南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1143-1152.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.04
收稿日期:2024-12-20
出版日期:2025-06-20
发布日期:2025-06-27
通讯作者:
师林
E-mail:eillyjun@163.com;shilin293@qq.com
作者简介:何丽君,在读硕士研究生,主治医师,E-mail: eillyjun@163.com
基金资助:
Lijun HE1( ), Xiaofei CHEN1, Chenxin YAN1, Lin SHI1,2(
), Xiaofei CHEN1, Chenxin YAN1, Lin SHI1,2( )
)
Received:2024-12-20
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-06-27
Contact:
Lin SHI
E-mail:eillyjun@163.com;shilin293@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 通过网络药理学、分子对接和体外实验探究扶正化积汤治疗非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)的作用机制。 方法 通过TCMSP、SwissTargetPrediction数据库筛选扶正化积汤活性成分及其作用靶点。通过在GeneCards、PharmGKB数据库获取NSCLC相关靶点,与扶正化积汤活性成分靶点取交集。利用STRING数据库建立蛋白相互作用(PPI)网络,使用Cytoscape3.8.2软件CytoNCA插件筛选PPI网络核心靶点,利用DAVID6.8数据库进行GO和KEGG通路富集分析。使用A549细胞开展体外实验进行靶点验证,CCK-8法检测扶正化积汤含药血清对A549细胞增殖的影响。Annexin V-FITC/PI染色检测含药血清对A549细胞凋亡的影响。Western blotting检测含药血清对关键通路中相关蛋白表达的影响。 结果 扶正化积汤活性成分共140个,药物和疾病交集靶点共707个,PPI网络核心靶点有TP53, AKT1,HIF1A, GAPDH,ALB,EGFR,CTNNB1, TNF等,GO分析显示主要生物学过程为转移酶、激酶、受体、水解酶、丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶、氧化还原酶等,KEGG通路富集显示主要信号通路为PI3K-AKT信号通路、Ras信号通路、钙离子信号通路、MAPK信号通路等。分子对接结果显示,药物有效成分与TP53、AKT1、HIF1A均有效对接。体外实验结果: CCK-8实验确定以2.5%、5%、10%为扶正化积汤含药血清的低、中、高浓度(P<0.05,P<0.01,P<0.0001)。细胞凋亡实验显示扶正化积汤含药血清不同程度促进A549细胞凋亡(P<0.01,P<0.001)。Western blotting结果显示,扶正化积汤下调A549细胞中HIF1A、p-AKT 308和TP53蛋白的表达水平(P<0.05,P<0.01,P<0.001,P<0.0001)。 结论 扶正化积汤可能通过调控HIF1A,p-AKT 308,TP53蛋白的表达,抑制A549细胞增殖,发挥治疗NSCLC的潜在作用。
何丽君, 陈晓菲, 闫陈昕, 师林. 扶正化积汤治疗非小细胞肺癌的分子机制:基于网络药理学及体外实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152.
Lijun HE, Xiaofei CHEN, Chenxin YAN, Lin SHI. Inhibitory effect of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction against non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and the possible molecular mechanism[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152.
