Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 2385-2393.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.11.11
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bowen SONG1( ), Renjie ZHOU1, Ying XU2, Jinran SHI2, Zhizhi ZHANG2, Jing LI2, Zhijun GENG2, Xue SONG2, Lian WANG1,2, Yueyue WANG2, Lugen ZUO1,2(
), Renjie ZHOU1, Ying XU2, Jinran SHI2, Zhizhi ZHANG2, Jing LI2, Zhijun GENG2, Xue SONG2, Lian WANG1,2, Yueyue WANG2, Lugen ZUO1,2( )
)
Received:2025-04-22
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-11-28
Contact:
Lugen ZUO
E-mail:songbowen@stu.bbmu.edu.cn;zuolugen@126.com
Supported by:Bowen SONG, Renjie ZHOU, Ying XU, Jinran SHI, Zhizhi ZHANG, Jing LI, Zhijun GENG, Xue SONG, Lian WANG, Yueyue WANG, Lugen ZUO. Elevated TMCO1 expression in gastric cancer is associated poor prognosis and promotes malignant phenotypes of tumor cells by inhibiting apoptosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(11): 2385-2393.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.11.11

Fig.1 TMCO1 expression is elevated in gastric cancer tissues in positive correlation with the expression of Ki67. A: Expression of TMCO1 in different human tumors (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Normal). B: Expression levels of TMCO1 in gastric cancer (*P<0.05). C, D: Immunohistochemistry for detecting TMCO1 expression in gastric cancer tissues and adjacent tissues and the relative IOD values (*P<0.05 vs adjacent tissue). E, F: Immunohistochemistry for detecting Ki67 expression in gastric cancer and adjacent tissues and the relative IOD value (*P<0.05 vs adjacent tissue). G, H: Correlation analysis of TMCO1 and Ki67 expressions.
| Factor | n | TMCO1 expression [n, (%)] | χ² | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=52) | High (n=52) | ||||
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 72 | 40 (55.6%) | 32 (44.4%) | 2.889 | 0.089 |
| Female | 32 | 12 (37.5%) | 20 (62.5%) | ||
| Age (year) | |||||
| ˂60 | 49 | 28 (57.1%) | 21 (42.9%) | 1.891 | 0.169 |
| ≥60 | 55 | 24 (43.6%) | 31 (56.4%) | ||
| CEA (μg/L) | |||||
| ˂5 | 40 | 28 (70.0%) | 12 (30.0%) | 10.400 | 0.001 |
