Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (7): 1345-1354.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.07.14
Huaixiang TAO1,2( ), Jinguang LUO1,2, Zhiyuan WEN1, Genming YU1,2, Xiao SU1, Xinwei WANG1, Han GUAN1, Zhijun CHEN1(
), Jinguang LUO1,2, Zhiyuan WEN1, Genming YU1,2, Xiao SU1, Xinwei WANG1, Han GUAN1, Zhijun CHEN1( )
)
Received:2023-12-18
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-07-25
Contact:
Zhijun CHEN
E-mail:2240489402@qq.com;byczj@bbmc.edu.cn
Huaixiang TAO, Jinguang LUO, Zhiyuan WEN, Genming YU, Xiao SU, Xinwei WANG, Han GUAN, Zhijun CHEN. High STING expression exacerbates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by regulating the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway and promoting inflammation and apoptosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1345-1354.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.07.14
| Gene | Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| STING | F:GTCCCTTGCACATGGTGTTG |
| R:CAGGTCATGCTGTCGCCTAT | |
| KIM-1 | F:AGAAGACCCACAACTACAAGGC |
| R:TAGATGTTGGAGGAGTGGAGGT | |
| IL-1β | F:GCCTGTGTTTTCCTCCTTGC |
| R:TGCTGCCTAATGTCCCCTTG | |
| IL-6 | F:GTGGCTAAGGACCAAGACCAT |
| R:TCTGACCACAGTGAGGAATGTC | |
| TNF-α | F:AGCCGATGGGTTGTACCTTG |
| R:ATAGCAAATCGGCTGACGGT | |
| GAPDH | F:TGGAAAGCTGTGGCGTGAT |
| R:AGATCCACGACGGACACATT |
Tab.1 Primer sequence for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| STING | F:GTCCCTTGCACATGGTGTTG |
| R:CAGGTCATGCTGTCGCCTAT | |
| KIM-1 | F:AGAAGACCCACAACTACAAGGC |
