南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 1867-1879.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.07
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2025-03-27
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-09-28
通讯作者:
金华
E-mail:qinhu992024@163.com;ya790312@sina.com
作者简介:呼 琴,在读博士研究生,E-mail: qinhu992024@163.com
基金资助:Received:2025-03-27
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Hua JIN
E-mail:qinhu992024@163.com;ya790312@sina.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨清肾颗粒对慢性肾脏病(CKD)湿热证患者miR-23b及Nrf2通路及氧化应激干预作用。 方法 通过TCMSP、UniProt检索并映射清肾颗粒调控靶点,利用Small RNA测序技术筛选慢性肾衰竭湿热证的疾病基因,构建“活性成分-交集靶点-疾病”网络。利用KEGG通路富集分析及分子对接,明确清肾颗粒通过Nrf2通路影响CKD的靶点。临床试验:纳入60例CKD3~5期且表现为湿热证的非透析患者,设观察组和对照组,30例/组,另设20例正常组。对照组接受西医常规治疗,观察组在此基础上加用清肾颗粒,疗程8周。检测指标包括PBMC中miR-23b-5p、Nrf2和HO-1蛋白的表达水平,肾功能指标(Scr、eGFR),以及血清中ROS、AOPP、 PON-1的含量。 结果 清肾颗粒经筛选得到6种主要活性成分,10个关键靶点(ACTB、JUN、PTEN、ESR1、GSK3B、PPARG、PIK3CA、APP、PIK3R1、BECN1)。通过Small RNA测序,发现miR-23b-5p基因表达上调。KEGG通路分析显示Nrf2通路发挥重要作用。分子对接揭示核心靶点与活性成分结合活性良好,NFE2L2与木犀草素结合活性最好。清肾颗粒能降低患者血清Scr及ROS和AOPP水平,升高eGFR及血清PON-1水平(P<0.05);升高PBMC中的 Nrf2和HO-1蛋白水平(P<0.05);升高miR-23b-5p的表达水平(P<0.05)。 结论 miR-23b表达及Nrf2通路异常可能是CKD湿热证患者的关键干预靶点。清肾颗粒能通过多种活性成分作用于多靶点改善CKD湿热证患者肾功能,其治疗效果可能与 miR-23b 表达的上调、Nrf2 抗氧化通路活性的增强以及机体氧化应激水平的降低密切相关。
呼琴, 金华. 清肾颗粒通过调控miR-23b及Nrf2通路改善慢性肾脏病湿热证患者的肾功能:基于网络药理学和临床试验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1867-1879.
Qin HU, Hua JIN. Qingshen Granules improves renal function of patients with chronic kidney disease damp-heat syndrome by activating the miR-23b and Nrf2 pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1867-1879.
| Group | Age (year) | Course | Gender | CKD staging | Underlying medical conditions | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | 3 | 4 | 5 | Chronic nephritis | Hypertension | Diabetes | Polycystic kidney disease | |||||
| Normal (n=20) | 51.55±8.17 | - | 11 | 9 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Control (n=30) | 48.73±9.13 | 3.74±1.92 | 17 | 13 | 1 | 17 | 12 | 12 | 7 | 7 | 4 | ||
