Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (8): 1732-1742.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.08.17
Ziliang WANG1,2( ), Xiaohua CHEN1, Jingjing YANG1, Chen YAN3, Zhizhi ZHANG3, Bingyi HUANG1,2, Meng ZHAO1,2, Song LIU1,2, Sitang GE2, Lugen ZUO2, Deli CHEN2(
), Xiaohua CHEN1, Jingjing YANG1, Chen YAN3, Zhizhi ZHANG3, Bingyi HUANG1,2, Meng ZHAO1,2, Song LIU1,2, Sitang GE2, Lugen ZUO2, Deli CHEN2( )
)
Received:2025-02-25
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-09-05
Contact:
Deli CHEN
E-mail:wangziliang1115@163.com;13965295950@139.com
Ziliang WANG, Xiaohua CHEN, Jingjing YANG, Chen YAN, Zhizhi ZHANG, Bingyi HUANG, Meng ZHAO, Song LIU, Sitang GE, Lugen ZUO, Deli CHEN. High expression of SURF4 promotes migration, invasion and proliferation of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting tight junction proteins[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1732-1742.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.08.17
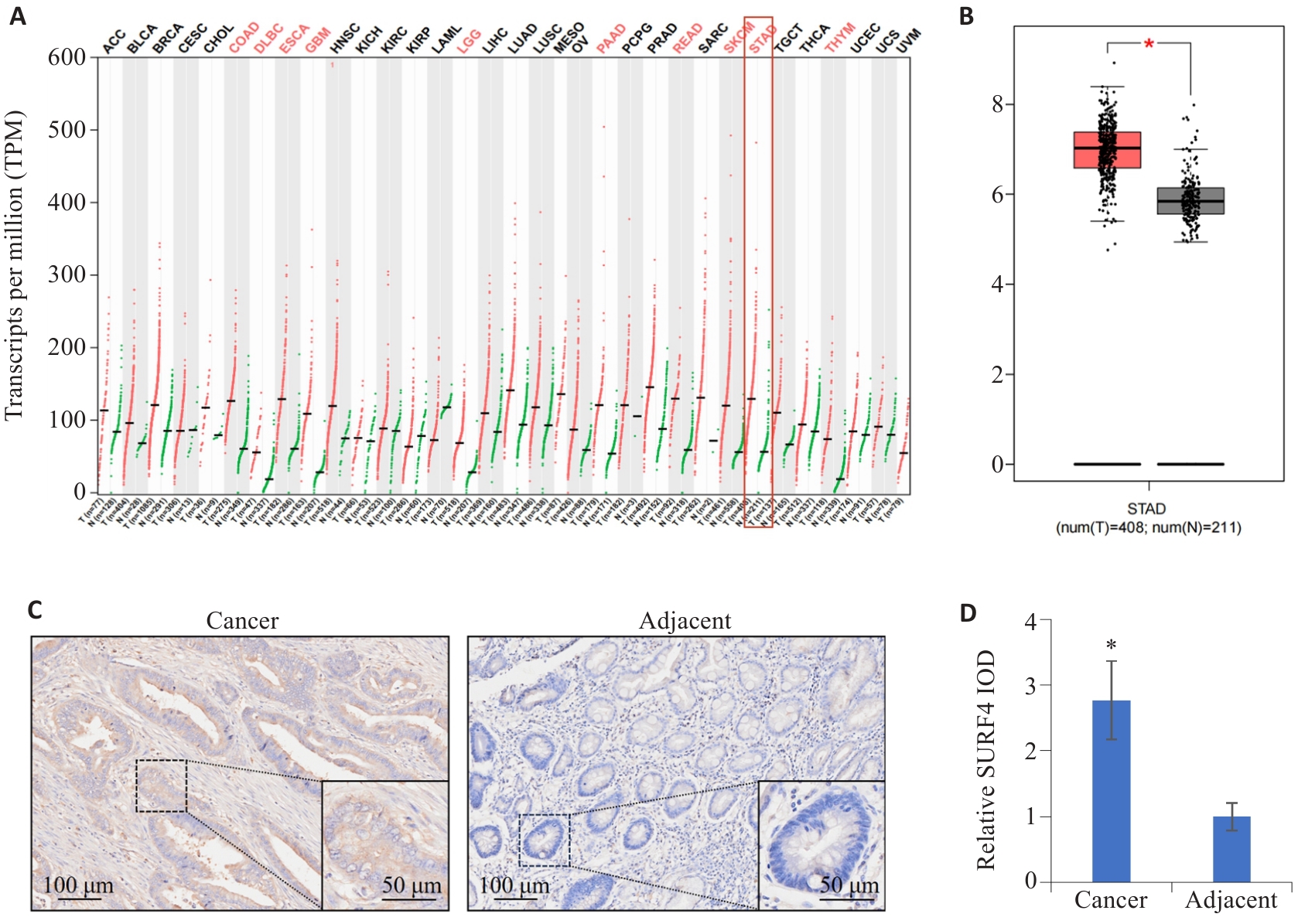
Fig.1 Distribution characteristics of SURF4 in different cancers. A: Expression of SURF4 in different human cancers. B: Expression of SURF4 in gastric cancer. *P<0.05. C: Distribution characteristics of SURF4 in gastric cancer and adjacent tissues detected by immunohistochemistry. D: Relative IOD value of SURF4. n=155. *P<0.05 vs adjacent.
