Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2561-2572.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.04
Previous Articles Next Articles
Jinzhi XIA1,5( ), Yue CHEN3,5, Lü REN3,5, Jing LI1,2, Xue SONG2,4, Lu TAO2,4, Jianguo HU1,2(
), Yue CHEN3,5, Lü REN3,5, Jing LI1,2, Xue SONG2,4, Lu TAO2,4, Jianguo HU1,2( )
)
Received:2025-05-16
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Jianguo HU
E-mail:Jinzhixia0511@163.com;jghu9200@bbmu.edu.cn
Supported by:Jinzhi XIA, Yue CHEN, Lü REN, Jing LI, Xue SONG, Lu TAO, Jianguo HU. Kahweol improves motor function of mice with spinal cord injury by inhibiting microglial activation via regulating the IκBα/NF-κB pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2561-2572.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.04
| Gene (mice) | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | TGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTAC | GAGTTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCA |
| TNF-α | CAGGCGGTGCCTATGTCTC | CGATCACCCCGAAGTTCAGTAG |
| IL-6 | TCTATACCACTTCACAAGTCGGA | GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT |
| IL-1β | GAAATGCCACCTTTTGACAGTG | TGGATGCTCTCATCAGGACAG- |
Tab.1 Primer sequences (5' to 3') for RT-qPCR
| Gene (mice) | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | TGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTAC | GAGTTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCA |
| TNF-α | CAGGCGGTGCCTATGTCTC | CGATCACCCCGAAGTTCAGTAG |
| IL-6 | TCTATACCACTTCACAAGTCGGA | GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT |
| IL-1β | GAAATGCCACCTTTTGACAGTG | TGGATGCTCTCATCAGGACAG- |
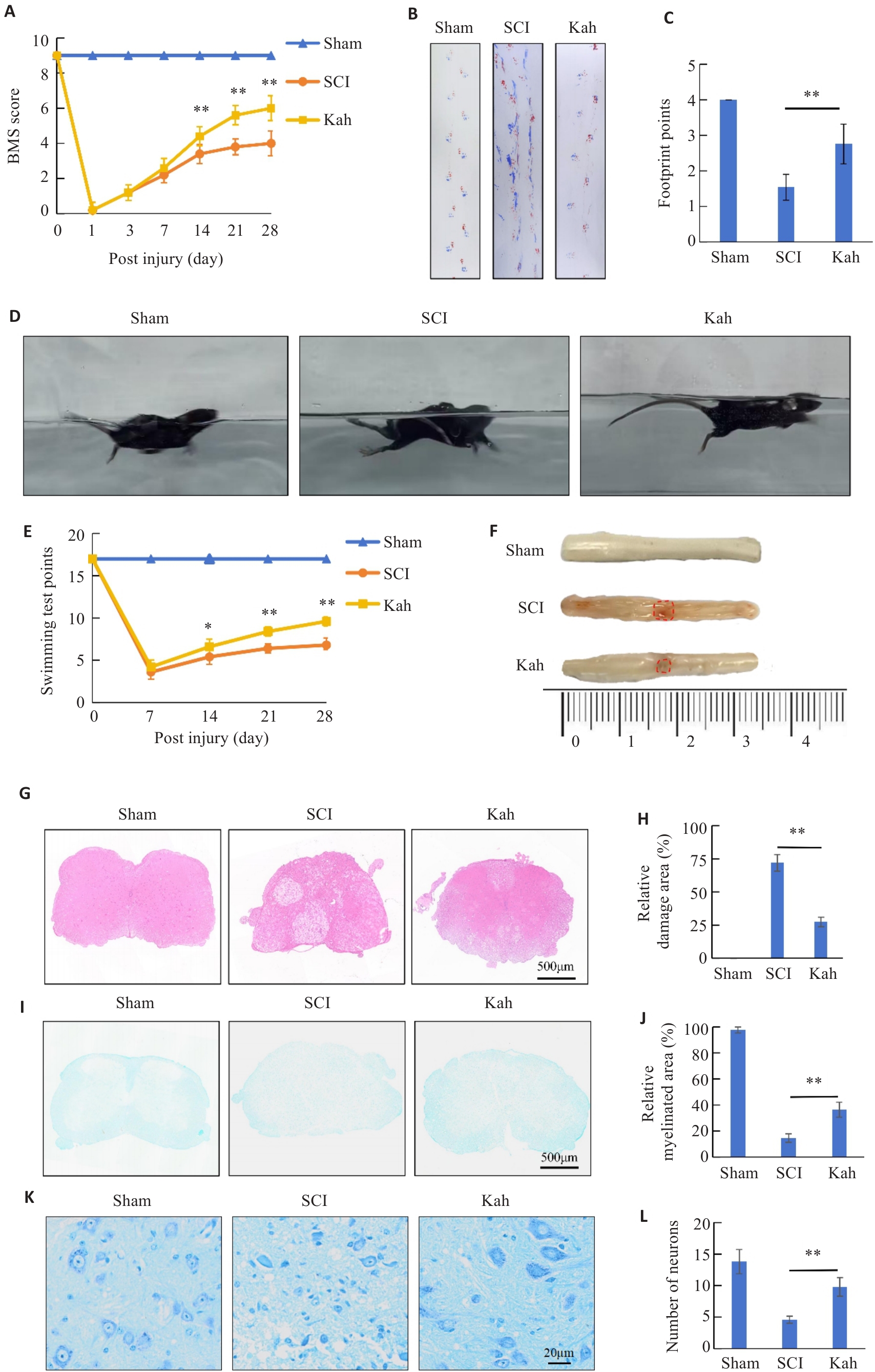
Fig.1 Kahweol (Kah) improves motor function and alleviates spinal cord tissue pathologies of SCI mice. A: BMS Score. B, C: Footprint score. D, E: Swimming experiments. F: Dorsal view of fresh spinal cords on days 7. G: HE staining. H: Quantitative analysis of the lesion areas in the 3 groups. I: LFB staining. J: Quantitative analysis of residual myelination in the 3 groups. K: Nissl staining. L: Quantitative analysis of the number of motor neurons in the 3 groups. n=5 in each group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
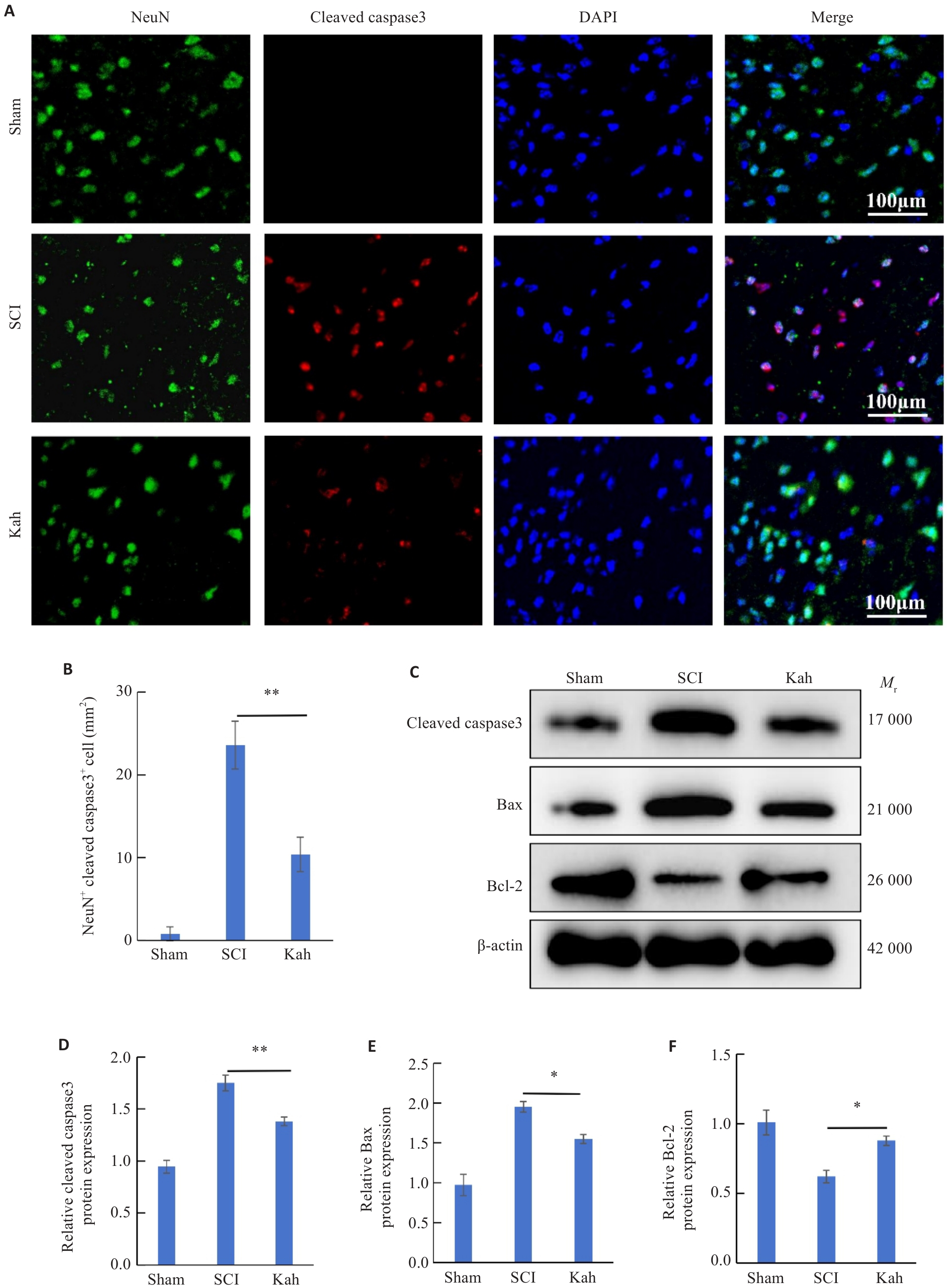