| Observation (n=30) | 50.03±9.64 | 3.91±2.04 | 16 | 14 | 5 | 11 | 14 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 4 | ||
表1 研究对象的一般资料比较
Tab.1 Comparison of general data of the participants
| Group | Age (year) | Course | Gender | CKD staging | Underlying medical conditions | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | 3 | 4 | 5 | Chronic nephritis | Hypertension | Diabetes | Polycystic kidney disease | |||||
| Normal (n=20) | 51.55±8.17 | - | 11 | 9 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Control (n=30) | 48.73±9.13 | 3.74±1.92 | 17 | 13 | 1 | 17 | 12 | 12 | 7 | 7 | 4 | ||
| Observation (n=30) | 50.03±9.64 | 3.91±2.04 | 16 | 14 | 5 | 11 | 14 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 4 | ||
| miRNA_id | log2 Fold Change | qValue | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-let-7b-3p | 8.206372 | 1.35×10-5 | Up |
| hsa-let-7f-2-3p | 9.086326 | 0.0016 | Up |
| …… | …… | …… | …… |
| hsa-miR-20a-5p | 10.3875 | 1.37×10-5 | Up |
| hsa-miR-21-5p | 5.334294 | 0.000371 | Up |
| hsa-miR-23b-5p | -4.50953 | 0.003782 | Down |
| hsa-miR-26b-5p | 4.938481 | 0.003172 | Up |
| hsa-miR-27a-3p | 4.084065 | 0.005144 | Up |
| hsa-miR-30d-3p | -2.49269 | 0.049808 | Down |
表2 两组差异miRNA的表达
Tab.2 Expression of differential miRNAs between the two groups
| miRNA_id | log2 Fold Change | qValue | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-let-7b-3p | 8.206372 | 1.35×10-5 | Up |
| hsa-let-7f-2-3p | 9.086326 | 0.0016 | Up |
| …… | …… | …… | …… |
| hsa-miR-20a-5p | 10.3875 | 1.37×10-5 | Up |
| hsa-miR-21-5p | 5.334294 | 0.000371 | Up |
| hsa-miR-23b-5p | -4.50953 | 0.003782 | Down |
| hsa-miR-26b-5p | 4.938481 | 0.003172 | Up |
| hsa-miR-27a-3p | 4.084065 | 0.005144 | Up |
| hsa-miR-30d-3p | -2.49269 | 0.049808 | Down |
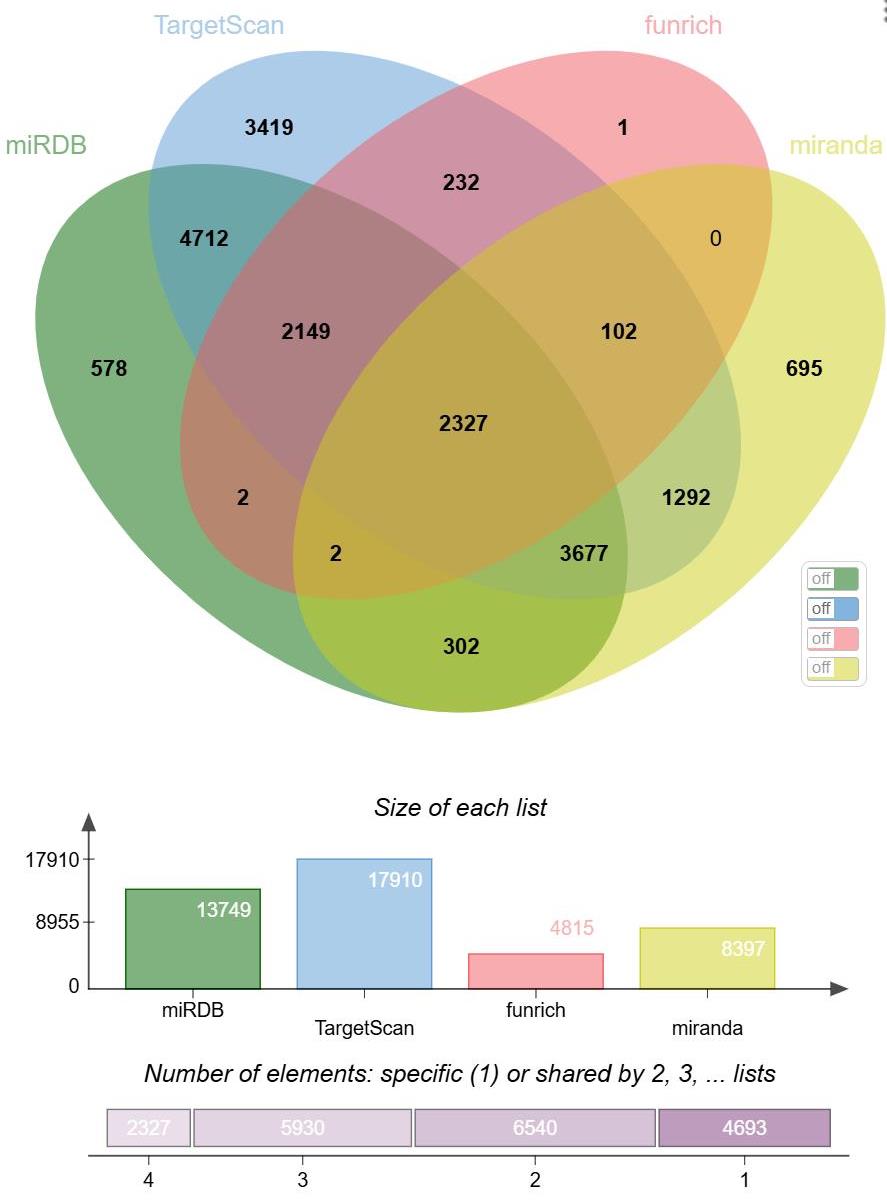
图2 miRNA靶基因预测韦恩图
Fig.2 Venn diagram of miRNA target gene prediction. 1: Elements exist only in a single list (one of miRDB, TargetScan, funrich, miranda) and are not shared with other lists. 2: Elements exist in two lists simultaneously. 3: Elements exist in three lists simultaneously. 4: Elements exist in four lists simultaneously.