| ≥5 | 64 | 24 (37.5%) | 40 (62.5%) | ||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | |||||
| ˂37 | 38 | 29 (76.3%) | 9 (23.7%) | 16.587 | ˂0.001 |
| ≥37 | 66 | 23 (34.8%) | 43 (65.2%) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | |||||
| ˂5 | 46 | 26 (56.5%) | 20 (43.5%) | 1.403 | 0.236 |
| ≥5 | 58 | 26 (44.8%) | 32 (55.2%) | ||
| Cancer cell type | |||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 70 | 36 (51.4%) | 34 (48.6%) | 0.175 | 0.676 |
| Other | 34 | 16 (47.1%) | 18 (52.9%) | ||
| T stage | |||||
| 1-2 | 37 | 24 (64.9%) | 13 (35.1%) | 5.076 | 0.024 |
| 3-4 | 67 | 28 (41.8%) | 39 (58.2%) | ||
| N stage | |||||
| 0-1 | 42 | 27 (64.3%) | 15 (35.7%) | 5.751 | 0.016 |
| 2-3 | 62 | 25 (40.3%) | 37 (59.7%) | ||
Tab.1 Correlation between TMCO1 expression levels and parameters of gastric cancer progression
| Factor | n | TMCO1 expression [n, (%)] | χ² | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=52) | High (n=52) | ||||
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 72 | 40 (55.6%) | 32 (44.4%) | 2.889 | 0.089 |
| Female | 32 | 12 (37.5%) | 20 (62.5%) | ||
| Age (year) | |||||
| ˂60 | 49 | 28 (57.1%) | 21 (42.9%) | 1.891 | 0.169 |
| ≥60 | 55 | 24 (43.6%) | 31 (56.4%) | ||
| CEA (μg/L) | |||||
| ˂5 | 40 | 28 (70.0%) | 12 (30.0%) | 10.400 | 0.001 |
| ≥5 | 64 | 24 (37.5%) | 40 (62.5%) | ||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | |||||
| ˂37 | 38 | 29 (76.3%) | 9 (23.7%) | 16.587 | ˂0.001 |
| ≥37 | 66 | 23 (34.8%) | 43 (65.2%) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | |||||
| ˂5 | 46 | 26 (56.5%) | 20 (43.5%) | 1.403 | 0.236 |
| ≥5 | 58 | 26 (44.8%) | 32 (55.2%) | ||
| Cancer cell type | |||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 70 | 36 (51.4%) | 34 (48.6%) | 0.175 | 0.676 |
| Other | 34 | 16 (47.1%) | 18 (52.9%) | ||
| T stage | |||||
| 1-2 | 37 | 24 (64.9%) | 13 (35.1%) | 5.076 | 0.024 |
| 3-4 | 67 | 28 (41.8%) | 39 (58.2%) | ||
| N stage | |||||
| 0-1 | 42 | 27 (64.3%) | 15 (35.7%) | 5.751 | 0.016 |
| 2-3 | 62 | 25 (40.3%) | 37 (59.7%) | ||