| Code | ID | Name | Relevance | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DZ8 | MOL006709 | 8-Hydroxypinoresinol | 149 | Eucommia |
| FBX3 | MOL002714 | baicalein | 83 | Pinellia |
| HQ2 | MOL000239 | Jaranol | 81 | Astragalus |
| DS10 | MOL000006 | luteolin | 80 | Codonopsis |
| DZ25 | MOL000098 | quercetin | 80 | Eucommia |
| DZ4 | MOL000422 | kaempferol | 80 | Eucommia |
| HQ15 | MOL000422 | kaempferol | 80 | Astragalus |
| HQ20 | MOL000098 | quercetin | 80 | Astragalus |
| HQ5 | MOL000354 | isorhamnetin | 80 | Astragalus |
| HQ8 | MOL000378 | 7-O-methylisomucronulatol | 80 | Astragalus |
表1 扶正化积汤治疗非小细胞肺癌的关键药物成分
Tab.1 Key active components of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
| Code | ID | Name | Relevance | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DZ8 | MOL006709 | 8-Hydroxypinoresinol | 149 | Eucommia |
| FBX3 | MOL002714 | baicalein | 83 | Pinellia |
| HQ2 | MOL000239 | Jaranol | 81 | Astragalus |
| DS10 | MOL000006 | luteolin | 80 | Codonopsis |
| DZ25 | MOL000098 | quercetin | 80 | Eucommia |
| DZ4 | MOL000422 | kaempferol | 80 | Eucommia |
| HQ15 | MOL000422 | kaempferol | 80 | Astragalus |
| HQ20 | MOL000098 | quercetin | 80 | Astragalus |
| HQ5 | MOL000354 | isorhamnetin | 80 | Astragalus |
| HQ8 | MOL000378 | 7-O-methylisomucronulatol | 80 | Astragalus |
| Target | Sample | Estimated ΔG (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| TP53 | DZ8 | -9.40 |
| TP53 | FBX3 | -9.90 |
| TP53 | HQ2 | -9.50 |
| TP53 | DS10 | -10.40 |
| TP53 | DZ25 | -10.20 |
| TP53 | DZ4 | -9.80 |
| TP53 | HQ5 | -9.60 |
