南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 1485-1496.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.08.07
• • 上一篇
于官正1,2( ), 程炜强2, 涂星1(
), 程炜强2, 涂星1( ), 张满2, 李鸿1,2, 聂娟2
), 张满2, 李鸿1,2, 聂娟2
收稿日期:2024-04-07
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-09-06
通讯作者:
涂星
E-mail:1760453902@qq.com;2015030@hbmzu.edu.cn
作者简介:于官正,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 1760453902@qq.com
基金资助:
Guanzheng YU1,2( ), Weiqiang CHENG2, Xing TU1(
), Weiqiang CHENG2, Xing TU1( ), Man ZHANG2, Hong LI1,2, Juan NIE2
), Man ZHANG2, Hong LI1,2, Juan NIE2
Received:2024-04-07
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-09-06
Contact:
Xing TU
E-mail:1760453902@qq.com;2015030@hbmzu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 基于UPLC-QE-MS与网络药理学挖掘隔山消防治溃疡性结肠炎(UC)的靶点及通路,并结合代谢组学技术探讨作用机制。 方法 采用UPLC-QE-MS技术鉴定隔山消醇提物化学成分,基于Swiss Target Prediction、GeneCards、Pubchem等数据库筛选相应靶点,获取核心PPI,进行GO、KEGG富集分析。将40只雄性C57小鼠随机分为正常组、模型组、美沙拉嗪组(0.2 g/kg)、隔山消组(2.28 g/kg),每组10只,除正常组外,其余各组自由饮用2.5% DSS诱导UC模型,造模期间给药组给予药物灌胃干预。通过体质量变化率、DAI得分评价治疗效果;HE及AB-PAS染色观察结肠组织病理变化;Western blotting技术检测JAK2、STAT3蛋白水平;代谢组学技术鉴别差异代谢物并挖掘代谢通路。 结果 鉴定出隔山消醇提物化学成分240个,其中甾体类(高含量)19个,得到隔山消(甾体类)靶点177个,UC基因5406个,隔山消与UC交集基因117个,JAK2、STAT3等为核心PPI,在脂质与动脉粥样硬化等通路富集显著。动物实验结果显示,经隔山消治疗后,小鼠体质量变化率上升、DAI评分显著下降(P<0.05),肠组织病理改变明显缓解,JAK2、STAT3蛋白水平显著降低(P<0.05)。鉴定出正常组、模型组及隔山消组之间交集差异代谢物83个,以甘油磷脂、类花生酸、氨基酸成分为主,与甘油磷脂代谢等通路相关。整合分析显示隔山消治疗UC的核心靶点参与了代谢物的调节。 结论 隔山消可通过调节JAK2、STAT3等核心靶点表达及内源性代谢物水平来缓解脂质及氨基酸代谢紊乱,发挥治疗UC的作用。
于官正, 程炜强, 涂星, 张满, 李鸿, 聂娟. 隔山消治疗溃疡性结肠炎的机制:基于UPLC-QE-MS、网络药理学及代谢组学技术[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1485-1496.
Guanzheng YU, Weiqiang CHENG, Xing TU, Man ZHANG, Hong LI, Juan NIE. Therapeutic mechanism of Cynanchum wilfordii for ulcerative colitis: an analysis using UPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology and metabolomics[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1485-1496.
