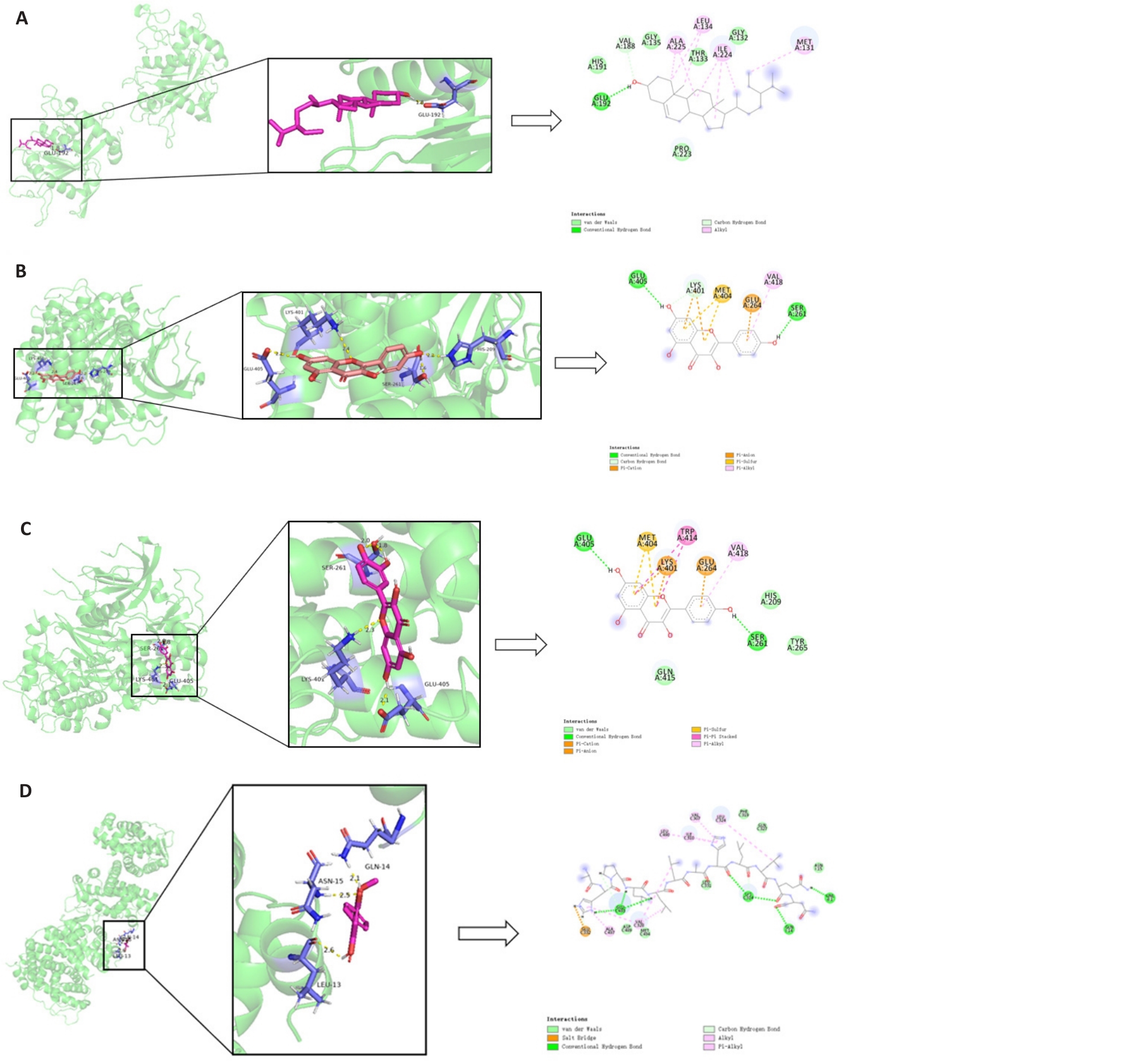
图16 活性成分与关键靶点分子对接结果图
Fig.16 Docking results of the active components with the key target molecules. A: Beta-Sitosterol-TNF. B: kaempferol-AKT1. C: Quercetin-AKT1. D: Wogonin-ESR1.