| TP53 | HQ8 | -8.70 |
| AKT1 | DZ8 | -10.80 |
| AKT1 | FBX3 | -10.20 |
| AKT1 | HQ2 | -9.70 |
| AKT1 | DS10 | -11.10 |
| AKT1 | DZ25 | -9.70 |
| AKT1 | DZ4 | -9.70 |
| AKT1 | HQ5 | -9.50 |
| AKT1 | HQ8 | -9.40 |
| HIF1A | HQ8 | -4.80 |
| HIF1A | DZ8 | -5.50 |
| HIF1A | HQ2 | -4.90 |
| HIF1A | HQ5 | -5.00 |
| HIF1A | FBX3 | -5.40 |
| HIF1A | DZ4 | -4.90 |
| HIF1A | DZ25 | -5.10 |
| HIF1A | DS10 | -6.00 |
表2 扶正化积汤治疗NSCLC核心成分与核心靶点分子TP53、AKT1、HIF1A对接的结合能
Tab.2 Binding energies of the core active components of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction for NSCLC treatment for docking with the core target molecules TP53, AKT1, and HIF1A
| Target | Sample | Estimated ΔG (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| TP53 | DZ8 | -9.40 |
| TP53 | FBX3 | -9.90 |
| TP53 | HQ2 | -9.50 |
| TP53 | DS10 | -10.40 |
| TP53 | DZ25 | -10.20 |
| TP53 | DZ4 | -9.80 |
| TP53 | HQ5 | -9.60 |
| TP53 | HQ8 | -8.70 |
| AKT1 | DZ8 | -10.80 |
| AKT1 | FBX3 | -10.20 |
| AKT1 | HQ2 | -9.70 |
| AKT1 | DS10 | -11.10 |
| AKT1 | DZ25 | -9.70 |
| AKT1 | DZ4 | -9.70 |
| AKT1 | HQ5 | -9.50 |
| AKT1 | HQ8 | -9.40 |
| HIF1A | HQ8 | -4.80 |
| HIF1A | DZ8 | -5.50 |
| HIF1A | HQ2 | -4.90 |
| HIF1A | HQ5 | -5.00 |
| HIF1A | FBX3 | -5.40 |
| HIF1A | DZ4 | -4.90 |
| HIF1A | DZ25 | -5.10 |
| HIF1A | DS10 | -6.00 |
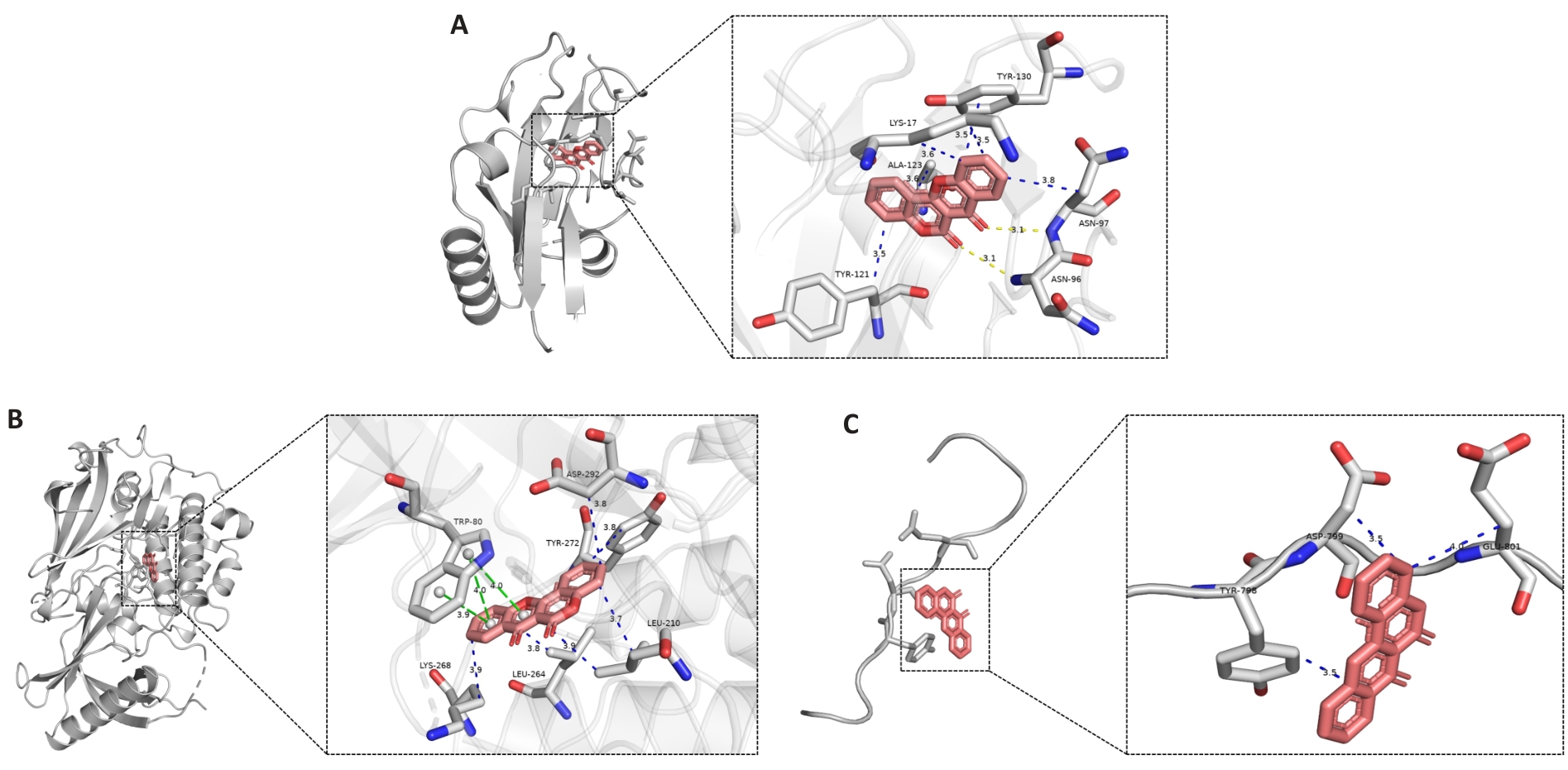
图6 分子对接结果可视化
Fig.6 Visualization of the results of molecular docking analysis. A: Docked molecular conformation of TP53 with DS10; B: Molecular conformation of AKT1 docked with DS10; C: Molecular conformation of HIF1A docked with DS10.
