Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (8): 1633-1642.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.08.08
Chuyu DENG1( ), Xueying WANG1, Lixiang GAN1, Dayu WANG1, Xiaoyan ZHENG2, Chunzhi TANG1(
), Xueying WANG1, Lixiang GAN1, Dayu WANG1, Xiaoyan ZHENG2, Chunzhi TANG1( )
)
Received:2025-02-08
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-09-05
Contact:
Chunzhi TANG
E-mail:tanyacyd@163.com;jordan664@163.com
Supported by:Chuyu DENG, Xueying WANG, Lixiang GAN, Dayu WANG, Xiaoyan ZHENG, Chunzhi TANG. Electroacupuncture at Zusanli improves blood lipid disorders in hyperlipidemic mice by improving gut microbiota structure[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1633-1642.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.08.08
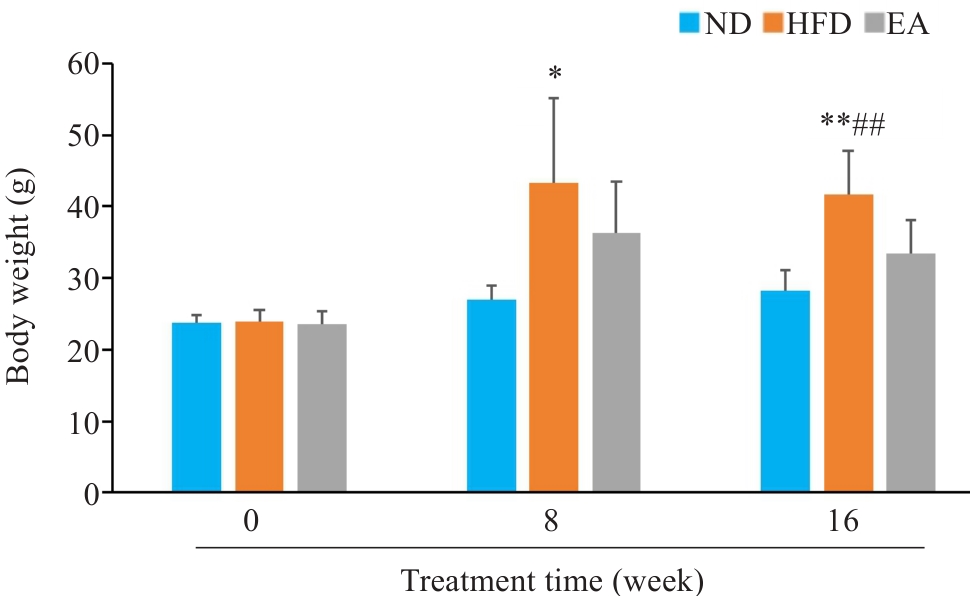
Fig.2 Weight changes of the mice in each group at 8 and 16 weeks (Mean±SD, n=10). *P<0.05, **P<0.01vs ND, ##P<0.01 vs EA. ND:Normal diet group; HFD: High fat diet group; EA: High fat diet and electroacupuncture group.
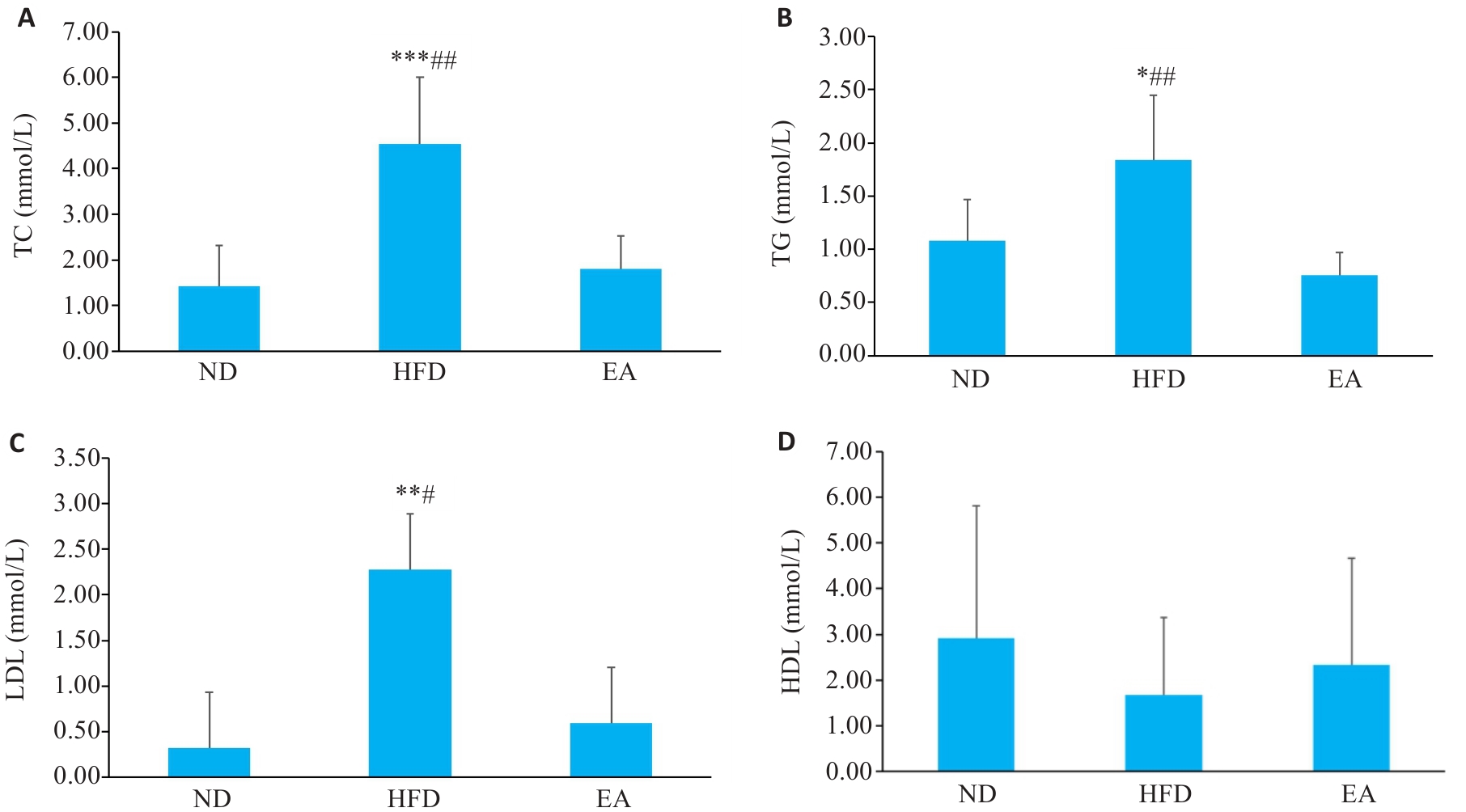
Fig.3 Comparison of TC (A), TG (B), LDL-c (C) and HDL-c (D) levels of the mice among the groups (Mean±SD, n=6). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs ND, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs EA. ND:Normal diet group; HFD: High fat diet group; EA: High fat diet and electroacupuncture group.
