南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 347-358.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.02.16
• • 上一篇
刘莹1,2( ), 李柏睿1, 李永财1, 常禄博1, 王娇1, 杨琳1, 颜永刚1,2, 屈凯3, 刘继平1,4, 张岗1(
), 李柏睿1, 李永财1, 常禄博1, 王娇1, 杨琳1, 颜永刚1,2, 屈凯3, 刘继平1,4, 张岗1( ), 沈霞1,2(
), 沈霞1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-17
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2025-03-03
通讯作者:
张岗,沈霞
E-mail:farewell991007@163.com;jay_gumling2003@aliyun.com;jxrain@163.com
作者简介:刘 莹,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: farewell991007@163.com
基金资助:
Ying LIU1,2( ), Borui LI1, Yongcai LI1, Lubo CHANG1, Jiao WANG1, Lin YANG1, Yonggang YAN1,2, Kai QV3, Jiping LIU1,4, Gang ZHANG1(
), Borui LI1, Yongcai LI1, Lubo CHANG1, Jiao WANG1, Lin YANG1, Yonggang YAN1,2, Kai QV3, Jiping LIU1,4, Gang ZHANG1( ), Xia SHEN1,2(
), Xia SHEN1,2( )
)
Received:2024-11-17
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-03-03
Contact:
Gang ZHANG, Xia SHEN
E-mail:farewell991007@163.com;jay_gumling2003@aliyun.com;jxrain@163.com
摘要:
目的 基于网络药理学、代谢组学和16srDNA探究加味逍遥丸(JWXYP)改善抑郁样行为的功效物质及作用机制。 方法 通过TCMSP、TCMIP等数据库,筛选加味逍遥丸治疗抑郁症的功效物质群、关键靶点及通路。将SD大鼠随机分为空白(Control)组、模型(CUMS)组、阳性组(1.8 mg/kg)组和加味逍遥丸低、中、高(JWXYP,1.44、2.88、4.32 g·kg-1·d-1)组(n=6)。通过行为学实验评估大鼠抑郁样行为, HE染色观察肝脏和海马病理变化,ELISA检测血清和脑组织生化指标。血清代谢组学采用OPLS-DA方法筛选差异代谢物并进行通路分析。盲肠内容物进行16srDNA基因测序分析肠道菌群变化。 结果 网络药理学研究发现,加味逍遥丸中的薄荷酮和丹皮酚等关键成分可通过血脑屏障,调节炎症通路保护神经系统。动物实验显示,加味逍遥丸均显著改善模型大鼠的体质量、糖水偏好率及旷场中央区域活动时间(P<0.05);明显减少肝脏炎性细胞浸润和细胞坏死,改善海马神经元结构;降低血清中肿瘤坏死因子-α、白细胞介素-1β、白细胞介素-6水平以及脂多糖结合蛋白,上调外周血和大脑中5-羟色胺、血管活性肠肽的浓度(P<0.05),其中高剂量效果最为显著(P<0.01)。代谢组学分析显示,加味逍遥丸干预的差异代谢物包括吲哚-3-乙酰胺、乙酰左旋肉碱、3-甲基-L-组氨酸等,涉及次级胆汁酸生物合成、精氨酸和脯氨酸代谢和D-氨基酸代谢等多条通路(P<0.05)。16srDNA分析发现,加味逍遥丸组的Chao1、Observed和Shannon指数均明显升高,肠道菌群丰富度和均匀度增加,且菌鼠乳杆菌、肠乳酸杆菌的丰度显著提高。 结论 加味逍遥丸通过调节神经递质、抗炎抗氧化以及肠道菌群三条途径相互作用,改善情绪和认知功能减轻抑郁样症状。
刘莹, 李柏睿, 李永财, 常禄博, 王娇, 杨琳, 颜永刚, 屈凯, 刘继平, 张岗, 沈霞. 加味逍遥丸通过神经递质调节、抗炎抗氧化及肠道菌群调控改善大鼠的抑郁样行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 347-358.
Ying LIU, Borui LI, Yongcai LI, Lubo CHANG, Jiao WANG, Lin YANG, Yonggang YAN, Kai QV, Jiping LIU, Gang ZHANG, Xia SHEN. Jiawei Xiaoyao Pills improves depression-like behavior in rats by regulating neurotransmitters, inhibiting inflammation and oxidation and modulating intestinal flora[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 347-358.