Fig.2 Kah attenuates neuronal apoptosis in the spinal cord of SCI mice. A: Immunofluorescent staining for NeuN and cleaved caspase3. B: Quantification analysis of the number of NeuN+ cleaved caspase3+ cells. C-F: Western blotting and quantitative analysis of protein expression levels. n=3 in each group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
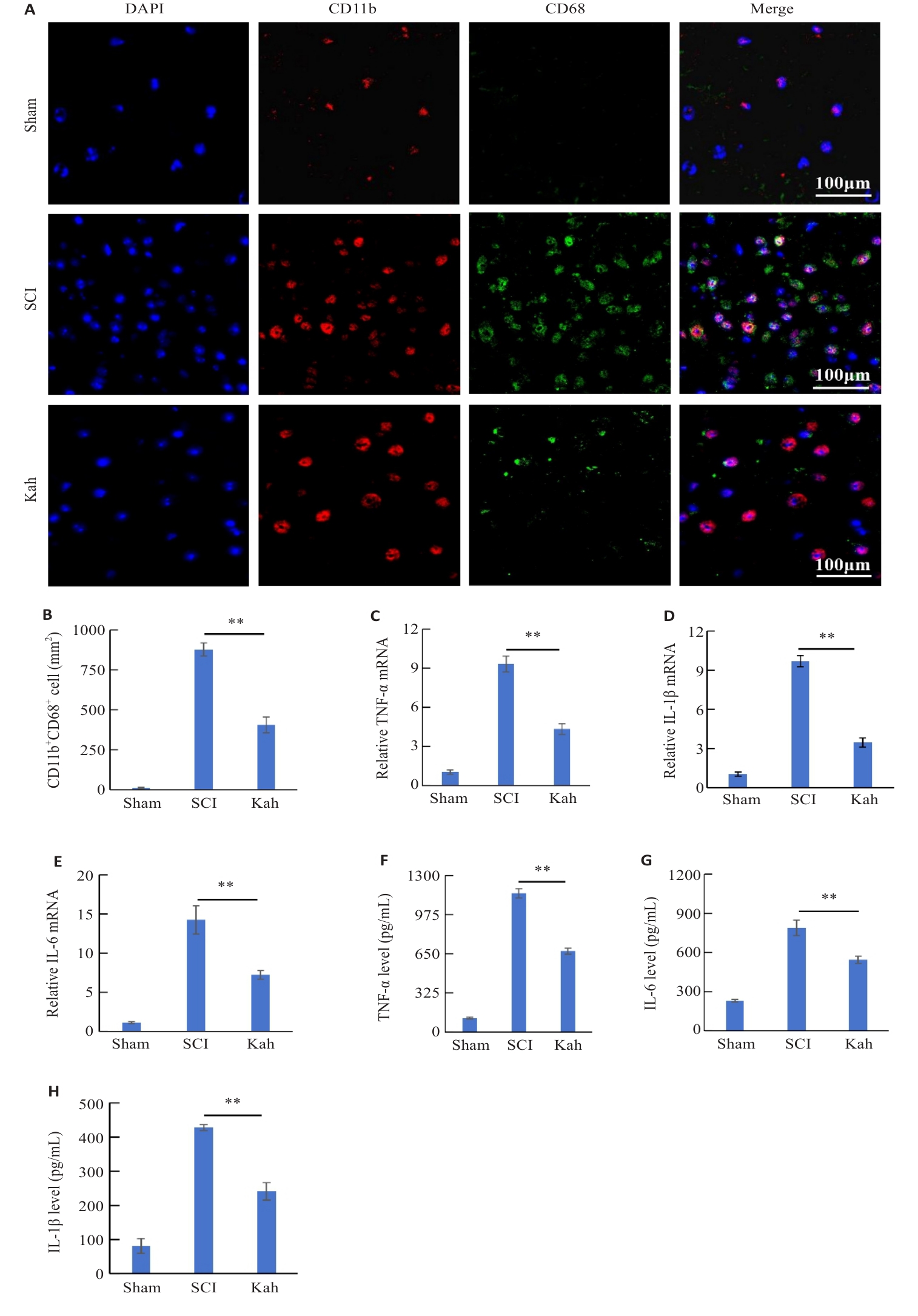
Fig. 3 Kah reduces the expressions of inflammation-related factors and inhibits microglial activation in the spinal cord of SCI mice. A: Immunofluorescent staining for CD11b and CD68. B: Quantification analysis of the number of the CD11b+ CD68+ cells. C-E: Effect of Kah on mRNA levels of TNF‑α, IL-6 and IL-1β. F-H: Quantification of protein levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β. n=3 in each group. **P<0.01.
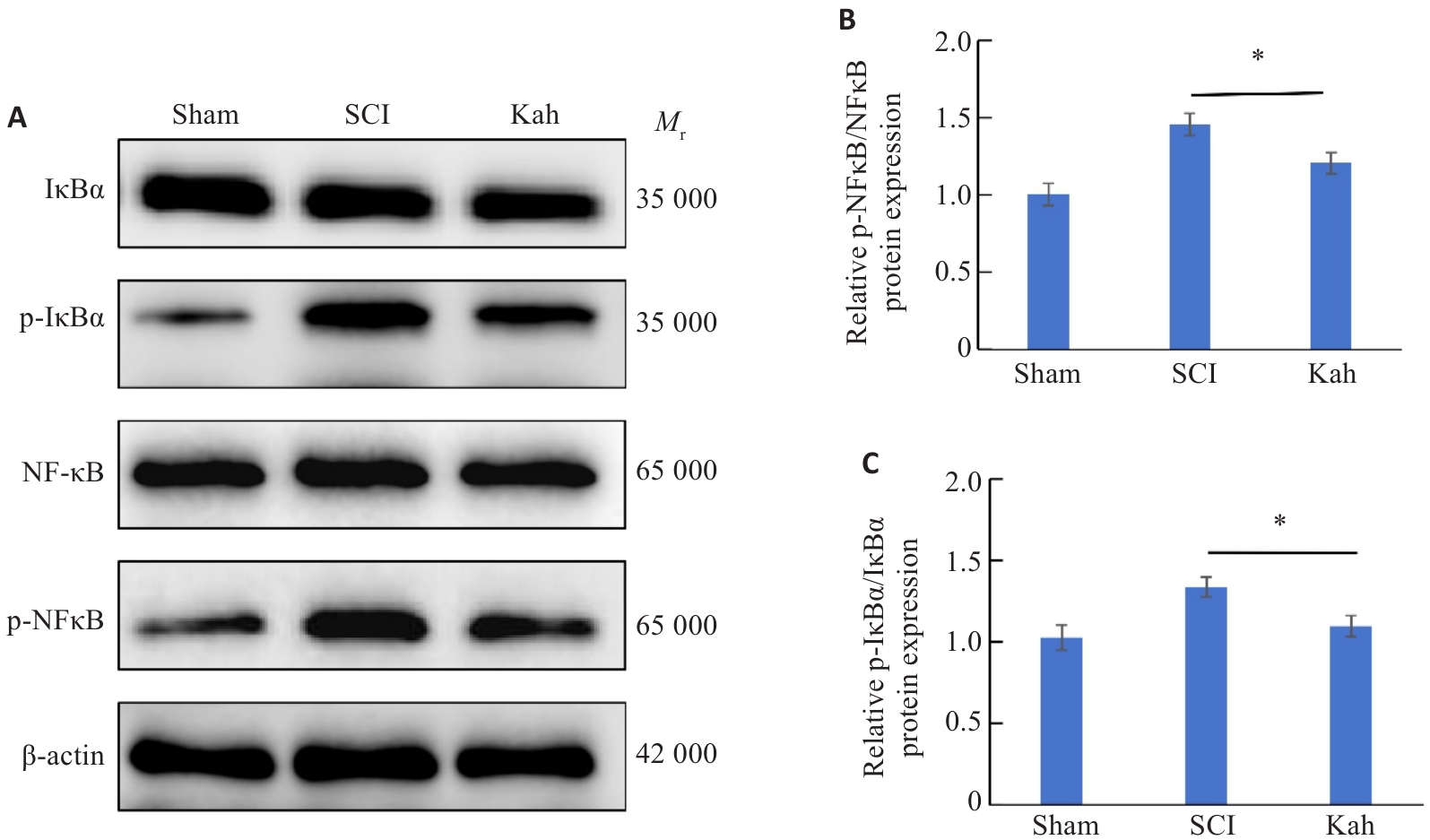
Fig. 4 The protective effect of Kah in SCI mice may be related to the NF-κB signaling pathway. A-C: Proteins expressions of NF-κB, p-NF-κB, IκBα and p-IκBα in the spinal cord of SCI mice detected by Western blotting and quantitative analysis of protein levels. n=3 in each group. *P<0.05.