| R:TAGATGTTGGAGGAGTGGAGGT | |
| IL-1β | F:GCCTGTGTTTTCCTCCTTGC |
| R:TGCTGCCTAATGTCCCCTTG | |
| IL-6 | F:GTGGCTAAGGACCAAGACCAT |
| R:TCTGACCACAGTGAGGAATGTC | |
| TNF-α | F:AGCCGATGGGTTGTACCTTG |
| R:ATAGCAAATCGGCTGACGGT | |
| GAPDH | F:TGGAAAGCTGTGGCGTGAT |
| R:AGATCCACGACGGACACATT |
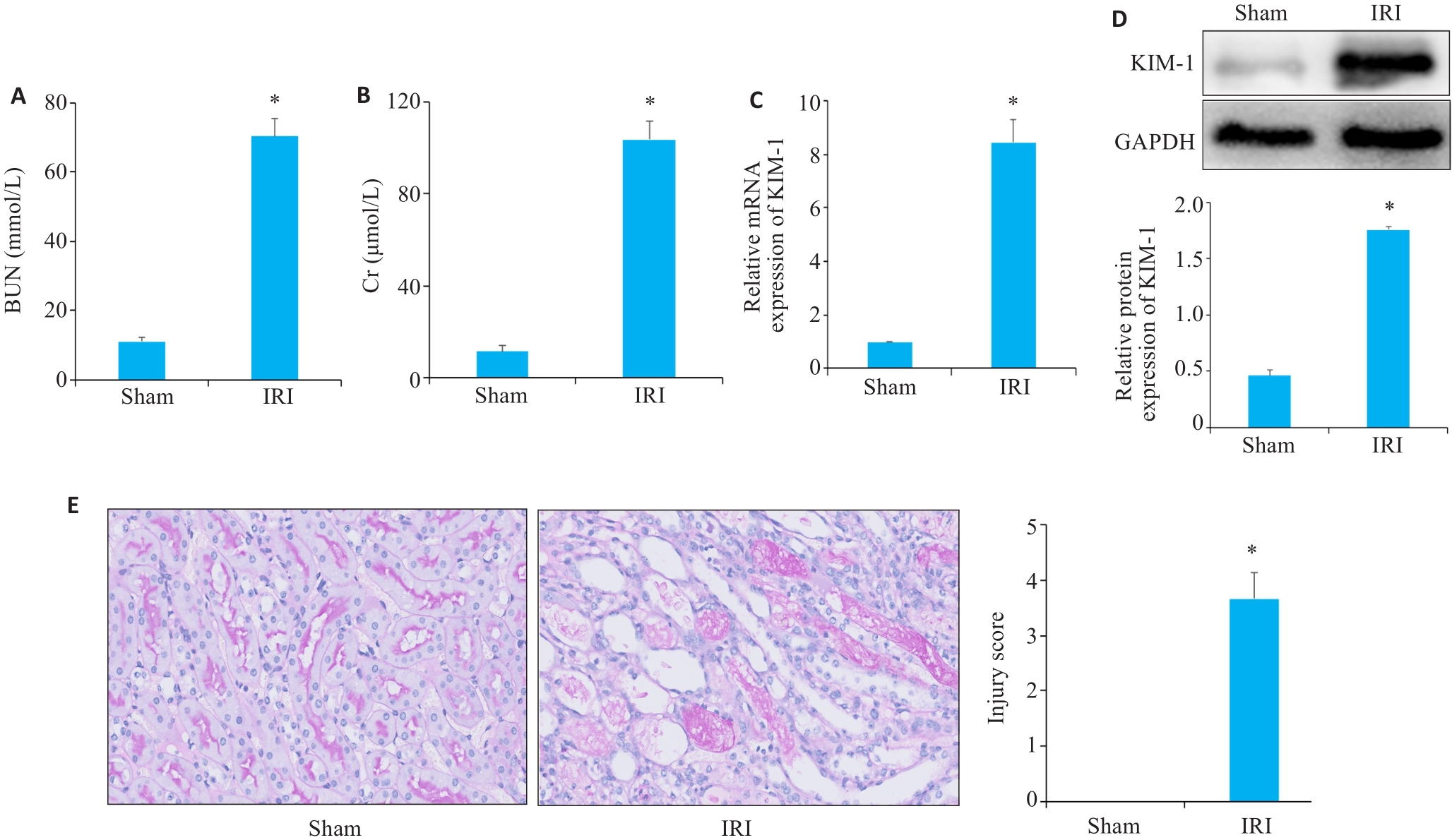
Fig.2 Serum biochemistry, Western blotting, RT-qPCR and PAS staining for assessing the effect of ischemia-reperfusion modeling. A, B: Serum BUN (A) and Cr (B) levels of the mice in sham and IRI group. C: RT-qPCR analysis of KIM-1 in Sham and IRI groups mice. D: Western blotting of KIM-1 in sham and IRI group. E: PAS staining of renal tissue from mice in sham and IRI groups (Original magnification: ×400). *P<0.05 vs Sham group.
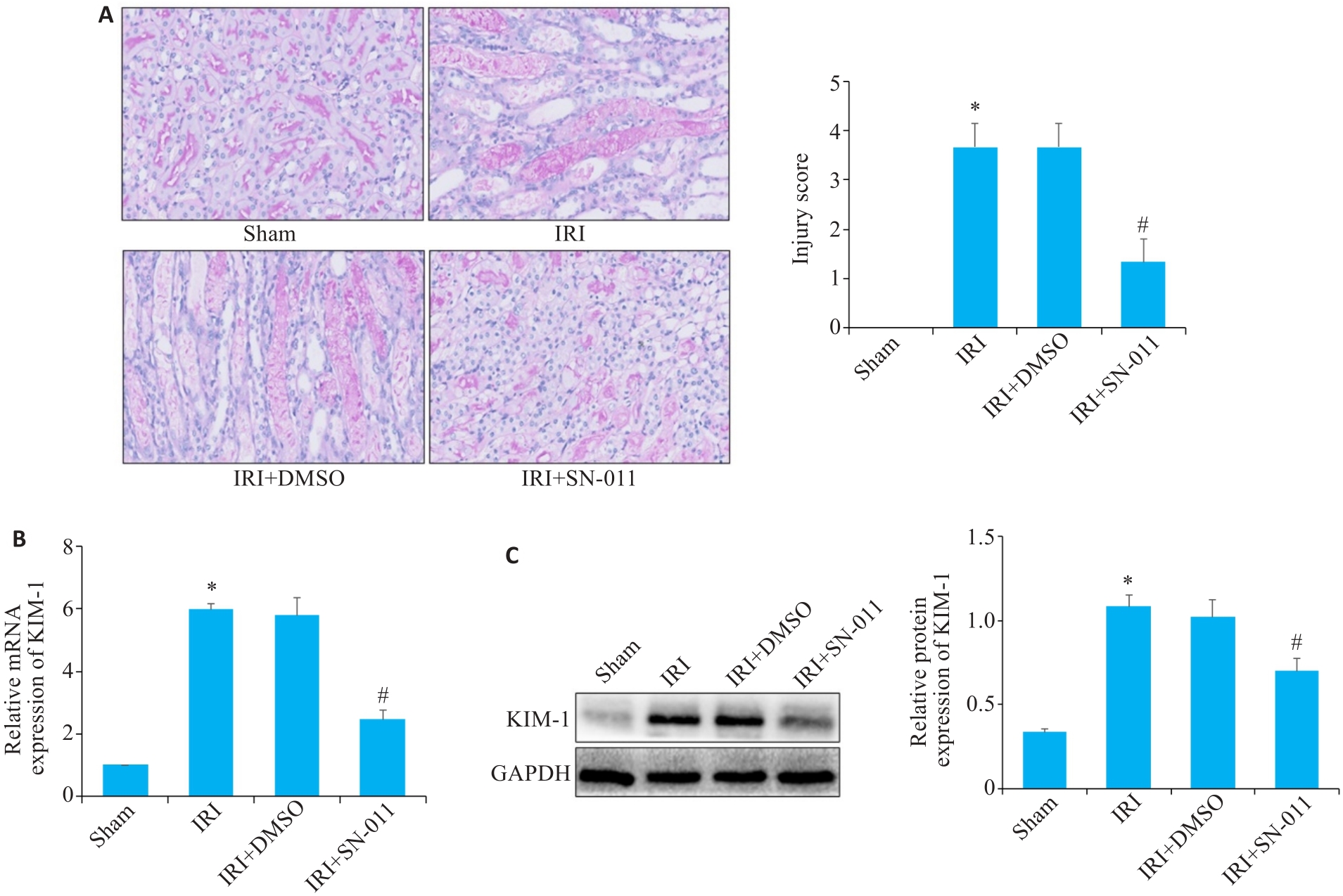
