Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2573-2584.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.05
Xiaofeng LI1( ), Taochun YE1,2,5, Lu XI1,3,5, Chunqiao LI1,4,5, Huihui LIU1,3,5(
), Taochun YE1,2,5, Lu XI1,3,5, Chunqiao LI1,4,5, Huihui LIU1,3,5( )
)
Received:2025-06-20
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Huihui LIU
E-mail:bitou780@163.com;gzylhh@163.com
Supported by:Xiaofeng LI, Taochun YE, Lu XI, Chunqiao LI, Huihui LIU. Acupuncture alleviates chronic airway inflammation in obese asthmatic mice by downregulating Vnn1 and FAM126B[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2573-2584.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.05
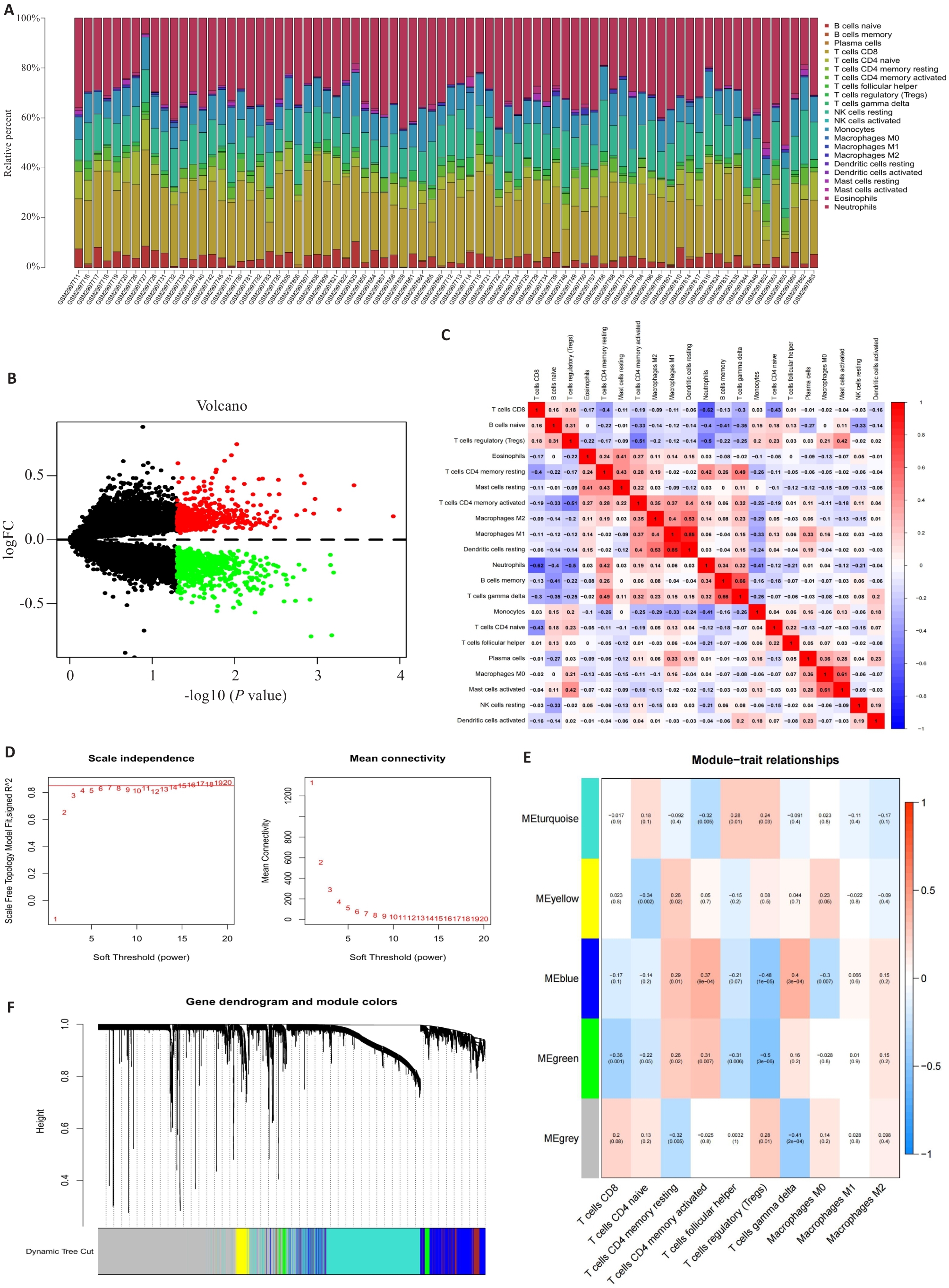
Fig.1 Analysis of the differentially expressed genes (DEGs): Immune Infiltration and WGCNA. A: Stacked bar graph showing immune infiltration of multiple samples from GSE110551. B: Volcano plots showing the differences in gene expressions. C: Heat map showing the connections among different immune cell types. D: Selection of a soft threshold in a weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA). E: Results of hierarchical clustering based on gene expression data. F: Heat map showing connections of different modules and the specific features of each cell.