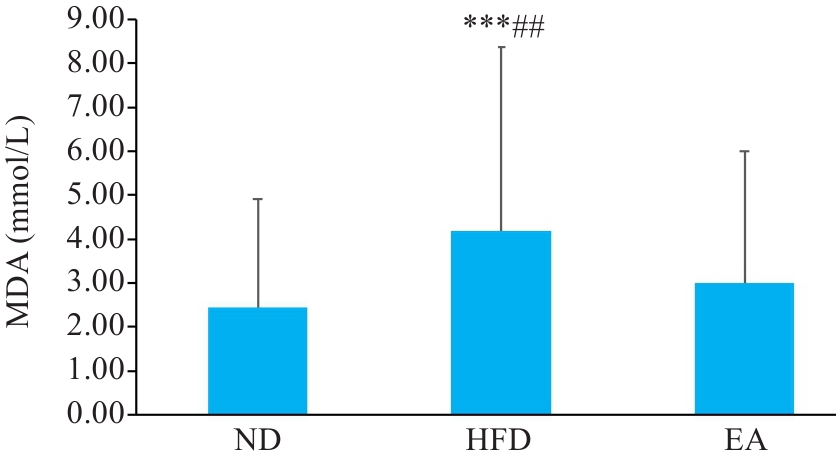
Fig.4 Comparison of serum MDA levels of the mice among the 3 groups (Mean±SD, n=6). ***P<0.001 vs ND, ##P<0.01 vs EA. ND: Normal diet group; HFD: High fat diet group; EA: High fat diet and electroacupuncture group.
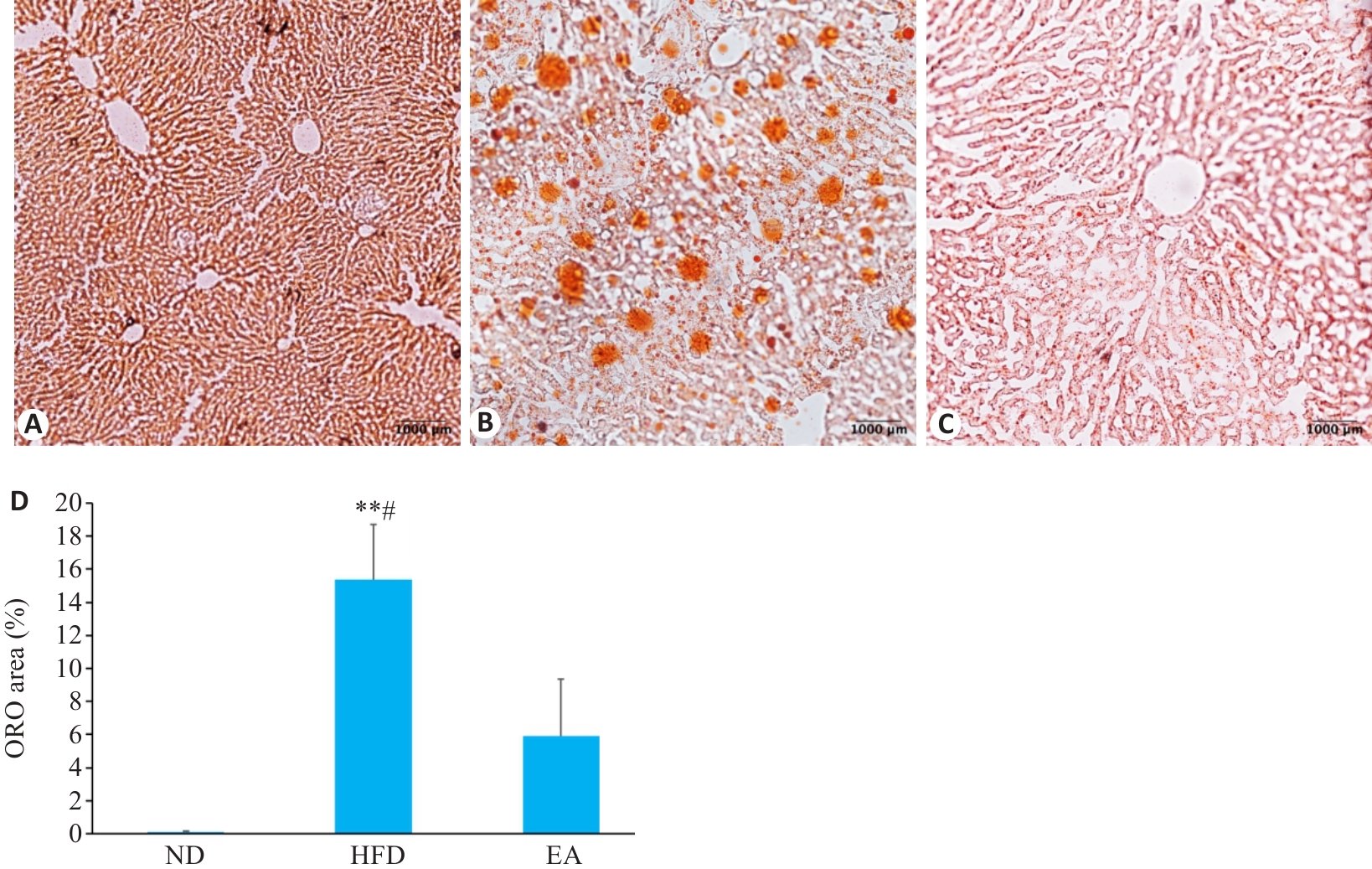
Fig.5 Lipid droplet accumulation in the liver of the mice (Oil Red Staining,Scale=1000 μm). A: ND group. B: HFD group. C: EA group. D: Comparison of Oil Red O stained area (%) among the 3 groups (Mean±SD, n=3). **P<0.01vs ND, #P<0.05 vs EA group. ND: Normal diet group; HFD: High fat diet group; EA: High fat diet and electroacupuncture group.