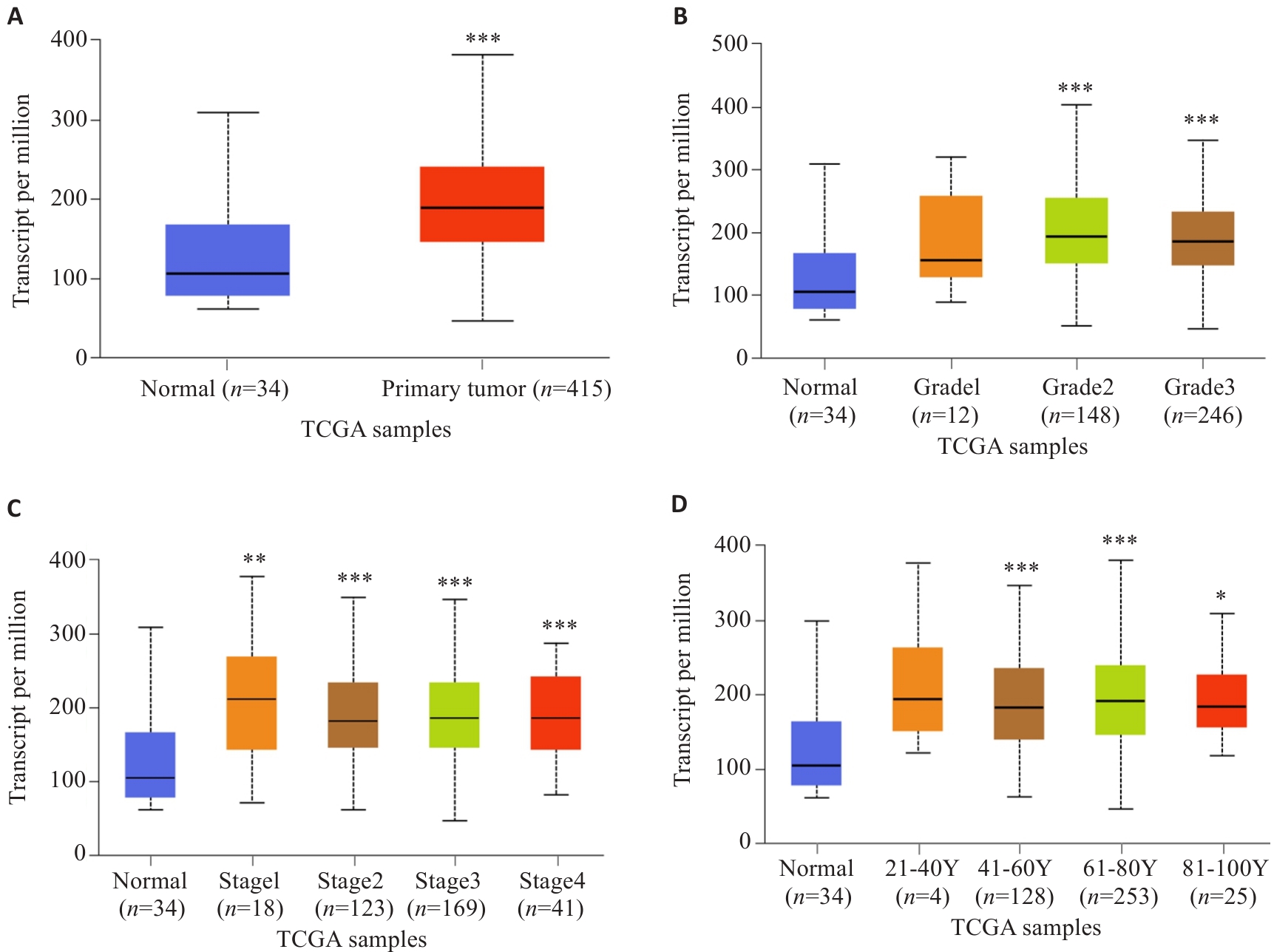
Fig.2 Analysis of expression levels of SURF4 in gastric cancer patients with different pathological parameters based on UALCAN database. A: Sample type. B: Tumor grading. C: Cancer staging. D: Age. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Normal.