| Key ingredients | Target | Affinity (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| ACTB | -2.88 | |
| PTEN | -2.55 | |
| Quercetin | PPARG | -5.31 |
| PIK3CA | -4.9 | |
Kaempferol Apigenin Luteolin | NFE2L2 ACTB PTEN PPARG PIK3CA NFE2L2 ACTB PTEN PPARG PIK3CA NFE2L2 ACTB PTEN PPARG PIK3CA NFE2L2 | -4.8 -3.61 -3.5 -4.1 -2.63 -4.96 -3.21 -2.34 -4.13 -4.05 -6.0 -4.34 -3.58 -4.26 -4.19 -5.38 |
表3 活性成分与核心靶点的结合能
Tab.3 Binding energy of the active ingredients to the core targets
| Key ingredients | Target | Affinity (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| ACTB | -2.88 | |
| PTEN | -2.55 | |
| Quercetin | PPARG | -5.31 |
| PIK3CA | -4.9 | |
Kaempferol Apigenin Luteolin | NFE2L2 ACTB PTEN PPARG PIK3CA NFE2L2 ACTB PTEN PPARG PIK3CA NFE2L2 ACTB PTEN PPARG PIK3CA NFE2L2 | -4.8 -3.61 -3.5 -4.1 -2.63 -4.96 -3.21 -2.34 -4.13 -4.05 -6.0 -4.34 -3.58 -4.26 -4.19 -5.38 |
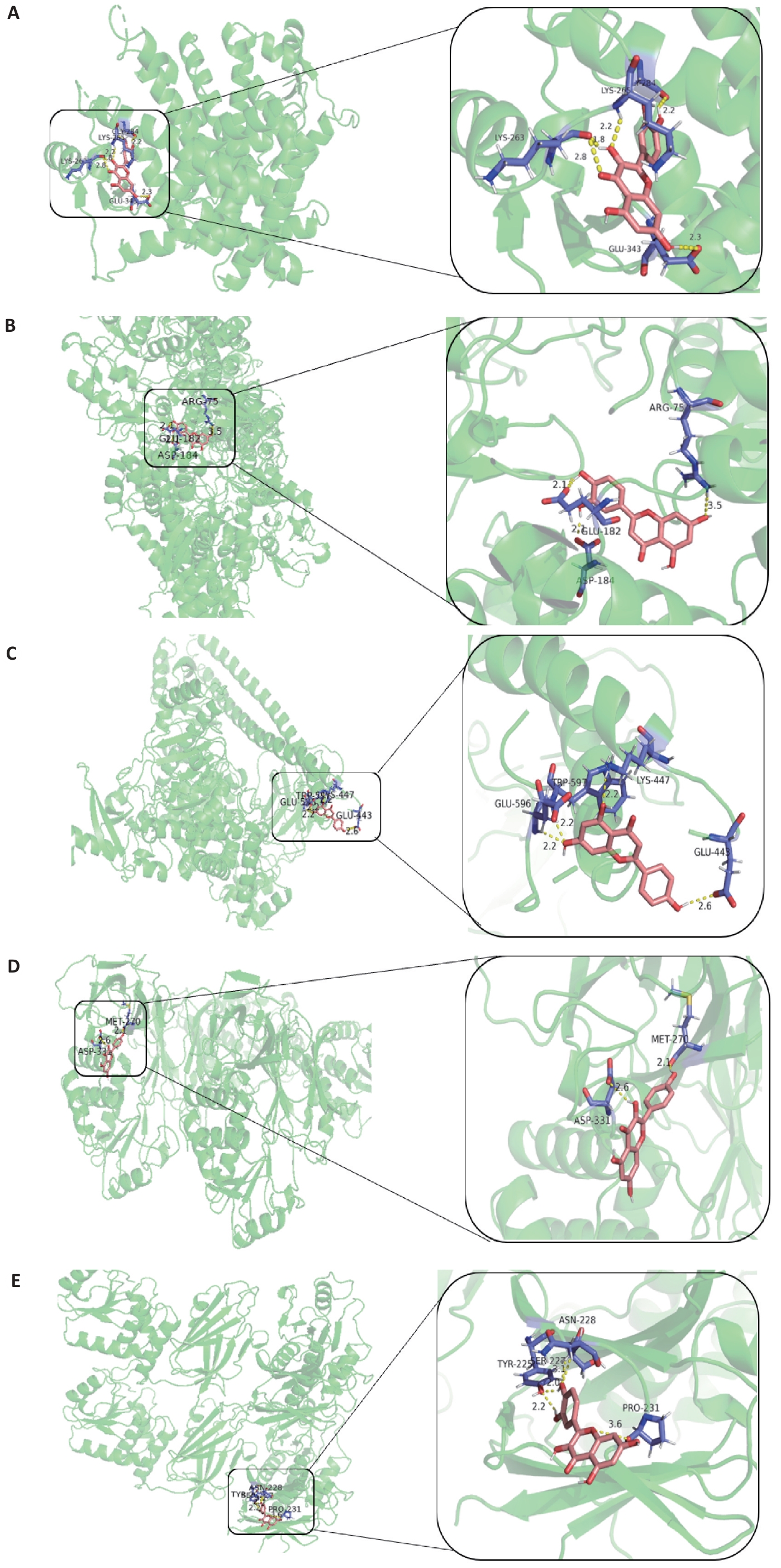
图8 分子对接及结合位点图
Fig.8 Molecular docking and the binding sites. A: Quercetin-PPARG. B: luteolin-ACTB. C: Apigenin-PIK3CA. D: Kaempferol-PTEN. E: Quercetin-PTEN.
| Group | TCM syndrome scores | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | ||
| Control | 11.98±1.69 | 10.87±2.14 | |
| Observation | 12.60±1.11 | 8.53±2.19*▲ | |
表4 中医症候积分比较
Tab.4 Comparison of TCM syndrome scores (n=30, Mean±SD)