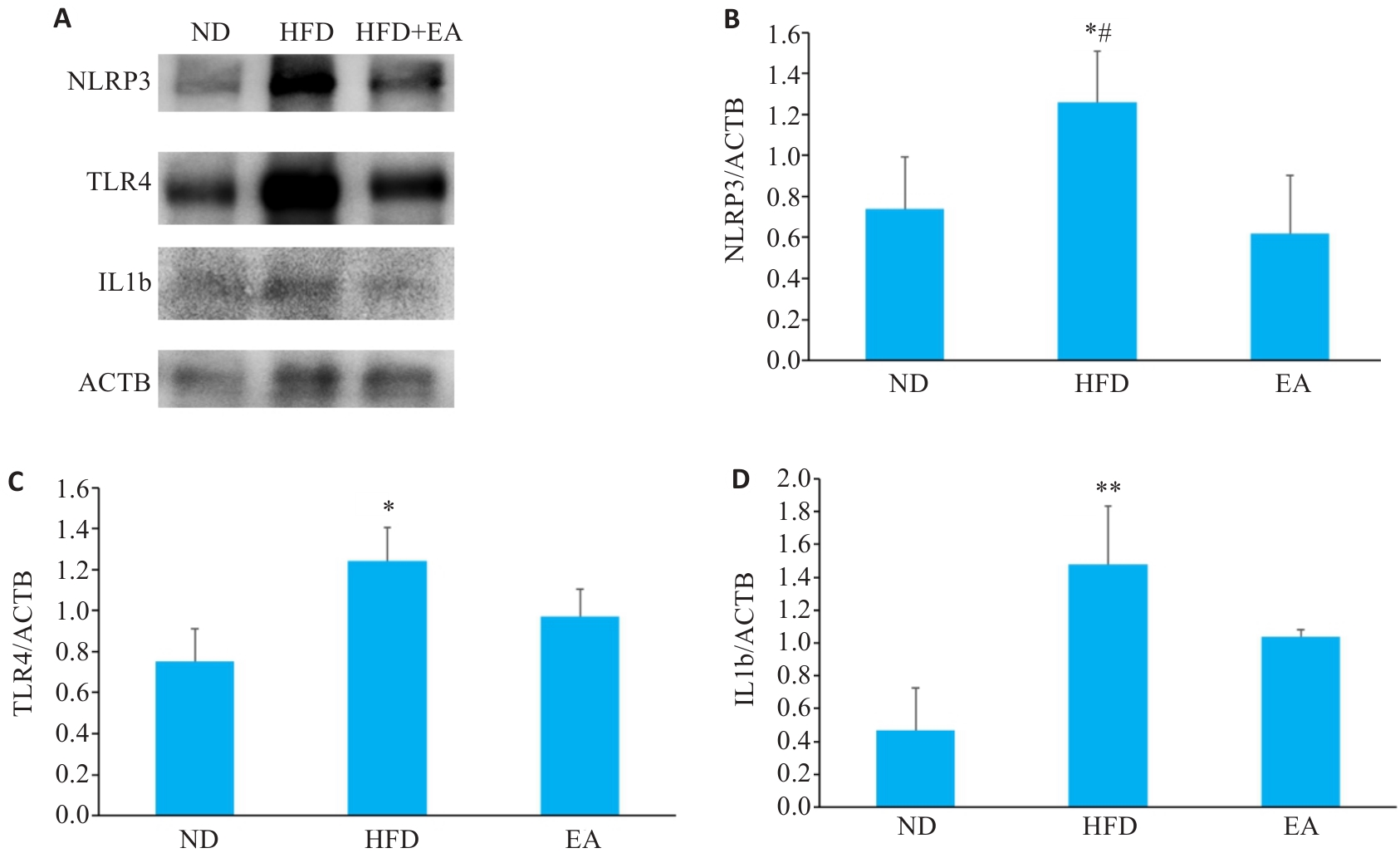
Fig.6 NLRP3, TLR4 and IL-1b protein expressions in mouse colon tissues detected by Western blotting (Mean±SD, n=4). A: Protein band of NLRP3, TLR4 and IL-1b. B-D: Bar chart of gray scale values of the protein bands. *P<0.05, **P<0.01vs ND group; #P<0.05 vs EA group. ND: Normal diet group; HFD: High fat diet group; EA: High fat diet and electroacupuncture group.