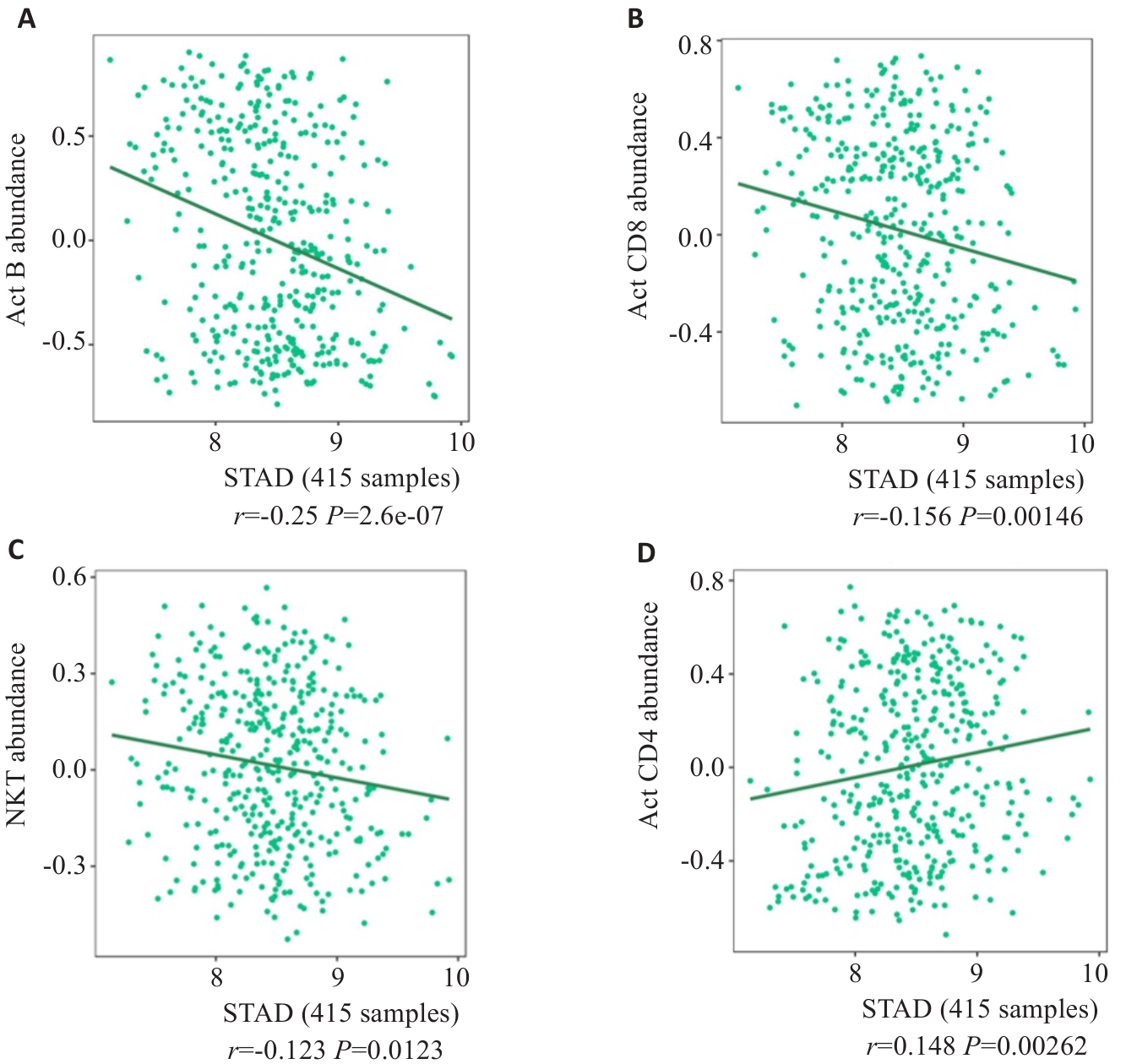
Fig.3 Relationship between SURF4 expression level and immune microenvironment of gastric cancer analyzed using TISIBD data platform. A: Activated B cells. B: CD8+ effector memory T cells. C: NK cells. D: CD4+ thymocytes.
| Factors | n | SURF4 expression | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=77) | High (n=78) | ||||
| Gender | 0.919 | 0.338 | |||
| Male | 114 | 54 (47.4) | 60 (52.6) | ||
| Female | 41 | 23 (56.1) | 18 (43.9) | ||
| Age (year) | 1.459 | 0.227 | |||
| <60 | 65 | 36 (55.4) | 29 (44.6) | ||
| ≥60 | 90 | 41 (45.6) | 49 (54.4) | ||
| CEA (μg/L) | 10.874 | <0.001 | |||
| <5 | 80 | 50 (62.5) | 30 (37.5) | ||
| ≥5 | 75 | 27 (36.0) | 48 (64.0) | ||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | 8.080 | 0.004 | |||
| <37 | 87 | 52 (59.8) | 35 (40.2) | ||
| ≥37 | 68 | 25 (36.8) | 43 (63.2) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | 0.156 | 0.693 | |||
| <5 | 87 | 42 (48.3) | 45 (51.7) | ||
| ≥5 | 68 | 35 (51.5) | 33 (48.5) | ||
| Histological type | 1.455 | 0.228 | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 112 | 59 (52.7) | 53 (47.3) | ||
| Other | 43 | 18 (41.9) | 25 (58.1) | ||
| T stage | 8.836 | 0.003 | |||
| 1-2 | 78 | 48 (61.5) | 30 (38.5) | ||
| 3-4 | 77 | 29 (37.7) | 48 (62.3) | ||
| N stage | 5.441 | 0.020 | |||
| 0-1 | 70 | 42 (60.0) | 28 (40.0) | ||
| 2-3 | 85 | 35 (41.2) | 80 (58.8) | ||
Tab.1 Relationship between SURF4 expression levels and clinicopathological parameters in 155 patients with gastric cancer [n(%)]