Fig.5 RT-qPCR, Western blotting and PAS staining for detecting renal tissue injury. A: PAS staining of kidney tissues from mice in the sham, IRI, IRI+DMSO and IRI+SN-011 groups (×400). B, C: RT-qPCR and Western blotting of the expressions of KIM-1 in sham, IRI, IRI+DMSO and IRI+SN-011 groups. *P<0.05 vs Sham; #P<0.05 vs IRI.
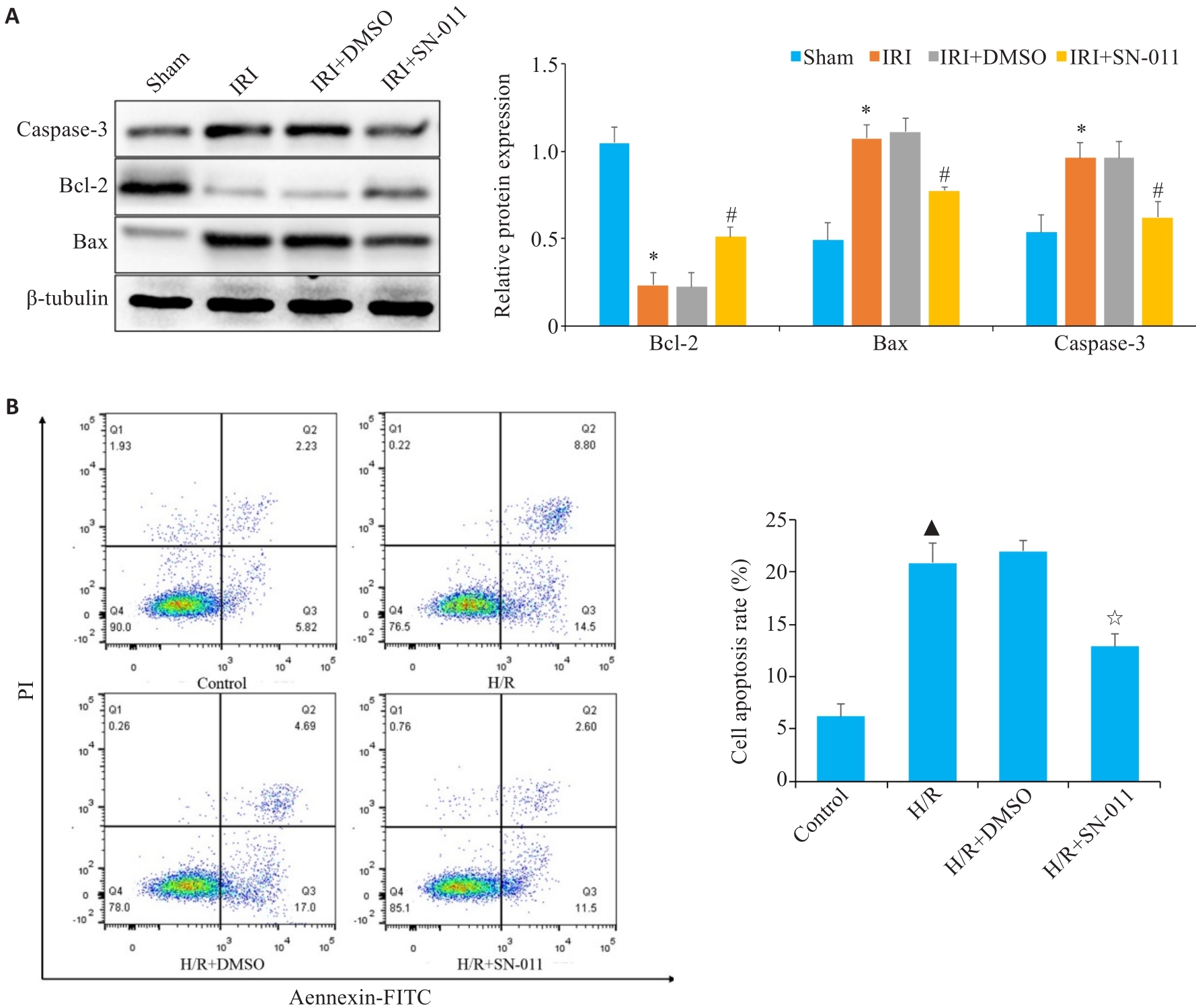
Fig.7 Cell apoptosis analyzed using Western blotting and flow cytometry. A: Western blotting of relative expression levels of caspase-3, Bcl-2 and Bax in mouse kidney tissue from sham, IRI, IRI+DMSO and IRI+SN-011 groups. B: Flow cytometric analysis of HK-2 cell apoptosis in control, H/R, H/R+DMSO, and H/R+SN-011 groups. *P<0.05 vs Sham; #P<0.05 vs IRI; ▲P<0.05 vs control; ☆P<0.05 vs H/R.