| NO. | tR/min | Chemical compound | Chemical formula | Ionization mode | m/z | Theoretical m/z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11.54 | Qingyangshengenin B | C49H78O16 | M-H, M+FA-H | 967.5273 | 967.5272 |
| 2 | 9.72 | Qingyangshengenin A | C49H72O17 | M+NH4, M+Na | 955.4642 | 955.4662 |
| 3 | 5.53 | Convallatoxin | C29H42O10 | M+FA-H | 595.2765 | 595.2760 |
| 4 | 9.7 | Caudatin | C28H42O7 | M-H, M+FA-H | 535.2915 | 535.2912 |
| 5 | 10.22 | Cynatratoside A | C28H40O8 | M+H-H2O | 487.2679 | 487.2690 |
| 6 | 6.45 | Qingyangshengenin | C28H36O8 | M+Na | 523.2292 | 523.2303 |
| 7 | 7.33 | 5beta-Dihydrocortisol | C21H32O5 | M+H | 365.2315 | 365.2323 |
| 8 | 9.13 | Acetylarenobufagin | C26H34O7 | M+Na | 481.2214 | 481.2196 |
| 9 | 9.36 | Polyphyllin VI | C39H62O13 | M+K | 777.3818 | 777.3822 |
| 10 | 9.2 | Oleandrin | C32H48O9 | M+Na | 599.3215 | 599.3190 |
| 11 | 10.47 | Gracillin | C45H72O17 | M-H2O-H | 865.4589 | 865.4591 |
| 12 | 7.57 | 19-Oxocinobufagin | C26H32O7 | 2M-H | 911.4252 | 911.4223 |
| 13 | 10.28 | Dioscin | C45H72O16 | M+FA-H | 913.4814 | 913.4802 |
| 14 | 11.52 | (25R)-Spirost-4-en-3,12-dion | C27H38O4 | M+NH4 | 444.3099 | 444.3109 |
| 15 | 10.14 | 3-O-Acetylbufotalin | C28H38O7 | M+Na | 509.2527 | 509.2509 |
| 16 | 11.57 | Timosaponin A1 | C33H54O8 | M+Na | 601.3699 | 601.3711 |
| 17 | 5.83 | Bufarenogin | C24H32O6 | 2M+Na | 855.4328 | 855.4289 |
| 18 | 5.38 | Digoxigenin | C23H34O5 | M+H-H2O | 373.236 | 373.2373 |
| 19 | 4.82 | Rubrosterone | C19H26O5 | M+NH4 | 352.2113 | 352.2119 |
表1 隔山消甾体类鉴定结果
Tab.1 Results of identification of the steroids in Cynanchum wilfordii