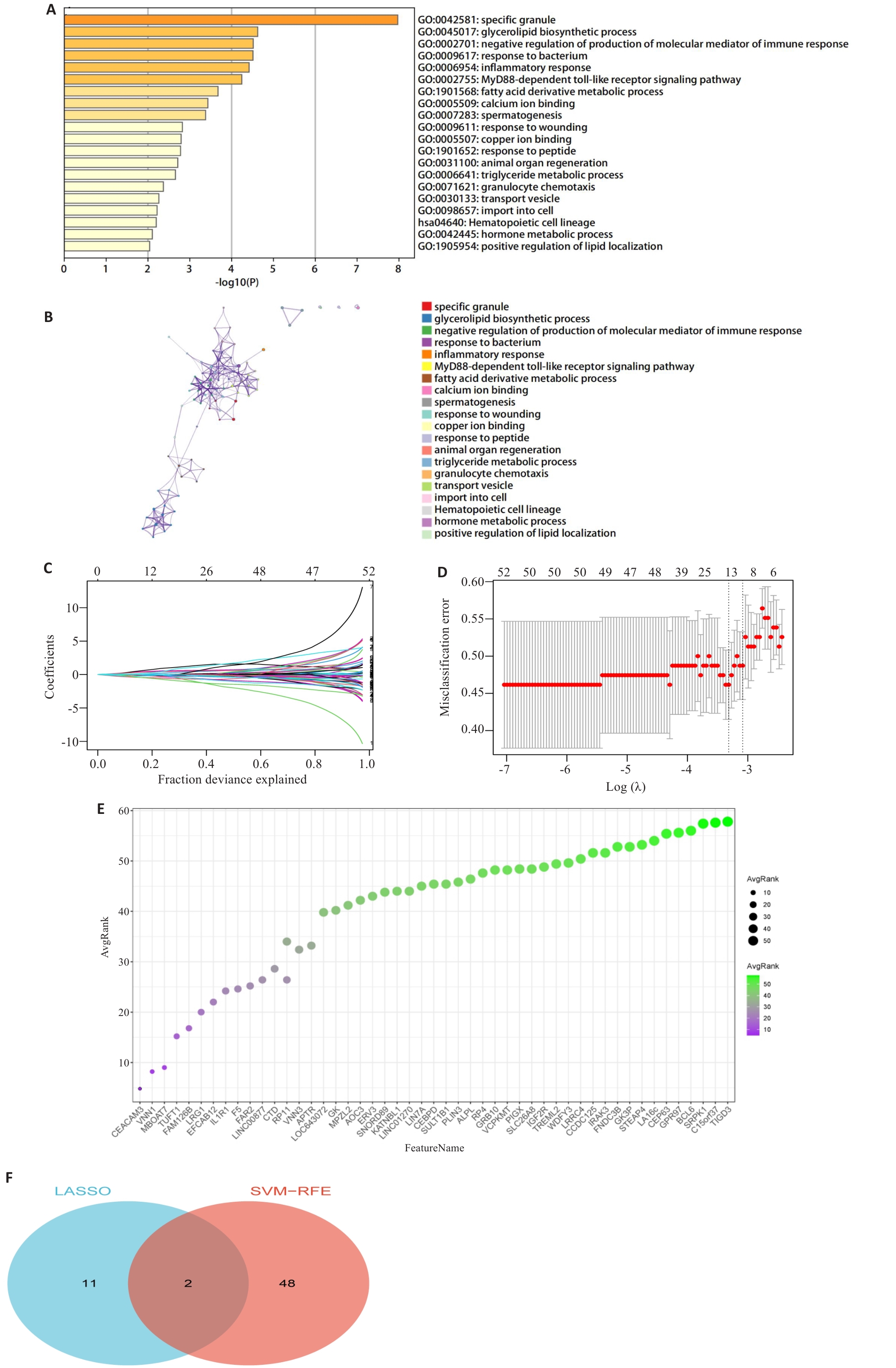
Fig.2 Screening of the DEGs using GO/KEGG enrichment analysis and machine learning. A,B: Results of pathway analysis of genes in the green module using the Metascape website. C: Lasso regression curve diagram. D: Selection of the optimal λ value to balance model complexity and predictive performance. E: Evaluation of feature genes in obesity-asthma using the Support Vector Machine Recursive Feature Elimination (SVM-RFE) algorithm. F: Venn diagram of LASSO and SVM-RFE: two intersecting genes, FAM126B and VNN1, were obtained.