| Group | TCM syndrome scores | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | ||
| Control | 11.98±1.69 | 10.87±2.14 | |
| Observation | 12.60±1.11 | 8.53±2.19*▲ | |
| Group | Scr (μmol/L) | eGFR(mL/min) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | △Scr | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | △eGFR | |||
| Control | 328.51±109.32 | 322.25±110.45 | 6.26±20.57 | 19.33±9.20 | 19.78±9.19 | 0.45±1.51 | ||
| Observation | 317.81±114.33 | 298.47±108.61* | 19.34±23.86▲ | 20.02±9.31 | 21.68±10.15* | 1.65±2.15▲ | ||
表5 两组患者Scr、eGFR比较
Tab.5 Comparison of Scr and eGFR between the two groups of patients (n=30, Mean±SD)
| Group | Scr (μmol/L) | eGFR(mL/min) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | △Scr | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | △eGFR | |||
| Control | 328.51±109.32 | 322.25±110.45 | 6.26±20.57 | 19.33±9.20 | 19.78±9.19 | 0.45±1.51 | ||
| Observation | 317.81±114.33 | 298.47±108.61* | 19.34±23.86▲ | 20.02±9.31 | 21.68±10.15* | 1.65±2.15▲ | ||
| Group | n | Nrf2/β-actin | HO-1/β-actin | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | |||
| Normal | 20 | 1.04±0.06 | - | 1.10±0.09 | - | |
| Control | 30 | 0.42±0.07△ | 0.48±0.09* | 0.32±0.06 | 0.36±0.11* | |
| Observation | 30 | 0.45±0.07△ | 0.55±0.12*▲ | 0.33±0.06 | 0.42±0.10*▲ | |