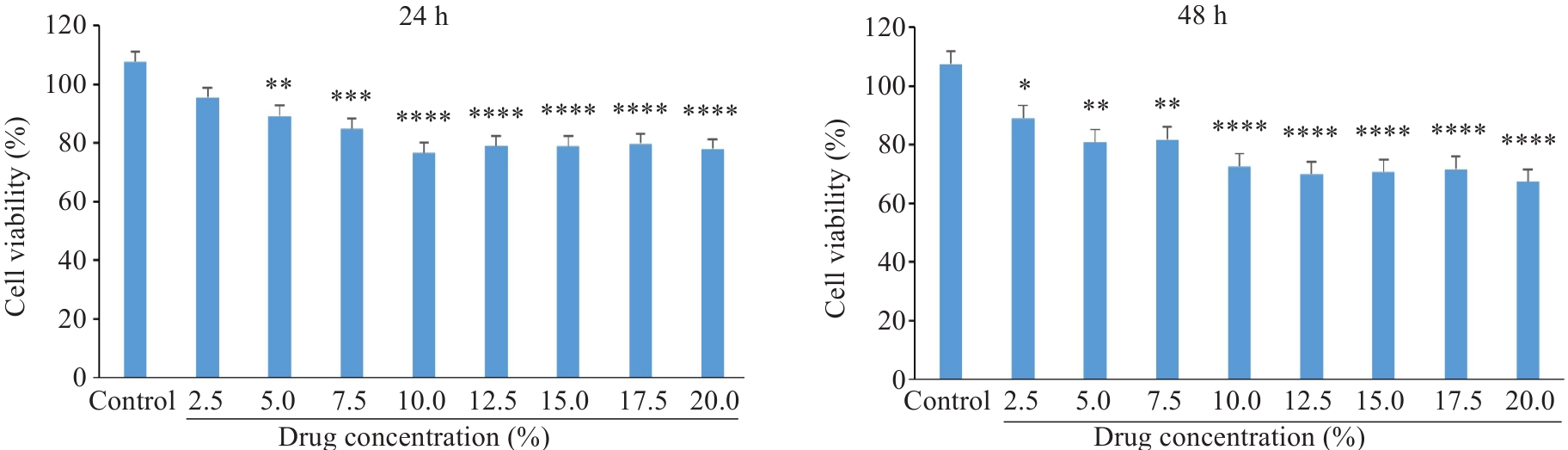
图7 扶正化积汤含药血清对A549细胞增殖能力的影响
Fig.7 Changes in proliferation of A549 cells treated with Fuzheng Huaji Decoction-medicated serum detected by CCK-8 assay. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs control group.