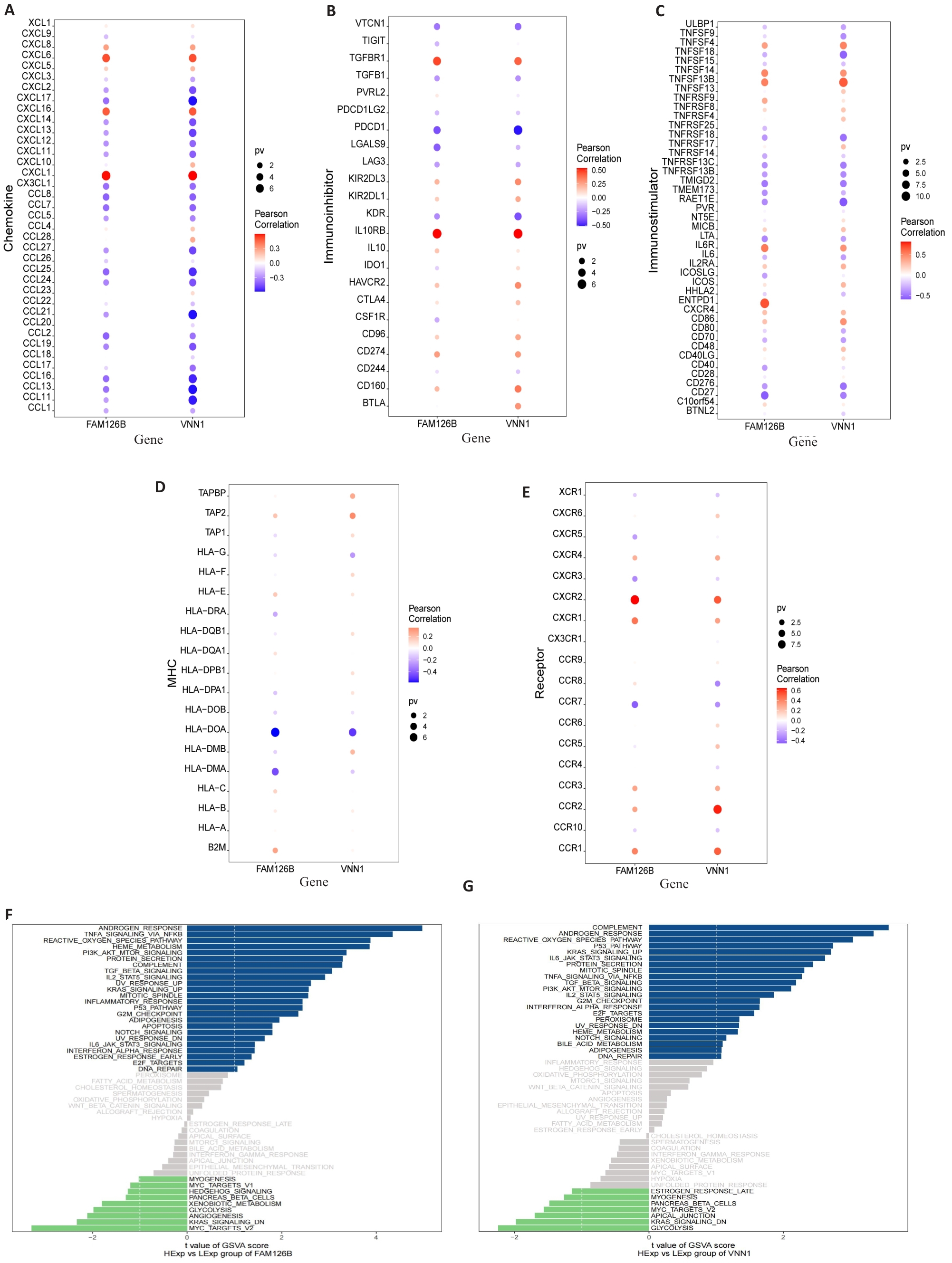
Fig.3 Immunological factors associated with FAM126B and VNN1 and GSVA analysis. A-E: Bubble plots showing the correlation between different chemokines, immunosuppressive factors, immunostimulatory factors, MHC, chemokine receptors, and the two specific genes (FAM126B and VNN1). F-G: GSVA bar charts for FAM126B and VNN1. Patients with high FAM126B and VNN1 expressions exhibit enrichment in different signaling pathways.