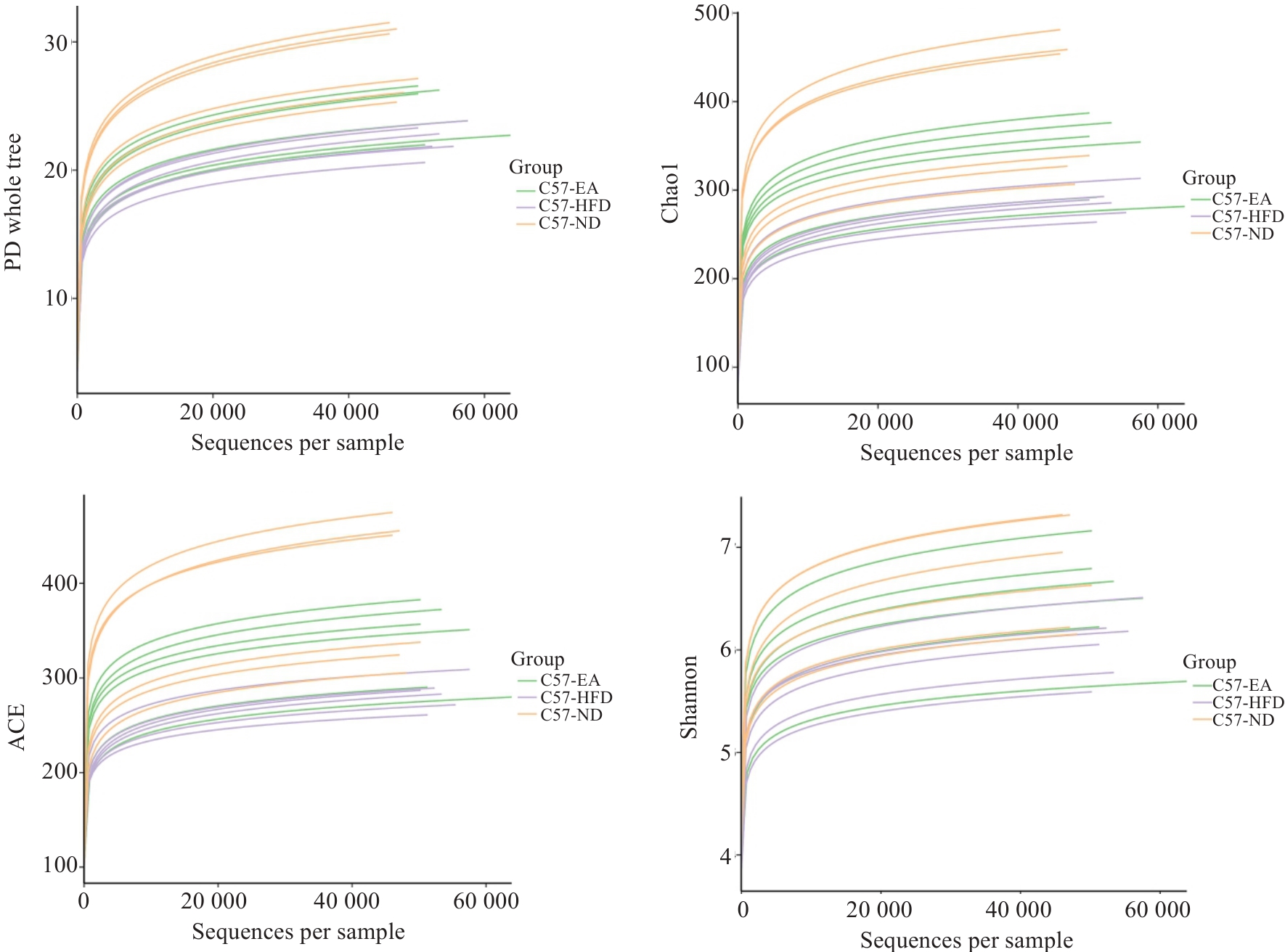
Fig.7 ASV and diversity index dilution curve in the 3 groups. ND: Normal diet group; HFD: High fat diet group; EA: High fat diet and electroacupuncture group.
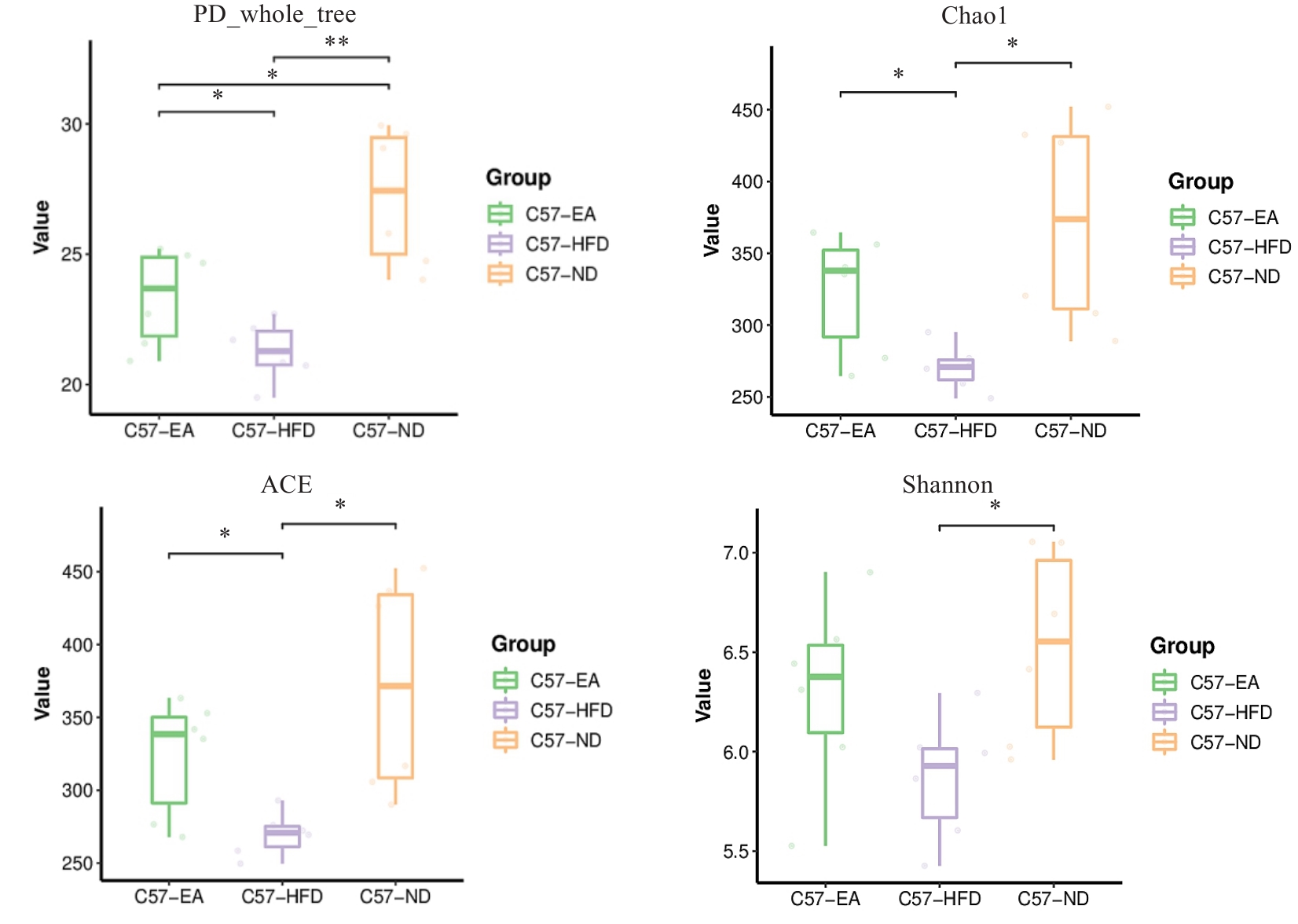
Fig.8 Fig.8 Alpha diversity related boxplot. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. ND: Normal diet group; HFD: High fat diet group; EA: High fat diet and electroacupuncture group.