表6 PBMC中Nrf2、HO-1比较
Tab.6 Comparison of Nrf2 and HO-1 in PBMCs among the 3 groups (Mean±SD)
| Group | n | Nrf2/β-actin | HO-1/β-actin | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | |||
| Normal | 20 | 1.04±0.06 | - | 1.10±0.09 | - | |
| Control | 30 | 0.42±0.07△ | 0.48±0.09* | 0.32±0.06 | 0.36±0.11* | |
| Observation | 30 | 0.45±0.07△ | 0.55±0.12*▲ | 0.33±0.06 | 0.42±0.10*▲ | |
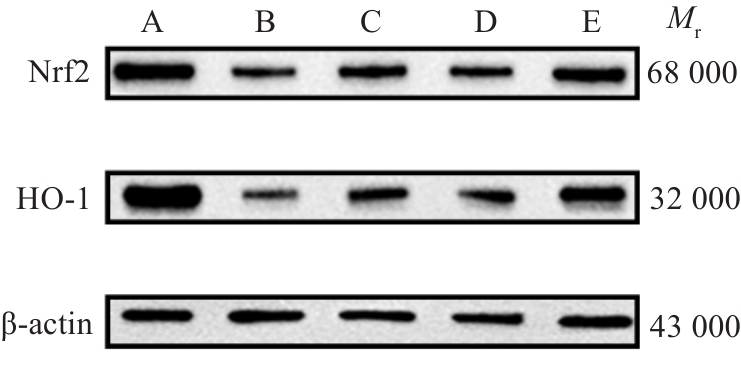
图9 各组PBMC中Nrf2、HO-1比较
Fig.9 Nrf2 and HO-1 in the PBMCs in each group. A:Normal group. B: Control group(Pre-treatment).C: Control group (Post-treatment). D:Observation group(Pre-treatment). E: Observation group(Post-treatment).
| Group | n | ROS (U/mL) | PON-1 (U/L) | AOPP (μmol/L) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | ||||
| Normal | 20 | 21707.25±844.70 | - | 79.40±5.25 | - | 2045.52±156.85 | - | ||
| Control | 30 | 36181.78±2904.00△ | 35090.40±3001.58* | 47.94±9.58 | 50.84±12.18* | 3596.73±236.77 | 3493.55±236.38* | ||
| Observation | 30 | 36019.23±2370.14△ | 30176.07±2850.72*▲ | 51.28±9.24 | 60.50±13.29*▲ | 3527.61±347.18 | 2825.24±311.16*▲ | ||
表7 血清ROS、PON-1、AOPP水平比较
Tab.7 Comparison of serum ROS, PON-1 and AOPP levels among the 3 groups before and after treatment (Mean±SD)
| Group | n | ROS (U/mL) | PON-1 (U/L) | AOPP (μmol/L) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | ||||