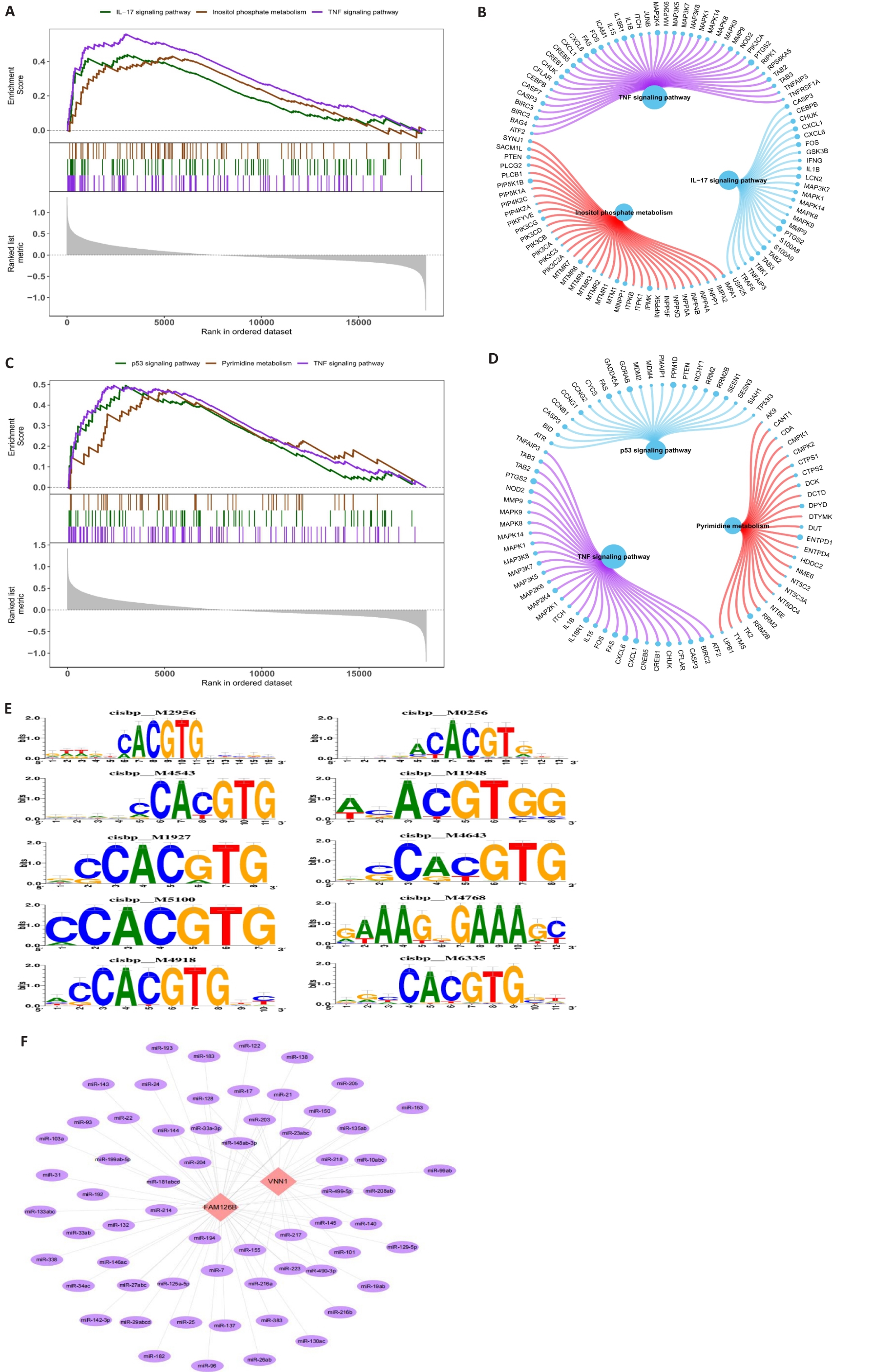
Fig.4 GSEA analysis of FAM126B and VNN1, co-regulation enrichment analysis of multiple transcription factors, and mRNA-miRNA relationships. A,B: GSEA results and network diagram of FAM126B, enriched in the IL-17 signaling pathway, inositol phosphate metabolism, and TNF signaling pathway. C, D: GSEA results and network diagram for VNN1, enriched in the p53 signaling pathway, pyrimidine metabolism, and TNF signaling pathway. E: Enrichment analysis and motif-TF annotation of transcription factors. F: miRNA network diagram for FAM1268 and VNN1 using Cytoscape.