| Factors | n | SURF4 expression | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=77) | High (n=78) | ||||
| Gender | 0.919 | 0.338 | |||
| Male | 114 | 54 (47.4) | 60 (52.6) | ||
| Female | 41 | 23 (56.1) | 18 (43.9) | ||
| Age (year) | 1.459 | 0.227 | |||
| <60 | 65 | 36 (55.4) | 29 (44.6) | ||
| ≥60 | 90 | 41 (45.6) | 49 (54.4) | ||
| CEA (μg/L) | 10.874 | <0.001 | |||
| <5 | 80 | 50 (62.5) | 30 (37.5) | ||
| ≥5 | 75 | 27 (36.0) | 48 (64.0) | ||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | 8.080 | 0.004 | |||
| <37 | 87 | 52 (59.8) | 35 (40.2) | ||
| ≥37 | 68 | 25 (36.8) | 43 (63.2) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | 0.156 | 0.693 | |||
| <5 | 87 | 42 (48.3) | 45 (51.7) | ||
| ≥5 | 68 | 35 (51.5) | 33 (48.5) | ||
| Histological type | 1.455 | 0.228 | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 112 | 59 (52.7) | 53 (47.3) | ||
| Other | 43 | 18 (41.9) | 25 (58.1) | ||
| T stage | 8.836 | 0.003 | |||
| 1-2 | 78 | 48 (61.5) | 30 (38.5) | ||
| 3-4 | 77 | 29 (37.7) | 48 (62.3) | ||
| N stage | 5.441 | 0.020 | |||
| 0-1 | 70 | 42 (60.0) | 28 (40.0) | ||
| 2-3 | 85 | 35 (41.2) | 80 (58.8) | ||
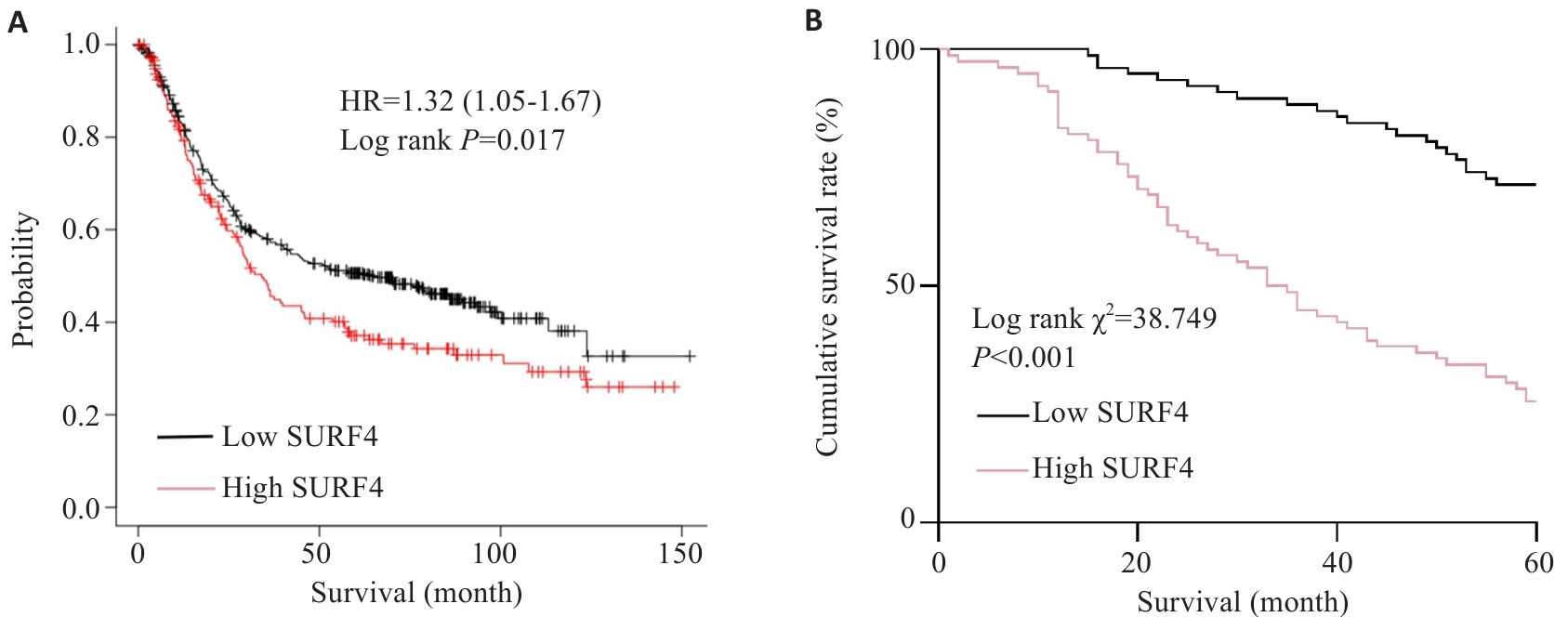
Fig.4 Relationship between SURF4 expression and 5-year survival of the patients after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer. A: Relationship between SURF4 expression and overall survival. B: Postoperative survival of patients in high expression group and low expression group.