| Normal | 20 | 21707.25±844.70 | - | 79.40±5.25 | - | 2045.52±156.85 | - | ||
| Control | 30 | 36181.78±2904.00△ | 35090.40±3001.58* | 47.94±9.58 | 50.84±12.18* | 3596.73±236.77 | 3493.55±236.38* | ||
| Observation | 30 | 36019.23±2370.14△ | 30176.07±2850.72*▲ | 51.28±9.24 | 60.50±13.29*▲ | 3527.61±347.18 | 2825.24±311.16*▲ | ||
| Group | n | miR-23b-5p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | ||
| Normal | 20 | 1.05±0.19 | - |
| Control | 30 | 0.35±0.09△ | 0.39±0.14 |
| Observation | 30 | 0.38±0.11△ | 0.53±0.19*▲ |
表8 PBMC中miR-23b-5p比较
Tab.8 Comparison of miR-23b-5p in PBMCs among the 3 groups (Mean±SD)
| Group | n | miR-23b-5p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | ||
| Normal | 20 | 1.05±0.19 | - |
| Control | 30 | 0.35±0.09△ | 0.39±0.14 |
| Observation | 30 | 0.38±0.11△ | 0.53±0.19*▲ |
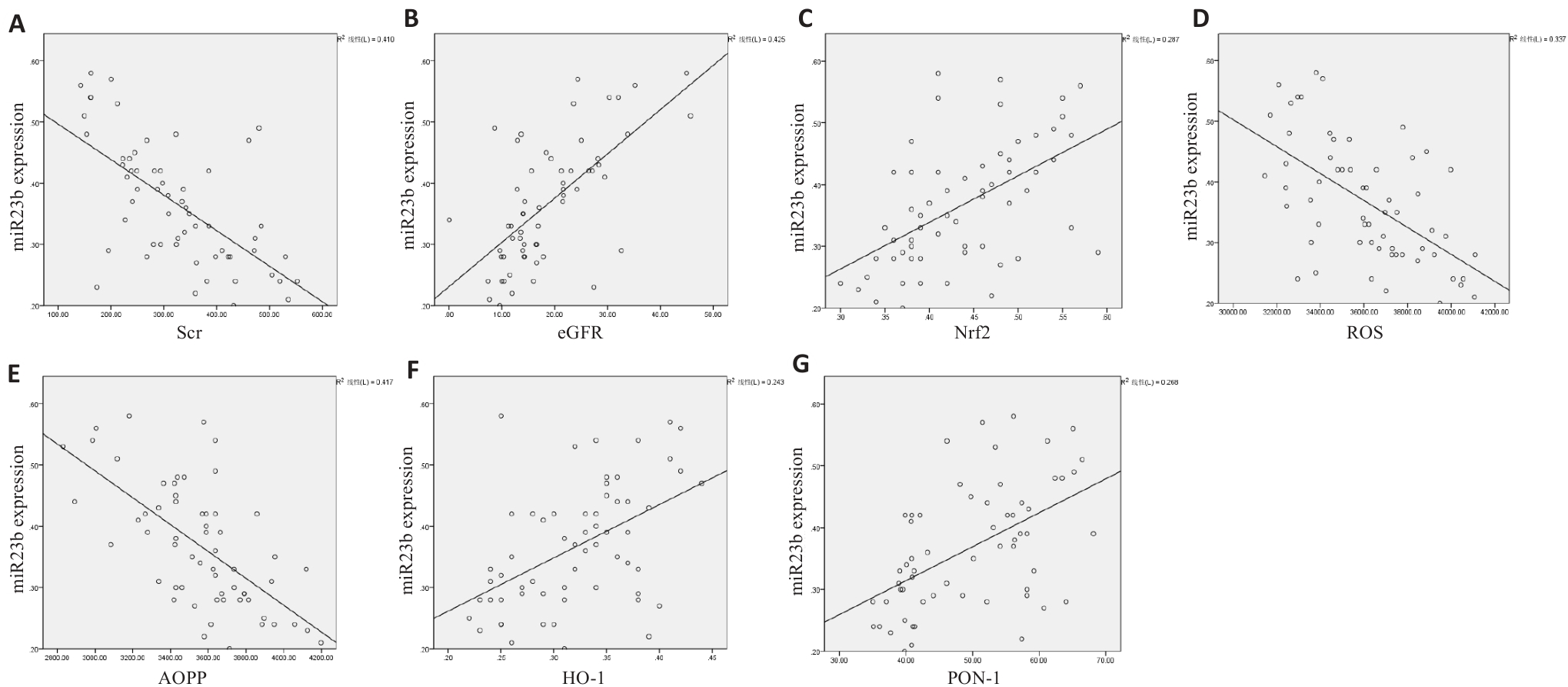
图10 miR-23b-5p表达量的相关性分析
Fig10 Correlation analysis of miR-23b-5p expression. A: miR-23b-5p and Scr (negative correlation). B: miR-23b-5p and eGFR (positive correlation). C: miR-23b-5p and Nrf2 (positive correlation). D: miR-23b-5p and ROS (negative correlation). E: miR-23b-5p and AOPP (negative correlation). F: miR-23b-5p and HO-1 (positive correlation). G: miR-23b-5p and PON1 (positive correlation).