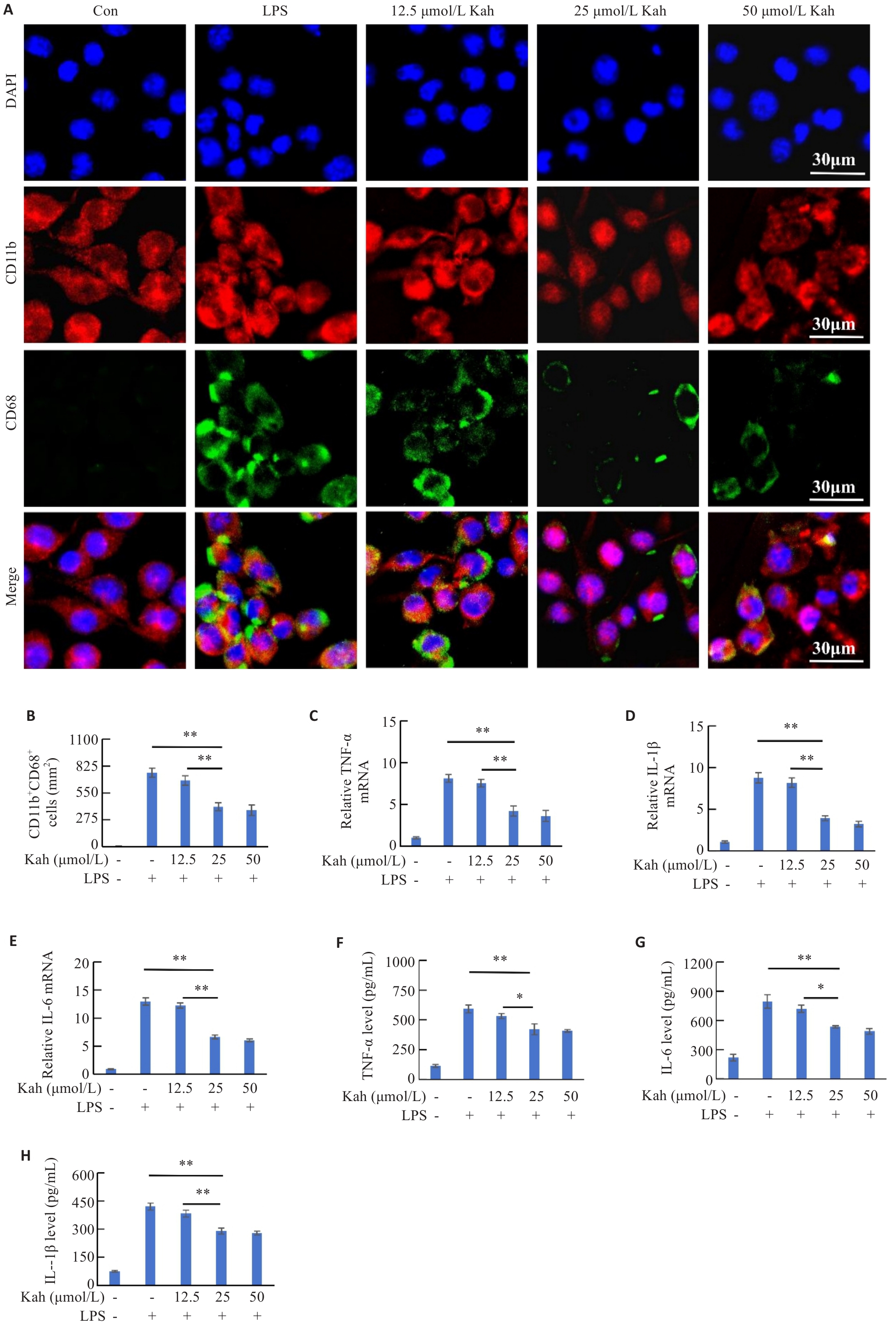
Fig.5 Kah inhibits LPS-induced microglial activation and expressions of inflammatory cytokines. A: Immunofluorescent staining for CD11b and CD68. B: Quantification analysis of the number of the CD11b+ CD68+ cells. C-E: Effect of Kah on mRNA levels of TNF‑α, IL-6 and IL-1β. F-H: Quantification of protein levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β. n=3 in each group. *P<0.05, **P<0.001.