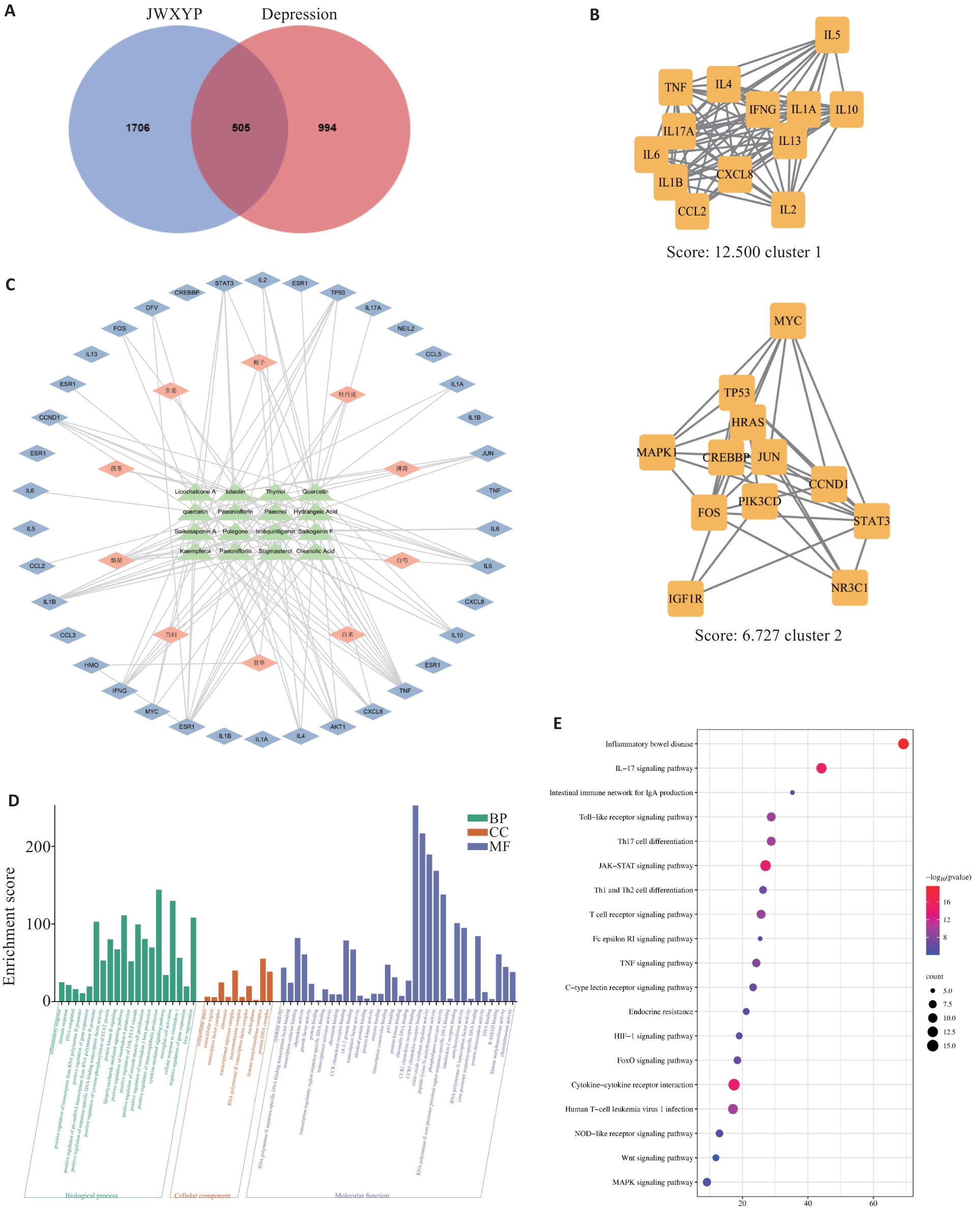
图1 网络药理学结果
Fig.1 Network pharmacology results. A: JWXYP and depression intersection genes. B: MCODE algorithm for screening the key targets. C: Chinese medicine-component-target network diagram. D: GO analysis of the key genes. E: Bubble map of KEGG analysis of the key genes.
| Compound | MW | OB(%) | BBB | DL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | 302.25 | 46.43 | -0.77 | 0.28 |
| Luteolin | 286.25 | 36.16 | -0.84 | 0.25 |
| Kaempferol | 286.25 | 41.88 | -0.55 | 0.24 |
| Thymol | 150.24 | 41.47 | 1.68 | 0.03 |
| Stigmasterol | 412.77 | 43.83 | 1 | 0.76 |
| Paeonol | 166.19 | 28.79 | 0.84 | 0.04 |
| Oleanolic acid | 456.78 | 29.02 | 0.07 | 0.76 |
| Saikosaponin A | 781.1 | 32.39 | -2.93 | 0.09 |
| Pulegone | 152.26 | 51.6 | 1.74 | 0.03 |
| Isoliquiritigenin | 256.27 | 85.32 | -0.41 | 0.15 |
| Paeoniflorin | 480.51 | 53.87 | -1.86 | 0.79 |
| Saikogenin F | 472.78 | 25.88 | -0.71 | 0.63 |
| Licochalcone A | 338.43 | 40.79 | -0.21 | 0.29 |
表1 化学成分理化性质表
Tab.1 Physicochemical properties of the bioactive compounds in Jiawei Xiaoyao Pills (JWXYP)
| Compound | MW | OB(%) | BBB | DL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | 302.25 | 46.43 | -0.77 | 0.28 |
| Luteolin | 286.25 | 36.16 | -0.84 | 0.25 |
| Kaempferol | 286.25 | 41.88 | -0.55 | 0.24 |
| Thymol | 150.24 | 41.47 | 1.68 | 0.03 |
| Stigmasterol | 412.77 | 43.83 | 1 | 0.76 |
| Paeonol | 166.19 | 28.79 | 0.84 | 0.04 |
| Oleanolic acid | 456.78 | 29.02 | 0.07 | 0.76 |