Fig.3 High expression of TMCO1 is associated with decreased postoperative 5-year survival rate of gastric cancer patients. A: Kaplan-Meier (KM) online platform analysis. B: KM survival curves for analyzing clinical data of patients in our hospital. C: Predictive value of TMCO1 for 5-year survival after radical gastrectomy.
| Factor | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log-rank χ2 | P | HR | 95% CI | P | ||
| Gender (male vs female) | 0.041 | 0.840 | ||||
| Age (˂60 years vs ≥60 years) | 3.189 | 0.074 | ||||
| TMCO1 expression (high vs low) | 44.369 | ˂0.001 | 3.449 | 1.966-6.053 | ˂0.001 | |
| CEA (˂5 μg/L vs ≥5 μg/L) | 29.662 | ˂0.001 | 2.513 | 1.394-4.530 | 0.002 | |
| CA19-9 (˂37 kU/L vs ≥37 kU/L) | 33.690 | ˂0.001 | 2.934 | 1.593-5.405 | ˂0.001 | |
| Tumor size (˂5 cm vs ≥5 cm) | 3.084 | 0.079 | ||||
| Cancer cell type (adenocarcinoma vs other) | 1.336 | 0.248 | ||||
| T stage (T1-T2 vs T3-T4) | 20.352 | ˂0.001 | 2.217 | 1.265-3.887 | 0.005 | |
| N stage (N0-N1 vs N2-N3) | 26.017 | ˂0.001 | 2.202 | 1.218-3.981 | 0.009 | |
Tab.2 Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis of prognostic factors influencing 5-year survival of gastric cancer patients
| Factor | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log-rank χ2 | P | HR | 95% CI | P | ||
| Gender (male vs female) | 0.041 | 0.840 | ||||
| Age (˂60 years vs ≥60 years) | 3.189 | 0.074 | ||||
| TMCO1 expression (high vs low) | 44.369 | ˂0.001 | 3.449 | 1.966-6.053 | ˂0.001 | |
| CEA (˂5 μg/L vs ≥5 μg/L) | 29.662 | ˂0.001 | 2.513 | 1.394-4.530 | 0.002 | |
| CA19-9 (˂37 kU/L vs ≥37 kU/L) | 33.690 | ˂0.001 | 2.934 | 1.593-5.405 | ˂0.001 | |
| Tumor size (˂5 cm vs ≥5 cm) | 3.084 | 0.079 | ||||
| Cancer cell type (adenocarcinoma vs other) | 1.336 | 0.248 | ||||
| T stage (T1-T2 vs T3-T4) | 20.352 | ˂0.001 | 2.217 | 1.265-3.887 | 0.005 | |
| N stage (N0-N1 vs N2-N3) | 26.017 | ˂0.001 | 2.202 | 1.218-3.981 | 0.009 | |
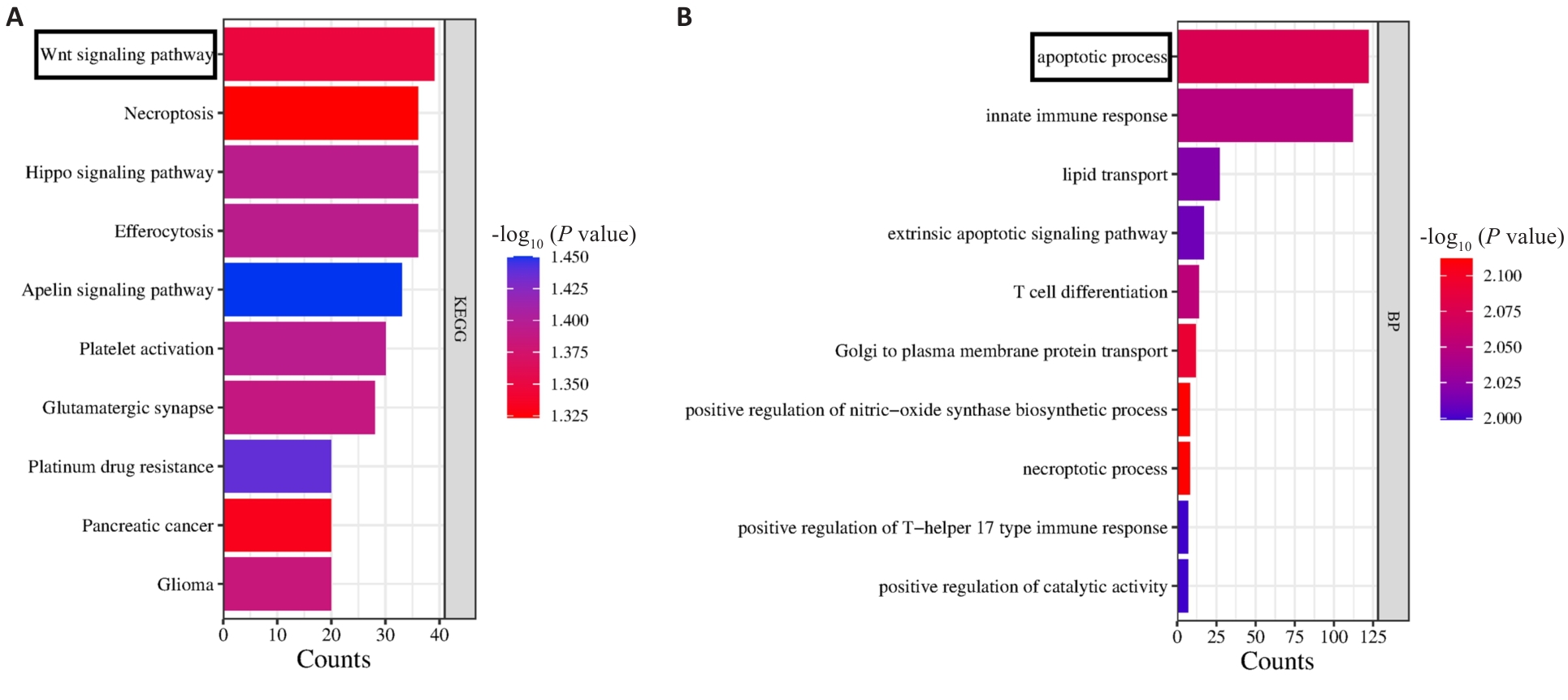
Fig.4 KEGG and GO enrichment analysis of TMCO1. A: KEGG enrichment analysis shows that TMCO1 is related to the Wnt signaling pathway. B: GO enrichment analysis shows that TMCO1 is associated with cell apoptosis process.