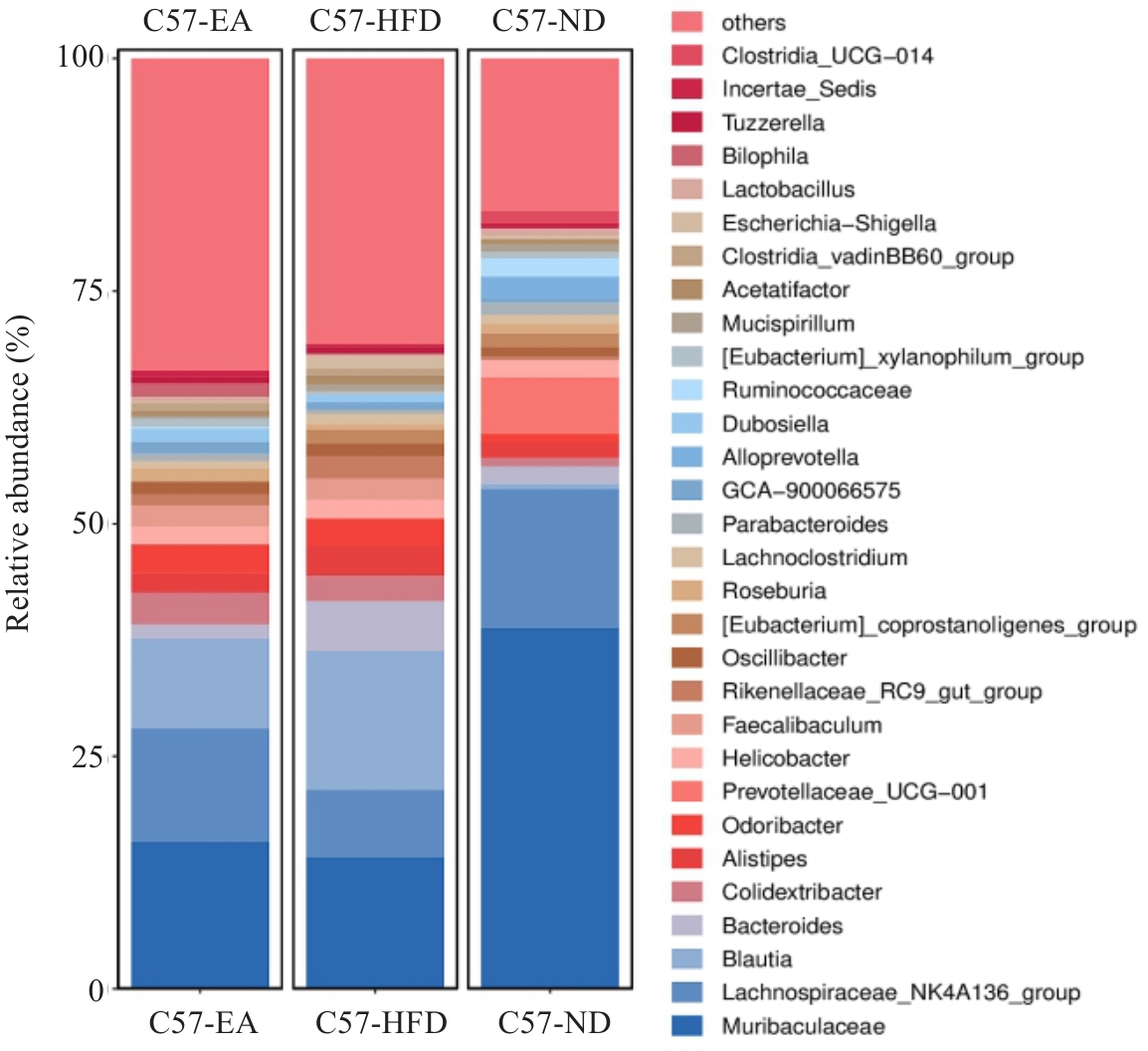
Fig.11 Bar chart of gut microbiota community structure at the genus level. ND:Normal diet group; HFD: High fat diet group; EA: High fat diet and electroacupuncture group.