| Saikosaponin A | 781.1 | 32.39 | -2.93 | 0.09 |
| Pulegone | 152.26 | 51.6 | 1.74 | 0.03 |
| Isoliquiritigenin | 256.27 | 85.32 | -0.41 | 0.15 |
| Paeoniflorin | 480.51 | 53.87 | -1.86 | 0.79 |
| Saikogenin F | 472.78 | 25.88 | -0.71 | 0.63 |
| Licochalcone A | 338.43 | 40.79 | -0.21 | 0.29 |
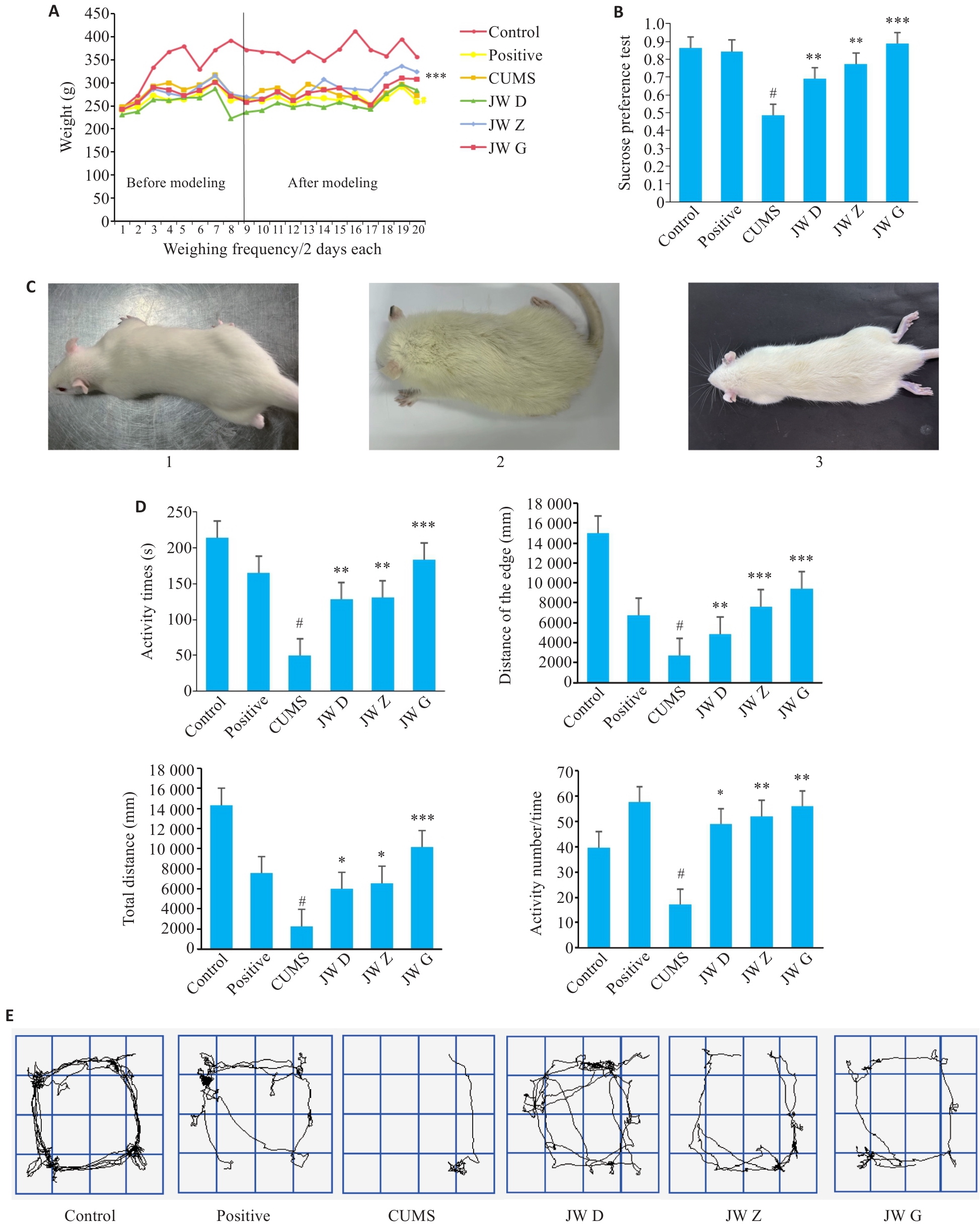
图2 大鼠模型建立及行为学测试结果测定
Fig.2 Establishment of depression rat models and behavioral test results of the rats. A: Body weight curves of rats in each group. B: Sugar water preference test. C: External hair of rats before modeling (1), after modeling (2) and after drug treatment (3). D: Open- field test of the rats (activity time, distance of the edge, total distance, and number of activities). E: Trajectory diagram of the rats in open field test. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs model group (CUMS); #P<0.05 vs control group.
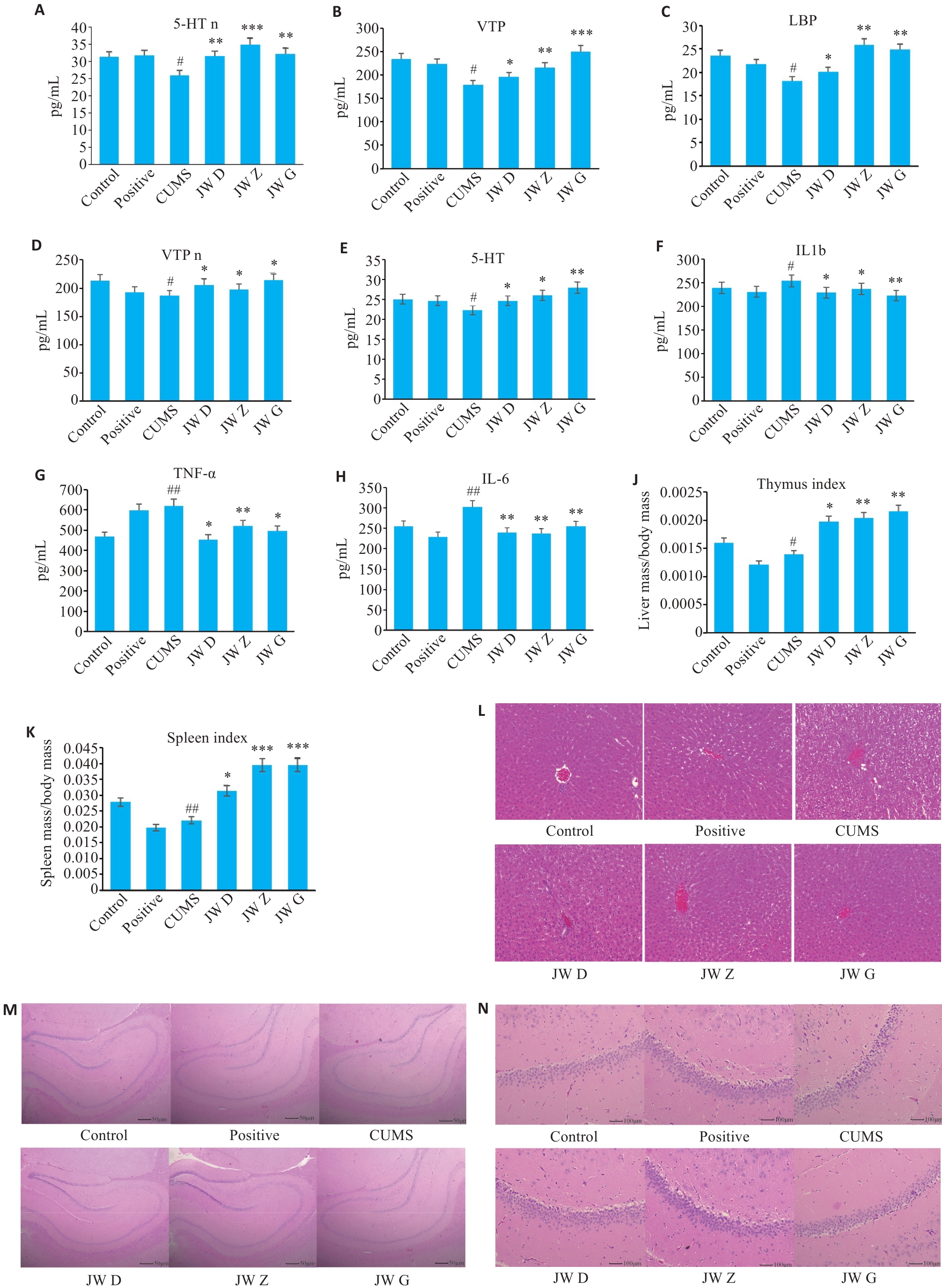
图3 ELISA结果、肝脾指数、肝脏照片及HE染色结果
Fig.3 ELISA results, liver and spleen index, liver and hippocampus HE staining results. A, D: Content of VIP and 5-HT in the brain tissues. B, C, E-H: Serum levels of IL-6, TNF-α, VIP, 5-HT, ILβ and LBP. J, K: Thymus index and spleen index. L: HE staining of the liver tissues in each group (Original magnification: ×100). M: HE staining of rat hippocampus (×100). N: HE staining of hippocampal CA1 region of the rats (×200) . *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs model group (CUMS); #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs control group.
