Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1048-1058.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.06.05
Li LI1,2( ), Mengzhe WANG1,2, Saisai LIU1,2, Xiaonan ZHANG1,2, Jie CHEN1,2, Weiting TAO1,2, Shai LI2,4, Zhiwen QING2,3, Quanfang TAO2,3, Yi LIU2,3, Li Huang1,2(
), Mengzhe WANG1,2, Saisai LIU1,2, Xiaonan ZHANG1,2, Jie CHEN1,2, Weiting TAO1,2, Shai LI2,4, Zhiwen QING2,3, Quanfang TAO2,3, Yi LIU2,3, Li Huang1,2( ), Shidi ZHAO1,2(
), Shidi ZHAO1,2( )
)
Received:2023-11-02
Online:2024-06-20
Published:2024-07-01
Contact:
Li Huang, Shidi ZHAO
E-mail:19556126120@163.com;zi05@163.com;zhsdi@126.com
Li LI, Mengzhe WANG, Saisai LIU, Xiaonan ZHANG, Jie CHEN, Weiting TAO, Shai LI, Zhiwen QING, Quanfang TAO, Yi LIU, Li Huang, Shidi ZHAO. Soy isoflavones alleviates calcium overload in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion by inhibiting the Wnt/Ca2+ signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1048-1058.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.06.05
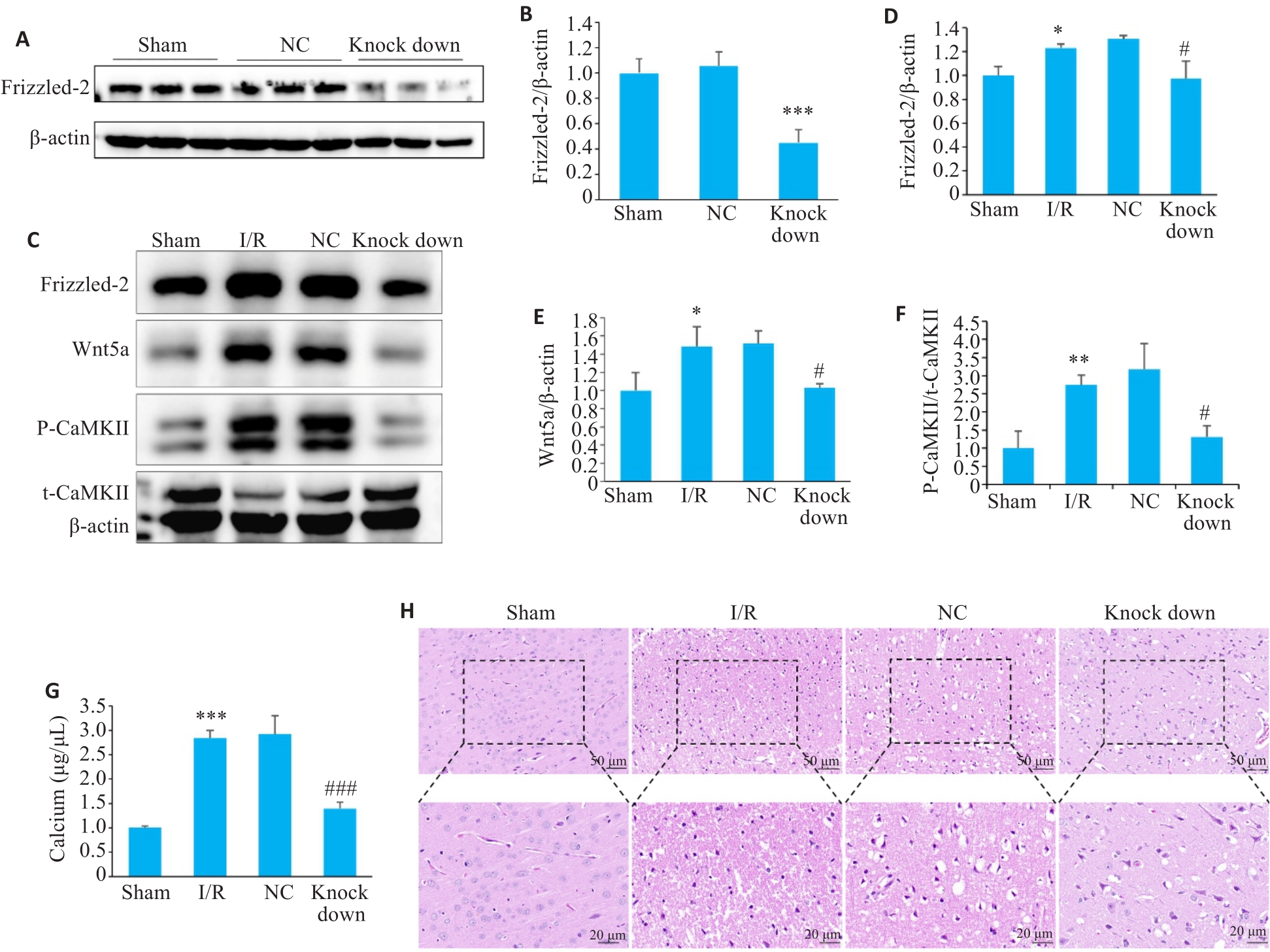
Fig.1 Effect of inhibition of Wnt/Ca2+ signaling pathway on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury in rats. A, B: Expression of Frizzled-2 in the brain tissue of sham-operated rats detected by Western blotting (n=3). C-F: Western blotting for detecting expressions of Frizzled-2, Wnt5a and P-CaMK II in the brain tissues of rats in each group (n=3). G: Ca2+ level in the brain tissues of the rats (n=6). H: HE staining of the brain tissues of the rats. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Sham group; #P<0.05, ###P<0.001 vs I/R group.
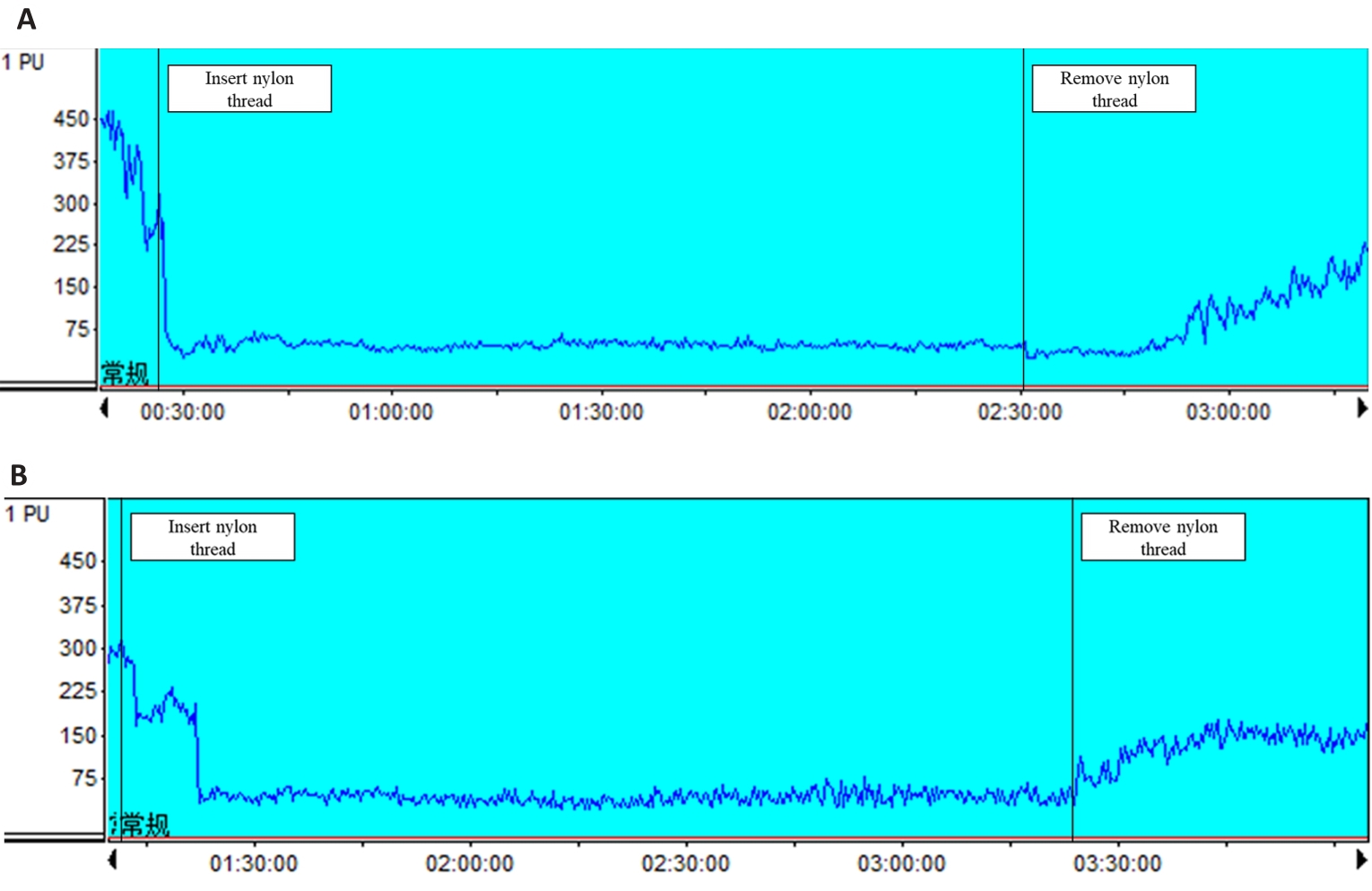
Fig.2 Dynamic changes of regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF). A: Changes of rCBF in I/R group. B: Changes of rCBF in soy isoflavones (SI)-pretreated group.
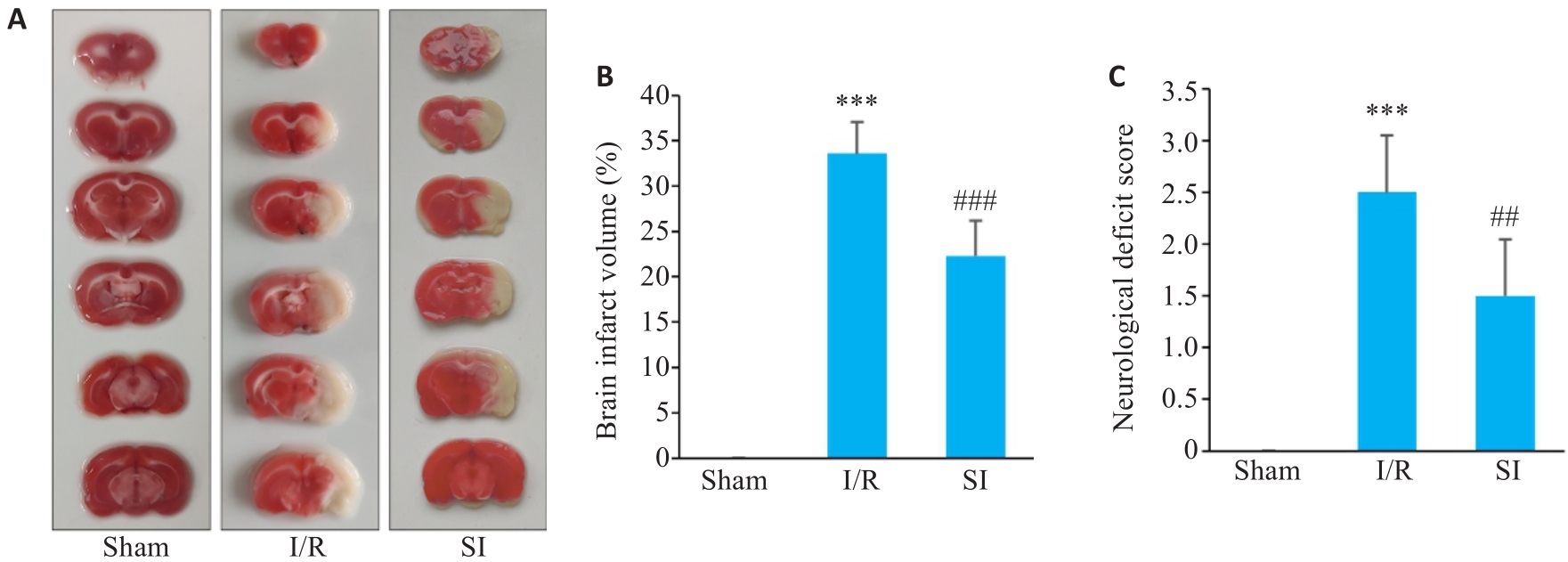
Fig.3 Brain infarct volume and neurological deficit scores of the rats with sham operation, cerebral I/R injury and soy isoflavones (SI) pretreatment. A, B: Brain infarct volume (n=5). C: Neurological deficit scores (n=6). ***P<0.001 vs Sham group; ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs I/R group.