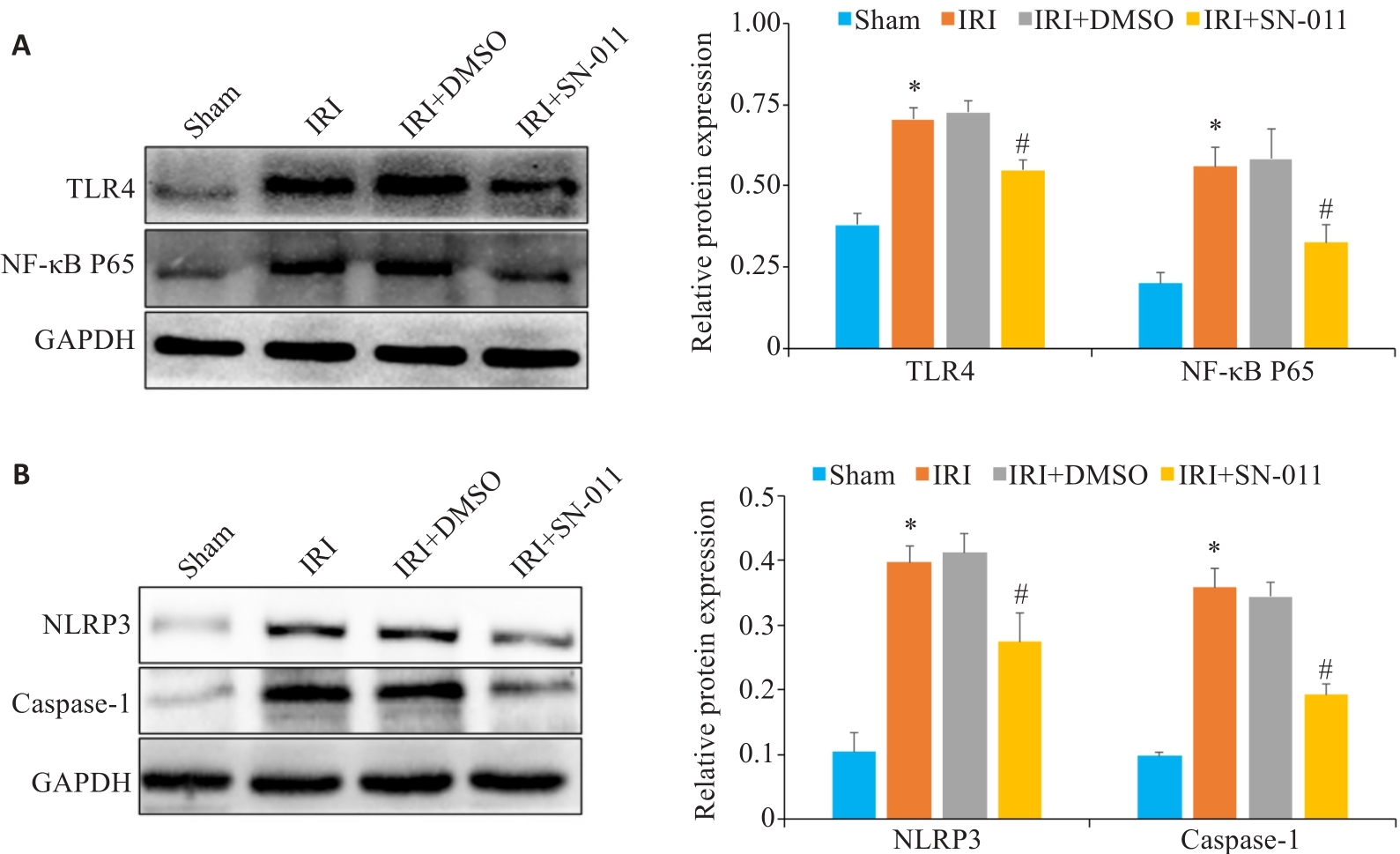
Fig.8 Western blotting for detecting TLR4, NF‑κB P65, NLRP3, and caspase-1 protein expressions in the renal tissue. A: Western blotting of TLR4 and NF-κB P65 in mouse kidney tissues from sham, IRI, IRI+DMSO and IRI+SN-011 groups. B: Western blotting of NLRP3 and caspase-1 in mice kidney tissue from the sham, IRI, IRI+DMSO and IRI+SN-011 groups. *P<0.05 vs Sham; #P<0.05 vs IRI.