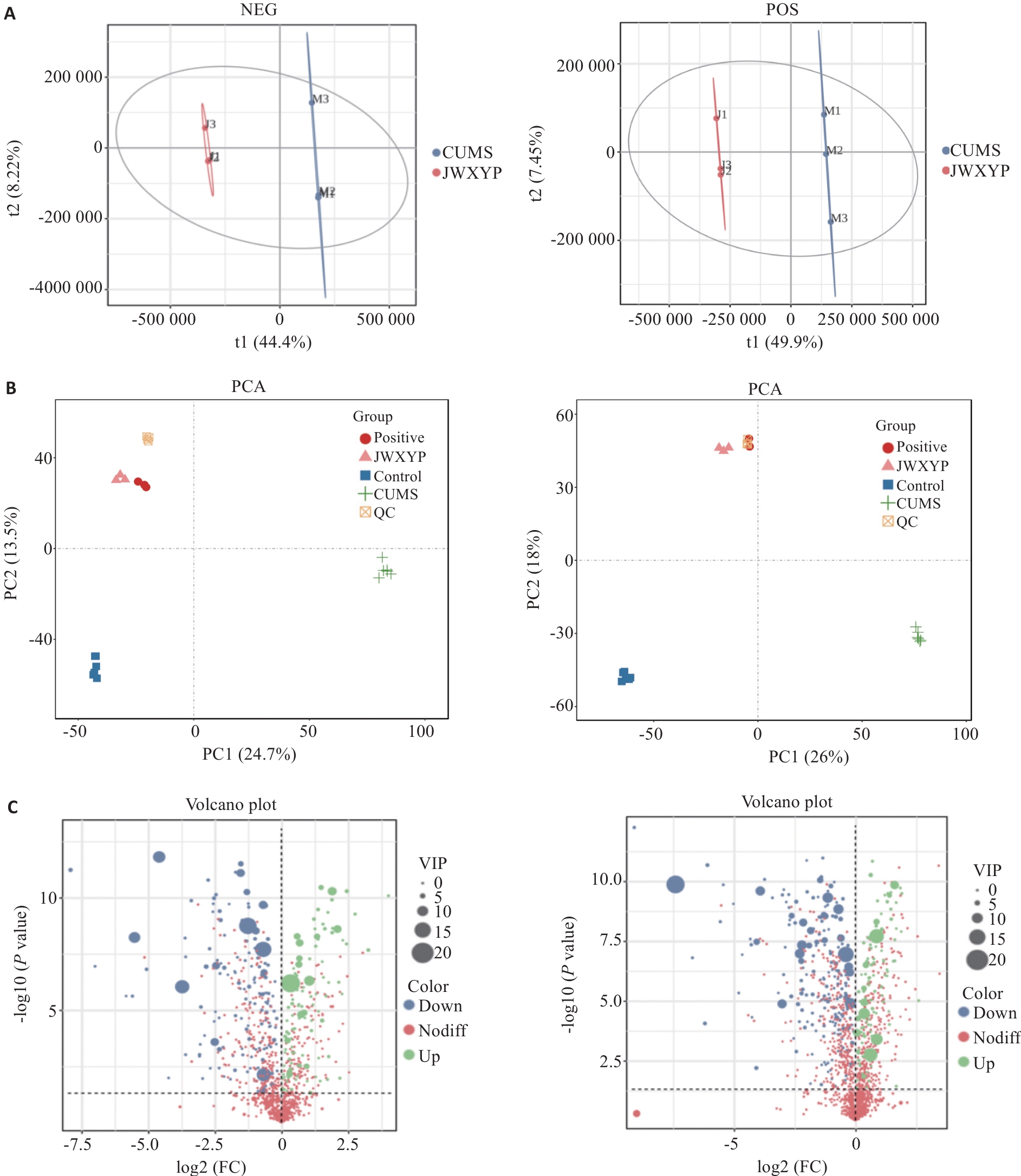
图4 差异代谢物的鉴定及多元统计分析
Fig.4 Identification of differential metabolites and multivariate statistical analysis. A: Principal component analysis. B: Partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA). C: Differential metabolite volcano plot analysis. The threshold of the difference was VIP≥1 and T-test P<0.05 in the OPLS-DA model.