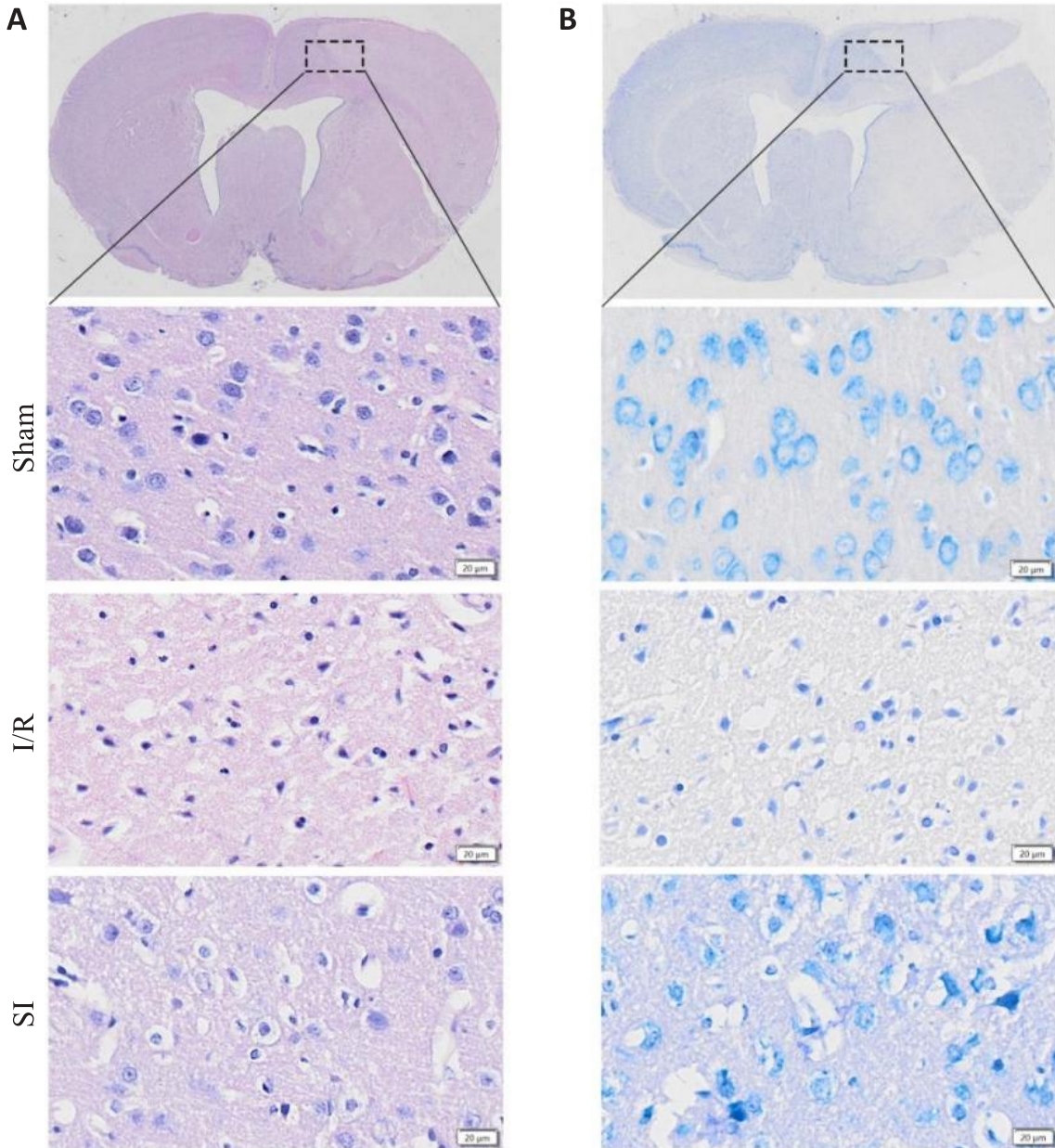
Fig.4 HE staining (A) and Nissl staining (B) of the rats with sham operation, cerebral I/R injury and soy isoflavones (SI) pretreatment before modeling (scale bar=20 μm).