| 1 | Hoste EAJ, Kellum JA, Selby NM, et al. Global epidemiology and outcomes of acute kidney injury[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2018, 14(10): 607-25. |
| 2 | Zuk A, Bonventre JV. Acute kidney injury[J]. Annu Rev Med, 2016, 67: 293-307. |
| 3 | Arai S, Kitada K, Yamazaki T, et al. Apoptosis inhibitor of macrophage protein enhances intraluminal debris clearance and ameliorates acute kidney injury in mice[J]. Nat Med, 2016, 22(2): 183-93. |
| 4 | Inagi R, Ishimoto Y, Nangaku M. Proteostasis in endoplasmic reticulum: new mechanisms in kidney disease[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2014, 10(7): 369-78. |
| 5 | Yan MJ, Tang CY, Ma ZW, et al. DNA damage response in nephrotoxic and ischemic kidney injury[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2016, 313: 104-8. |
| 6 | Malek M, Nematbakhsh M. Renal ischemia/reperfusion injury; from pathophysiology to treatment[J]. J Renal Inj Prev, 2015, 4(2): 20-7. |
| 7 | Fang R, Wang CG, Jiang QF, et al. NEMO-IKKβ are essential for IRF3 and NF-κB activation in the cGAS-STING pathway[J]. J Immunol, 2017, 199(9): 3222-33. |
| 8 | Fang R, Jiang QF, Guan YK, et al. Golgi apparatus-synthesized sulfated glycosaminoglycans mediate polymerization and activation of the cGAMP sensor STING[J]. Immunity, 2021, 54(5): 962-75.e8. |
| 9 | Ren P, Cao JL, Lin PL, et al. Molecular mechanism of luteolin regulating lipoxygenase pathway against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion injury in H9c2 cardiomyocytes based on molecular docking[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi, 2021, 46(21): 5665-73. |
| 10 | Bi R, Yang YL, Liao HW, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis induces an inflammatory response via the cGAS-STING signaling pathway in a periodontitis mouse model[J]. Front Microbiol, 2023, 14: 1183415. |
| 11 | Pressly JD, Park F. DNA repair in ischemic acute kidney injury[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2017, 312(4): F551-5. |
| 12 | Hu HL, Zou C. Mesenchymal stem cells in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury: biological and therapeutic perspectives[J]. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther, 2017, 12(3): 183-7. |
| 13 | Inagi R. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the kidney as a novel mediator of kidney injury[J]. Nephron Exp Nephrol, 2009, 112(1): e1-9. |
| 14 | Cao Q, Wang YP, Niu ZG, et al. Potentiating tissue-resident type 2 innate lymphoid cells by IL-33 to prevent renal ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2018, 29(3): 961-76. |
| 15 | Havasi A, Borkan SC. Apoptosis and acute kidney injury[J]. Kidney Int, 2011, 80(1): 29-40. |
| 16 | Yang DH, Tang M, Zhang MM, et al. Downregulation of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 4 protects against kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Kidney Int, 2023, 103(4): 719-34. |
| 17 | Li XR, Liao J, Su XJ, et al. Human urine-derived stem cells protect against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat model via exosomal miR-146a-5p which targets IRAK1 [J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(21): 9561-78. |
| 18 | Wang J, Xiong MR, Fan Y, et al. Mecp2 protects kidney from ischemia-reperfusion injury through transcriptional repressing IL-6/STAT3 signaling[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12(8): 3896-910. |
| 19 | van Timmeren MM, van den Heuvel MC, Bailly V, et al. Tubular kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) in human renal disease[J]. J Pathol, 2007, 212(2): 209-17. |
| 20 | Gkirtzimanaki K, Kabrani E, Nikoleri D, et al. IFNα impairs autophagic degradation of mtDNA promoting autoreactivity of SLE monocytes in a STING-dependent fashion[J]. Cell Rep, 2018, 25(4): 921-33.e5. |
| 21 | Gao YP, Zhang NN, Zeng ZH, et al. LncRNA PCAT1 activates SOX2 and suppresses radioimmune responses via regulating cGAS/STING signalling in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2022, 12(4): e792. |
| 22 | Li X, Liu YJ, Wang Y, et al. Epoxy triglyceride enhances intestinal permeability via caspase-1/NLRP3/GSDMD and cGAS-STING pathways in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mice[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2023, 71(10): 4371-81. |
| 23 | Wu JJ, Zhao L, Hu HG, et al. Agonists and inhibitors of the STING pathway: potential agents for immunotherapy[J]. Med Res Rev, 2020, 40(3): 1117-41. |
| 24 | Barber GN. STING: infection, inflammation and cancer[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2015, 15(12): 760-70. |