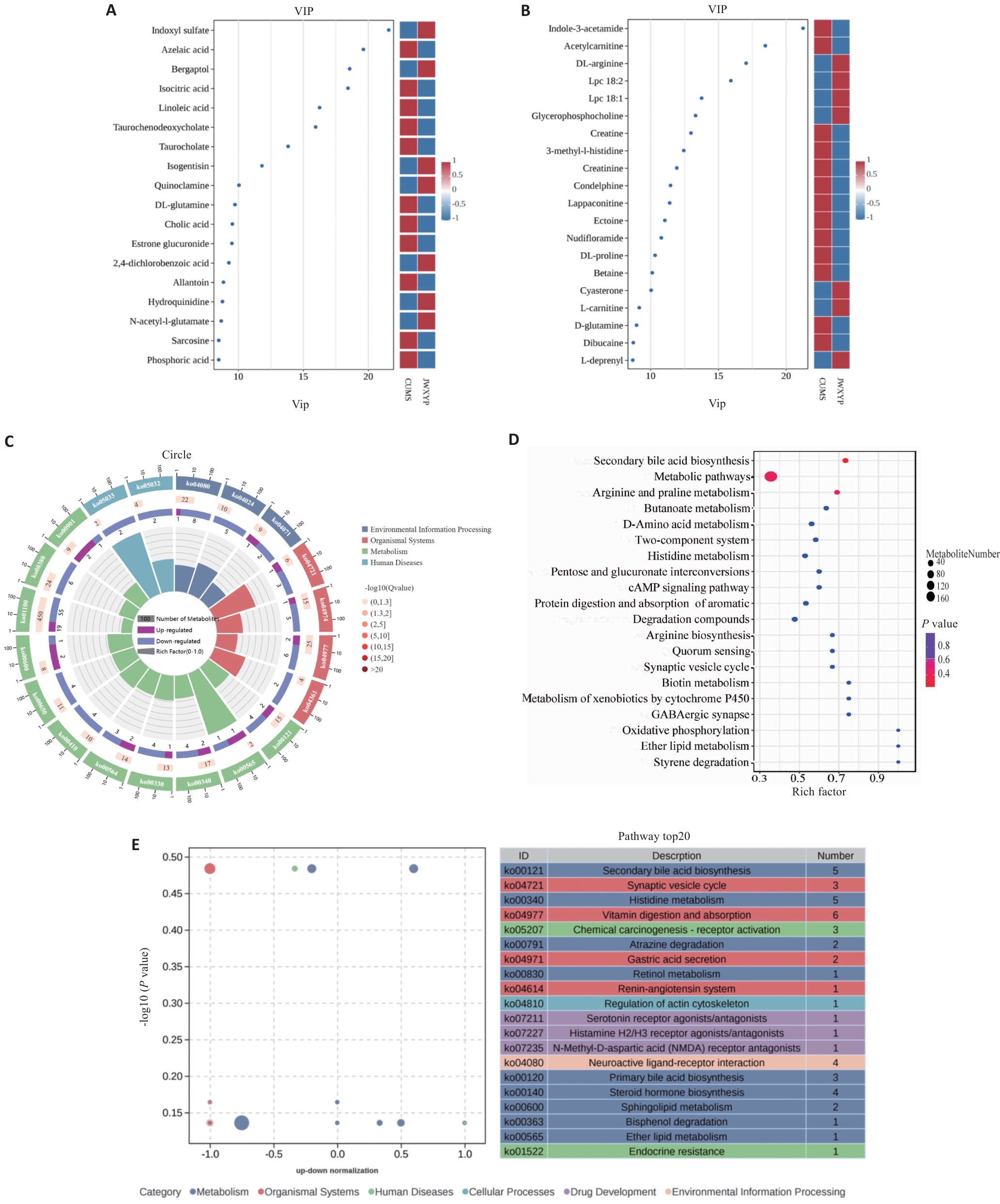
图5 血清代谢物的影响及代谢通路分析
Fig.5 Effects of serum metabolites and metabolic pathway analysis. A: VIP (importance of variables in projection) diagram of OPLS-DA in POS mode. B: VIP diagram of OPLS-DA in NEG mode. C: KEGG enrichment circle diagram (CUMS vs JWJWXYP). D: KEGG enriched bubble diagram of the top 20 pathways with the smallest Q value. E: Metabolic pathway and classification between JWXYP and CUMS groups.
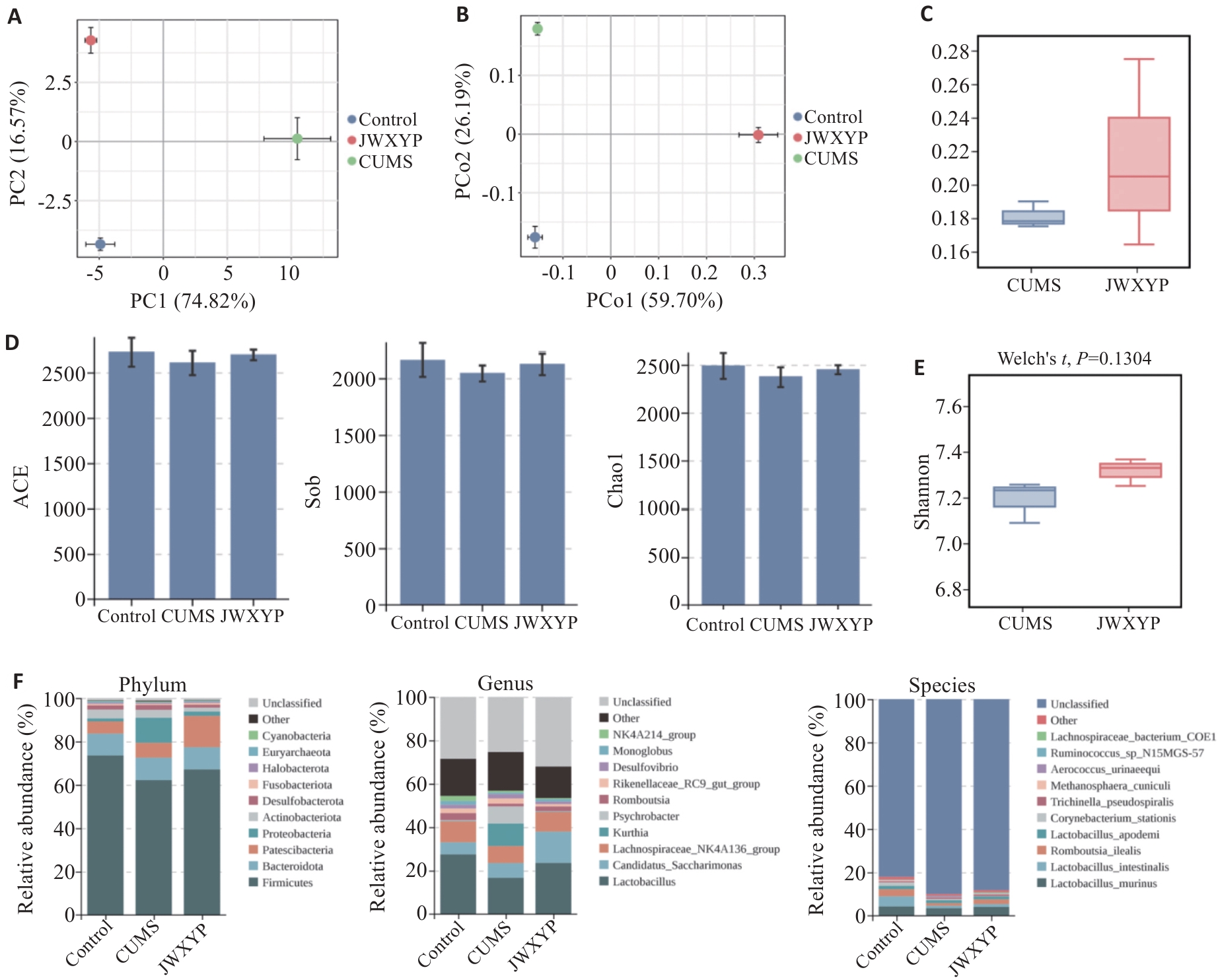
图6 肠道菌群物种丰度及差异物种
Fig.6 Intestinal flora species abundance and differential species. A: Distribution of samples in PC1 and PC2 dimensions. B: PCA analysis and PCoA analysis of the distribution