Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1023-1030.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.05.15
Guanglü HE1,3( ), Wanyu CHU1,3, Yan LI1,3, Xin SHENG1,3, Hao LUO3, Aiping XU3, Mingjie BIAN3, Huanhuan ZHANG2, Mengya WANG3(
), Wanyu CHU1,3, Yan LI1,3, Xin SHENG1,3, Hao LUO3, Aiping XU3, Mingjie BIAN3, Huanhuan ZHANG2, Mengya WANG3( ), Chao ZHENG1(
), Chao ZHENG1( )
)
Received:2024-07-20
Online:2025-05-20
Published:2025-05-23
Contact:
Mengya WANG, Chao ZHENG
E-mail:1596104580@qq.com;wangmy@wnmc.edu.cn;chaozheng10@fudan.edu.cn
Supported by:Guanglü HE, Wanyu CHU, Yan LI, Xin SHENG, Hao LUO, Aiping XU, Mingjie BIAN, Huanhuan ZHANG, Mengya WANG, Chao ZHENG. Orexin-A promotes motor function recovery of rats with spinal cord injury by regulating ionotropic glutamate receptors[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 1023-1030.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.05.15
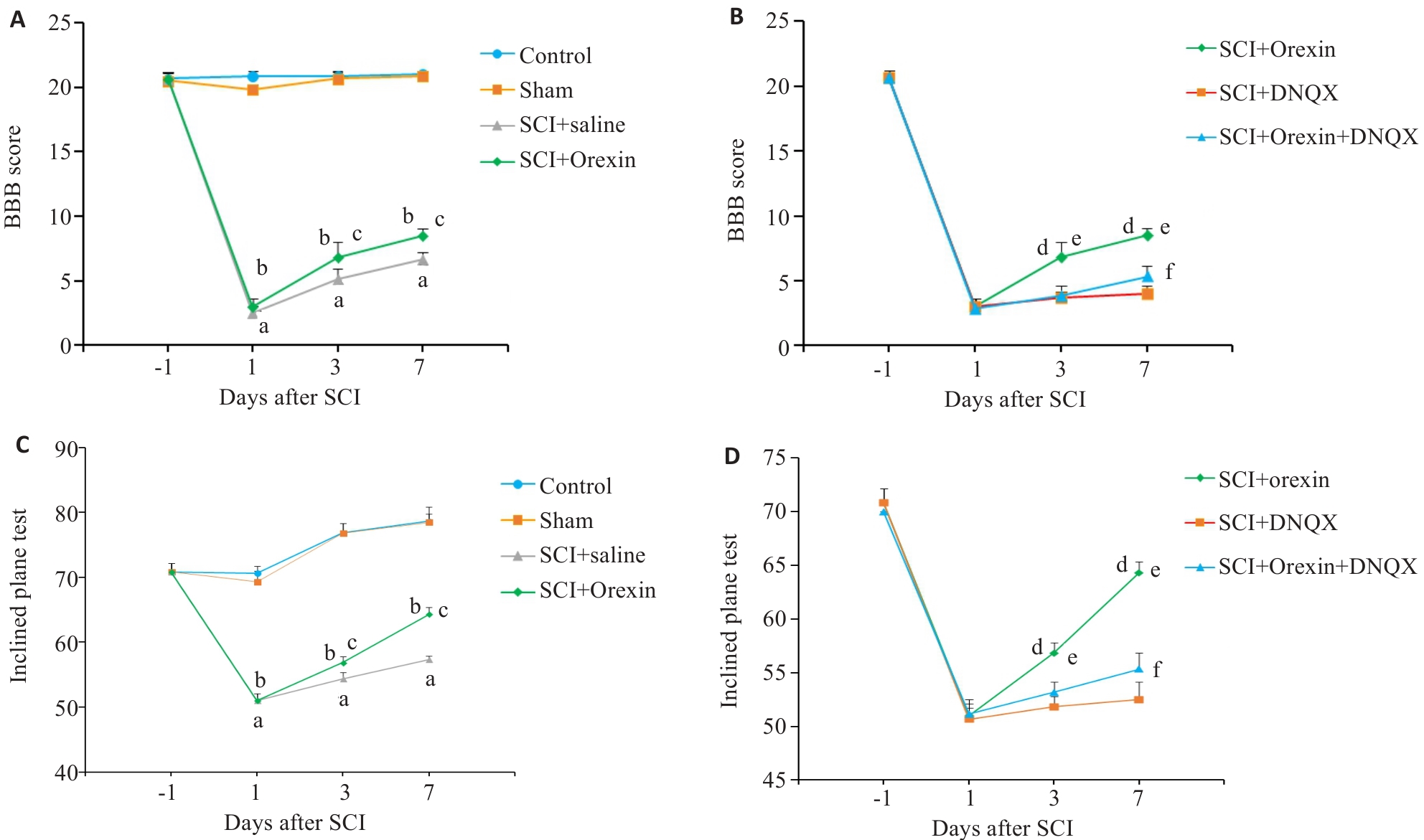
Fig.1 Results of behavioral test of the rats in different groups. A, B: BBB scores in the 6 groups. C: Results of inclined plane test in the 6 groups. D: Comparisons of inclined plane test among SCI+Orexin group, SCI+DNQX group and SCI+Orexin+DNQX group。 aP<0.01, bP<0.01 vs Sham group; cP<0.01 vs SCI+Saline group; dP<0.01, fP<0.01 vs SCI+DNQX group; eP<0.01 vs SCI+Orexin+DNQX group.