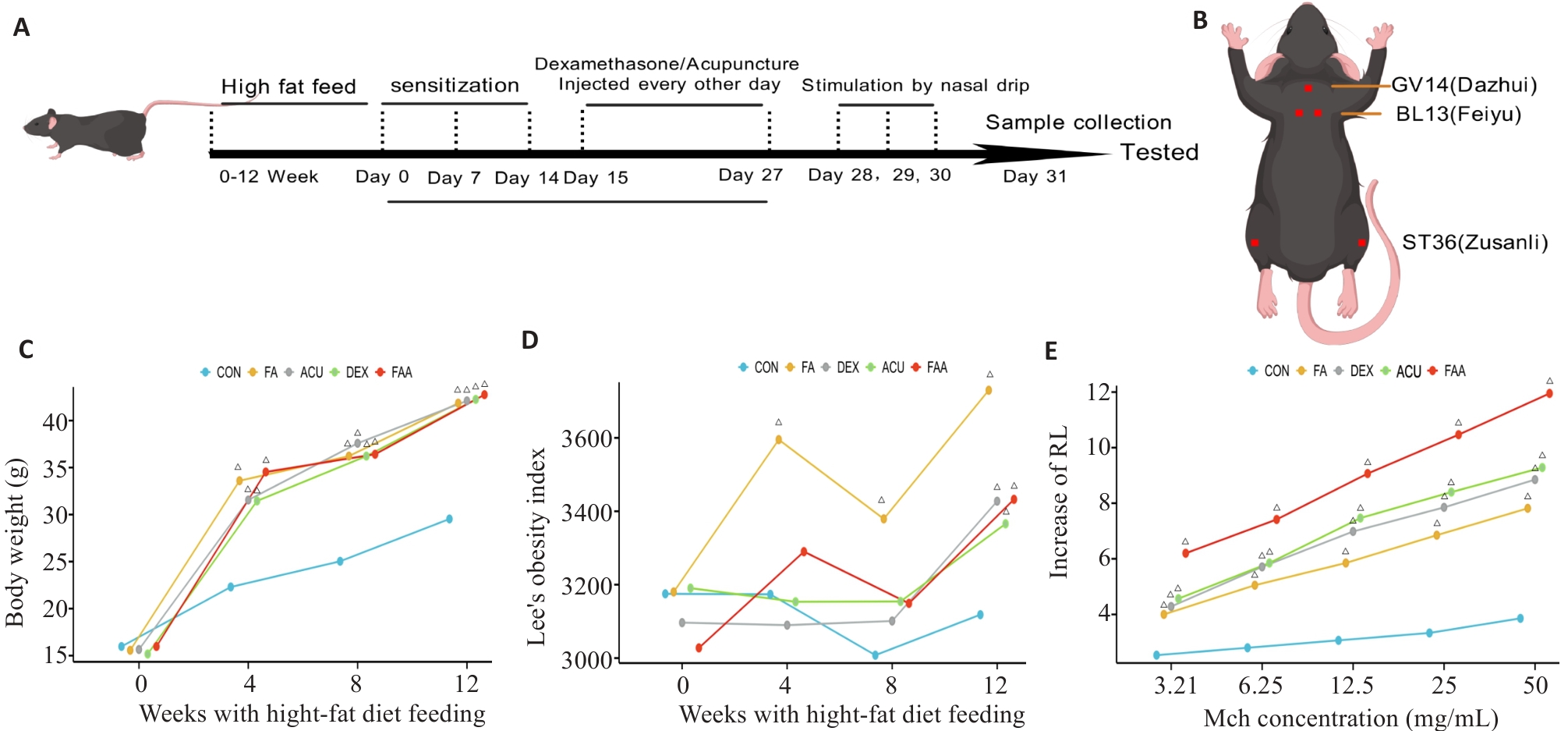
Fig.5 Obese asthma modeling in mice and weekly changes of the related parameters of the mice. A: Flow chart of animal experiment. B: Location of mice acupoints. C: Line chart of body weight changes of the mice. D: Line chart of lee's index in mice. E: Line chart of RF test of the mice. △P<0.05 vs COH. CON: Normal feeding group; FA: High-fat diet feeding group; ACU: High-fat feeding group with OVA sensitization and treatment with acupuncture; DEX: High-fat feeding group with OVA sensitization and 2 mg/kg dexamethasone gavage; FAA: High-fat feeding and OVA sensitization group.

Fig.6 HE staining of the lung tissues and blood routine results in each group. A-F: Pathological inflammatory cell infiltration in mice, including lymphocytes, eosinophils, and neutrophils (×100). The inflammation score was 0 in CON group, 1 in FA group, 3 in ACU group, 4 in DEX group, and 5 in FAA group. G: Mouse blood routine test results for neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocyte and eosinophils. △P<0.05 vs CON group; ○P<0.05 vs FA group; &P<0.05 vs ACU group; *P<0.05 vs DXE group.