Fig.5 High expression of TMCO1 inhibits apoptosis and promotes proliferation of gastric cancer cells. A, D: Validation of TMCO1 overexpression and TMCO1 silencing in HGC-27 cells. B: CCK8 assay for assessing HGC-27 cell proliferation. C, E: TMCO1 regulates the expression of proliferation-associated proteins Ki67 and PCNA in HGC-27 cells. F, G: Flow cytometry for analyzing apoptosis of HGC-27 cells. *P<0.05, ***P˂0.001, ****P˂0.0001 vs Vector group.

Fig.6 TMCO1 overexpression promotes migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. A, C, D: Cell migration and invasion of HGC-27 cells. B, E: Wound-healing assay. *P<0.05 vs Vector group.
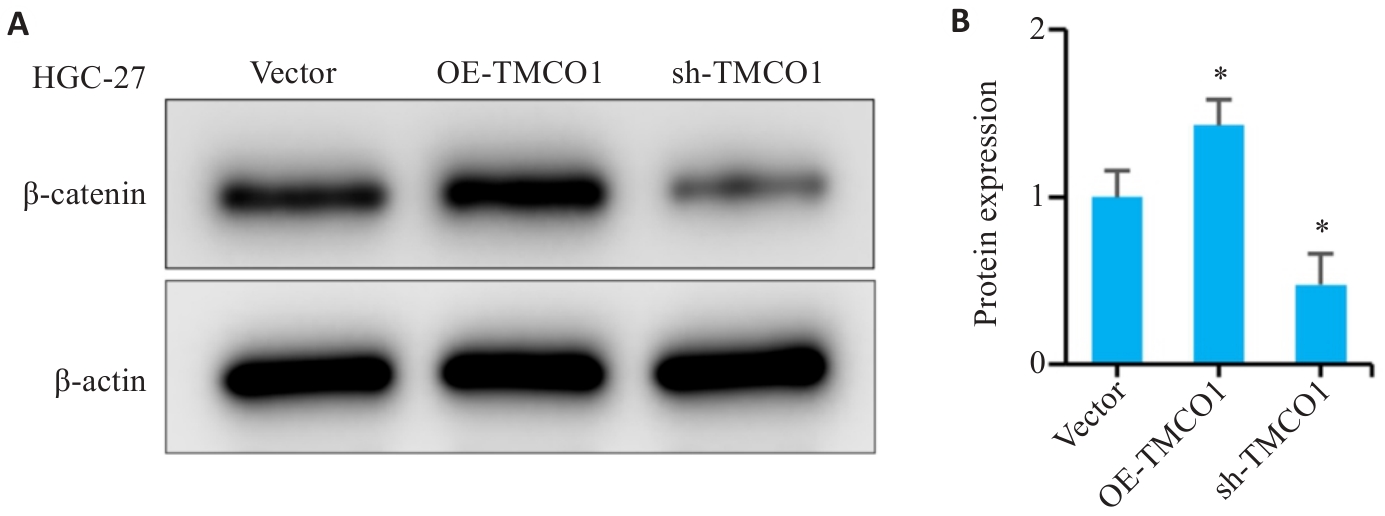
Fig.7 TMCO1 regulates the Wnt signaling pathway in gastric cancer cells. A: Detection of β‑catenin protein expression in HGC-27 cells with TMCO1 overexpression or silencing by Western blotting. B: Analysis of the IOD values of β‑catenin in HGC-27 cells. *P<0.05 vs Vector group.