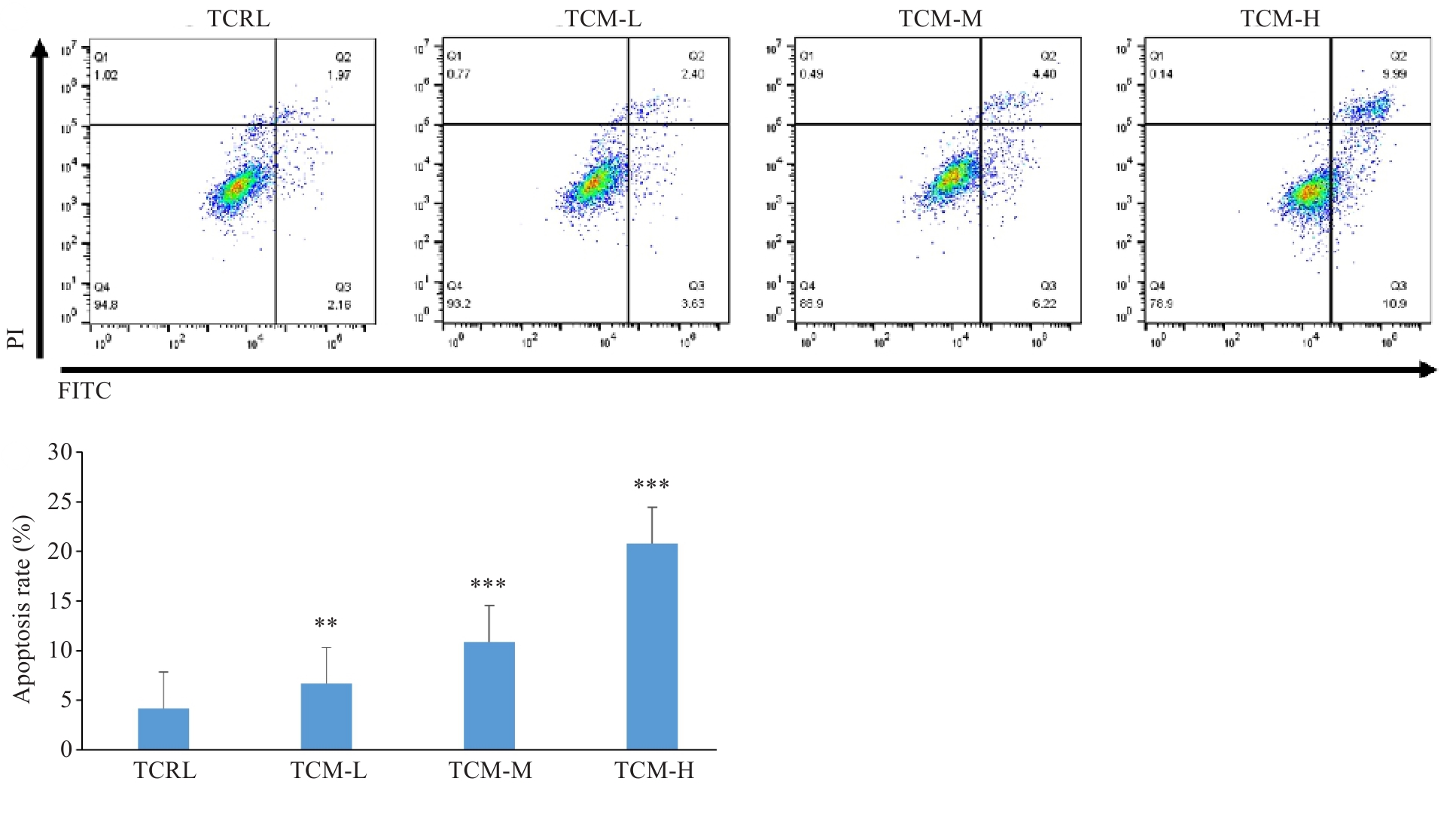
图8 扶正化积汤含药血清对A549细胞的细胞凋亡检测
Fig.8 Apoptosis of A549 cells treated with Fuzheng Huaji Decoction-medicated serum detected by annexin V-FITC/PI staining. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs TCRL.