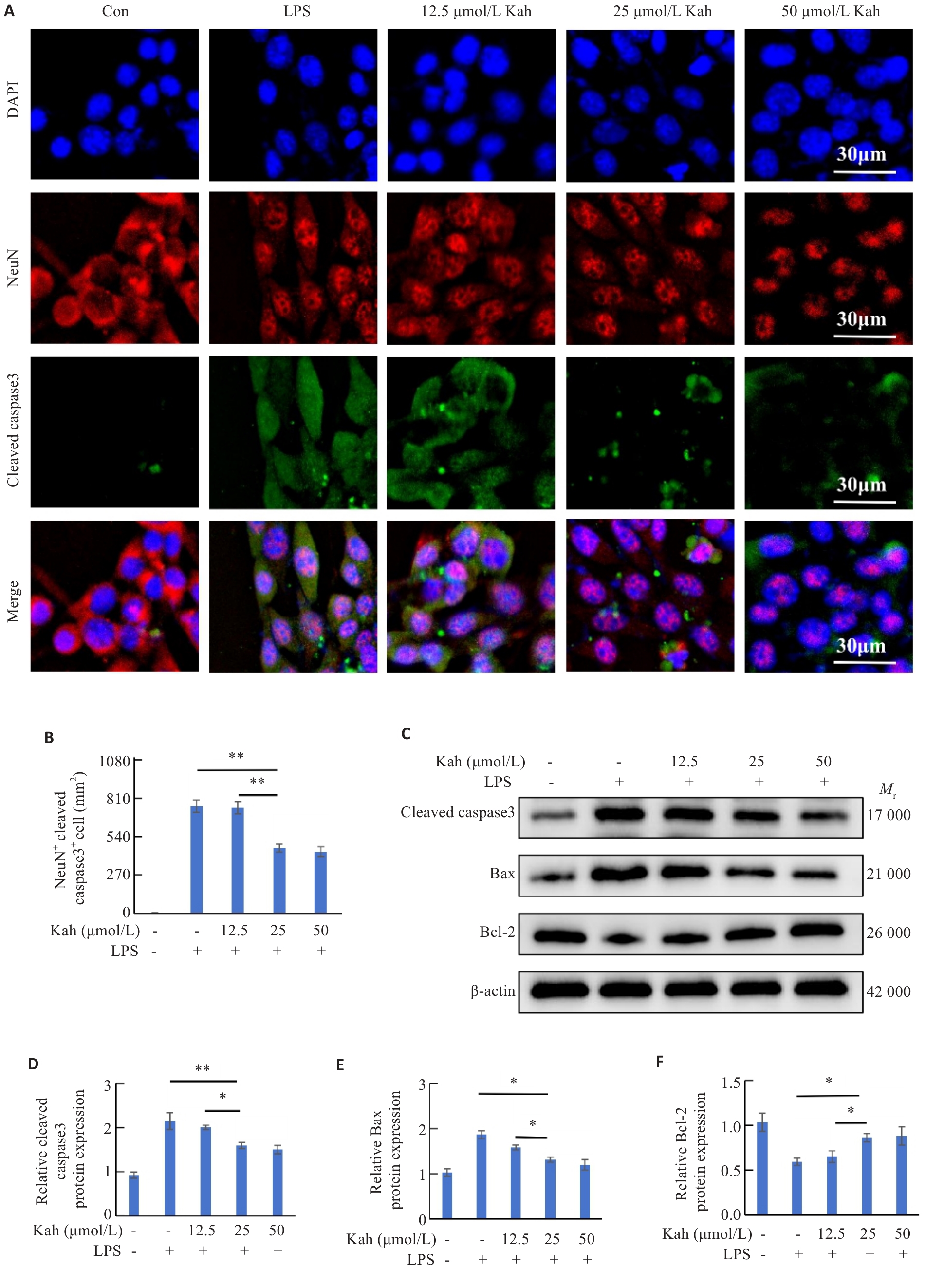
Fig.6 Kah attenuates neuronal apoptosis caused by microglial activation. A: Immunofluorescent staining for NeuN and cleaved caspase-3. B: Quantification analysis of the number of the NeuN+/cleaved caspase-3+ cells. C-F: Western blotting analysis and quantitative analysis of protein expression levels. n=3 in each group. *P<0.05, **P<0.001.
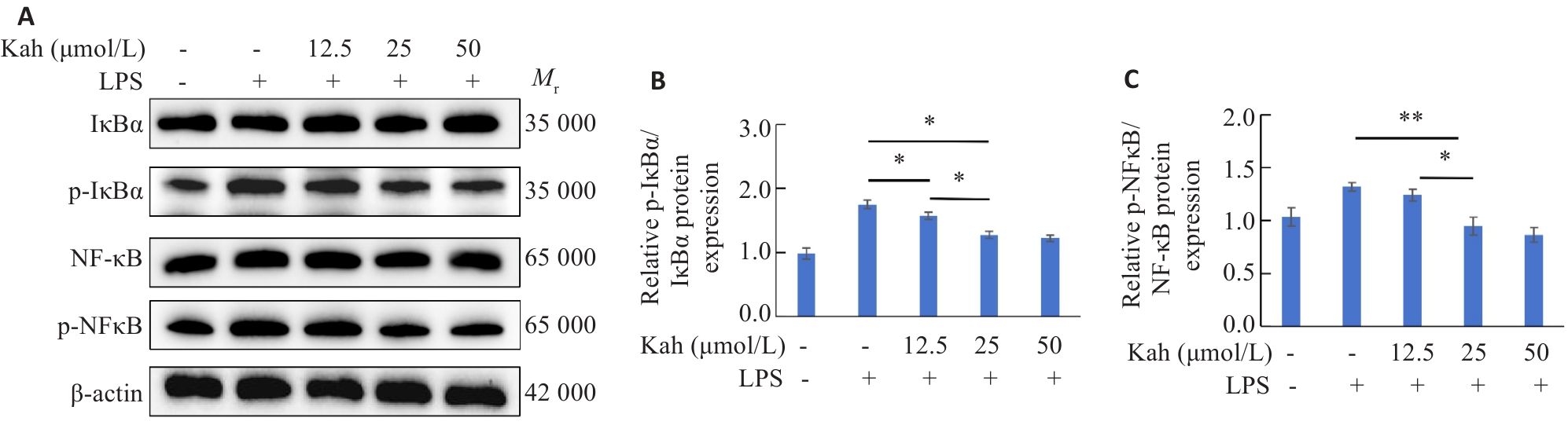
Fig.7 Kah inhibits the NF-kB signaling pathway. A-C: Proteins expressions of NF-κB, p-NF-κB, IκBα and p-IκBα in BV2 cells detected by Western blotting and quantitative analysis of protein levels. n=3 in each group. *P<0.05, **P<0.001.