| [1] | GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10225): 709-33. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(19)32977-0 |
| [2] | Ruiz-Ortega M, Rayego-Mateos S, Lamas S, et al. Targeting the progression of chronic kidney disease[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2020, 16(5): 269-88. doi:10.1038/s41581-019-0248-y |
| [3] | Zhao H, Ma SX, Shang YQ, et al. microRNAs in chronic kidney disease[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2019, 491: 59-65. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2019.01.008 |
| [4] | Aranda-Rivera AK, Cruz-Gregorio A, Pedraza-Chaverri J, et al. Nrf2 activation in chronic kidney disease: promises and pitfalls[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2022, 11(6): 1112. doi:10.3390/antiox11061112 |
| [5] | DiseaseKidney: Improving Global Outcomes CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease[J]. Kidney Int, 2024, 105(4S): S117-314. |
| [6] | 王亿平, 陈 芳, 王 东, 等. 清肾颗粒对慢性肾衰竭湿热证患者氧化应激的干预作用[J]. 中成药, 2017, 39(1): 46-50. |
| [7] | 金 华, 王亿平, 王 东, 等. 清肾颗粒对慢性肾衰竭湿热证患者氧化应激介导的NF-κB信号通路活化的影响[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2017, 28(12): 2841-3. |
| [8] | 李文娟, 王亿平. 湿热证与慢性肾衰竭病证关系浅析[J]. 安徽中医学院学报, 2004, 23(2): 58-9. |
| [9] | 邵光新.慢性肾功能衰竭中医证候学临床回顾性调查研究[D].合肥:安徽中医学院,2007. |
| [10] | 慢性肾脏病蛋白营养治疗专家共识[J]. 国外医学 内分泌学分册, 2005, 25(6): 437-8. |
| [11] | 中国高血压防治指南修订委员会, 高血压联盟(中 国, 中国医疗保健国际交流促进会高血压病学分会, 等. 中国高血压防治指南(2024年修订版)[J]. 中华高血压杂志: 中英文, 2024, 32(7): 603-700. |
| [12] | 孙雪峰. 《中国肾性贫血诊疗的临床实践指南》解读[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2021, 41(9): 785-8. |
| [13] | National Clinical Research Center of Kidney Diseases. 中国慢性肾脏病矿物质和骨异常诊治指南概要[J]. 肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志, 2019, 28(1): 52-7. |
| [14] | Lai KM, Wang JJ, Lin SY, et al. Sensing of mitochondrial DNA by ZBP1 promotes RIPK3-mediated necroptosis and ferroptosis in response to diquat poisoning[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2024, 31(5): 635-50. doi:10.1038/s41418-024-01279-5 |
| [15] | Zhang JC, Zhao XM, Zhu HL, et al. Apigenin protects against renal tubular epithelial cell injury and oxidative stress by high glucose via regulation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2019, 25: 5280-8. doi:10.12659/msm.915038 |
| [16] | Jin H, Wang YP, Wang D, et al. Effects of Qingshen Granules on the oxidative stress-NF/kB signal pathway in unilateral ureteral obstruction rats[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2018, 2018: 4761925. doi:10.1155/2018/4761925 |
| [17] | Lin DW, Hsu YC, Chang CC, et al. Insights into the molecular mechanisms of NRF2 in kidney injury and diseases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(7): 6053. doi:10.3390/ijms24076053 |
| [18] | Ryoo IG, Shin DH, Kang KS, et al. Involvement of Nrf2-GSH signaling in TGFβ1-stimulated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition changes in rat renal tubular cells[J]. Arch Pharm Res, 2015, 38(2): 272-81. doi:10.1007/s12272-014-0380-y |
| [19] | Wang J, Zhu HB, Huang LQ, et al. Nrf2 signaling attenuates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and renal interstitial fibrosis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathways[J]. Exp Mol Pathol, 2019, 111: 104296. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104296 |
| [20] | 陈 诺, 金 华, 呼 琴, 等. 清肾颗粒对腺嘌呤致肾纤维化大鼠Nrf2/ARE信号通路及氧化应激的干预作用[J]. 中医药临床杂志, 2023, 35(5): 976-82. |
| [21] | Yu DM, Yang XH, Zhu Y, et al. Knockdown of plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 (PVT1) inhibits high glucose-induced proliferation and renal fibrosis in HRMCs by regulating miR-23b-3p/early growth response factor 1 (EGR1)[J]. Endocr J, 2021, 68(5): 519-29. doi:10.1507/endocrj.ej20-0642 |
| [22] | Zhao BH, Li HZ, Liu JT, et al. microRNA-23b targets ras GTPase-activating protein SH3 domain-binding protein 2 to alleviate fibrosis and albuminuria in diabetic nephropathy[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2016, 27(9): 2597-608. doi:10.1681/asn.2015030300 |