| NO. | tR/min | Chemical compound | Chemical formula | Ionization mode | m/z | Theoretical m/z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11.54 | Qingyangshengenin B | C49H78O16 | M-H, M+FA-H | 967.5273 | 967.5272 |
| 2 | 9.72 | Qingyangshengenin A | C49H72O17 | M+NH4, M+Na | 955.4642 | 955.4662 |
| 3 | 5.53 | Convallatoxin | C29H42O10 | M+FA-H | 595.2765 | 595.2760 |
| 4 | 9.7 | Caudatin | C28H42O7 | M-H, M+FA-H | 535.2915 | 535.2912 |
| 5 | 10.22 | Cynatratoside A | C28H40O8 | M+H-H2O | 487.2679 | 487.2690 |
| 6 | 6.45 | Qingyangshengenin | C28H36O8 | M+Na | 523.2292 | 523.2303 |
| 7 | 7.33 | 5beta-Dihydrocortisol | C21H32O5 | M+H | 365.2315 | 365.2323 |
| 8 | 9.13 | Acetylarenobufagin | C26H34O7 | M+Na | 481.2214 | 481.2196 |
| 9 | 9.36 | Polyphyllin VI | C39H62O13 | M+K | 777.3818 | 777.3822 |
| 10 | 9.2 | Oleandrin | C32H48O9 | M+Na | 599.3215 | 599.3190 |
| 11 | 10.47 | Gracillin | C45H72O17 | M-H2O-H | 865.4589 | 865.4591 |
| 12 | 7.57 | 19-Oxocinobufagin | C26H32O7 | 2M-H | 911.4252 | 911.4223 |
| 13 | 10.28 | Dioscin | C45H72O16 | M+FA-H | 913.4814 | 913.4802 |
| 14 | 11.52 | (25R)-Spirost-4-en-3,12-dion | C27H38O4 | M+NH4 | 444.3099 | 444.3109 |
| 15 | 10.14 | 3-O-Acetylbufotalin | C28H38O7 | M+Na | 509.2527 | 509.2509 |
| 16 | 11.57 | Timosaponin A1 | C33H54O8 | M+Na | 601.3699 | 601.3711 |
| 17 | 5.83 | Bufarenogin | C24H32O6 | 2M+Na | 855.4328 | 855.4289 |
| 18 | 5.38 | Digoxigenin | C23H34O5 | M+H-H2O | 373.236 | 373.2373 |
| 19 | 4.82 | Rubrosterone | C19H26O5 | M+NH4 | 352.2113 | 352.2119 |
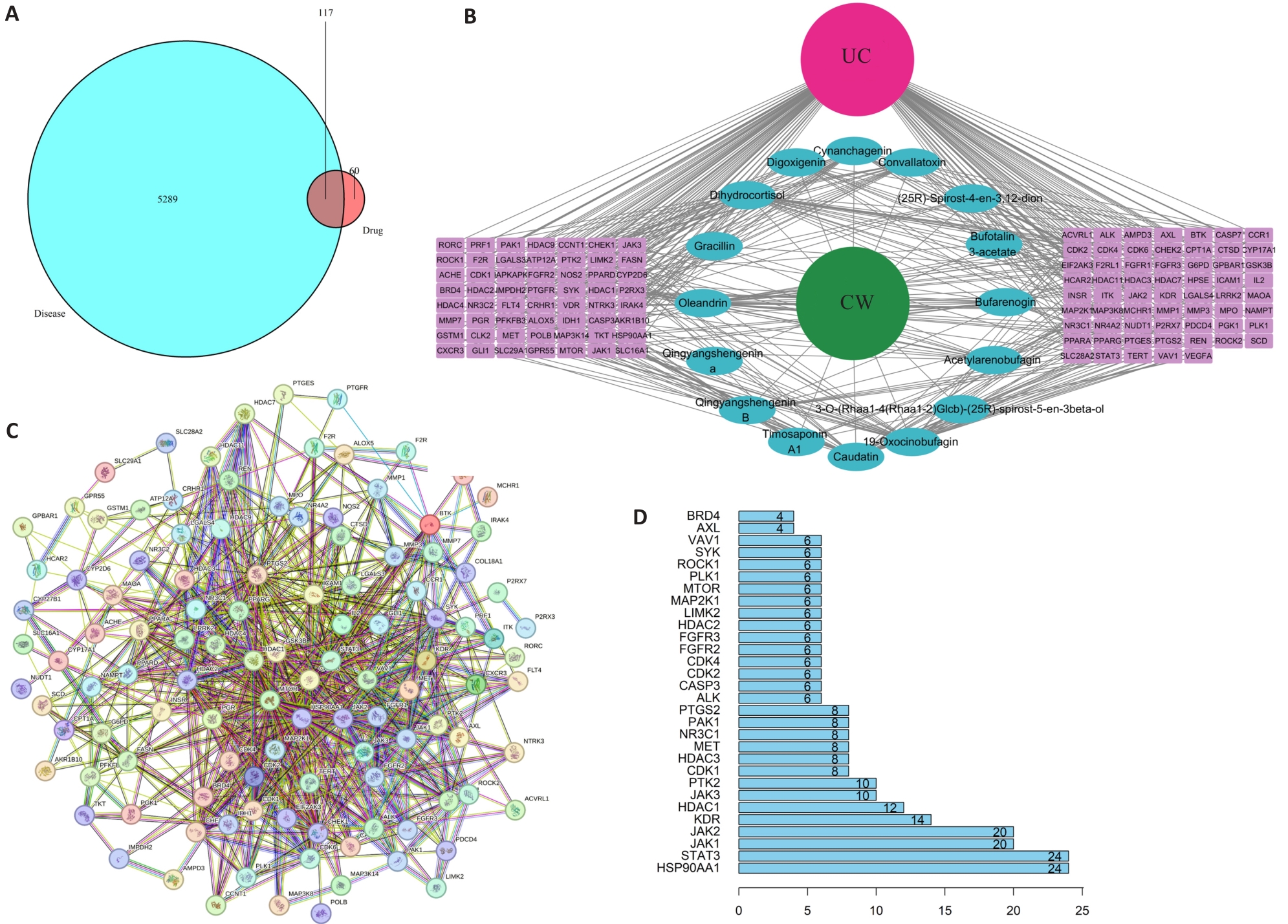
图1 Venn图、网络调控图及核心PPI
Fig.1 Venn diagrams, network regulation charts and core PPI. A: Venn diagram. B: Network regulation charts. C: PPI network. D: Core PPI. CW: Cynanchum wilfordii.