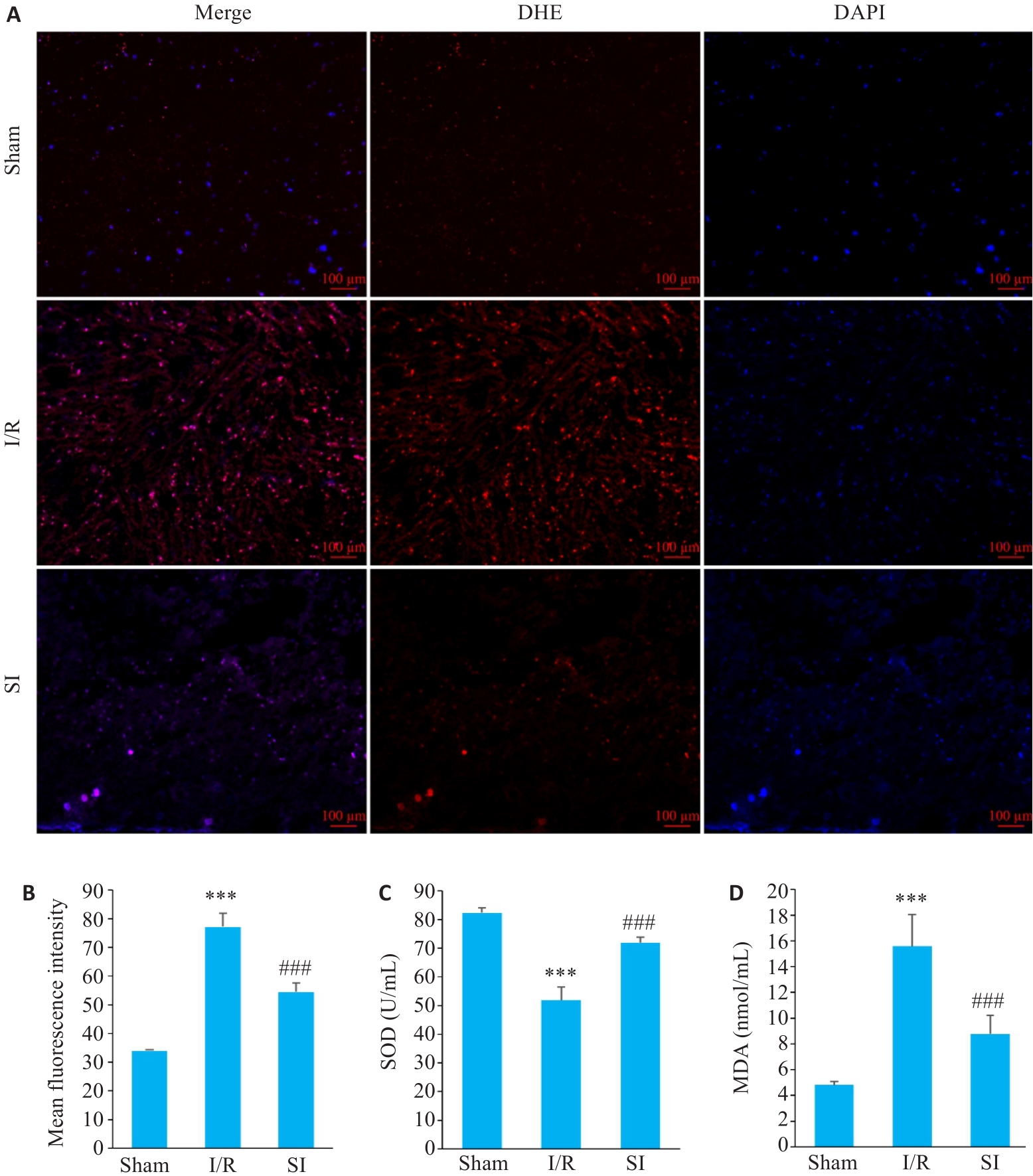
Fig.6 Changes of oxidative stress level in the brain tissue of the rats in the 3 groups. A, B: Immunofluorescence assay for detecting ROS level in the brain tissues (n=3). C: SOD activity in the brain tissue (n=6); D: Content of MDA in the brain tissue (n=6). ***P<0.001 vs Sham group; ###P<0.001 vs I/R group.

Fig.8 Western blotting (A) and immunohistochemistry (B, original magnification:×400) for detecting protein expression of Wnt5a, Frizzled-2 and P-CaMK II in the brain tissues of the rats in the 3 groups. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Sham group; #P<0.05 vs I/R group.
| 1 | Zhang XX, Wang XB, Xue ZW, et al. Prevention properties on cerebral ischemia reperfusion of medicine food homologous Dioscorea yam-derived diosgenin based on mediation of potential targets[J]. Food Chem, 2021, 345: 128672. |
| 2 | Poh L, Kang SW, Baik SH, et al. Evidence that NLRC4 inflammasome mediates apoptotic and pyroptotic microglial death following ischemic stroke[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2019, 75: 34-47. |
| 3 | Lou Z, Wang AP, Duan XM, et al. Upregulation of NOX2 and NOX4 mediated by TGF‑β signaling pathway exacerbates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion oxidative stress injury[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 46(5): 2103-13. |
| 4 | Stegner D, Klaus V, Nieswandt B. Platelets as modulators of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2505. |
| 5 | Lipton P. Ischemic cell death in brain neurons[J]. Physiol Rev, 1999, 79(4): 1431-568. |
| 6 | Martin HGS, Wang YT. Blocking the deadly effects of the NMDA receptor in stroke[J]. Cell, 2010, 140(2): 174-6. |
| 7 | Han YL, Li XW, Yang L, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury due to inhibition of NOX2-mediated calcium homeostasis dysregulation in mice[J]. J Ginseng Res, 2022, 46(4): 515-25. |
| 8 | Xu ZX, Xu BY, Xia T, et al. Relationship between intracellular Ca²⁺ and ROS during fluoride-induced injury in SH-SY5Y cells[J]. Environ Toxicol, 2013, 28(6): 307-12. |
| 9 | Mäkitie RE, Haanpää M, Valta H, et al. Skeletal characteristics of WNT1 osteoporosis in children and young adults[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2016, 31(9): 1734-42. |
| 10 | Li N, Wu XT, Zhuang W, et al. Soy and isoflavone consumption and multiple health outcomes: umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies and randomized trials in humans[J]. Mol Nutr Food Res, 2020, 64(4): e1900751. |
| 11 | Applegate CC, Rowles JL, Ranard KM, et al. Soy consumption and the risk of prostate cancer: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Nutrients, 2018, 10(1): 40. |