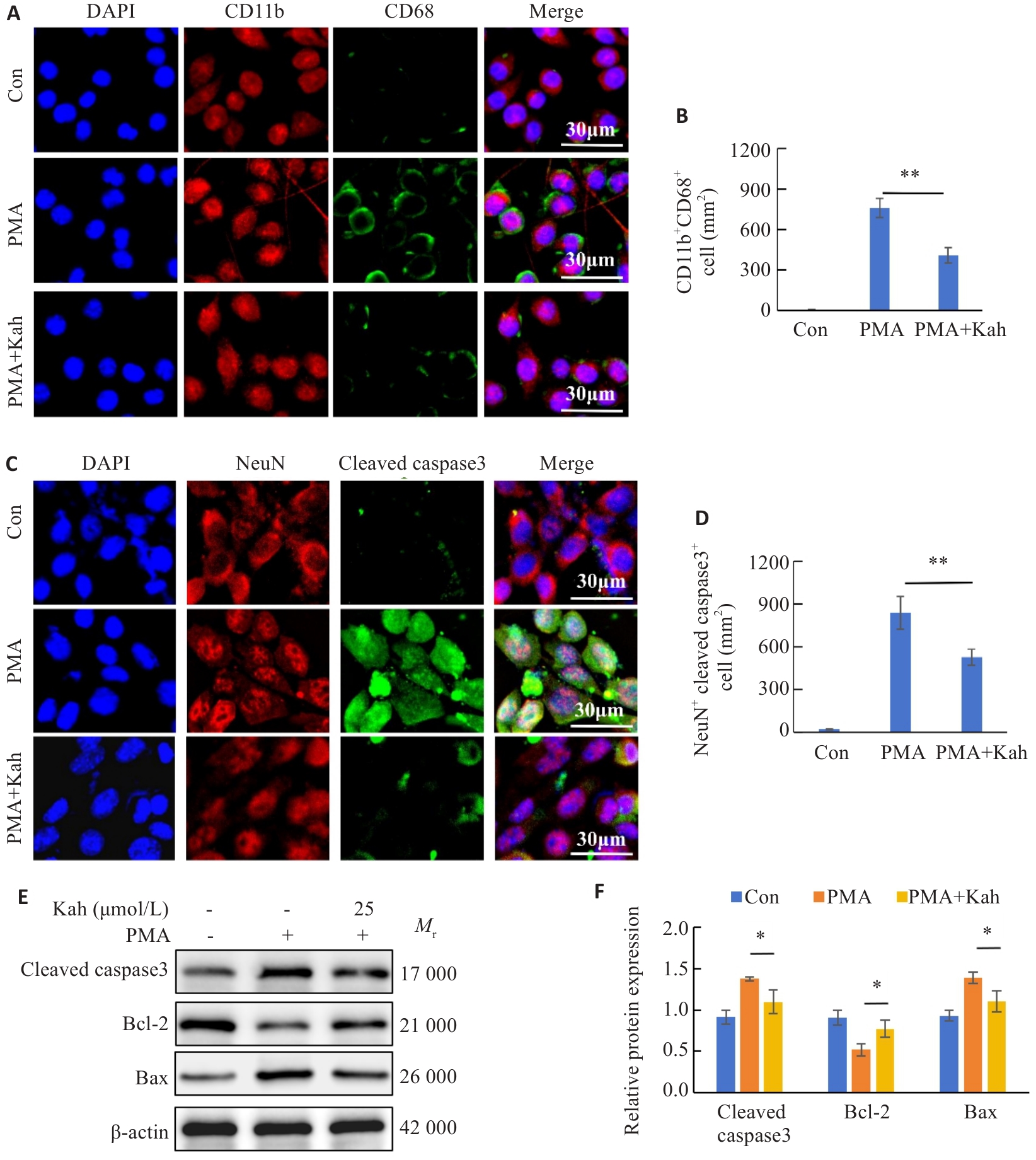
Fig.8 Kah attenuates microglial activation and neuronal apoptosis by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. A: Immunofluorescent staining for CD11b and CD68. B: Quantification analysis of the number of CD11b+CD68+ cells. C: Immunofluorescent staining for NeuN and cleaved caspase3. D: Quantification analysis of the number of the NeuN+ cleaved caspase3+ cells. E, F: Western blotting and quantitative analysis of protein expression levels. n=3 in each group. *P<0.05, **P<0.001.