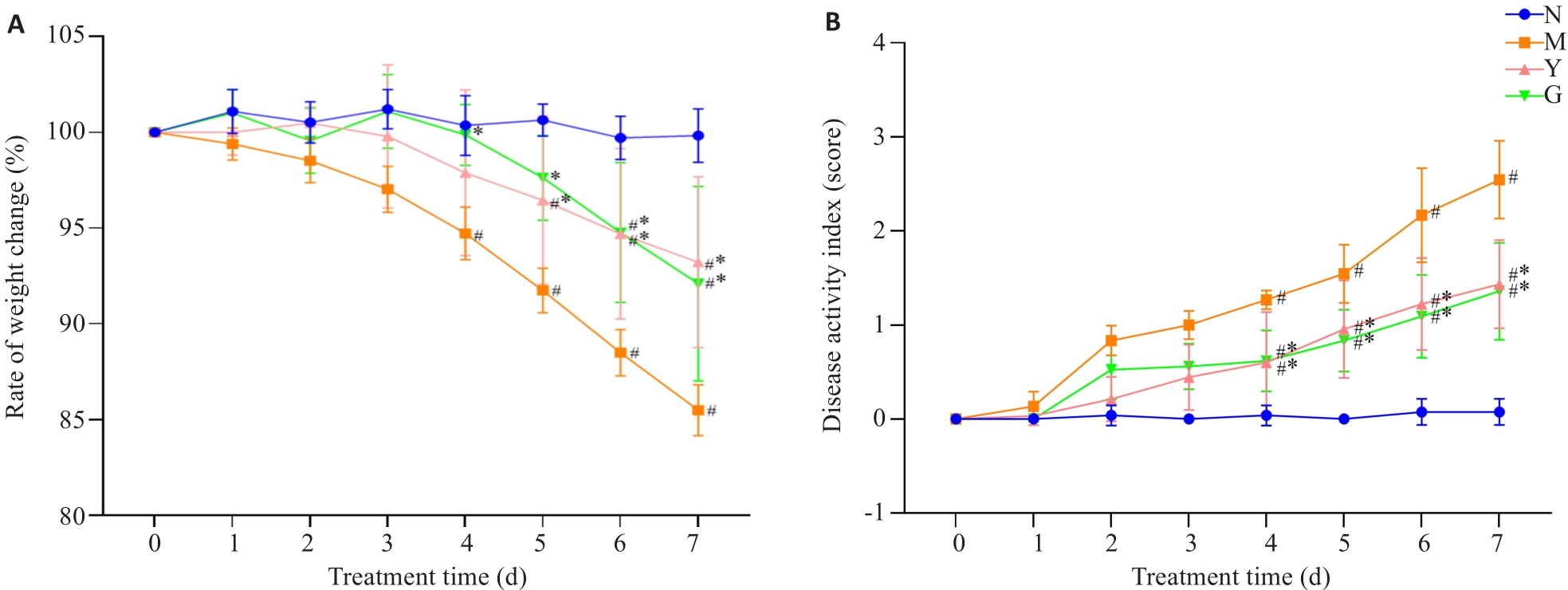
图4 体质量变化率及DAI评分
Fig.4 Weight change rate and DAI score of the mouse models of UC. A: Weight change rate. B: DAI score. N: Normal group. M: Model group. Y: Mesalazine group. G: Cynanchum wilfordii Group. #P<0.05 vs normal group; *P<0.05 vs model group.