| 25 | Lu L, Zhou HM, Ni M, et al. Innate immune regulations and liver ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Transplantation, 2016, 100(12): 2601-10. |
| 26 | DeWolf SE, Kasimsetty SG, Hawkes AA, et al. DAMPs released from injured renal tubular epithelial cells activate innate immune signals in healthy renal tubular epithelial cells[J]. Transplantation, 2022, 106(8): 1589-99. |
| 27 | Raup-Konsavage WM, Wang YM, Wang WW, et al. Neutrophil peptidyl arginine deiminase-4 has a pivotal role in ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury[J]. Kidney Int, 2018, 93(2): 365-74. |
| 28 | Salvadori M, Rosso G, Bertoni E. Update on ischemia-reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation: Pathogenesis and treatment[J]. World J Transplant, 2015, 5(2): 52-67. |
| 29 | Liu CH, Wang QD, Niu L. Sufentanil inhibits Pin1 to attenuate renal tubular epithelial cell ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating the PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 pathway[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2023, 55(8): 1903-16. |
| 30 | Wu B, Xu MM, Fan C, et al. STING inhibitor ameliorates LPS-induced ALI by preventing vascular endothelial cells-mediated immune cells chemotaxis and adhesion[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2022, 43(8): 2055-66. |
| 31 | Liu R, Li JY, Shao JC, et al. Innate immune response orchestrates phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetases to support DNA repair[J]. Cell Metab, 2021, 33(10): 2076-89.e9. |
| 32 | Yang B, Li X, Fu Y, et al. MEK inhibition remodels the immune landscape of mutant KRAS tumors to overcome resistance to PARP and immune checkpoint inhibitors[J]. Cancer Res, 2021, 81(10): 2714-29. |
| 33 | Zhang YN, Dong YL, Hao WP, et al. Increased cGAS/STING signaling components in patients with Mooren's ulcer[J]. Int J Ophthalmol, 2021, 14(11): 1660-5. |
| 34 | Hong Z, Mei JH, Li CH, et al. STING inhibitors target the cyclic dinucleotide binding pocket[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2021, 118(24): e2105465118. |
| 35 | Diao FF, Bai J, Jiang CL, et al. The papain-like protease of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus impedes STING translocation from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus by deubiquitinating STIM1[J]. J Virol, 2023, 97(4): e0018823. |
| 36 | Yang BX, Xie XR, Wu ZY, et al. DNA damage-mediated cellular senescence promotes hand-foot syndrome that can be relieved by thymidine prodrug[J]. Genes Dis, 2022, 10(6): 2557-71. |
| 37 | Ablasser A, Chen ZJ. cGAS in action: expanding roles in immunity and inflammation[J]. Science, 2019, 363(6431): eaat8657. |
| 38 | Gulen MF, Koch U, Haag SM, et al. Signalling strength determines proapoptotic functions of STING[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8(1): 427. |
| 39 | Lehnardt S, Massillon L, Follett P, et al. Activation of innate immunity in the CNS triggers neurodegeneration through a Toll-like receptor 4-dependent pathway[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2003, 100(14): 8514-9. |
| 40 | Wang L, Yang JW, Lin LT, et al. Acupuncture attenuates inflammation in microglia of vascular dementia rats by inhibiting miR-93-mediated TLR4/MyD88/NF‑κB signaling pathway[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2020, 2020: 8253904. |
| 41 | Zhang NX, Guan C, Liu ZY, et al. Calycosin attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing NF‑κB mediated inflammation via PPARγ/EGR1 pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 970616. |
| 42 | Alaaeldin R, Bakkar SM, Mohyeldin RH, et al. Azilsartan modulates HMGB1/NF-κB/p38/ERK1/2/JNK and apoptosis pathways during renal ischemia reperfusion injury[J]. Cells, 2023, 12(1): 185. |
| 43 | Ding HS, Huang Y, Qu JF, et al. Panaxynol ameliorates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing NLRP3-induced pyroptosis and apoptosis via HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB axis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 121: 110222. |
| 44 | Liu YY, Lei ZL, Chai H, et al. Salidroside alleviates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury during liver transplant in rat through regulating TLR-4/NF‑κB/NLRP3 inflammatory pathway[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 13973. |
| 45 | Li N, Zhou H, Wu HM, et al. STING-IRF3 contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction, inflammation, apoptosis and pyroptosis by activating NLRP3[J]. Redox Biol, 2019, 24: 101215. |