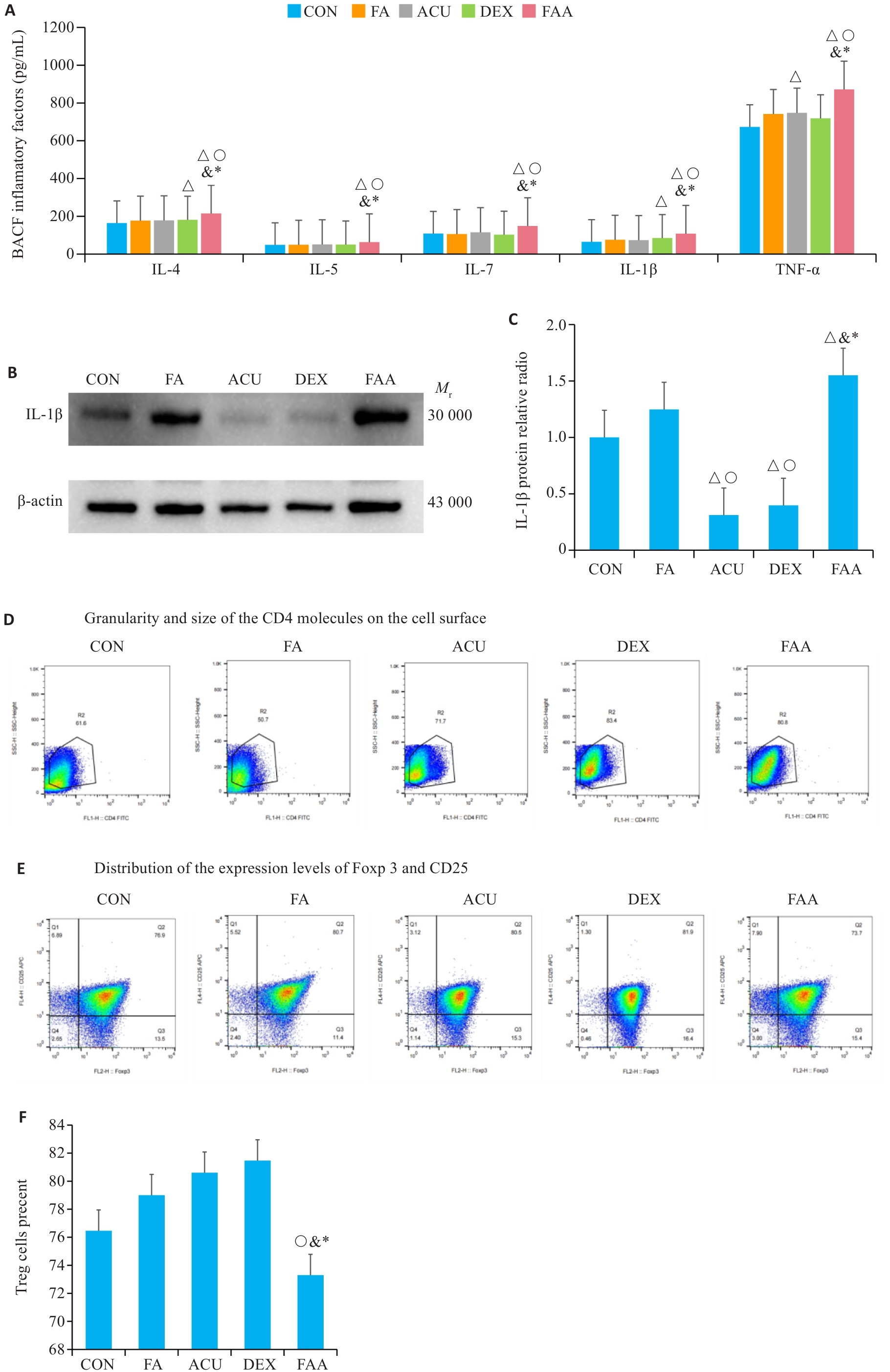
Fig.7 Therapeutic effects of acupuncture and dexamethasone in the mouse models. A: ELISA detection results of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for IL-4, IL-5, IL-17, IL-1β, and TNF-α. B, C: Western blotting for detecting IL-1β expressions in each group. D-F: Flow cytometry for analysis of Treg cells. △P<0.05 vs CON group; ○P<0.05 vs FA group; &P<0.05 vs ACU group; *P<0.05 vs DXE group.
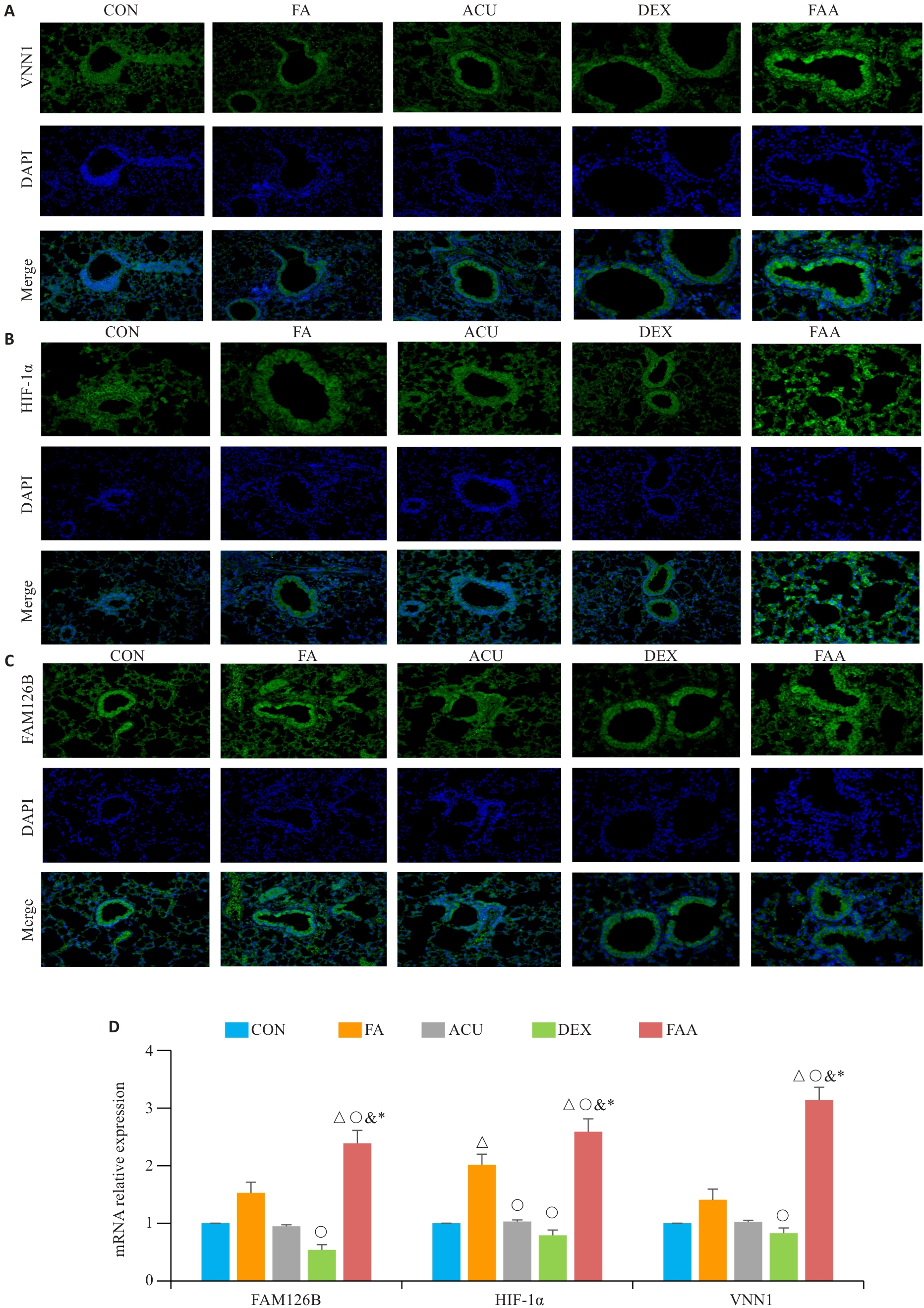
Fig.8 Expression of HIF-1α, FAM126B and Vnn1 in mice with obese asthma. A-C: Immunofluorescence staining of Vnn1, FAM126B, and HIF-1α in the lung tissues (×100). D: Bar charts showing mRNA expression levels of HIF-1α, Vnn-1 and FAM126B in the lung tissues. △P<0.05 vs CON group; ○P<0.05 vs FA group; &P<0.05 vs ACU group; *P<0.05 vs DXE group.
| [1] | Grasemann H, Holguin F. Oxidative stress and obesity-related asthma[J]. Paediatr Respir Rev, 2021, 37: 18-21. doi:10.1016/j.prrv.2020.05.004 |
| [2] | Bhatraju NK, Agrawal A. Mitochondrial dysfunction linking obesity and asthma[J]. Ann Am Thorac Soc, 2017, 14(): S368-73. doi:10.1513/annalsats.201701-042aw |
| [3] | van der Wiel E, Ten Hacken NHT, van den Berge M, et al. Eosinophilic inflammation in subjects with mild-to-moderate asthma with and without obesity: disparity between sputum and biopsies[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2014, 189(10): 1281-4. doi:10.1164/rccm.201310-1841le |
| [4] | Wang YF, Zhao L, Gao LW, et al. Health policy and public health implications of obesity in China[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2021, 9(7): 446-61. doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(21)00118-2 |
| [5] | Rabadán-Chávez G, Díaz de la Garza RI, Jacobo-Velázquez DA. White adipose tissue: Distribution, molecular insights of impaired expandability, and its implication in fatty liver disease[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA Mol Basis Dis, 2023, 1869(8): 166853. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166853 |
| [6] | Kim HY, Lee HJ, Chang YJ, et al. Interleukin-17-producing innate lymphoid cells and the NLRP3 inflammasome facilitate obesity-associated airway hyperreactivity[J]. Nat Med, 2014, 20(1): 54-61. doi:10.1038/nm.3423 |
| [7] | Silverpil E, Lindén A. IL-17 in human asthma[J]. Expert Rev Respir Med, 2012, 6(2): 173-86. doi:10.1586/ers.12.12 |