| [1] | Martynyuk T, Ricard J, Bracchi-Ricard V, et al. Mitigating sTNF/TNFR1 activation on VGluT2+spinal cord interneurons improves immune function after mid-thoracic spinal cord injury[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2025, 123: 633-43. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2024.10.021 |
| [2] | Anjum A, Yazid MD, Fauzi Daud M, et al. Spinal cord injury: pathophysiology, multimolecular interactions, and underlying recovery mechanisms[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(20): E7533. doi:10.3390/ijms21207533 |
| [3] | Ma H, Wang C, Han L, et al. Tofacitinib promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury by regulating microglial polarization via JAK/STAT signaling pathway[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2023, 19(15): 4865-82. doi:10.7150/ijbs.84564 |
| [4] | Kunnumakkara AB, Shabnam B, Girisa S, et al. Inflammation, NF-κB, and chronic diseases: how are they linked?[J]. Crit Rev Immunol, 2020, 40(1): 1-39. doi:10.1615/critrevimmunol.2020033210 |
| [5] | Zhao HS, Mei XF, Yang DF, et al. Resveratrol inhibits inflammation after spinal cord injury via SIRT-1/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2021, 762: 136151. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2021.136151 |
| [6] | Song C, Zhang K, Luo C, et al. Inhibiting the NF-κB/DRP1 axis affords neuroprotection after spinal cord injury via inhibiting polarization of pro-inflammatory microglia[J]. Front Biosci: Landmark Ed, 2024, 29(8): 307. doi:10.31083/j.fbl2908307 |
| [7] | Fei M, Li Z, Cao YW, et al. microRNA-182 improves spinal cord injury in mice by modulating apoptosis and the inflammatory response via IKKβ/NF-κB[J]. Lab Investig, 2021, 101(9): 1238-53. doi:10.1038/s41374-021-00606-5 |
| [8] | Wang H, Lin F, Wu Y, et al. Carrier-free nanodrug based on co-assembly of methylprednisolone dimer and rutin for combined treatment of spinal cord injury[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(13): 12176-87. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c00360 |
| [9] | Baroudi M, Rezk A, Daher M, et al. Management of traumatic spinal cord injury: a current concepts review of contemporary and future treatment[J]. Injury, 2024, 55(6): 111472. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2024.111472 |
| [10] | Socała K, Szopa A, Serefko A, et al. Neuroprotective effects of coffee bioactive compounds: a review[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 22(1): E107. doi:10.3390/ijms22010107 |
| [11] | Eldesouki S, Qadri R, Abu Helwa R, et al. Recent updates on the functional impact of kahweol and cafestol on cancer[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(21): 7332. doi:10.3390/molecules27217332 |
| [12] | Seo HY, Kim MK, Lee SH, et al. Kahweol ameliorates the liver inflammation through the inhibition of NF-κB and STAT3 activation in primary kupffer cells and primary hepatocytes[J]. Nutrients, 2018, 10(7): E863. doi:10.3390/nu10070863 |
| [13] | Lee HF, Lin JS, Chang CF. Acute kahweol treatment attenuates traumatic brain injury neuroinflammation and functional deficits[J]. Nutrients, 2019, 11(10): E2301. doi:10.3390/nu11102301 |
| [14] | Hwang YP, Jeong HG. The coffee diterpene kahweol induces heme oxygenase-1 via the PI3K and p38/Nrf2 pathway to protect human dopaminergic neurons from 6-hydroxydopamine-derived oxidative stress[J]. FEBS Lett, 2008, 582(17): 2655-62. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2008.06.045 |
| [15] | Xue MT, Sheng WJ, Song X, et al. Atractylenolide III ameliorates spinal cord injury in rats by modulating microglial/macrophage polarization[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2022, 28(7): 1059-71. doi:10.1111/cns.13839 |
| [16] | Duan FX, Shi YJ, Chen J, et al. Neuroprotective effects of P7C3 against spinal cord injury in rats[J]. Exp Biol Med: Maywood, 2019, 244(18): 1680-7. doi:10.1177/1535370219888620 |
| [17] | Kim JY, Leem J, Kim GM. Kahweol protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice through inhibiting oxidative stress, hepatocyte death, and inflammation[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2022, 2022: 8121124. doi:10.1155/2022/8121124 |
| [18] | Kim JY, Jo J, Leem J, et al. Kahweol ameliorates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through pleiotropic effects in mice[J]. Biomedicines, 2020, 8(12): E572. doi:10.3390/biomedicines8120572 |
| [19] | Basso DM, Fisher LC, Anderson AJ, et al. Basso Mouse Scale for locomotion detects differences in recovery after spinal cord injury in five common mouse strains[J]. J Neurotrauma, 2006, 23(5): 635-59. doi:10.1089/neu.2006.23.635 |
| [20] | Xu YB, Geng ZJ, Sun Y, et al. Complanatuside A improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury through inhibiting JNK signaling-mediated microglial activation[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2024, 965: 176287. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.176287 |
| [21] | Liu S, Wu Q, Wang LY, et al. Coordination function index: a novel indicator for assessing hindlimb locomotor recovery in spinal cord injury rats based on catwalk gait parameters[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2024, 459: 114765. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2023.114765 |
| [22] | Jiang D, Gong F, Ge X, et al. Neuron-derived exosomes-transmitted miR-124-3p protect traumatically injured spinal cord by suppressing the activation of neurotoxic microglia and astrocytes[J]. J Nanobiotechnology, 2020, 18(1): 105. doi:10.1186/s12951-020-00665-8 |
| [23] | Lei P, Li Z, Hua Q, et al. Ursolic acid alleviates neuroinflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage by mediating microglial pyroptosis via the NF-κB/NLRP3/GSDMD pathway[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(19): 14771. doi:10.3390/ijms241914771 |
| [24] | Zhang Y, Jia J. Betaine mitigates amyloid‑β‑associated neuroinfl-ammation by suppressing the NLRP3 and NF‑κB signaling pathways in microglial cells[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2023, 94(s1): S9-19. doi:10.3233/jad-230064 |
| [25] | Shen T, Park YC, Kim SH, et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB/signal transducers and activators of transcription-1-mediated inflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages are a major inhibitory target of kahweol, a coffee diterpene[J]. Biol Pharm Bull, 2010, 33(7): 1159-64. doi:10.1248/bpb.33.1159 |
| [26] | Li G, Fu T, Wang W, et al. Pretreatment with kahweol attenuates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via improving mitochondrial homeostasis in a CaMKKII/AMPK-dependent pathway[J]. Mol Nutr Food Res, 2023, 67(19): e2300083. doi:10.1002/mnfr.202300083 |