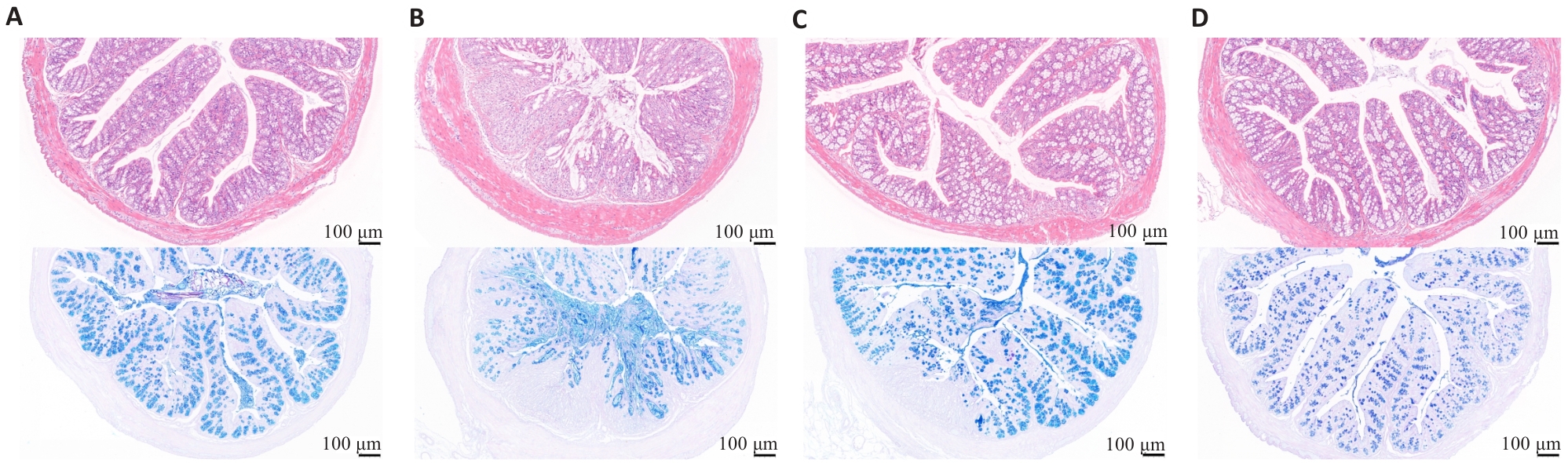
图5 HE染色及AB-PAS染色
Fig.5 HE staining and AB-PAS staining of the colon tissue of the mice. A: Normal group. B: Model group. C: mesalazine group. D: Cynanchum wilfordii Group.
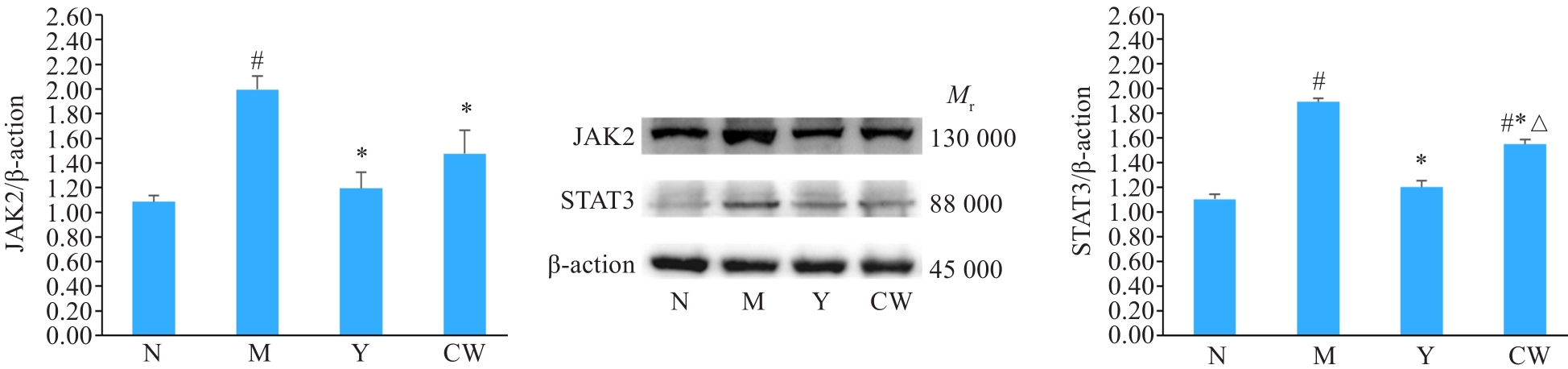
图6 各组小鼠结肠组织中JAK2和STAT3蛋白表达
Fig.6 Expression of JAK2 and STAT3 proteins in the colon tissue of the mice detected by Western blotting. CW: Cynanchumwilfordii Group. #P<0.05 vs normal group; *P<0.05 vs model group;△P<0.05 vs mesalazine group.