| Factor | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log rank χ2 | P | HR | 95% CI | P | |
| Gender (Male vs female) | 2.023 | 0.155 | - | - | - |
| Age (≥60 years vs <60 years) | 2.691 | 0.101 | - | - | - |
| SURF4 expression (low vs high) | 38.749 | <0.001 | 3.106 | 1.853-5.206 | <0.001 |
| CEA (≥5 μg/L vs <5 μg/L) | 34.667 | <0.001 | 1.853 | 1.092-3.146 | 0.022 |
| CA19-9 (≥37kU/L vs <37kU/L) | 35.752 | <0.001 | 1.949 | 1.125-3.378 | 0.017 |
| Tumor size (≥5 cm vs <5 cm) | 0.044 | 0.833 | - | - | - |
| Histological type (Adenocarcinoma vs other) | 0.013 | 0.910 | - | - | - |
| T stage (T3-T4 vs T1-T2) | 31.071 | <0.001 | 2.774 | 1.661-4.635 | <0.001 |
| N stage (N2-N3 vs N0-N1) | 28.779 | <0.001 | 2.641 | 1.515-4.604 | <0.001 |
Tab.2 Cox regression analysis of prognostic factors for 5-year survival after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer
| Factor | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log rank χ2 | P | HR | 95% CI | P | |
| Gender (Male vs female) | 2.023 | 0.155 | - | - | - |
| Age (≥60 years vs <60 years) | 2.691 | 0.101 | - | - | - |
| SURF4 expression (low vs high) | 38.749 | <0.001 | 3.106 | 1.853-5.206 | <0.001 |
| CEA (≥5 μg/L vs <5 μg/L) | 34.667 | <0.001 | 1.853 | 1.092-3.146 | 0.022 |
| CA19-9 (≥37kU/L vs <37kU/L) | 35.752 | <0.001 | 1.949 | 1.125-3.378 | 0.017 |
| Tumor size (≥5 cm vs <5 cm) | 0.044 | 0.833 | - | - | - |
| Histological type (Adenocarcinoma vs other) | 0.013 | 0.910 | - | - | - |
| T stage (T3-T4 vs T1-T2) | 31.071 | <0.001 | 2.774 | 1.661-4.635 | <0.001 |
| N stage (N2-N3 vs N0-N1) | 28.779 | <0.001 | 2.641 | 1.515-4.604 | <0.001 |
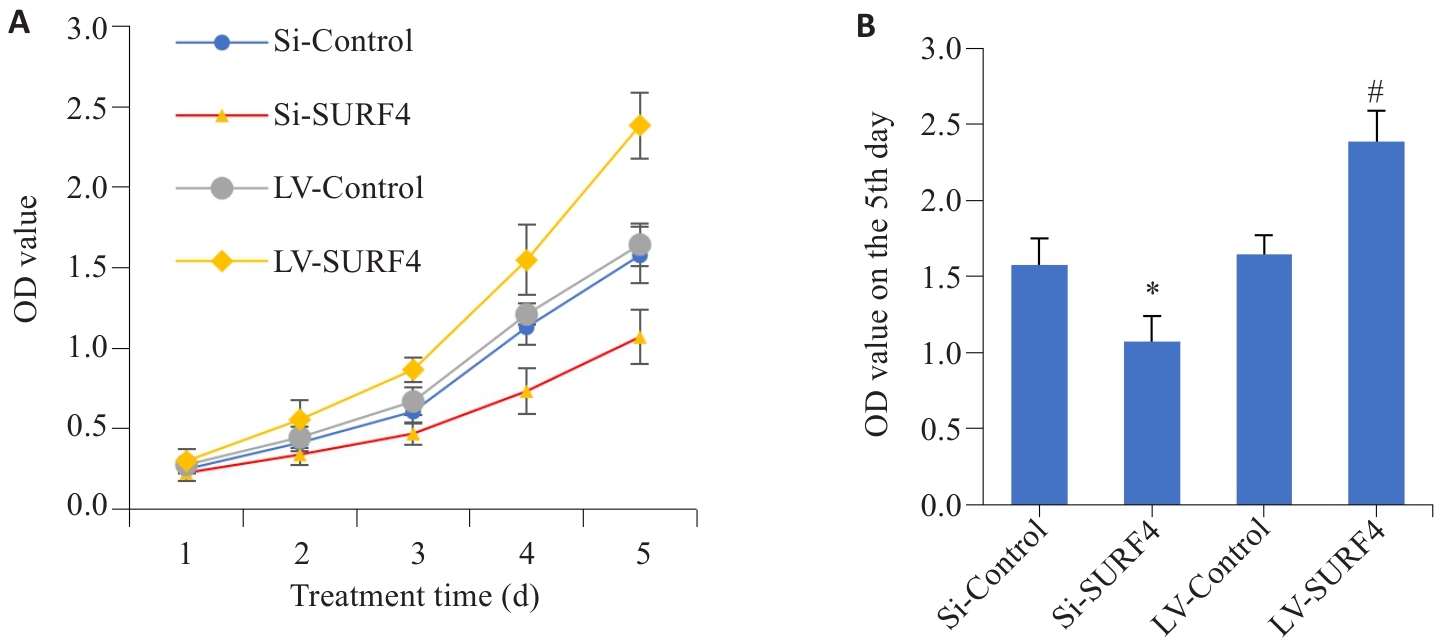
Fig.7 Effect of SURF4 expression level on proliferation of gastric cancer HGC-27 cells. A: Cell proliferation from day 1 to day 5. B: Comparison of cell proliferation on day 5 (n=4). LV: overexpression; Si: SiRNA. *P<0.05 vs Si-Control; #P<0.05 vs LV-Control.