| [27] | Liu H, Zhang J, Xu X, et al. SARM1 promotes neuroinflammation and inhibits neural regeneration after spinal cord injury through NF-κB signaling[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(9): 4187-206. doi:10.7150/thno.49054 |
| [28] | Ryu Y, Ogata T, Nagao M, et al. The swimming test is effective for evaluating spasticity after contusive spinal cord injury[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(2): e0171937. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0171937 |
| [29] | Metz GAS, Merkler D, Dietz V, et al. Efficient testing of motor function in spinal cord injured rats[J]. Brain Res, 2000, 883(2): 165-77. doi:10.1016/s0006-8993(00)02778-5 |
| [30] | Davidson LT, Evans MC. Congenital and acquired spinal cord injury and dysfunction[J]. Pediatr Clin North Am, 2023, 70(3): 461-81. doi:10.1016/j.pcl.2023.01.017 |
| [31] | de Oliveira MR, de Souza ICC, Fürstenau CR. Mitochondrial protection promoted by the coffee diterpene kahweol in methylglyoxal-treated human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells[J]. Neurotox Res, 2020, 37(1): 100-10. doi:10.1007/s12640-019-00107-w |
| [32] | Meng TY, Zhang YF, Huang J, et al. Rubusoside mitigates neuroinflammation and cellular apoptosis in Parkinson's disease, and alters gut microbiota and metabolite composition[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 124: 155309. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155309 |
| [33] | Mitchell JP, Carmody RJ. Chapter two NF-κB and the transcriptional control of inflammation[J]. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol, 2018, 335: 41-84. doi:10.1016/bs.ircmb.2017.07.007 |
| [34] | Wei J, Li T, Lin S, et al. Dihydrotestosterone reduces neuroinflammation in spinal cord injury through NF-κB and MAPK pathway[J]. Cell Mol Biol: Noisy-le-grand, 2024, 70(1): 213-8. doi:10.14715/cmb/2024.70.1.29 |
| [1] | Shufen ZHANG, Tianrong HUANG, Canhong YANG, Jiayi CHEN, Tianming LÜ, Jiafa ZHANG. Sulforaphane reduces reactive astrocyte-mediated neuron apoptosis in vitro by inhibiting the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in Aβ42 oligomer-activated astrocytes [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2026, 46(1): 191-199. |
| [2] | Bing XIA, Jin PENG, Jiuyang DING, Jie WANG, Guowei TANG, Guojie LIU, Yun WANG, Changwu WAN, Cuiyun LE. ATF3 regulates inflammatory response in atherosclerotic plaques in mice through the NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1131-1142. |
| [3] | Yujia YANG, Lifang YANG, Yaling WU, Zhaoda DUAN, Chunze YU, Chunyun WU, Jianyun YU, Li YANG. Cannabidiol inhibits neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in rats with multiple concussions by regulating the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1240-1250. |
| [4] | Guanglü HE, Wanyu CHU, Yan LI, Xin SHENG, Hao LUO, Aiping XU, Mingjie BIAN, Huanhuan ZHANG, Mengya WANG, Chao ZHENG. Orexin-A promotes motor function recovery of rats with spinal cord injury by regulating ionotropic glutamate receptors [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 1023-1030. |
| [5] | Yue CHEN, Linyu XIAO, Lü REN, Xue SONG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. Monotropein improves motor function of mice with spinal cord injury by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to suppress neuronal apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 774-784. |
| [6] | Yongxin MAI, Shuting ZHOU, Ruijia WEN, Jinfang ZHANG, Dongxiang ZHAN. Aucubin alleviates knee osteoarthritis in mice by suppressing the NF‑κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2104-2110. |
| [7] | Yiming SUN, Xinran XU, Xuerui ZHUO, Hui CAI, Yan WANG. C1q-neutralizing antibodies improves postpartum depressive-like behaviors in mice by regulating the C1q/C3 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2111-2117. |
| [8] | Na ZHONG, Huijie WANG, Wenying ZHAO, Zhengui SUN, Biao GENG. High RNF7 expression enhances PD-1 resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells by promoting CXCL1 expression and myeloid-derived suppressor cell recruitment via activating NF-κB signaling [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1704-1711. |
| [9] | Hanjun ZUO, Zhaoda DUAN, Zhao WANG, Tao GUO, Jinsha SHI, Haolong SHI, Juanjuan LI. Gastrodin improves microglia-mediated inflammatory response after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats via PI3K/AKT pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1712-1719. |
| [10] | Na ZHAO, Mengdi SHEN, Rui ZHAO, Di AO, Zetan LUO, Yinliang ZHANG, Zhidong XU, Fangtian FAN, Hailun ZHENG. column:Sanguinarine alleviates ulcerative colitis in mice by regulating the Nrf2/NF-κB pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1467-1475. |
| [11] | Linyu XIAO, Ting DUAN, Yongsheng XIA, Yue CHEN, Yang SUN, Yibo XU, Lei XU, Xingzhou YAN, Jianguo HU. Linarin inhibits microglia activation-mediated neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis in mouse spinal cord injury by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1589-1598. |
| [12] | MAN Hao, WANG Jianwei, WU Mao, SHAO Yang, YANG Junfeng, LI Shaoshuo, LÜ Jinye, ZHOU Yue. Jisuikang formula promotes spinal cord injury repair in rats by activating the YAP/PKM2 signaling axis in astrocytes [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(4): 636-643. |
| [13] | Jinsha SHI, Haonan ZHANG, Xinglin ZHANG, Haolong SHI, Hanjun ZUO, Tao GUO, Zhao WANG, Hang YU, Juanjuan LI. Gastrodin alleviates microglia-mediated inflammatory responses in neonatal mice with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage by regulating CCR5/AKT signaling [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(10): 1850-1857. |
| [14] | SUN Xiaopeng, SHI Hang, ZHANG Lei, LIU Zhong, LI Kewei, QIAN Lingling, ZHU Xingyu, YANG Kangjia, FU Qiang, DING Hua. Exosomes from ectoderm mesenchymal stem cells inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial M1 polarization and promotes survival of H2O2-exposed PC12 cells by suppressing inflammatory response and oxidative stress [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 119-128. |
| [15] | SUN Yang, XU Yibo, XIAO Linyu, ZHU Guoqing, LI Jing, SONG Xue, XU Lei, HU Jianguo. Acetylcorynoline inhibits microglia activation by regulating EGFR/MAPK signaling to promote functional recovery of injured mouse spinal cord [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(6): 915-923. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||