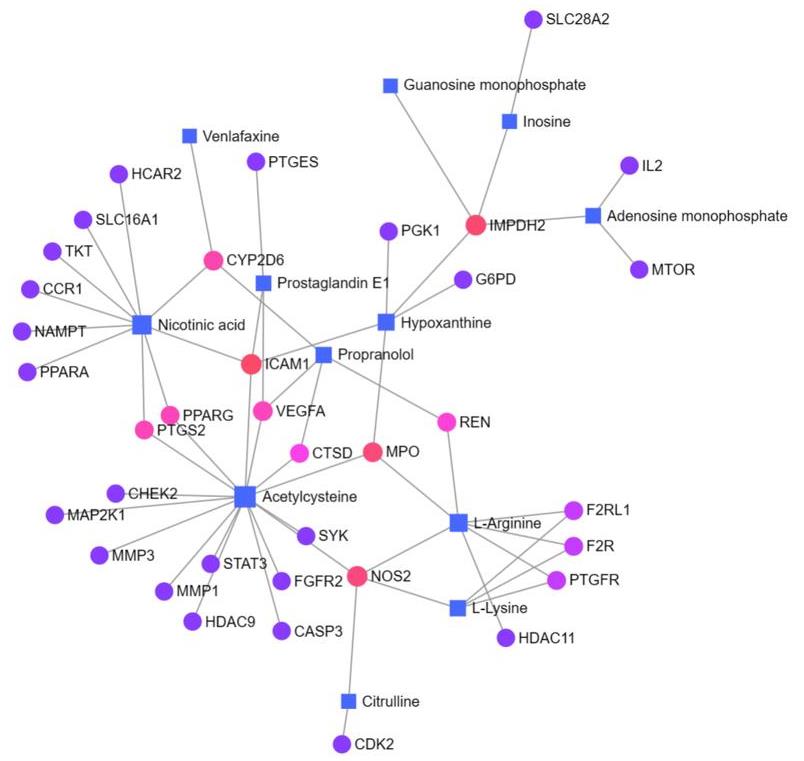
图12 代谢物-靶点基因网络
Fig.12 Metabolite-target gene network. Squares represent differential genes, circles represent the core target. The darker the color, the stronger the correlation.
| 1 | Ordás I, Eckmann L, Talamini M, et al. Ulcerative colitis[J]. Lancet, 2012, 380(9853): 1606-19. |
| 2 | Ukil A, Maity S, Das PK. Protection from experimental colitis by theaflavin-3, 3'-digallate correlates with inhibition of IKK and NF-kappaB activation[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2006, 149(1): 121-31. |
| 3 | Gao X, Li J, Pang XP, et al. Animal models and pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis[J]. Comput Math Methods Med, 2022, 2022: 5927384. |
| 4 | Du L, Ha C. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis[J]. Gastroenterol Clin North Am, 2020, 49(4): 643-54. |
| 5 | 周长琳, 郑学宝, 黄晓其, 等. 黄芩汤通过调节ILC3s-Th细胞反应减轻小鼠的溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(2): 256-63. |
| 6 | Sun Y, Zhang Z, Zheng CQ, et al. Mucosal lesions of the upper gastrointestinal tract in patients with ulcerative colitis: a review[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2021, 27(22): 2963-78. |
| 7 | 王 康, 缪志伟, 董 筠, 等. 基于STAT3/NF-kB/IL-6通路研究加味黄芩汤治疗溃疡性结肠炎的作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(2): 196-202. |
| 8 | 张 照, 杨 菊, 王加伟, 等.左金丸对DSS诱导的溃疡性结肠炎的作用及其机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2023, 29(16): 1-11. |
| 9 | 沈 洪, 唐志鹏, 唐旭东, 等.消化系统常见病溃疡性结肠炎中医诊疗指南(基层医生版)[J].中华中医药杂志, 2019, 34(9): 4155-60. |
| 10 | 孙 佳, 刘利琴, 勾 健, 等. 基于 “双态” 在体肠循环灌流模型研究隔山消提取物肠吸收特性差异[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2022, 47(23): 6340-7. |
| 11 | 勾 健, 吴宗芹, 孟 欣, 等. 基于UHPLC Q-Exactive Plus Orbitrap HRMS高分辨质谱技术的隔山消提取物化学成分分析[J]. 中国新药杂志, 2024, 33(5): 489-98. |
| 12 | Ru JL, Li P, Wang JN, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines[J]. J Cheminform, 2014, 6: 13. |
| 13 | 谢泽宇, 许一笑, 郑梦圆, 等. 基于网络药理学探究合欢皮-白蒺藜药对抑制肝星状细胞系LX2的抗焦亡作用[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2023, 48(2): 481-91. |
| 14 | 胡雪黎, 周昌园, 徐 睿, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS技术的土家族药三颗针干预溃疡性结肠炎的代谢组学研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2023, 48(9): 2490-9. |
| 15 | Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS, et al. Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium experimental murine colitis[J]. Lab Invest, 1993, 69(2): 238-49. |