of samples in PCo1 and PCo2 dimensions. C: β diversity box plot. D: Shaanon diversity index: ACE, Sob, Chao1 and Shannon index of Control, CIHMS and JWXYP groups. E: Distribution of Shannon index. F: Relative abundance of species at the phylum, class and species levels in control, CUMS and JWXYP groups.
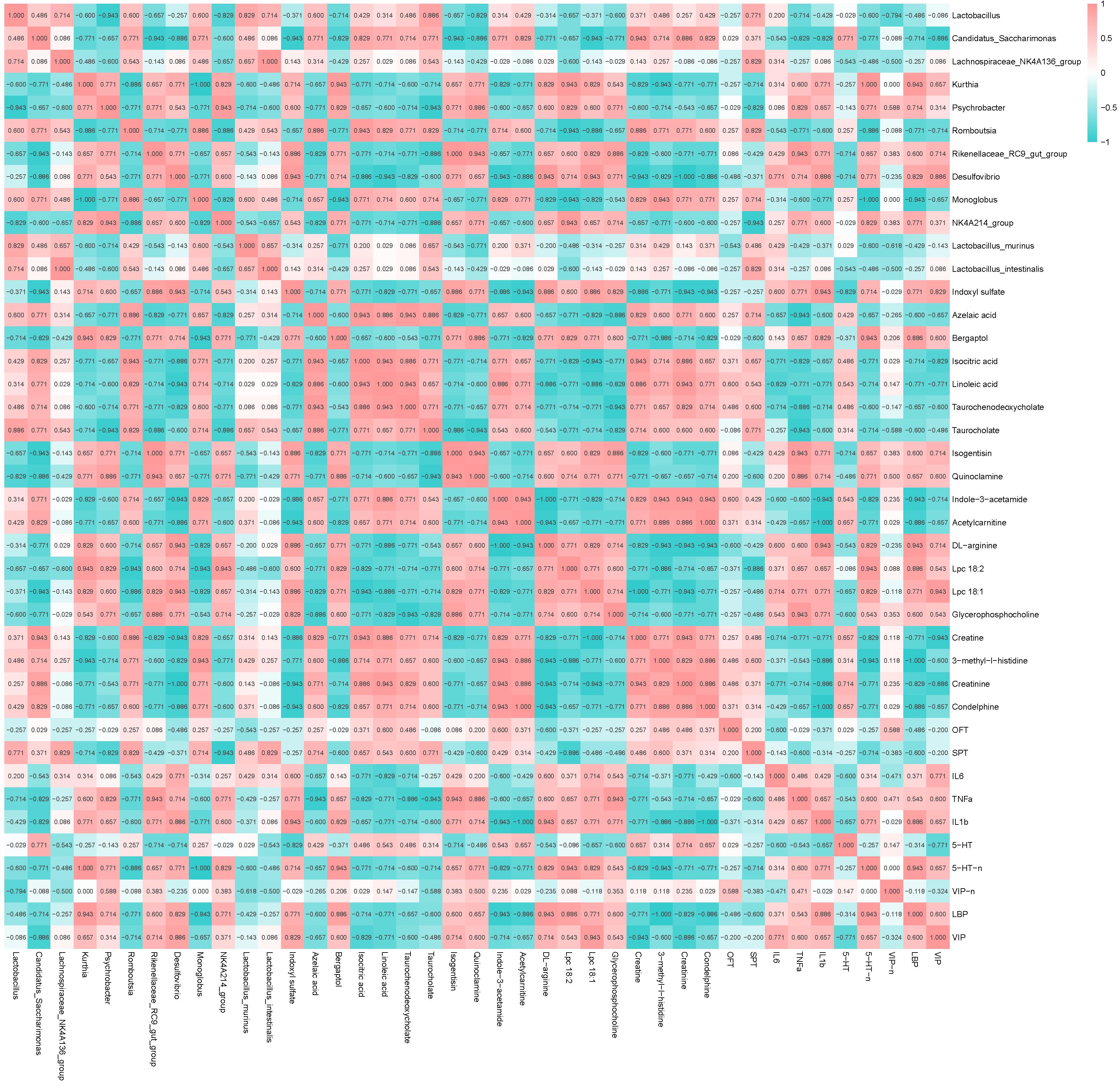
图7 组内分析采用Spearman分析对加味逍遥丸干预CUMS诱导的抑郁相关成分、大鼠体内差异代谢物、差异肠道菌群
Fig.7 Spearman analysis of depression-related components, differential metabolites and differential intestinal flora in JWXYP-treated rats with CUMS-induced depression. P value and color depth represent the degree of correlation.*P<0.05, **P<0.01,***P<0.001, JW vs CUMS group.