| [1] | Wei ZHANG, Mengmeng DENG, Yao ZENG, Chenfei LIU, Feifei SHANG, Wenhao XU, Haoyi JIANG, Fengchao WANG, Yanqing YANG. 2,6-dimethoxy-1,4-benzoquinone alleviates septic shock in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1024-1032. |
| [2] | Li LI, Mengzhe WANG, Saisai LIU, Xiaonan ZHANG, Jie CHEN, Weiting TAO, Shai LI, Zhiwen QING, Quanfang TAO, Yi LIU, Li Huang, Shidi ZHAO. Soy isoflavones alleviates calcium overload in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion by inhibiting the Wnt/Ca2+ signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1048-1058. |
| [3] | Zhixian REN, Beixian ZHOU, Linxin WANG, Jing LI, Rongping ZHANG, Xiping PAN. Inhibitory effect of 5-hydroxy-6,7-dimethoxyflavone on H1N1 influenza virus-induced ferroptosis and inflammation in A549 cells and its possible mechanisms [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1070-1078. |
| [4] | Jie CHEN, Chenxu LIU, Chun WANG, Li LI, Weiting TAO, Jingru XUN, Honghui TANG, Li HUANG. Exogenous leptin improves cerebral ischemia-reperfusion-induced glutamate excitotoxic injury in mice by up-regulating GLT-1 and GLAST expression in astrocytes [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1079-1087. |
| [5] | CAO Jiafan, SUN Yue, DING Xin, LI Shengwen, CHEN Bo, LAN Tian. Arbutin ameliorates liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting macrophage recruitment and regulating the Akt/NF-κB and Smad signaling pathways [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(4): 652-659. |
| [6] | XI Jin, ZHANG Min, ZHANG Yongyu, ZHANG Chen, ZHANG Yulu, WANG Rui, SHEN Lin, LI Jing, SONG Xue. Upregulating KLF11 ameliorates intestinal inflammation in mice with 2, 4, 6-trinitrobenesulfonic acid-induced colitis by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(4): 765-772. |
| [7] | CHEN Guodong, LUO Suxin. Colchicine alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by activating AMPK [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 226-235. |
| [8] | FANG Shangping, SUN Renke, SU Hui, ZHAI Kecheng, XIANG Yu, GAO Yangmengna, GUO Wenjun. Chlorogenic acid alleviates acute kidney injury in septic mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasomes and the caspase-1 canonical pyroptosis pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 317-323. |
| [9] | GUI Jianjun, SUN Xiaodong, WEN Shu, LIU Xin, QIN Bingqing, SANG Ming. Resveratrol protects dopaminergic neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease by regulating the gut-brain axis via inhibiting the TLR4 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 270-279. |
| [10] | LING Xuguang, XU Wenwen, PANG Guanlai, HONG Xuxing, LIU Fengqin, LI Yang. Tea polyphenols ameliorates acute lung injury in septic mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasomes [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 381-386. |
| [11] | WU Guangyang, SONG Tianli, TANG Lang, WANG Yiming, LIU Xu, HUANG Sheng. Total saponins of Panax japonicus alleviates CCl4-induced acute liver injury in rats by regulating the PI3K/AktNF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 244-251. |
| [12] | WU Ruojie, LIU Rui, ZHANG Yisu, LI Xiaohong. Parecoxib sodium down-regulates CXCL8-CXCR1/2 to improve inflammatory microenvironment and promote patient recovery following laparoscopic radical resection of rectal cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 363-369. |
| [13] | XU Xiaohui, FENG Jinmei, LUO Ying, HE Xinyu, ZANG Jinbao, HUANG Daochao. Adeno-associated virus-mediated hepatocyte-specific NDUFA13 overexpression protects against CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting hepatic NLRP3 activation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 201-209. |
| [14] | SUN Xiaopeng, SHI Hang, ZHANG Lei, LIU Zhong, LI Kewei, QIAN Lingling, ZHU Xingyu, YANG Kangjia, FU Qiang, DING Hua. Exosomes from ectoderm mesenchymal stem cells inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial M1 polarization and promotes survival of H2O2-exposed PC12 cells by suppressing inflammatory response and oxidative stress [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 119-128. |
| [15] | XU Guiling, GONG Zhaoqian, WANG Junrao, MA Yanyan, XU Maosheng, CHEN Meijia, HU Dapeng, LIANG Jianpeng, ZHAO Wengqu, ZHAO Haijin. Effects of type 2 inflammation on bronchodilator responsiveness of large and small airways in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 93-99. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||