| 1 | 贵州省药品监督管理局. 贵州省中药材民族药材质量标准2019年版 第二册[M]. 中国医药科技出版社, 2019: 149. |
| 2 | Chen L, Li JS, Ke X, et al. Chemical profiling and the potential active constituents responsible for wound healing in Periploca forrestii Schltr[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2018, 224: 230-41. |
| 3 | Chen HG, Liang Q, Zhou X, et al. Preparative separation of the flavonoid fractions from Periploca forrestii Schltr. ethanol extracts using macroporous resin combined with HPLC analysis and evaluation of their biological activities[J]. J Sep Sci, 2019, 42(3): 650-61. |
| 4 | 贾敏如, 张 艺. 中国民族药辞典[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2016: 603. |
| 5 | 张贵源, 龚莉莉, 党荣敏, 等. 黑骨藤对Pristionchus pacificus线虫神经损伤的治疗实验[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2012, 23(11): 2758-9. |
| 6 | 张贵源, 龚莉莉, 余跃生, 等. 黑骨藤对PC12细胞氧化损伤的保护研究[J]. 宁夏农林科技, 2012, 53(8): 139-40. |
| 7 | Wu H, Cao YJ, Qu YX, et al. Integrating UPLC-QE-Orbitrap-MS technology and network pharmacological method to reveal the mechanism of Bailemian capsule to relieve insomnia[J]. Nat Prod Res, 2022, 36(10): 2554-8. |
| 8 | Liu Y, Sun MY, Sun JQ, et al. Identification of novel serum metabolic signatures to predict chronic kidney disease among Chinese Elders using UPLC-Orbitrap-MS[J]. J Nutr Health Aging, 2024, 28(3): 100036. |
| 9 | 刘灿黄, 章泽恒, 汪 辉, 等. UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS 法定性分析丹膝颗粒的化学成分[J]. 药品评价, 2022, 19(4): 201-9. |
| 10 | 李泮霖, 李楚源, 刘孟华, 等. 基于UFLC-Triple-Q-TOF-MS/MS技术的金银花、山银花化学成分比较[J]. 中南药学, 2016, 14(4): 363-9. |
| 11 | 吴 欢, 占 远, 陈海芳, 等. UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS对紫花地丁中化学成分的快速表征[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2016, 22(24): 70-5. |
| 12 | 贾志鑫, 丛诗语, 潘明霞, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS的速效救心丸化学成分定性分析[J]. 药物评价研究, 2023, 46(2): 330-41. |
| 13 | 王 梦, 田 伟, 甄亚钦, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS技术的彝族药姜味草化学成分分析[J]. 中国药学杂志, 2022, 57(20): 1717-25. |
| 14 | 刘 爽, 戴宇滢, 赵爽同, 等. 基于UHPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap-MS技术分析桂附地黄丸的化学成分及入血成分[J]. 中南药学, 2023, 21(8): 2069-75. |
| 15 | 朱高峰, 蒋成英, 王建塔, 等. UPLC-Q-TOF-MSE技术结合UNIFI数据库定性分析见血清醇提取物化学成分[J]. 广东化工, 2020, 47(20): 36-8. |
| 16 | 肖 岩, 马博稷, 李冰涛, 等. 青钱柳醇提物中化学成分的UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28(16): 196-204. |
| 17 | 张忠立, 石文康, 左月明, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS技术的不同产地肺形草化学成分的研究[J]. 中南药学, 2023, 21(2): 312-9. |
| 18 | 许如玲, 范君婷, 董惠敏, 等. 经典名方黄芪桂枝五物汤标准煎液化学成分的UPLC-Q-TOF-MS分析[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2020, 45(23): 5614-30. |
| 19 | 姜奇瑶, 刘臣臣, 陈惠玲, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS和UPLC的六君子汤化学成分定性与定量分析[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2024,30(06):169-78. |
| 20 | 于小杰. 基于LC-MS技术的芪归银方药效物质基础研究[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2014. |
| 21 | 孔 娇, 刘传鑫, 张 娜, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF/HRMSE小陷胸汤化学成分定性分析[J]. 药物评价研究, 2020, 43(7): 1273-82. |
| 22 | 凌 霄, 李伟霞, 王晓艳, 等. UPLC-Q-TOF-MS分析芍药汤水煎液化学成分[J]. 中国现代中药, 2021, 23(1): 48-56. |
| 23 | 张 宝, 李 悦, 陈婷婷, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-Exactive-Plus-Orbitrap-MS技术分析蛇含委陵菜的化学成分[J]. 中药材, 2023, 46(12): 3014-22. |
| 24 | Wang L, Pan XQ, Jiang LS, et al. The biological activity mechanism of chlorogenic acid and its applications in food industry: a review[J]. Front Nutr, 2022, 9: 943911. |
| 25 | 肖炜明, 卜 平, 龚卫娟. 汉黄芩素抗肿瘤和免疫调节作用的研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2014, 39(16): 3004-9. |