| [1] | Joshi SS, Badgwell BD. Current treatment and recent progress in gastric cancer[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 264-79. doi:10.3322/caac.21657 |
| [2] | Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(3): 229-63. doi:10.3322/caac.21834 |
| [3] | Guan WL, He Y, Xu RH. Gastric cancer treatment: recent progress and future perspectives[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2023, 16(1): 57. doi:10.1186/s13045-023-01451-3 |
| [4] | Wang Y, Zhang L, Yang Y, et al. Progress of gastric cancer surgery in the era of precision medicine[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2021, 17(4): 1041-9. doi:10.7150/ijbs.56735 |
| [5] | Jiang YM, Zhou KN, Sun ZP, et al. Non-invasive tumor microenvironment evaluation and treatment response prediction in gastric cancer using deep learning radiomics[J]. Cell Rep Med, 2023, 4(8): 101146. doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101146 |
| [6] | Zeng HM, Zheng RS, Sun KX, et al. Cancer survival statistics in China 2019-2021: a multicenter, population-based study[J]. J Natl Cancer Cent, 2024, 4(3): 203-13. doi:10.1016/j.jncc.2024.06.005 |
| [7] | Evan GI, Vousden KH. Proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer[J]. Nature, 2001, 411(6835): 342-8. doi:10.1038/35077213 |
| [8] | Li Y, Li LX, Liu H, et al. CPNE1 silencing inhibits cell proliferation and accelerates apoptosis in human gastric cancer[J]. Eur J Pharm Sci, 2022, 177: 106278. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2022.106278 |
| [9] | Wang JH, Hou Q, Qu J, et al. Polyhedral magnetic nanoparticles induce apoptosis in gastric cancer stem cells and suppressing tumor growth through magnetic force generation[J]. J Control Release, 2024, 373: 370-84. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.07.041 |
| [10] | Liu J, Li SM, Tang YJ, et al. Jaceosidin induces apoptosis and inhibits migration in AGS gastric cancer cells by regulating ROS-mediated signaling pathways[J]. Redox Rep, 2024, 29(1): 2313366. doi:10.1080/13510002.2024.2313366 |
| [11] | Dong J, Kang S, Cao F, et al. The relationship between TMCO1 and CALR in the pathological characteristics of prostate cancer and its effect on the metastasis of prostate cancer cells[J]. Open Life Sci, 2024, 19(1): 20220972. doi:10.1515/biol-2022-0972 |
| [12] | Sun G, Gong S, Lan S, et al. TMCO1 regulates cell proliferation, metastasis and EMT signaling through CALR, promoting ovarian cancer progression and cisplatin resistance[J]. Cell Mol Biol: Noisy-le-grand, 2024, 70(1): 99-109. doi:10.14715/cmb/2024.70.1.14 |
| [13] | Gao L, Ye Z, Liu JH, et al. TMCO1 expression promotes cell proliferation and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transformation in human gliomas[J]. Med Oncol, 2022, 39(5): 90. doi:10.1007/s12032-022-01687-y |
| [14] | Yang KY, Zhao S, Feng H, et al. Ca2+ homeostasis maintained by TMCO1 underlies corpus callosum development via ERK signaling[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(8): 674. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-05131-x |
| [15] | Bong AHL, Robitaille M, Lin S, et al. TMCO1 is upregulated in breast cancer and regulates the response to pro-apoptotic agents in breast cancer cells[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2024, 10(1): 421. doi:10.1038/s41420-024-02183-0 |
| [16] | Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhao M, et al. VEGF mediates tumor growth and metastasis by affecting the expression of E-cadherin and N-cadherin promoting epithelial to mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer[J]. Clin Med Insights Oncol, 2023, 17: 11795549231175715. doi:10.1177/11795549231175715 |
| [17] | Ding LL, Zhang M, Zhang T, et al. MFGE8 promotes gastric cancer progression by activating the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signaling[J]. Cell Signal, 2025, 125: 111486. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111486 |
| [18] | Pang Y, Liu Y, Chen S, et al. Biological role of SPAG5 in the malignant proliferation of gastric cancer cells[J]. Nan Fang Yi Ke da Xue Xue Bao, 2024, 44(8): 1497-507. |