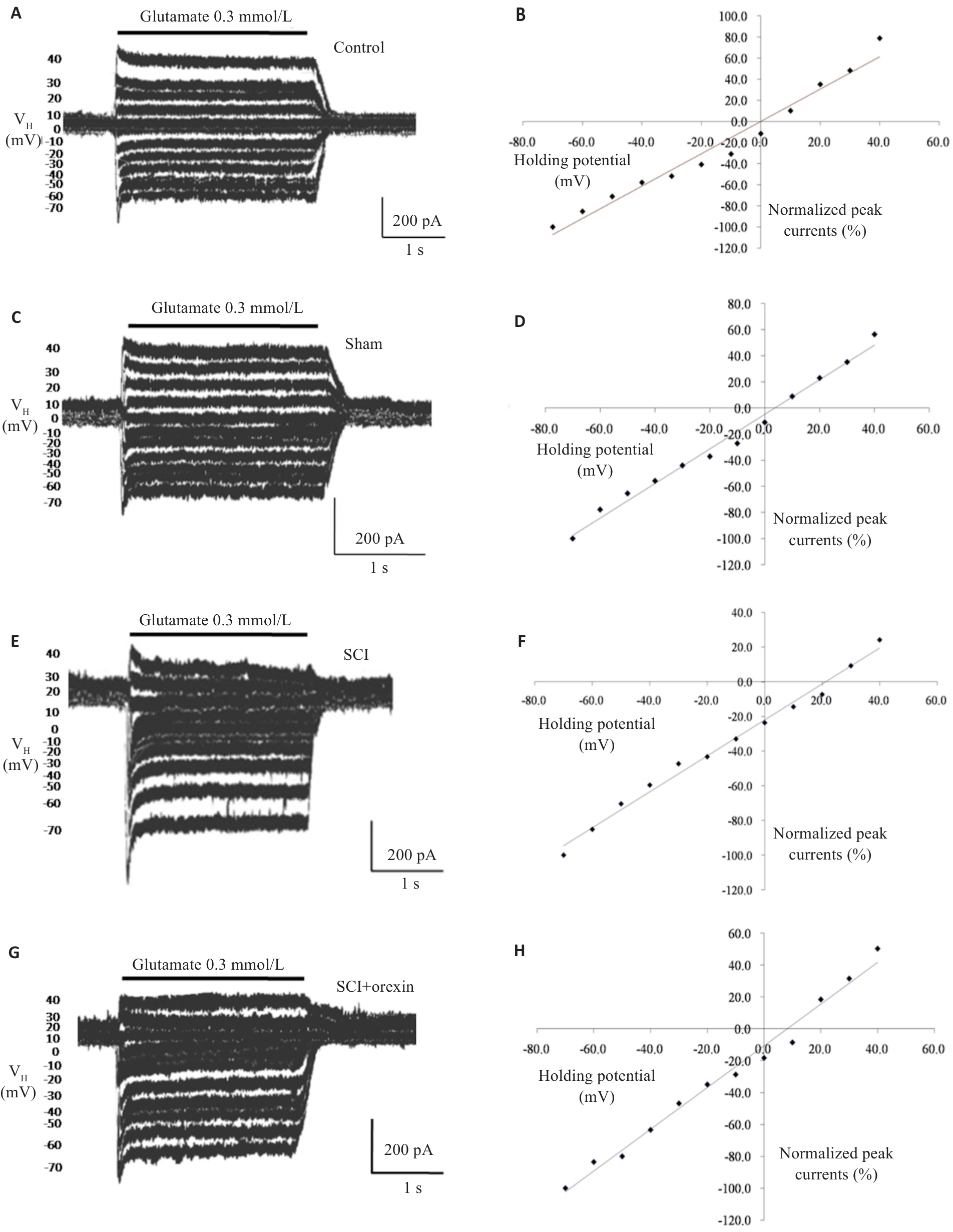
Fig.3 Effect of orexin on reversal potential of glutamate-induced currents in spinal cord ventral horn neurons of rats after spinal cord injury (SCI). A, B: Changes in glutamate-induced currents in normal group under different holding potentials (-70 to +40 mV) and linear fit of the current-voltage relationship curve (the intersection point on the X-axis represents reversal potential of glutamate-induced currents). C, D: Changes in glutamate-induced currents in Sham group under different holding potentials and linear fit of the current-voltage relationship curve. E, F: Changes in glutamate-induced currents in SCI group under different holding potentials and linear fit of the current-voltage relationship curve. G, H: Changes in glutamate-induced currents in SCI+Orexin group under different holding potentials and linear fit of the current-voltage relationship curve.
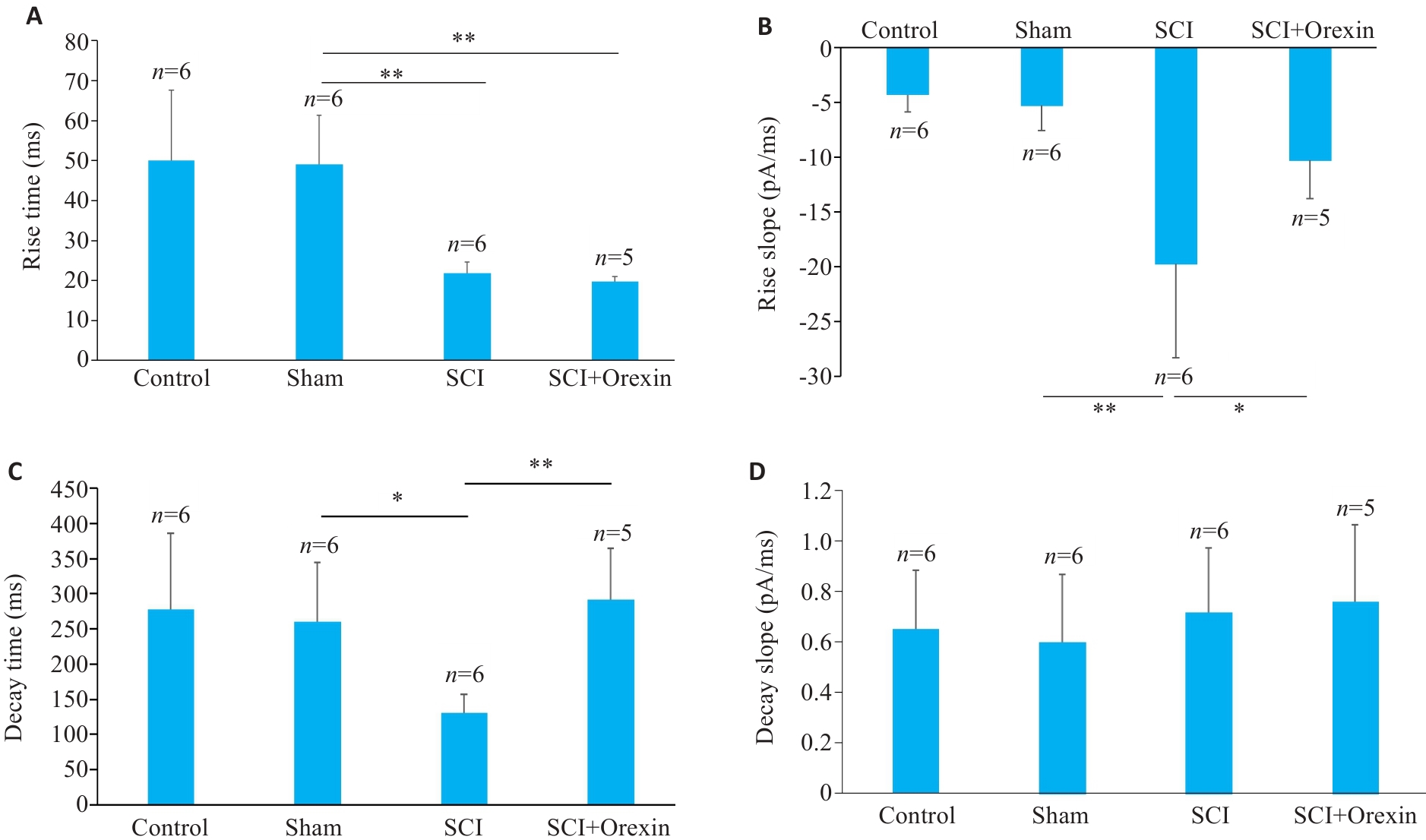
Fig.5 Comparisons of the dynamic index of glutamate currents in spinal cord ventral horn neurons among the groups. A: Comparison of the rise time of glutamate current. B: Comparison of the rise slope of glutamate current. C: Comparisons of decay time of glutamate current. D: Comparison of decay slope of glutamate current. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
| 1 | Wagner FB, Mignardot JB, Le Goff-Mignardot CG, et al. Targeted neurotechnology restores walking in humans with spinal cord injury[J]. Nature, 2018, 563(7729): 65-71. |
| 2 | Angeli CA, Boakye M, Morton RA, et al. Recovery of over-ground walking after chronic motor complete spinal cord injury[J]. N Engl J Med, 2018, 379(13): 1244-50. |
| 3 | Sakurai T, Amemiya A, Ishii M, et al. Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior[J]. Cell, 1998, 92(4): 573-85. |
| 4 | Chieffi S, Carotenuto M, Monda V, et al. Orexin system: the key for a healthy life[J]. Front Physiol, 2017, 8: 357. |
| 5 | Yamuy J, Fung SJ, Xi MC, et al. State-dependent control of lumbar motoneurons by the hypocretinergic system[J]. Exp Neurol, 2010, 221(2): 335-45. |