Fig.8 Effect of SURF4 knockdown and overexpression on migration, invasion and EMT of HGC-27 gastric cancer cells. A, D: Results of scratch assay. B, E: Effect of SURF4 knockdown and overexpression on migration ability of HGC-27 cells. C, F: Invasion ability of HGC-27 cells with SURF4 knockdown and overexpression. G-I: Expressions of E-cadherin and N-cadherin protein in HGC-27 cells with SURF4 knockdown and overexpression. *P<0.05 vs Si-Control; #P<0.05 vs LV-Control(n=4).
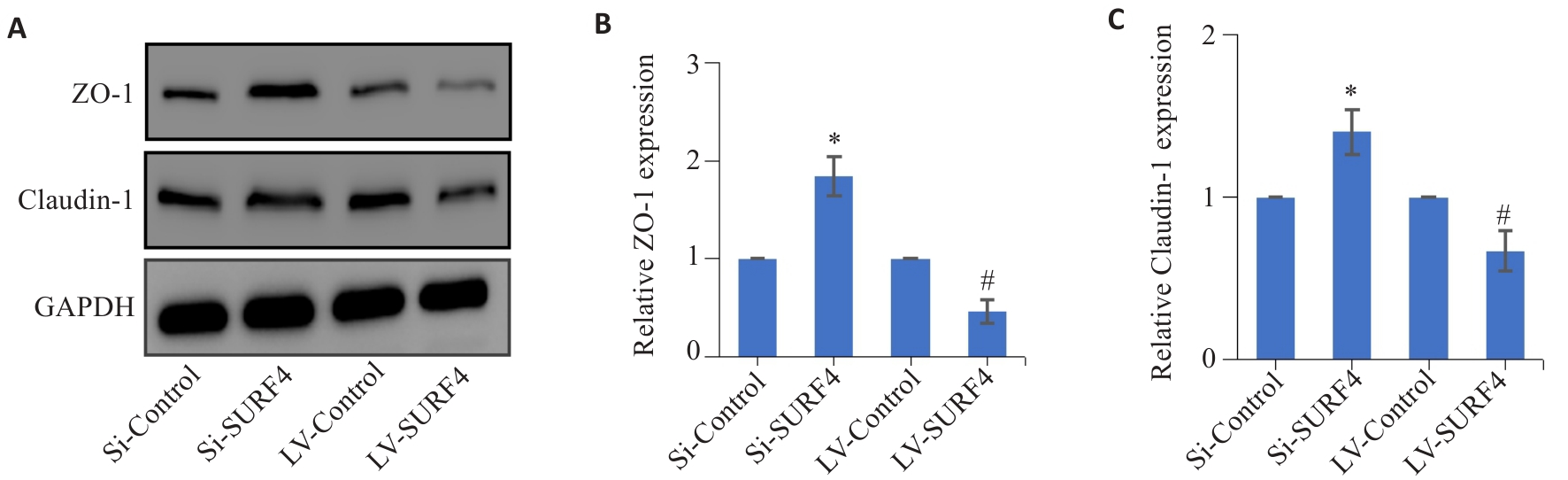
Fig.9 Effect of SURF4 knockdown and overexpression on tight junction protein expression in HGC-27 cells detected by Western blotting. A-C: Expressions of ZO-1 and Caudin-1 protein in HGC-27 gastric cancer cells. *P<0.05 vs Si-Control; #P<0.05 vs LV-Control (n=4).