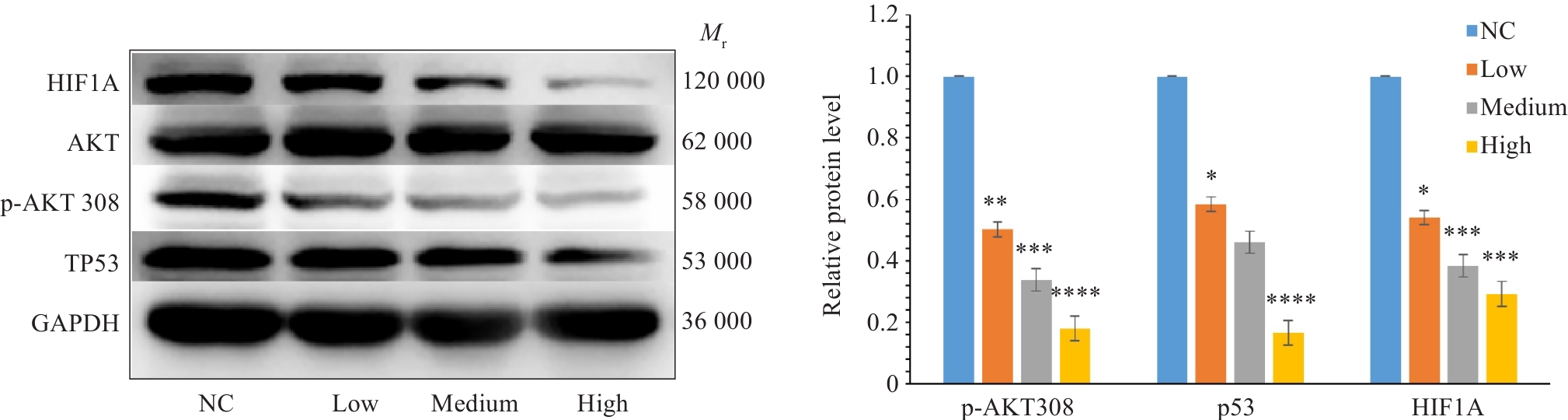
图9 扶正化积汤含药血清对关键通路相关蛋白表达的影响
Fig.9 Effect of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction-medicated serum on expressions of HIF1A, p-AKT 308 and TP53 proteins in A549 cells detected by Western blotting proteins in A549 cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs NCgroup.
| 1 | 郭 祯, 王 伟, 王 红, 等. 2022年全球肺癌终生罹患风险和死亡风险分析[J]. 中国肿瘤, 2025, 34(2): 81-8. doi:10.11735/j.issn.1004-0242.2025.02.A001 |
| 2 | Chen P, Liu Y, Wen Y, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer in China[J]. Cancer Commun: Lond, 2022, 42(10): 937-70. doi:10.1002/cac2.12359 |
| 3 | Gao S, Li N, Wang S, et al. Lung cancer in people's republic of China[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2020, 15(10): 1567-76. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2020.04.028 |
| 4 | Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. The biology and mana-gement of non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Nature, 2018, 553(7689): 446-54. doi:10.1038/nature25183 |
| 5 | Hendriks LEL, Remon J, Faivre-Finn C, et al. Non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2024, 10(1): 71. doi:10.1038/s41572-024-00551-9 |
| 6 | Miller KD, Nogueira L, Devasia T, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2022[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2022, 72(5): 409-36. doi:10.3322/caac.21731 |
| 7 | 贺佐梅, 徐 云, 邓天好, 等. 7435份非小细胞肺癌病案中医用药规律分析[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报, 2022, 42(7): 1157-63. |
| 8 | 骆文斌, 吴承玉. 肺癌病因病机研究[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2009, 11(3): 16-7. |
| 9 | 张鹏飞, 张惠娟, 梁建庆, 等. 基于“扶正祛邪”理论探讨中医药治疗非小细胞肺癌的规律及机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2025, 42(8): 1-17. |
| 10 | 王思云, 柯 斌, 陈晓菲, 等. 加味龟鹿二仙胶汤通过抑制MAPKAP1/mTORC2/AKT通路抗NSCLC血管拟态形成[J/OL]. 中药材, 2024, (11): 2835-42. |
| 11 | 吴 静, 彭 丞, 胡学谦, 等. 非小细胞肺癌的中西医治疗研究进展[J]. 中国现代医生, 2022, 60(26): 123-7. |
| 12 | 赵亚东, 王福庆, 高亚军. 加味玉屏风散对中晚期肺癌化疗后肺脾气虚型患者生活质量及免疫功能的影响[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2024, 33(1): 83-6. |
| 13 | 贺佳文, 韩 冰, 卢佳萱, 等. 从肿瘤微环境的重塑探索扶正解毒法治疗肿瘤的机制[J]. 环球中医药, 2024, 17(2): 273-6. |
| 14 | 赵延华, 周仲瑛, 吴勉华, 等. 基于癌毒理论探讨“抗癌解毒药”[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2022, 37(12): 7146-9. |
| 15 | 杨 柱, 唐东昕, 郭 斌, 等. 刘尚义治疗肿瘤用药经验数据挖掘分析[J]. 中医杂志, 2016, 57(19): 1641-5. doi:10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2016.19.006 |
| 16 | 黄雯琪, 杨 柱, 唐东昕, 等. 基于数据挖掘分析刘尚义教授治疗肺癌的临床用药特点[J]. 长春中医药大学学报, 2017, 33(3): 418-21. doi:10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2017.03.024 |
| 17 | 叶懿祥, 陈冬梅, 贾立群, 等. 黄芪抗肿瘤药理作用机制与临床应用研究进展[J]. 世界中医药, 2023, 18(11): 1615-20. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2023.11.022 |