| 6 | Carpi M, Mercuri NB, Liguori C. Orexin receptor antagonists for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease and associated sleep disorders[J]. Drugs, 2024, 84(11): 1365-78. |
| 7 | Becquet L, Abad C, Leclercq M, et al. Systemic administration of orexin A ameliorates established experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by diminishing neuroinflammation[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2019, 16(1): 64. |
| 8 | Hwang YT, Piguet O, Hodges JR, et al. Sleep and orexin: a new paradigm for understanding behavioural-variant frontotemporal dementia[J]? Sleep Med Rev, 2020, 54: 101361. |
| 9 | Lee MG, Hassani OK, Jones BE. Discharge of identified orexin/hypocretin neurons across the sleep-waking cycle[J]. J Neurosci, 2005, 25(28): 6716-20. |
| 10 | Mileykovskiy BY, Kiyashchenko LI, Siegel JM. Behavioral correlates of activity in identified hypocretin/orexin neurons[J]. Neuron, 2005, 46(5): 787-98. |
| 11 | Takakusaki K, Takahashi K, Saitoh K, et al. Orexinergic projections to the cat midbrain mediate alternation of emotional behavioural states from locomotion to cataplexy[J]. J Physiol, 2005, 568(Pt 3): 1003-20. |
| 12 | Zhang J, Li B, Yu L, et al. A role for orexin in central vestibular motor control[J]. Neuron, 2011, 69(4): 793-804. |
| 13 | Yamuy J, Fung SJ, Xi MC, et al. Hypocretinergic control of spinal cord motoneurons[J]. J Neurosci, 2004, 24(23): 5336-45. |
| 14 | Kang JW, Ren BK, Huang LH, et al. Orexin-a alleviates ferroptosis by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in traumatic brain injury[J]. Aging, 2024, 16(4): 3404-19. |
| 15 | Russell Huie J, Stuck ED, Lee KH, et al. AMPA receptor phosphorylation and synaptic colocalization on motor neurons drive maladaptive plasticity below complete spinal cord injury[J]. eNeuro, 2015, 2(5): ENEURO.0091-15.2015. |
| 16 | Follwell MJ, Ferguson AV. Cellular mechanisms of orexin actions on paraventricular nucleus neurones in rat hypothalamus[J]. J Physiol, 2002, 545(3): 855-67. |