| [1] | Yang WJ, Zhao HP, Yu Y, et al. Updates on global epidemiology, risk and prognostic factors of gastric cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2023, 29(16): 2452-68. doi:10.3748/wjg.v29.i16.2452 |
| [2] | Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(1): 12-49. doi:10.3322/caac.21820 |
| [3] | Zheng RS, Chen R, Han BF, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022[J]. Chin J Oncol, 2024, 46(3): 221-31. |
| [4] | Huang CM, Liu H, Hu YF, et al. Laparoscopic vs open distal gastrectomy for locally advanced gastric cancer: five-year outcomes from the CLASS-01 randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Surg, 2022, 157(1): 9-17. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2021.7583 |
| [5] | Li GZ, Doherty GM, Wang JP. Surgical management of gastric cancer: a review[J]. JAMA Surg, 2022, 157(5): 446-54. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2022.0182 |
| [6] | Joshi SS, Badgwell BD. Current treatment and recent progress in gastric cancer[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 264-79. doi:10.3322/caac.21657 |
| [7] | Kelly RJ, Ajani JA, Kuzdzal J, et al. Adjuvant nivolumab in resected esophageal or gastroesophageal junction cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 384(13): 1191-203. doi:10.1056/nejmoa2032125 |
| [8] | 史佳炜. 胃癌D2根治术后淋巴结阳性患者辅助免疫联合化疗对比单纯辅助化疗的临床疗效和安全性分析[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2024. |
| [9] | Ward ZJ, Gaba Q, Atun R. Cancer incidence and survival for 11 cancers in the commonwealth: a simulation-based modelling study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2024, 25(9): 1127-34. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(24)00336-x |
| [10] | Wu ZH, Qu BC, Yuan MX, et al. CRIP1 reshapes the gastric cancer microenvironment to facilitate development of lymphatic metastasis[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2023, 10(26): e2303246. doi:10.1002/advs.202303246 |
| [11] | Xiao J, Cao SQ, Wang JW, et al. Leptin-mediated suppression of lipoprotein lipase cleavage enhances lipid uptake and facilitates lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2024, 44(8): 855-78. doi:10.1002/cac2.12583 |
| [12] | Won Y, Jang B, Lee SH, et al. Oncogenic fatty acid metabolism rewires energy supply chain in gastric carcinogenesis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2024, 166(5): 772-86.e14. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2024.01.027 |
| [13] | Augustin JE, Soussan P, Bass AJ. Targeting the complexity of ERBB2 biology in gastroesophageal carcinoma[J]. Ann Oncol, 2022, 33(11): 1134-48. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2022.08.001 |
| [14] | 赵 燕, 于 鸿. 管家基因SURF4的生理功能及其与肿瘤的关系[J]. 中华生物医学工程杂志, 2022, 28(6): 704-8. |
| [15] | Zhai JT, Han JS, Li C, et al. High SURF4 expression is associated with poor prognosis of breast cancer[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2022, 14(22): 9317-37. doi:10.18632/aging.204409 |
| [16] | Yue YF, Xia LL, Xu SS, et al. SURF4 maintains stem-like properties via BIRC3 in ovarian cancer cells[J]. J Gynecol Oncol, 2020, 31(4): e46. doi:10.3802/jgo.2020.31.e46 |
| [17] | Kim J, Lee HS, Hong CM, et al. Novel endogenous endoplasmic reticulum transmembrane protein SURF4 suppresses cell death by negatively regulating the STING-STAT6 axis in myeloid leukemia[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2023, 43(3): 395-9. doi:10.1002/cac2.12390 |
| [18] | Yu J, Meng SB, Xuan TT, et al. Identification of hsa-miR-193a-5p-SURF4 axis related to the gut microbiota-metabolites- cytokines in lung cancer based on Mendelian randomization study and bioinformatics analysis[J]. Discov Oncol, 2024, 15(1): 475. doi:10.1007/s12672-024-01359-5 |
| [19] | Yang WS, Cui XH, Sun DP, et al. POU5F1 promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells by reducing the ubiquitination level of TRAF6[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(12): 802. doi:10.1038/s41419-023-06332-8 |
| [20] | Kim J, Hong CM, Park SM, et al. SURF4 has oncogenic potential in NIH3T3 cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 502(1): 43-7. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.116 |
| [21] | Thrift AP, Wenker TN, El-Serag HB. Global burden of gastric cancer: epidemiological trends, risk factors, screening and prevention[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2023, 20(5): 338-49. doi:10.1038/s41571-023-00747-0 |
| [22] | Huang JJ, Lucero-Prisno DE, Zhang L, et al. Updated epidemiology of gastrointestinal cancers in east Asia[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 20(5): 271-87. doi:10.1038/s41575-022-00726-3 |
| [23] | Lei ZN, Teng QX, Tian Q, et al. Signaling pathways and therapeutic interventions in gastric cancer[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7(1): 358. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01190-w |
| [24] | 左芦根, 王 炼, 杨 子, 等. 高表达CAMSAP2通过上调TGF-β信号促进胃癌细胞的侵袭和转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1460-8. doi:10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.09.02 |
| [25] | Carter P, Kang YB. Tumor heterogeneity and cooperating cancer hallmarks driven by divergent EMT programs[J]. Cancer Res, 2025, 85(1): 12-4. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-24-4309 |