| [8] | Burbank AJ, Schworer SA, Sood A, et al. Airway IL-1β associates with IL-5 production following dust mite allergen inhalation in humans[J]. Respir Res, 2021, 22(1): 309. doi:10.1186/s12931-021-01903-9 |
| [9] | Kudo M, Melton AC, Chen C, et al. IL-17A produced by αβ T cells drives airway hyper-responsiveness in mice and enhances mouse and human airway smooth muscle contraction[J]. Nat Med, 2012, 18(4): 547-54. doi:10.1038/nm.2684 |
| [10] | Crotty Alexander LE, Akong-Moore K, Feldstein S, et al. Myeloid cell HIF-1α regulates asthma airway resistance and eosinophil function[J]. J Mol Med (Berl), 2013, 91(5): 637-44. doi:10.1007/s00109-012-0986-9 |
| [11] | Byun Y, Choi YC, Jeong Y, et al. miR-200c downregulates HIF-1α and inhibits migration of lung cancer cells[J]. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 2019, 24: 28. doi:10.1186/s11658-019-0152-2 |
| [12] | 刘慧慧, 刘嘉羿, 彭美玉, 等. 针刺对气道重塑小鼠TGF-β1/Smads通路的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(11): 1372-7. |
| [13] | Athar M, Manhas A, Rana N, et al. Computational and bioinformatics tools for understanding disease mechanisms[J]. Biocell, 2024, 48(6): 935-44. doi:10.32604/biocell.2024.049891 |
| [14] | China Association of Acupuncture and Moxibustion. 实验动物常用穴位名称与定位 第3部分: 小鼠[J]. 世界针灸杂志: 英文版, 2025, 35(2): 160-6. |
| [15] | Gomez-Llorente MA, Romero R, Chueca N, et al. Obesity and asthma: a missing link[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(7): 1490. doi:10.3390/ijms18071490 |
| [16] | Frohnert BI, Bernlohr DA. Glutathionylated products of lipid peroxidation: a novel mechanism of adipocyte to macrophage signaling[J]. Adipocyte, 2014, 3(3): 224-9. doi:10.4161/adip.28851 |
| [17] | Li RJ, Wen YX. Association of body mass index with asthma occurrence and persistence in adolescents: a retrospective study of NHANES (2011–2018)[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(9): e20092. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20092 |
| [18] | Uribe-Querol E, Rosales C. Neutrophils actively contribute to obesity-associated inflammation and pathological complications[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(12): 1883. doi:10.3390/cells11121883 |
| [19] | Bartucci R, Salvati A, Olinga P, et al. Vanin 1: its physiological function and role in diseases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(16): 3891. doi:10.3390/ijms20163891 |
| [20] | Chen SY, Zhang WX, Tang CQ, et al. Vanin-1 is a key activator for hepatic gluconeogenesis[J]. Diabetes, 2014, 63(6): 2073-85. doi:10.2337/db13-0788 |