| 17 | Borgland SL, Storm E, Bonci A. Orexin B/hypocretin 2 increases glutamatergic transmission to ventral tegmental area neurons[J]. Eur J Neurosci, 2008, 28(8): 1545-56. |
| 18 | Lambe EK, Aghajanian GK. Hypocretin (orexin) induces calcium transients in single spines postsynaptic to identified thalamocortical boutons in prefrontal slice[J]. Neuron, 2003, 40(1): 139-50. |
| 19 | Niknia S, Kaeidi A, Hajizadeh MR, et al. Neuroprotective and antihyperalgesic effects of orexin-a in rats with painful diabetic neuropathy[J]. Neuropeptides, 2019, 73: 34-40. |
| 20 | Jin N, Zhu SY, Yang XY, et al. Orexin-a potentiates Glycine currents by activating OX1R and IP3/Ca2+/PKC signaling pathways in spinal cord ventral horn neurons[J]. Brain Res Bull, 2021, 169: 196-204. |
| 21 | Thomas A, Miller A, Roughan J, et al. Efficacy of intrathecal morphine in a model of surgical pain in rats[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(10): e0163909. |
| 22 | Rana S, Sieck GC, Mantilla CB. Diaphragm electromyographic activity following unilateral midcervical contusion injury in rats[J]. J Neurophysiol, 2017, 117(2): 545-55. |
| 23 | Fan L, Li XB, Liu T. Asiaticoside inhibits neuronal apoptosis and promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury in rats[J]. J Mol Neurosci, 2020, 70(12): 1988-96. |
| 24 | Anjum A, Yazid MD, Fauzi Daud M, et al. Spinal cord injury: pathophysiology, multimolecular interactions, and underlying recovery mechanisms[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(20): 7533. |
| 25 | Reshamwala R, Eindorf T, Shah M, et al. Induction of complete transection-type spinal cord injury in mice[J]. J Vis Exp, 2020(159): (159). |
| 26 | Pan LL, Qi RR, Wang JQ, et al. Evidence for a role of orexin/hypocretin system in vestibular lesion-induced locomotor abnormalities in rats[J]. Front Neurosci, 2016, 10: 355. |
| 27 | Yan GL, Li FG, Tao ZW, et al. Effects of vestibular damage on the sleep and expression level of orexin in the hypothalamus of rats and its correlation with autophagy and Akt tumor signal pathway[J]. J Oncol, 2022, 2022: 2514555. |