| [1] | Fan S, Chen S, Lin L. Research progress of gut microbiota and obesity caused by high-fat diet[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2023, 13: 1139800. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2023.1139800 |
| [2] | Frazier K, Kambal A, Zale EA, et al. High-fat diet disrupts REG3γ and gut microbial rhythms promoting metabolic dysfunction[J]. Cell Host Microbe, 2022, 30(6): 809-23.e6. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2022.03.030 |
| [3] | Tong Y, Gao H, Qi Q, et al. High fat diet, gut microbiome and gastrointestinal cancer[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(12): 5889-910. doi:10.7150/thno.56157 |
| [4] | Sanmiguel C, Gupta A, Mayer EA. Gut microbiome and obesity: a plausible explanation for obesity[J]. Curr Obes Rep, 2015, 4(2): 250-61. doi:10.1007/s13679-015-0152-0 |
| [5] | Yao XT, Yang CX, Jia XR, et al. High-fat diet consumption promotes adolescent neurobehavioral abnormalities and hippocampal structural alterations via microglial overactivation accompanied by an elevated serum free fatty acid concentration[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2024, 119: 236-50. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2024.04.005 |
| [6] | Le Chatelier E, Nielsen T, Qin J, et al. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers[J]. Nature, 2013, 500(7464): 541-6. |
| [7] | Asadi A, Shadab Mehr N, Mohamadi MH, et al. Obesity and gut-microbiota-brain axis: a narrative review[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2022, 36(5): e24420. doi:10.1002/jcla.24420 |
| [8] | Ding S, Chi MM, Scull BP, et al. High-fat diet: bacteria interactions promote intestinal inflammation which precedes and correlates with obesity and insulin resistance in mouse[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(8): e12191. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012191 |
| [9] | Kim KA, Gu W, Lee IA, et al. High fat diet-induced gut microbiota exacerbates inflammation and obesity in mice via the TLR4 signaling pathway[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(10): e47713. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0047713 |
| [10] | Yu WF, Yin GL, Chen SW, et al. Diosgenin attenuates metabolic-associated fatty liver disease through the hepatic NLRP3 inflam-masome-dependent signaling pathway[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 138: 112581. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112581 |
| [11] | Engin AB. Message transmission between adipocyte and macro-phage in obesity[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2024, 1460: 273-95. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_9 |
| [12] | Lan Q, Chen J, Yang Y. Chromofungin mitigates free fatty acids-induced endothelial inflammation via inhibition of NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain-associated protein 3 mediated by adenosine 5'-monophosphate-activated protein kinase[J]. Biotechnol Appl Biochem, 2025, 72(2): 460-8. doi:10.1002/bab.2676 |
| [13] | Rajamanickam V, Desouza CV, Castillo RT, et al. Blocking thrombo-xane-prostanoid receptor signaling attenuates lipopolysaccharide- and stearic acid-induced inflammatory response in human PBMCs[J]. Cells, 2024, 13(16): 1320. doi:10.3390/cells13161320 |
| [14] | Ciesielska A, Matyjek M, Kwiatkowska K. TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2021, 78(4): 1233-61. doi:10.1007/s00018-020-03656-y |
| [15] | Zhang SY, Xu QP, Shi LN, et al. Soluble CD4 effectively prevents excessive TLR activation of resident macrophages in the onset of sepsis[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 236. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01438-z |
| [16] | Jia CW, Xiang ZQ, Zhang PF, et al. Selenium-SelK-GPX4 axis protects nucleus pulposus cells against mechanical overloading-induced ferroptosis and attenuates senescence of intervertebral disc[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2024, 81(1): 49. doi:10.1007/s00018-023-05067-1 |
| [17] | 余晨歌, 黄 晶, 席艳, 等. 单纯高脂饮食诱导2型糖尿病小鼠模型的构建及病理改变的评价 [J]. 生理学报, 2024, 76(03): 385-93. |
| [18] | Duan Y, Zeng L, Zheng C, et al. Inflammatory links between high fat diets and diseases[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 2649. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.02649 |
| [19] | 伊丽米古丽·阿卜杜扎伊尔. 温针灸足三里对高血脂症血脂影响的临床分析[J]. 中西医结合心血管病电子杂志, 2016, 4(22): 156. |
| [20] | 兰彩莲, 万 隆, 萨喆燕, 等. 电针足三里和丰隆对高脂血症新西兰兔血脂影响[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2016, 18(10): 85-7. doi:10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2016.10.025 |
| [21] | 汪 倩, 陈以国. 丰隆与足三里联合异功降脂饮对血脂异常的协同增效作用[J]. 湖北中医杂志, 2020, 42(4): 21-3. |
| [22] | 邢海辉, 圣海蓉, 王玲玲. 足三里调脂作用临床研究[J]. 吉林中医药, 2009, 29(12): 1058-60. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1003-5699.2009.12.027 |
| [23] | Taha MM, Abdelghany AI, Draz RS. Lipid profile response to electroacupuncture in non-alcoholic fatty liver patients with hyperlipidemia[J]. J Acupunct Meridian Stud, 2021, 14(1): 21-6. doi:10.51507/j.jams.2021.14.1.21 |
| [24] | Zhu LL, Wei WM, Zeng ZH, et al. Impact of electro-acupuncture on lipid metalolism in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Sichuan da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban, 2012, 43(6): 847-50. |
| [25] | Xu Q, Wu HX, Zhu HB, et al. Grain-sized moxibustion at Zusanli (ST36) promotes hepatic autophagy in rats with hyperlipidemia by regulating the ULK1 and TFEB expression through the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(5): e15316. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15316 |
| [26] | 刘云龙, 李姗姗, 杨永瑞, 等. 电针“足三里” 调节胃肠功能异常的分子机制研究进展[J]. 针刺研究, 2023, 48(10): 1048-54. |