| [21] | Berruyer C, Martin FM, Castellano R, et al. Vanin-1-/ - mice exhibit a glutathione-mediated tissue resistance to oxidative stress[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2004, 24(16): 7214-24. doi:10.1128/mcb.24.16.7214-7224.2004 |
| [22] | Wei Y, Dong M, Zhong L, et al. Regulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity and immunologic function contributed to the anti-inflammatory effect of acupuncture in the OVA-induced murine asthma model[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2017, 636: 177-83. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2016.11.001 |
| [23] | Shi LZ, Wang RN, Huang GH, et al. HIF1alpha-dependent glycolytic pathway orchestrates a metabolic checkpoint for the differentiation of TH17 and Treg cells[J]. J Exp Med, 2011, 208(7): 1367-76. doi:10.1084/jem.20110278 |
| [24] | Huerta-Yepez S, Baay-Guzman GJ, Bebenek IG, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor promotes murine allergic airway inflammation and is increased in asthma and rhinitis[J]. Allergy, 2011, 66(7): 909-18. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2011.02594.x |
| [25] | Zhu YP, Wu F, Gui WW, et al. A positive feedback regulatory loop involving the lncRNA PVT1 and HIF-1α in pancreatic cancer[J]. J Mol Cell Biol, 2021, 13(9): 676-89. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjab042 |
| [26] | Guo JL, Wang GQ, Liu T, et al. Acupuncture improves chronic cerebral ischemia by inhibiting the CKLF1/HIF-1α/VEGF/Notch1 signaling pathway[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2025, 31(3): e70246. doi:10.1111/cns.70246 |
| [27] | Liu HH, Liu JY, Peng MY, et al. Effect of acupuncture on TGF-β1/Smads pathway in mice with airway remodeling mic[J]. J South Med Univ, 2018, 38(11): 1372-7. |
| [28] | Xiao C, Biagini Myers JM, Ji H, et al. Vanin-1 expression and methylation discriminate pediatric asthma corticosteroid treatment response[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2015, 136(4): 923-31.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2015.01.045 |
| [29] | Zhang ZZ, He YW, Liu H, et al. NLRP3 regulates ferroptosis via the JAK2/STAT3 pathway in asthma inflammation: Insights from in vivo and in vitro studies[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 143(Pt 2): 113416. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113416 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||