| 12 | 赵士弟, 陈 耀, 姜丽娜, 等. 大豆异黄酮对脑缺血/再灌注诱导的线粒体损伤和脑细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2014, 30(12): 2172-8. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2014.12.010 |
| 13 | 赵士弟, 陈 耀, 董银凤, 等. 大豆异黄酮对全脑缺血/再灌注大鼠海马神经细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报: 医学版, 2015, 35(4): 521-9. |
| 14 | 李 晒, 李 丽, 闵思敏, 等. 大豆异黄酮可减轻大鼠脑缺血/再灌注损伤: 基于抑制铁死亡及炎症级联反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 323-31. |
| 15 | Kühl M, Sheldahl LC, Malbon CC, et al. Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II is stimulated by Wnt and Frizzled homologs and promotes ventral cell fates in Xenopus [J]. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275(17): 12701-11. |
| 16 | Brossia-Root LJ, Cotroneo TM, Hish G. Anesthesia and Analgesia for Research Animals[M]. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2019: 13-34. |
| 17 | Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats[J]. Stroke, 1989, 20(1): 84-91. |
| 18 | Paxinos G.《大鼠脑立体定位图谱》[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2005. |
| 19 | Kristián T, Siesjö BK. Calcium in ischemic cell death[J]. Stroke, 1998, 29(3): 705-18. |
| 20 | Al-Mufti F, Amuluru K, Roth W, et al. Cerebral ischemic reperfusion injury following recanalization of large vessel occlusions[J]. Neurosurgery, 2018, 82(6): 781-9. |
| 21 | Soares ROS, Losada DM, Jordani MC, et al. Ischemia/reperfusion injury revisited: an overview of the latest pharmacological strategies[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(20): 5034. |
| 22 | Mao R, Zong NN, Hu YJ, et al. Neuronal death mechanisms and therapeutic strategy in ischemic stroke[J]. Neurosci Bull, 2022, 38(10): 1229-47. |
| 23 | Manzanero S, Santro T, Arumugam TV. Neuronal oxidative stress in acute ischemic stroke: sources and contribution to cell injury[J]. Neurochem Int, 2013, 62(5): 712-8. |
| 24 | Wang YL, Tian YX, Zhao JX, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on gene expression in calcium signaling pathway in hippocampal cells in mice with cerebral ischemia reperfusion[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2017, 37(2): 252-60. |
| 25 | Hu Y, Deng H, Xu SX, et al. MicroRNAs regulate mitochondrial function in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2015, 16(10): 24895-917. |
| 26 | Schanne FA, Kane AB, Young EE, et al. Calcium dependence of toxic cell death: a final common pathway[J]. Science, 1979, 206(4419): 700-2. |
| 27 | Uddin MS, Kabir MT. Emerging signal regulating potential of genistein against Alzheimer's disease: a promising molecule of interest[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2019, 7: 197. |