| [26] | Verstappe J, Berx G. A role for partial epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in enabling stemness in homeostasis and cancer[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2023, 90: 15-28. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.02.001 |
| [27] | Ang HL, Mohan CD, Shanmugam MK, et al. Mechanism of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer and its regulation by natural compounds[J]. Med Res Rev, 2023, 43(4): 1141-200. doi:10.1002/med.21948 |
| [28] | Yu S, He J, Xie KP. Zonula occludens proteins signaling in inflammation and tumorigenesis[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2023, 19(12): 3804-15. doi:10.7150/ijbs.85765 |
| [29] | 丛 馨, 张 艳, 俞光岩, 等. 上皮细胞间紧密连接功能的研究进展[J]. 生理学报, 2016, 68(4): 492-504. doi:10.13294/j.aps.2016.0057 |
| [30] | 谭眉灵, 龙春姣, 蒋 旺, 等. 呼吸系统中上皮-间质转化的研究进展及细胞黏附连接调控机制[J]. 生理学报, 2020, 72(5): 605-16. doi:10.13294/j.aps.2020.0043 |
| [31] | Du FQ, Xie YW, Wu SZ, et al. Expression and targeted application of claudins family in hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases[J]. J Hepatocell Carcinoma, 2024, 11: 1801-21. doi:10.2147/jhc.s483861 |
| [32] | Kim HS, Lee SI, Choi YR, et al. GNAQ-regulated ZO-1 and ZO-2 act as tumor suppressors by modulating EMT potential and tumor-repressive microenvironment in lung cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(10): 8801. doi:10.3390/ijms24108801 |
| [33] | Tsuboi T, Matsuzaki T, Takekoshi S, et al. Significance of ZO-1, an intercellular adhesion molecule, as a prognostic marker in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Tokai J Exp Clin Med, 2024, 49(1): 1-8. |
| [34] | García-García CA, Cruz-Gregorio A, Pedraza-Chaverri J, et al. NDMA enhances claudin-1 and-6 expression viaCYP2E1/ROS in AGS cells[J]. Toxicol In Vitro, 2025, 102: 105952. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2024.105952 |
| [1] | Siyuan MA, Bochao ZHANG, Chun PU. Circ_0000437 promotes proliferation, invasion, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells by targeting the let-7b-5p/CTPS1 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1682-1696. |
| [2] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [3] | Jinlong PANG, Xinli ZHAO, Zhen ZHANG, Haojie WANG, Xingqi ZHOU, Yumei YANG, Shanshan LI, Xiaoqiang CHANG, Feng LI, Xian LI. Overexpression of multimerin-2 promotes cutaneous melanoma cell invasion and migration and is associated with poor prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1479-1489. |
| [4] | Xuan WU, Jiamin FANG, Weiwei HAN, Lin CHEN, Jing SUN, Qili JIN. High PRELID1 expression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542. |
| [5] | Kang WANG, Haibin LI, Jing YU, Yuan MENG, Hongli ZHANG. High expression of ELFN1 is a prognostic biomarker and promotes proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1543-1553. |
| [6] | Xinrui HOU, Zhendong ZHANG, Mingyuan CAO, Yuxin DU, Xiaoping WANG. Salidroside inhibits proliferation of gastric cancer cells by regulating the miR-1343-3p-OGDHL/PDHB glucose metabolic axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1226-1239. |
| [7] | Zhennan MA, Fuquan LIU, Xuefeng ZHAO, Xiaowei ZHANG. High expression of DTX2 promotes proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 829-836. |
| [8] | Yi ZHANG, Yu SHEN, Zhiqiang WAN, Song TAO, Yakui LIU, Shuanhu WANG. High expression of CDKN3 promotes migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating the p53/NF-κB signaling pathway and inhibiting cell apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [9] | Lu TAO, Zhuoli WEI, Yueyue WANG, Ping XIANG. CEACAM6 inhibits proliferation and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 566-576. |
| [10] | Qingqing HUANG, Wenjing ZHANG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Lian WANG, Xue SONG, Zhijun GENG, Lugen ZUO, Yueyue WANG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. High MYO1B expression promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor patient prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 622-631. |
| [11] | Huali LI, Ting SONG, Jiawen LIU, Yongbao LI, Zhaojing JIANG, Wen DOU, Linghong ZHOU. Prognosis-guided optimization of intensity-modulated radiation therapy plans for lung cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 643-649. |
| [12] | Xue SONG, Yue CHEN, Min ZHANG, Nuo ZHANG, Lugen ZUO, Jing LI, Zhijun GENG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Yueyue WANG, Lian WANG, Jianguo HU. GPSM2 is highly expressed in gastric cancer to affect patient prognosis by promoting tumor cell proliferation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 229-238. |
| [13] | Tianwei TANG, Luan LI, Yuanhan CHEN, Li ZHANG, Lixia XU, Zhilian LI, Zhonglin FENG, Huilin ZHANG, Ruifang HUA, Zhiming YE, Xinling LIANG, Ruizhao LI. High serum cystatin C is an independent risk factor for poor renal prognosis in IgA nephropathy [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 379-386. |
| [14] | Xiaorui CHEN, Qingzheng WEI, Zongliang ZHANG, Jiangshui YUAN, Weiqing SONG. Overexpression of CHMP2B suppresses proliferation of renal clear cell carcinoma cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 126-136. |
| [15] | Yaobin WANG, Liuyan CHEN, Yiling LUO, Jiqing SHEN, Sufang ZHOU. Predictive value of NUF2 for prognosis and immunotherapy responses in pan-cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 137-149. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||