| 16 | Saber S, El-Kader EMA. Novel complementary coloprotective effects of metformin and MCC950 by modulating HSP90/NLRP3 interaction and inducing autophagy in rats[J]. Inflammo-pharmacology, 2021, 29(1): 237-51. |
| 17 | 席 进, 张 敏, 张永玉, 等. 上调KLF11可改善结肠炎模型小鼠的肠道炎症: 基于抑制JAK2/STAT3信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 765-72. |
| 18 | Lu Z, Xiong WN, Xiao SM, et al. Huanglian Jiedu Decoction ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice via the JAK2/STAT3 signalling pathway[J]. Chin Med, 2020, 15: 45. |
| 19 | 刘星赐, 吴东升, 曹 晖, 等. 基于LC-MS研究芍药汤对溃疡性结肠炎大鼠粪便代谢产物的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2023, 29(9): 61-70. |
| 20 | 张 婷, 陈 烨, 王中秋, 等. 炎症性肠病患者肠道菌群结构的变化及其与炎性指标的关系[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2013, 33(10): 1474-7, 1498. |
| 21 | 龚顺航, 杨 杰, 张金涛, 等. 基于HMGCR及PPARα信号通路探究雪莲果浸膏对高脂血症大鼠脂质代谢的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(11): 1977-83. |
| 22 | 张甜甜, 项楚涵, 夏 勇, 等. M1型巨噬细胞非靶向脂质组学分析[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2021, 37(4): 711-7. |
| 23 | 杨 慧, 蒋且英, 刘 漩, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS技术白术多糖干预溃疡性结肠炎的代谢组学研究[J]. 中草药, 2023, 54(15): 4895-904. |
| 24 | Cho WH, Yeo HJ, Yoon SH, et al. Lysophosphatidylcholine as a prognostic marker in community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization: a pilot study[J]. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis, 2015, 34(2): 309-15. |
| 25 | 戎晓娟, 孔令霏, 康雨彤, 等. 基于脂质代谢组学的卵白蛋白诱导小鼠过敏性哮喘机制研究[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2023, 39(3): 477-83. |
| 26 | 朱 洁, 侯宝龙, 程 雯, 等. 基于血清代谢组学探究色胺酮抗小鼠溃疡性结肠炎的作用机制[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2023, 48(8): 2193-202. |
| 27 | Nakanishi M, Menoret A, Tanaka T, et al. Selective PGE(2) suppression inhibits colon carcinogenesis and modifies local mucosal immunity[J]. Cancer Prev Res, 2011, 4(8): 1198-208. |
| 28 | Li MH, Zeng YX, Ge LL, et al. Evaluation of the influences of low dose polybrominated diphenyl ethers exposure on human early retinal development[J]. Environ Int, 2022, 163: 107187. |
| 29 | Diederen K, Li JV, Donachie GE, et al. Exclusive enteral nutrition mediates gut microbial and metabolic changes that are associated with remission in children with Crohn’s disease[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 18879. |
| 30 | Mammedova JT, Sokolov AV, Freidlin IS, et al. The mechanisms of L-arginine metabolism disorder in endothelial cells[J]. Biochemistry, 2021, 86(2): 146-55. |