| 1 | Chang LJ, Wei Y, Hashimoto K. Brain-gut-microbiota axis in depression: a historical overview and future directions[J]. Brain Res Bull, 2022, 182: 44-56. |
| 2 | Kim IB, Park SC, Kim YK. Microbiota-gut-brain axis in major depression: a new therapeutic approach[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2023, 1411: 209-24. |
| 3 | Liu SH, Guo RJ, Liu F, et al. Gut microbiota regulates depression-like behavior in rats through the neuroendocrine-immune-mitocho-ndrial pathway[J]. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat, 2020, 16: 859-69. |
| 4 | 吴 丹, 高 耀, 向 欢, 等. 逍遥散“异病同治” 抑郁症和糖尿病的网络药理学作用机制研究[J]. 中草药, 2019, 50(8): 1818-27. |
| 5 | 于冰清, 邵欣欣, 付晓凡, 等. 抗抑郁中药复方的组方特点及作用机制研究[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(11): 3344-52. |
| 6 | 宋)宋太医局编 (宋)陈 承, (宋)裴宗元, 宋)陈师文校正. 太平惠民和剂局方[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社, 2020. |
| 7 | Li ZX, Zhao YX, Cheng JL, et al. Integrated plasma metabolomics and gut microbiota analysis: the intervention effect of Jiawei Xiaoyao San on liver depression and spleen deficiency liver cancer rats[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 906256. |
| 8 | Xie JQ, Xu DD, Wang C, et al. Jiawei Xiaoyao San in treatment of anxiety disorder and anxiety: a review[J]. Chin Herb Med, 2023, 15(2): 214-21. |
| 9 | 平 凡, 朱 琳, 沈 霞, 等. 基于炎症因子、雌激素及骨稳态的多向调控研究肉桂-熟地黄防治骨质疏松的分子作用机制[J]. 药学学报, 2022, 57(12): 3644-52. |
| 10 | 王艳霞, 沈 霞, 颜永刚, 等. 基于UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS的大黄治疗血瘀证的多元统计分析及代谢调控机制研究[J]. 药学学报, 2022, 57(4): 1115-22. |
| 11 | 朱 琳, 刘 莹, 申 洁, 等. 基于功效实验-网络药理学-HPLC探讨大黄-桃仁配伍活血化瘀的物质基础及分子作用机制[J]. 药学学报, 2024, 59(7): 2126-34. |
| 12 | 沈 霞, 裴丽珊, 高 静, 等. 基于系统药理学逍遥散治疗抑郁症的分子机制初探[J]. 中南药学, 2019, 17(9): 1476-84. |
| 13 | 裴丽珊, 沈 霞, 颜永刚, 等. 基于血管内皮生长因子信号通路/肿瘤坏死因子信号通路的桃核承气汤防治脑卒中双向调节分子网络机制[J]. 药学学报, 2020, 55(5): 898-906. |
| 14 | Yan LJ, Xu X, He ZY, et al. Antidepressant-like effects and cognitive enhancement of coadministration of Chaihu Shugan San and fluoxetine: dependent on the BDNF-ERK-CREB signaling pathway in the hippocampus and frontal cortex[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 2794263. |
| 15 | Zhou XM, Liu CY, Liu YY, et al. Xiaoyaosan alleviates hippocampal glutamate-induced toxicity in the CUMS rats via NR2B and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 586788. |
| 16 | 乔明亮, 梁 硕, 孟 毅, 等. 柴胡皂苷A调节cAMP/PKA/CREB信号通路对失眠大鼠的改善作用及机制研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2024, 35(5): 633-8. |
| 17 | 于泽胜, 路腾飞, 周好波, 等. 柴胡白芍药对对慢性温和不可预知性应激抑郁模型大鼠脑内单胺类神经递质的影响[J]. 中草药, 2016, 47(16): 2887-92. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2016.16.019 |
| 18 | 左洁仪, 徐汪洋, 陈洪栋, 等. 槲皮素通过调控FoxO3a/TXNIP通路对神经细胞焦亡的影响[J]. 中药材, 2024, 47(5): 1271-6. |
| 19 | 李 红, 万珊珊, 刘志新, 等. 甘草查尔酮A通过PI3K/Akt信号通路对胶质瘤U87细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭和氧化损伤的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2024, 40(5): 678-82. |
| 20 | 何 芳, 丁 敏, 甄海宁, 等. 芍药苷通过STAT3抑制IL-13诱导的BEAS-2B细胞氧化应激和自噬[J]. 中国医院药学杂志, 2024, 44(13): 1535-40. |
| 21 | 庞彬彬, 陈 震, 邢怡桥. 芍药苷调节RhoA/ROCK信号通路对实验性自身免疫性葡萄膜炎小鼠Th17/Treg免疫平衡的影响[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2024, 35(4): 506-12. |
| 22 | Yang J, Zheng P, Li YF, et al. Landscapes of bacterial and metabolic signatures and their interaction in major depressive disorders[J]. Sci Adv, 2020, 6(49): eaba8555. |
| 23 | Amin N, Liu J, Bonnechere B, et al. Interplay of metabolome and gut microbiome in individuals with major depressive disorder vs control individuals[J]. JAMA Psychiatry, 2023, 80(6): 597-609. |
| 24 | 郭天灏, 程海波. 肠道菌群与氨基酸代谢的相互作用研究进展[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2023, 38(10): 4851-7. |
| 25 | Vang S, Longley K, Steer CJ, et al. The unexpected uses of urso- and tauroursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of non-liver diseases[J]. Glob Adv Health Med, 2014, 3(3): 58-69. |
| 26 | Cheng L, Huang C, Chen Z. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced depression like behavior in mice via the inhibition of neuroinflammation and oxido-nitrosative stress[J]. Pharmacology, 2019, 103(1/2): 93-100. |