| 28 | Chen LR, Chen KH. Utilization of isoflavones in soybeans for women with menopausal syndrome: an overview[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(6): 3212. |
| 29 | Basak K, Manjunatha M, Dutta PK. Review of laser speckle-based analysis in medical imaging[J]. Med Biol Eng Comput, 2012, 50(6): 547-58. |
| 30 | 刘 宇, 孟 然, 闫 峰, 等. 激光多普勒血流仪评价活体大鼠大脑中动脉栓塞模型成功的可行性分析[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2011, 27(3): 620-4. |
| 31 | Shin S, Fu JL, Shin WK, et al. Association of food groups and dietary pattern with breast cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Nutr, 2023, 42(3): 282-97. |
| 32 | Uifălean A, Schneider S, Ionescu C, et al. Soy isoflavones and breast cancer cell lines: molecular mechanisms and future perspectives[J]. Molecules, 2015, 21(1): E13. |
| 33 | Sahin I, Bilir B, Ali S, et al. Soy isoflavones in integrative oncology: increased efficacy and decreased toxicity of cancer therapy[J]. Integr Cancer Ther, 2019, 18: 1534735419835310. |
| 34 | Castelló-Ruiz M, Torregrosa G, Burguete MC, et al. Soy-derived phytoestrogens as preventive and acute neuroprotectors in experimental ischemic stroke: influence of rat strain[J]. Phytomedicine, 2011, 18(6): 513-5. |
| 35 | Zins K, Schäfer R, Paulus P, et al. Frizzled2 signaling regulates growth of high-risk neuroblastomas by interfering with β‑catenin-dependent and β‑catenin-independent signaling pathways[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(29): 46187-202. |
| 36 | Zhao CH, Bu XM, Wang W, et al. GEC-derived SFRP5 inhibits Wnt5a-induced macrophage chemotaxis and activation[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(1): e85058. |
| 37 | Maeda K, Takahashi N, Kobayashi Y. Roles of Wnt signals in bone resorption during physiological and pathological states[J]. J Mol Med, 2013, 91(1): 15-23. |
| 38 | 刘 丽, 龙鼎新. Wnt信号通路在神经系统发育中的作用研究进展[J]. 中南医学科学杂志, 2017, 45(3): 303-6. |
| 39 | Wang RY, Wang M, He SB, et al. Targeting calcium homeostasis in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: an overview of regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic reagents[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 872. |
| 40 | Pittas K, Vrachatis DA, Angelidis C, et al. The role of calcium handling mechanisms in reperfusion injury[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2018, 24(34): 4077-89. |
| 41 | Zhou SS, He F, Chen AH, et al. Suppression of rat Frizzled-2 attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced Ca2+ accumulation in rat H9c2 cells[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2012, 318(13): 1480-91. |