| 31 | Seim GL, Britt EC, Fan J. Analysis of arginine metabolism using LC-MS and isotopic labeling[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2019, 1978: 199-217. |
| [1] | 赵娜, 沈梦迪, 赵睿, 奥迪, 骆泽谭, 张银亮, 徐志东, 范方田, 郑海伦. 血根碱通过调控Nrf2/NF-κB通路缓解小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1467-1475. |
| [2] | 胡司淦, 程增为, 李敏, 高世毅, 高大胜, 康品方. 冠状动脉慢性完全闭塞病变侧支循环的建立与胰岛素抵抗的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 780-786. |
| [3] | 宋泽军, 董海滨, 马 娜, 任渝棠, 姜 泊. 改进的MAYO内镜评分对活动期溃疡性结肠炎疗效有较高的评估价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1204-1213. |
| [4] | 王旋成, 朱一帆, 周海琳, 黄宗声, 陈鸿炜, 张嘉豪, 杨珊伊, 陈广辉, 张淇淞. 血清非靶向代谢组学联合靶向胆汁酸代谢组学筛查结直肠癌的潜在生物标志物[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 443-453. |
| [5] | 库尔班乃木·卡合曼, 赵健锋, 穆凯代斯·艾合买提, 王汉铭, 朱稷蔚, 潘文涛, 卡思木江·阿西木江. 屎肠球菌QH06能减轻溃疡性结肠炎大鼠的结肠黏膜损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(7): 976-987. |
| [6] | 宋泽军, 张明君, 任渝棠, 姜 泊. 改良Mayo内镜评分对溃疡性结肠炎有较高的评估价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(7): 997-1005. |
| [7] | 刘文虎, 汤建才, 常晋霞. RUNX3调控胃癌细胞对曲妥珠单抗耐药的机制:基于超效高液相色谱-四极杆/静电场轨道阱质谱的代谢组学分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(4): 498-508. |
| [8] | 王佳媛, 袁依依, 张 坤, 孙 翔, 卜 歆, 董 健, 吴有盛, 田红英, 沈 岚. NDRG2通过调控肝癌细胞磷脂和甘油三酯代谢抑制肝细胞癌的生长:基于代谢组学分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(12): 1765-1773. |
| [9] | 华 慧, 董 昕, 张雨钊, 方 凡, 张蓓蓓, 李向阳, 于 倩, 郑葵阳, 颜 超. 华支睾吸虫来源的分子伴侣rCsHscB对小鼠慢性溃疡性结肠炎有治疗作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(5): 664-670. |
| [10] | 周长琳, 郑学宝, 黄晓其, 苏冀彦, 李木霞, 陈志维, 李敏瑶, 迟宏罡. 黄芩汤通过调节ILC3s-Th细胞反应减轻小鼠的溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(2): 256-263. |
| [11] | 王 康,缪志伟,董 筠,叶 柏. 基于 STAT3/NF-kB/IL-6 通路研究加味黄芩汤治疗溃疡性结肠炎的作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(02): 196-202. |
| [12] | 刘秀红,杜亚军,刘国星,但国梅,童 鑫,肖 娟. 奇任醇通过抑制炎症细胞因子和诱导淋巴细胞凋亡减轻小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(12): 1387-1392. |
| [13] | 张磊,范志娟,康华,王宇凡,刘树业,单忠强. HPLC/MS分析乙肝相关性肝细胞癌的血清代谢轮廓分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(01): 49-. |
| [14] | 王晶,李春林,白璐璐,唐强虎,张瑞源,Ting-Li Han,郭玉明,Philip N.Baker,夏茵茵,涂白杰. 苯并[a]芘暴露大鼠的皮层代谢组学研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(02): 162-. |
| [15] | 林安娜,李雨晴,钟慕晓,刘江,代倩,朱薇,张亚历. 炎性细胞因子在溃疡性结肠炎患者中的表达及其对预后的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(12): 1712-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||