| [23] | Liu HF, Wang XH, Liu SF, et al. Effects and mechanism of miR-23b on glucose-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2016, 70: 149-60. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2015.11.016 |
| [24] | Li HZ, Chen ZC, Chen WT, et al. microRNA-23b-3p deletion induces an IgA nephropathy-like disease associated with dysregulated mucosal IgA synthesis[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2021, 32(10): 2561-78. doi:10.1681/asn.2021010133 |
| [25] | Li M, Peng YF, Chen WJ, et al. Active Nrf2 signaling flexibly regulates HO-1 and NQO-1 in hypoxic Gansu Zokor (Eospalax cansus)[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol, 2023, 264: 110811. doi:10.1016/j.cbpb.2022.110811 |
| [26] | Zhao YF, Fan XT, Wang QM, et al. ROS promote hyper-methylation of NDRG2 promoters in a DNMTS-dependent manner: Contributes to the progression of renal fibrosis[J]. Redox Biol, 2023, 62: 102674. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2023.102674 |
| [27] | Xiang Q, Cheng ZR, Wang JT, et al. Allicin attenuated advanced oxidation protein product-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial apoptosis in human nucleus pulposus cells[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2020, 2020: 6685043. doi:10.1155/2020/6685043 |
| [28] | Zuo J, Chaykovska L, Chu C, et al. Head-to-head comparison of oxidative stress biomarkers for all-cause mortality in hemodialysis patients[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2022, 11(10): 1975. doi:10.3390/antiox11101975 |
| [29] | Morris G, Puri BK, Bortolasci CC, et al. The role of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, apolipoprotein A and paraoxonase-1 in the pathophysiology of neuroprogressive disorders[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2021, 125: 244-63. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.02.037 |
| [1] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | 王立明, 陈宏睿, 杜燕, 赵鹏, 王玉洁, 田燕歌, 刘新光, 李建生. 益气滋肾方通过抑制PI3K/Akt/NF-κB通路改善小鼠慢性阻塞性肺疾病的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [3] | 朱胤福, 李怡燃, 王奕, 黄颖而, 龚昆翔, 郝文波, 孙玲玲. 桂枝茯苓丸活性成分常春藤皂苷元通过抑制JAK2/STAT3通路抑制宫颈癌细胞的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [4] | 何丽君, 陈晓菲, 闫陈昕, 师林. 扶正化积汤治疗非小细胞肺癌的分子机制:基于网络药理学及体外实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [5] | 李国永, 黎仁玲, 刘艺婷, 柯宏霞, 李菁, 王新华. 牛蒡子治疗小鼠病毒性肺炎后肺纤维化的机制:基于代谢组学、网络药理学和实验验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [6] | 管丽萍, 颜燕, 卢心怡, 李智峰, 高晖, 曹东, 侯晨曦, 曾靖宇, 李欣怡, 赵洋, 王俊杰, 方会龙. 复方积雪草减轻小鼠日本血吸虫引起的肝纤维化:通过调控TLR4/MyD88通路抑制炎症-纤维化级联反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [7] | 唐培培, 谈勇, 殷燕云, 聂晓伟, 黄菁宇, 左文婷, 李玉玲. 调周滋阴方治疗早发性卵巢功能不全的疗效、安全性及作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [8] | 梁晓涛, 熊一凡, 刘雪琪, 梁小珊, 朱晓煜, 谢炜. 活血疏风颗粒通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB通路改善慢性偏头痛小鼠的中枢敏化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| [9] | 冉念东, 刘杰, 徐剑, 张永萍, 郭江涛. 黑骨藤正丁醇萃取成分治疗大鼠阿尔茨海默病的药效学及作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 785-798. |
| [10] | 徐皓男, 张放, 黄钰莹, 姚其盛, 管悦琴, 陈浩. 百蕊草通过调节肠道菌群和调控EGFR/PI3K/Akt信号通路改善小鼠抗生素相关性腹泻[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [11] | 高俊杰, 叶开, 吴竞. 槲皮素通过调控TP53基因抑制肾透明细胞癌的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [12] | 刘莹, 李柏睿, 李永财, 常禄博, 王娇, 杨琳, 颜永刚, 屈凯, 刘继平, 张岗, 沈霞. 加味逍遥丸通过神经递质调节、抗炎抗氧化及肠道菌群调控改善大鼠的抑郁样行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 347-358. |
| [13] | 褚乔, 王小娜, 续佳颖, 彭荟林, 赵裕琳, 张静, 陆国玉, 王恺. 白头翁皂苷D通过多靶点和多途径抑制三阴性乳腺癌侵袭转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [14] | 龙秀鹏, 陶顺, 阳绅, 李素云, 饶利兵, 李莉, 张哲. 槲皮素通过抑制MAPK信号通路改善心力衰竭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 187-196. |
| [15] | 徐朦, 陈丽娜, 吴金玉, 刘丽丽, 施美, 周灏, 张国梁. “白花蛇舌草-半枝莲”治疗原发性肝癌的机制研究:基于网络药理学、分子对接及体外实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 80-89. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