| 27 | Peng LY, Shi HT, Tan YR, et al. Baicalin inhibits APEC-induced lung injury by regulating gut microbiota and SCFA production[J]. Food Funct, 2021, 12(24): 12621-33. |
| 28 | Amin N, Liu J, Bonnechere B, et al. Interplay of metabolome and gut microbiome in individuals with major depressive disorder vs control individuals[J]. JAMA Psychiatry, 2023, 80(6): 597-609. |
| 29 | 李雅青, 王玉静, 许嘉乾, 等. 乳酸菌对抑郁症的影响及其可能的作用机制[J]. 微生物学通报,2024: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.240596 . |
| 30 | Mela DJ. A proposed simple method for objectively quantifying free sugars in foods and beverages[J]. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2020, 74(9): 1366-8. |
| 31 | 吴振宁, 王 琦, 秦雪梅, 等. 肠道菌群及其代谢产物在中药治疗抑郁症中的研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2023, 54(14): 4713-21. |
| 32 | Raidoo S, Tschann M, Kaneshiro B, et al. Impact of insurance coverage for abortion in hawai'i on gestational age at presentation and type of abortion, 2010-2013[J]. Hawaii J Health Soc Welf, 2020, 79(4): 117-22. |
| 33 | Gao K, Mu CL, Farzi A, et al. Tryptophan metabolism: a link between the gut microbiota and brain[J]. Adv Nutr, 2020, 11(3): 709-23. |
| 34 | Zhang FL, Chen XW, Wang YF, et al. Microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites indole-3-lactic acid is associated with intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury via positive regulation of YAP and Nrf2[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21(1): 264. |
| 35 | Wang QW, Jia DJC, He JM, et al. Lactobacillus intestinalis primes epithelial cells to suppress colitis-related Th17 response by host-microbe retinoic acid biosynthesis[J]. Adv Sci, 2023, 10(36): e2303457. |
| 36 | 国立东, 王丽群. 综述乳酸菌对抑郁症的改善作用[J]. 中国食品学报, 2020, 20(7): 317-25. |
| 37 | Michaudel C, Sokol H. The gut microbiota at the service of immunometabolism[J]. Cell Metab, 2020, 32(4): 514-23. |
| 38 | Mihajlovic M, Wyss HM, Sijbesma RP. Effects of surfactant and urea on dynamics and viscoelastic properties of hydrophobically assembled supramolecular hydrogel[J]. Macromolecules, 2018, 51(13): 4813-20. |
| [1] | 徐皓男, 张放, 黄钰莹, 姚其盛, 管悦琴, 陈浩. 百蕊草通过调节肠道菌群和调控EGFR/PI3K/Akt信号通路改善小鼠抗生素相关性腹泻[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [2] | 高俊杰, 叶开, 吴竞. 槲皮素通过调控TP53基因抑制肾透明细胞癌的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [3] | 褚乔, 王小娜, 续佳颖, 彭荟林, 赵裕琳, 张静, 陆国玉, 王恺. 白头翁皂苷D通过多靶点和多途径抑制三阴性乳腺癌侵袭转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [4] | 龙秀鹏, 陶顺, 阳绅, 李素云, 饶利兵, 李莉, 张哲. 槲皮素通过抑制MAPK信号通路改善心力衰竭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 187-196. |
| [5] | 徐朦, 陈丽娜, 吴金玉, 刘丽丽, 施美, 周灏, 张国梁. “白花蛇舌草-半枝莲”治疗原发性肝癌的机制研究:基于网络药理学、分子对接及体外实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 80-89. |
| [6] | 刘青, 刘敬, 郑逸航, 雷金, 黄建华, 刘思妤, 刘芳, 彭群龙, 张远芳, 王俊杰, 李玉娟. 积雪草活性成分槲皮素通过介导STAT3磷酸化抑制IL-23/IL-17A炎症轴发挥抗银屑病作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 90-99. |
| [7] | 陈星梅, 刘琴文, 李镱, 钟晓宇, 樊奇灵, 马柯, 罗柳婷, 官道刚, 朱志博. 茵陈蒿汤治疗肝纤维化的核心功能成分群以及潜在通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1508-1517. |
| [8] | 张珊苑, 蔡巧燕, 祁江晗, 殷恺馨, 何晨晨, 高铸烨, 张铃, 褚剑锋. 清心解瘀颗粒抗动脉粥样硬化的药效学及调控机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1518-1528. |
| [9] | 张钰明, 夏士程, 张淋淋, 陈梦茜, 刘晓婧, 高琴, 叶红伟. 金银花提取物对小鼠阿霉素肝脏损伤的保护作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1571-1581. |
| [10] | 王瑾瑾, 崔文飞, 窦雪伟, 尹冰磊, 牛钰琪, 牛羚, 闫国立. 鬼箭羽通过调节EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂耐药信号通路延缓糖尿病肾病的进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1243-1255. |
| [11] | 王琳月, 戚文月, 高记华, 田茂生, 许建成. 痛痒消洗剂可促进大鼠肛瘘术后的创面愈合[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1256-1265. |
| [12] | 张文祥, 顾惠贤, 陈鹏德, 吴思宇, 马洪艳, 姚蓝. 复方玉液汤通过调控PI3K/Akt信号通路抑制糖尿病大鼠心肌细胞凋亡和炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1306-1314. |
| [13] | 黄燕, 覃璐璐, 管少兴, 管宴萍, 韦玉茹, 操艾伶, 李冬梅, 韦桂宁, 苏启表. 金缕半枫荷的水提取物抑制胰腺癌的作用机制:活性成分、关键靶点和信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1336-1344. |
| [14] | 刘佳进, 缪长宏, 徐健康, 余伟杰, 陈继鑫, 唐好知, 刘爱峰. 肠道菌群与色素沉着绒毛结节性滑膜炎之间的因果关系:基于孟德尔随机化分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1397-1406. |
| [15] | 任志军, 刁建新, 王奕婷. 芎归汤通过抑制氧化应激诱导的心肌凋亡减轻小鼠心梗后心衰引起的心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1416-1424. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||