| 18 | 杨振耀, 张晓青, 王成志, 等. 黄芪甲苷抗肿瘤机制及其在肺癌中的研究进展[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2024, 42(8): 1-18. |
| 19 | 张 颖, 王 淳, 于 丹, 等. 黄芪多糖抑制肺腺癌A549/DDP细胞移植瘤裸鼠EMT改善顺铂耐药的机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28(6): 79-85. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20220527 |
| 20 | 屈子怡. 黄芪多糖联合化疗对晚期NSCLC的临床疗效及相关机制研究[D]. 天津: 天津中医药大学, 2022. |
| 21 | 武洪杨, 范向荣. 冬凌草甲素抗肿瘤作用机制研究进展[J]. 国际中医中药杂志, 2022, 44(5): 599-601. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn115398-20210511-00102 |
| 22 | 夏子昊, 赵光利, 肖翔文, 等.中药蜈蚣的研究进展[J].中药与临床,2023,14(01):103-8. |
| 23 | 张珂洋, 张永清, 杨春淼, 等. 全蝎的炮制历史沿革、化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2024, 49(4): 868-83. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230814.202 |
| 24 | Prejac J, Dedić Plavetić N, Gotovac Jerčić K, et al. A first report of a rare TP53 variant associated with Li-Fraumeni syndrome manifesting as invasive breast cancer and malignant solitary fibrous tumor[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2021, 19(1): 254. doi:10.1186/s12957-021-02370-8 |
| 25 | 邓世超. 不同信号通路在非小细胞肺癌中的预测价值研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2022. |
| 26 | La Fleur L, Falk-Sörqvist E, Smeds P, et al. Mutation patterns in a population-based non-small cell lung cancer cohort and prognostic impact of concomitant mutations in KRAS and TP53 or STK11[J]. Lung Cancer, 2019, 130: 50-8. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.01.003 |
| 27 | Lawrence MS, Stojanov P, Mermel CH, et al. Discovery and saturation analysis of cancer genes across 21 tumour types[J]. Nature, 2014, 505(7484): 495-501. doi:10.1038/nature12912 |
| 28 | Rao G, Pierobon M, Kim IK, et al. Inhibition of AKT1 signaling promotes invasion and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer cells with K-RAS or EGFR mutations[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 7066. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-06128-9 |
| 29 | Lin H, Ai D, Liu Q, et al. Modified podophyllotoxin phenoxyacetamide phenylacetate derivatives: tubulin/AKT1 dual-targeting and potential anticancer agents for human NSCLC[J]. J Nat Prod, 2023, 86(7): 1844-54. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.3c00384 |
| 30 | Zhang L, Gong Y, Zhang L, et al. Gou Qi Zi inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis through the PI3K/AKT1 signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 1034750. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.1034750 |