| [19] | Jayaraman S, Pazhani J, PriyaVeeraraghavan V, et al. PCNA and Ki67: Prognostic proliferation markers for oral cancer[J]. Oral Oncol, 2022, 130: 105943. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2022.105943 |
| [20] | Gao L, Xu Z, Huang Z, et al. CPI-613 rewires lipid metabolism to enhance pancreatic cancer apoptosis via the AMPK-ACC signaling[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2020, 39(1): 73. doi:10.1186/s13046-020-01579-x |
| [21] | Cong X, Chen T, Li S, et al. Dihydroartemisinin enhances sensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma HNE1/DDP cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by promoting ROS production[J]. Nan Fang Yi Ke da Xue Xue Bao, 2024, 44(8): 1553-60. |
| [22] | Zhu Q, Huang B, Wei L, et al. Overexpression of LncRNA MEG3 promotes ferroptosis and enhances chemotherapy sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to cisplatin[J]. Nan Fang Yi Ke da Xue Xue Bao, 2024, 44(1): 17-24. |
| [23] | Justus CR, Marie MA, Sanderlin EJ, et al. Transwell in vitro cell migration and invasion assays[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2023, 2644: 349-59. doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-3052-5_22 |
| [24] | Zuo L, Lin J, Ge S, et al. Preoperative visceral fat index predicts the survival outcomes of patients with gastric cancer after surgery[J]. Oncol Lett, 2024, 27(3): 99. doi:10.3892/ol.2024.14233 |
| [25] | Zheng S, Zhao D, Hou G, et al. iASPP suppresses Gp78-mediated TMCO1 degradation to maintain Ca2+ homeostasis and control tumor growth and drug resistance[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2022, 119(6): e2111380119. doi:10.1073/pnas.2111380119 |
| [26] | Li J, Liu C, Li Y, et al. TMCO1-mediated Ca2+ leak underlies osteoblast functions via CaMKII signaling[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 1589. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09653-5 |
| [27] | Zheng SL, Wang XW, Zhao D, et al. Calcium homeostasis and cancer: insights from endoplasmic reticulum-centered organelle communications[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2023, 33(4): 312-23. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2022.07.004 |
| [28] | Marchi S, Giorgi C, Galluzzi L, et al. Ca2+ fluxes and cancer[J]. Mol Cell, 2020, 78(6): 1055-69. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.017 |
| [29] | Moyer A, Tanaka K, Cheng EH. Apoptosis in cancer biology and therapy[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2025, 20(1): 303-28. doi:10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-051222-115023 |
| [30] | Di Y, Zhang X, Wen X, et al. MAPK signaling-mediated RFNG phosphorylation and nuclear translocation restrain oxaliplatin-induced apoptosis and ferroptosis[J]. Adv Sci: Weinh, 2024, 11(38): e2402795. doi:10.1002/advs.202402795 |
| [31] | Luo Z, Yu G, Lee HW, et al. The Nedd8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 induces autophagy and apoptosis to suppress liver cancer cell growth[J]. Cancer Res, 2012, 72(13): 3360-71. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-12-0388 |
| [32] | Lei ZN, Teng QX, Tian Q, et al. Signaling pathways and therapeutic interventions in gastric cancer[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7(1): 358. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01190-w |
| [33] | Chen X, Lu H, Wang Z, et al. Role of Abelson interactor 2 in progression and prognosis of gastric cancer and its regulatory mechanisms[J]. Nan Fang Yi Ke da Xue Xue Bao, 2024, 44(9): 1653-61. |
| [34] | Zhang W, Zhang N, Yang Z, et al. Overexpression of BZW1 promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells by regulating Wnt/β‑catenin signaling and promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. Nan Fang Yi Ke da Xue Xue Bao, 2024, 44(2): 354-62. |
| [35] | Majumder S, Crabtree JS, Golde TE, et al. Targeting Notch in oncology: the path forward[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2021, 20(2): 125-44. doi:10.1038/s41573-020-00091-3 |
| [36] | Guo W, Wang H, Li C. Signal pathways of melanoma and targeted therapy[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2021, 6(1): 424. doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00827-6 |