| [27] | 王 成, 袁 君, 郭彦玎, 等. 艾灸“足三里”对膝关节骨关节炎与类风湿性关节炎大鼠膝关节滑膜巨噬细胞极化的影响的比较研究 [J]. 针刺研究, 2023, 48(10): 993-1000. doi:10.13702/j.1000-0607.20220952 |
| [28] | 许 骞, 陆成轩, 吴奂汐, 等. 不同灸程45 ℃“足三里”温和灸对高脂血症大鼠腹主动脉炎性因子的影响[J]. 针刺研究, 2023, 48(9): 923-932. doi:10.13702/j.1000-0607.20221039 |
| [29] | Wang J, Zhu H, Song X, et al. Electroacupuncture regulates gut microbiota to reduce depressive-like behavior in rats[J]. Front Microbiol, 2024, 15: 1327630. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2024.1327630 |
| [30] | 吴小丽, 黄光瑞, 李晓璐, 等. 针灸调节肠道菌群研究进展[J]. 上海中医药大学学报, 2021, 35(2): 103-8. doi:10.16306/j.1008-861x.2021.02.017 |
| [31] | 赵彩娇, 谌桑妮, 李 鑫, 等. 艾灸“足三里”对衰老大鼠氧化应激和肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中国针灸, 2024, 44(3): 303-8. |
| [32] | 王婧雯, 郑淑霞, 林 晟, 等. 基于16S rDNA高通量测序研究电针对腹泻型肠易激综合征大鼠肠道菌群的调节作用[J]. 环球中医药, 2023, 16(5): 846-51. |
| [33] | 徐梦月, 白 娟, 王 强. 基于16S rDNA测序探究电针干预对自发性高血压大鼠肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中医药导报, 2023, 29(5): 6-11. |
| [34] | 蒋志明, 刘 磊, 张 辽, 等. “脑肠同调”法针刺对缺血性脑卒中患者运动功能及肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中国针灸, 2024, 44(7): 740-8. |
| [35] | Lagkouvardos I, Pukall R, Abt B, et al. Corrigendum: The Mouse Intestinal Bacterial Collection (miBC) provides host-specific insight into cultured diversity and functional potential of the gut microbiota [J]. Nat Microbiol, 2016, 1(11): 16219. doi:10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.219 |
| [36] | Li Y, Chen M, Ma Y, et al. Regulation of viable/inactivated/lysed probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum H6 on intestinal microbiota and metabolites in hypercholesterolemic mice[J]. NPJ Sci Food, 2022, 6(1): 50. doi:10.1038/s41538-022-00167-x |
| [37] | Yan C, Huang SH, Ding HF, et al. Adverse effect of oxidized cholesterol exposure on colitis is mediated by modulation of gut microbiota[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2023, 459: 132057. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.132057 |
| [38] | Wang X, Wang Z, Cao J, et al. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites mediate the neuroprotective effect of melatonin in cognitive impairment induced by sleep deprivation[J]. Microbiome, 2023, 11(1): 17. doi:10.1186/s40168-022-01452-3 |
| [39] | 王娇娇. 电针介导lncRNA TUG1靶向miR-127/NF-κB轴调节腹泻型肠易激综合征炎性因子的研究[D], 2022. |
| [40] | Liu S, Wang Z, Su Y, et al. A neuroanatomical basis for electroacupuncture to drive the vagal-adrenal axis[J]. Nature, 2021, 598(7882): 641-5. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04001-4 |
| [41] | Bonaz B, Sinniger V, Pellissier S. Vagal tone: effects on sensitivity, motility, and inflammation[J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2016, 28(4): 455-62. doi:10.1111/nmo.12817 |
| [42] | Zhang R, Lao L, Ren K, et al. Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on persistent pain[J]. Anesthesiology, 2014, 120(2): 482-503. doi:10.1097/aln.0000000000000101 |
| [43] | Tian SL, Wang XY, Ding GH. Repeated electro-acupuncture attenuates chronic visceral hypersensitivity and spinal cord NMDA receptor phosphorylation in a rat irritable bowel syndrome model[J]. Life Sci, 2008, 83(9/10): 356-63. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2008.06.027 |
| [44] | Wu LZ, Cui CL, Tian JB, et al. Suppression of morphine withdrawal by electroacupuncture in rats: dynorphin and κ‑opioid receptor implicated[J]. Brain Res, 1999, 851(1/2): 290-6. doi:10.1016/s0006-8993(99)02069-7 |
| [45] | Zhang XN, He W, Wan HY, et al. Electroacupuncture and moxibustion-like stimulation activate the cutaneous and systemic hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axes in the rat[J]. Acupunct Med, 2022, 40(3): 232-40. doi:10.1177/09645284211055745 |
| [46] | Zhou F, Jiang H, Kong N, et al. Electroacupuncture attenuated anxiety and depression-like behavior via inhibition of hippocampal inflammatory response and metabolic disorders in TNBS-induced IBD rats[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 8295580. doi:10.1155/2022/8295580 |
| [47] | 兰彩莲, 许金森, 萨喆燕, 等. 基于液相色谱-质谱联用技术探讨电针对高脂血症大鼠胆汁酸代谢的影响[J]. 福建中医药, 2024, 55(6): 14-20. |
| [48] | Zhao ZQ. Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia[J]. Prog Neurobiol, 2008, 85(4): 355-75. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2008.05.004 |
| [49] | Koh A, De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, et al. From dietary fiber to host physiology: short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites[J]. Cell, 2016, 165(6): 1332-45. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.041 |
| [50] | 王婧雯. 电针足三里对IBS-D模型大鼠肠道菌群、TRPV1及相关因子的影响[D]; 福建中医药大学, 2023. |
| [51] | 楼 屹, 朱之青, 谢莉莉, 等. 电针足三里对脓毒症大鼠肠上皮细胞间紧密连接结构的影响[J]. 新中医, 2022, 54(15): 163-8. |
| [52] | 季春莲, 占靓卉, 郑静茹, 等. 电针预处理对脓毒症小鼠肠黏膜屏障功能保护作用及MLCK/MLC信号通路的调节作用[J]. 上海针灸杂志, 2023, 42(10): 1092-101. |
| [53] | 王 景, 白栓成. TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3通路抑制炎症反应作用的研究[J]. 中国当代医药, 2024, 31(11): 180-5. |
| [54] | Zhou LL, Liu T, Huang B, et al. Excessive deubiquitination of NLRP3-R779C variant contributes to very-early-onset inflam-matory bowel disease development[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2021, 147(1): 267-79. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.09.003 |
| [55] | 赵保胜, 霍海如, 姜廷良. Toll样受体4的研究及现状[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2007, 12(1): 19-22. |
| [56] | 陈双兰, 刘 蓉, 刘青松, 等. TLR4在炎症性肠病癌变中作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2023, 39(4): 626-30. |
| [57] | 王燕燕, 吴 瑾. TLR4在新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎中的研究进展[J]. 临床儿科杂志, 2020, 38(11): 877-80. |
| [58] | 许文静. 肠道菌群失调在新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎中的研究进展[J]. 中国社区医师, 2023, 39(9): 7-9. |