| 31 | Zhang J, Wu Y, Lin YH, et al. Prognostic value of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and prolyl 4-hydroxylase beta polypeptide overex-pression in gastric cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2018, 24(22): 2381-91. doi:10.3748/wjg.v24.i22.2381 |
| 32 | Lee SH, Golinska M, Griffiths JR. HIF-1-independent mechanisms regulating metabolic adaptation in hypoxic cancer cells[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(9): 2371. doi:10.3390/cells10092371 |
| 33 | 刘燕翔, 张 锦, 郑玉双, 等. PGC-1α、HIF1A在胃癌中的表达与临床病理特征及预后的关系[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2024, 33(6): 709-13. |
| 34 | 李海燕, 王锦伟, 金英英, 等. 缺氧对肺癌细胞中lncRNA H19的表达及耐药机制的研究[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2023, 33(4): 388-92. |
| [1] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | 王立明, 陈宏睿, 杜燕, 赵鹏, 王玉洁, 田燕歌, 刘新光, 李建生. 益气滋肾方通过抑制PI3K/Akt/NF-κB通路改善小鼠慢性阻塞性肺疾病的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [3] | 朱胤福, 李怡燃, 王奕, 黄颖而, 龚昆翔, 郝文波, 孙玲玲. 桂枝茯苓丸活性成分常春藤皂苷元通过抑制JAK2/STAT3通路抑制宫颈癌细胞的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [4] | 李国永, 黎仁玲, 刘艺婷, 柯宏霞, 李菁, 王新华. 牛蒡子治疗小鼠病毒性肺炎后肺纤维化的机制:基于代谢组学、网络药理学和实验验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [5] | 管丽萍, 颜燕, 卢心怡, 李智峰, 高晖, 曹东, 侯晨曦, 曾靖宇, 李欣怡, 赵洋, 王俊杰, 方会龙. 复方积雪草减轻小鼠日本血吸虫引起的肝纤维化:通过调控TLR4/MyD88通路抑制炎症-纤维化级联反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [6] | 李丹丹, 楚佳鑫, 闫妍, 徐文隽, 朱行春, 孙韵, 丁浩峰, 任丽, 朱博. 姜黄素通过下调HIF-1α通路抑制非小细胞肺癌脂质代谢[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 1039-1046. |
| [7] | 唐培培, 谈勇, 殷燕云, 聂晓伟, 黄菁宇, 左文婷, 李玉玲. 调周滋阴方治疗早发性卵巢功能不全的疗效、安全性及作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [8] | 梁晓涛, 熊一凡, 刘雪琪, 梁小珊, 朱晓煜, 谢炜. 活血疏风颗粒通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB通路改善慢性偏头痛小鼠的中枢敏化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| [9] | 冉念东, 刘杰, 徐剑, 张永萍, 郭江涛. 黑骨藤正丁醇萃取成分治疗大鼠阿尔茨海默病的药效学及作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 785-798. |
| [10] | 徐皓男, 张放, 黄钰莹, 姚其盛, 管悦琴, 陈浩. 百蕊草通过调节肠道菌群和调控EGFR/PI3K/Akt信号通路改善小鼠抗生素相关性腹泻[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [11] | 高俊杰, 叶开, 吴竞. 槲皮素通过调控TP53基因抑制肾透明细胞癌的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [12] | 刘莹, 李柏睿, 李永财, 常禄博, 王娇, 杨琳, 颜永刚, 屈凯, 刘继平, 张岗, 沈霞. 加味逍遥丸通过神经递质调节、抗炎抗氧化及肠道菌群调控改善大鼠的抑郁样行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 347-358. |
| [13] | 褚乔, 王小娜, 续佳颖, 彭荟林, 赵裕琳, 张静, 陆国玉, 王恺. 白头翁皂苷D通过多靶点和多途径抑制三阴性乳腺癌侵袭转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [14] | 龙秀鹏, 陶顺, 阳绅, 李素云, 饶利兵, 李莉, 张哲. 槲皮素通过抑制MAPK信号通路改善心力衰竭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 187-196. |
| [15] | 徐朦, 陈丽娜, 吴金玉, 刘丽丽, 施美, 周灏, 张国梁. “白花蛇舌草-半枝莲”治疗原发性肝癌的机制研究:基于网络药理学、分子对接及体外实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 80-89. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||