| 42 | Hu X, Zhou CJ, He GL, et al. Inhibition of Frizzled-2 by small interfering RNA protects rat hepatic BRL-3A cells against cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by Hypoxia/Reoxygenation[J]. Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 43(3): 107-16. |
| 43 | Niu LJ, Xu RX, Zhang P, et al. Suppression of Frizzled-2-mediated Wnt/Ca²⁺ signaling significantly attenuates intracellular calcium accumulation in vitro and in a rat model of traumatic brain injury[J]. Neuroscience, 2012, 213: 19-28. |
| 44 | Xu XF, Zhang MF, Xu FY, et al. Wnt signaling in breast cancer: biological mechanisms, challenges and opportunities[J]. Mol Cancer, 2020, 19(1): 165. |
| 45 | Wu QJ, Tymianski M. Targeting NMDA receptors in stroke: new hope in neuroprotection[J]. Mol Brain, 2018, 11(1): 15. |
| 46 | Lai TW, Zhang S, Wang YT. Excitotoxicity and stroke: identifying novel targets for neuroprotection[J]. Prog Neurobiol, 2014, 115: 157-88. |
| [1] | SUN Wei, CHEN Ping, TANG Xiaohang, GU Yingmin, TIAN Xuesong. An improved 4-vessel intermittent occlusion method for establishing rat models of global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(7): 1194-1203. |
| [2] | CAO Tianran, LIU Qingfang, PAN Meimin, ZHANG Xuehong. LncRNA SNHG8 inhibits miR-494-3p expression to alleviate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(12): 2015-2022. |
| [3] | . DJ-1 alleviates oxidative stress injury by activating the Nrf2 pathway in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(5): 679-686. |
| [4] | . Mitochondrial calcium overload in the masseter muscle of rats with occlusal interference: ionic changes and regulation by calmodulin kinase II [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2018, 38(06): 755-. |
| [5] | . Effect of 2,3-butanedione monoxime on calcium paradox-induced heart injury in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2016, 36(05): 633-. |
| [6] | LIU Zhao-hui, MA Dong-liang, JIN Hui, MA Yan-bing, HU Hai-tao Department of Anatomy and Histology-Embryology, Key Laboratory of Environment and Genes Related of Disease, Ministry of Education, School of Medicine, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710061, China. Protective effect of adeno-associated viral vector-mediated expression of human brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rat neurons against beta-amyloid-induced Alzheimer’s disease in vitro [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2006, 26(10): 1388-1393. |
| [7] | MA Ren-qiang1, CHEN Jian-wen1, PANG Jian-xin2, LAN Xiu-jian3, QIU Can-hua3. Protective effects of total paeony glycoside against global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in gerbils [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2005, 25(04): 471-473. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||