| [37] | Zheng T, Sun M, Liu L, et al. GPR116 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis in gastric cancer[J]. Medicine: Baltimore, 2021, 100(48): e28059. doi:10.1097/md.0000000000028059 |
| [38] | Li Y, Zhang M, Zheng X. High expression of NLRC5 is associated with prognosis of gastric cancer[J]. Open Med: Wars, 2018, 13: 443-9. doi:10.1515/med-2018-0066 |
| [1] | Ying WANG, Jing LI, Yidi WANG, Mingyu HUA, Weibin HU, Xiaozhi ZHANG. Construction and verification of a prognostic model combining anoikis and immune prognostic signatures for primary liver cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1967-1979. |
| [2] | Yu ZHANG, Haitao LI, Yuqing PAN, Jiexian CAO, Li ZHAI, Xi ZHANG. Pan-cancer analysis of MZB1 expression and its association with immune infiltration and clinical prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 2006-2018. |
| [3] | Ziliang WANG, Xiaohua CHEN, Jingjing YANG, Chen YAN, Zhizhi ZHANG, Bingyi HUANG, Meng ZHAO, Song LIU, Sitang GE, Lugen ZUO, Deli CHEN. High expression of SURF4 promotes migration, invasion and proliferation of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting tight junction proteins [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1732-1742. |
| [4] | Xiaoyu CHANG, Hanwen ZHANG, Hongting CAO, Ling HOU, Xin MENG, Hong TAO, Yan LUO, Guanghua LI. Heat stress affects expression levels of circadian clock gene Bmal1 and cyclins in rat thoracic aortic endothelial cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1353-1362. |
| [5] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [6] | Jinlong PANG, Xinli ZHAO, Zhen ZHANG, Haojie WANG, Xingqi ZHOU, Yumei YANG, Shanshan LI, Xiaoqiang CHANG, Feng LI, Xian LI. Overexpression of multimerin-2 promotes cutaneous melanoma cell invasion and migration and is associated with poor prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1479-1489. |
| [7] | Xuan WU, Jiamin FANG, Weiwei HAN, Lin CHEN, Jing SUN, Qili JIN. High PRELID1 expression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542. |
| [8] | Kang WANG, Haibin LI, Jing YU, Yuan MENG, Hongli ZHANG. High expression of ELFN1 is a prognostic biomarker and promotes proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1543-1553. |
| [9] | Yanxiu MO, Yang SHU, Yulan MO, Juntong LIU, Ouou XU, Huafei DENG, Qiben WANG. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated CDC20 gene knockout inhibits cervical cancer cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1200-1211. |
| [10] | Xinrui HOU, Zhendong ZHANG, Mingyuan CAO, Yuxin DU, Xiaoping WANG. Salidroside inhibits proliferation of gastric cancer cells by regulating the miR-1343-3p-OGDHL/PDHB glucose metabolic axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1226-1239. |
| [11] | Yujia YANG, Lifang YANG, Yaling WU, Zhaoda DUAN, Chunze YU, Chunyun WU, Jianyun YU, Li YANG. Cannabidiol inhibits neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in rats with multiple concussions by regulating the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1240-1250. |
| [12] | Yue CHEN, Linyu XIAO, Lü REN, Xue SONG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. Monotropein improves motor function of mice with spinal cord injury by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to suppress neuronal apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 774-784. |
| [13] | Fei CHU, Xiaohua CHEN, Bowen SONG, Jingjing YANG, Lugen ZUO. Moslosooflavone ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by suppressing intestinal epithelium apoptosis via inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 819-828. |
| [14] | Yi ZHANG, Yu SHEN, Zhiqiang WAN, Song TAO, Yakui LIU, Shuanhu WANG. High expression of CDKN3 promotes migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating the p53/NF-κB signaling pathway and inhibiting cell apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [15] | Qingqing HUANG, Wenjing ZHANG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Lian WANG, Xue SONG, Zhijun GENG, Lugen ZUO, Yueyue WANG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. High MYO1B expression promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor patient prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 622-631. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||