| 28 | Iacobucci GJ, Popescu GK. Ca2+-dependent inactivation of GluN2A and GluN2B NMDA receptors occurs by a common kinetic mechanism[J]. Biophys J, 2020, 118(4): 798-812. |
| 29 | Fani G, Mannini B, Vecchi G, et al. Aβ oligomers dysregulate calcium homeostasis by mechanosensitive activation of AMPA and NMDA receptors[J]. ACS Chem Neurosci, 2021, 12(4): 766-81. |
| 30 | Yasuda R, Hayashi Y, Hell JW. CaMKII: a central molecular organizer of synaptic plasticity, learning and memory[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2022, 23(11): 666-82. |
| 31 | Kosenkov AM, Gaidin SG, Sergeev AI, et al. Fast changes of NMDA and AMPA receptor activity under acute hyperammonemia in vitro [J]. Neurosci Lett, 2018, 686: 80-6. |
| 32 | Plaza-Zabala A, Li X, Milovanovic M, et al. An investigation of interactions between hypocretin/orexin signaling and glutamate receptor surface expression in the rat nucleus accumbens under basal conditions and after cocaine exposure[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2013, 557 Pt B(0 0): 101-6. |
| 33 | Dong YJ, Jiang NH, Zhan LH, et al. Soporific effect of modified Suanzaoren Decoction on mice models of insomnia by regulating Orexin-A and HPA axis homeostasis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 143: 112141. |
| 34 | Palomba L, Motta A, Imperatore R, et al. Role of 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol and CB1 receptors in orexin-A-mediated prevention of oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced neuronal injury[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(6): 1507. |
| 35 | Zhang DX, Cui Y, Zhao MM, et al. Orexin-a exerts neuroprotective effect in experimental intracerebral hemorrhage by suppressing autophagy via OXR1-mediated ERK/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2022, 16: 1045034. |
| 36 | Nepovimova E, Janockova J, Misik J, et al. Orexin supplementation in narcolepsy treatment: a review[J]. Med Res Rev, 2019, 39(3): 961-75. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||