| [59] | 吴俊东, 耿智隆, 杨勇丽, 等. NLRP3炎症小体激活机制及其在脓毒症中的作用[J]. 医学综述, 2021, 27(3): 459-64, 470. |
| [60] | 郑沁薇, 郝微微, 王凯强, 等. NLRP3炎症小体对炎症性肠病免疫机制影响的研究进展[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2019, 27(6): 6. |
| [61] | 张燕燕, 陈月桥, 裴 浩, 等. 从"肝与大肠相通"理论探讨NLRP3信号通路与急性肝衰竭肠道微生态的相关性[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2024, (4). |
| [62] | 蔡燕. NLRP3炎症小体在重症急性胰腺炎小鼠肠粘膜屏障功能障碍中的作用[D], 南昌大学, 2018. |
| [63] | Epstein AA, Janos SN, Menozzi L, et al. Subventricular zone stem cell niche injury is associated with intestinal perforation in preterm infants and predicts future motor impairment[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2024, 31(4): 467-83. e6. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2024.03.001 |
| [64] | 丁晓蕊. 萝卜硫素通过Nrf2抑制NLRP3/IL-1β轴减轻溃疡性结肠炎的炎症反应[D]. 滨州: 滨州医学院, 2019. |
| [65] | 许 骞, 刘力源, 张荣贤, 等. 基于mTOR/HIF-1α/VEGF信号通路探讨麦粒灸“足三里” 对高脂饮食大鼠血管损伤和氧化应激的影响[J]. 中国针灸, 2024, 44(4): 433-40. |
| [66] | Kim YW, Byzova TV. Oxidative stress in angiogenesis and vascular disease[J]. Blood, 2014, 123(5): 625-31. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-09-512749 |
| [67] | 苏世杰, 林东新, 刘壮壮,等. 基于AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α通路探讨泽泻汤改善高脂饮食诱导小鼠认知障碍的作用机制[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2023, 38(9): 4154-60. |
| [68] | 郑晓清, 魏 伟, 李惠红, 等. 泽泻汤对高热量饮食诱导认知功能损害模型小鼠的认知功能及脑组织神经炎症的影响[J]. 中医杂志, 2024, 65(4): 395-403. |
| [1] | Kun WANG, Haiyan ZUO, Jiaojiao ZHANG, Xin WU, Wenhui WANG, Shengbing WU, Meiqi ZHOU. Electroacupuncture improves myocardial injury in rats with acute myocardial ischemia by inhibiting HPA axis hyperactivity via modulating hippocampal glutamatergic system [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1599-1607. |
| [2] | Zhengyuan FAN, Zihan SHEN, Ya LI, Tingting SHEN, Gaofeng LI, Suyun LI. Protective effect of Bufei Yishen Formula against cigarette smoke extract-induced human bronchial epithelial cell damage and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1372-1379. |
| [3] | Haiyi ZHOU, Siyi HE, Ruifang HAN, Yongge GUAN, Lijuan DONG, Yang SONG. Moxibustion promotes endometrial repair in rats with thin endometrium by inhibiting the NLRP3/pyroptosis axis via upregulating miR-223-3p [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1380-1388. |
| [4] | Dongning TANG, Yunyun KANG, Wenjie HE, Qing XIA. Electroacupuncture combined with rehabilitation training improves neurological function of mice with cerebral ischemia by promoting astrocyte transdifferentiation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1434-1441. |
| [5] | Yuexuan ZHU, Zhangrui ZHU, Peng WU. Pentosan polysulfate alleviates cyclophosphamide-induced interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome in mice by modulating gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1270-1279. |
| [6] | Zhihua TIAN, Qingqing YANG, Xin CHEN, Fangfang ZHANG, Baimao ZHONG, Hong CAO. Spermine suppresses GBP5-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages to relieve vital organ injuries in neonatal mice with enterovirus 71 infection [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 901-910. |
| [7] | Anbang ZHANG, Xiuqi SUN, Bo PANG, Yuanhua WU, Jingyu SHI, Ning ZHANG, Tao YE. Electroacupuncture pretreatment alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting ferroptosis through the gut-brain axis and the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 911-920. |
| [8] | Fenlan BIAN, Shiyao NI, Peng ZHAO, Maonanxing QI, Bi TANG, Hongju WANG, Pinfang KANG, Jinjun LIU. Asiaticoside alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 977-985. |
| [9] | Xiaotao LIANG, Yifan XIONG, Xueqi LIU, Xiaoshan LIANG, Xiaoyu ZHU, Wei XIE. Huoxue Shufeng Granule alleviates central sensitization in chronic migraine mice via TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| [10] | Yalei SUN, Meng LUO, Changsheng GUO, Jing GAO, Kaiqi SU, Lidian CHEN, Xiaodong FENG. Amentoflavone alleviates acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting cell pyroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 692-701. |
| [11] | Zhengwang ZHU, Linlin WANG, Jinghan ZHAO, Ruixue MA, Yuchun YU, Qingchun CAI, Bing WANG, Pingsheng ZHU, Mingsan MIAO. Tuihuang Mixture improves α‑naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestasis in rats by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasomes via regulating farnesoid X receptor [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 718-724. |
| [12] | Jiachun LUO, Sodnomjamts Batzaya, Xuefeng GAO, Jingyu CHEN, Zhengying YU, Shasha XIONG, Hong CAO. Akkermansia muciniphila gavage improves gut-brain interaction disorders in gp120 transgenic mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 554-565. |
| [13] | Mingyuan LI, Wei ZHANG, Mengqing HUA. Bardoxolone methyl alleviates acute liver injury in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1662-1669. |
| [14] | Linyu XIAO, Ting DUAN, Yongsheng XIA, Yue CHEN, Yang SUN, Yibo XU, Lei XU, Xingzhou YAN, Jianguo HU. Linarin inhibits microglia activation-mediated neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis in mouse spinal cord injury by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1589-1598. |
| [15] | Huaixiang TAO, Jinguang LUO, Zhiyuan WEN, Genming YU, Xiao SU, Xinwei WANG, Han GUAN, Zhijun CHEN. High STING expression exacerbates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by regulating the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway and promoting inflammation and apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1345-1354. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||