| 26 | 王 玉, 于桂芳, 胡军华, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS及网络药理学探讨麻杏止哮颗粒治疗哮喘的有效成分和作用机制[J]. 中草药, 2023, 54(17): 5508-21. |
| 27 | Dey M, Singh RK. Neurotoxic effects of aluminium exposure as a potential risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Pharmacol Rep, 2022, 74(3): 439-50. |
| 28 | Gilbert PE, Brushfield AM. The role of the CA3 hippocampal subregion in spatial memory: a process oriented behavioral assessment[J]. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry, 2009, 33(5): 774-81. |
| 29 | 周丽莎, 朱书秀, 望庐山. 核桃仁提取物对老年痴呆模型大鼠Ach、ChAT及AchE活性的影响[J]. 中国医院药学杂志, 2011, 31(6): 446-9. |
| 30 | Chen ZR, Huang JB, Yang SL, et al. Role of cholinergic signaling in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(6): 1816. |
| 31 | Meng XW, Cui J, He GB. Bcl-2 is involved in cardiac hypertrophy through PI3K-Akt pathway[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021, 2021: 6615502. |
| 32 | Beroske L, Van den Wyngaert T, Stroobants S, et al. Molecular imaging of apoptosis: the case of caspase-3 radiotracers[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(8): 3948. |
| 33 | Fan SS, Liu XY, Wang Y, et al. Thymus quinquecostatus Celak. ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via dual antioxidant actions: Activating Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and directly scavenging ROS[J]. Phytomedicine, 2021, 91: 153673. |
| [1] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | 王立明, 陈宏睿, 杜燕, 赵鹏, 王玉洁, 田燕歌, 刘新光, 李建生. 益气滋肾方通过抑制PI3K/Akt/NF-κB通路改善小鼠慢性阻塞性肺疾病的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [3] | 朱胤福, 李怡燃, 王奕, 黄颖而, 龚昆翔, 郝文波, 孙玲玲. 桂枝茯苓丸活性成分常春藤皂苷元通过抑制JAK2/STAT3通路抑制宫颈癌细胞的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [4] | 何丽君, 陈晓菲, 闫陈昕, 师林. 扶正化积汤治疗非小细胞肺癌的分子机制:基于网络药理学及体外实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [5] | 李国永, 黎仁玲, 刘艺婷, 柯宏霞, 李菁, 王新华. 牛蒡子治疗小鼠病毒性肺炎后肺纤维化的机制:基于代谢组学、网络药理学和实验验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [6] | 管丽萍, 颜燕, 卢心怡, 李智峰, 高晖, 曹东, 侯晨曦, 曾靖宇, 李欣怡, 赵洋, 王俊杰, 方会龙. 复方积雪草减轻小鼠日本血吸虫引起的肝纤维化:通过调控TLR4/MyD88通路抑制炎症-纤维化级联反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [7] | 唐培培, 谈勇, 殷燕云, 聂晓伟, 黄菁宇, 左文婷, 李玉玲. 调周滋阴方治疗早发性卵巢功能不全的疗效、安全性及作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [8] | 梁晓涛, 熊一凡, 刘雪琪, 梁小珊, 朱晓煜, 谢炜. 活血疏风颗粒通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB通路改善慢性偏头痛小鼠的中枢敏化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| [9] | 徐皓男, 张放, 黄钰莹, 姚其盛, 管悦琴, 陈浩. 百蕊草通过调节肠道菌群和调控EGFR/PI3K/Akt信号通路改善小鼠抗生素相关性腹泻[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [10] | 高俊杰, 叶开, 吴竞. 槲皮素通过调控TP53基因抑制肾透明细胞癌的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [11] | 刘莹, 李柏睿, 李永财, 常禄博, 王娇, 杨琳, 颜永刚, 屈凯, 刘继平, 张岗, 沈霞. 加味逍遥丸通过神经递质调节、抗炎抗氧化及肠道菌群调控改善大鼠的抑郁样行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 347-358. |
| [12] | 褚乔, 王小娜, 续佳颖, 彭荟林, 赵裕琳, 张静, 陆国玉, 王恺. 白头翁皂苷D通过多靶点和多途径抑制三阴性乳腺癌侵袭转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [13] | 龙秀鹏, 陶顺, 阳绅, 李素云, 饶利兵, 李莉, 张哲. 槲皮素通过抑制MAPK信号通路改善心力衰竭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 187-196. |
| [14] | 徐朦, 陈丽娜, 吴金玉, 刘丽丽, 施美, 周灏, 张国梁. “白花蛇舌草-半枝莲”治疗原发性肝癌的机制研究:基于网络药理学、分子对接及体外实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 80-89. |
| [15] | 刘青, 刘敬, 郑逸航, 雷金, 黄建华, 刘思妤, 刘芳, 彭群龙, 张远芳, 王俊杰, 李玉娟. 积雪草活性成分槲皮素通过介导STAT3磷酸化抑制IL-23/IL-17A炎症轴发挥抗银屑病作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 90-99. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||